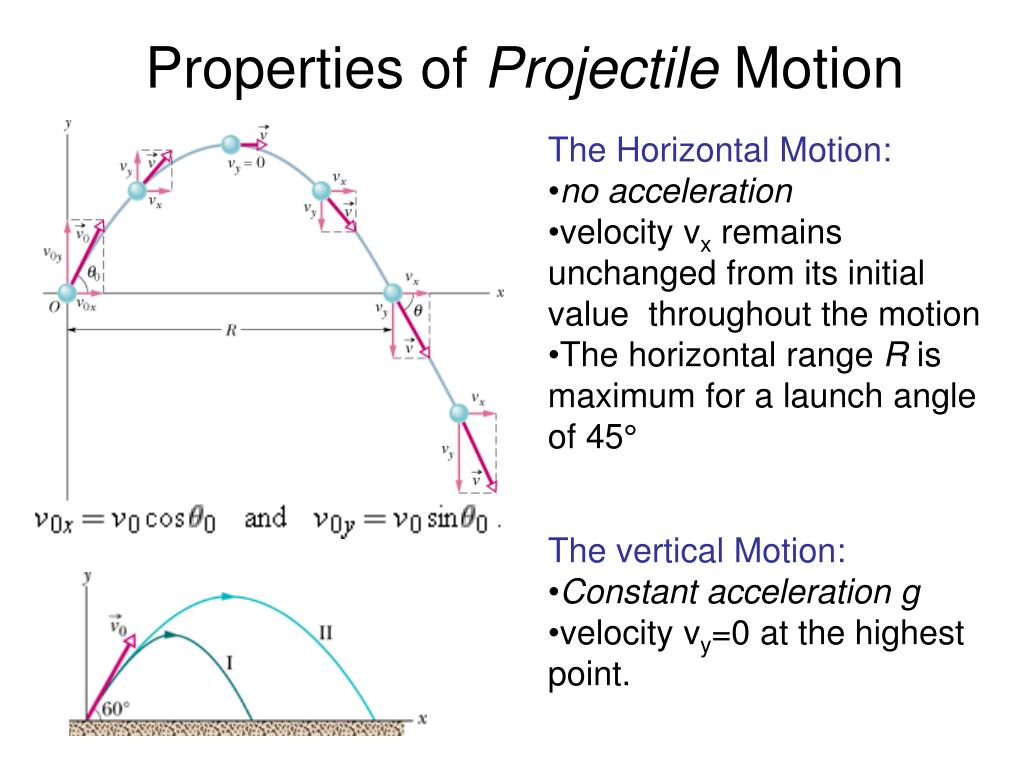
Stomach muscle separation during pregnancy
Diastasis Recti (Abdominal Separation): Symptoms & Treatment
Overview
Diastasis recti happens when a person's abdomen stretches during pregnancy and creates a gap in the abdominal muscles.What is diastasis recti?
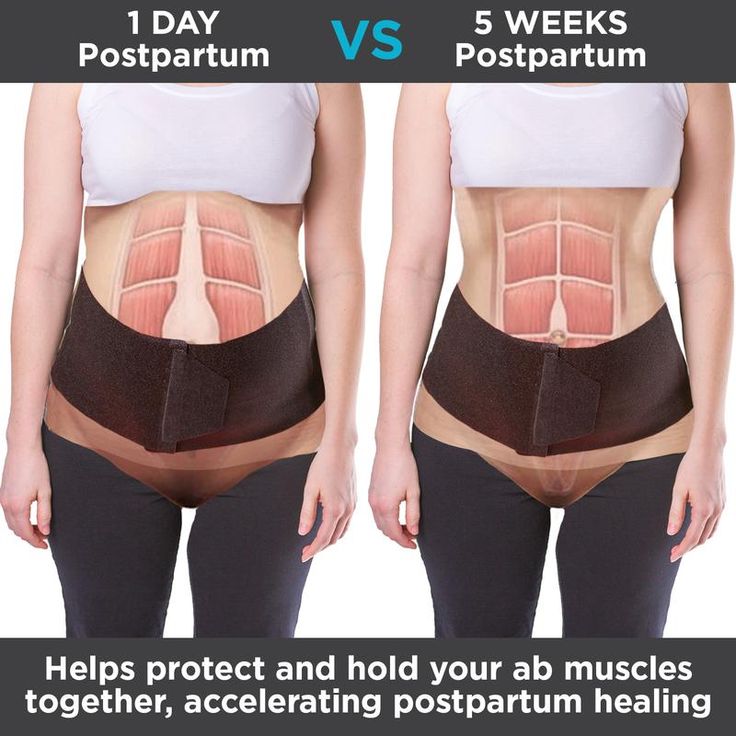
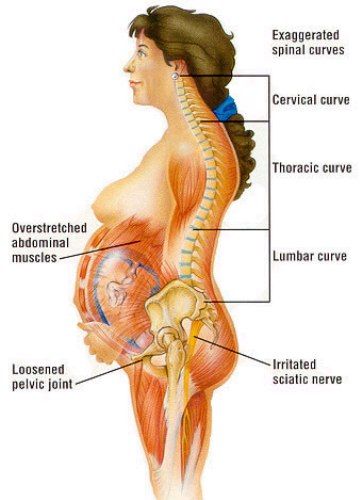
Diastasis recti (diastasis rectus abdominis or diastasis) is the separation of the rectus abdominis muscles during and after pregnancy. The rectus abdominis runs vertically along the front of your stomach. It's frequently referred to as someone's "six-pack abs." It's divided into left and right sides by a band of tissue called the linea alba that runs down the middle. As your uterus expands during pregnancy, the abdominals are stretched and the linea alba thins and pulls apart. This band of tissue gets wider as it's pushed outward.
Once you deliver your baby, the linea alba can heal and come back together. It's highly elastic and retracts backs (like a rubber band). When the tissue loses its elasticity from being overstretched, the gap in the abdominals will not close as much as it should. This is diastasis recti.
If you have diastasis, your belly may appear to stick out just above or below the belly button, making you appear pregnant months or years after giving birth.
Why does diastasis recti happen?
Pregnancy puts a lot of pressure on your abdomen (abs). The abdomen is made up of left and right ab muscles and a thin band of connective tissue (linea alba) in between. They are pushed outward and stretched to make room for the growing baby. Diastasis recti occurs when the linea alba is overstretched and doesn't come back together. The left and right sides of the abdominals stay separated. It's also referred to as an "ab gap" or abdominal separation.
Who gets diastasis recti?
Diastasis recti is most common in pregnant and postpartum women (it can also be seen in men and infants). Diastasis recti usually develops in the third trimester. There is increased pressure on the abdominal wall because the baby is growing quickly during this time. Most people don't notice diastasis recti until the postpartum period.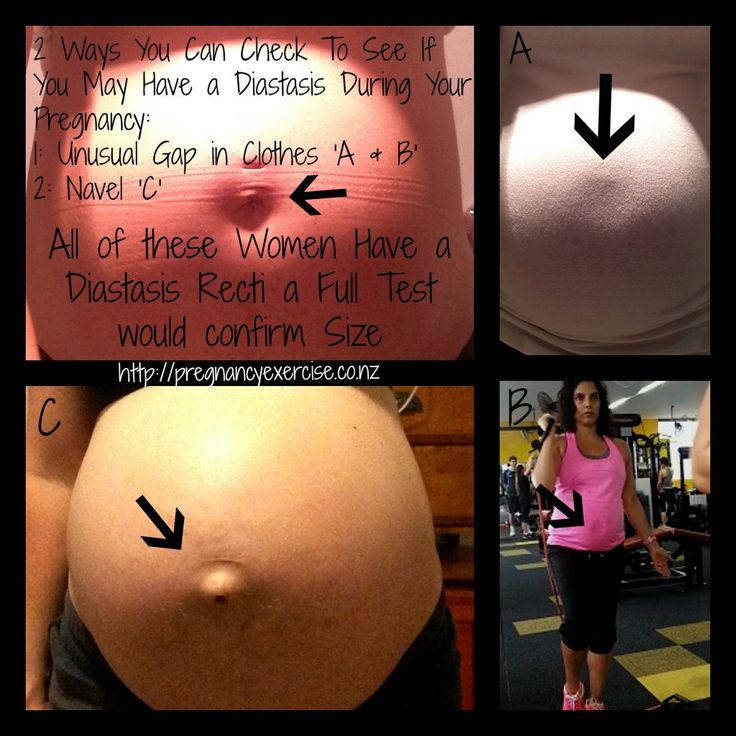
How common is diastasis recti?
Diastasis recti is extremely common in those who are pregnant and during the postpartum period. It affects 60% of people. It usually resolves itself within eight weeks of delivery. About 40% of those who have diastasis recti still have it by six months postpartum.
Symptoms and Causes
What are the symptoms of diastasis recti?
Most people don't notice signs of diastasis recti until they are postpartum. You can have diastasis recti during pregnancy, but it's hard to distinguish because your abdomen is stretched.
Common signs of diastasis recti during the postpartum period are:
- A visible bulge or "pooch" that protrudes just above or below the belly button.
- Softness or jelly-like feeling around your belly button.
- Coning or doming when you contract your ab muscles.
- Difficulty lifting objects, walking or performing everyday tasks.
- Pain during sex.
- Pelvic or hip pain.
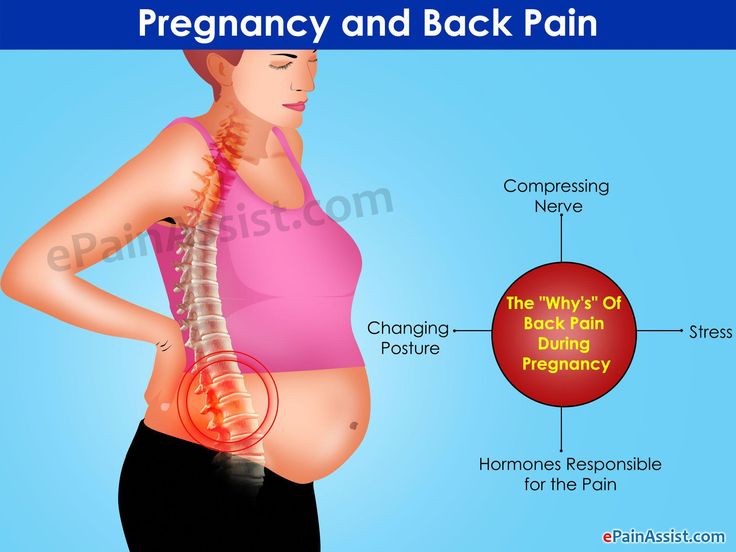
- Low back pain.
- Poor posture.
- Urine leaking when you sneeze or cough.
- Constipation.
- Feeling weak in your abdominals.
What does diastasis recti feel like?
Diastasis recti is not painful. You may feel pain associated with some of the side effects of diastasis, but the ab separation itself doesn't hurt. You may feel weakness in your core when doing once easy tasks, like lifting a laundry basket. Some people feel a jelly-like texture in the space between the left and right abdominals when contracting the ab muscles.
How do I know if I have diastasis recti?
There are some common signs that can signal you have diastasis recti. One of the most common signs of diastasis recti is a bulge in your midsection that doesn't go away, even after exercising or losing weight gained during pregnancy. Another sign is that your belly cones or domes when you lean back on a chair or get up out of bed. You can check for diastasis recti on your own, but it is always a good idea to speak with your healthcare provider about your symptoms.
What are the risk factors for developing diastasis recti?
Several factors can increase your risk for developing diastasis recti:
- Having multiple pregnancies (especially back-to-back).
- Being over 35 years old.
- Having multiples (such as twins or triplets).
- Having a heavy or big baby.
- Being extremely petite.
- Vaginal delivery. Pushing can increase abdominal pressure.
Diagnosis and Tests
How is diastasis recti diagnosed?
Your healthcare provider will evaluate if diastasis is present, where it's located and how severe it is. Diastasis recti can occur above the belly button, below the belly button and at the belly button.
Your provider will use their hands and fingers to feel the abdominal area for gaps and muscle tone. Some providers may use ultrasound, measuring tape or a tool called a caliper for a more accurate measurement. This exam typically occurs at your postpartum appointment before being cleared for exercise.
An abdominal gap wider than 2 centimeters is considered diastasis recti. Diastasis recti is also measured in finger widths, for example, two or three fingers' separation.
Your healthcare provider may recommend movements for diastasis recti or they may refer you to a specialist for additional treatment.
How do I test myself for diastasis recti?
You can test yourself for diastasis recti:
- Lie on your back with your knees bent and feet flat on the floor.
- Lift your shoulders slightly off the ground, keeping one hand behind your head for support. Almost like you are doing a sit-up. Look down at your belly.
- Move your other hand above your belly button area, palms down and fingers towards your toes.
- Use your fingers to feel for a gap between the abs. See how many fingers can fit in the gap between your right and left abdominals.
If you feel a gap of two or more finger widths, discuss your concerns with your healthcare provider. They should confirm diastasis recti with a proper diagnosis and recommend appropriate care.
They should confirm diastasis recti with a proper diagnosis and recommend appropriate care.
Management and Treatment
How can I fix diastasis recti?
To fix diastasis recti, you'll need to perform gentle movements that engage the abdominal muscles. Before starting an exercise program, be sure it's safe for diastasis recti. Work with a fitness professional or physical therapist who has experience with diastasis recti. They can create a treatment plan to make sure you are performing the movements correctly and progressing to more challenging movements at the right time.
Certain movements will make abdominal separation worse. During the postpartum period, there are some modifications you should make:
- Avoid lifting anything heavier than your baby.
- Roll onto your side when getting out of bed or sitting up. Use your arms to push yourself up.
- Skip activities and movements that push your abdominals outward (like crunches and sit-ups).
Some people use binding devices (elastic belly bands) to help hold their belly in and support the lower back. Wearing binders can't heal diastasis recti and will not strengthen your core muscles. It can be a good reminder of your diastasis recti and promote good posture.
Wearing binders can't heal diastasis recti and will not strengthen your core muscles. It can be a good reminder of your diastasis recti and promote good posture.
Can you fix diastasis recti without surgery?
Yes, it's possible to fix diastasis recti without surgery. Surgery is rarely performed to fix diastasis recti. Healthcare providers will recommend physical therapy or at-home exercises to help heal diastasis before surgical methods. Surgery is performed in cases of hernia (when an organ pushes through the linea alba) or if a woman wants diastasis recti surgery (a tummy tuck).
What are the best exercises for diastasis recti?
The best exercises for diastasis recti are those that engage the deep abdominals. Most diastasis recti exercises involve deep breathing and slow, controlled movements. Unfortunately, many of the most common ab exercises (like crunches) can worsen your diastasis. Before starting abdominal exercises, ask your healthcare provider to check you for diastasis recti.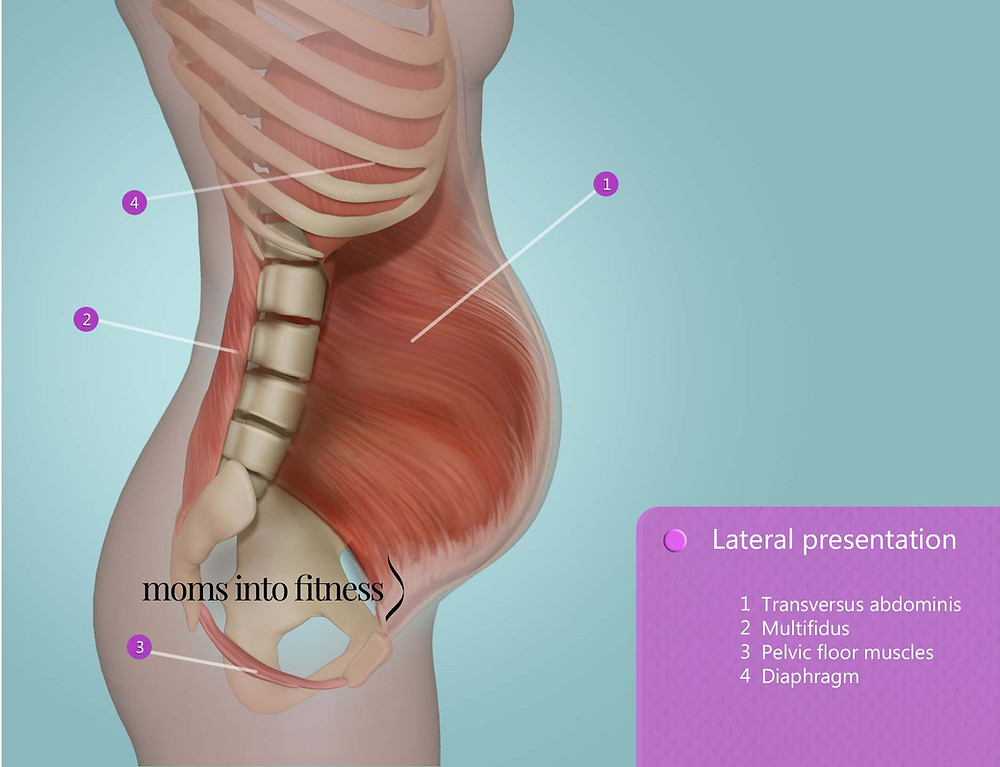
What movements make diastasis recti worse?
Any movement that bulges the abdominal wall forward can cause more damage to your diastasis recti. Everyday movements like getting out of bed or up off a chair can worsen diastasis. Try to be mindful about how you are using your abdominals as you go about your day.
These exercise movements should be avoided if you have diastasis recti:
- Crunches or sit-ups of any kind.
- Planks or push-ups (unless using modifications).
- Downward dog, boat pose and other yoga poses.
- Double leg lifts, scissors and other Pilates moves.
- Any exercise that causes your abdominals to bulge, cone or dome.
Prevention
How do I prevent diastasis recti?
Some abdominal separation is normal and expected with pregnancy. There are some things you can do to lower your risk for developing diastasis recti:
- Healthy weight gain during pregnancy: Exercising and eating healthy foods to keep weight gain within a healthy range.

- Proper posture and deep breathing: Stand up straight with your shoulders back. Take deep breaths that allow your ribs to expand and not just your belly.
- Safe core exercises: Avoid exercises like sit-ups and crunches that put pressure on your abdominals after 12 weeks of pregnancy and postpartum.
- Don't strain while lifting: Certain day-to-day activities like lifting grocery bags or your children can put undue strain on your abdominals.
- Log roll when getting out of bed: If you're pregnant or postpartum, roll to one side and use your arms to push up out of bed.
Outlook / Prognosis
How long will it take to heal my diastasis recti?
The amount of time it takes to heal diastasis recti depends on the amount of ab separation and how consistent you are with strengthening exercises. After several weeks postpartum, this gap will start to close as your muscles regain strength. If you're making modifications to your lifestyle and performing exercises with good form, you're more likely to notice progress.
If you're making modifications to your lifestyle and performing exercises with good form, you're more likely to notice progress.
Can I get diastasis recti again?
Yes, you can heal your diastasis recti and get it again. Your risk for diastasis recti increases the more times you are pregnant. Think of the linea alba as a rubber band that is continuously stretched. Over time, the rubber band will lose its elasticity. The linea alba may not regain its original shape or form after being stretched through multiple pregnancies.
Is it too late to fix my diastasis recti?
It's never too late to repair your diastasis recti. With the proper exercises, you can fix your ab separation years after you've delivered your last baby.
Are there complications from diastasis recti?
If left untreated or in severe cases of diastasis recti, complications can include:
- Umbilical hernia.
- Increase in back pain.
- Pain during sex.
- Urinary incontinence.

- Pelvic and hip pain.
Living With
When should I see my healthcare provider?
Diastasis recti is a common and easily treated condition. If you have more than a two-finger gap between your abdominals or are experiencing pain, contact your healthcare provider for a diagnosis. They may want you to see a physical therapist or pelvic floor specialist to help strengthen your abdominal muscles.
A note from Cleveland Clinic:
Diastasis recti can make you appear pregnant years after your last baby. Discuss your concerns with your healthcare provider so they can diagnose and treat you. Getting treatment can help you feel more confident in your body and correct any pain you are experiencing.
Abdominal separation (diastasis recti) | Pregnancy Birth and Baby
Abdominal separation (diastasis recti) | Pregnancy Birth and Baby beginning of content4-minute read
Listen
What is abdominal separation?
Some women find their stomach muscles weaken and separate during and after pregnancy.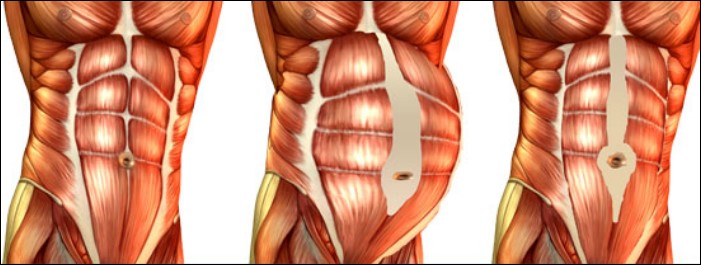 This is known as abdominal separation, ‘diastasis recti’ or ‘recti divarication’. It is a common condition and often gets better in the first 8 weeks after having your baby.
This is known as abdominal separation, ‘diastasis recti’ or ‘recti divarication’. It is a common condition and often gets better in the first 8 weeks after having your baby.
Abdominal separation occurs when the growing uterus causes the 2 long, parallel muscles of your stomach to separate from each other. These muscles run from your chest to your pelvis, just under the skin, down the middle of your belly.
Abdominal separation is partly due to the pressure of your growing baby, and partly due to the hormonal changes that take place during pregnancy. It usually starts in the second half of pregnancy.
Abdominal separation is more common in women who have had more than 1 child, are aged over 35 or who are having twins or triplets (or more). It can also occur in a small-statured woman who is having a larger-than-average baby.
It is sometimes known as ‘DRAM’ (diastasis of rectus abdominis muscle).
What are the signs and symptoms of abdominal separation?
If you have abdominal separation after the birth of your baby, you may be able to see a gap between the two bands of abdominal muscles.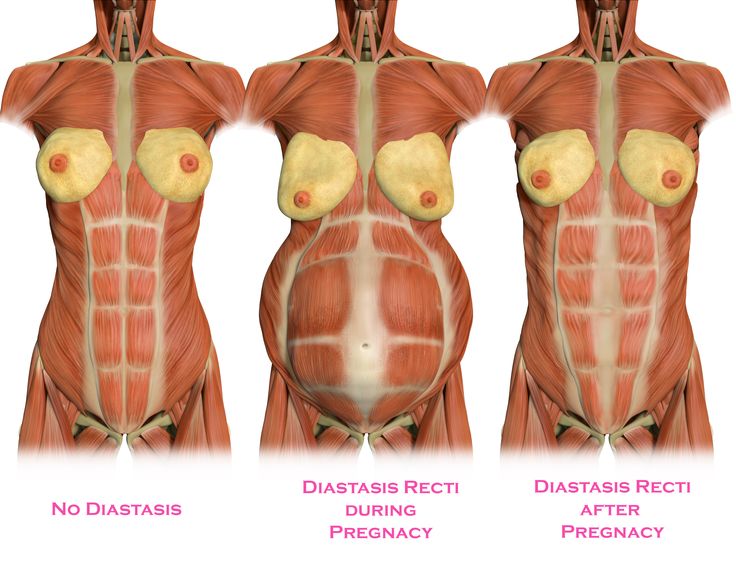 You can see this gap more clearly if you lie flat on your back and lift your head up.
You can see this gap more clearly if you lie flat on your back and lift your head up.
You might also notice a physical canoe-shaped bulge in the middle of your stomach, especially when your abdominal muscles are active.
Some women with abdominal separation also get lower back pain, as the separation prevents the stomach muscles from supporting the back.
How is abdominal separation diagnosed?
Your GP, midwife or physiotherapist can check how big your abdominal separation is by measuring it with their fingers or a measuring tape, or by doing an ultrasound.
Does abdominal separation go away by itself?
Abdominal separation usually goes away after the birth of the baby. That said, up to 1 in 3 women still report problems with abdominal separation 12 months after the birth.
How can abdominal separation be prevented during pregnancy?
Strengthening your core muscles before you get pregnant or in the early stages of pregnancy might help prevent abdominal separation.
It’s best to avoid putting excess strain on your abdominal muscles while pregnant. Avoid sit-ups or planks. Try to avoid constipation and if you have a cough, get it treated.
How is abdominal separation after the birth treated?
It’s important to stop the separation from getting worse. Try these tips:
- Avoid lifting anything heavier than your baby.
- Roll onto your side when getting out of bed or sitting up.
- Choose gentle exercises (rather than intense ones) that strengthen the deeper stomach muscles.
- Skip activities and movements that can make abdominal separation worse, such as sit-ups (crunches), oblique curls and some yoga poses (ask your GP, midwife or physiotherapist for advice).
You can also wear a supportive brace or compression underwear to help support your back and resolve the muscle separation.
There is a good chance that with time and care, the muscles will come back together. If that doesn’t work as well as you’d like, surgery after you’ve had your baby is an option.
Surgery often involves using stitches to repair the abdominal wall and reduce the gap between the muscles. This can improve quality of life and muscle strength, especially when separation is wider than 3cm.
Where to get help
If you notice anything unusual about your stomach muscles or experience any symptoms, see your GP, midwife or physiotherapist. You can find a physiotherapist near you using the healthdirect service finder.
You can also contact Pregnancy, Birth and Baby on 1800 882 436 to speak with a maternal child health nurse.
Sources:
Royal Women’s Hospital (Abdominal muscle separation), Surgical Endoscopy (The general surgeon’s perspective of rectus diastasis), King Edward Memorial Hospital (Physiotherapy after childbirth), Pelvic Floor First (Re-thinking abdominal training in pregnant and postnatal women)Learn more here about the development and quality assurance of healthdirect content.
Last reviewed: September 2020
Back To Top
Related pages
- Yoga and Pilates during pregnancy
- Looking after your body after having a baby
- Pelvic floor exercises
- Safe return to exercise after pregnancy
- Exercising during pregnancy
- Physiotherapy advice after pregnancy
Need more information?
Disclaimer
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is not responsible for the content and advertising on the external website you are now entering.
OKNeed further advice or guidance from our maternal child health nurses?
1800 882 436
Video call
- Contact us
- About us
- A-Z topics
- Symptom Checker
- Service Finder
- Linking to us
- Information partners
- Terms of use
- Privacy
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is funded by the Australian Government and operated by Healthdirect Australia.
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is provided on behalf of the Department of Health
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby’s information and advice are developed and managed within a rigorous clinical governance framework. This website is certified by the Health On The Net (HON) foundation, the standard for trustworthy health information.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
This information is for your general information and use only and is not intended to be used as medical advice and should not be used to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any medical condition, nor should it be used for therapeutic purposes.
The information is not a substitute for independent professional advice and should not be used as an alternative to professional health care. If you have a particular medical problem, please consult a healthcare professional.
Except as permitted under the Copyright Act 1968, this publication or any part of it may not be reproduced, altered, adapted, stored and/or distributed in any form or by any means without the prior written permission of Healthdirect Australia.
Support this browser is being discontinued for Pregnancy, Birth and Baby
Support for this browser is being discontinued for this site
- Internet Explorer 11 and lower
We currently support Microsoft Edge, Chrome, Firefox and Safari. For more information, please visit the links below:
- Chrome by Google
- Firefox by Mozilla
- Microsoft Edge
- Safari by Apple
You are welcome to continue browsing this site with this browser. Some features, tools or interaction may not work correctly.
Diastasis of the rectus abdominis muscles and diastasis of the womb. Solvable problems of pregnancy. Interview with Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor M.A. Chechnevoy
— What is muscle diastasis and what is pubic symphysis diastasis?
— Pregnancy is an amazing and wonderful time, but it is also a period of additional loads, which undoubtedly becomes a test of strength for the female body.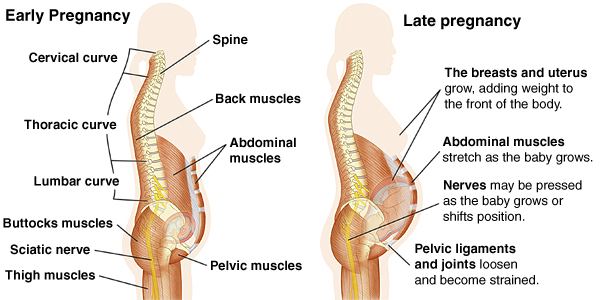
The previously existing everyday point of view that pregnancy rejuvenates and gives strength is not confirmed by anything. During the bearing of a child, significant additional loads are placed on the mother's body, which often lead to the manifestation of problems that were invisible before pregnancy. nine0005
Diastasis of the rectus abdominis muscles is a divergence of the inner edges of the muscles along the white line of the abdomen (connective tissue structure) at a distance of more than 27 mm. Pubic diastasis is one of the manifestations of pregnancy-associated pelvic girdle pain. This pathology affects the entire pelvic ring, sacroiliac joints and symphysis. And they certainly have common causes for the appearance.
The formation of such problems is facilitated by a decrease in the strength of connective tissue collagen. One of the reasons is an innate predisposition, the so-called connective tissue dysplasia, when the tissues are very elastic, extensible. During pregnancy, the body of a woman increases the production of the hormone relaxin, which reduces the synthesis of collagen and enhances its breakdown. This is provided by nature to create maximum elasticity of the birth canal. However, other structures, such as the anterior abdominal wall and the pubic symphysis, also fall under the action of relaxin. nine0005
This is provided by nature to create maximum elasticity of the birth canal. However, other structures, such as the anterior abdominal wall and the pubic symphysis, also fall under the action of relaxin. nine0005
— How does diastasis of the muscles and diastasis of the pubis affect pregnancy and childbirth?
- The divergence of the rectus abdominis muscles is observed in about 40% of pregnant women. During pregnancy, it does not give serious complications that threaten the life of the mother or the condition of the fetus. However, the inferiority of the work of the rectus abdominis muscles forces the redistribution of the load on the back muscles, which can lead to lumbar-pelvic pain and, accordingly, discomfort in the back. During childbirth, the abdominal muscles are involved in attempts, and the violation of their anatomy and function can affect the birth act. nine0005
With diastasis of the pubis, things are more complicated. As already mentioned, this is only one of the manifestations of a violation of the structure and function of the pubic joint (symphysiopathy) during pregnancy. It occurs in about 50% of pregnant women in varying degrees of severity: in 25% of cases it leads to restriction of the mobility of the pregnant woman, in 8% - to severe disorders up to disability.
It occurs in about 50% of pregnant women in varying degrees of severity: in 25% of cases it leads to restriction of the mobility of the pregnant woman, in 8% - to severe disorders up to disability.
With symphysiopathy, the ligaments of the pubic articulation and the cartilages that connect the pubic bones are affected. All this leads to severe pain in the pubic joint, pelvic bones, lower back, as well as to a violation of gait and the inability to stand up or lie down without outside help. Women with pelvic girdle pain syndrome experience significant levels of discomfort, disability, and depression, with associated social and economic problems. These include impaired sexual activity during pregnancy, chronic pain syndrome, risk of venous thromboembolism due to prolonged immobility, and even seeking early induction of labor or caesarean section to stop pain. nine0005
During childbirth, this patient may experience rupture of the pubic symphysis and may require surgery to repair it.
— How to prevent the development of muscle and pelvic diastasis during pregnancy and childbirth? What factors increase the likelihood of its development?
- There is no recipe that will be one hundred percent. There is a wonderful term in the medical literature called "lifestyle modification". Whatever diseases we study, be it symphysiopathy, diabetes mellitus or preeclampsia, the risk group for pathology is always overweight women. You need to prepare for pregnancy, you need to be in good physical shape. During pregnancy, weight gain should be monitored. The recommendation to "eat for two" is not just wrong, but extremely harmful. Pregnant women should maintain reasonable physical activity. Weak and flabby abdominal muscles, combined with the large size of the fetus, undoubtedly increase the risk of diastasis. nine0005
The risk factors for symphysiopathy in numerous studies are hard physical labor and previous injuries of the pelvic bones. Factors such as time elapsed from previous pregnancies, smoking, use of hormonal contraception, epidural anesthesia, mother's ethnicity, number of previous pregnancies, bone density, weight and gestational age of the fetus (post-term fetus) are not associated with an increased risk of symphysiopathy.
— How to diagnose diastasis recti and diastasis pubis? nine0004
— In most cases, diastasis rectus abdominis can be diagnosed clinically. It happens that inspection, palpation and simple measurements are enough.
In the standing position, you can see the divergence of the muscles when the woman does not have subcutaneous fat. In this case, diastasis is defined as a vertical defect between the rectus muscles.
With tension of the abdominal press, a longitudinal protrusion is observed in the diastasis zone. Such a protrusion is especially noticeable if the patient in the supine position is asked to raise her head and legs. If necessary, you can measure the width of the defect simply with a ruler. nine0005
Ultrasound may be the most accurate diagnostic method. With ultrasound, the inner edges of the rectus muscles are clearly visible and the distance between them at different levels can be measured.
Computed tomography is used in the diagnosis of diastasis extremely rarely, mainly in scientific research.
For the diagnosis of symphysiopathy and diastasis pubis there is no one test as a "gold standard".
The first place, of course, is the questioning and examination of the patient. We pay attention to the gait of the pregnant woman, to how she sits down, lies down and how she gets up. Symphysiopathy is characterized by a “duck gait”, when a pregnant woman rolls from foot to foot. On palpation in the area of the womb, pain and swelling are noted. The so-called pain provocative tests are used, for example, a mat-test (pulling up an imaginary rug, mat with your foot towards you). nine0005
The following questionnaires are used to assess quality of life, pain and disability: Health-Related Quality of Life (HRQL), Oswestry Disability Index (ODI), Disability Rating Index (DRI), Edinburgh Postpartum Depression Scale (EPDS), Pregnancy Mobility Index (PMI), and Pelvic Ring Score (PGQ).
Of the instrumental methods, ultrasound is the most widely used, less often computed or magnetic resonance imaging. Ultrasound allows you to assess the condition of the ligaments of the pubic joint and the interpubic disc, the severity of the changes and the risk of natural childbirth. nine0005
Ultrasound allows you to assess the condition of the ligaments of the pubic joint and the interpubic disc, the severity of the changes and the risk of natural childbirth. nine0005
— What is the treatment for diastasis recti or pubis?
— Primary prevention: when planning and during pregnancy, it is necessary to strengthen all muscle groups of the pelvic girdle, as well as the pelvic diaphragm.
More often, diastasis of the rectus muscles disappears on its own during the first months after childbirth. Special physical exercises to correct the work of muscles, to tone them and restore their basic functions should be performed under the guidance of a competent instructor. There are types of physical exercises that can, on the contrary, worsen the situation with diastasis of the rectus abdominis muscles. In some cases, when there is no effect from physiotherapy exercises, it is necessary to resort to surgical correction of the defect. Currently, both endoscopic and open surgery are practiced. The choice of method depends on the size and localization of the defect. nine0005
The choice of method depends on the size and localization of the defect. nine0005
With symphysiopathy, therapeutic exercises reduce lumbar and pelvic pain. Acupuncture and wearing a pelvic bandage have a positive effect on symphysiopathy.
Initial treatment of pubic symphysis should be conservative even if symptoms are severe. Treatment includes bed rest and the use of a pelvic brace or corset that tightens the pelvis. Early appointment of physiotherapy with dosed therapeutic exercises will help to avoid complications associated with prolonged immobilization. Walking should be done with assistive devices such as walkers. nine0005
In most cases (up to 93%), the symptoms of dysfunction of the pelvic ring, including the pubic joint, progressively subside and completely disappear six months after birth. In other cases, it persists, becoming chronic. However, if the diastasis exceeds 40 mm, then surgical treatment may be required. Most studies recommend surgery only after failure of conservative treatment, inadequate enlargement of diastasis, or its recurrence. Several procedures have been described, including external fixation and open reduction of the pubic bones with internal fixation. nine0005
Several procedures have been described, including external fixation and open reduction of the pubic bones with internal fixation. nine0005
The best advice for prevention, diagnosis and treatment: ask a competent doctor all the questions that worry you. Only the joint efforts of the doctor and the patient can overcome all problems and find the best solutions.
Diastasis of the rectus abdominis muscles - symptoms, signs, degrees, causes and treatment in men and women in Moscow in the "SM-Clinic"
The surgeon deals with the treatment of this disease
Book online Request a call
- What is diastasis rectus abdominis?
- About disease
- Species
- Symptoms of diastasis recti
- Causes of diastasis recti
- Diagnostics of diastasis of the rectus abdominis muscles
- Expert opinion
- Treatment of diastasis recti
- Surgical treatment of diastasis recti nine0085 Prevention
- Rehabilitation after surgery
- Questions and Answers
- Sources
About the disease
The disease is based on stretching and expansion of the white line of the abdomen - a tendon that is located between the rectus muscles, connects and holds them.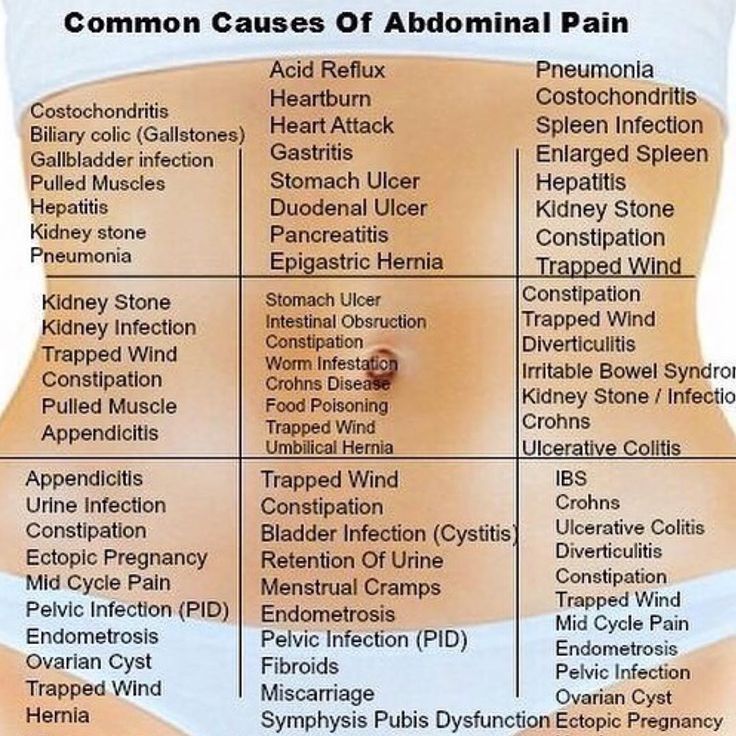 This is a strip of connective tissue, consisting of several layers, located vertically in the middle of the abdomen from the xiphoid process to the pubic joint. nine0005
This is a strip of connective tissue, consisting of several layers, located vertically in the middle of the abdomen from the xiphoid process to the pubic joint. nine0005
Due to an increase in intra-abdominal pressure or a violation of the properties of the connective fibers, the structure of the tendon changes, it weakens, becomes thinner and stretches. The trigger mechanism is prolonged pressure on the abdominal wall associated with pregnancy or visceral obesity. An aggravating factor is the loosening of the white line against the background of collagenopathy, the effects of relaxin, the immaturity of cellular structures, etc.
As a result, the white line becomes thinner and stretched. Normally, its dimensions are restored with a gradual decrease in the abdomen or as the properties of the connective tissue normalize. Thus, physiological diastasis is eliminated during the neonatal period or in women after childbirth. nine0005
If abdominal training is started early in the postpartum period, this leads to contraction of the rectus muscles and a simultaneous increase in intra-abdominal pressure, and the white line is fixed in a stretched position and does not hold the internal organs well. As a result, unaesthetic vertical folds form on the abdomen, a rounded protrusion appears, dysfunction of the digestive tract occurs and the risk of hernia formation increases.
As a result, unaesthetic vertical folds form on the abdomen, a rounded protrusion appears, dysfunction of the digestive tract occurs and the risk of hernia formation increases.
Species
Depending on the magnitude of the stretching of the tendon ligament, there are 3 degrees of diastasis of the rectus abdominis muscles:
- first - the muscles move away from each other by 2.5-5 cm;
- second - ligaments diverge by 5-8 cm;
- third - the line is stretched more than 8 cm.
According to the localization of the place of maximum stretching, supra-umbilical, sub-umbilical and mixed forms of diastasis are distinguished.
According to the degree of involvement of other muscles of the anterior abdominal wall, the pathology is classified into types:
- A - classical divergence of muscles after natural childbirth; nine0086
- B - relaxation of the lower lateral sections of the muscles;
- C - expansion affects the region of the ribs and the xiphoid process;
- D - diastasis is combined with a curvature of the waistline.
Symptoms of diastasis of the rectus abdominis muscles
Manifestations of BPMD increase as the pathology progresses. In women, a vivid clinical picture manifests itself abruptly (shortly after childbirth), while in men the disease develops gradually.
At the onset of the disease, there may be no symptoms at all. The patient then notices a characteristic rounded vertical protrusion in the center of the abdomen. With deliberate tension of the press, the inner edges of the rectus muscles and the groove between them are clearly visible. Due to muscle dysfunction, pain in the spine, lower back, fatigue, and posture disorders are possible.
With the progression of the pathology, manifestations of dysfunction of the gastrointestinal tract join:
- heartburn; nine0085 belching;
- flatulence;
- abdominal pain;
- constipation.
In the third stage of diastasis, patients are faced with the formation of hernias, which are formed due to structural defects in the white line.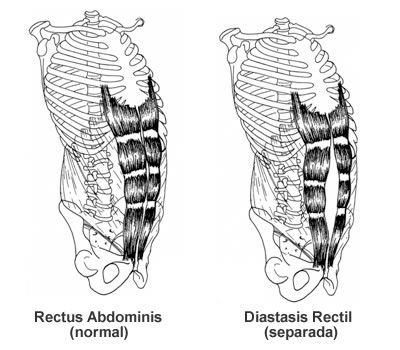 Possible ptosis (omission) of internal organs and serious disturbances in the work of the intestines (in severe cases, intestinal obstruction develops). Women often experience urinary incontinence, renal colic.
Possible ptosis (omission) of internal organs and serious disturbances in the work of the intestines (in severe cases, intestinal obstruction develops). Women often experience urinary incontinence, renal colic.
Causes of diastasis recti
Increase the risk of developing diastasis pathology of the connective tissue and increased pressure in the abdominal cavity. In different categories of patients, the causes of the development of PMSD are different.
Divergence of muscles in children is due to the failure of the musculature and tendons. After 2-12 months after birth, the muscles come into tone, the ligaments and tendons are strengthened - the process resolves itself. In premature babies and infants with intrauterine developmental pathologies, this may take longer. With Down syndrome, there is a risk of maintaining diastasis for life. nine0005
Pregnancy is the provocateur of diastasis of the rectus abdominis muscles in women. The growing uterus puts considerable pressure on the linea alba, stretching it. Under the action of hormones, the synthesis of collagen fibers is inhibited, the ligaments become looser. But a few months after the birth, the white line of the abdomen is normally restored.
Under the action of hormones, the synthesis of collagen fibers is inhibited, the ligaments become looser. But a few months after the birth, the white line of the abdomen is normally restored.
In men, BMD is often provoked by obesity, physical activity and hereditary collagenopathies. The risk of diastasis increases with a tendency to constipation, as well as with chronic respiratory diseases accompanied by coughing. nine0005
Treatment of pathology by conservative methods is possible with a small diastasis. At the later stages of development, the pathological divergence of muscles is eliminated with the help of abdominal plastic surgery.
Get advice
If you experience these symptoms, we recommend that you make an appointment with your doctor. Timely consultation will prevent negative consequences for your health.
You can find out more about the disease, prices for treatment and sign up for a consultation with a specialist by phone:
+7 (495) 292-39-72
Request a call back Book online
Why SM-Clinic?
1
Treatment is carried out in accordance with clinical recommendations
2
A comprehensive assessment of the nature of the disease and treatment prognosis
Modern diagnostic equipment and own laboratory
4
High level of service and a weighted price policy
Diagnosis of diastasis of the rectus abdominis muscles
Identification of BPMD is not difficult, since the disease has characteristic clinical manifestations.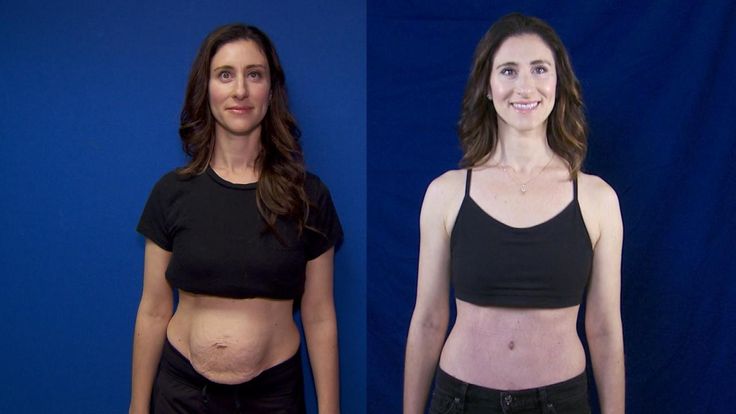 With signs of diastasis, you should contact the surgeon.
With signs of diastasis, you should contact the surgeon.
An increase in the space between the rectus muscles is determined during palpation of the abdomen. To conduct the test, the patient is asked to lie on his back, legs slightly bent at the knees, and then tighten the abdominal muscles, raising his head and shoulder blades. In patients with obesity, the doctor is not always able to fully explore the width of the white line. nine0005
The exact size of the sprain is determined by ultrasound. This diagnostic method also allows you to detect complications (hernia, displacement of internal organs). In order to differentiate the symptoms of diastasis and manifestations of chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract or the genitourinary system, consultations of specialized specialists are prescribed.
Expert opinion
Surgeons warn that diastasis rectus abdominis is asymptomatic for a long time. Therefore, in the presence of predisposing factors (recent pregnancy and childbirth, chronic constipation, obesity) or non-specific complaints, you should independently feel the white line of the abdomen in the navel.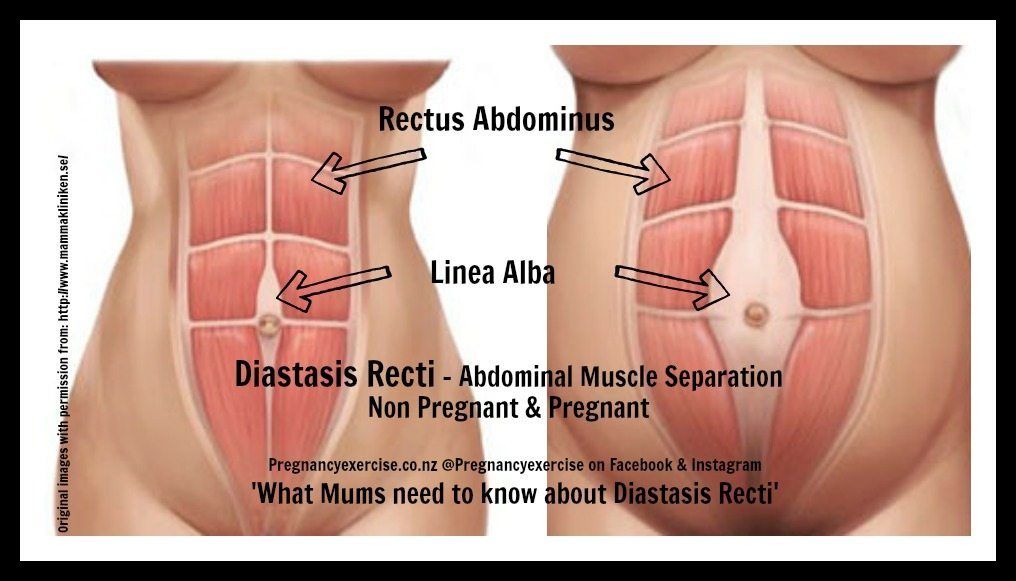 If the distance between the rectus muscles is more than 2.5 cm, contact the surgeon. Also, do not delay the visit in any doubtful cases. Only a doctor can establish the correct diagnosis, self-examination does not exclude the need for an in-person consultation. nine0005
If the distance between the rectus muscles is more than 2.5 cm, contact the surgeon. Also, do not delay the visit in any doubtful cases. Only a doctor can establish the correct diagnosis, self-examination does not exclude the need for an in-person consultation. nine0005
Egiev Valery Nikolaevich, surgeon, oncologist, doctor of medical sciences, professor, head of the department of surgery and oncology, FPC MR MI PFUR
Treatment of diastasis recti
Functional diastasis in newborns and puerperas does not require treatment. Doctors use expectant tactics, recommend adhering to the principles of rational nutrition, doing massages, and doing gymnastics. The observation period can last up to 12 months. If after this time the problem persists, the surgeon decides on an operative method of correction. nine0005
Conservative treatment
Patients are prescribed a diet to prevent constipation and excessive gas formation, as well as to gradually reduce weight. In the postpartum period, incl.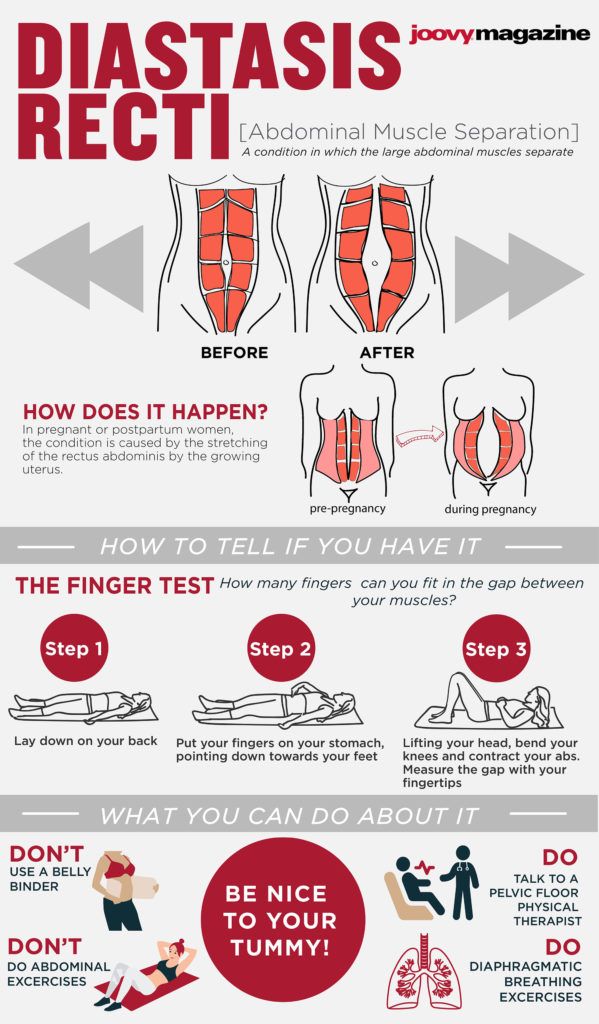 after a caesarean section, women are advised to wear a bandage, support the stomach during sneezing and coughing. The general strengthening of the muscles allows you to quickly restore the tone of the anterior abdominal wall, so patients are prescribed exercise therapy, swimming, yoga classes. It is important to exclude any training of the abdominal muscles. You can not perform exercises in the knee-elbow position, as well as in the emphasis (bar). Such loads can be resumed after the restoration of the size of the white line. Conservative treatment is effective only at the 1st stage of BPMD. nine0005
after a caesarean section, women are advised to wear a bandage, support the stomach during sneezing and coughing. The general strengthening of the muscles allows you to quickly restore the tone of the anterior abdominal wall, so patients are prescribed exercise therapy, swimming, yoga classes. It is important to exclude any training of the abdominal muscles. You can not perform exercises in the knee-elbow position, as well as in the emphasis (bar). Such loads can be resumed after the restoration of the size of the white line. Conservative treatment is effective only at the 1st stage of BPMD. nine0005
Surgical treatment of diastasis of the rectus abdominis muscles
In case of complicated and uncomplicated diastasis of the rectus abdominis muscles of the 2-3rd degree, surgical treatment is indicated. It is possible to use the following surgical techniques:
- Tension plastic using own tissues. It involves stitching the edges of the muscles with the removal of excess connective tissue.
 To date, it is not used due to the high risk of recurrence.
To date, it is not used due to the high risk of recurrence. - Tension-free repair with a mesh prosthesis. It implies the introduction of an endoprosthesis under the site of stretching. nine0086
- Tension plastic with prosthesis installation. It involves the removal of excess connective tissue, suturing the edges of the muscles and strengthening the zone with a polypropylene mesh.
- Combined technique. Includes muscle suturing, mesh strengthening, removal of excess adipose tissue and stretched skin.
Prevention
To reduce the risk of developing diastasis rectus abdominis, you should keep your body in shape - engage in regular exercise, train your muscles. However, do not overdo it: lifting weights can, on the contrary, become the main cause of muscle divergence. nine0005
It is also important to eat a nutritious and balanced diet - a lack of nutrients will lead to a decrease in the elasticity of the connective tissue.
It is necessary to control your weight - body mass index should not exceed 26 kg/m3.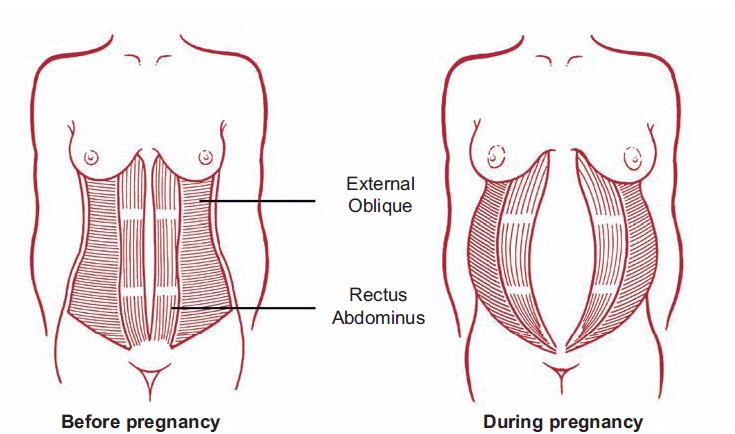 Obesity, especially of the abdominal type, is an important risk factor for BLV.
Obesity, especially of the abdominal type, is an important risk factor for BLV.
Prevention and timely treatment of chronic lung diseases accompanied by cough, pathologies of the digestive system, occurring with constipation, will reduce the possibility of increasing intra-abdominal pressure and, as a result, the likelihood of diastasis. nine0005
Rehabilitation after surgery
After surgery, the patient is under inpatient observation, receiving analgesic and antibiotic therapy. Full recovery lasts 1-3 months. During this period, the patient is prescribed a diet to normalize defecation, it is recommended to avoid significant physical exertion, weight lifting. To prevent excess tension, it is necessary to wear a bandage.
Questions and Answers
A surgeon deals with the treatment of pathology. nine0005
In the stronger sex, obesity and connective tissue dysplasia are considered to be the main cause of BMD. Sharp weight loss or weight gain, excessive passion for power loads are capable of provoking muscle divergence. If a man or close relatives have hernias, varicose veins, valgus flat feet, hemorrhoids, this is regarded as an increased tendency to PMSD.
If a man or close relatives have hernias, varicose veins, valgus flat feet, hemorrhoids, this is regarded as an increased tendency to PMSD.
There is no need to rush in this matter. Just the desire to quickly get in shape is the main reason for the progression of diastasis in women. Physical activity can be resumed 1-2 months after delivery. You can start with hiking or yoga. Abdominal exercises can be performed soon after the white line is reduced to 2 cm. It is advisable to pay attention to the diet. A smooth decrease in weight and volume of visceral fat will ensure gradual and timely muscle contraction. Sharp weight loss, on the contrary, can increase diastasis. nine0005
You can lie on a hard surface on your back, tense your abs. With gentle movements of the fingers, you should begin to probe the stomach in the middle in the navel. With a normal width of the white line and with diastasis, a depression will be found - this is the median ligament. If its width is equal to or greater than the width of two fingers, you should contact the surgeon. Constipation, bloating and abdominal pain should be alarming. If there are such symptoms, it is necessary to get to the surgeon in the near future.
Constipation, bloating and abdominal pain should be alarming. If there are such symptoms, it is necessary to get to the surgeon in the near future.
Pathogenesis and treatment of ventral hernias and diastasis of the rectus abdominis muscles: Abstract of the thesis / Zagirov U.Z. - nineteen95.
Comparative aspects of methods for eliminating diastasis of the rectus abdominis muscles / Topchiev MA, Bondarev VA, Elderov S.Sh.// Astrakhan medical journal. - 2010.
Jessen M. L., Öberg S., Rosenberg J. Treatment Options for Abdominal Rectus Diastasis // Front Surg. - 2019. - No. 6. - R. 65
>
Diseases referred by a surgeon
Esophageal ulcer Appendicitis Ascites Atheroma femoral hernia Crohn's disease Bursitis Hernia Hernia of the white line of the abdomen hiatal hernia Cholelithiasis Keratoma salivary gland cyst Lipoma Bowel obstruction Oleogranuloma kidney tumor Acute pancreatitis Inguinal hernia Peritonitis Barrett's esophagus Polycystic kidney disease Postoperative hernia Umbilical hernia Stomach cancer Reflux esophagitis (GERD) Thyroiditis Furuncle (boil) Furunculosis cholestasis Cholecystitis Chronic cholecystitis Erosive gastritis Peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum
All doctors
VDNKh metro station
Belorusskaya metro station
Lesnaya, 57, pp.