Thrush in babies pictures bottom
Yeast Diaper Rash: Symptoms, Pictures, Home Remedies
Diaper rashes are a common problem for babies. But, a yeast diaper rash is different than regular diaper rash. With a regular diaper rash, an irritant causes the rash. But with a yeast diaper rash, yeast (Candida) causes the rash.
A yeast diaper rash is different than regular diaper rash. With a regular diaper rash, an irritant causes the rash. But with a yeast diaper rash, yeast (Candida) causes the rash.
Yeast is a living microorganism. It naturally lives on skin but can be hard to tame when there’s an overgrowth.
Anyone using a diaper can develop a yeast diaper rash. Read on to learn how to identify, treat, and prevent this type of diaper rash.
Yeast diaper rashes require different treatment than a standard diaper rash, so it’s important to be able to identify the type of rash.
| Yeast diaper rash symptoms | Regular diaper rash symptoms |
|---|---|
| red skin with dots or pimples | pink to reddish skin that’s smooth or chapped |
| rash doesn’t respond to standard diaper creams and takes a while to treat | rash responds to standard diaper creams and clears up in 2-3 days |
| rash may occur more in the folds of legs, genitals, or buttocks | rash may occur on smoother surfaces of the buttocks or on the vulva |
| rash may occur along with thrush infection in baby’s mouth | rash doesn’t usually occur along with oral thrush |
| may have satellite spots of rash outside the border of the rest of the rash | rash is localized to one area |
Yeast can be present on the skin and in other parts of the body with no symptoms or negative effects. However, if the yeast overgrows, it can cause an infection in the area. Overgrowth often happens in warm, moist areas or where a regular diaper rash already exists.
The goal of treating a yeast infection in the diaper area is to heal the skin and reduce exposure to yeast.
The following home remedies may help treat the infection.
Keep the area clean
Gently and thoroughly clean the whole diaper area every time you change the diaper. It can help remove yeast and also reduce the risk of other infections.
It’s also important to thoroughly wash your hands and anything your baby laid on during the diaper change. This can help prevent the spread of the yeast.
Keep the area dry
Change your baby more frequently. If you notice their diaper is wet, change them right away. Yeast thrives in warm, damp areas, so keeping the area dry can help stop the spread of the yeast.
In addition to more frequent diaper changes, also allow baby’s bottom to air dry between changes. Gently pat the area dry, but avoid rubbing, which can further irritate the skin. You can use a hair dryer on the low, cool setting to help speed up the drying process.
Gently pat the area dry, but avoid rubbing, which can further irritate the skin. You can use a hair dryer on the low, cool setting to help speed up the drying process.
Have diaper-free time
Give baby extended time without any diaper on to further help dry out the diaper area. This can get messy, so consider having diaper-free time in areas of your home that are easy to clean, or put a towel or play mat under baby to help catch any messes.
To further reduce the risk of messes, have diaper-free time immediately after a diaper change. If baby has recently gone to the bathroom, they’re less likely to need to go again anytime soon.
For younger babies, you can do diaper-free time during their usual tummy time. For sitting babies, place books and engaging toys around them to try and keep them entertained on the towel.
Avoid irritants
The infected area will be tender. Irritating products can make discomfort worse, like soap and bubble bath.
You may also want to hold off on using wipes during diaper changes.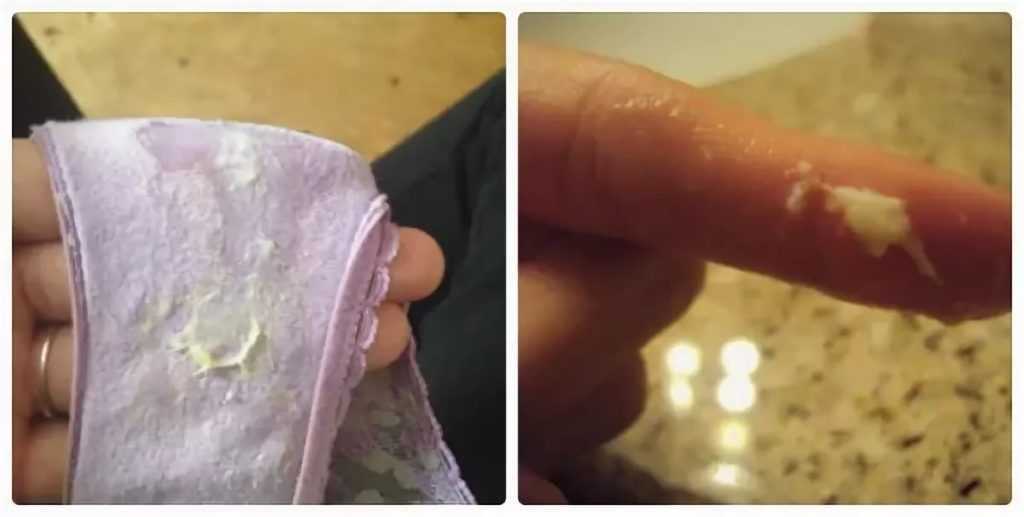 Instead, use a clean towel that’s been dampened in warm water to clean the diaper area.
Instead, use a clean towel that’s been dampened in warm water to clean the diaper area.
Use antifungal creams
The above measures can help treat the symptoms of a yeast diaper rash and may help it to go away faster, but most yeast rashes need further treatment. Ask your doctor about using an antifungal or yeast cream. Many can be purchased over the counter.
Ask your pharmacist or doctor for specific instructions, such as how often to use each day and for how long to use the treatment.
You can also ask your doctor about applying gentian violet. This is a dark purple ointment known to kill yeast, but it may not be as effective as other antifungal treatments. If you do use it, be very careful when applying, as it stains clothing.
Are natural remedies safe to use?
Ask your doctor before using natural remedies like vinegar or oils. Natural doesn’t always mean safe.
If your doctor gives you the OK, remember that a small amount goes a long way, so be sure to dilute products well.
Does baby powder help?
There’s mixed information about whether or not it’s safe to use baby powder to try to keep the diaper area dry and help prevent a yeast rash. Many believe yeast will feed on cornstarch. Cornstarch is the main ingredient in many baby powders.
As part of an older study from 1984, researchers tested for this and found no correlation between cornstarch use and increased yeast growth.
However, baby powder hasn’t been shown to treat a yeast diaper rash that’s already present. In fact, it’s not recommended to use baby powder on children, as inhaling it can damage their lungs.
Always see a doctor if your baby is very fussy, seems sick, or the rash looks infected. Doctors can help create a treatment plan to alleviate pain and help your baby heal fast.
Also see a doctor if the rash has lasted for more than a few days or isn’t responding to treatment.
In many cases, a doctor can identify a yeast infection through a physical examination of the rash. Sometimes, though, the doctor may need to scrape off a bit of skin to test for yeast or bacterial infection in the rash.
Sometimes, though, the doctor may need to scrape off a bit of skin to test for yeast or bacterial infection in the rash.
Most diaper rashes can be treated without prescriptions. Rarely, a diaper rash may be serious and affect other parts of the body. Severe yeast infections may be treated with medicated suppositories or oral antifungal medication.
Sometimes what appears as a yeast rash can actually be a bacterial infection. This is a serious issue. It may require antibiotics to treat and prevent further complications.
Possible complications from diaper rash include scabbing skin, bleeding, and irritability.
In extreme cases, a yeast diaper rash can infect other parts of the body, like skin and blood. This is more serious and needs to be urgently treated by a doctor.
Babies with a yeast diaper rash may also develop thrush. If you breastfeed, you may develop a yeast rash on your breasts.
Most diaper rashes should improve after two to three days of treatment. However, yeast infections can take several weeks to heal since the yeast is a living organism that needs to be killed.
However, yeast infections can take several weeks to heal since the yeast is a living organism that needs to be killed.
You’ll know your baby has recovered once the rash has disappeared and the skin is healed.
Call your doctor if diaper rash is persistent, doesn’t improve, gets worse with treatment, or is very painful.
The steps to prevent a yeast diaper rash are similar to many of the steps you can use to treat it at home.
Diaper rashes are very common since diapers are often warm and moist. Keeping your baby clean and as dry as possible is the best way to prevent rashes and a yeast diaper rash.
Consider these preventive tips:
- Regularly bathe baby in warm water. Clean their diaper area each time you change their diaper.
- Change diapers often. Avoid leaving baby in a wet diaper.
- Let baby’s bottom air-dry for as long as possible after every diaper change. Patting baby’s bum with a soft cloth or using a blow dryer on the cool-air setting may help speed up the process.

- Give baby regular diaper-free time.
- Don’t use rubber pants or diapers that prevent air flow. These can trap moisture near skin.
- Consider using a diaper cream to help protect your baby’s skin. Creams provide a barrier from urine and stool, which can irritate skin and make it prone to developing a rash.
- Avoid baby products that contain fragrances and dyes, such as lotions or soaps. These additives can irritate the skin.
- Don’t give baby unnecessary antibiotics, as they can cause an imbalance of healthy bacteria and yeasts in the body.
A yeast diaper rash is different than a regular diaper rash because it involves a microorganism (yeast) and not just irritated skin.
Treating a yeast diaper rash can be more difficult than treating a regular diaper rash. Most yeast diaper rashes can be treated at home, but see a doctor if your baby is very uncomfortable, the rash isn’t improving or keeps recurring, or if you think your baby has thrush.
Yeast Diaper Rash: Symptoms, Pictures, Home Remedies
Diaper rashes are a common problem for babies. But, a yeast diaper rash is different than regular diaper rash. With a regular diaper rash, an irritant causes the rash. But with a yeast diaper rash, yeast (Candida) causes the rash.
A yeast diaper rash is different than regular diaper rash. With a regular diaper rash, an irritant causes the rash. But with a yeast diaper rash, yeast (Candida) causes the rash.
Yeast is a living microorganism. It naturally lives on skin but can be hard to tame when there’s an overgrowth.
Anyone using a diaper can develop a yeast diaper rash. Read on to learn how to identify, treat, and prevent this type of diaper rash.
Yeast diaper rashes require different treatment than a standard diaper rash, so it’s important to be able to identify the type of rash.
| Yeast diaper rash symptoms | Regular diaper rash symptoms |
|---|---|
| red skin with dots or pimples | pink to reddish skin that’s smooth or chapped |
| rash doesn’t respond to standard diaper creams and takes a while to treat | rash responds to standard diaper creams and clears up in 2-3 days |
| rash may occur more in the folds of legs, genitals, or buttocks | rash may occur on smoother surfaces of the buttocks or on the vulva |
| rash may occur along with thrush infection in baby’s mouth | rash doesn’t usually occur along with oral thrush |
| may have satellite spots of rash outside the border of the rest of the rash | rash is localized to one area |
Yeast can be present on the skin and in other parts of the body with no symptoms or negative effects.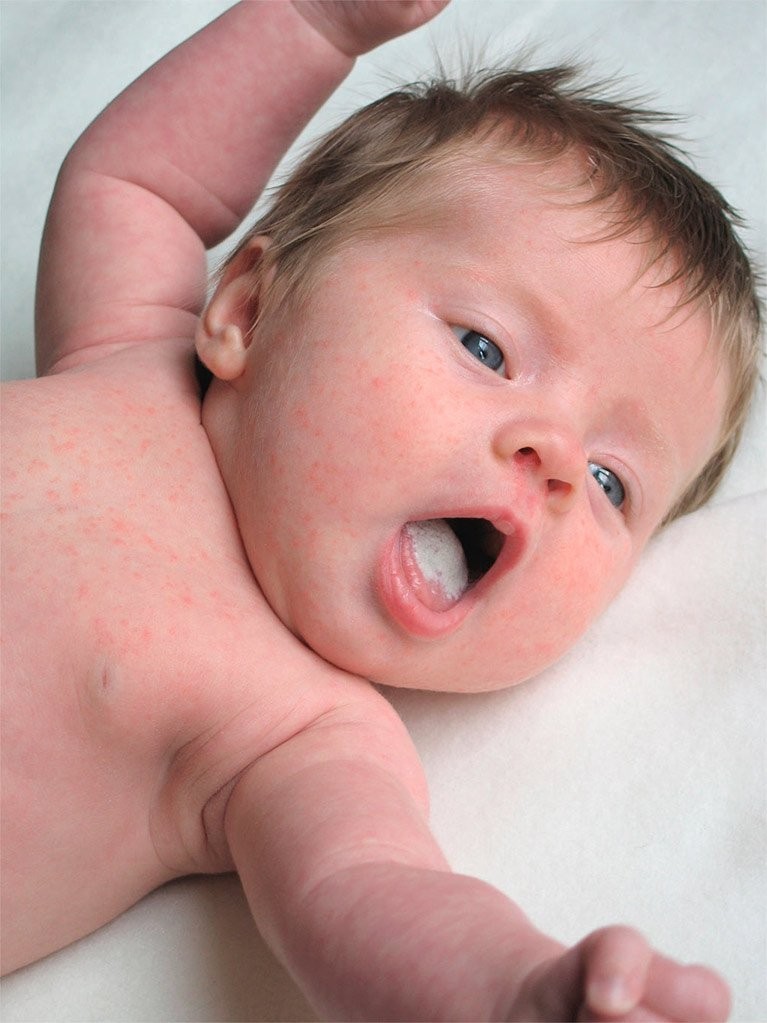 However, if the yeast overgrows, it can cause an infection in the area. Overgrowth often happens in warm, moist areas or where a regular diaper rash already exists.
However, if the yeast overgrows, it can cause an infection in the area. Overgrowth often happens in warm, moist areas or where a regular diaper rash already exists.
The goal of treating a yeast infection in the diaper area is to heal the skin and reduce exposure to yeast.
The following home remedies may help treat the infection.
Keep the area clean
Gently and thoroughly clean the whole diaper area every time you change the diaper. It can help remove yeast and also reduce the risk of other infections.
It’s also important to thoroughly wash your hands and anything your baby laid on during the diaper change. This can help prevent the spread of the yeast.
Keep the area dry
Change your baby more frequently. If you notice their diaper is wet, change them right away. Yeast thrives in warm, damp areas, so keeping the area dry can help stop the spread of the yeast.
In addition to more frequent diaper changes, also allow baby’s bottom to air dry between changes.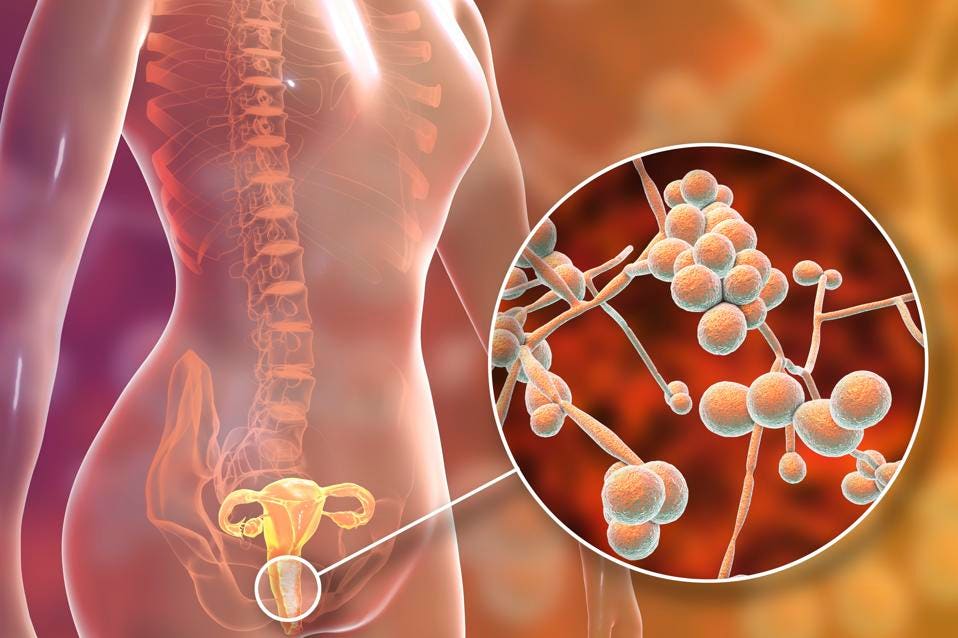 Gently pat the area dry, but avoid rubbing, which can further irritate the skin. You can use a hair dryer on the low, cool setting to help speed up the drying process.
Gently pat the area dry, but avoid rubbing, which can further irritate the skin. You can use a hair dryer on the low, cool setting to help speed up the drying process.
Have diaper-free time
Give baby extended time without any diaper on to further help dry out the diaper area. This can get messy, so consider having diaper-free time in areas of your home that are easy to clean, or put a towel or play mat under baby to help catch any messes.
To further reduce the risk of messes, have diaper-free time immediately after a diaper change. If baby has recently gone to the bathroom, they’re less likely to need to go again anytime soon.
For younger babies, you can do diaper-free time during their usual tummy time. For sitting babies, place books and engaging toys around them to try and keep them entertained on the towel.
Avoid irritants
The infected area will be tender. Irritating products can make discomfort worse, like soap and bubble bath.
You may also want to hold off on using wipes during diaper changes. Instead, use a clean towel that’s been dampened in warm water to clean the diaper area.
Instead, use a clean towel that’s been dampened in warm water to clean the diaper area.
Use antifungal creams
The above measures can help treat the symptoms of a yeast diaper rash and may help it to go away faster, but most yeast rashes need further treatment. Ask your doctor about using an antifungal or yeast cream. Many can be purchased over the counter.
Ask your pharmacist or doctor for specific instructions, such as how often to use each day and for how long to use the treatment.
You can also ask your doctor about applying gentian violet. This is a dark purple ointment known to kill yeast, but it may not be as effective as other antifungal treatments. If you do use it, be very careful when applying, as it stains clothing.
Are natural remedies safe to use?
Ask your doctor before using natural remedies like vinegar or oils. Natural doesn’t always mean safe.
If your doctor gives you the OK, remember that a small amount goes a long way, so be sure to dilute products well.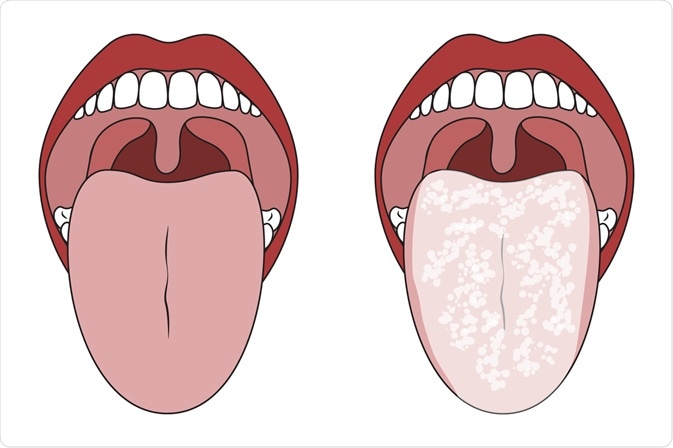
Does baby powder help?
There’s mixed information about whether or not it’s safe to use baby powder to try to keep the diaper area dry and help prevent a yeast rash. Many believe yeast will feed on cornstarch. Cornstarch is the main ingredient in many baby powders.
As part of an older study from 1984, researchers tested for this and found no correlation between cornstarch use and increased yeast growth.
However, baby powder hasn’t been shown to treat a yeast diaper rash that’s already present. In fact, it’s not recommended to use baby powder on children, as inhaling it can damage their lungs.
Always see a doctor if your baby is very fussy, seems sick, or the rash looks infected. Doctors can help create a treatment plan to alleviate pain and help your baby heal fast.
Also see a doctor if the rash has lasted for more than a few days or isn’t responding to treatment.
In many cases, a doctor can identify a yeast infection through a physical examination of the rash. Sometimes, though, the doctor may need to scrape off a bit of skin to test for yeast or bacterial infection in the rash.
Sometimes, though, the doctor may need to scrape off a bit of skin to test for yeast or bacterial infection in the rash.
Most diaper rashes can be treated without prescriptions. Rarely, a diaper rash may be serious and affect other parts of the body. Severe yeast infections may be treated with medicated suppositories or oral antifungal medication.
Sometimes what appears as a yeast rash can actually be a bacterial infection. This is a serious issue. It may require antibiotics to treat and prevent further complications.
Possible complications from diaper rash include scabbing skin, bleeding, and irritability.
In extreme cases, a yeast diaper rash can infect other parts of the body, like skin and blood. This is more serious and needs to be urgently treated by a doctor.
Babies with a yeast diaper rash may also develop thrush. If you breastfeed, you may develop a yeast rash on your breasts.
Most diaper rashes should improve after two to three days of treatment.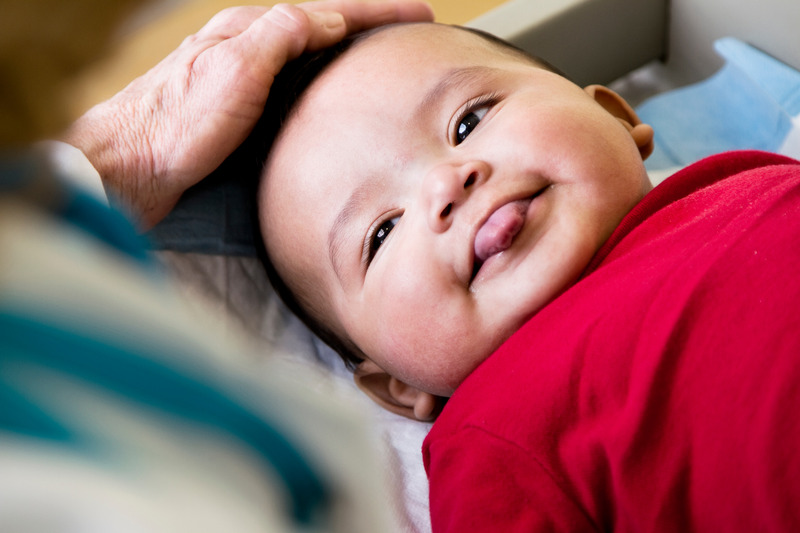 However, yeast infections can take several weeks to heal since the yeast is a living organism that needs to be killed.
However, yeast infections can take several weeks to heal since the yeast is a living organism that needs to be killed.
You’ll know your baby has recovered once the rash has disappeared and the skin is healed.
Call your doctor if diaper rash is persistent, doesn’t improve, gets worse with treatment, or is very painful.
The steps to prevent a yeast diaper rash are similar to many of the steps you can use to treat it at home.
Diaper rashes are very common since diapers are often warm and moist. Keeping your baby clean and as dry as possible is the best way to prevent rashes and a yeast diaper rash.
Consider these preventive tips:
- Regularly bathe baby in warm water. Clean their diaper area each time you change their diaper.
- Change diapers often. Avoid leaving baby in a wet diaper.
- Let baby’s bottom air-dry for as long as possible after every diaper change. Patting baby’s bum with a soft cloth or using a blow dryer on the cool-air setting may help speed up the process.

- Give baby regular diaper-free time.
- Don’t use rubber pants or diapers that prevent air flow. These can trap moisture near skin.
- Consider using a diaper cream to help protect your baby’s skin. Creams provide a barrier from urine and stool, which can irritate skin and make it prone to developing a rash.
- Avoid baby products that contain fragrances and dyes, such as lotions or soaps. These additives can irritate the skin.
- Don’t give baby unnecessary antibiotics, as they can cause an imbalance of healthy bacteria and yeasts in the body.
A yeast diaper rash is different than a regular diaper rash because it involves a microorganism (yeast) and not just irritated skin.
Treating a yeast diaper rash can be more difficult than treating a regular diaper rash. Most yeast diaper rashes can be treated at home, but see a doctor if your baby is very uncomfortable, the rash isn’t improving or keeps recurring, or if you think your baby has thrush.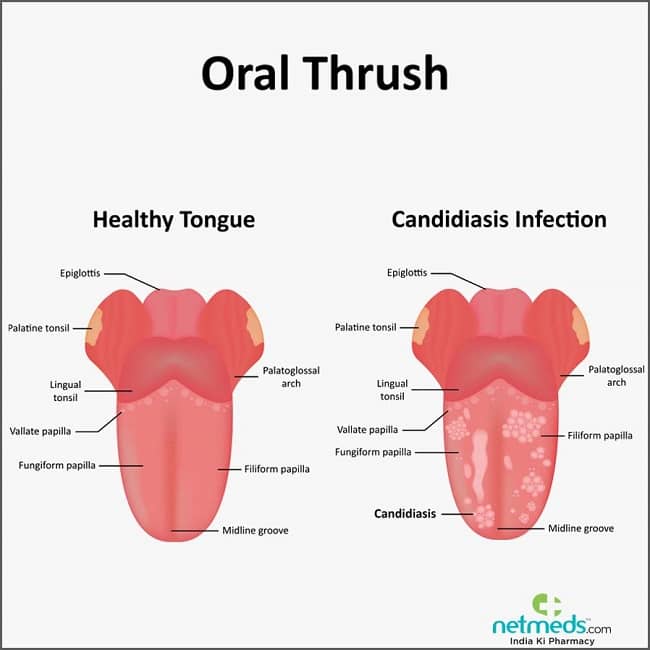
Candidiasis in the mouth of a child
Contents
What kind of disease is candidiasisSymptomsCausesTreatmentMethods of therapyPreventive measures
Many parents are aware of such a common problem in children as thrush, which is characterized by the appearance of white plaque on the tissues of the oral cavity. In medicine, this pathological condition has the term "candidiasis" and refers to fungal diseases.
Most often, candidiasis develops in the mouth of a child in the first year of life. Symptoms of thrush greatly disturb the baby, but timely treatment allows you to quickly and without consequences get rid of the fungus. nine0003
What kind of disease is candidiasis
According to statistics, about 30% of infants are faced with candidiasis. The causative agent of the disease is the Candida fungus. These specific microorganisms are normally present in the body of every person, even in the absence of health problems, but only in small quantities.
Oral candidiasis in children is much more common, since the immune system of babies is not yet formed and is not able to withstand pathogenic microorganisms and the effects of negative external factors. nine0003
With a weakened immune system and the concomitant effect of provoking factors, the fungus begins to actively multiply, affecting the mucous membranes. Without therapeutic treatment, candidiasis is eliminated in exceptional cases. If thrush is not treated, complications arise, and the infection itself spreads throughout the body.
Symptoms
Oral candidiasis in children can have a different form of manifestation and severity of symptoms: mild, moderate and severe. As a rule, each form corresponds to the stage of development of the disease. If therapy is not carried out in a timely manner, then the signs of a fungal infection become more intense and the number of symptoms increases. nine0003
With a mild form of the disease, a red rash appears on the oral mucosa, which is covered with a white coating on top.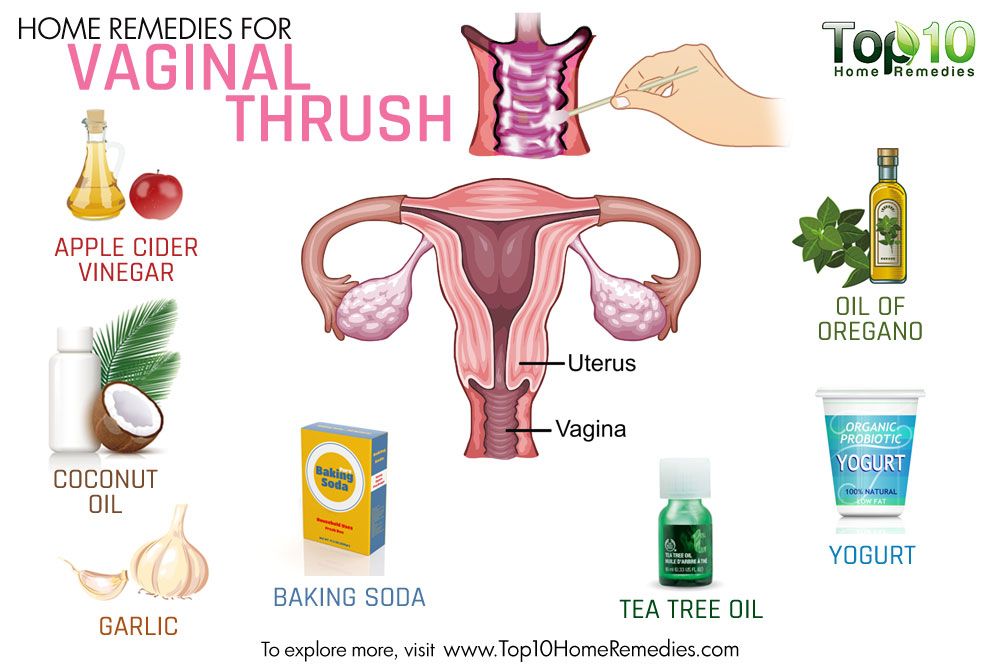 At the next stage, the child has swelling of the tissues and the formation of localized white spots with a touch of curd consistency. Gradually, these spots merge into a large affected area. When plaque is removed, bleeding sores open. If the thrush starts, then the fungus already spreads to the entire oral cavity, including the lips, tongue and throat. All fabrics are completely covered with cheesy bloom. nine0003
At the next stage, the child has swelling of the tissues and the formation of localized white spots with a touch of curd consistency. Gradually, these spots merge into a large affected area. When plaque is removed, bleeding sores open. If the thrush starts, then the fungus already spreads to the entire oral cavity, including the lips, tongue and throat. All fabrics are completely covered with cheesy bloom. nine0003
Common symptoms of candidiasis in children include:
-
burning sensation and itching in the mouth;
-
discomfort and pain when eating;
-
frequent spitting up in babies;
-
the formation of cracks in the corners of the lips;
-
temperature rise. nine0003
Children of the first two years of life report their condition with refusal to eat, constant whims and causeless crying. It is not difficult to see signs of candidiasis, so if a child has a sharp rise in temperature or refuses to eat, pediatricians and dentists recommend checking the oral cavity for white plaque. If you suspect thrush, it is undesirable to delay a visit to a specialist, since the fungal infection progresses rapidly. nine0003
If you suspect thrush, it is undesirable to delay a visit to a specialist, since the fungal infection progresses rapidly. nine0003
Reasons
The main reason for the development of candidiasis of the oral mucosa in children is a weakened immune system. If a child is born prematurely, then the likelihood of having thrush is very high. Children who are breastfed or have congenital pathologies are also often exposed to fungal infection.
Provoking factors include:
-
the presence of vaginal candidiasis in the mother during pregnancy - the child can become infected when passing through the birth canal; nine0003
-
insufficient hygiene of the female breast during breastfeeding - the fungus is often localized precisely on the nipples because of the favorable environment for it;
-
poor processing of the child's initial things - bottles, nipples, and so on;
-
the habit of parents to lick the nipples - even if the adult does not have signs of thrush, a fungus may be present in the mouth, which will be transmitted to the child; nine0003
-
long-term use of drugs of the "antibiotics" group - drugs help to reduce one's own immunity;
-
frequent regurgitation in infants - after regurgitation, an increased acidic environment, favorable for the fungus, remains inside the oral cavity;
-
excessive and frequent dry mouth - the absence of saliva, as a protective agent against the activity of pathological microorganisms.
 nine0003
nine0003
Infection with Candida fungus in children older than 2 years can occur as a result of unwashed foods, raw milk or running water. If a child over 3 years of age has suddenly developed signs of thrush, one should be examined not only for a fungal infection, but also for other possible diseases that may be accompanied by a “fading” of the immune system.
Treatment
Children's fungal diseases can be dealt with by a pediatrician, infectious disease specialist or dermatologist. If we are talking about the treatment of thrush of the oral cavity, then the dentist can also carry out therapy. nine0003
The diagnosis of "candidiasis" is determined in most cases on the basis of a specialist examination of the oral cavity. If there is any doubt, the doctor directs the patient for additional examinations. To confirm the disease, a laboratory method is used to study a smear taken from the mouth for the presence of a fungus.
Treatment of thrush in children involves an integrated approach. If the disease is not advanced, then local therapy is carried out in combination with the adoption of measures to strengthen the immune system. In severe form, oral candidiasis in children is treated with systemic drugs, local remedies and compliance with preventive recommendations. nine0003
If the disease is not advanced, then local therapy is carried out in combination with the adoption of measures to strengthen the immune system. In severe form, oral candidiasis in children is treated with systemic drugs, local remedies and compliance with preventive recommendations. nine0003
Methods of therapy
Treatment of candidiasis begins with the treatment of the oral cavity. The first procedure is already performed at the reception. Antiseptic agents are used to remove plaque. The doctor may then apply an antifungal agent.
The parent should carefully monitor the actions of the dentist, as in the future they will have to independently process the oral cavity at home. The necessary drugs will be prescribed by a specialist. Local antifungal agents are dangerous in case of overdose, especially for the child's body, so you must strictly follow the doctor's recommendations. nine0003
In advanced cases, medications are prescribed in the form of solutions, drops or tablets. There are only a few drugs for the treatment of candidiasis in children. Replacing them with adult counterparts is dangerous. The dosage must be strictly observed.
There are only a few drugs for the treatment of candidiasis in children. Replacing them with adult counterparts is dangerous. The dosage must be strictly observed.
A mandatory addition to the main therapy is hygiene, good sleep, proper nutrition and taking measures to strengthen immunity (eating healthy foods, if necessary, pharmacy vitamins, walking. nine0003
Preventive measures
In order to prevent and even shorten the course of therapy, it is recommended to rinse the mouth (if the child is older than 3-4 years), or use antiseptic sprays several times a day.
It is not difficult to prevent oral candidiasis in children. The responsible approach of parents to the health of the child from the moment of planning conception and pregnancy will help to avoid fungal infections in babies.
symptoms, causes, diagnosis, prices and treatment
Vaginal candidiasis is an unpleasant, and in case of complications, dangerous disease that causes discomfort, even pain in the lower abdomen. It also affects the general condition of a woman, who begins to feel weak and irritable.
It also affects the general condition of a woman, who begins to feel weak and irritable.
This is one of the most common infectious diseases of the vagina and vulva, since its causative agent is always present in a small amount in the human body. It lives on the mucous membranes that line the mouth, esophagus, stomach, intestines, and genitals. A decrease in immunity automatically triggers the active reproduction of Candida fungal microorganisms, which leads to candidiasis, or thrush. We will talk about this in more detail in our article. nine0003
Contents:
- Symptoms
- Complications
- Causes
- Diagnostics
- How treatment is carried out
- Consequences
- Prophylaxis
Symptoms of vaginal candidiasis
They can be pronounced, but sometimes the pathology is hidden. The disease has an acute and chronic form, it can also be uncomplicated and complicated. Most common symptoms:
- The woman experiences burning and itching, which is aggravated after hygiene procedures.

- Discharge becomes curdled or creamy.
- A characteristic sour smell appears.
- Problems with urination may begin.
- A woman experiences discomfort during intercourse.
Symptoms of vaginal candidiasis worse before menstruation. During a gynecological examination, the doctor can determine that the mucous membrane is swollen and irritated, a white or greenish coating has appeared on the walls of the vagina. nine0003
Complications of vaginal candidiasis
Stenosis. Due to candidiasis, the walls of the vagina become inflamed and become less elastic, and the lumen narrows. As a result, sexual intercourse causes a feeling of discomfort in a woman.
Salpingitis. The infection rises from the vagina and causes inflammation of the fallopian tube. However, it is often not limited to this, and one or both ovaries are affected in the patient. This disease is characterized by pain in the lower abdomen, fever, general malaise, and nausea with vomiting is also possible. Salpingitis with oophoritis can cause infertility, adhesions, and the development of pathologies of the abdominal organs. nine0003
Salpingitis with oophoritis can cause infertility, adhesions, and the development of pathologies of the abdominal organs. nine0003
Urethritis. The mucous membrane of the urethra becomes inflamed. The disease is accompanied by pain, burning redness. The urine may contain blood or pus.
Cystitis. The infection travels from the urethra to the bladder, and it becomes inflamed. The symptoms of this and the previous diseases are similar. The patient experiences pain in the lower abdomen, as well as frequent urge to urinate, although the bladder is not full enough. Body temperature may rise.
Important! Vaginal candidiasis increases the risk of complications during pregnancy and infection of the unborn child, which can lead to his death or premature birth. nine0003
Causes of thrush
The causative agent that causes this disease is yeast-like fungi of the genus Candida. They live on the mucous membrane of the vagina and in small quantities do not cause noticeable harm.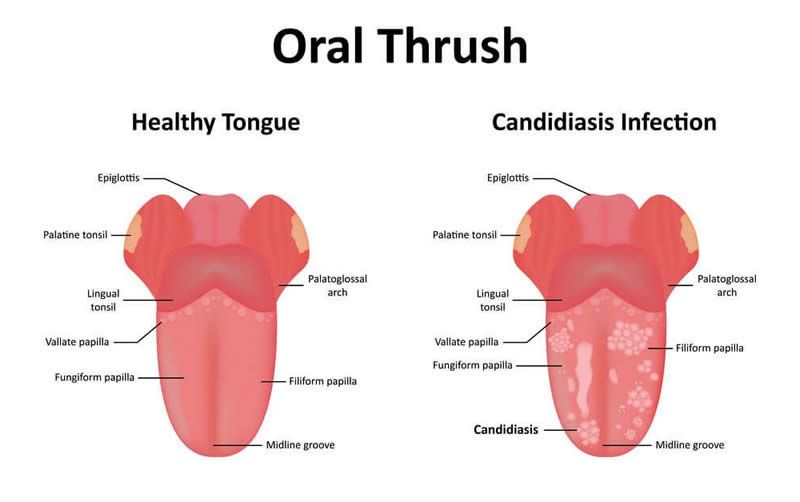 Moreover, their presence encourages beneficial bacteria to become stronger and more competitive. However, when the body weakens, they begin to multiply actively and cause disease. Candidiasis can occur:
Moreover, their presence encourages beneficial bacteria to become stronger and more competitive. However, when the body weakens, they begin to multiply actively and cause disease. Candidiasis can occur:
- as a result of wearing synthetic underwear, mechanical damage to the vagina, or a contraceptive method such as an intrauterine device; nine0030
- as a concomitant disease in other, more global pathologies: diabetes mellitus, immunodeficiency states, allergies, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and genitourinary system, oncology;
- due to taking medications: antibiotics, corticosteroids, chemotherapy, as well as during radiation therapy;
- during menstruation. Thrush also often occurs during pregnancy, as the woman's immunity weakens at this time. nine0047
- flucanosole,
- clotrimazole,
- levomekol
- flucostat,
- nystatin,
- pimafucin, etc.

- Do not use pads every day. It is also recommended to avoid wearing underwear made of synthetic fabrics.

Diagnosis of vaginal candidiasis
Pathology is detected on the basis of the woman's complaints and medical examination, as well as laboratory tests. Microscopy of vaginal smears and serological diagnostics are carried out. Cultural and molecular biological methods are also used.
Cultural and molecular biological methods are also used.
When diagnosing vaginal candidiasis, it is very important to differentiate it from other pathologies, such as genital herpes, aerobic vaginitis, as well as eczema, lichen planus, etc. nine0003
Important! For successful treatment, it is necessary to correctly identify the disease and its causes. Only then the drugs will be selected correctly. Having made a mistake when making a diagnosis and starting to be treated on her own, a woman can harm herself. In addition, with vaginal candidiasis, drugs are prescribed depending on the degree of damage and other factors. Therefore, if you experience discomfort, it is recommended to contact the clinic.
How thrush is treated
Antifungals interfere with the synthesis of ergosterol, which is found in microorganism cells. As a result, they either slow down their growth or die completely. For the treatment of thrush use:
Doctors select drugs from different groups (antibiotics, triazoles, combined drugs, etc.), since each patient may have a different clinical picture.
Topical preparations are commonly used in the treatment of acute vaginal candidiasis. They do not enter the blood, but act locally. These include suppositories, creams, ointments, vaginal tablets. For example, econazole, clindacin, macmiror. In a chronic process, drugs in the form of tablets are connected. nine0003
Important! During pregnancy and lactation, many drugs are either categorically contraindicated, or can only be used under medical supervision.
Some women experience a lack of effectiveness of drugs. This is because candida forms a substance that coats the colony and protects it from the effects of drugs. In such cases, the gynecologist corrects the treatment by prescribing drugs that can overcome the protective film.
Sequelae of vaginal candidiasis
If you see a doctor in time, the outcome of the treatment of vaginal thrush is usually favorable. If you start the disease or choose drugs on your own, the process can become chronic. In addition, as a result of unsuccessful treatment, microorganisms often become resistant to the antibiotic.
If you start the disease or choose drugs on your own, the process can become chronic. In addition, as a result of unsuccessful treatment, microorganisms often become resistant to the antibiotic.
It happens in the following way. An incorrectly selected medicine does not have a strong enough effect on fungal microorganisms. Some of them survive, while beneficial bacteria that help the immune system destroy pathogenic microflora die. There is nothing to stop Candida from multiplying, and it also passes on its antibiotic resistance to the next generation. As a result, the drug stops working. nine0003
To avoid this, you should adhere to the treatment regimen prescribed by the gynecologist based on the examination and tests. In addition, it is necessary to protect yourself with barrier methods of contraception or refrain from sexual activity for a while.