Is indigestion a sign of early pregnancy
Heartburn, gas, tender breasts, and more
Think you might be pregnant? Here are the most common pregnancy signs in the first month.
When you’re hoping to be pregnant and you haven’t missed your period yet—or it’s a day or two late—it’s pretty easy to interpret nearly any physical symptom as a sign of pregnancy. It’s not uncommon to feel symptoms in the first week or two of your pregnancy—or even earlier. “Some women experience pregnancy symptoms from the moment of conception,” says Karen Nordahl, a general practitioner and obstetrician in Vancouver and co-author of Fit to Deliver. “Usually, this is second- or third-time moms who remember a particular sensation, such as increased gas.” But many first-time moms miss these early pregnancy signs because the very first symptoms aren’t necessarily the ones we associate with having a baby on the way. So, yes, while some women experience nausea or hypersensitivity to smells, these seven symptoms are among the most common during the first few weeks of pregnancy.
Digestive changes are one of the most common early pregnancy signs, says Nordahl. If you feel a burning sensation in your chest after scarfing down your usual black coffee and egg-salad sandwich from the deli near your office, it might not be that the deli changed the recipe to include green onions or switched coffee brands; it could actually be pregnancy-related heartburn. One telltale sign of heartburn is that the burning sensation can feel worse when you bend over or lie down. It’s safe to reach for an antacid to relieve the burning, but also try to avoid certain foods, such as citrus fruits.
2. Pregnancy sign: Sore breastsBefore you start cursing your bra for suddenly feeling more like a contraption from the hardware store than the lacy lingerie that took a serious chunk out of your paycheque, consider that your newly sore boobs could be a sign that you’re pregnant. Breast tenderness is another common early pregnancy sign, according to Nordahl. For many women, what can make this symptom particularly confusing is that breast soreness is also a very common sign of your period. But early on in your pregnancy, your breasts may hurt because they’re expanding in preparation for producing milk.
Breast tenderness is another common early pregnancy sign, according to Nordahl. For many women, what can make this symptom particularly confusing is that breast soreness is also a very common sign of your period. But early on in your pregnancy, your breasts may hurt because they’re expanding in preparation for producing milk.
Being gassy—or, less eloquently, “farty”—is no problem when you’re chillaxing alone in your threadbare sweatpants, but it’s next-level horrifying when you’re out and about anywhere else. Unfortunately, it’s one of the more common early pregnancy signs. Expect flatulence during not only the first few weeks of pregnancy but also the next nine months. Inevitably, your unruly gas will strike right in the middle of a work meeting or during a cool-down in your silent yoga class.
Can’t zip up those light-wash jeans that fit like a glove a few weeks ago? It could be that extra-large soda and popcorn you inhaled while transfixed on the onscreen hunk at the cinema last night, but it could also be a sign that you’re expecting. Like breast tenderness, abdominal bloating is a symptom that’s common before your period, making it hard to tell apart from monthly premenstrual symptoms. The usual tactic to fight extra bloating and constipation is to ease up on excess salt and stay hydrated with water, both of which are good habits, whether you’re pregnant or not. But you might also want to buy a pregnancy test.
5. Pregnancy sign: Lower pelvic crampingPelvic cramping as an early pregnancy sign? Yep, it can be, according to Nordahl. That might seem counterintuitive, as cramps are super-typical symptoms of Aunt Flow. You were probably hoping that being pregnant meant you could kiss cramps goodbye, but sadly that’s not the case. Light cramps can be caused by early pregnancy hormonal shifts and implantation of the fertilized egg on your uterine lining.
Light cramps can be caused by early pregnancy hormonal shifts and implantation of the fertilized egg on your uterine lining.
The unusual sensation of feeling “full” is yet another early symptom of pregnancy. “Fullness can be experienced before a period is missed, but a first-time mom may miss it,” says Nordahl. “A second- or third-time mom may pick up on it right away, especially if she is actively trying to conceive.” If you’re getting a feeling of déjà vu from previous pregnancies that you’re experiencing at the gut level (literally), congrats, you could be preggo!
7. Pregnancy sign: A missed periodWell, duh, of course a missed period is the most common of early pregnancy signs. For many women who haven’t been pregnant before, this is usually the first symptom they notice, explains Nordahl. But hindsight is often 20/20. “A first-time mom usually thinks back and realizes that a few things were different but wasn’t sure what they meant,” she says.
Read more:
Due date calculator
Pregnancy by week: Follow along as your baby grows
Pregnancy food guide
See more on Getting Pregnant
Your Pregnancy Week by Week
Subscribe to Today’s Parent’s pregnancy newsletter for weekly updates on baby’s development, how you’re feeling and what to expect next.- Email*
- Your child's due date*
Month223456789101112
Day12345678910111213141516171819202122232425262728293031
Year2024202320222021
- CAPTCHA
- Consent*
Yes, I would like to receive Today's Parent's Pregnancy by Week newsletter. I understand I can unsubscribe at any time.**
FILED UNDER: Being pregnant FirstResponse0519 getting pregnant health service seo Ovulation Pregnancy pregnancy symptoms
Is Heartburn a Sign of Early Pregnancy?| TUMS
There are so many noticeable changes going on in your body when you’re pregnant. But there are also subtle symptoms of pregnancy you may have before you know you're pregnant. You might be wondering, is heartburn an early pregnancy sign?
But there are also subtle symptoms of pregnancy you may have before you know you're pregnant. You might be wondering, is heartburn an early pregnancy sign?
Let’s take a look at heartburn and how it might relate to pregnancy symptoms, as well as how to manage some discomfort you might be experiencing.
So, Is Heartburn an Early Sign of Pregnancy?It is—for some women.
Let’s back up a second and define “heartburn” because, for some women, it might be the first time they’ve experienced this digestive symptom. Heartburn is a term that describes a burning sensation in your chest. You feel heartburn when stomach acid refluxes, or seeps back up, into your esophagus, the part of the digestive track that connects your mouth to your stomach.
While every woman’s body is different, and you can certainly experience heartburn and indigestion without being pregnant, heartburn can occur at any point in a pregnancy1. So, a woman may experience heartburn as an early pregnancy symptom—even before she knows she’s pregnant.
If you have recently been experiencing symptoms of heartburn and indigestion and think you might be pregnant, see your doctor.
Will I experience heartburn while I am pregnant?Possibly—and likely. Many women experience heartburn beyond their first trimester of pregnancy2. There are a few reasons why:
Hormones relax muscles…During pregnancy, a rising level of the hormone progesterone relaxes the valve (known as the lower esophageal sphincter) that separate the stomach and esophagus. As a result, stomach acids can flow back into your esophagus2 and lead to some of the classic uncomfortable heartburn feelings that come with acid indigestion.
…and slow digestionAdditional hormones slow digestion, which mean food may stay in your stomach longer2 and lead to a higher likelihood of acid indigestion.
The uterus crowds other organsLater, as a pregnancy progresses and the uterus expands, it puts pressure on other organs in the abdomen3—including the stomach.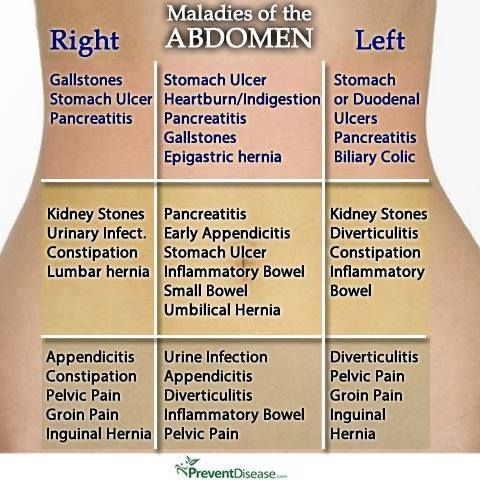
So, a stomach getting pushed out of place, with the food in it lingering longer, and a valve to the throat that’s a bit looser. The result? Heartburn.
A baby with lots of hair?You might have heard the old wives’ tale that having heartburn while pregnant means you’ll deliver a baby with a more hair on its head. One small scientific study years ago did find a correlation4! Make of that what you will.
Treatment for Heartburn and Acid Indigestion During Early PregnancyBefore jumping into the possible treatment options for pesky heartburn, confirm you are indeed pregnant with your trusted health care provider. They can help you better understand how to approach your symptoms and decide next steps.
If you are indeed pregnant and experiencing heartburn, we recommend taking the following measures to keep your heartburn symptoms at bay.3
- Avoid foods that flare up your symptoms. These might include spicy foods, fried foods or meals, caffeine such as coffee or soda.
 Create a journal of foods that you’ve noticed might cause upset stomach.
Create a journal of foods that you’ve noticed might cause upset stomach. - Stay away from large meals just before bedtime. This can trigger acid reflux due to your sleeping position.
- Sleep with a pillow wedge that raises your head to deter acid reflux.
- Consult with your doctor to determine whether an antacid, like TUMS, would be right for you.
While it’s no fun to experience heartburn and acid indigestion, talk to your care provider about the many tools and resources to help you manage. Whether together you decide you should use TUMS to help manage your symptoms or find comfort in pairing antacids with other preventative measures, you have options.
Read more about heartburn and pregnancy and other heartburn and indigestion-related issues.
Sources
- Simerpal Kaur Gill, Caroline Maltepe and Gideon Koren. The effect of heartburn and acid reflux on the severity of nausea and vomiting of pregnancy.
 Canadian Journal of Gastroenterology, April 2009. 23(4):270-272. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2711677/
Canadian Journal of Gastroenterology, April 2009. 23(4):270-272. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2711677/ - Juan C Vazquez. Heartburn in pregnancy. BMJ (British Medical Journal) Clinic Evidence, 2015; 2015: 1411. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4562453/
- Pregnancy – signs and symptoms. Department of Health, State Government of Victoria, Australia. https://www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au/health/HealthyLiving/pregnancy-signs-and-symptoms.
- Kathleen A. Costigan, Heather L. Sipsma and Janet A. DiPietro. Pregnancy Folklore Revisited: The Case of Heartburn and Hair. Birth: Issues in Perinatal Care, November 2006. Volume 33, Issue 4 p. 311-314. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/j.1523-536X.2006.00128.x
Toxemia, Intestinal Problems, and Heartburn
Find out how pregnancy affects your digestive tract, which trimesters are more likely to cause indigestion and nausea, and what to do to manage them.

During pregnancy, the burden on the mother's body increases. The body needs more nutrients, the body produces additional hormones. And the growing fetus puts pressure on neighboring organs, including the stomach and intestines. We tell you what symptoms are observed in each trimester, how to cope with toxicosis and get rid of heartburn.
Contents:
- 2. Toxicosis and pregnancy
- 3. Causes, risks and treatment of diarrhea during pregnancy
- 4. Heartburn and stomach pain during pregnancy
- 5. Bloating, constipation and microbiota during pregnancy
- 6. Note
Changes in the work of the gastrointestinal tract by trimesters of pregnancy
The average duration of pregnancy is 40 weeks, which are usually divided into trimesters in accordance with the stages of intrauterine development of the child.
Each trimester is accompanied by a number of changes in the body, including in the gastrointestinal tract:
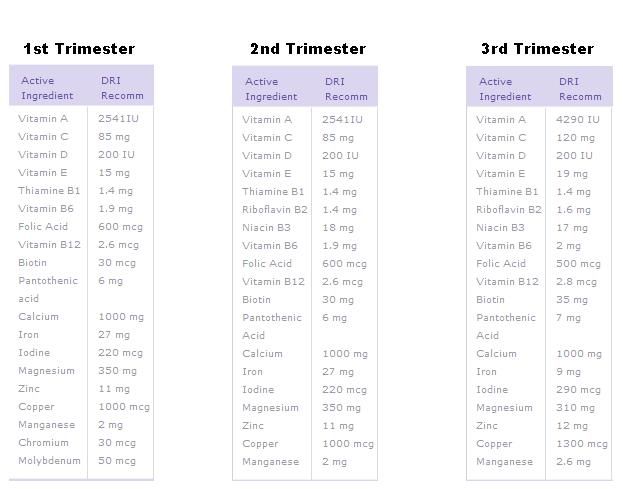
| The first trimester 1–13 weeks | 900 26 weeks | Third trimester of pregnancy 27–40 weeks |
| Morning sickness Morning sickness Zapor Intestinal disorder increased appetite TREAM to certain products Acid reflux | Constipation Acid Office 9000 9000 9000 9000 Flatulence Constipation Heartburn Violation of the outflow of bile Hemorrhoids |
The Atlas Genetic Test will help you find out how your genes affect the level of female sex hormones necessary for fertility and pregnancy.

Causes of gastrointestinal problems during pregnancy
Every pregnancy is accompanied by inevitable changes in the functioning of the digestive system. They are most often caused by hormonal changes and increased stress on organs, but they can also be associated with lifestyle and health conditions, for example:
- Sedentary lifestyle and unbalanced diet;
- Certain drugs, including calcium or aluminum antacids;
- Viral and bacterial infections;
- Intolerance to certain nutrients and allergic reactions;
- Stress;
- Diseases of the thyroid gland.
If you have chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and you are planning a pregnancy, try to consult your doctor in advance. Symptoms of conditions such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) or acid reflux are more likely to get worse during pregnancy. Your doctor will help prepare your body and create a prevention plan to help relieve symptoms during this time.
Irritable bowel syndrome, or IBS, is a functional bowel disease that causes frequent abdominal pain, impaired peristalsis, bloating, constipation, or diarrhea.
Morning sickness, vomiting and general malaise during pregnancy
Morning sickness and morning sickness during early pregnancy are common, because the body undergoes important changes necessary for the development of the child.
up to 90%
women experience nausea during pregnancy
Doctors find it difficult to say with certainty why pregnant women feel sick in the morning. The main theory is hormonal changes. But there are some patterns associated with an increased risk of morning sickness:
- Multiple pregnancy;
- Toxicosis during previous pregnancy;
- History of morning sickness during pregnancy in close relatives;
- Tendency to motion sickness in transport;
- Use of oral contraceptives containing estrogen before pregnancy;
- Frequent migraines;
- BMI 30 and above;
- Elevated levels of stress hormones
Risks of severe morning sickness and how to reduce nausea
Nausea and vomiting are usually not associated with a risk for mother and child and disappear by 16-20 weeks of pregnancy, but it is not necessary to wait so long - there are ways that can help reduce nausea and enjoy the process of waiting for a new person:
- Get plenty of rest - fatigue increases toxicosis;
- Avoid smells and foods that cause nausea;
- Eat something right after waking up.
 A toast or a slice of bread will help reduce nausea;
A toast or a slice of bread will help reduce nausea; - Avoid hunger - empty stomach increases nausea. Eat small meals often, prefer low-fat, high-carbohydrate foods;
- Try ginger - studies show it helps with nausea;
- Sip as often as possible and prefer still water.
In rare cases, pregnant women may develop hyperemesis gestationis or excessive vomiting. This is a serious condition that can lead to dehydration, kidney damage, seizures, abnormal heart rhythms, and even death.
Signs of dehydration include dry mouth, dizziness, dark urine, infrequent urination and/or dizziness.
Symptoms of excessive pregnancy vomiting:
- frequent nausea for a long time and regular vomiting after meals;
- dry skin and lips;
- sudden weight loss;
- low blood pressure (below 90/60).
If symptoms of excessive pregnancy vomiting occur, do not wait until the condition resolves on its own. It is necessary to seek medical help as soon as possible - the doctor will prescribe treatment, help adjust the diet and lifestyle of the expectant mother.
It is necessary to seek medical help as soon as possible - the doctor will prescribe treatment, help adjust the diet and lifestyle of the expectant mother.
0.5–2%
pregnant women experience excessive vomiting
Diarrhea in pregnancy
The word "diarrhea" comes from the Greek language and literally means "to flow through". This is a condition during which bowel movements or bowel movements occur three times a day or more often. This phenomenon is especially typical for the third trimester of pregnancy, but it can also occur earlier.
Symptoms of diarrhea:
- Three or more bowel movements per day
- Urgent urge to have a bowel movement
- Abdominal pain and cramps
- Bloating
Causes of diarrhea during pregnancy poisoning, dysbacteriosis, bacterial and viral infections:
| Gastroenteritis | Use of lactose and gluten in case of intolerance to these nutrients |
| Bacterial infections: listeriosis or salmonella | Chronic gastrointestinal diseases: Crohn's disease, IBS, ulcerative colitis |
| Certain antibiotics and antacids to reduce acidity | Laxatives |
| Sugar substitutes such as sorbitol | Overconsumption of certain foods |
Tip: If you have recently returned from a vacation in an exotic country with nausea and diarrhea and find out you are pregnant, see your doctor as soon as possible.
Gastroenteritis
One common cause of diarrhea during pregnancy is gastroenteritis or stomach flu. It is caused by bacterial or viral infections: norovirus, rotavirus, E. coli, salmonella, which enter the body through contact with contaminated surfaces, dishes, food and water.
Gastroenteritis usually lasts about three days. However, severe illness is a health hazard, especially during pregnancy, as it can cause dehydration, electrolyte imbalance, and lead to preterm labor.
The main symptoms of gastroenteritis are diarrhea without blood, nausea and vomiting, stomach cramps and pain, slight fever, headache and muscle pain.
Take extra precautions to reduce your risk of getting sick: frequent handwashing and surface disinfection. If the expectant mother has small children, they are not recommended to use the same cutlery.
Risks of diarrhea during pregnancy
Usually diarrhea during pregnancy is not a cause for concern. However, you should consult a doctor if the following symptoms occur during this period:
However, you should consult a doctor if the following symptoms occur during this period:
- Diarrhea for more than two days;
- Blood or mucus stools;
- Sudden weight loss;
- Pain in the abdomen;
- Dehydration.
How to treat diarrhea during pregnancy
If you have diarrhea during pregnancy, drink plenty of fluids, avoid foods high in fat and sugar, avoid dairy products, and caffeinated drinks.
Dehydration is a serious risk, especially during pregnancy, so electrolyte balance should be restored first with fluids and simple foods:
| Moderate fruit juices | Drinks without alcohol and caffeine |
| Bananas | Potato |
| Rice | Toast |
| Rusks | Light soups and broths |
| Pasta | Applesauce |
Find out about your body's ability to break down lactose and gluten with the Atlas Microbiota Test.
Stomach pain and heartburn during pregnancy
Many women experience stomach pain during pregnancy, especially in the upper part of the stomach, as well as heartburn - a burning sensation in the chest and esophagus.
This is more common in the third trimester, after about 27 weeks. This is an unpleasant but natural phenomenon during pregnancy: the baby grows inside the uterus and presses on other organs, including the stomach. And hormones cause the muscles to relax, which causes acid from the stomach to enter the esophagus and irritate it. In addition, pain can be caused by problems with certain organs such as the gallbladder, or inflammation of the pancreas.
Symptoms of heartburn during pregnancy:
- Burning in chest and esophagus;
- Feeling of overeating, heaviness or bloating;
- Belching, including with acid and/or food particles;
- Nausea.
It is unlikely that you will be able to avoid cramps and heartburn during pregnancy. However, some tips can help reduce their frequency:
However, some tips can help reduce their frequency:
Nutrition : try to avoid overeating - eat easily digestible food in small portions; do not eat three hours before bedtime; watch your posture while eating - so the pressure on your stomach will be less.
Smoking and alcohol: In addition to known harms to mothers and babies, tobacco smoke also relaxes the muscles in the lower esophagus, allowing acid to enter the esophagus. And alcohol provokes heartburn and acid reflux.
Although stomach pain and heartburn often accompany pregnancy, abdominal pain, especially in the third trimester, should be taken seriously. It can be a sign of preterm labor or placental abruption, and puts mother and baby at risk.
If you experience severe abdominal pain during pregnancy that is accompanied by the following symptoms, seek medical attention as soon as possible:
| Abdominal pain and fever | Bleeding |
| Regular convulsions | Unusual vaginal discharge / spotting |
| Vomiting | Low back pain |
| Pain or burning when urinating | Severe pain that lasts 30-60 minutes |
Bloating, constipation and microbiota during pregnancy
Excessive gas and constipation during pregnancy can be caused by hormonal changes, such as increased production of progesterone. This hormone, essential for nourishing the uterus and fetus, relaxes the muscles of the body, including the muscles in the intestines, which slows down digestion and increases flatulence. A similar reaction of the body can be observed before each menstruation, when the production of progesterone increases.
This hormone, essential for nourishing the uterus and fetus, relaxes the muscles of the body, including the muscles in the intestines, which slows down digestion and increases flatulence. A similar reaction of the body can be observed before each menstruation, when the production of progesterone increases.
Flatulence - bloating of the abdomen due to the accumulation of gases.
Here are a few simple rules that will help improve bowel movements and avoid constipation and bloating:
- If you don't usually eat a lot of fiber and indigestible foods like legumes, try to gradually introduce them into your diet;
- Avoid carbonated drinks and fatty foods;
- Move more;
- Drink plenty of fluids.
If bloating and constipation are accompanied by severe pain that lasts more than 30 minutes, or if you have been constipated for two or more weeks, see your doctor.
Gut microbiota and bacteria during pregnancy
A woman's body goes through many changes during pregnancy, and this can affect the microbiota, the bacterial ecosystem that lives in the gut. Trillions of microorganisms do important work for the whole body: they synthesize vitamins and essential acids, keep your intestines working and protect it from disease and inflammation.
Trillions of microorganisms do important work for the whole body: they synthesize vitamins and essential acids, keep your intestines working and protect it from disease and inflammation.
The additional influx of female hormones that accompanies pregnancy alters gut function and affects the microbiota. This is good, because the bacterial community is constantly adjusting to external and internal conditions in order to keep up with the needs of the body.
To keep your gut bacteria running smoothly, they need your help. Provide them with healthy foods and plant fibers. Fruits, vegetables, whole grains, nuts, and seeds contain prebiotics, special substances that beneficial bacteria feed on. When properly balanced, the bacteria even increase your body's defenses against harmful microorganisms that can cause gastroenteritis during pregnancy.
The Atlas Microbiota Test will help you understand how to prepare your intestines for future pregnancy and reduce the risk of digestive problems.
☝️ Take note
Now you have all the necessary knowledge and tools to help you deal with digestive problems during pregnancy. They are quite varied and quite natural, but in some cases it is necessary to immediately seek medical help:
- Vomiting blood;
- Blood in stool;
- Diarrhea for more than two days;
- Constipation for more than two weeks;
- Sudden weight loss;
- Severe pain interfering with daily activities;
- Difficulty breathing;
- Pain when swallowing or difficulty swallowing;
- Excessive fatigue.
More articles on the causes of digestive problems in the blog:
- 7 foods that cause gas and bloating
- Lindsey J Wegrzyniak, Treatment of Hyperemesis Gravidarum, 2012
- Edwards A. et al., The Maternal Gut Microbiome During Pregnancy, 2018
- National Health and Safety (NHS), Vomiting and morning sickness in pregnancy
- Kudzai Kanhutu, Travel and pregnancy: an infectious diseases perspective, 2011
- CDC, Pregnant travelers
- U.
 S. Department of Health and Human Services, Agency for healthcare research and quality, Abdominal Pain in Early Pregnancy
S. Department of Health and Human Services, Agency for healthcare research and quality, Abdominal Pain in Early Pregnancy - Robyn Horsager-Boehrer, M.D., UT Southwestern Medical Center, Should pregnant moms be concerned about gastroenteritis?, 2018
- International Foundation for Gastrointestinal Disorders, Pregnancy and Irritable Bowel Syndrome, 2016
- NHS Vomiting and morning sickness in pregnancy
- NHS, Severe vomiting in pregnancy
- Lindsey J Wegrzyniak et al., Treatment of Hyperemesis Gravidarum, 2012
- Karen Miles, Diarrhea during pregnancy, 2020
- Cleveland Clinic, Diarrhea
- You and your hormones, Progesterone
- Traci C. Johnson, MD, Pregnancy, Bloating, 2020
First signs of pregnancy before delay, early symptoms
Significant hormonal changes occur during pregnancy. This causes a number of symptoms. Some women experience pregnancy symptoms right away, while others may only have a few. About the first signs of pregnancy at an early stage and when exactly the initial signs of pregnancy appear are described in the article.
About the first signs of pregnancy at an early stage and when exactly the initial signs of pregnancy appear are described in the article.
At what time do the first signs of pregnancy appear
The answer to the question of when the first signs of pregnancy appear is rather ambiguous, because some women do not feel any signs at all during the first few weeks. At what week do the first signs of pregnancy appear in others? When do the first signs of pregnancy appear after conception? Symptoms of very early pregnancy (such as breast tenderness) may appear before a missed period, as early as six to seven days after conception, while other early signs of pregnancy (such as spotting) may appear about a week after ovulation. We will tell you more about the first signs of pregnancy before menstruation and when the signs of pregnancy appear.
What are the earliest signs of pregnancy?
The first signs of pregnancy in the early stages:
- delayed menstruation - 29%;
- nausea - 25%;
- mood swings - from 14 to 23%;
- breast changes - 17%;
- pain in the lower abdomen - 15%;
- depression - 15%;
- fatigue, drowsiness - 13%
- decrease in immunity - 6%;
- the first signs of pregnancy - discharge or implantation bleeding - only 3%.

Physiological first signs of pregnancy
What are the very first symptoms of pregnancy?
The most common physiological signs of pregnancy include:
- Tender and enlarged breasts. Signs of pregnancy in the first days after conception include breast changes (1-2 weeks after conception). The area around the nipples, called the areola, may also darken.
- Drowsiness and fatigue. Fatigue is also among the signs of pregnancy in the first days after conception. During early pregnancy, levels of the hormone progesterone rise dramatically, which can cause drowsiness.
- Nausea with vomiting. When do these signs of pregnancy appear? Morning sickness, which can appear at any time of the day or night, often appears between the second and eighth weeks after conception.
- Dizziness and fainting .
 This may be due to dilation of blood vessels, lowering blood pressure and blood sugar levels.
This may be due to dilation of blood vessels, lowering blood pressure and blood sugar levels.
- Spasms. Some women experience symptoms of pregnancy in the early days, such as mild uterine cramps.
- Headaches and back pains. Many pregnant women complain of frequent headaches, while others experience back pain.
- Insomnia - another first sign of pregnancy before the test. Causes can include stress, physical discomfort, and hormonal changes.
- Change in taste preferences. Like most other symptoms of pregnancy, these eating habits can be attributed to hormonal changes.
- Temperature. Early signs of pregnancy include fever (37-37.5).
- Delayed menses. How long does it take for the first signs of pregnancy to appear? If you are of childbearing age and a week or more has passed without your expected period, you may be pregnant.
 However, this symptom can be misleading if you have an irregular menstrual cycle.
However, this symptom can be misleading if you have an irregular menstrual cycle.
- Bloody discharge - early signs of pregnancy . This bleeding, known as implantation bleeding, occurs when a fertilized egg attaches to the lining of the uterus, approximately 10 to 14 days after conception.
- Bloating, heartburn. Hormonal changes can cause problems with the stomach and esophagus - these are common signs of pregnancy at 2 weeks.
- Constipation . Hormonal changes cause the digestive system to slow down, which can lead to constipation (signs of pregnancy after a delay).
- Frequent urination. You may urinate more than usual, a common sign of pregnancy at 5 weeks. During pregnancy, the amount of blood in the body increases, causing the kidneys to process excess fluid that enters the bladder.
- Runny nose.
 The appearance of this symptom is associated with excessive production of the hormone estrogen.
The appearance of this symptom is associated with excessive production of the hormone estrogen.
- Exacerbation of chronic diseases. This is a sign of pregnancy after ovulation.
- Increased salivation. Also associated with hormonal changes.
- Sense of smell enhancement . Signs of pregnancy in the first two weeks may cause sensitivity to certain smells and the sense of taste may change.
Emotional first signs of pregnancy
The first signs of pregnancy before delay (the earliest signs of pregnancy) include psycho-emotional symptoms.
- Mood swings.
- Irritability.
- Vulnerability, tearfulness.
- Capriciousness.
- Depression.
These are all emotional signs of early pregnancy that many women report. They describe feelings of heightened emotion or even bouts of crying, which are associated with rapid changes in hormone levels in the body. Also, signs of pregnancy at week 4 can make you feel PMS-style cranky. In addition, about 15% of women suffer from depression or anxiety during pregnancy. And after childbirth, these conditions suffer even more. In this case, it is better to seek help from a doctor.
Also, signs of pregnancy at week 4 can make you feel PMS-style cranky. In addition, about 15% of women suffer from depression or anxiety during pregnancy. And after childbirth, these conditions suffer even more. In this case, it is better to seek help from a doctor.
Do everything you can to improve your mood: get plenty of rest, eat well, get enough sleep, do things you love, and pamper yourself.
However, be aware that mood swings can be caused by a number of conditions other than pregnancy.
Influence of early pregnancy on daily routine
Early signs of pregnancy, mainly those that bring discomfort, can cause a change in daily routine. Here are some tips on what you can do with some of them:
- In case of toxicosis, avoid too hot or too cold food - this provokes an attack of vomiting. Eat often - at least 5-6 times a day, but in small portions.
- For nausea or vomiting, try ginger, chamomile, or vitamin B6.
- Drink plenty of water, in small sips between meals, to replenish lost fluids.
 Teas, juices, fruit drinks are also suitable.
Teas, juices, fruit drinks are also suitable. - For back pain, wear shoes or shoe insoles designed for pregnant women and avoid high heels. Sleep on a firm mattress.
- For chest discomfort, wear a special bra that supports enlarged breasts.
- For constipation, eat more fiber-rich foods such as wheat bran and fresh vegetables and fruits.
- If you suffer from headaches and mood swings, try stress reduction techniques such as yoga or meditation.
- Be outdoors more often, at least half an hour a day. This helps to reduce the symptoms of toxicosis, calm the nervous system.
- Maintain daily physical activity for as long as you feel comfortable doing certain activities.
- Eat a balanced diet with enough protein, fat and carbohydrates.
Important! All these tips are advisory in nature, be sure to consult your doctor if you encounter discomfort.
What to do if you find early signs of pregnancy
To make sure the signs of pregnancy are accurate, you can use the following methods to diagnose early pregnancy:
- Donate blood for hCG.
 This method can be used a few days after conception. This type of pregnancy test is done using a small sample of blood that is analyzed in a hospital. It determines whether there is a pregnancy hormone in your body and in what quantity. Its accuracy is 99%.
This method can be used a few days after conception. This type of pregnancy test is done using a small sample of blood that is analyzed in a hospital. It determines whether there is a pregnancy hormone in your body and in what quantity. Its accuracy is 99%. - Use test strip. It can be used at home from the first days of delay. To determine pregnancy, dip the reagent area of the test strip into the urine. Accuracy: 99%. You can buy Evitest or HomeTest test strips in our pharmacy.
- Use jet or electronic test. They can be used at home a few days before your expected period. You need to remove its protective cap, substitute the test under the stream of urine for 10 seconds, and after 3-5 minutes get the result. Accuracy: 97%. In our pharmacy you can buy Evitest or Alpe inkjet tests.
- Get your first ultrasound. You can use this method at 3-4 weeks from the start of a missed period. At this time, ultrasound will show the very fact of uterine pregnancy, and the place of attachment of the fetal egg is also determined.