Symptoms after ovulation day
Early Pregnancy Signs 10 Days Past Ovulation
Ovulation is when the ovaries release a mature egg, and it happens around the 14th day of your menstrual cycle. Although the average cycle is about 28 days long, some people have slightly longer or shorter cycles.
Once the egg is released, you’ll either become pregnant or get your period. The latter occurs when the egg dies (after just one day) and is shed by the body, along with the uterine lining.
Is 10 DPO a good time to take a pregnancy test?
During ovulation, three specific hormones reach peak levels: luteinizing hormone, estrogen, and follicle-stimulating hormone. They’re responsible for triggering the release of an egg each month.
Progesterone levels spike right after ovulation, and this change in hormones can lead to premenstrual syndrome (PMS) symptoms. These include breast tenderness, nausea, fatigue, cramps, headaches, food cravings, and bloating. Progesterone production stops around 10 days past ovulation. Your period should then start around 14 or 15 days after ovulation.
After ovulation, you may experience various symptoms of PMS, whether or not you’re pregnant. If these PMS symptoms disappear at about 10 DPO, you’re probably not pregnant and a test may be unnecessary.
If your period doesn’t come when expected and you’re experiencing potential signs of early pregnancy, it’s a good idea to take a pregnancy test.
After fertilization, implantation usually happens between 6 and 10 days past ovulation. When you’re pregnant, your body secretes human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), a substance that pregnancy tests can detect in your urine (you can use our online hCG calculator to track your hCG levels at home if it turns out you are pregnant). Since hCG levels increase around the date of your missed period, waiting until then to take a pregnancy test will give you the most reliable results. One thing to keep in mind is that some tests are more sensitive than others, and results could be inconsistent.
Common pregnancy symptoms at 10 DPO
While they don’t necessarily indicate pregnancy, some common early-pregnancy symptoms such as fatigue, cramps, breast tenderness, and nausea could pop up after ovulation.
If you decide to take a test and get a negative result but still miss your period, consult with your health care provider. They’ll try to determine the exact cause of these symptoms. In rare cases, these symptoms could indicate an ectopic pregnancy or another medical complication.
If you are pregnant, you’ll likely experience the following symptoms:
Fatigue or exhaustion
Increased levels of progesterone can trigger fatigue, nausea, and constipation, among other things. If you’ve been feeling unusually exhausted, engaging in relaxing activities could help you regain energy. Go for leisurely walks or spend time engaging in your favorite hobbies.
Abdominal cramps
Mild cramping and a dull pressure in the lower abdomen are often early signs of pregnancy. To alleviate the pain, start exercising more, drink plenty of water, get soothing massages, and practice good sleep habits. If your cramps become severe, be sure to visit your health care provider.
To alleviate the pain, start exercising more, drink plenty of water, get soothing massages, and practice good sleep habits. If your cramps become severe, be sure to visit your health care provider.
Digestive issues
Elevated hormone levels can also significantly impact your digestive system. Progesterone is notorious for slowing down digestion as it relaxes smooth muscles throughout the body. This, in turn, leads to occasional gas, constipation, and bloating.
Backaches
Similarly, a spike in progesterone in the first trimester might cause backaches by softening the supporting discs and ligaments of your back. This is how your body naturally prepares itself for pregnancy and childbirth.
Breast tenderness
Both PMS and early pregnancy are marked by tender or swollen breasts due to increased blood flow to tissues in this region.
Nausea
Once again, progesterone is the number one culprit, producing nausea and vomiting. When coupled with gas, bloating, and constipation, it can create a loss of appetite.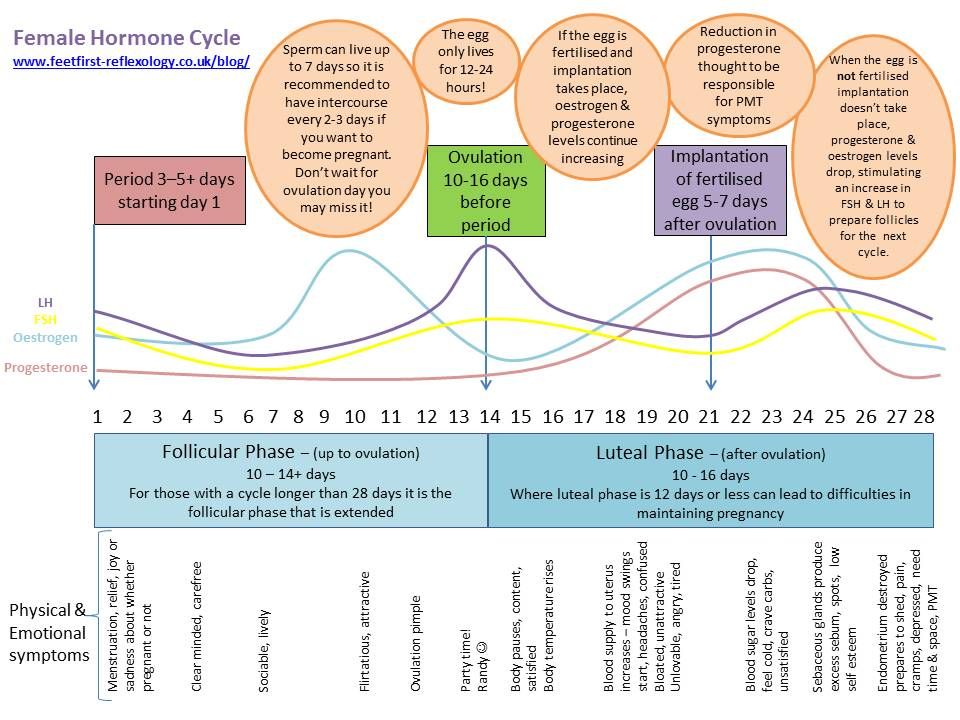
Many people feel nauseous when they’re pregnant thanks to their sensitivity to certain odors like perfume or cigarette smoke. Even the slightest whiff can trigger intense discomfort.
Headaches
Another common symptom in the first trimester is frequent headaches that are brought on by hormonal surges and excessive blood flow.
Is it possible to get positive test results at 10 DPO?
Yes, it is. Certain types of tests are capable of detecting pregnancy five full days before your first missed period. That means you might actually see a 10 days past ovulation BFP (big fat positive).
Which symptoms appear even when you’re not pregnant?
It’s possible to get a 10 DPO BFN (big fat negative) after experiencing early pregnancy symptoms. These might include:
- Mild cramping
- Nausea
- Dizziness
- Swollen or tender breasts
- Headaches
- Hot flashes
- Backaches
- Frequent urination
- Heartburn
If you’ve been trying to conceive and have some of the above symptoms approximately 10 days past ovulation, take a pregnancy test.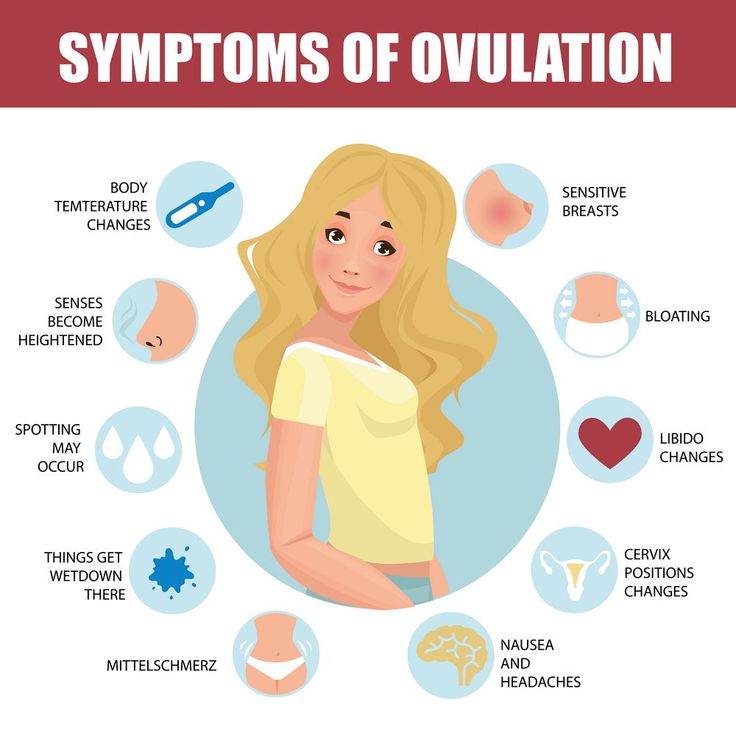 Blood hCG tests are more sensitive than urine hCG tests and can deliver more accurate results at this early stage. If you receive a 10 DPO BFN, take the test again at 11 or 14 DPO, when hCG concentrations should be higher.
Blood hCG tests are more sensitive than urine hCG tests and can deliver more accurate results at this early stage. If you receive a 10 DPO BFN, take the test again at 11 or 14 DPO, when hCG concentrations should be higher.
What to expect in the 2-week wait
For couples trying to get pregnant, the days following ovulation mark the infamously difficult 2-week wait.
However, knowing what is happening in the body, as well as the typical pregnancy symptoms that occur on different days past ovulation (DPO), can make the wait a little easier.
Many women wonder if every twinge and ache could be a sign of pregnancy. However, the early symptoms of pregnancy are often similar to the symptoms of an impending period. Some, like muscle aches and pains, are also a part of everyday life.
It is not possible to know for sure if a woman is pregnant until a pregnancy test confirms it. Also, pregnancy symptoms, and when they occur, vary significantly between individuals.
In this article, we look at what is happening in the body around the time of ovulation, and what early signs women might notice in the early DPO.
While some women experience many early pregnancy symptoms, others experience few or no symptoms at all.
Also, early pregnancy symptoms can be very similar to the symptoms experienced around the time of ovulation, during PMS, and by those taking fertility medications.
This is why DPO symptoms are not a reliable measure of whether or not a woman has become pregnant. Women should talk with a doctor about their specific symptoms.
Days 0–7 past ovulation
Ovulation is the moment an ovary releases an egg.
As soon as an ovary releases an egg, the luteal phase of the menstrual cycle begins. The luteal phase ends with a menstrual period unless pregnancy occurs.
Women will not experience any pregnancy symptoms during the earliest part of the luteal phase. This is because pregnancy does not occur until the fertilized egg implants into the wall of the uterus.
During the luteal phase, the body produces more progesterone, which is a hormone that helps sustain an early pregnancy.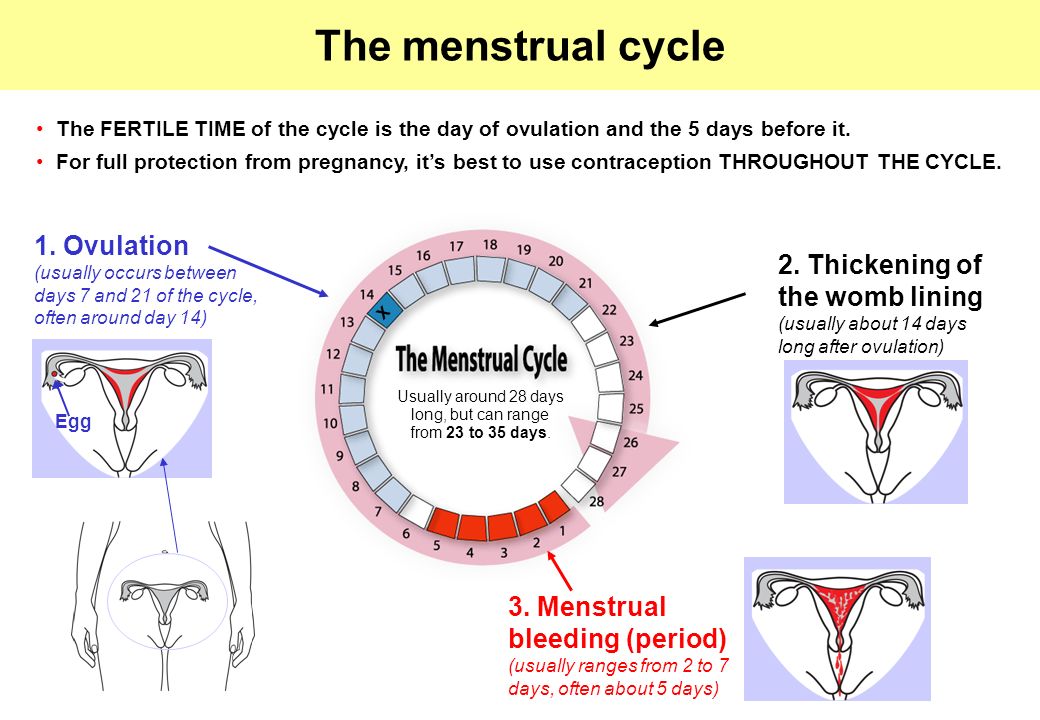 The levels of progesterone peak at 6–8 days after ovulation, even when a woman does not become pregnant.
The levels of progesterone peak at 6–8 days after ovulation, even when a woman does not become pregnant.
Progesterone levels can affect a woman’s mood and body — this means that after a week or so, they may experience similar symptoms in early pregnancy as they do before a period.
When a fertilized egg reaches the uterus, it implants itself into the wall of the uterus. This is called implantation and marks the start of pregnancy. Implantation typically happens 6–12 days after fertilization.
This is the time when women may begin to experience pregnancy symptoms, including:
- breast tenderness
- bloating
- food cravings
- increased nipple sensitivity
- headaches and muscle aches
However, these symptoms may also occur in those who are not pregnant. This is because of the increased levels of progesterone that are present during the last stages of the menstrual cycle.
Days 7–10 past ovulation
When the fertilized egg implants itself in the uterus, around one-third of women will notice light bleeding or spotting, which is called implantation bleeding.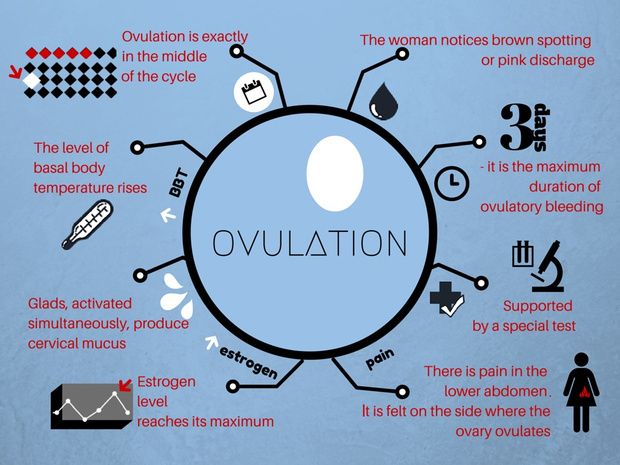
This spotting typically lasts only a day or two and is very light in flow. Implantation bleeding is one of the earliest signs of pregnancy since it happens around the time the woman becomes pregnant.
However, even when a woman notices bleeding around the time of implantation, they may still not get a positive pregnancy test. They may have a very early miscarriage called a chemical pregnancy, or the bleeding might be due to something else.
At implantation, the body begins producing a pregnancy hormone called human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG). Known as the pregnancy hormone, hCG — along with progesterone and estrogen — is responsible for early pregnancy symptoms. It is also the hormone that pregnancy tests identify.
However, it can take several days for hCG to reach to a detectable level, so pregnancy tests may not pick up the hormone, and symptoms may not develop immediately.
Days 11–14 past ovulation
A few days after implantation, hCG levels may be high enough to cause early pregnancy symptoms.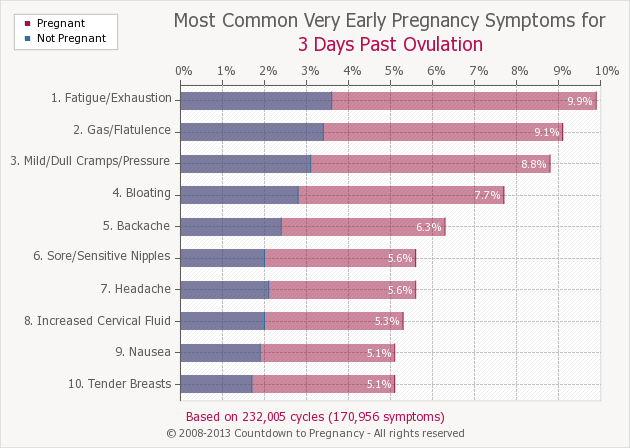 However, this is also the phase of the menstrual cycle when a woman is most likely to experience symptoms that mean they are about to get their period.
However, this is also the phase of the menstrual cycle when a woman is most likely to experience symptoms that mean they are about to get their period.
Women who are aware of how their body behaves each month might be better able to identify whether their symptoms are due to pregnancy or regular menstruation.
Some other symptoms of early pregnancy include:
- darkening in the color of the nipples
- fatigue
- food cravings or increased hunger
- increased need to use the bathroom
- gastrointestinal changes, such as cramping or diarrhea
By the time a woman has experienced several early pregnancy symptoms, it is possible that the hCG levels are high enough that a pregnancy test can indicate a pregnancy. However, hCG levels vary, so this is not always the case.
Share on PinterestNausea is a common symptom of early pregnancy.
As pregnancy progresses and hCG levels rise even more, many women begin experiencing more symptoms.
Some of the most common include:
- dizziness or lightheadedness due to hormonal shifts and changes in the blood pressure and heart rate
- nausea, especially when hungry
- vomiting
- strong aversions to certain foods or smells
- changes in the sense of smell
- fatigue
- bloating and water retention
Whether a woman is trying to get pregnant or trying to avoid a pregnancy, the 2-week wait can be frustrating.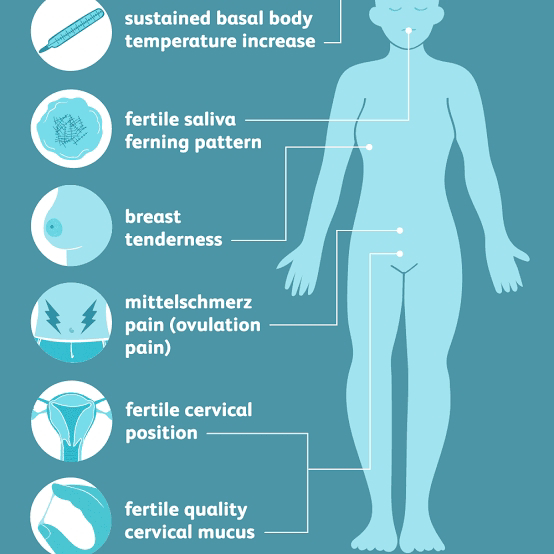
Some women track their ovulation by looking out for physical symptoms or using ovulation tests. It is important to note that the only way to detect ovulation is through medical testing.
However, home ovulation tests can be misleading, particularly if a woman has a condition that affects ovulation.
No symptom alone can confirm early pregnancy, and many women experience no early pregnancy symptoms at all. The only way to establish a pregnancy is by taking a pregnancy test.
Signs of ovulation | Clinic MEdel
OVULATION (from lat. ovum - egg) - release of a mature egg capable of fertilization from the ovarian follicle into the abdominal cavity; stage of the menstrual cycle (ovarian cycle). Ovulation in women of childbearing age occurs periodically (every 21-35 days). The frequency of ovulation is regulated by neurohumoral mechanisms, mainly gonadotropic hormones of the anterior pituitary gland and ovarian follicular hormone. Ovulation contributes to the accumulation of follicular fluid and thinning of the ovarian tissue located above the protruding pole of the follicle. The rhythm of ovulation , which is constant for every woman, undergoes changes within 3 months after an abortion, within a year after childbirth, and also after 40 years, when the body is preparing for the premenopausal period. Stops ovulation with the onset of pregnancy and after the extinction of menstrual function. Setting a deadline ovulation is important when choosing the most effective time for fertilization, artificial insemination and in vitro fertilization.
Ovulation contributes to the accumulation of follicular fluid and thinning of the ovarian tissue located above the protruding pole of the follicle. The rhythm of ovulation , which is constant for every woman, undergoes changes within 3 months after an abortion, within a year after childbirth, and also after 40 years, when the body is preparing for the premenopausal period. Stops ovulation with the onset of pregnancy and after the extinction of menstrual function. Setting a deadline ovulation is important when choosing the most effective time for fertilization, artificial insemination and in vitro fertilization.
Signs of ovulation
Subjective signs of ovulation may be short-term pain in the lower abdomen. objective signs of ovulation are an increase in mucous discharge from the vagina and a decrease in rectal (basal) temperature on the day of ovulation with an increase in it the next day, an increase in the content of progesterone in the blood plasma, etc.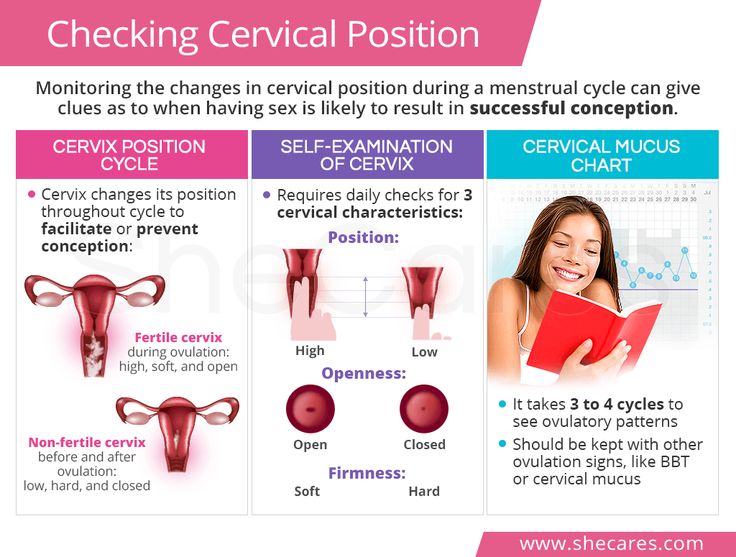 Violation of ovulation is due to dysfunction of the hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian system and can be caused by inflammation of the genitals, dysfunction of the adrenal cortex or thyroid gland, systemic diseases, tumors of the pituitary and hypothalamus , stressful situations. Lack of ovulation at childbearing age (anovulation) is manifested by a violation of the rhythm of menstruation by the type of oligomenorrhea (menstruation lasting 1-2 days), amenorrhea, dysfunctional uterine bleeding. Absence ovulation (anovulation) is always the cause of a woman's infertility. Methods for restoring ovulation are determined by the cause that caused anovulation, and require an appointment with a gynecologist and special treatment.
Violation of ovulation is due to dysfunction of the hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian system and can be caused by inflammation of the genitals, dysfunction of the adrenal cortex or thyroid gland, systemic diseases, tumors of the pituitary and hypothalamus , stressful situations. Lack of ovulation at childbearing age (anovulation) is manifested by a violation of the rhythm of menstruation by the type of oligomenorrhea (menstruation lasting 1-2 days), amenorrhea, dysfunctional uterine bleeding. Absence ovulation (anovulation) is always the cause of a woman's infertility. Methods for restoring ovulation are determined by the cause that caused anovulation, and require an appointment with a gynecologist and special treatment.
Some women experience peak sexual arousal on days 90,003 of ovulation 90,004. However, the use of a physiological method of contraception against pregnancy, based on sexual abstinence during ovulation , is especially difficult for young spouses, whose frequency of sexual intercourse reaches a fairly high level.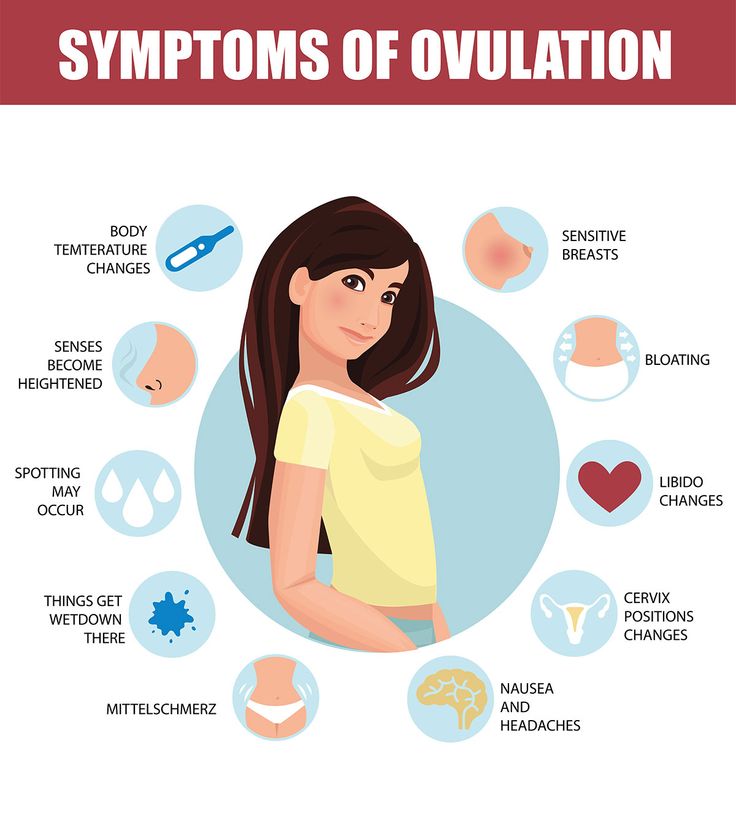 In addition, with strong love excitement and nervous stress, additional ovulation can occur (especially with episodic, irregular intercourse), and then not one, but two eggs mature in one menstrual cycle. This should be remembered when choosing one or another method of contraception.
In addition, with strong love excitement and nervous stress, additional ovulation can occur (especially with episodic, irregular intercourse), and then not one, but two eggs mature in one menstrual cycle. This should be remembered when choosing one or another method of contraception.
As soon as every healthy girl at the age of 11-15 begins to menstruate, which is an indicator of her body's readiness for childbearing, then there are problems associated with counting the days of the menstrual cycle and the legitimate question why menstruation does not occur, or vice versa, why the long-awaited pregnancy does not occur. . This makes a woman think and wait all the time, be in the dark about what happens to her every month. And so every month for decades.
Length of menstruation and cycle
Ideal menstruation lasts 3-5 days and repeats every 28 days. However, for some women, this cycle takes 19 days or even less, while for others it lasts from 35 to 45 days, which is a feature of their body, and not a violation of menstrual function. The duration of menstruation also, depending on the organism, can vary within a week. All this should not cause alarm in a woman, but a delay of more than two months, called opsometry or more than six months - amenorrhea, should alert the woman and make sure to find out the cause with a gynecologist.
The duration of menstruation also, depending on the organism, can vary within a week. All this should not cause alarm in a woman, but a delay of more than two months, called opsometry or more than six months - amenorrhea, should alert the woman and make sure to find out the cause with a gynecologist.
Length of menstrual cycle
The menstrual cycle is a complex physiological process that continues in women up to 45-55 years. It is regulated by the so-called sex centers located in the middle part of the diencephalon - the hypothalamus. The changes that occur during the menstrual cycle are most pronounced in the uterus and ovaries. In the ovary, under the influence of hormones produced by the ovarian follicles, partly by the adrenal cortex and testes, the main follicle, which contains the egg, grows and matures. The mature follicle ruptures and the egg, together with the follicular fluid, enters the abdominal cavity, and then into the fallopian tube. The process of rupture of the follicle and the release of a mature (suitable for fertilization) egg from its cavity is called ovulation , which, with a 28-day cycle, occurs most often between the 13th and 15th days.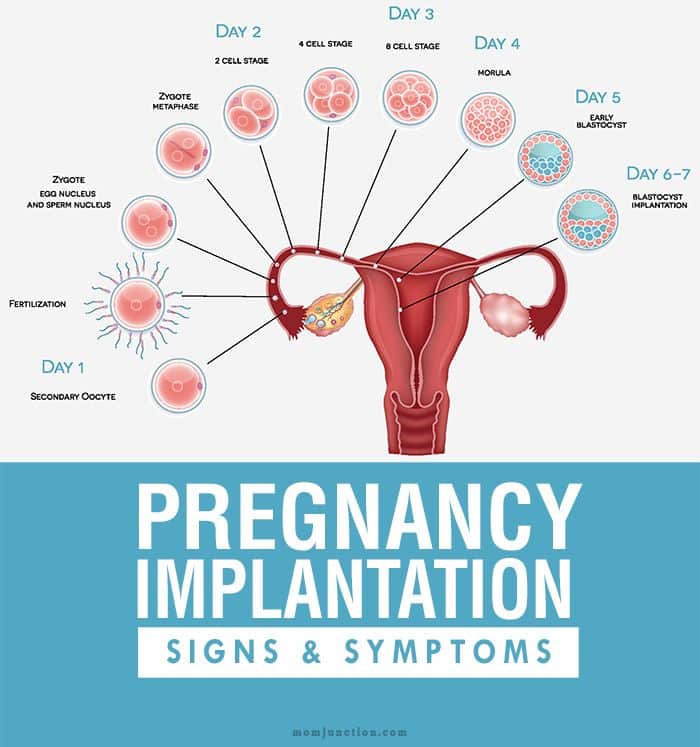
Corpus luteum, estrogen, progesterone
A corpus luteum forms at the site of the ruptured follicle. These morphological changes in the ovary are accompanied by the release of sex steroid hormones - estrogens and progesterone. Estrogens are secreted by the maturing follicle, and progesterone by the corpus luteum.
The release of estrogen has two maxima - during ovulation and during the period of maximum activity of the corpus luteum. So, for example, if the normal estrogen content is about 10 µg/l, then during ovulation it is about 50 µg/l, and during pregnancy, especially towards the end of it, the estrogen content in the blood increases to 70-80 µg/l per due to a sharp increase in the biosynthesis of estrogens in the placenta.
Together with progesterone, estrogens promote the implantation (introduction) of a fertilized egg, maintain pregnancy and promote childbirth. Estrogens play an important role in the regulation of many biochemical processes, are involved in carbohydrate metabolism, lipid distribution, stimulate the synthesis of amino acids, nucleic acids and proteins. Estrogens contribute to the deposition of calcium in bone tissue, delay the release of sodium, potassium, phosphorus and water from the body, that is, increase their concentration both in the blood and in electrolytes (urine, saliva, nasal secretions, tears) of the body.
Estrogens contribute to the deposition of calcium in bone tissue, delay the release of sodium, potassium, phosphorus and water from the body, that is, increase their concentration both in the blood and in electrolytes (urine, saliva, nasal secretions, tears) of the body.
The secretion of estrogens is controlled by the anterior pituitary gland and its genadotropic hormones: follicle-stimulating (FSH) and luteinizing (LH).
Under the influence of estrogens in the first phase of the menstrual cycle, called folliculin, regeneration occurs in the uterus, that is, the restoration and growth of its mucous membrane - the endometrium, the growth of glands that stretch in length and become convoluted. The mucous membrane of the uterus thickens 4-5 times. In the glands of the cervix, the secretion of mucous secretion increases, the cervical canal expands, and becomes easily passable for spermatozoa. In the mammary glands, the epithelium grows inside the milk ducts.
In the second phase, called luteal (from the Latin word luteus - yellow), under the influence of progesterone, the intensity of metabolic processes in the body decreases. The growth of the mucous membrane of the body of the uterus stops, it becomes loose, edematous, a secret appears in the glands, which creates favorable conditions for attaching a fertilized egg to the mucous membrane and developing the embryo. The glands stop secreting mucus, the cervical canal closes. In the mammary glands, from the overgrown epithelium of the end sections of the milk ducts, alveoli arise, capable of producing and secreting milk.
The growth of the mucous membrane of the body of the uterus stops, it becomes loose, edematous, a secret appears in the glands, which creates favorable conditions for attaching a fertilized egg to the mucous membrane and developing the embryo. The glands stop secreting mucus, the cervical canal closes. In the mammary glands, from the overgrown epithelium of the end sections of the milk ducts, alveoli arise, capable of producing and secreting milk.
If pregnancy does not occur, the corpus luteum dies, the functional layer of the endometrium is rejected, and menstruation occurs. Monthly bleeding varies from three to seven days, the amount of blood lost is from 40 to 150 g.
It should be noted that different women have a noticeable difference in the timing of ovulation . And even for the same woman, the exact timing of the onset fluctuates in different months. In some women, cycles are characterized by exceptional irregularity. In other cases, cycles may be longer or shorter than the average - 14 days. In rare cases, it happens that in women with a very short cycle ovulation occurs around the end of the period of menstrual bleeding, but still, in most cases, ovulation occurs quite regularly.
In rare cases, it happens that in women with a very short cycle ovulation occurs around the end of the period of menstrual bleeding, but still, in most cases, ovulation occurs quite regularly.
If, for one reason or another, ovulation does not occur , the endometrial layer in the uterus is thrown out during menstruation. If the fusion of the egg and sperm has occurred, then the cytoplasm of the egg begins to vibrate very strongly, as if the egg is experiencing an orgasm. Sperm penetration is the final stages of egg maturation. All that remains of a spermatozoon is its nucleus, where 23 chromosomes are densely packed (half the set of a normal cell). The sperm nucleus is now rapidly approaching the egg nucleus, which also contains 23 chromosomes. The two cores are slowly touching. Their shells dissolve and they merge, as a result of which they are divided into pairs and form 46 chromosomes. Of the 23 chromosomes of the sperm, 22 are completely analogous to the chromosomes of the egg. They determine all the physical characteristics of a person except gender. In the remaining pair from the egg there is always an X chromosome, and from the sperm there can be an X or Y chromosome. Thus, if there are 2 XX chromosomes in this set, then a girl will be born, if XY, then a boy.
They determine all the physical characteristics of a person except gender. In the remaining pair from the egg there is always an X chromosome, and from the sperm there can be an X or Y chromosome. Thus, if there are 2 XX chromosomes in this set, then a girl will be born, if XY, then a boy.
Studies conducted at the National Institute of Environmental Medical Problems (North Carolina) showed that the time of conception in relation to the time of onset of ovulation depends not only on the actual conception of a child, but also on its gender.
The probability of conception is maximum on day of ovulation and is estimated at about 33%. A high probability is also noted on the day before ovulation - 31%, two days before it - 27%. Five days before ovulation the probability of conception is estimated to be 10% four days before ovulation - 14% and three days - 16%. Six days before ovulation and the day after ovulation, the probability of conception during sexual intercourse is very small.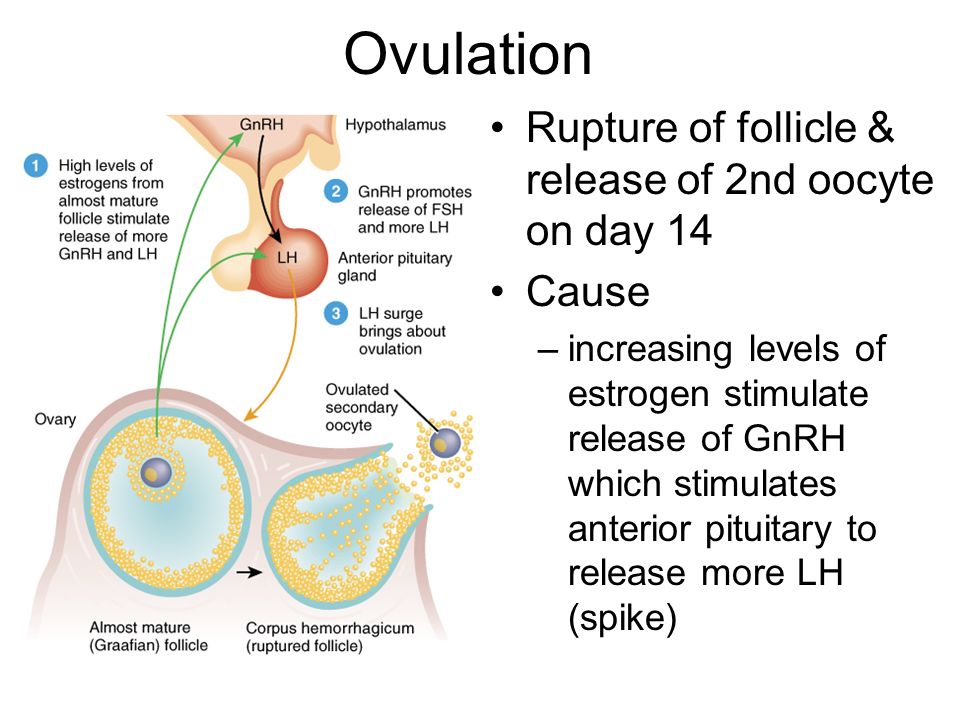
Considering that the average “lifespan” of spermatozoa is 2-3 days (in rare cases it reaches 5-7 days), and the female egg remains viable for about 12-24 hours, then the maximum duration of the “dangerous” period is 6- 9days and the “dangerous” period corresponds to the phase of slow rise (6-7 days) and rapid decline (1-2 days) before and after the day of ovulation , respectively. Ovulation , as noted above, divides the menstrual cycle into two phases: the follicle maturation phase, which, with an average cycle duration of 10-16 days, and the luteal phase (corpus luteum phase), which is stable, independent of the duration of the menstrual cycle and is 12-16 days. The phase of the corpus luteum is referred to as the period of absolute infertility, it begins 1-2 days after ovulation and ends with the onset of a new menstruation.
Causes and symptoms of late ovulation: is it common?
During ovulation, one of the ovaries releases an egg.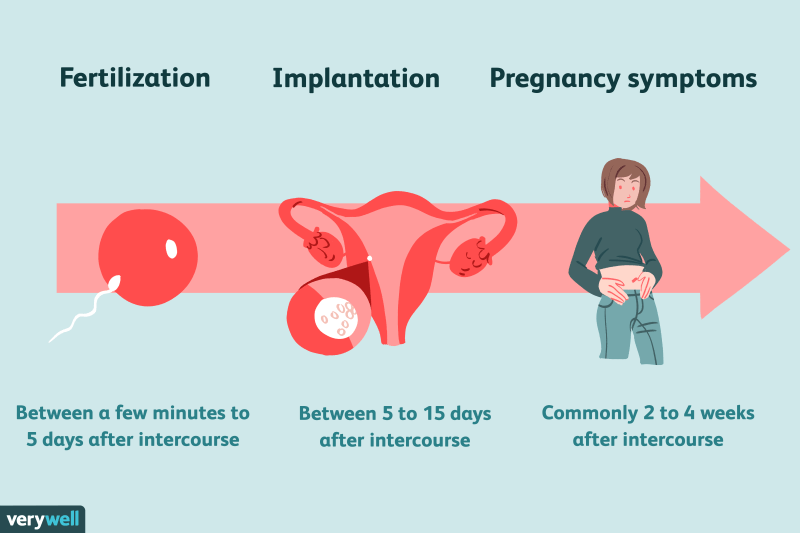 It enters the fallopian tube, where it can be fertilized by sperm. If fertilization has occurred, the resulting zygote attaches itself to the lining of the uterus.
It enters the fallopian tube, where it can be fertilized by sperm. If fertilization has occurred, the resulting zygote attaches itself to the lining of the uterus.
If fertilization does not occur, the egg is shed from the body along with the lining of the uterus during menstruation.
Women with a 28-day menstrual cycle will ovulate around day 14. Therefore, with a regular cycle, ovulation occurs about 14 days before the next period.
This makes it much easier for women with regular cycles to keep track of their periods and ovulation.
If you want to get pregnant, you are more likely to conceive if you have sex on the day of ovulation or within 5 days before it.
Is it common to ovulate late? Many women have irregular cycles. According to the study, only 10% of women ovulated on the 14th day. So 28 days is just an average. The duration of your cycle can normally be from 21 to 35 days. This doesn't mean you're less fertile, but it can make it harder to predict when you'll ovulate.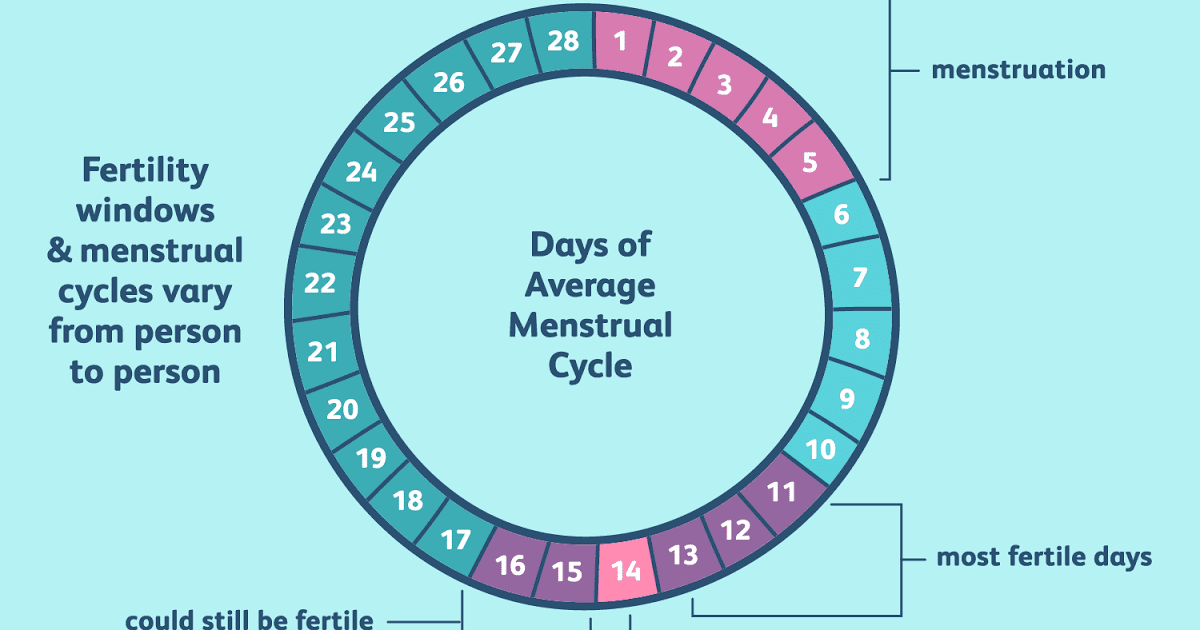 In addition, with an irregular cycle, it is more difficult to determine when sex is most likely to lead to conception.
In addition, with an irregular cycle, it is more difficult to determine when sex is most likely to lead to conception.
If ovulation occurs after the 21st day of the cycle, it can be considered late.
Late ovulation has many causes. Here are the most common ones.
Medicines
Some medicines may affect ovulation and fertility. These include:
- antidepressants;
- chemotherapy preparations for oncology;
- thyroid medicines;
- steroids.
See Patient Information or talk to your doctor if you think a medication you are taking may be affecting your ovulation or fertility.
Breastfeeding
One of the natural results of breastfeeding is a change in the menstrual cycle. During the entire period of breastfeeding, periods may be absent or irregular. Accordingly, ovulation may not occur.
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a common condition that affects the functioning of the ovaries.
Main signs of PCOS:
- irregular menses;
- high levels of male sex hormones;
- enlarged ovaries with many follicles.
In women with PCOS, follicle maturation and egg release often do not occur, i.e. ovulation does not occur.
Symptoms of PCOS may include:
- irregular or absent menses;
- have difficulty conceiving;
- there is increased hair growth on the face and body;
- observed hair loss, increased oily skin, increased body weight.
Talk to your doctor if you suspect you have PCOS.
Thyroid dysfunction
The thyroid gland is located in the front of the neck. It produces hormones that control heart rate, body temperature and other important indicators of the body. An overactive or underactive thyroid can cause problems with ovulation.
Symptoms of hyperthyroidism include:
- irritability;
- mood swings;
- fatigue or weakness;
- irregular or unusually fast heart rate.
Symptoms of hypothyroidism:
- fatigue;
- weight gain;
- depression;
- muscle pain.
See your doctor for advice on diagnosing and treating thyroid problems.
Stress
It is natural to experience stress during the day or week. Personal or work issues and a host of other factors can cause you anxiety.
But when there is too much stress in life or it lasts too long, it can seriously affect your body. If your periods have become irregular or you're having trouble getting pregnant (despite having regular sex), stress may be the cause.
If you think stress is affecting your life and overall well-being, talk to your doctor. He will recommend the appropriate treatment.
Although many women do not ovulate on the 14th day, it is usually considered late if it occurs after the 21st day of the cycle. The best way to track this is to watch for signs of ovulation using any of the following methods.
- Measurement of basal body temperature. Basal body temperature is the lowest body temperature in 24 hours. Using a thermometer, you can keep track of changes in your basal temperature. Before ovulation, BBT, as a rule, falls, and immediately after ovulation, it rises sharply.
- Cervical mucus monitoring. Cervical mucus is a discharge that can be found on underwear for a month. For most of the cycle, these secretions are thick and sticky, but during ovulation, they can become thinner and more stringy. Their number at this time also, as a rule, increases.
- Track changes in the cervix. At ovulation, it becomes softer, moister and more open. You can notice this by inserting your fingers into the vagina and feeling for the cervix. This sign is more difficult to observe and usually requires some practice.
Ovulation often causes other symptoms that you may notice:
- breast tenderness;
- abdominal discomfort;
- increased sexual desire.
Doctors are increasingly using ultrasound to detect ovulation. Check with your doctor if you can use this method.
You may find it useful to add your symptoms and feelings to our application. This way you can see patterns in your cycle.
This is very simple but gives very accurate predictions. Confirmation of something is that more and more women are getting pregnant with Flo.
Women who ovulate at the end of their cycle report that their attempts to get pregnant may not be successful. Even if you know about late ovulation, it is difficult to predict when sex is most likely to lead to conception. Many women lose heart, especially if they know that friends or relatives have conceived without any problems.
First of all, don't get discouraged! Millions of women around the world ovulate late but still manage to conceive. Focus on what to do to increase your chances of getting pregnant. The simplest, yet most important thing you can do is watch your cycle. The better you understand it, the easier it will be for you to determine when you are (or are about to) ovulate.
Once the egg is released from the ovary, it begins its journey down the fallopian tube to the uterus. From that moment on, she has 12–24 hours to be fertilized with sperm. Not much time at first glance. However, remember: spermatozoa can live in your fallopian tubes for up to 5 days. Therefore, if you had sex a few days before ovulation, the chances of fertilizing an egg are still high.
When planning a pregnancy with your partner, keep in mind methods that will help increase your chances of conceiving.
- Tracking changes in cervical mucus. Get in the habit of watching the nature of your secretions. Before ovulation, you may notice that the amount of discharge has increased. In addition, they can become stretchy: you can probably stretch them up to a few centimeters between two fingers. All this points to the approach of ovulation - it's time for intimacy with a partner! Immediately after ovulation, cervical mucus becomes thicker and cloudier, and its amount decreases.
- Observation of changes in the cervix. Practice getting to know her by inserting your finger into the vagina while sitting on the toilet or squatting. But remember: hands should be clean and nails short! For most of the cycle, the cervix is hard, dry, and closed. As ovulation approaches, you will feel it getting softer, wetter, and more open.
- Ovulation tests. Using home tests to determine fertile days is quite effective. You can read more about this in the article The Complete Guide to Ovulation Tests.
Late ovulation may affect the ability to conceive. With an irregular cycle, it can be more difficult to track and predict ovulation. This makes it harder to predict when sex is more likely to result in conception.
If you have any of the conditions or symptoms described above, talk to your doctor. The doctor will talk about possible treatment options, and possibly lifestyle changes to improve your fertility and health.