How to tell if your child has strep throat
Strep Throat: All You Need to Know
Increase in Invasive Group A Strep Infections, 2022–2023
CDC is looking into an increase in invasive group A strep (iGAS) infections among children in the United States. iGAS infections include necrotizing fasciitis and streptococcal toxic shock syndrome.
Español (Spanish) | Print
Worried your sore throat may be strep throat? Doctors can do a quick test to see if a sore throat is strep throat. Antibiotics can help people with strep throat feel better faster and prevent spreading it to others.
- Bacteria cause strep throat
- How you get strep throat
- Pain, fever, but no cough is common
- Some people are at increased risk
- A simple test gives fast results
- Antibiotics are used for treatment
- Not everyone needs antibiotics
- Serious complications are not common
- Protect yourself and others
Bacteria cause strep throat
Viruses cause most sore throats. However, strep throat is an infection in the throat and tonsils caused by bacteria called group A Streptococcus (group A strep).
How you get strep throat
Group A strep bacteria are very contagious. Generally, people spread the bacteria to others through
- Respiratory droplets
- Direct contact
Rarely, people can spread group A strep bacteria through food that is not handled properly (visit CDC’s food safety page).
It usually takes two to five days for someone exposed to group A strep bacteria to become ill with strep throat.
Respiratory droplets
Group A strep bacteria often live in the nose and throat. People who are infected spread the bacteria by talking, coughing, or sneezing, which creates respiratory droplets that contain the bacteria.
People can get sick if they:
- Breathe in respiratory droplets that contain the bacteria
- Touch something with those droplets on it and then touch their mouth or nose
- Drink from the same glass or eat from the same plate as a person infected with group A strep bacteria
Direct contact
People can also spread group A strep bacteria from infected sores on their skin. Other people can get sick if they:
Other people can get sick if they:
- Touch sores on the skin caused by group A strep bacteria (impetigo) or come into contact with fluid from the sores
It is important to know that some infected people do not have symptoms or seem sick. People sick with strep throat are much more contagious than those who do not have symptoms.
A sore throat that starts quickly, pain with swallowing, and fever are some of the common signs and symptoms of strep throat.
Pain, fever, but no cough is common
In general, strep throat is a mild infection, but it can be very painful. The most common symptoms of strep throat include:
- Sore throat that can start very quickly
- Pain when swallowing
- Fever
- Red and swollen tonsils, sometimes with white patches or streaks of pus
- Petechiae — pronounced pi-TEE-kee-eye — on the soft or hard palate (tiny, red spots on the roof of the mouth)
- Swollen lymph nodes in the front of the neck
Other symptoms may include a headache, stomach pain, nausea, or vomiting — especially in children. Someone with strep throat may also have a rash; it is known as scarlet fever.
Someone with strep throat may also have a rash; it is known as scarlet fever.
Some symptoms suggest a viral cause rather than group A strep
The following symptoms suggest a virus is the cause of the illness instead of strep throat:
- Cough
- Runny nose
- Hoarseness (changes in your voice that make it sound breathy, raspy, or strained)
- Conjunctivitis (pink eye)
- Up to 3 in 10 children with a sore throat have strep throat
- About 1 in 10 adults with a sore throat has strep throat
Some people are at increased risk
Anyone can get strep throat, but there are some factors that can increase the risk of getting this common infection.
Age
Strep throat is more common in children than adults. It is most common in children 5 through 15 years old. It is very rare in children younger than 3 years old.
Adults who are at increased risk for strep throat include:
- Parents of school-aged children
- Adults who are often in contact with children
Group settings
Close contact with another person with strep throat is the most common risk factor for illness. For example, if someone has strep throat, the bacteria often spread to other people in their household.
For example, if someone has strep throat, the bacteria often spread to other people in their household.
Infectious illnesses tend to spread wherever large groups of people gather. Crowded settings can increase the risk of getting a group A strep infection. These settings include:
- Schools
- Daycare centers
- Military training facilities
A simple test gives fast results
A doctor will determine what type of illness you have by asking about symptoms and doing a physical exam. If they think you might have strep throat, they will swab your throat to test for strep throat. There are two types of tests for strep throat: a rapid strep test and throat culture.
Rapid strep test
A rapid strep test involves swabbing the throat and running a test on the swab. The test quickly shows if group A strep bacteria are causing the illness.
- If the test is positive, doctors can prescribe antibiotics.
- If the test is negative, but a doctor still suspects strep throat, then the doctor can take a throat culture swab.
Throat culture
A throat culture takes time to see if group A strep bacteria grow from the swab. While it takes more time, a throat culture sometimes finds infections that the rapid strep test misses.
Culture is important to use in children and teens since they can get rheumatic fever from an untreated strep throat infection. For adults, it is usually not necessary to do a throat culture following a negative rapid strep test. Adults are generally not at risk of getting rheumatic fever following a strep throat infection.
Antibiotics are used for treatment
Doctors treat strep throat with antibiotics. Benefits of antibiotics include:
- Decreasing how long someone is sick
- Decreasing symptoms (feeling better)
- Preventing the bacteria from spreading to others
- Preventing serious complications like rheumatic fever
Someone with strep throat should start feeling better in just a day or two after starting antibiotics. Call the doctor if you or your child are not feeling better after taking antibiotics for 48 hours.
Call the doctor if you or your child are not feeling better after taking antibiotics for 48 hours.
When to return to work, school after illness
People with strep throat should stay home from work, school, or daycare until they:
- No longer have a fever
AND
- Have taken antibiotics for at least 12 hours
Antibiotic dos and don’ts
- Do take the prescription exactly as the doctor says to.
- Don’t stop taking the medicine, even if you or your child feels better, unless the doctor says to stop.
You can find more guidance on taking antibiotics on CDC’s Antibiotic Do’s & Don’ts Page.
Not everyone needs antibiotics
Someone who tests positive for strep throat but has no symptoms (called a “carrier”) usually does not need antibiotics. They are less likely to spread the bacteria to others and very unlikely to get complications.
If a carrier gets a sore throat illness caused by a virus, the rapid strep test can be positive. In these cases, it can be hard to know what is causing the sore throat.
In these cases, it can be hard to know what is causing the sore throat.
If someone keeps getting a sore throat after taking the right antibiotics, they may be a strep carrier and have a viral throat infection. Talk to a doctor if you think you or your child may be a strep carrier.
Serious complications are not common
Complications can occur after a strep throat infection. This can happen if the bacteria spread to other parts of the body.
Complications can include:
- Abscesses (pockets of pus) around the tonsils or in the neck
- Swollen lymph nodes in the neck
- Sinus infections
- Ear infections
- Rheumatic fever (a disease that can affect the heart, joints, brain, and skin)
- Post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis (a kidney disease)
Wash your hands often to help prevent germs from spreading.
Protect yourself and others
People can get strep throat more than once. Having strep throat does not protect someone from getting it again in the future. While there is no vaccine to prevent strep throat, there are things people can do to protect themselves and others.
While there is no vaccine to prevent strep throat, there are things people can do to protect themselves and others.
Good hygiene
The best way to keep from getting or spreading group A strep is to wash your hands often. This is especially important after coughing or sneezing and before preparing foods or eating.
To prevent group A strep infections, you should:
- Cover your mouth and nose with a tissue when you cough or sneeze.
- Put your used tissue in the waste basket.
- Cough or sneeze into your upper sleeve or elbow, not your hands, if you don’t have a tissue.
- Wash your hands often with soap and water for at least 20 seconds.
- Use an alcohol-based hand rub if soap and water are not available.
You should also wash glasses, utensils, and plates after someone who is sick uses them. These items are safe for others to use once washed.
Antibiotics
Antibiotics help prevent someone with strep throat from spreading the bacteria to others.
Scarlet fever
Impetigo
Necrotizing fasciitis
Cellulitis
- Conjunctivitis (Pink Eye)
- Food Safety Homepage
- Handwashing: When and How to Wash Your Hands
- Hygiene Etiquette and Practice: Coughing and Sneezing
- PANDAS — Questions and Answers
- Sore Throats and Antibiotic Use
Top of Page
Strep Throat (for Parents) - Nemours KidsHealth
What Is Strep Throat?
Strep throat is an infection caused by a type of bacteria (group A streptococcus). Strep bacteria are the most common cause of bacterial sore throat in children and teens.
Strep throat usually needs treatment with antibiotics. With the proper medical care — and plenty of rest and fluids — most kids get back to school and play within a few days.
What Are the Signs & Symptoms of Strep Throat?
Symptoms of strep throat include:
- sore throat
- fever
- red and swollen tonsils
- painful or swollen neck glands
Not all sore throats are strep throats.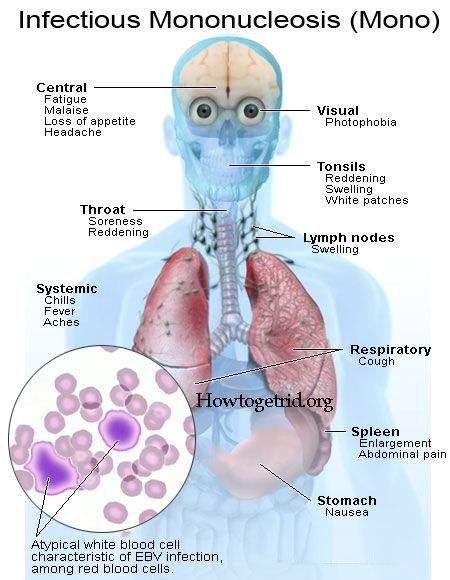 Often, kids have a sore throat because of a
Often, kids have a sore throat because of a
virus, which will usually clear up without medical treatment.
Kids who do have strep throat might get other symptoms within about 3 days, such as:
- red and white patches in the throat
- trouble swallowing
- a headache
- lower stomach pain
- general discomfort, uneasiness, or ill feeling
- loss of appetite
- nausea
- rash
Is Strep Throat Contagious?
Strep throat is very contagious. Anybody can get it, but most cases are in school-age kids and teens. Infections are common during the school year, with peaks in winter and early spring, when big groups of kids and teens are in close contact.
How Do People Get Strep Throat?
The bacteria that cause strep throat tend to hang out in the nose and throat. So normal activities like sneezing, coughing, or shaking hands can easily spread an infection from one person to another.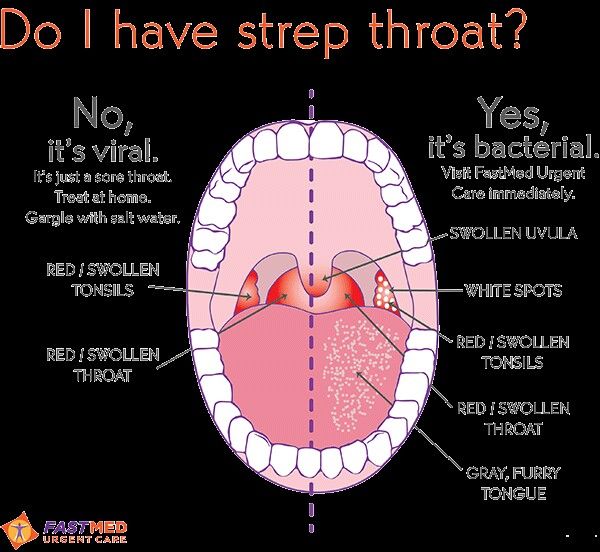
Kids with untreated strep throat are more likely to spread the infection when their symptoms are most severe, but can still infect others for up to 3 weeks.
That's why it's so important to teach kids to wash their hands. well and often. This can lower their chances of getting contagious diseases like strep throat.
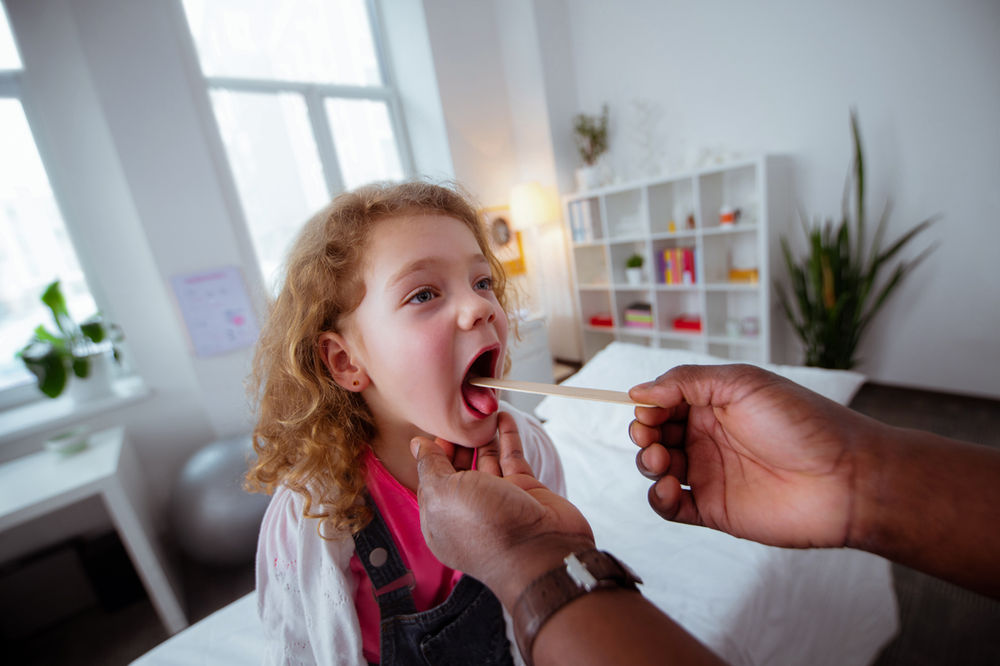
How Is Strep Throat Diagnosed?
If your child has a sore throat and other strep throat symptoms, call your doctor. The doctor will likely do a rapid strep test in the office, using a cotton swab to take a sample of the fluids at the back of the throat. The test only takes about 5 minutes.
If it's positive, your child has strep throat. If it's negative, the doctor will send a sample to a lab for a throat culture. The results are usually available within a few days.
How Is Strep Throat Treated?
Doctors usually prescribe about 10 days of antibiotic medicine to treat strep throat. Within about 24 hours after starting on antibiotics, your child probably won't have a fever and won't be contagious. By the second or third day, other symptoms should start to go away.
By the second or third day, other symptoms should start to go away.
Even when kids feel better, they should take the antibiotics as prescribed. This is the best way to kill the harmful bacteria. Otherwise, bacteria can stay in the throat and symptoms can come back. Completing all the antibiotics also prevents other health problems that a strep infection can cause, such as rheumatic fever (which can cause heart damage), scarlet fever, blood infections, or kidney disease.
To prevent spreading strep throat to others in your home:
- Keep your child's eating utensils, dishes, and drinking glasses separate and wash them in hot, soapy water after each use.
- Make sure your child doesn't share food, drinks, napkins, handkerchiefs, or towels with other family members.
- Teach your child to cover all sneezes or coughs. If a tissue isn't handy, kids should sneeze or cough into their elbow, not their hands.
- Remind everyone to wash their hands well and often.
- Give your child a new toothbrush after the antibiotic treatment starts and they're no longer contagious.
How Can I Help My Child Feel Better?
Home care can help your child feel better while battling strep throat. Give plenty of liquids to prevent dehydration, such as water or ginger ale, especially if your child had a fever. Avoid orange juice, grapefruit juice, lemonade, or other acidic beverages, which can irritate a sore throat. Warm liquids like soups, sweetened tea, or hot chocolate can be soothing.
For fever and pain, your doctor may suggest an over-the-counter medicine, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen. Follow the package directions on how much to give and when.
Talk to your doctor about when your child can return to normal activities. Most kids can go back to school when they've taken antibiotics for at least 24 hours and no longer have a fever.
Reviewed by: Rachel S. Schare, MD
Date reviewed: April 2022
Angina in a child.
 Diagnosis and treatment of tonsillitis in children at the Fantasy clinic in Moscow
Diagnosis and treatment of tonsillitis in children at the Fantasy clinic in Moscow We treat children according to the principles of evidence-based medicine: we choose only those diagnostic and treatment methods that have proven their effectiveness. We will never prescribe unnecessary examinations and medicines!
Make an appointment via WhatsApp
Prices Doctors
The first children's clinic of evidence-based medicine in Moscow
No unnecessary examinations and drugs! We will prescribe only what has proven effective and will help your child.
Treatment according to world standards
We treat children with the same quality as in the best medical centers in the world.
The best team of doctors in Fantasy!
Pediatricians and subspecialists Fantasy - highly experienced doctors, members of professional societies. Doctors constantly improve their qualifications, undergo internships abroad.
Ultimate safety of treatment
We have made children's medicine safe! All our staff work according to the most stringent international standards JCI
We have fun, like visiting best friends
Game room, cheerful animator, gifts after the reception. We try to make friends with the child and do everything to make the little patient feel comfortable with us.
We try to make friends with the child and do everything to make the little patient feel comfortable with us.
You can make an appointment by calling or by filling out the form on the site
Other services under "Pediatric otolaryngology (ENT diseases)"
- Consultation of a pediatric ENT doctor
Manipulations, procedures, operations
- Opening of a tonsil cyst in children
- Removal of a foreign body from the ear or nose of a child
- Stopping nosebleeds in children
- Opening of abscesses and hematomas of the nasal septum in children
- Reposition of the bones of the nose for a child
- Opening and drainage of hematomas in a child
- Removal of adenoids in children
- Shunting of the eardrums for a child installation of ventilation tubes
- Washing the lacunae of the tonsils for a child
Frequent calls
- Snoring in a child: causes and treatment
- Obstructive sleep apnea syndrome (OSAS) in children
- Hearing impairment in children: diagnosis and treatment
- Allergic rhinitis in a child: diagnosis and treatment
- Sulfur plug in a child
- Laryngitis in children: treatment
- Enlarged cervical lymph nodes in a child
- Treatment of adenoids without surgery
- Otitis media in children: diagnosis and treatment
Online payment
Documents online
Online services
Diseases - blog of pediatricians of the children's clinic "RebenOK"
Diseases - blog of pediatricians of the children's clinic "RebenOK"- Learn more
- Constipation pains in early pregnancy

- 18Th week of pregnancy no movement

- Runny nose pregnant
- How to make your child feel better when sick

- How are twins born

- How to help child with diarrhea

- Loss of a newborn

- Pelvic floor muscle strengthening exercises

- Having a cold and pregnant

- Red spots on bottom of baby feet

- How long do you have to terminate a pregnancy


