The start of a miscarriage
Miscarriage - NHS
A miscarriage is the loss of a pregnancy during the first 23 weeks.
Symptoms of a miscarriage
The main sign of a miscarriage is vaginal bleeding, which may be followed by cramping and pain in your lower abdomen.
If you have vaginal bleeding, contact a GP or your midwife.
Most GPs can refer you to an early pregnancy unit at your local hospital straight away if necessary.
You may be referred to a maternity ward if your pregnancy is at a later stage.
But bear in mind that light vaginal bleeding is relatively common during the first trimester (first 3 months) of pregnancy and does not necessarily mean you're having a miscarriage.
Causes of a miscarriage
There are potentially many reasons why a miscarriage may happen, although the cause is not usually identified.
The majority are not caused by anything you have done.
It's thought most miscarriages are caused by abnormal chromosomes in the baby.
Chromosomes are genetic "building blocks" that guide the development of a baby.
If a baby has too many or not enough chromosomes, it will not develop properly.
In most cases, a miscarriage is a one-off event and most people go on to have a successful pregnancy in the future.
Preventing a miscarriage
The majority of miscarriages cannot be prevented.
But there are some things you can do to reduce the risk of a miscarriage.
Avoid smoking, drinking alcohol and using drugs while pregnant.
Being a healthy weight before getting pregnant, eating a healthy diet and reducing your risk of infection can also help.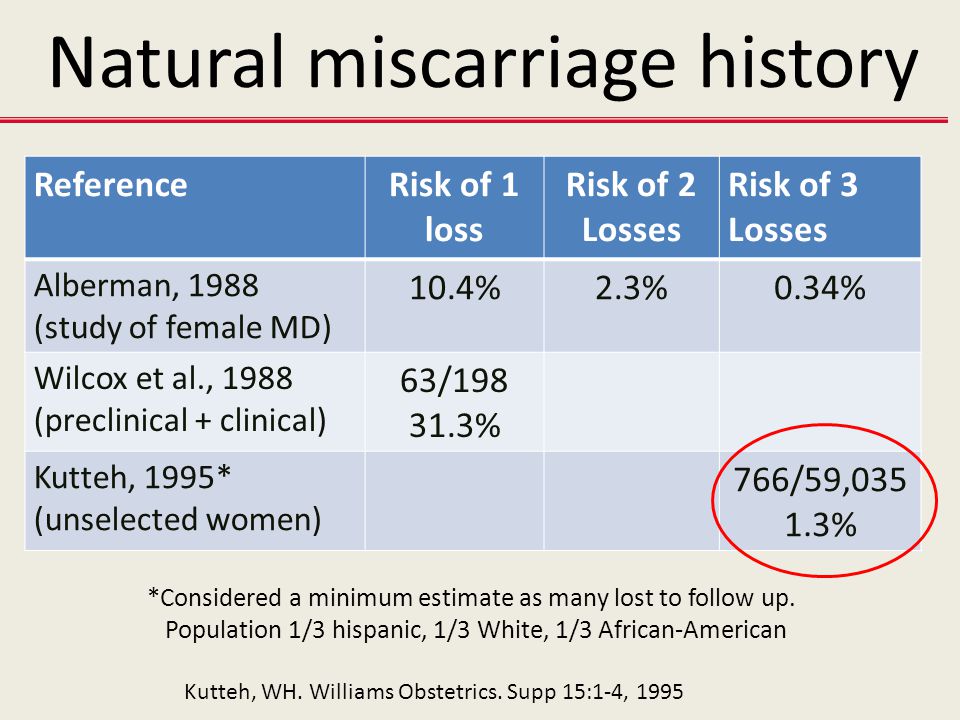
What happens if you think you're having a miscarriage
If you have the symptoms of a miscarriage, you'll usually be referred to a hospital for tests.
In most cases, an ultrasound scan can determine if you're having a miscarriage.
When a miscarriage is confirmed, you'll need to talk to your doctor or midwife about the options for the management of the end of the pregnancy.
Often the pregnancy tissue will pass out naturally in 1 or 2 weeks.
Sometimes medicine to assist the passage of the tissue may be recommended, or you can choose to have minor surgery to remove it if you do not want to wait.
After a miscarriage
A miscarriage can be an emotionally and physically draining experience.
You may have feelings of guilt, shock and anger.
Advice and support are available at this time from hospital counselling services and charity groups.
You may also find it beneficial to have a memorial for the baby you lost.
You can try for another baby as soon as your symptoms have settled and you're emotionally and physically ready.
It's important to remember that most miscarriages are a one-off and are followed by a healthy pregnancy.
How common are miscarriages?
Miscarriages are much more common than most people realise.
Among people who know they're pregnant, it's estimated about 1 in 8 pregnancies will end in miscarriage.
Many more miscarriages happen before a person is even aware they're pregnant.
Losing 3 or more pregnancies in a row (recurrent miscarriages) is uncommon and only affects around 1 in 100 women.
Page last reviewed: 09 March 2022
Next review due: 09 March 2025
Miscarriage | Pregnancy Birth and Baby
The loss of a baby through miscarriage can be very distressing. A miscarriage generally occurs for reasons outside your control and nothing can be done to prevent or stop it from happening. Most women who have had a miscarriage will go on to have a healthy pregnancy in the future.
What is a miscarriage?
A miscarriage is the loss of your baby before 20 weeks of pregnancy. The loss of a baby after 20 weeks is called a stillbirth.
Up to 1 in 5 confirmed pregnancies end in miscarriage before 20 weeks, but many other women miscarry without having realised they are pregnant.
Common signs of miscarriage include:
- cramping tummy pain, similar to period pain
- vaginal bleeding
If you think you are having a miscarriage, see your doctor or go to your local emergency department.
Many women experience vaginal spotting in the first trimester that does not result in pregnancy loss.
What are the types of miscarriage?
There are several types of miscarriage — threatened, inevitable, complete, incomplete or missed.
Other types of pregnancy loss include an ectopic pregnancy, molar pregnancy and a blighted ovum.
Threatened miscarriage
When your body is showing signs that you might miscarry, that is called a 'threatened miscarriage'. You may have light vaginal bleeding or lower abdominal pain. It can last days or weeks and the cervix is still closed.
The pain and bleeding may resolve and you can go on to have a healthy pregnancy and baby. Or things may get worse and you go on to have a miscarriage.
There is rarely anything a doctor, midwife or you can do to prevent a miscarriage. In the past bed rest was recommended, but there is no scientific proof that this helps at this stage.
Inevitable miscarriage
Inevitable miscarriages can come after a threatened miscarriage or without warning.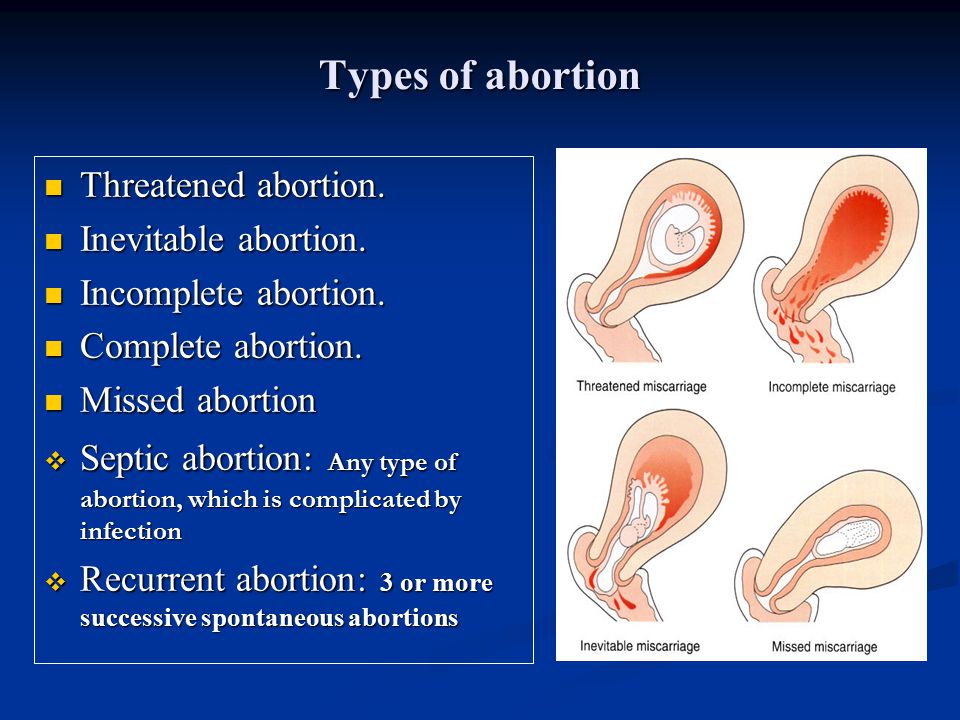 There is usually a lot more vaginal bleeding and strong lower stomach cramps. During the miscarriage your cervix opens and the developing fetus will come away in the bleeding.
There is usually a lot more vaginal bleeding and strong lower stomach cramps. During the miscarriage your cervix opens and the developing fetus will come away in the bleeding.
Complete miscarriage
A complete miscarriage has taken place when all the pregnancy tissue has left your uterus. Vaginal bleeding may continue for several days. Cramping pain much like labour or strong period pain is common — this is the uterus contracting to empty.
If you have miscarried at home or somewhere else with no health workers present, you should have a check-up with a doctor or midwife to make sure the miscarriage is complete.
Incomplete miscarriage
Sometimes, some pregnancy tissue will remain in the uterus. Vaginal bleeding and lower abdominal cramping may continue as the uterus continues trying to empty itself. This is known as an 'incomplete miscarriage'.
Your doctor or midwife will need to assess whether or not a short procedure called a ‘dilatation of the cervix and curettage of the uterus’ (often known as a ‘D&C’) is necessary to remove any remaining pregnancy tissue. This is an important medical procedure done in an operating theatre.
This is an important medical procedure done in an operating theatre.
Missed miscarriage
Sometimes, the fetus has died but stayed in the uterus. This is known as a 'missed miscarriage'.
If you have a missed miscarriage, you may have a brownish discharge. Some of the symptoms of pregnancy, such as nausea and tiredness, may have faded. You might have noticed nothing unusual. You may be shocked to have a scan and find the fetus has died.
If this happens, you should discuss treatment and support options with your doctor.
Recurrent miscarriage
A small number of women have repeated miscarriages. If this is your third or more miscarriage in a row, it’s best to discuss this with your doctor who may be able to investigate the causes, and refer you to a specialist.
A miscarriage can occur suddenly or over a number of weeks. The symptoms are usually vaginal bleeding and lower tummy pain. It is important to see your doctor or go to the emergency department if you have signs of a miscarriage.
The most common sign of a miscarriage is vaginal bleeding, which can vary from light red or brown spotting to heavy bleeding. If it is very early in the pregnancy, you may think that you have your period.
Other signs may include:
- cramping pain in your lower tummy, which can vary from period-like pain to strong labour-like contractions
- passing fluid from your vagina
- passing of blood clots or pregnancy tissue from your vagina
What really happens during a miscarriage?
WARNING — This article contains some graphic descriptions of what you might see during a miscarriage.
What should I do if I think I’m having a miscarriage?
If you are concerned that you are having a miscarriage, call your doctor or midwife for advice and support.
Keep in mind that many women experience vaginal spotting in the first trimester of pregnancy that does not result in a miscarriage.
If you are alone, consider calling your partner or a friend for help and support.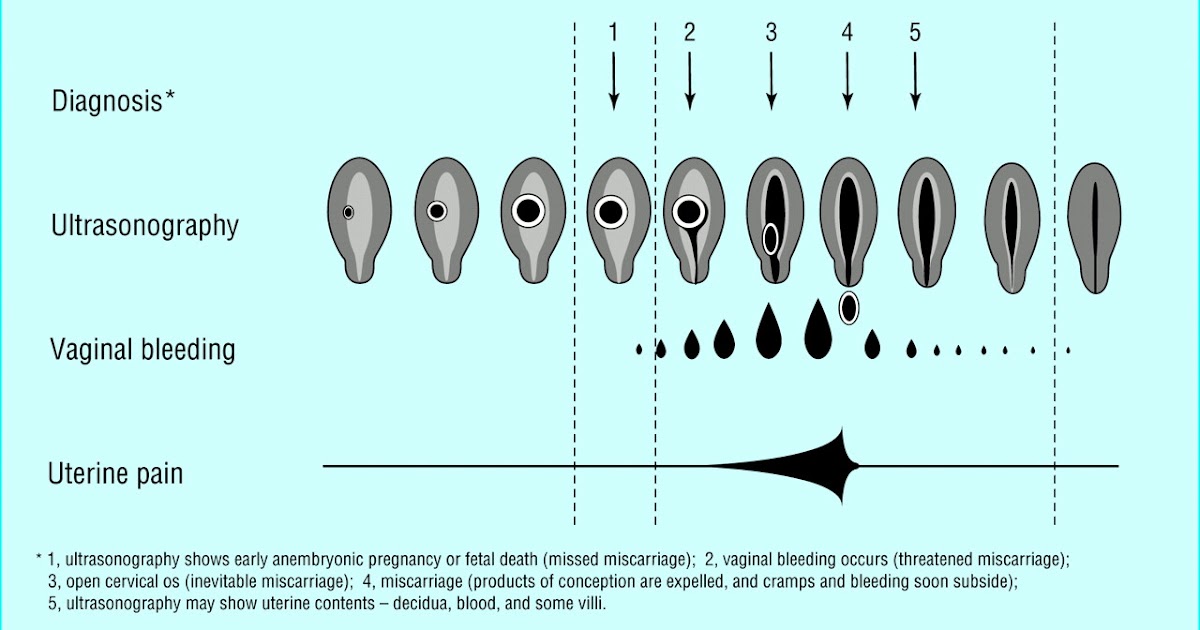
If you have very heavy bleeding, strong pain or feel unwell, call triple zero (000) or have someone take you to your nearest emergency department.
How is a miscarriage managed?
Unfortunately, nothing can prevent a miscarriage from happening once it has begun. What happens now depends on your own health and what is happening to you.
Each approach has benefits and risks. You should discuss these with your doctor.
Expectant or natural management
Also called ‘watch and wait’, expectant management may be recommended in early pregnancy. This involves going home and waiting until the pregnancy tissue has passed from your womb by itself. This can happen quickly, or it may take a few weeks.
Medical management
You may be offered medication that speeds up the passing of the pregnancy tissue. You may be asked to stay in hospital until the tissue has passed, or you may be advised to go home.
Surgical management
You may be advised to have a form of minor surgery called a 'dilatation and curettage' (also called a D&C or a curette).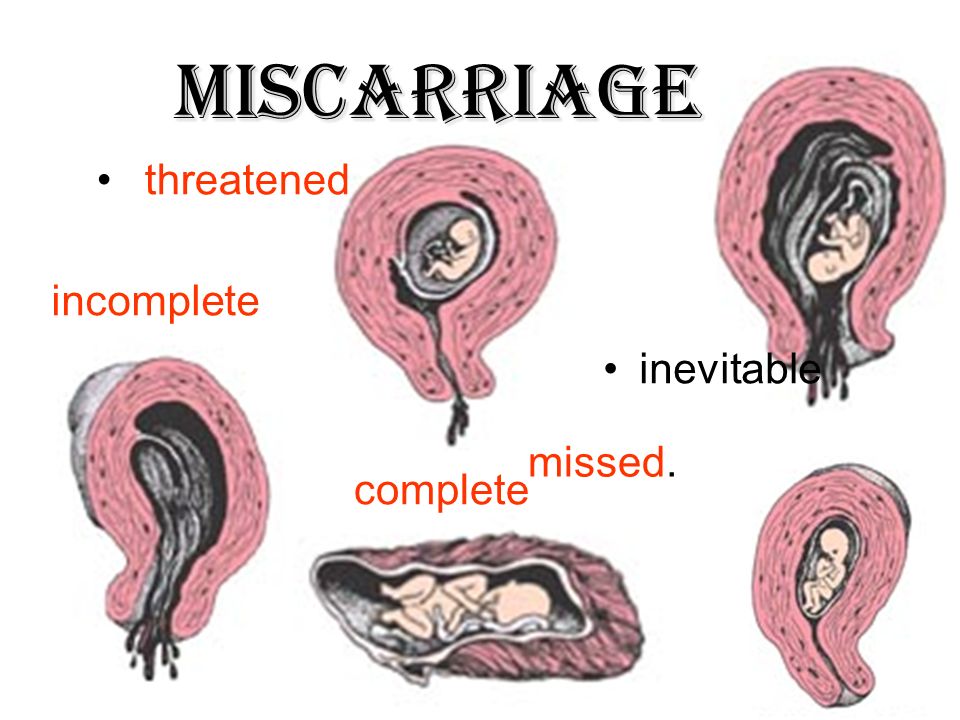 This procedure is often recommended if you have heavy bleeding, significant pain or signs of infection. It may also be recommended if expectant or medical management has failed. You may also decide that you prefer this option.
This procedure is often recommended if you have heavy bleeding, significant pain or signs of infection. It may also be recommended if expectant or medical management has failed. You may also decide that you prefer this option.
This procedure is done under general anaesthesia in an operating theatre. It takes 5-10 minutes once you are asleep. The doctor opens the cervix and removes the remaining pregnancy tissue.
How is a miscarriage treated?
Once it is confirmed that you are having a miscarriage, your doctor may offer or recommend treatment. There are many options. All have benefits and risks — discuss these with your doctor.
If the miscarriage is complete
If it seems the miscarriage is complete, you should still see your doctor for a check-up. You may be advised to have an ultrasound to make sure your uterus is empty.
If you go to hospital
If you go to your hospital’s emergency department, you will be seen first by a triage nurse, who will assess how urgently you need to be seen by a doctor. Depending on your symptoms, you will either be taken in to see a doctor immediately, or you will be asked to wait.
Depending on your symptoms, you will either be taken in to see a doctor immediately, or you will be asked to wait.
If you are waiting to be seen and your symptoms become worse or you feel like you need to go to the toilet, let the staff know immediately.
What happens if I miscarry at home?
Some women miscarry at home before they have a chance to see their doctor or get to the hospital.
If this happens, then:
- use pads to manage the bleeding
- if you can, save any pregnancy tissue that you pass, as your doctor may recommend it is tested to see why your miscarriage happened
- take medications such as paracetamol if you have pain
- rest
- call your doctor or midwife
There is a chance you may see your baby in the tissue that you pass, but often the baby is too small to recognise, or may not be found at all. It is normal to want to look at the remains, but you may decide you do not want to. There is no right or wrong thing to do.
Some women miscarry while on the toilet. This can also happen if you are out and about, or in hospital. There is no right or wrong way to handle this.
Why do miscarriages happen?
Many women wonder if their miscarriage was their fault. In most cases, a miscarriage has nothing to do with anything you have or have not done. There is no evidence that exercising, stress, working or having sex causes a miscarriage.
Most parents do not ever find out the exact cause. However, it is known that miscarriages often happen because the baby fails to develop properly, usually due to a chromosomal abnormality that was spontaneous, not inherited.
Occasionally, miscarriage is caused by:
- hormonal abnormalities
- immune system and blood clotting problems
- medical conditions such as thyroid problems or diabetes
- severe infections causing high fevers (not common colds)
- physical problems with your womb or cervix
What are the risk factors for miscarriage?
Women are more likely to have miscarriages if they:
- are older
- smoke
- drink alcohol in the first trimester
- drink too much caffeine in coffee, tea or energy drinks
- have had several previous miscarriages
Can you prevent a miscarriage?
Living healthily — no cigarettes, no alcohol and little to no caffeine — can decrease your risk of miscarriage. It’s a good idea to avoid contact with people who have a serious infectious illness when you’re pregnant.
It’s a good idea to avoid contact with people who have a serious infectious illness when you’re pregnant.
Who can I talk to for advice and support?
Talk to your doctor or midwife for information and advice on what do and how to look after yourself if you experience a miscarriage.
Your hospital should be able to provide details of available support services, such as bereavement support.
SANDS is an independent organisation that provides support for miscarriage, stillbirth and newborn death. You can call them on 1300 072 637 or visit www.sands.org.au.
You can also call Pregnancy, Birth and Baby on 1800 882 436, 7am to midnight (AET) to speak to a maternal child health nurse for advice and emotional support.
Speak to a maternal child health nurse
Call Pregnancy, Birth and Baby to speak to a maternal child health nurse on 1800 882 436 or video call. Available 7am to midnight (AET), 7 days a week.
Learn more here about the development and quality assurance of healthdirect content.
Miscarriage, symptoms - Health Clinic 365 Yekaterinburg
Causes of miscarriage
Questions to the doctor about miscarriage
Diagnosis of miscarriage
Treatment and prevention of miscarriage
According to statistics, 10 to 20% of all pregnancies end in miscarriage. However, the real numbers could be much higher, as a large number of miscarriages happen very early, and women are not even aware of their pregnancy. Most miscarriages happen due to abnormal development of the fetus.
Miscarriage is quite common, but this fact does not make things any easier. It is always difficult to cope with the realization that there was a pregnancy, but no child. Try to deal with the situation psychologically and understand what could be causing the miscarriage, what increases the risk of it, and what type of treatment might be needed.
Miscarriage symptoms .
Most miscarriages occur before 12 weeks. Signs and symptoms of a miscarriage include:
- Vaginal bleeding or spotting (although quite common in early pregnancy)
- Pain or cramps in the abdomen or lower back
- Fluid vaginal discharge or tissue fragments
It is important to consider the fact that in early pregnancy, spotting or vaginal bleeding is quite common. In most cases, women who experience light bleeding during the first three months have an uneventful pregnancy thereafter. In some cases, even with heavy bleeding, the pregnancy does not end in a miscarriage.
In most cases, women who experience light bleeding during the first three months have an uneventful pregnancy thereafter. In some cases, even with heavy bleeding, the pregnancy does not end in a miscarriage.
Some women who have a miscarriage develop an infection in the uterus. This infection, also called septic miscarriage, can cause:
- Fever (feeling hot, chills)
- Body pains
- Thick, foul-smelling vaginal discharge
When to see a doctor.
Call your doctor if:
- Bleeding, even if only light spotting occurs
- Profuse, liquid vaginal discharge without pain or bleeding
- Isolation of tissue fragments from the vagina
You can put a piece of tissue to be isolated in a clean container and take it to your doctor for examination. It is unlikely that the study will give any accurate results, but if it is determined that the fragments of the excreted tissue are from the placenta, the doctor will be able to conclude that the symptoms that appear are not associated with the presence of a tubal (ectopic) pregnancy.
You can get more detailed information about miscarriage from the gynecologists of the Health 365 clinic in Yekaterinburg.
Prices
Gynecologist, initial appointment
2300 i
Early miscarriage - symptoms and how to prevent it
The term "early miscarriage" refers to a spontaneous abortion that occurs in the first 6-8 weeks of pregnancy. It can occur before 20 weeks of pregnancy for reasons related to the natural states of the fair sex. According to statistics, the logical outcome of every fifth pregnancy is a miscarriage. However, quite often a woman does not even know that she was pregnant by the time the fetus is rejected by the body.
In addition, a curious pattern was revealed: more often than a natural one, a pregnancy induced artificially ends in a miscarriage. For example, in vitro fertilization, unfortunately, does not always lead to a successful pregnancy and the birth of a baby on time.
Why can an early miscarriage occur?
Here are the most common causes, each of which significantly increases the risk of miscarriage:
- the future mother has some infectious diseases, as well as STDs;
- intoxication of a woman's body for various reasons, including as a result of her living in an ecologically unfavorable region;
- all kinds of metabolic disorders in the body;
- hormonal disruptions, including those caused by a malfunction of the thyroid gland;
- various neoplasms in the uterus and others, as well as the cervix, pathologies;
- future mother leading a life far from a healthy lifestyle. May include drinking alcohol, smoking, taking psychotropic and narcotic drugs, as well as malnutrition;
- obesity;
- immune status disorders;
- cardiac diseases;
- diabetes mellitus;
- too early for pregnancy or, conversely, the patient's overly mature age at times increases the risk of miscarriage;
- various pathologies of chromosomes and genes;
- prolonged exposure to stress or severe psycho-emotional trauma in a woman.

The timing of a miscarriage may depend, among other things, on the patient's genetic predisposition to miscarriage. Finally, often its specific cause remains unexplained to the end.
Symptoms of miscarriage
A pregnant woman should urgently seek medical help if she has the following warning signs:
- bleeding from the vagina;
- spotting discharge from the genital tract. They can have both light pink and intense red or brownish tint;
- convulsions;
- severe pain in the lumbar region;
- abdominal pain, etc.
All of the above signs can be symptoms of a miscarriage. Timely provision of qualified medical care is the key to maintaining pregnancy.
Life after miscarriage
If a woman could not bear the pregnancy - an early miscarriage crossed out all her plans - then she needs to calm down and take all measures to prevent such complications in the future.