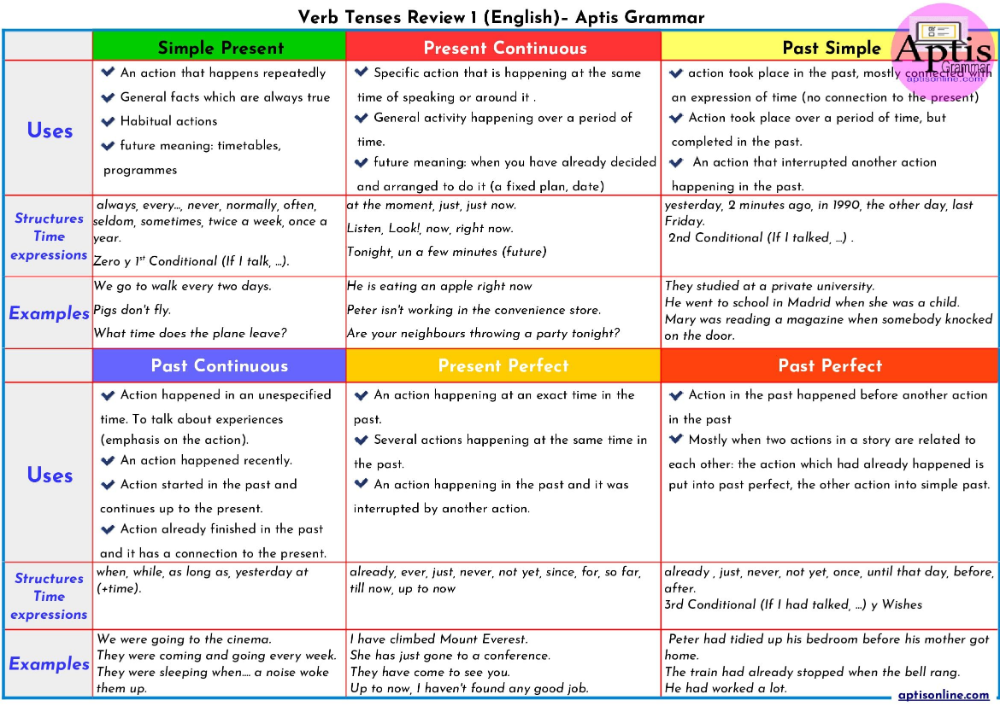
Swollen lady parts during pregnancy
How to Ease Vaginal Swelling During Pregnancy
Swelling is a common side effect of pregnancy, especially when it comes to your feet and hands. But there’s one area that can also swell during pregnancy that doesn’t get a lot of attention: Your vagina. If you notice you have a swollen vagina during pregnancy, know you’re not the only woman going through this! Still, we’re guessing you might have questions about why this is happening. Here’s what you need to know, plus how to minimize the swelling and ease any discomfort.
In this article:
Symptoms of vaginal swelling during pregnancy
What causes vaginal swelling during pregnancy?
How to reduce vaginal swelling during pregnancy
How to prevent vaginal swelling during pregnancy
Symptoms of Vaginal Swelling During Pregnancy
Every woman and every pregnancy is different—which means the symptoms of vaginal swelling during pregnancy can differ from person to person. In general, though, you might experience the following:
• Noticeable swelling. You’re probably familiar on at least some level with what your vulva and vaginal area usually feels like. If it’s swollen, it can feel noticeably bigger or puffier, says Frederick Friedman, Jr., MD, associate professor of obstetrics, gynecology and reproductive science at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York City. “There may just be a general feeling of swelling or fullness in the vaginal area,” adds Julie Lamppa, APRN, CNM, a certified nurse midwife at Mayo Clinic, which can lead to overall discomfort.
• Bumps. Some women who experience vaginal swelling during pregnancy can have varicose veins surface in their vulvar area, which can cause swelling and a bumpy feel down there, Lamppa says.
• Itchiness. This isn’t the case for every woman, but itchiness can sometimes accompany vaginal swelling, Lamppa says.
What Causes Vaginal Swelling During Pregnancy?
There are several reasons why you might develop vaginal swelling in pregnancy. Here are some of the most common ones:
Here are some of the most common ones:
• An increase in blood volume. Your blood volume increases during pregnancy to help support the growing baby. As your uterus grows, there’s also an increase in pressure of the blood vessels in your pelvis, Lamppa explains. The combination of these two things can lead to swelling.
• Varicose veins in your vulva. Varicose veins are swollen, bumpy veins that develop when valves let blood pool in one spot or flow backward. Just like you can develop varicose veins in your legs, you can also develop these in your vulva during pregnancy, Lamppa says. “These aren’t dangerous, but they can be alarming to women when they suddenly show up.”
• A yeast infection. Yeast infections are common among moms-to-be, and they can also lead to a swollen vagina during pregnancy, Friedman says. “The inflammation that results from the infection can cause more swelling,” he explains.
• Excess fluid.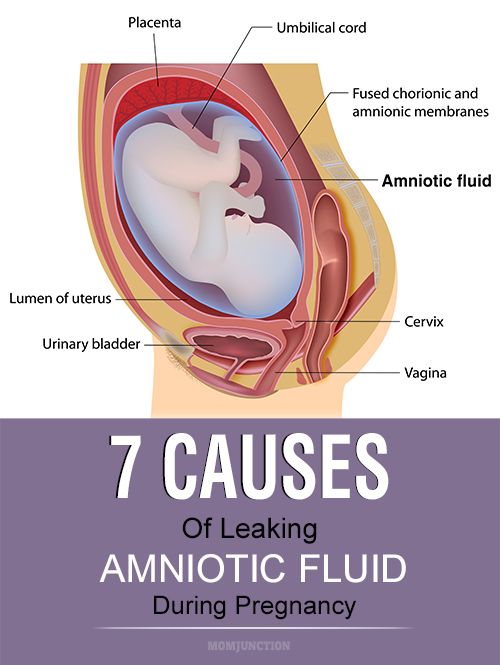 Excess fluid can get trapped in your body’s tissues during pregnancy, and that can cause swelling down there, Friedman says.
Excess fluid can get trapped in your body’s tissues during pregnancy, and that can cause swelling down there, Friedman says.
How to Reduce Vaginal Swelling During Pregnancy
If you suspect that your vaginal swelling is due to excess fluid, compression or support stockings might help. “There are products on the market that you can buy that give vulvar support,” Lamppa says. (Just check in with your doctor first to make sure it’s okay for you to use.)
For direct relief, Lamppa recommends applying a cool pack directly to your vulva. That should help with discomfort as well as cut down on some of the swelling.
If you’re experiencing vaginal swelling along with symptoms of a yeast infection—such as an itchy vaginal area during pregnancy, accompanied by white vaginal discharge—Lamppa recommends seeing your doctor for an evaluation. If they determine that you do, in fact, have a yeast infection, your care provider will likely recommend that you use an over-the-counter cream.
How to Prevent Vaginal Swelling During Pregnancy
Sorry, but there isn’t a ton you can do to lower the odds you’ll experience vaginal swelling during pregnancy, given that it’s a normal side effect of being pregnant, Lamppa says. However, doing your best to avoid sitting or standing for long periods of time may be helpful, Friedman suggests.
While it’s pretty common, it’s a good idea to flag any vaginal swelling during pregnancy for your care provider so they can help pinpoint the cause and get you sweet relief ASAP.
Updated January 2020
Expert bios:
Frederick Friedman, Jr., MD, is an associate professor of obstetrics, gynecology and reproductive science at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai. He also serves as director for both the division of obstetrics and the division of generalists in the department of obstetrics, gynecology and reproductive science at the Mount Sinai Health System, and maintains a clinical practice in general obstetrics and gynecology.
Julie Lamppa, APRN, CNM, is a certified nurse midwife and medical editor at Mayo Clinic, and maintains a midwifery practice in Rochester, New York.
*Please note: The Bump and the materials and information it contains are not intended to, and do not constitute, medical or other health advice or diagnosis and should not be used as such. You should always consult with a qualified physician or health professional about your specific circumstances. *
Plus, more from The Bump:
Swelling in Pregnancy: Why It Happens and How to Deal
How Your Vaginal Discharge Can Change During Pregnancy
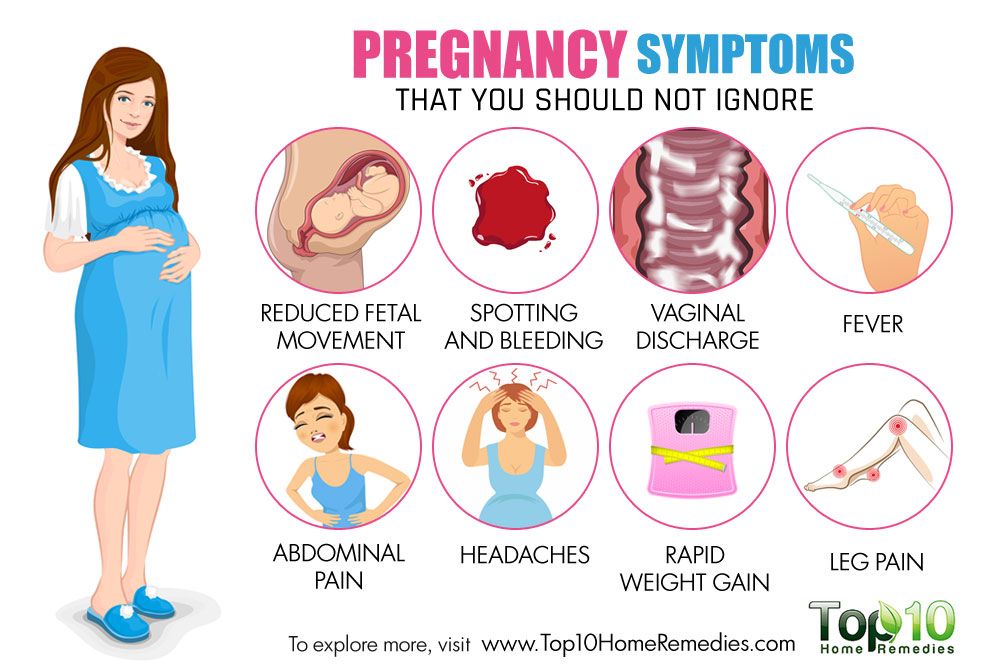
10 Surprising Pregnancy Symptoms No One Warned You About
Swollen labia: Why it happens during pregnancy and postpartum
- Baby
- Postpartum Health
By Maggie Getz
|
|
February 11, 2022
Many women experience swollen labia during pregnancy because of the increased blood flow to the area; some women even develop blue or purple veins on their labia, also known as vulvar varicosities, due to the growing uterus compressing the veins in the pelvis. There’s not much you can do to prevent swollen labia, but you can find relief by avoiding sitting or standing for long periods of time.
There’s not much you can do to prevent swollen labia, but you can find relief by avoiding sitting or standing for long periods of time.
Photo credit: iStock / nd3000
- Labia swelling: What does it mean?
- Is it normal to have swollen labia during pregnancy?
- How can I get relief from swollen labia during pregnancy and beyond?
- Will I continue to experience swollen labia postpartum?
- Should I ever be concerned about swollen labia?
Labia swelling: What does it mean?
Some women find that their labia – the lips that surround the opening of the vagina – feel swollen during pregnancy. FYI, the labia has two folds of skin: The outer folds are called the labia majora and the inner folds are the labia minora. The area may not look very swollen, but it may feel full, irritated, or even itchy. The skin of your labia may also appear darker.
All of your external genitalia – including labia, vaginal opening, urethral opening, and clitoris – are known as the vulva. The changes to your vulva during pregnancy are due to increased blood flow to the area from the demands of your growing uterus and baby.
The changes to your vulva during pregnancy are due to increased blood flow to the area from the demands of your growing uterus and baby.
Is it normal to have swollen labia during pregnancy?
Having swollen labia during pregnancy may start as early as your first trimester and may grow more intense as your pregnancy progresses. This could be because your uterus and baby are getting larger and applying more pressure to the area. And you may feel more pressure late in pregnancy when your baby "drops." This happens when the baby's head moves lower into the pelvis in preparation for labor.
You may also notice blue or purple veins on your swollen labia minora or majora. These varicose veins (known as vulvar varicosities) are caused by your growing uterus compressing the veins in your pelvis and increasing the pressure inside them. Changes in pregnancy hormones also cause your veins to widen and relax, allowing them to swell.
What's more, the increase in your blood volume during pregnancy limits how quickly your blood returns from your lower body to your heart.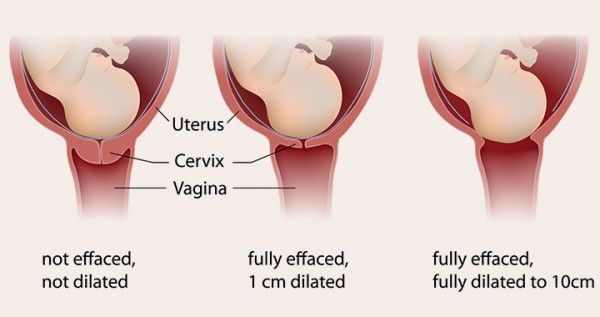 The result is that blood accumulates in the veins of your legs and vulva, causing them to bulge.
The result is that blood accumulates in the veins of your legs and vulva, causing them to bulge.
You may notice that your symptoms are worse after standing, exercise, or sex. If you develop varicose veins in your labia during pregnancy, they tend to go away within six weeks after delivery.
However, if you have swollen labia minora with a lump, it could be a sign of a vaginal boil or Bartholin's cyst. This might also be an explanation for why there is swelling on one side of your labia. A Bartholin cyst forms when fluid gets stuck in your Bartholin's glands, which are on either side of your vulva. If the fluid in the Bartholin's cyst gets infected, you may develop pus around the area.
Pus around a small bump on your vulva can also be a vaginal boil, which you can develop from an infected hair follicle or an injury, like a cut from shaving. Vaginal boils look like small, red bumps that are swollen and painful. while a Bartholin cyst is painless, if the cyst gets infected, it will become very painful. Bartholin cysts usually go away on their own, but you can talk to your doctor about trying some at-home remedies, like a sitz bath. If you have a Bartholin cyst that becomes infected or a vaginal boil, you'll likely need antibiotics that your doctor can prescribe.
Bartholin cysts usually go away on their own, but you can talk to your doctor about trying some at-home remedies, like a sitz bath. If you have a Bartholin cyst that becomes infected or a vaginal boil, you'll likely need antibiotics that your doctor can prescribe.
Either way, if you develop swollen labia during pregnancy, you should bring it up to your doctor to make sure it isn't a more serious issue; it will also put your mind at ease about any other changes to your vagina.
How can I get relief from swollen labia during pregnancy and beyond?
While there's not much you can do to prevent swollen labia during pregnancy, you can find some relief from the discomfort by trying the following tips:
- Change position frequently. Avoid standing or sitting for long periods of time.
- Put your feet up. Elevate your legs above your heart (prop them on pillows) while lying down to help promote circulation.
- Use cold compresses.
 Apply a cold pack covered in a cloth to your vulva to ease your discomfort.
Apply a cold pack covered in a cloth to your vulva to ease your discomfort. - Use a support garment. Look for a compression band, support strap, or underwear designed for vulvar varicosities. Some also provide support for the lower abdomen and lower back.
Will I continue to experience swollen labia postpartum?
It's common for your labia to be swollen and sore after a vaginal birth. The miraculous process of giving birth does tend to traumatize the tissues in the vaginal area. Fortunately, your body's ability to heal is equally miraculous.
The tender treatment you're probably already giving your perineum – ice packs for the first 12 to 24 hours and warm, soothing sitz baths after that – will do wonders for your labia, too.
The amount of time it takes the swelling to go down depends on the cause of the swelling. Bartholin cysts rarely go away, while swelling due to fluid retention or varicose veins usually gest better within days or weeks of giving birth. And two weeks postpartum, you should definitely be on the mend. If you haven't noticed significant improvement by then, ask your health provider about it. (For more details on postpartum care for the vaginal area, see our article on caring for a sore perineum.)
And two weeks postpartum, you should definitely be on the mend. If you haven't noticed significant improvement by then, ask your health provider about it. (For more details on postpartum care for the vaginal area, see our article on caring for a sore perineum.)
Should I ever be concerned about swollen labia?
If you develop swollen labia postpartum, it's usually nothing to worry about and will heal on its own. However, you should still bring it up with your provider so they can keep a close eye on the area.
If you aren't pregnant and develop swollen labia, it could be a symptom of vulvitis, or inflammation of the vulva. Pinpointing what causes vulvitis can be difficult, but using vaginal sprays and deodorants and douching are common triggers. In addition to swelling, you may experience extreme itchiness, redness, clear, fluid-filled blisters, and scaly patches of skin. Because these symptoms are commonly shared with other vaginal issues, like bacterial vaginosis and a yeast infection, see your healthcare provider for a proper diagnosis and treatment.
Learn more:
- 12 icky pregnancy side effects
- Pregnancy symptoms you should never ignore
Sources
BabyCenter's editorial team is committed to providing the most helpful and trustworthy pregnancy and parenting information in the world. When creating and updating content, we rely on credible sources: respected health organizations, professional groups of doctors and other experts, and published studies in peer-reviewed journals. We believe you should always know the source of the information you're seeing. Learn more about our editorial and medical review policies.
University of Rochester. Anatomy of Vulva. https://www.urmc.rochester.edu/encyclopedia/content.aspx?contenttypeid=34&contentid=19522-1 [Accessed February 2022]
Mayo Clinic. Bartholin’s cyst. 2020. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/bartholin-cyst/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20369981 [Accessed February 2022]
Cleveland Clinic. Vaginal Boil. 2021. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/21651-vaginal-boil [Accessed February 2022]
2021. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/21651-vaginal-boil [Accessed February 2022]
Johns Hopkins Medicine. Vulvitis. https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/vulvitis [Accessed February 2022]
Show more
advertisement | page continues below
advertisement
Featured video
All pregnancy, parenting, and birth videos >
Edema during pregnancy | Nutriclub
What you need to know about edema: why they appear, how to deal with them, how to distinguish ordinary physiological edema from a symptom of a serious illness
It is believed that edema inevitably accompanies the pregnancy of most women - you just need to endure their unaesthetic appearance. However, swelling can be a signal of health problems and pose a danger to both the expectant mother and the development of the fetus. Nutriclub understands when to worry if you have swelling.
- Edema - excessive accumulation of fluid in the interstitial space - occurs quite often in pregnant women. Swelling can occur at any time and in different parts of the body.
- Edema on the face (especially bags under the eyes and severe swelling of the eyelids) are especially noticeable and cause maximum dissatisfaction, because they directly affect the appearance.
- Very often, pregnant women have swollen legs, especially after a long walk. That is why it is so important to get comfortable shoes for the entire period of pregnancy.
- Hands tend to swell in women who work at a computer or do needlework. Rings begin to press, fingers look like “sausages”. In such cases, you need to temporarily abandon jewelry.
- Pregnant women often mistake swelling of the nasal mucosa for a runny nose or allergies. The latter is more likely because allergic reactions tend to get worse during pregnancy. Also in pregnant women, due to changes in hormonal levels, a condition called rhinitis of pregnancy can develop, which is accompanied by severe nasal congestion.
 It is better to take tests and be sure to discuss the situation with a doctor who will prescribe a drug that is allowed during pregnancy. Ignoring nasal congestion is not recommended - breathing problems in the mother can make it difficult for oxygen to reach the child.
It is better to take tests and be sure to discuss the situation with a doctor who will prescribe a drug that is allowed during pregnancy. Ignoring nasal congestion is not recommended - breathing problems in the mother can make it difficult for oxygen to reach the child.
All these edemas can be both physiological and pathological.
Physiological edema of pregnant women
Physiological usually do not cause complications. They are explained by natural changes in the body of the expectant mother: the uterus puts pressure on neighboring organs, slowing down blood circulation, and sodium accumulates in the blood - it slows down the excretion of fluid from the body. At the same time, during pregnancy, the total amount of fluid circulating throughout the body almost doubles (part of it is contained in the amniotic fluid and placenta).
At the same time, a woman's hormonal background changes, which may be the cause of the legendary “salty” craving, which, in turn, provokes thirst and excessive fluid intake.
Summer heat or stuffiness in transport and premises, physical overload also affects health and appearance.
Physiological edema is considered natural at any stage of pregnancy - and does not pose a threat to the woman's health.
But at the first sign of swelling, you should definitely contact your obstetrician-gynecologist. The doctor will prescribe the necessary examinations and tests to exclude pathological edema, indicating health problems and complications of pregnancy.
Pathological edema during pregnancy
Pathological edema in the early stages may signal hypothyroidism - a condition in which there is a lack of thyroid hormones in the body. Doctors try to identify the disease before the appearance of swelling - pregnant women with a deficiency or excess body weight, with severe toxicosis, a blood test for thyroid hormones is prescribed. If the results are not normal, treatment is prescribed.
Also, starting from the first trimester, edema may appear due to problems with the kidneys. It is very important to take a urine test every two weeks, as recommended in the antenatal clinic. Erythrocytes, high leukocytes, a protein that should not be in the urine - a reason for referral to a urologist and ultrasound of the kidneys. It is important to exclude an infection in the kidneys, and if it is diagnosed, it should be treated qualitatively. Otherwise, premature obstructed labor or the birth of a child with a low weight are possible.
It is very important to take a urine test every two weeks, as recommended in the antenatal clinic. Erythrocytes, high leukocytes, a protein that should not be in the urine - a reason for referral to a urologist and ultrasound of the kidneys. It is important to exclude an infection in the kidneys, and if it is diagnosed, it should be treated qualitatively. Otherwise, premature obstructed labor or the birth of a child with a low weight are possible.
Starting from the 20th week, swelling may indicate varicose veins. Circulatory disturbance due to uterine pressure leads to the formation of "knots" and pain in the legs. If you suspect varicose veins, you will be referred to a phlebologist who will give the necessary recommendations.
Edema also accompanies heart failure, which is considered a serious complication of pregnancy. In this case, the appearance of edema is preceded by shortness of breath and cyanosis of the mucous membranes.
However, most often, pathological swelling indicates late toxicosis - gestosis. This is a problem in the third trimester of pregnancy, but the first signs can begin to appear between the 18th and 20th weeks. Preeclampsia almost always requires the help of a doctor and the presence of a pregnant woman in a hospital.
This is a problem in the third trimester of pregnancy, but the first signs can begin to appear between the 18th and 20th weeks. Preeclampsia almost always requires the help of a doctor and the presence of a pregnant woman in a hospital.
What is gestosis and why is it dangerous?
However, gestosis, in addition to edema, has other symptoms: high blood pressure, protein in the sea (it is normally absent), nausea, vomiting, headaches, convulsions, fever, drowsiness, or, conversely, severe arousal.
There are four degrees of preeclampsia. The first degree is known as dropsy of pregnant women, it is mainly expressed in edema. The second degree is edema, protein in the urine, a violation of pressure. The third degree of preeclampsia is called preeclampsia. It is characterized by a decrease in cerebral circulation and even hemorrhage. In the most severe, fourth stage of the disease, convulsions (eclampsia) are observed. A pregnant woman may have a stroke or placental abruption.
Thus, even if everyone around them says that edema is completely natural, and they do not cause discomfort to the pregnant woman herself, it is very important to inform the doctor about the first appearance of swelling - precisely in order to make sure that the edema is physiological, and not pathological, and no complications for the development of the fetus and the process of childbirth will not entail.
When should a pregnant woman see a doctor immediately?
The following problems can be considered the reason for an urgent visit to a doctor:
- swelling visible already in the morning, immediately after getting up;
- edema accompanied by high blood pressure;
- edema becomes very severe: it is impossible to clench the hand into a fist, shoes are painful and uncomfortable to wear, it is difficult to open the eyes due to swelling;
- regular shortness of breath, palpitations;
- headaches do not go away for several days;
- regularly experience nausea and vomiting after the 12th week;
- Urges for small needs are rare and are accompanied by the release of urine of a dark color;
- there are pains in the upper part of the abdomen;
- painful convulsions appear;
What helps with swelling during pregnancy?
If, according to the results of examination and analysis, it is established that the edema is physiological, it is possible to get rid of them (or at least reduce them) using the following methods.
- Avoid fried, smoked, spicy, pickled and sweet foods. Steam or bake, eat fruits and vegetables regularly.
- The use of salt should be limited - it contains sodium, it is he who retains fluid in the body.
- Many advise to limit the use of water, even in the form of broth. In fact, it threatens with dehydration. It is better to drink plain water in small sips - and consume most of the daily allowance of one and a half to two liters in the morning. Soda should be excluded.
- It is contraindicated to stay in heat or stuffy rooms for a long time.
- On the recommendation of a doctor, you can wear special compression underwear, while giving up tight tights, uncomfortable shoes and heels.
- Sleep at least 8-10 hours. It is also recommended to lie down every day for 15-20 minutes with legs raised up, do foot massage and foot baths with sea salt.
When using any materials from the site nutriclub.ru, a link to the site is required.

© Nutriclub, 2020
You will also be interested
- Nutriclub - healthy nutrition and child development
- Pregnancy
- Mom's health and well-being
- Edema during pregnancy | Nutriclub
reasons, what to do, how to reduce
PreviousNext
- Is swelling during pregnancy normal?
- Where can edema appear?
- How to detect edema?
- Are swelling during pregnancy dangerous?
- How to reduce swelling during pregnancy?
- If swelling disappears during pregnancy, is it good?
Contents:
Pregnancy is a happy time in anticipation of a miracle, but even it has a few "fly in the ointment" that few people manage to avoid. Perhaps the most famous of them are toxicosis, digestive problems, back pain and, of course, swelling. Why do pregnant women swell? By what signs can you understand that it is time to start treatment? What can be done to prevent or reduce swelling? Let's discuss the causes and consequences.
Perhaps the most famous of them are toxicosis, digestive problems, back pain and, of course, swelling. Why do pregnant women swell? By what signs can you understand that it is time to start treatment? What can be done to prevent or reduce swelling? Let's discuss the causes and consequences.
Is swelling during pregnancy normal?
More likely yes than no. The key causes of edema during pregnancy are an increase in fluid in the woman's body and a high level of progesterone 1 . This hormone begins to be actively produced even during ovulation, preparing the uterus for egg implantation. Its concentration remains consistently high in a woman's blood throughout pregnancy, providing many important functions associated with fetal development. Unfortunately, it has such a side effect.
Interesting fact
Many women experience swelling before menstruation 2 . It's also progesterone. The hormone level rises in the second half of the menstrual cycle, which leads to this result.
The fact that one of the causes of edema during pregnancy is the production of a very important hormone does not mean at all that you need to accept this situation with humility. It all depends on the severity of the condition: slight swelling in pregnant women is almost inevitable, but if they become significant, it is worth thinking about treatment.
What other changes appear in the body during pregnancy, read here.
Where can edema appear?
Edema during pregnancy is most often localized on the feet, ankles and lower legs. The reasons are clear: excess liquid first collects at the very bottom - where gravity pulls it. Usually everything starts with pastosity - mild swelling with blanching and a decrease in skin elasticity.
The next favorite place for pastosity and swelling is the hands. Also, excess fluid often leaves a mark on the face, along with edema, nasal debt may appear - the so-called "pregnant rhinitis" 3 .
Important to know!
Most people consider cold drops and sprays to be among the most harmless medicines. Just not during pregnancy - many of them are dangerous for the fetus 4 ! Be sure to consult your doctor before treating a runny nose.
And even in the early stages of pregnancy, a woman's body temperature rises to a more comfortable fetus - just above 37 ° C. This does not mean at all that you have caught a cold or caught a virus. To learn more about basal temperature, read our article.
How to detect swelling?
Severe swelling during pregnancy is hard not to notice. When puffiness is not so pronounced, especially if the accumulation of excess fluid occurs slowly, the following signs will help to detect them:
-
There is a suspicious weight trend. If you follow the diet recommended by your doctor, but the weekly weight gain exceeds the norm for this period of pregnancy, most likely water is retained somewhere in the body.

-
Rings get stuck on the fingers, tight shoes. Signs of pastosity during pregnancy are easiest to detect by things picked up by hand or leg - they begin to press. By the way, it is better to remove the rings while there is such an opportunity.
-
The face is rounded. Every day you see your face in the mirror and you will surely notice if its forms begin to blur, smooth out.
-
There are traces of rubber bands. Many women today wear "footprints" - short socks that are almost invisible from the shoes. Perhaps the high "classic" is not so elegant, but it is an excellent tool for the early diagnosis of edema during pregnancy. If their elastic bands leave embossed marks on the legs, it means that excess fluid is collecting in the tissues.
-
There are unusual sensations in the fingers. If you feel tingling, burning, or numbness in your fingers, if there is pain or tension when you bend your fingers or step on your toes, it is most likely a sign of swelling.

Is swelling during pregnancy dangerous?
Edema is an excess accumulation of fluid in tissues 5 . As you can see, in this definition there is no clarification “in the tissues located directly under the skin”, internal organs can also swell. Often, swelling of the arms, legs, face in pregnant women is just the tip of the iceberg. Hidden from the eyes, internal stagnation of water can cause dysfunction of organs, general dehydration, and impaired oxygen transport. Ultimately, this can threaten the fetus with an insufficient supply of nutrients and oxygen starvation. Severe swelling during pregnancy affects not only the beauty of the expectant mother, but also the health of her baby.
Medicine divides edema during pregnancy into physiological and pathological. The former refers to almost inevitable changes associated with a hormonal shift and a general increase in fluid circulating in the body. The latter are a sign of various internal problems, such as kidney disease, heart failure, varicose veins, preeclampsia (late toxicosis) and others. Physiological edema usually does not require treatment - to reduce them, it is enough to follow a healthy lifestyle. In pathological cases, it is necessary to find the cause and eliminate it.
Physiological edema usually does not require treatment - to reduce them, it is enough to follow a healthy lifestyle. In pathological cases, it is necessary to find the cause and eliminate it.
Your doctor will be able to distinguish physiological from pathological edema based on the results of the examination and tests. In particular, the presence of protein in the urine is an alarming sign. Between visits to the doctor, you yourself can suspect a pathology if the edema grows too quickly, starts to rise above the shins, and when you press on the swollen places, dents remain on the skin, which slowly resolve.
What else can go wrong while carrying a baby? Watch a video lesson on the pathologies of pregnancy from the fertility specialist Anna Ilyina.
How to reduce swelling during pregnancy?
Pharmaceutical treatment is the last resort and is used only in extreme cases. Usually it is enough to adjust the lifestyle and acquire a few good habits. We'll give you 12 simple tips to help reduce water retention 1 .
We'll give you 12 simple tips to help reduce water retention 1 .
-
Observe the regime of the day. Try not to overwork during the day and have a good rest. The duration of sleep during pregnancy should be at least 8 hours, and if your body has such a need, even 9-10 hours.
-
Walk more. Your assistants in the treatment of edema during pregnancy are fresh air and reasonable physical activity. If in ordinary life you are used to walking only from the elevator to the parked car and back, something needs to be done about it.
-
Wear comfortable shoes. Even if you really love high-heeled shoes, even if you have complexes without them because of your own height, you will have to give them up for a while. Uncomfortable shoes exacerbate swelling during pregnancy, and soft shoes with low heels help fight it. If your feet still hurt at the end of the day, visit an orthopedic salon and ask a specialist to make custom insoles for you.

-
Change your posture more often. When your body becomes numb, it swells. Try not to sit or stand without moving for a long time. Both at work and at home, periodically leave your favorite chair to stretch a little. And while you are sitting in it, do not freeze in one position - move your arms and legs, change the position of your body.
-
Let's rest our feet. To prevent swelling in the legs, it is necessary to periodically raise them higher. So you facilitate the work of the circulatory system and allow it to pump out a little excess fluid from the legs. It is ideal to lie on your back with your legs up, but even if you just put them on a nearby chair during lunch in a corporate kitchen, this is not bad.
-
Exercise. In the fight against puffiness during pregnancy, simple physical exercises are useful - tilts, turns, etc. Statics will also help: kneel, then lower yourself on your elbows, stand in this position for 5 minutes.
 Yoga classes for pregnant women also allow you to disperse the fluid.
Yoga classes for pregnant women also allow you to disperse the fluid. -
Lie on your side. In late pregnancy, your body itself will tell you the correct position for rest - lying on your side. In the early stages, it is also the most useful: in this position, the kidneys work most efficiently, utilizing excess water.
-
Drink, and do not limit yourself in this. You might think: the less I drink, the less swelling there will be. No, you can't drive them away like that, but getting dehydrated is easy. Drink as much as you want, but only clean water, fruit drinks or decoctions without sugar. Soda, juices from the store and other sugary drinks should be excluded from the diet.
-
Observe nutritional balance. During pregnancy, eat more protein foods, avoid pastries, bread, sweets and other carbohydrate-rich foods, limit the amount of fat in the diet. Completely give up "empty calories" - snacks and fast food.
-
Arrange fasting days. Treat yourself with a diet once a week. It's not about sitting on the water all day. There are many recipes for a tasty and quite nutritious "unloading" - from a kefir or banana diet to a chicken breast day or fruit smoothies.
-
Control your sodium intake. Sodium salts hold fluid in tissues, and the most famous of them is ordinary table salt. To prevent severe swelling during pregnancy, limit your daily salt intake to one level teaspoon, even less is better. When calculating, do not forget that salt enters the body not only from the salt shaker. It is found in many food ingredients (meat, fish, dairy products, tomatoes, etc.), and in almost all semi-finished and finished products - from sausage to bread. Over time, you may even come to love the natural taste of food without or with minimal salt added - it is quite good.
-
Take natural diuretics. Rosehip, hawthorn, chamomile, lingonberry, bearberry - in the pharmacy you can find a lot of natural remedies to combat edema.
 Discuss the purchase with your doctor: during pregnancy, you should consult with him before taking any medications, even herbal ones.
Discuss the purchase with your doctor: during pregnancy, you should consult with him before taking any medications, even herbal ones.
Compression stockings 6 can be worn to prevent swelling and varicose veins. Consult a doctor - he will tell you what is better to buy and how to use.
If swelling disappears during pregnancy, is it good?
If you've recently changed your diet, are spending more time outdoors, or are taking other activities, that's very good. So your treatments are working and you are on the right track.
Another thing is when edema during pregnancy disappears by itself, without any changes in your life. A few days before the planned date of delivery, this is normal: progesterone has done its job, and its level drops 7 , releasing excess water. If the birth is still far away, a spontaneous decrease in edema is at least a suspicious sign. Contact your doctor to establish the cause of the body's unexpected gift and decide what to do about it.