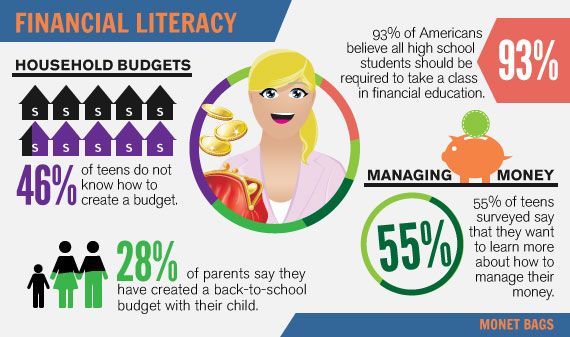
Sweeping to induce labor
Does It Speed Up Your Labor?
Written by WebMD Editorial Contributors
In this Article
- Understanding Labor Induction
- How Membrane Sweeping Works
- Pros and Cons of Membrane Sweeping
- Risks of Not Having Labor Induced
When you near the end of your pregnancy, your medical team watches you closely for signs that they may need to induce your labor. If your baby needs to be born sooner than everyone else counted on, membrane sweeping, also called sweep and stretch or membrane stripping, may be the labor-induction method your doctor chooses.
Understanding Labor Induction
Usually, a woman’s body goes into labor without much prompting, in preparation for a baby’s birth. But if you or your baby is at risk, your doctor may want to induce your labor sooner.
There may be other, practical reasons why a doctor may want to induce. But labor induction techniques should not be used before 39 weeks’ gestation unless there is a medical reason.
Your cervix prepares for labor by:
- Ripening, which is also called softening
- Opening, also called dilation
- Thinning, also called effacement
These things may start to happen but then stall. Or your water may break, but contractions don’t follow. In these cases, a doctor may choose to induce labor, to stimulate the body’s progress.
Other conditions that call for inducing labor include:
- Status of one or two weeks past the estimated due date
- High blood pressure
- Placenta detached from the uterus
- Infection
- Lung disease
- Diabetes
If your doctor doesn’t try membrane sweeping or another labor induction method, it increases your risk for a cesarean section delivery. While a C-section is sometimes necessary, it is considered higher-risk, so your doctor may want to avoid doing one if possible.
How Membrane Sweeping Works
Your doctor inserts a gloved finger into your vagina and up into your cervix to separate your water (amniotic) sac, or bag, from your uterus without breaking the sac. Your doctor uses this technique to urge your body to release prostaglandins, hormones that stimulate labor. As the water sac separates from your uterus, your cervix may soften and contractions may begin.
Your doctor uses this technique to urge your body to release prostaglandins, hormones that stimulate labor. As the water sac separates from your uterus, your cervix may soften and contractions may begin.
Your membranes can only be swept once your cervix opens enough for your doctor to insert a finger. Membrane sweeping to induce labor works for one in eight women. It’s one of the less risky labor-induction techniques.
Pros and Cons of Membrane Sweeping
Pros of membrane sweeping. The idea of forcing your body into labor may be daunting, but this technique has been used for decades.
Compare membrane sweeping to other ways to induce labor:
- Taking medicine that softens your cervix
- Taking medicine that causes your uterus to contract
- Using a balloon catheter to encourage the cervix to open
- Having medicine inserted vaginally to ripen your cervix
When membrane sweeping works and labor begins, there’s no need to help labor along with drugs like oxytocin, by breaking your water, or by using other, more invasive methods.
It’s considered a safe way to speed up your labor without increasing your risk for infection. It can also prevent you from needing to deliver via C-section.
Cons of membrane sweeping. You may start to feel uncomfortable afterward, with irregular contractions and some bleeding. In addition, if membrane sweeping brings on too many contractions, your uterus may be overstimulated.
Too many contractions can put you at risk for:
- Irregular fetal heart rate
- Too much pressure on your umbilical cord
- Uterine tear
- Increased risk of cesarean birth
- Fetal death
Medical problems you may have had before or during your pregnancy can also contribute to these complications. Your doctor will weigh the pros and cons of membrane sweeping before using it to induce your labor.
Risks of Not Having Labor Induced
Your health. If your doctor wants to sweep your membranes or use any other labor-induction technique around the time of your due date, take this into account: If you let your pregnancy go past full-term, you will be at greater risk of a difficult delivery as your baby continues to grow in utero. You’re also at an increased risk for a type of high blood pressure that's associated with pregnancy, after your due date.
You’re also at an increased risk for a type of high blood pressure that's associated with pregnancy, after your due date.
Your baby’s health. Your baby is also at risk as your pregnancy stretches on. With each passing week, the placenta becomes less effective at passing nutrients and blood to your baby. A baby that grows larger than your birth canal will allow for, may be stressed during delivery. A C-section may become unavoidable.
Staying pregnant longer can increase the risk of your baby passing their first meconium stool in utero. If your baby breathes meconium in the birth canal, it greatly increases their risk of developing an infection. A baby born after 42 weeks of gestation also has an increased risk of sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS).
Membrane sweep: One way to get your labor started
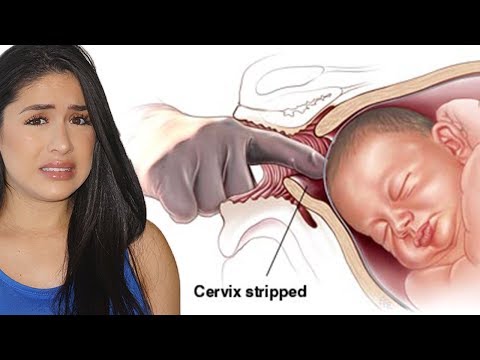
Membrane stripping (also known as a membrane sweep) is a procedure done to help induce labor if you're full term and your cervix is already somewhat dilated. Your practitioner inserts a finger through your cervix and manually separates your amniotic sac from the uterine lining. Many women find the procedure uncomfortable or even painful, but it only lasts a few minutes.
Your practitioner inserts a finger through your cervix and manually separates your amniotic sac from the uterine lining. Many women find the procedure uncomfortable or even painful, but it only lasts a few minutes.
What happens during membrane stripping?
Membrane stripping can be done during a regular office visit. Similar to an internal exam, your practitioner inserts a finger into your vagina and up through the cervix, then manually separates the amniotic sac from the lower part of your uterus with a sweeping motion. This triggers the release of prostaglandins, which may help further ripen your cervix and get contractions going.
When would I need a membrane sweep?
Your practitioner may suggest membrane stripping if you're near or past your due date. A pregnancy that goes longer than 41 or 42 weeks puts you and your baby at greater risk for problems. For example, the placenta may become less effective at delivering nutrients and oxygen to your baby, increasing the risk of a stillbirth or serious problem for your newborn.
If your practitioner is concerned that you or your baby aren't doing well, she may suggest a c-section or a quicker method of induction.
Is membrane stripping safe?
Yes, membrane stripping is safe when it's done at full term (39 to 41 weeks). Researchers have found that women who have membrane stripping aren’t more likely than other women to end up having a c-section or other complications.
Is membrane stripping effective?
Generally, yes. One study reported that 90 percent of women who had a membrane sweep delivered by 41 weeks, compared to 75 percent of women who didn't have one.
Membrane stripping might be most effective if you're past your due date.
Membrane stripping isn’t as effective as other methods of induction, such as using Pitocin. It’s generally only used in situations when there isn’t a pressing medical reason to induce.
What should I expect after a membrane stripping?
After the membrane sweep, you typically go home and wait for labor to start, usually within the next couple days. You may have some spotting and cramping during this time. However, if you’re having a lot of bleeding or pain, call your practitioner or go to the hospital.
You may have some spotting and cramping during this time. However, if you’re having a lot of bleeding or pain, call your practitioner or go to the hospital.
What's it like to have a membrane sweep?
Here's how BabyCenter Mom Michelle Stein describes it:
Advertisement | page continues below
"I've had four babies and three membrane sweeps. Each was a bit different.
Getting a membrane sweep feels kind of like a rough cervical check. During my first sweep, with my second baby, my whole body involuntarily recoiled. It’s a lot of pressure in a highly sensitive place. But although it was super uncomfortable for 10 seconds or so, I wouldn’t say it was particularly painful. I grimaced through the awkwardness and got through it by focusing my thoughts on the hope that labor wouldn’t be far away.
I got the sweep at an afternoon OB appointment and scheduled an induction for the following morning. By the time I showed up for the induction at 6 a.m., I was having regular contractions. They went ahead and gave me some Pitocin anyway. My daughter was born in less than four hours.
They went ahead and gave me some Pitocin anyway. My daughter was born in less than four hours.
When I had my membrane swept during my third pregnancy, I started spotting immediately. (This is a fairly common side effect.) I put on a panty liner when I got home and experienced mild, periodic cramping throughout that afternoon. By the time evening rolled around, actual contractions started. My husband and I headed to the hospital around 10:30 that night, and our third child was born about five hours later.
Since the membrane sweep worked so well with baby number three, I requested another during my fourth pregnancy. There was some initial spotting that time, after my OB did the sweep – but that’s it. I never even felt any cramping at all that day. This time, the sweep didn't work. I was bummed, for sure, because I was so ready to be done with that pregnancy and meet my baby. I was also hoping to avoid induction. But alas, I showed up at the hospital for my scheduled induction a few days later.
Even though my doctor gave me a heads-up that there's only a 50/50 chance that membrane sweep will jump-start labor, I had myself convinced that I would be having a baby within the next day. It was frustrating.
Nevertheless, I’d probably ask for a membrane sweep again if I were to have another child. Because from experience, heading into the hospital at 6 centimeters dilated with contractions two minutes apart and then giving birth three hours later without needing an induction is infinitely preferable to walking into a scheduled induction at less than 3 centimeters dilated with zero contractions and giving birth 19 hours later. But maybe that’s just me."
Was this article helpful?
Yes
No
Induction of labor or induction of labor
The purpose of this informational material is to familiarize the patient with the induction of labor procedure and to provide information on how and why it is performed.
In most cases, labor begins between the 37th and 42nd weeks of pregnancy. Such births are called spontaneous. If drugs or medical devices are used before the onset of spontaneous labor, then the terms "stimulated" or "induced" labor are used in this case.
Such births are called spontaneous. If drugs or medical devices are used before the onset of spontaneous labor, then the terms "stimulated" or "induced" labor are used in this case.
Labor should be induced when further pregnancy is for some reason unsafe for the mother or baby and it is not possible to wait for spontaneous labor to begin.
The purpose of stimulation is to start labor by stimulating uterine contractions.
When inducing labor, the patient must be in the hospital so that both mother and baby can be closely monitored.
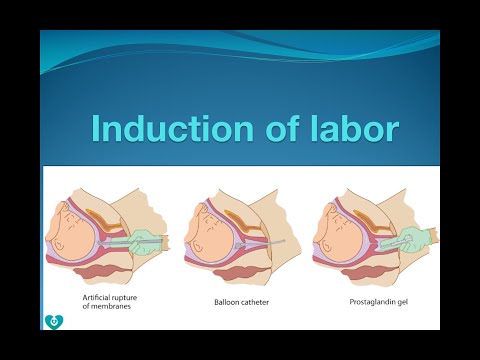
Labor induction methods
The choice of labor induction method depends on the maturity of the cervix of the patient, which is assessed using the Bishop scale (when viewed through the vagina, the position of the cervix, the degree of its dilatation, consistency, length, and the position of the presenting part of the fetus in the pelvic area are assessed). Also important is the medical history (medical history) of the patient, for example, a past caesarean section or operations on the uterus.
The following methods are used to induce (stimulate) labor:
- Oral misoprostol is a drug that is a synthetic analogue of prostaglandins found in the body. It prepares the body for childbirth, under its action the cervix becomes softer and begins to open.
- Balloon Catheter - A small tube is placed in the cervix and the balloon attached to the end is filled with fluid to apply mechanical pressure to the cervix. When using this method, the cervix becomes softer and begins to open. The balloon catheter is kept inside until it spontaneously exits or until the next gynecological examination.
- Amniotomy or opening of the fetal bladder - in this case, during a gynecological examination, when the cervix has already dilated sufficiently, the fetal bladder is artificially opened. When the amniotic fluid breaks, spontaneous uterine contractions will begin, or intravenous medication may be used to stimulate them.
- Intravenously injected synthetic oxytocin - acts similarly to the hormone of the same name produced in the body.
 The drug is given by intravenous infusion when the cervix has already dilated (to support uterine contractions). The dose of the drug can be increased as needed to achieve regular uterine contractions.
The drug is given by intravenous infusion when the cervix has already dilated (to support uterine contractions). The dose of the drug can be increased as needed to achieve regular uterine contractions.
When is it necessary to induce labor?
Labor induction is recommended when the benefits outweigh the risks.
Induction of labor may be indicated in the following cases:
- The patient has a comorbid condition complicating pregnancy (eg, high blood pressure, diabetes mellitus, preeclampsia, or some other condition).
- The duration of pregnancy is already exceeding the norm - the probability of intrauterine death of the fetus increases after the 42nd week of pregnancy.
- Fetal problems, eg, problems with fetal development, abnormal amount of amniotic fluid, changes in fetal condition, various fetal disorders.
- If the amniotic fluid has broken and uterine contractions have not started within the next 24 hours, there is an increased risk of inflammation in both the mother and the fetus.
 This indication does not apply in case of preterm labor, when preparation of the baby's lungs with a special medicine is necessary before delivery.
This indication does not apply in case of preterm labor, when preparation of the baby's lungs with a special medicine is necessary before delivery. - Intrauterine fetal death.
What are the risks associated with labor induction?
Labor induction is not usually associated with significant complications.
Occasionally, after receiving misoprostol, a patient may develop fever, chills, vomiting, diarrhea, and too frequent uterine contractions (tachysystole). In case of too frequent contractions to relax the uterus, the patient is injected intravenously relaxing muscles uterus medicine. It is not safe to use misoprostol if you have had a previous caesarean section as there is a risk of rupture of the uterine scar.
The use of a balloon catheter increases the risk of inflammation inside the uterus.
When using oxytocin, the patient may rarely experience a decrease in blood pressure, tachycardia (rapid heartbeat), hyponatremia (lack of sodium in the blood), which may result in headache, loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, depression strength and sleepiness.
Induction of labor, compared with spontaneous labor, increases the risk of prolonged labor, the need for instrumentation
(use of vacuum or forceps), postpartum hemorrhage, uterine rupture, the onset of too frequent uterine contractions and the associated deterioration of the fetus, prolapse umbilical cord, as well as premature detachment of the placenta.
If induction of labor is not successful
The time frame for induction of labor varies from patient to patient, on average labor begins within 24-72 hours. Sometimes more than one method is required.
The methods used do not always work equally quickly and in the same way on different patients. If the cervix does not dilate as a result of induction of labor, your doctor will tell you about your next options (which may include inducing labor later, using a different method, or delivering by caesarean section).
ITK833
This informational material was approved by the Women's Clinic on 01/01/2022.
How to induce labor naturally
There are at least seven ways to induce labor that are supported by science. Let's take a look at each of these "evidence-based" methods.
1. Sexual intercourse
Many women manage to induce natural childbirth through sex. This is because semen contains prostaglandins, the same hormone-like compounds found in cervical ripening drugs such as Cervidil.
The key to having sex for natural induction is not to do it once. With this natural method of labor induction, "3 times is the way to go." It is assumed that three ejaculations contain the same amount of prostaglandins as Cervidil.
Of course, at 40+ weeks of pregnancy, frequent sex is definitely not what the expectant mother dreams of, but it is definitely the best alternative to cervidil and pitocin, which can lead to more painful contractions and even rupture of the membranes or fetal distress.
2. Nipple Stimulation
Nipple Stimulation
Nipple stimulation can actually help induce labor or speed up stalled or slow labor. You should stimulate the entire breast, not just the nipples. Try a slow, rhythmic breast massage behind the areola.
You can do this yourself or ask your partner to help.
3. Evening Primrose Oil
Evening Primrose Oil contains prostaglandins that help prepare the cervix for childbirth. However, there is limited research on the efficacy and safety of evening primrose oil. Evening primrose oil can actually prolong labor by several hours when used vaginally. It can also cause early rupture of membranes, meaning your waters break before contractions begin.
Although many mothers claim that oil speeds up labor, there is still a risk, so it should be considered as a last resort.
4. Castor oil
Castor oil causes the intestines to contract, which can stimulate uterine contractions. But like evening primrose oil, this method should also be used with caution and only with the approval of your midwife or doctor.
Although many mothers have used it with great success and no other interventions. Yet it should be remembered that intestinal contractions cause terrible diarrhea. At best, this can be inconvenient; at worst, it can cause dehydration. If you and your birthing team decide to try this method, be sure to drink at least 500 ml of water to keep yourself hydrated and maintain healthy electrolyte levels.
5. Red raspberry leaf tea
Red raspberry leaf tea is a great way to tone the uterus during pregnancy and can also help induce labor.
Due to its stimulating effect, most midwives do not recommend drinking until the second trimester. For labor induction, increase the dose of this tea.
6. Eating dates
Research shows that eating dates during pregnancy helps women achieve greater cervical dilation, intact membranes, and more spontaneous labor when the time comes for delivery. Oxytocin use was significantly lower in women who consumed dates, and the average duration of the first stage of labor was shorter in women who consumed dates. As the study concludes, “dating dates during the last 4 weeks before delivery significantly reduced the need for labor induction and induction and resulted in more favorable labor.”
As the study concludes, “dating dates during the last 4 weeks before delivery significantly reduced the need for labor induction and induction and resulted in more favorable labor.”
What else can help induce labor?
While not backed by science, many moms claim these natural or "anecdotal" ways to induce labor.
1. Pamper yourself
Pamper yourself is a great way to relax and focus before having a baby. Sure, prenatal massage is great, but you might want to focus on the feet, which have special trigger points that can induce labor. A foot massage, reflexology, or even just a pedicure can be rewarding and definitely an enjoyable pastime.
2. Guided Relaxation
Soothing affirmations, guided meditation, and deep breathing can do wonders to help your body relax and prepare to welcome your baby. Fearful thoughts and anxiety can lead to the release of adrenaline and other stress hormones that stop the birth process.
Interestingly, before giving birth, cats go to a dark, quiet place. Darkness helps bypass stress hormones and increases levels of melatonin, a key hormone that can help trigger hormonal cascades. You can try this by turning off the lights, closing your eyes and focusing on your body and the amazing feat you are about to accomplish.
3. Nutrition
Follow your ideal pregnancy diet and remember to drink water. Childbirth is hard work and you will need all the support you can get. Although nutrition may not stimulate labor, it will definitely help you feel strong, prepared, and calm when labor actually begins.
4. Exercise
Moderate exercise is fantastic throughout pregnancy, and some women have been lucky enough to induce labor by walking, cycling, swimming, or other exercise. By moving our body, we can help the baby into its birth position and open up our pelvis for a faster delivery.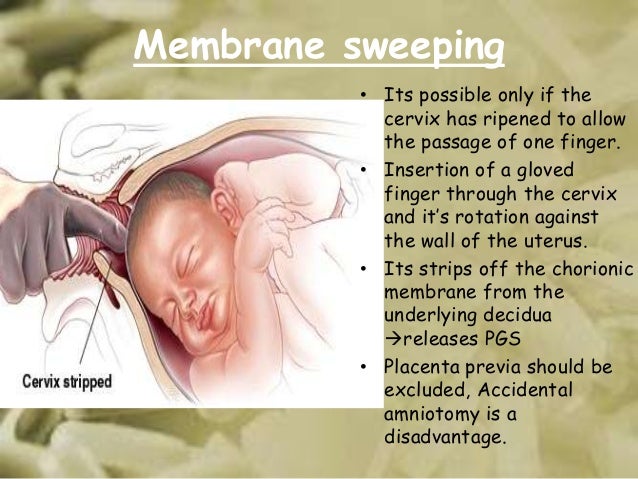 However, the main thing is not to overdo it. You don't want to be tired when labor starts.
However, the main thing is not to overdo it. You don't want to be tired when labor starts.
5. Acupuncture, acupressure and chiropractic
In addition to mental readiness, you and your child need to be physically ready, and acupuncture, acupressure and chiropractic can help with this. Acupuncture is a potentially useful way to induce labor, but there isn't a lot of solid research on this topic. However, acupuncture and acupressure have been used for many years to induce labor and are trusted by many women.
The idea of acupressure is that acupuncture and acupressure help to unblock any stagnant energy, which can help the child get into the correct position. Specifically, acupuncture points for inducing labor are found on the feet, arms, and back. They stimulate the thyroid, digestive and reproductive systems.
Chiropractic induction methods are based on the same idea. Opening and balancing the pelvis with chiropractic helps your baby get into the correct, deep position and stimulates your body for labor.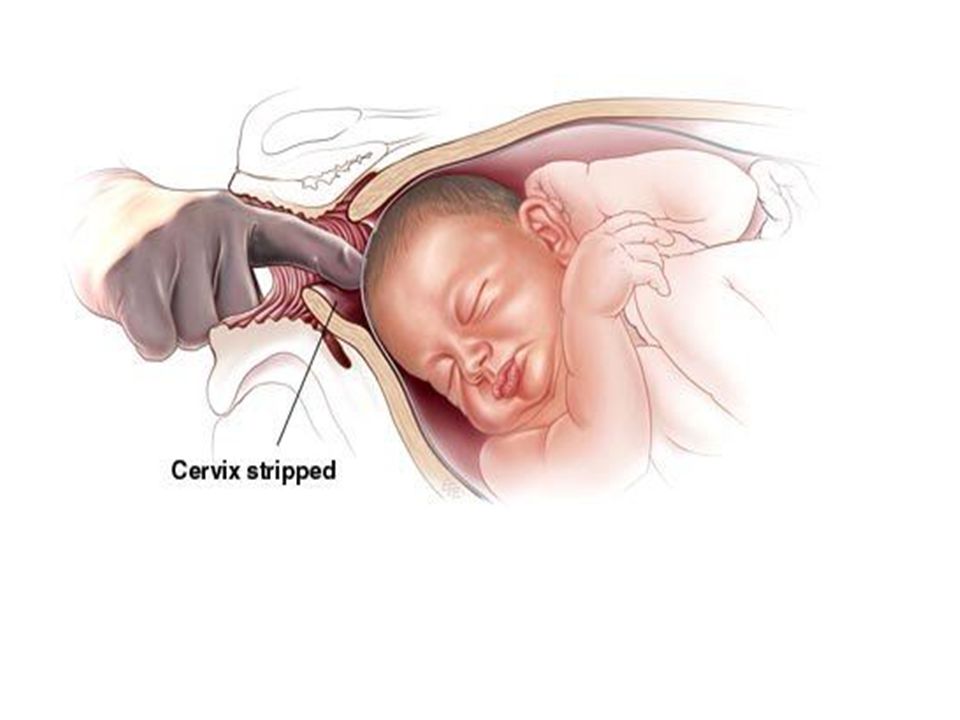
Find a suitable acupuncturist for pregnant women or contact a local mothers' group for recommendations.
6. Pineapple
The bromelain in pineapple and other tropical fruits is said to induce labor by stimulating the uterus. On the other hand, it may just be the stimulation of the intestines from eating a large amount of pineapple, which causes labor. Either way, it's a delightful way to induce labor naturally.
7. Spicy food
Some mothers use spicy food to induce labor. Like castor oil, spicy foods stimulate the intestines. Keep in mind that spicy foods can cause stomach upset, a side effect that is best avoided during childbirth.
8. Eggplant with Parmesan
Scalinis Restaurant near Atlanta, Georgia claims to have helped more than 300 women go into labor within 48 hours with their famous eggplant parmesan. Don't live near a restaurant? Dish you can try at home:
Ingredients:
3 medium eggplants
0. 5 cup flour
5 cup flour
6 eggs, beaten
2 cups Italian breadcrumbs
1L cups marinara sauce
1/2 cup grated romano cheese
1/2 cup grated parmesan cheese
200 gr mozzarella cheese, grated
2 cups ricotta cheese
How to cook:
After washing the eggplants, cut them into slices.
Lay the eggplant slices on a layer of paper towels and sprinkle with a little salt, then cover with another layer of paper towels and press down with something heavy. This will remove excess moisture. Let them sit for about an hour.
Working with one eggplant slice at a time, dust it with flour, then dip in beaten eggs, then coat well in breadcrumbs. Fry in hot olive oil on both sides until golden brown.
In a baking dish, alternate layers of marinara sauce, eggplant slices, ricotta, Parmesan, and Romano cheese until the baking dish is filled. Sprinkle with grated mozzarella cheese and bake for 25 minutes at 375°C. Let stand 10 minutes before serving.
Note. For a gluten-free option, use chickpea or buckwheat flour in place of flour and almond flour or semolina in place of breadcrumbs.
9. Homeopathic remedies
Homeopathic remedies are generally considered safe during pregnancy. Common homeopathic remedies used to induce labor include Pulsatilla 200C, Caullophyllum 200C, and Cimicifuga 200C. Some midwives recommend alternating all three times every three days until labor begins. Consult your gynecologist for dosage.
For more information on homeopathic remedies during pregnancy and childbirth, read Homeopathic Medicines for Pregnancy and Childbirth by Richard Moskowitz and Homeopathy for Pregnancy, Childbirth and Your Baby's First Year by Miranda Castro.
10. Special Exercises
This chart helps misplaced babies get into the ideal birthing position, which puts pressure on the cervix and stimulates labor.
This simple procedure has three parts, including:
1. Start in cat/cow pose with knees wide apart, then lower chest as low as possible and buttocks as high as possible. Swing while maintaining this position for 30 minutes. This helps the baby move out of the pelvis a little, allowing him to rotate and change his head position.
Start in cat/cow pose with knees wide apart, then lower chest as low as possible and buttocks as high as possible. Swing while maintaining this position for 30 minutes. This helps the baby move out of the pelvis a little, allowing him to rotate and change his head position.
2. Roll onto your left side, straighten your bottom leg, then lift your top leg as high as you can. Roll forward using pillows for support. Maintain this position for 30 minutes.
Do your best to move for at least 30 minutes. Lunges, walking up and down stairs in twos, sideways, sitting on a birth ball, and hula hoops are especially helpful because they put your pelvis in an asymmetrical position.
Which food induces labor?
As noted above, when it comes to food to induce labor, dates are the best choice. Research shows that dates reduce the need for induction and shorten labor. Pineapple and spicy foods can also help induce labor, although there isn't much evidence to support these theories, only a lot of anecdotal evidence.
How long does it take to have a baby after induction?
As with most aspects of childbirth, there is no hard and fast rule. Every woman is different: for some mothers, induction of labor can take only a few hours, for others it can take several days. And sometimes induction doesn't work at all.
Why does induction cause more pain?
Our body naturally produces oxytocin, a hormone that stimulates contractions. During induction, a woman is usually given a synthetic form of oxytocin, such as pitocin, to speed up contractions. This can cause labor to start too quickly, resulting in stronger and more intimate contractions.
What are the risks of induction?
The risks of induction vary depending on the method of induction, but the biggest risk is that the induction will fail. In 25% of cases, induction failed - this may mean that the mother is in labor for a long time, but a caesarean section may be required eventually. It can be physically taxing and emotionally draining for a mom.
It can be physically taxing and emotionally draining for a mom.
Other risks include:
Low fetal heart rate: The strong, frequent contractions caused by pitocin may cause discomfort to the baby.
Uterine rupture: The strong, frequent contractions caused by Pitocin can cause the uterus to rupture. This is most common in mothers who have previously had uterine surgery.
Excessive bleeding in the mother after childbirth: When stimulated, the uterus may not contract properly after childbirth.
Infection: Rupture of membranes can put mother and baby at increased risk of infection.
What if I miss my due date? Should I induce labor?
Absolutely not! You have the right to refuse anything that does not suit you, including induction of labor.
At 40 weeks gestation, there is no evidence that induction is necessary in a normal healthy pregnancy. Remember that your due date is determined by a number of factors, including the average length of pregnancies in your family, the accuracy of your due date calculation, and your individual child. Your baby and body are the ones who initiate labor and usually know when they are ready.
Your baby and body are the ones who initiate labor and usually know when they are ready.
If you have passed 41 weeks of pregnancy
There is no reason to consider induction in a normal healthy pregnancy before 41 weeks, and you may want to wait even longer before trying any of these methods. If you choose to go through 41 weeks without trying to induce labor, your healthcare provider will likely keep a close eye on you.
If you have passed 42 weeks of pregnancy
Natural induction of labor is still a priority and may increase the likelihood of other labor interventions. If mom and baby are healthy, it is perfectly reasonable and scientifically justified to give birth at 42 weeks.
How did other mothers induce labor?
I asked moms on my Facebook page about ways to induce labor naturally. Here are some of their responses:
- My water broke but my contractions didn't start. That night I went for acupuncture and two hours later I had a nice steady contraction rhythm! — Jill B.

- Massage of painful points, sex, walks. — Norma O.
- I have massaged the pressure points on the feet and around the ankles that are supposed to induce labor. That night I went into labor, that is, a week before the expected date of delivery! I also started drinking 1 cup of red raspberry leaf tea a day at 32 weeks pregnant and gradually increased it to 4 cups by the time I was due. — Jennifer B.
- A friend told me that she had read that pineapple can induce labor. Without thinking, the next day I ate almost a whole pineapple. That night I went into labor, a week early. — Stephanie N.
- With both of my kids, I've tried everything - spicy food, pineapple, even scrubbing floors/lunges vigorously. But both times the trick was to have sex with my husband and make him ejaculate inside me. I went into labor less than 12 hours after two times. — Lisa S.
- The first child was "delayed" for 3 days, so I stimulated naturally with evening primrose oil (oral and vaginal) and castor oil.