Sore calf muscle during pregnancy
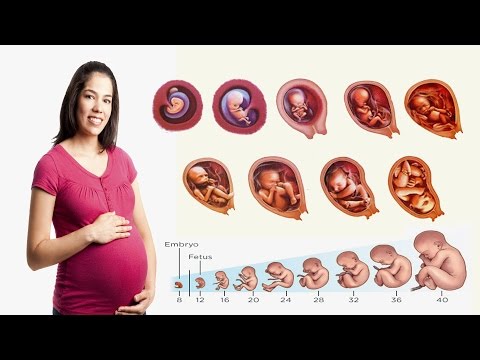
Leg cramps during pregnancy | Pregnancy Birth and Baby
Leg cramps during pregnancy | Pregnancy Birth and Baby beginning of content4-minute read
Listen
Leg pain can sometimes be a sign of a blood clot. If pain in your leg doesn’t go away, or if your leg is red, warm or swollen, see your doctor immediately.
Key facts
- Up to 3 in 10 people who are pregnant get leg cramps.
- Cramps are most common in your calf muscles.
- Cramps commonly happen at night in late pregnancy.
- To prevent leg cramps, try stretching your leg muscles before you go to bed and drink plenty of water.
- To ease a cramp, pull your toes up towards your ankle, rub the muscle, walk around or apply a heat pack.
What are leg cramps?
Leg cramps (pains) affect up to 3 in 10 people who are pregnant. They usually occur in your calf muscles, but can also occur in your thighs or feet. A cramp is a sign that your muscles are contracting very tightly when they shouldn’t be. This happens when acid builds up in your muscles.
Cramps usually happen at night. They are more common in your second and third trimesters.
Leg cramps are not the same as pelvic cramps.
What causes leg cramps during pregnancy?
There are many reasons suggested for cramps while you’re pregnant, such as changes to your metabolism, having a vitamin deficiency, being too active or not being active enough. However, nobody really knows why they occur in pregnancy.
How can I get rid of cramps?
To ease a leg cramp, you can try:
- stretching the muscle by pulling your toes hard up towards the front of your ankle
- rubbing the muscle firmly
- walking around
- a heat pack
If you have a partner, you could ask them to help.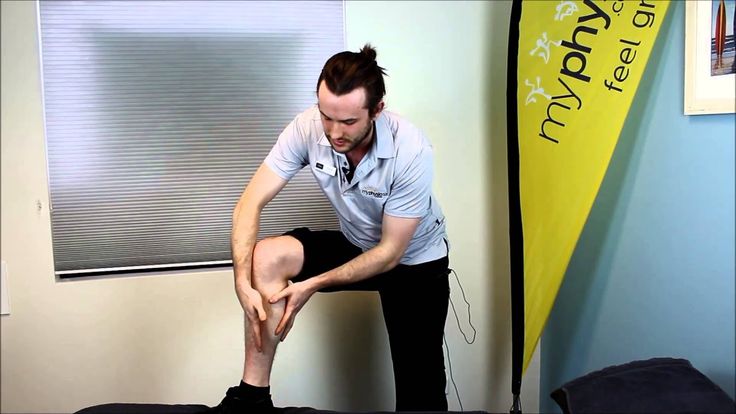
If your muscles are still sore after the cramp has gone, you can take paracetamol for pain relief.
How can I prevent leg cramps?
Things you can try that might help prevent cramps include:
- stretching your calf muscles before you go to bed
- drinking plenty of water
- having a warm bath before you go to bed
- eating a balanced diet
- avoiding stretching your leg while pointing your toes
Magnesium, calcium, vitamin B and vitamin C have been suggested as a treatment for cramps. It’s not clear whether any of these supplements work, but people often try magnesium and calcium. If you’re interested in trying supplements, talk to your doctor or midwife about whether they might be suitable for you.
When should I talk to my doctor or midwife about cramps?
If leg cramps are bothering you, talk to your doctor or midwife.
Leg pain can sometimes be a sign of a blood clot. If pain in your leg doesn’t go away, or if your leg is red, warm or swollen, see your doctor immediately.
Speak to a maternal child health nurse
Call Pregnancy, Birth and Baby to speak to a maternal child health nurse on 1800 882 436 or video call. Available 7am to midnight (AET), 7 days a week.
Sources:
Therapeutic Guidelines (Muscle cramps, including leg cramps in pregnant women), NSW Government (Having a baby), Queensland Health (6 weird things that may happen to your body during pregnancy), King Edward Memorial Hospital (Minor Symptoms or Disorders in Pregnancy King Edward Memorial Hospital Clinical Guidelines: Obstetrics & Midwifery), Queensland Health (VTE in pregnancy (a blood clot in the vein)), NPS (Magnesium, a treatment for leg cramps?), Royal Women’s Hospital (Common concerns in early pregnancy)Learn more here about the development and quality assurance of healthdirect content.
Last reviewed: July 2022
Back To Top
Related pages
- Common discomforts during pregnancy
- Swelling during pregnancy
- Varicose veins
Need more information?
Pregnancy at week 28
You are now in the third trimester and you'll probably be feeling many of the common discomforts of pregnancy, like a sore back, swelling, heartburn or cramps.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Common discomforts during pregnancy
Your body has a great deal to do during pregnancy. Sometimes the changes taking place will cause irritation or discomfort, and on occasions they may seem quite alarming.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Pregnancy health problems & complications | Raising Children Network
Many pregnancy health problems are mild, but always call your doctor if you’re worried about symptoms. A healthy lifestyle can help you avoid health problems.
A healthy lifestyle can help you avoid health problems.
Read more on raisingchildren.net.au website
Pregnancy - signs and symptoms - Better Health Channel
All women experience pregnancy differently, and you will experience different symptoms at different stages of your pregnancy.
Read more on Better Health Channel website
Sleep during pregnancy
Sleep can become a problem when you're pregnant. Here are some tips to help you get as much sleep as possible so you’re ready for your baby's arrival.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Pregnancy at week 33
Your baby's brain and nervous system are now fully developed, and the baby is continuing to gain weight. You'll probably also be feeling sore and tired.
You'll probably also be feeling sore and tired.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Pregnancy at week 25
As you are approaching the end of the second trimester, you might be starting to feel a bit uncomfortable as your baby continues to grow.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Pregnancy at week 26
Your baby is starting to put on fat and muscle and as your baby grows, your centre of gravity will shift, so you might find that you are starting to walk differently and maybe even a little clumsy.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Pregnancy and your mental health - Better Health Channel
Finding out you are pregnant can be a very exciting time. But it can also make you feel uncomfortable, unwell, worried and make you wonder how you are going to cope. And it doesn’t stop when the baby arrives. Some mums find it easy to adjust to life with a new baby. But others don’t!
But it can also make you feel uncomfortable, unwell, worried and make you wonder how you are going to cope. And it doesn’t stop when the baby arrives. Some mums find it easy to adjust to life with a new baby. But others don’t!
Read more on Better Health Channel website
Sclerotherapy - MyDr.com.au
Sclerotherapy is a treatment that involves the injection of a chemical solution into blood vessels, usually spider veins or superficial (surface) varicose veins on the legs.
Read more on myDr website
Disclaimer
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is not responsible for the content and advertising on the external website you are now entering.
OKNeed further advice or guidance from our maternal child health nurses?
1800 882 436
Video call
- Contact us
- About us
- A-Z topics
- Symptom Checker
- Service Finder
- Linking to us
- Information partners
- Terms of use
- Privacy
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is funded by the Australian Government and operated by Healthdirect Australia.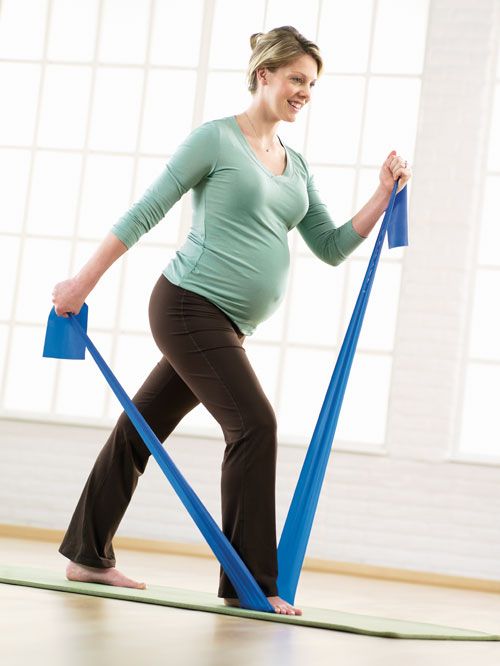
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is provided on behalf of the Department of Health
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby’s information and advice are developed and managed within a rigorous clinical governance framework. This website is certified by the Health On The Net (HON) foundation, the standard for trustworthy health information.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
This information is for your general information and use only and is not intended to be used as medical advice and should not be used to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any medical condition, nor should it be used for therapeutic purposes.
The information is not a substitute for independent professional advice and should not be used as an alternative to professional health care. If you have a particular medical problem, please consult a healthcare professional.
Except as permitted under the Copyright Act 1968, this publication or any part of it may not be reproduced, altered, adapted, stored and/or distributed in any form or by any means without the prior written permission of Healthdirect Australia.
Support this browser is being discontinued for Pregnancy, Birth and Baby
Support for this browser is being discontinued for this site
- Internet Explorer 11 and lower
We currently support Microsoft Edge, Chrome, Firefox and Safari. For more information, please visit the links below:
- Chrome by Google
- Firefox by Mozilla
- Microsoft Edge
- Safari by Apple
You are welcome to continue browsing this site with this browser. Some features, tools or interaction may not work correctly.
Leg Pain During Pregnancy: Exercises to Try
Leg Pain During Pregnancy: Exercises to TryMedically reviewed by Janine Kelbach, RNC-OB — By Natasha Freutel on February 24, 2016
While you await the arrival of your precious baby, you may be feeling new kinds of aches and pains. Leg and joint pain during the second or third trimester may be the result of added weight, changing body shape, and biomechanics. It can also be caused by fluid retention and joint laxity.
It can also be caused by fluid retention and joint laxity.
Pregnancy pain can have an impact on daily life and cause changes in sleep quantity and quality. Some common pregnancy aches include swollen and painful feet and legs, and calf cramps. Some women also report radiating pain down the back of the legs and hip pain.
Another common pregnancy symptom is swelling. Many pregnant women report swelling of the:
- face
- legs
- ankles
- feet
Mild swelling is a normal part of pregnancy. It happens because of the 50 percent increase in blood and bodily fluids needed to support the growing baby. But excessive swelling can be a sign of a more severe pregnancy complication. If you experience severe swelling, it’s important to be evaluated by a doctor.
Pregnancy back pain is widely studied, but there’s less research on hip, knee, and foot pain during pregnancy and postpartum. A study published in the Journal of Family Practice reports a high occurrence of low body pain among pregnant and postpartum women. It’s most likely related to changes in the way a pregnant woman moves due to a growing baby belly.
It’s most likely related to changes in the way a pregnant woman moves due to a growing baby belly.
Try these exercises to help decrease swelling, pain, and discomfort during pregnancy.
Swollen feet and ankles are common during pregnancy. This simple exercise helps increase circulation and blood flow to the feet to decrease swelling and pain.
Equipment needed: none
Muscles worked: ankle dorsiflexors, plantarflexors
- Lie on a bed with your feet slightly elevated on a pillow.
- Begin by pulling your toes toward your face to flex your feet, then point your toes away from you.
- Repeat 10 times continuously.
- Perform 3 sets.
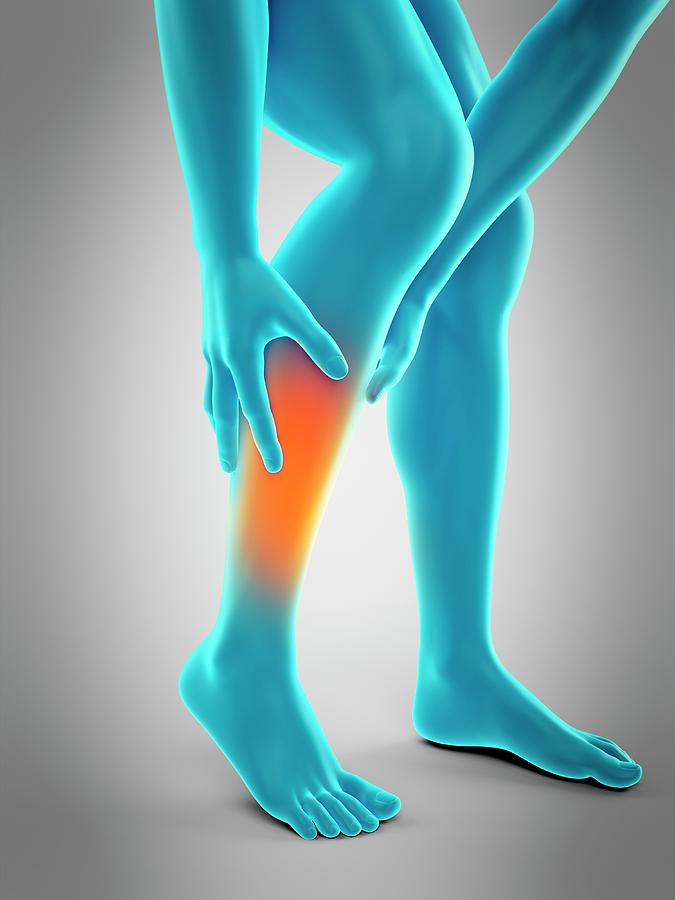
Some women suffer from sore calf muscles during pregnancy. This might be caused by weight gain, poor body mechanics, or improper footwear. Stretching can help promote relaxation of the muscles, leading to decreased pain.
Equipment needed: a wall
Muscles worked: gastrocnemius, soleus
- Stand to face a wall.
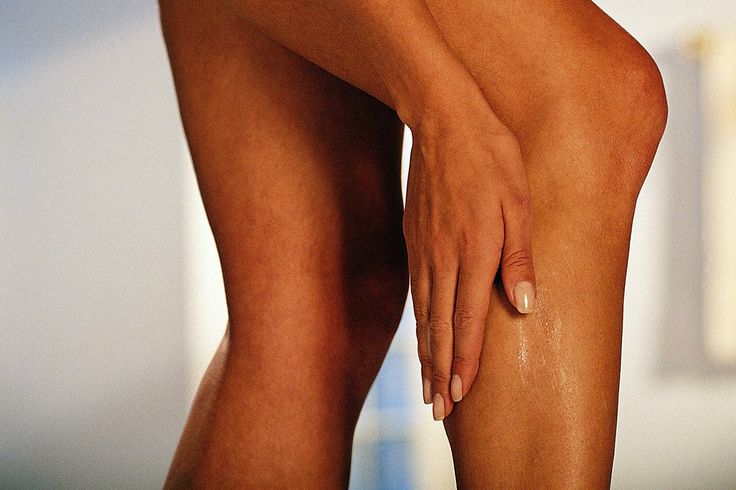 Place both hands on the wall for support.
Place both hands on the wall for support. - Put one foot up against the wall with your toes pointing toward the ceiling.
- Lean toward the wall, keeping your leg straight until you feel a stretch in the back of your lower leg.
- Hold for 20-30 seconds. Repeat on other leg.
Tight hamstrings can cause low back pain and discomfort during pregnancy. This exercise helps stretch the hamstrings. It also activates and strengthens the muscles of the buttocks.
Equipment needed: none
Muscles worked: hamstrings, glutes
- Stand with your feet parallel, hip-width apart.
- Put your hands behind your head and stand up tall, keeping your chest wide.
- Keep your legs relatively straight with a slight bend in your knees. Bend at the hips, moving them back as you lower yourself toward parallel. Bend until you feel a stretch in the back of your legs. Try to keep your back in a straight line.
- Move slowly through this movement 10 times.

- Perform 3 sets.
This exercise can increase strength and stability in the muscles of the lower back and core. It also works the quadriceps, the important muscles that support the ligaments of the knee.
Equipment needed: exercise ball
Muscles worked: gluteus maximus, hamstrings, deep core muscles
- Stand against a wall with an exercise ball positioned between your midback and the wall.
- Place your feet far enough away from the wall so that when you lower down into a squat, your knees can bend to 90 degrees. Having your feet too close to the wall will put stress on the knee joint. Feet should be parallel and a little wider than hip-width apart.
- Lower your body down into a sitting position while rolling the ball up your back.
- Hold for 1 second, return to starting position. Repeat 10 times.
Sciatic pain is common during pregnancy. It can cause shooting or aching pain down the buttocks, back of the leg, and foot. Foam rolling is a great way to soothe and relax tight muscles that may be contributing to increased pain.
Foam rolling is a great way to soothe and relax tight muscles that may be contributing to increased pain.
Equipment needed: foam roller
Muscles worked: hamstrings, calf muscles, glutes, piriformis
- Place a foam roller on the ground.
- Sit on the foam roller, supporting yourself with your hands behind you.
- Cross one foot over the other knee in a figure 4 position.
- Slowly move your buttocks back and forth over the foam roller until you find a tender spot.
- Continue this movement over the tender area for 30-60 seconds.
- Try rolling the foam roller down the back of your upper leg until you find another tender area.
- Repeat on other side.
Exercises and stretching can have a positive effect on mobility during pregnancy. They can also help decrease pain and dysfunction. The 2002 guidelines for physical activity during pregnancy recommend regular exercise for its overall health benefits to both mom and baby.
Always see your doctor before starting an exercise program to make sure it’s safe. Discontinue exercise and seek medical help if you have any of the following symptoms:
- vaginal bleeding
- dyspnoea before exertion
- dizziness
- headache
- chest pain
- muscle weakness
- calf pain or swelling
- preterm labor
- decreased fetal movement
- amniotic fluid leakage
Calf or leg pain can be a symptom of a more serious condition like a blood clot or thrombosis. Seek immediate medical attention if you have pain accompanied by redness, warmth, or swelling in the calf.
Share on Pinterest
Last medically reviewed on February 24, 2016
- Parenthood
- Pregnancy
- Pregnancy Health
How we reviewed this article:
Healthline has strict sourcing guidelines and relies on peer-reviewed studies, academic research institutions, and medical associations. We avoid using tertiary references. You can learn more about how we ensure our content is accurate and current by reading our editorial policy.
We avoid using tertiary references. You can learn more about how we ensure our content is accurate and current by reading our editorial policy.
- Artal, R., O’Toole, M., & White, S. (2003). Guidelines of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists for exercise during pregnancy and the postpartum period. British Journal of Sports Medicine, 37(1), 6-12
doi.org/10.1136/bjsm.37.1.6 - Dumas, G. A., & Reid, J. G. (1997). Laxity of knee cruciate ligaments during pregnancy. The Journal of Orthopaedic and Sports Physical Therapy, 26(1), 2-6
doi.org/10.2519/jospt.1997.26.1.2 - Swelling During Pregnancy. (2015)
americanpregnancy.org/pregnancy-health/swelling-during-pregnancy/ - Vullo, V. J., Richardson, J. K., & Hurvitz, E. A. (1996). Hip, knee, and foot pain during pregnancy and the postpartum period. The Journal of Family Practice, 43(1), 63–68
ncbi.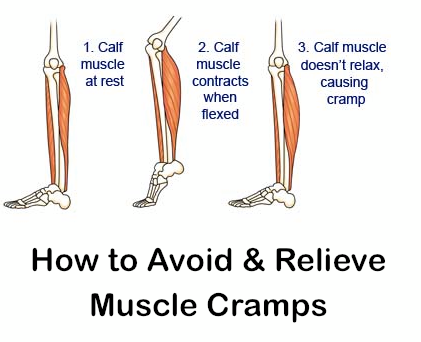 nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8691182
nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8691182
Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information becomes available.
Share this article
Medically reviewed by Janine Kelbach, RNC-OB — By Natasha Freutel on February 24, 2016
related stories
5 Stretches for Tailbone Pain During Pregnancy
Sciatica During Pregnancy: Symptoms, Causes, Treatments
Pregnancy Yoga Stretches for Back, Hips, and Legs
5 Ways to Perform Squats Safely During Pregnancy
Pregnancy Sciatica: 5 Natural Ways to Find Pain Relief Without Drugs
Read this next
5 Stretches for Tailbone Pain During Pregnancy
Medically reviewed by Janine Kelbach, RNC-OB
Many pregnant women experience uncomfortable tailbone pain. This gentle stretching routine will help ease some of the discomfort.
READ MORE
Sciatica During Pregnancy: Symptoms, Causes, Treatments
Medically reviewed by Beth Holloway, RN, MEd
Many pregnant women experience sciatic pain.
 Here's a look at the causes, symptoms, and ways to find relief.
Here's a look at the causes, symptoms, and ways to find relief. READ MORE
Pregnancy Yoga Stretches for Back, Hips, and Legs
Medically reviewed by Peggy Pletcher, M.S., R.D., L.D., CDE
Practicing yoga during pregnancy can help ease some of your aches and pains. Follow this gentle routine to stretch and relax your muscles.
READ MORE
5 Ways to Perform Squats Safely During Pregnancy
Medically reviewed by Peggy Pletcher, M.S., R.D., L.D., CDE
Performing squat exercises during pregnancy can be beneficial to both mom and baby. Here are five safe variations to try.
READ MORE
Pregnancy Sciatica: 5 Natural Ways to Find Pain Relief Without Drugs
Medically reviewed by Michael Weber, MD
A baby pushing on your bladder is uncomfortable enough without the added pain of sciatica.
 Here are some ways to find relief.
Here are some ways to find relief.READ MORE
Can Ectopic Pregnancy Be Diagnosed With Ultrasound?
Medically reviewed by Valinda Riggins Nwadike, MD, MPH
Ectopic pregnancy is a serious condition that requires accurate and swift diagnosis. Ultrasound for ectopic pregnancy diagnosis is just one tool your…
READ MORE
Is It Safe to Consume Flaxseeds During Pregnancy?
Given the inconclusive and conflicting stances about eating flaxseeds during pregnancy, it might be better to err on the side of caution.
READ MORE
Pregnancy After Miscarriage: Answers to Your Questions
Medically reviewed by Amanda Kallen, MD
Getting pregnant after a miscarriage can be an emotional experience, filled with joy but also anxiety and guilt. Learn more about pregnancy after…
READ MORE
What Is a Nurse Midwife and How to Tell If They Are Right for You
Medically reviewed by Meredith Wallis, MS, APRN, CNM, IBCLC
A nurse midwife is a nurse with education, training, and certification to provide prenatal, delivery, and women's care.
READ MORE
Your 6-Week Ultrasound: What to Expect
Medically reviewed by Valinda Riggins Nwadike, MD, MPH
We'll tell you all about the 6-week ultrasound, including why your doctor may have ordered it, what the risks are, and what it means if no heartbeat…
READ MORE
Muscle pain during pregnancy
Muscle pain during pregnancy is considered an inevitable phenomenon associated with natural processes, changes in the functioning of many organs and systems.
Literally from the first week of conception, the smooth muscles that line the hollow organs (uterus), striated muscles, the vascular and hormonal systems begin to “prepare” for childbirth. Such a general transformation of the body of the expectant mother really provokes discomfort of varying degrees of intensity, especially if the woman before pregnancy did not bother herself with sports, strengthening muscle fibers, and maintaining physical fitness.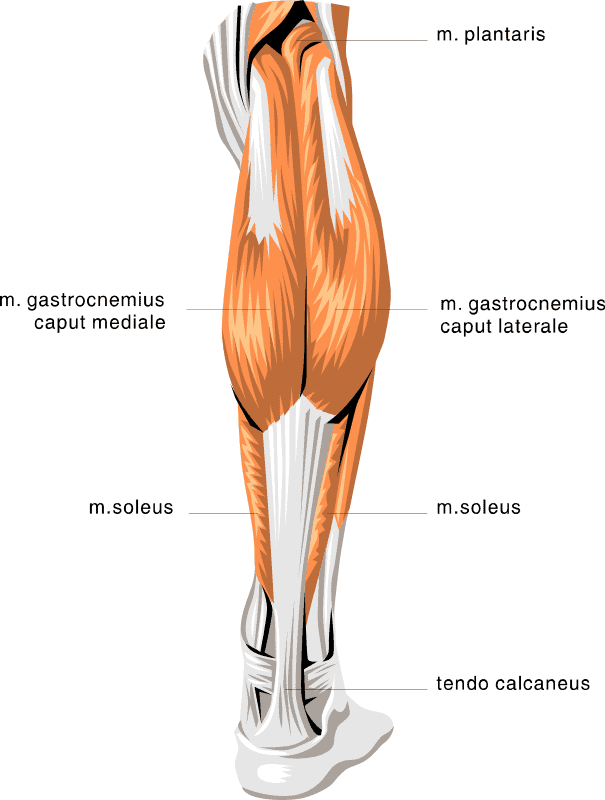 In this case, the contractile property of the muscles is initially reduced, and the activation of the function of muscle tissue provokes a pain symptom due to chronic hypertonicity, overstrain.
In this case, the contractile property of the muscles is initially reduced, and the activation of the function of muscle tissue provokes a pain symptom due to chronic hypertonicity, overstrain.
Causes of muscle pain during pregnancy
Pregnancy, in addition to bringing joyful expectation, sometimes causes quite understandable discomfort and even pain. Most often, pain is concentrated in muscle tissue and ligaments, since it is they who are subjected to increased stress, sprains.
The causes of muscle pain during pregnancy can be both physiological and pathological.
- Physiological causes of muscle pain in pregnant women.
- The woman's body becomes like a "double" - two hearts beat in it, her own and the heart of the fetus, respectively, an additional circle of blood flow appears.
- The heart muscle of a pregnant woman experiences an increased load and increases in size.

- The volume of blood flow increases to 6-7 liters.
- The body of a pregnant woman needs a double volume of oxygen for normal tissue nutrition, including muscle tissue.
- The spine and surrounding muscles are subjected to a special load, the weight of a pregnant woman can increase by 10-20 kilograms.
- 70-75% of women experience pain symptoms of varying intensity in the back due to temporary dysfunction of the spine.
- An increase in the size of the uterus inevitably entails a shift in the center of balance, gravity, respectively, the muscles of the lower back and pelvis are subjected to increased stress.
- The posture and gait of a woman changes, the muscles of the shoulder girdle, cervical, thoracic region have to work in hypertonicity mode.
- An increase in body weight leads to a violation of venous blood flow, respectively, the muscles of the legs hurt.
- Overeating or vice versa, lack of nutrients due to nausea and vomiting caused by toxicosis, can disrupt the vitamin-mineral balance, respectively, the muscle tissue does not receive proper nutrition, myalgia develops.
- Pathological causes of muscle pain during pregnancy:
- Disease of the cardiovascular system, reduced blood supply to muscle tissue.
- Atherosclerotic changes in the vascular system.
- Inflammatory processes in muscles, fascia, joints caused by infections.
- Neurological conditions associated with osteochondrosis of the spinal column.
- History of fibromyalgia.
- Local muscle injury (ossifying process).
- Nephropathology (pyelonephritis).
- Infectious pathologies, most often genital herpes.
- Inguinal hernia, umbilical hernia.
- Varicose veins, including vaginal varicose veins.
Before proceeding to the enumeration of the reasons, here are some statistics:
In what areas can muscle pain occur during pregnancy?
- The most susceptible to changes are the muscles of the abdominal region - the rectus abdominis muscles. Before pregnancy, these skeletal muscles performed the function of maintaining an elastic press, forming it.
 After conception, the rectus muscles must perform a completely different task - to support the growing uterus. Atonic, untrained abdominal muscles are at risk of painful sprains, resulting in pain.
After conception, the rectus muscles must perform a completely different task - to support the growing uterus. Atonic, untrained abdominal muscles are at risk of painful sprains, resulting in pain. - Muscles of the pelvis, which not only support the uterus and other organs in their proper places, but are also directly involved in the process of labor.
- The muscles of the back may ache due to an atypical shift in the center of gravity, excessive load on the growing body. The atonic muscle corset is not able to cope with the additional load, the muscles are stretched, inflamed, the woman feels back pain.
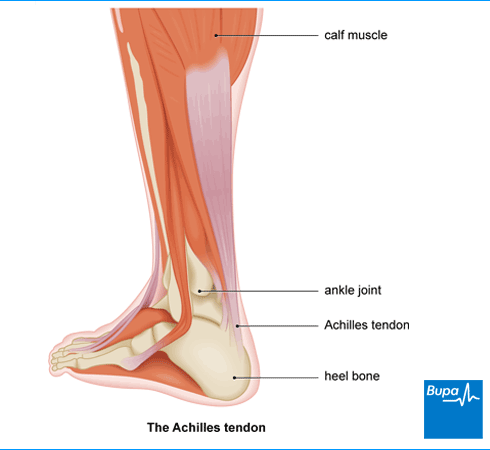
- Muscles of the legs that can hurt from the first trimester. The most typical cramps of the calf muscles during pregnancy, such a symptom most often develops in the initial phase of sleep, or at night, less often in the morning.
- Breast muscles, which, under the influence of changes in hormonal balance, increase due to increased blood circulation, activated lymph flow.

- Inguinal muscles can hurt for various reasons, but most often the pain symptom is due to physical overexertion or the effect of a specific hormone relaxin on the ligamentous apparatus. A pain symptom in the groin may not touch the muscle tissue, but the sensations are reflected precisely in the muscles, this happens with nephropathologies, diseases of the digestive tract, and even with constipation. Also, pain in the muscles of the groin during pregnancy can be caused by many non-physiological causes - varicose veins of the pubic joint, infectious diseases of the pelvic organs, and others.
- During pregnancy, the muscles of the vagina experience an increased vascular load, venous hemodynamics change, the elasticity of muscle tissue decreases, and pain appears.
- Statistics say that 70-75% of pregnant women experience pain in the lumbar region, the muscles of which are subject to increased stress due to increased body weight and physiological displacement of internal organs
It should be noted that during pregnancy, not all types of muscles spasm, there are those that, on the contrary, relax. Relaxation of smooth muscles, on the one hand, allows the delivery of oxygen and nutrients to the placenta, on the other hand, it can cause reflex radiating pain from excessively atonic organs (gall bladder, stomach, intestines).
Relaxation of smooth muscles, on the one hand, allows the delivery of oxygen and nutrients to the placenta, on the other hand, it can cause reflex radiating pain from excessively atonic organs (gall bladder, stomach, intestines).
Summarizing, we can say that the body of the expectant mother sometimes experiences an overwhelming load, comparable, according to experts, only with the intensity of the training of astronauts. Accordingly, a woman periodically feels pain symptoms, most often localized in the back, pelvic region, abdomen and legs.
Why muscles hurt during pregnancy
Why does a pregnant woman experience muscle pain? The simplest answer is this - due to systemic physiological changes in the body. The stages and types of transformation can be described as follows:
- Hormonal changes in the body.
- Progesterone and estrogen levels change, increased secretion of relaxin begins. Progesterone is needed to increase the tone of both the smooth muscles of the uterus and other muscle tissue, the production of progesterone in the first trimester is especially important so that the conception really goes into pregnancy and becomes fixed.
 In addition to influencing the state of the uterus, progesterone stimulates breast development, the muscles of the mammary glands soften, and the glands increase. In addition to the clearly beneficial effect on the body, progesterone inhibits the activity of the immune system so that it does not reject the embryo (fetus) that has invaded the uterus in the process of “recognition”. Thus, reduced immune protection is a potential risk of infectious, bacterial infections, diseases, often accompanied by muscle pain. Also, progesterone can contribute to the retention of salt and fluid in the body, which in turn disrupts the rate of normal blood circulation, venous outflow and provokes pain of a different nature, including myalgia.
In addition to influencing the state of the uterus, progesterone stimulates breast development, the muscles of the mammary glands soften, and the glands increase. In addition to the clearly beneficial effect on the body, progesterone inhibits the activity of the immune system so that it does not reject the embryo (fetus) that has invaded the uterus in the process of “recognition”. Thus, reduced immune protection is a potential risk of infectious, bacterial infections, diseases, often accompanied by muscle pain. Also, progesterone can contribute to the retention of salt and fluid in the body, which in turn disrupts the rate of normal blood circulation, venous outflow and provokes pain of a different nature, including myalgia. - An increased level of estrogen performs the task of activating the growth of the uterus, if there is too much estrogen, it works like diuretin, sometimes too actively. As a result, a violation of the water-salt, electrolyte balance develops and muscle pain appears
- Chorionic gonadotropin and somatomammotropin do not provoke myalgia by themselves, however, they accelerate all metabolic processes, and somewhat increase the muscle mass of the chest, less often than other zongs of the body (buttocks, feet).
- Diseases of the organs and blood supply systems of the small pelvis in history can also be the answer to the question - why do muscles hurt during pregnancy. Among them, the following are common and most often diagnosed:
- Ovarian cyst.
- Uterine fibroids.
- Adnexitis.
- VRVMT - varicose veins of the small pelvis
- Pain in the muscle tissue during pregnancy can also be caused by the following pathologies and acute conditions:
- Pyelonephritis.
- Inflammation of the appendix.
- Cholelithiasis.
- Incarcerated inguinal hernia.
- Infringement of the intervertebral disc.
- Threat of miscarriage.
- Constipation, flatulence.
- Sprain.
- Muscle injuries.
- Placental abruption.
- IBS - irritable bowel syndrome.
- Intestinal obstruction.
- Genital herpes.
- Symphysitis (third trimester).

- General venous insufficiency, vein occlusion.
- Urolithiasis.
- Braxton-Hicks contractions, false, training contractions.
Symptoms of muscle pain during pregnancy
Signs and symptoms of muscle pain in pregnant women are most often transient, more intense sensations, especially chronic ones, need immediate diagnosis, hospitalization and treatment.
Myalgia - pain in muscle tissue can be felt as:
- Shooting pain.
- Sharp, dagger pain (rare).
- Aching, pulling (often).
- Breaking.
- Burning, tingling.
Depending on the provoking factor, the symptoms of muscle pain during pregnancy can be temporary, situational, transient, or permanent, chronic. As a rule, discomfort in a particular area of the body in a future mother is transient, the pain may subside or even be neutralized during pregnancy, changing trimesters. This is due to constant changes in the body of a woman, which directly affect the state of muscle tissue..jpg)
Symptoms of physiologically acceptable conditions:
- Aching pain in the legs, subsiding with a change in body posture, at rest.
- Drawing pains in the back, relieved by light massage, relaxing procedures.
- Pain in the groin that improves with rest.
- Bursting, drawing pain in the back, in the pelvic region, due to a sprained ligament.
- Cramping pain associated with exercise cramps, Braxton-Hicks contractions.
Warning signs that require a doctor's call, examination and medical attention:
- Sudden, spontaneous severe pain with a tendency to worsen.
- Pain that does not subside at rest or with a change in posture, body position.
- Myalgia accompanied by fever.
- Muscle pain that lasts more than 2-3 days, not even sharp or intense.
- Cramping muscle pain with abnormal vaginal discharge (blood).
- Symptoms of "acute abdomen" - pain, drop in blood pressure, tachycardia, cyanosis of the skin.

Abdominal pain during pregnancy
A painful abdominal symptom in a pregnant woman is wrongly considered a common occurrence, a natural signal of muscle strain due to an increase in the uterus. Indeed, every day the uterus is getting bigger, this is especially noticeable in the second trimester, when the shifted center of balance provokes a change in the woman's gait. Pain in the abdominal muscles during pregnancy may indicate a pathological development of the process of bearing a fetus or other serious diseases - a cyst, inflammation of appendicitis. Fortunately, the pain symptom in pregnant women in the abdomen in 75-80% is due to tension and sprain of the round ligament, which performs the function of supporting the uterus. The bottom of the pelvis is lined with three-layer muscle tissue and fascia, which provides support for almost all organs of the reproductive system, as well as for the abdominal organs. The uterus is supported by thick ligaments, one of which, round, directly holds the uterus in place.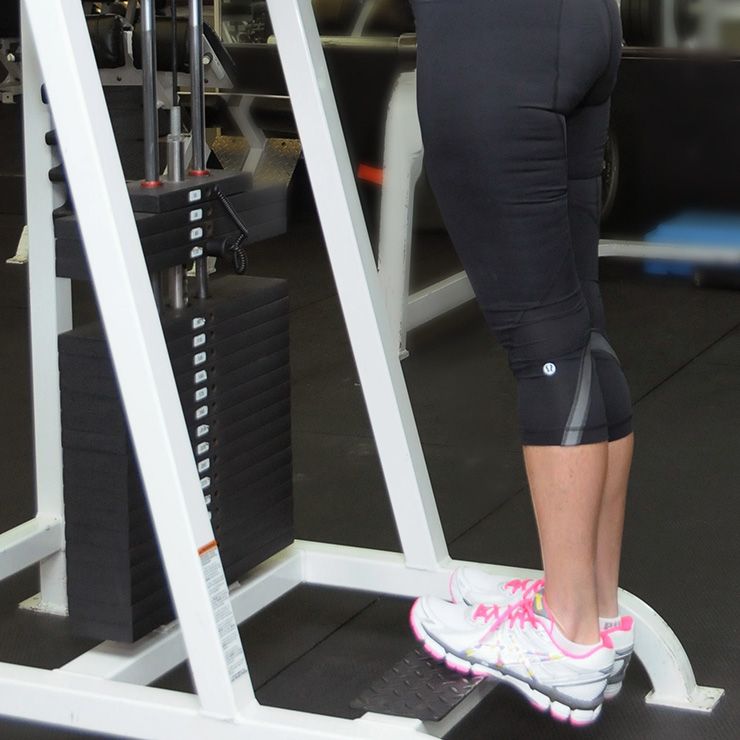 An increase in the size of the uterus provokes a stretching of the round ligament, which is quite naturally accompanied by pain in the abdomen.
An increase in the size of the uterus provokes a stretching of the round ligament, which is quite naturally accompanied by pain in the abdomen.
In the same way, the musculature is also subjected to stress, especially smooth (walls of the uterus) and abdominal muscles. If the expectant mother has not strengthened muscle tissue in advance through sports, exercise, the rectus and abdominal muscles during pregnancy are stretched or overstressed, as they have to participate in supporting the growing uterus. It is too fast stretching, muscle hypertonicity that provokes pain symptoms, while carrying a baby, the waist circumference can almost double, for example, from 65 to 100 centimeters.
The pain of the abdominal muscles during pregnancy most often does not require the intervention of a doctor and special treatment, however, a woman needs to be alert if the pain symptom does not subside when changing posture, rest, relaxation. Therefore, for any disturbing pain, it is better to consult with the attending gynecologist.
The list of the main emergency conditions in which a painful muscle symptom in the abdomen may appear:
- Obstetrical conditions:
- Threat of miscarriage.
- Septic miscarriage (acute abdomen clinic).
- Ectopic pregnancy, ectopic pregnancy.
- Fibromyoma.
- Placental abruption.
- Aneurysm rupture (splenic artery, renal artery, etc.).
- Distension and rupture of the uterus.
- General pathologies manifesting as abdominal pain, including muscle pain:
- Acute pyelonephritis.
- Appendicitis.
- Spontaneous hematoma in the rectus abdominis muscle (bleeding into muscle tissue).
- Acute cholecystitis.
- Cystitis (pain in the lower abdomen, in the perineum).
- Chronic inflammation of the ovary.
- Umbilical hernia.
- Groin hernia.
If your leg muscles hurt during pregnancy
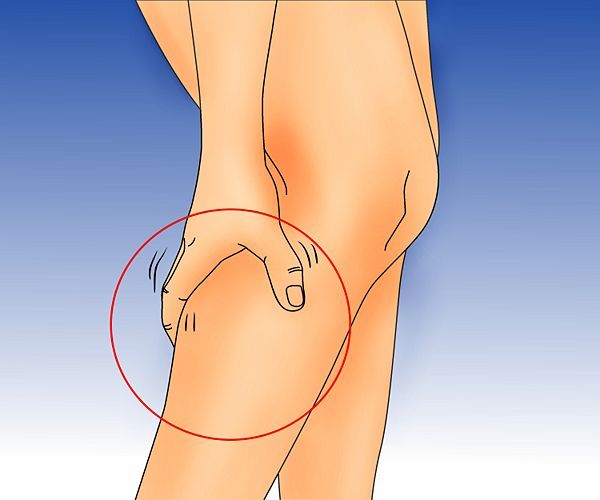
Most often, leg pain in pregnant women is either vascular disorders (varicose veins) that provoke aching, pulling pains, or convulsions, especially at night.
Why do leg muscles hurt during pregnancy?
- Flat feet, which, of course, was before pregnancy, but the period of gestation aggravates the load on the muscles and provokes their overstrain (hypertonicity). To prevent pain symptoms, which are most often localized in the calves of the legs and intensify when walking, a woman should purchase orthopedic insoles and choose shoes with a stable, medium heel with a fairly rigid sole that fixes the foot.
- Vascular dysfunctions. An increase in the weight of a pregnant woman inevitably entails an additional burden on the vascular system. If before pregnancy there was already a history of varicose veins, you should wear compression underwear, stockings to reduce pressure on the walls of blood vessels. Muscles with varicose veins hurt due to the fact that they do not receive proper nutrition.
- Non-compliance with the rules of a complete, rational diet, as a result of which the muscle tissue does not receive the necessary proteins, carbohydrates, vitamins and microelements.
 Often, convulsive syndrome is observed in women who adhere to a strict vegetarian diet.
Often, convulsive syndrome is observed in women who adhere to a strict vegetarian diet.
Often during pregnancy, the leg muscles in the calf area, that is, the calf muscles, hurt. Cramping is a severe pain that women describe as “bringing their legs together”. Night cramps of the calf muscles are the most common, which is due to the natural relaxation of the body and the dissonance between relaxation and chronic muscle hypertonicity. Also, hypnogogic convulsions, that is, muscle spasms before the deep sleep phase, often occur. Convulsive syndrome in 65% of cases is diagnosed in the middle of pregnancy, when the needs of the developing fetus are growing rapidly, and the resources of the mother's body are already significantly depleted.
Possible causes of seizures:
- Deficiency of B vitamins, magnesium, potassium, calcium.
- Persistence of bad habits - smoking, abuse of caffeinated drinks.
- Decreased blood sugar levels.
- Anemia, low hemoglobin level.

- Varicose veins.
- Syndromum venae cavae inferioris syndrome - the inferior pudendal vein, when in a horizontal position (at night) the uterus presses on a large vessel, venous outflow is disturbed, convulsions develop. This syndrome occurs in 80% of pregnant women in the third trimester.
- Misuse of diuretics to eliminate edema.
If the muscles between the legs hurt during pregnancy
Despite all the joyful and exciting moments of waiting for the baby, the period of gestation is accompanied by transient discomfort. In addition to the fact that the expectant mother has pain in the lower abdomen, in the lower back, there are many symptoms that can further complicate pregnancy, for example, the muscles between the legs hurt. In fact, such pain most likely does not appear in the muscles, but in the ligaments, nerve endings.
This is due to the increased secretion of a specific hormone - relaxin. Its main task is to reduce (inhibit) the contractile function of the uterus in the first trimester in order for the pregnancy to continue. In addition, later relaxin is needed to relax, soften the pelvic bones, symphysis, and prepare them for labor. Relaxin begins to be produced literally from the first week of conception, but the consequences of its influence are felt later, in the 2nd, and especially in the 3rd semester. Usually a pregnant woman complains of “muscles between her legs hurt” at precisely these times, pain is also felt in the hips, in the pubic region, and in the lower abdomen.
In addition, later relaxin is needed to relax, soften the pelvic bones, symphysis, and prepare them for labor. Relaxin begins to be produced literally from the first week of conception, but the consequences of its influence are felt later, in the 2nd, and especially in the 3rd semester. Usually a pregnant woman complains of “muscles between her legs hurt” at precisely these times, pain is also felt in the hips, in the pubic region, and in the lower abdomen.
Another reason that provokes a pain symptom in the groin, between the legs, may be a neurological factor - infringement of the sciatic nerve. Pinching of the nerve roots occurs due to the pressure of the growing uterus, and the pain is projected onto the buttocks, groin area, and lower limbs. Such pain cannot be attributed to true myalgia, although it affects muscle tissue.
Pregnancy, the muscles between the legs hurt - this condition can be caused by a banal overstrain, when a woman overestimates her own physical capabilities and continues to engage in sports exercises without taking into account her special position..jpg) Such cases are not uncommon among professional dancers, athletes who continue their activities during pregnancy.
Such cases are not uncommon among professional dancers, athletes who continue their activities during pregnancy.
What can relieve pain in the muscles between the legs?
- Rest and reasonable physical activity (no overload).
- Bandage supporting muscles, ligaments.
- Gentle physiotherapy treatments (by prescription only).
- Warm compresses.
- Performing a set of special exercises for pregnant women for preparatory muscle stretching.
If your groin muscles hurt during pregnancy
The entire period of pregnancy there is an increase in venous pressure, especially for the vessels of the lower extremities. This process is due to increased venous pressure of the enlarging uterus and at the same time slower pressure in the veins of the groin and legs. The growing uterus compresses the pelvic veins, the outflow of blood from the legs is difficult, this is one of the reasons why the groin muscles hurt during pregnancy.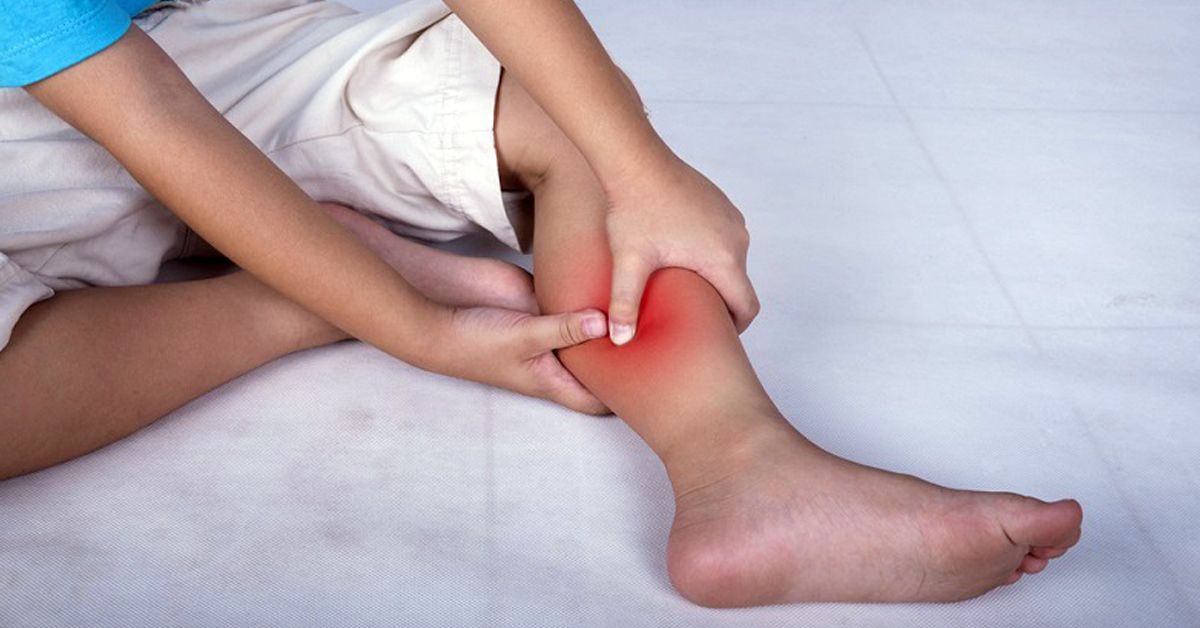
In addition, pain in the groin is explained by another physiologically acceptable reason.
In the second trimester, the round ligament is significantly stretched, the task of which is to support the uterus. Pain in the inguinal region during a sprain can be very acute, but short-term, it can be felt as a spasm, cramp, radiating down the abdomen.
In addition to physiological stretching, the following factors can explain why the groin muscles hurt during pregnancy:
- Inguinal hernia. The pain is localized to the right or left as a result of a decrease in the tone of the local supporting muscle tissue. As a result, intestinal loops can slip out under the pressure of an enlarging uterus right into the groin. A hernia looks like a bulge in the groin area, and when pinched by the muscles, it provokes pain. Strangulation is a medical emergency to avoid necrosis (blood supply cut off) and rupture of the intestine.
- Enlarged lymph nodes located in the groin.
 Enlarged lymph nodes may be a sign of an infectious inflammatory process in the pelvic organs. As a rule, a pregnant woman undergoes a thorough examination upon registration, and inflammations are recorded in the card. However, the very process of bearing a fetus can provoke an exacerbation of such diseases as adnexitis, parametritis, proctitis, endometritis, as a result, a pain symptom develops, including in the muscles.
Enlarged lymph nodes may be a sign of an infectious inflammatory process in the pelvic organs. As a rule, a pregnant woman undergoes a thorough examination upon registration, and inflammations are recorded in the card. However, the very process of bearing a fetus can provoke an exacerbation of such diseases as adnexitis, parametritis, proctitis, endometritis, as a result, a pain symptom develops, including in the muscles. - Urolithiasis also provokes pain, which in the form of renal colic can be reflected in the muscle tissues of the back, thighs or groin, depending on the location of the calculus. If the stone is localized low, the pain will manifest itself in the groin area.
- Pain in the muscles of the groin during pregnancy can be reflected when, due to the increased load on the spine, the nerve endings in the lumbosacral region are infringed.
- Bruise, blow to the groin.
- Genital herpes presenting as erythematous papules, pruritus, vaginal discharge, swollen lymph nodes, myalgia and pyrexia.
- VRVMT - varicose veins of the small pelvis, a disease that develops asymptomatically, but becomes acute during pregnancy. Venous hemodynamics is disturbed, pulling pains develop in the groin, in the legs.
When the muscles of the perineum hurt during pregnancy
The muscles of the intestines, gallbladder, esophagus and stomach are physiologically more relaxed during pregnancy, as they are directly involved in the nutrition of the fetus, but the muscles of the back, abdomen and perineal muscles, on the contrary, are subjected to increased stress and strain. This is perhaps the first and most common reason why the muscles of the perineum hurt during pregnancy.
In addition, the muscle tissue of the perineum can hurt due to the pressure of the growing uterus on the nerve endings and ligaments located in this area. As a rule, pain in the perineum after childbirth subsides irrevocably, which proves the physiological and natural nature of the pain symptom. An exception may be pain caused by a strong stretching of the perineum due to symphysitis, which develops in the second half of pregnancy.
An exception may be pain caused by a strong stretching of the perineum due to symphysitis, which develops in the second half of pregnancy.
Symphysitis, in turn, is explained by calcium deficiency in bone tissue, primary or secondary. Pain with symphysis is aching, pulling, the sensation of ache spreads in the pelvic region, in the groin, in the perineum, especially if a woman, lying in bed, tries to straighten her legs.
Overload and a kind of "softening" of the pelvic bones, which, in addition to being subjected to pressure from the uterus, "prepare" for childbirth (the body secretes relaxin for this), lead to a pain symptom. It can be felt as a pulling or shooting pain in the lumbar region, lower abdomen and in the muscle tissue of the perineum. As a compensatory consequence of muscle hypertonicity, hypotension develops, a decrease in the elasticity of the bladder, urethra. For expectant mothers, involuntary urination is typical even with slight tension in the muscles of the abdomen or back - with laughter, with coughing.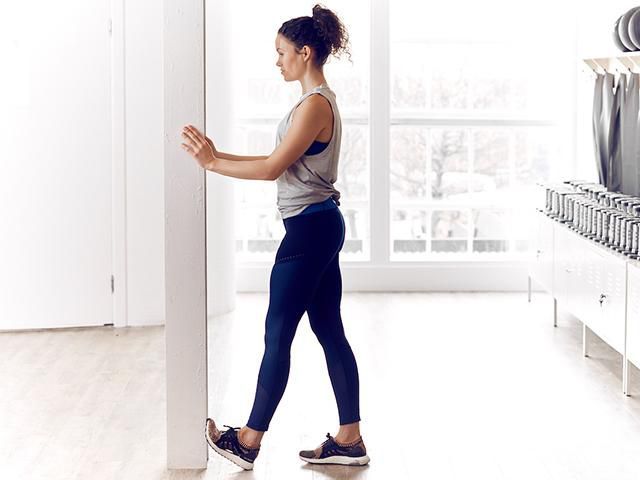 The same symptom is observed in some women when squatting or exerting pressure on the muscles of the perineum.
The same symptom is observed in some women when squatting or exerting pressure on the muscles of the perineum.
Also, during the period of gestation, a woman may have muscle pain in this area due to venous stasis, insufficiency. If you have a history of varicose veins when registering, most likely a pain symptom in the groin, perineum, and legs will be inevitable, but reversible with the right treatment.
Why do vaginal muscles hurt during pregnancy
The vagina is an organ that contains many nerve endings, receptors, blood vessels, so it is very dependent on the quality of the circulatory system.
Do vaginal muscles hurt during pregnancy? There may be several reasons:
- Weight load on the pelvic region, respectively, a decrease in active blood flow and a decrease in the supply of vaginal tissues. Congestion, swelling is a typical condition that accompanies pregnancy, the result of which is transient pain in the groin and vagina.
 In addition to the pain symptom, a woman may feel itching, tingling, which, as a rule, subside at rest, in a horizontal position (blood outflow).
In addition to the pain symptom, a woman may feel itching, tingling, which, as a rule, subside at rest, in a horizontal position (blood outflow). - Varicose veins, varicose veins of the labia. This pathological phenomenon can only be associated with the period of pregnancy, but can be observed before it. Varicose veins of the labia may be due to a weak valvular vascular system, overweight, inflammatory processes in the internal organs of the small pelvis, constant physical overstrain (carrying weights). In addition, pregnancy varicose veins can be explained by increased secretion of progesterone and estrogens, lengthening and expansion of the entire circulatory network, starting from the 10th week after conception. Uterine blood flow is activated during the entire period of gestation and reaches a peak (600-700 ml per minute) by the time of delivery. Accordingly, the fallopian tubes inevitably thicken and hyperemia, the cervix swells, the labia swells, and pain appears.
Symptoms of varicose veins can manifest themselves in the following signs:
- Drawing pain in the groin, in the vagina.

- Sensation of fullness in labia.
- Swelling of the vagina.
- Dryness, lack of lubrication, itching.
- Visible varicose nodules may appear on the labia, in the groin.
If the muscles of the vagina hurt during pregnancy, the cause can be looked for in the past. If a woman, long before conception, systematically took hormonal contraceptives or hormonal drugs for the treatment of a chronic disease, her vascular system got used to the help of hormones. During pregnancy, without the usual dose of hormonal substances, the vessels may not work at full strength, the venous outflow is disturbed, congestion develops in the lower abdomen and pain, including in the vagina
When abdominal muscles hurt during pregnancy
The abdominal muscles, which before conception were responsible for the condition and appearance of the press, during pregnancy should perform a completely different task. Support for the uterus and other internal organs is a new function of the rectus muscles, which are located in the anterior part of the peritoneum. The abdominal muscles are two muscles, the right rectus and the left rectus, which are connected in a place that is very poetically called the “white line” of the abdomen. The rectus muscles originate from the lower part of the sternum, from the lower ribs, extending down vertically along the abdominal region, reach the pubic bone, where they are fixed. The rectus muscles are crossed by specific tendon elements - jumpers, it is this combination of rectus and transverse muscles that gives the desired visual effect of the "cubes" of the press. However, for a normal pregnant woman, the cubes are not as important as the health of the baby and her own health, which is sometimes overshadowed by uncomfortable pain. Rectus muscles (abs) all 9months are subject to changes, because they must hold the growing uterus all the time. In this state, they are able to constantly close in place of the "white line" and gradually diverge evenly on the sides. It is this phenomenon that is called diastasis, it is this that explains why the abdominal muscles hurt during pregnancy.
The abdominal muscles are two muscles, the right rectus and the left rectus, which are connected in a place that is very poetically called the “white line” of the abdomen. The rectus muscles originate from the lower part of the sternum, from the lower ribs, extending down vertically along the abdominal region, reach the pubic bone, where they are fixed. The rectus muscles are crossed by specific tendon elements - jumpers, it is this combination of rectus and transverse muscles that gives the desired visual effect of the "cubes" of the press. However, for a normal pregnant woman, the cubes are not as important as the health of the baby and her own health, which is sometimes overshadowed by uncomfortable pain. Rectus muscles (abs) all 9months are subject to changes, because they must hold the growing uterus all the time. In this state, they are able to constantly close in place of the "white line" and gradually diverge evenly on the sides. It is this phenomenon that is called diastasis, it is this that explains why the abdominal muscles hurt during pregnancy.
Not every future mother may have diastasis, for those who previously went in for sports, led an active lifestyle, were on the move, strengthened the press, diastasis is observed very rarely. However, even in those who did not devote time to sports at all and “acquired” diastasis during pregnancy, it disappears 2-4 months after childbirth, such is the unique adaptive property of muscle tissue.
If the abdominal muscles hurt during pregnancy, this is considered quite acceptable, but under certain conditions and sensations:
- The abdominal muscles hurt only in the navel area, the pain is transient, appears after the 12th week and gradually subsides as the muscles are stretched adaptively.
- The rectus abdominis muscles hurt only during exercise.
- Pain in the abdominal area is not associated with an increase in body temperature, does not move down the abdomen and is not acute, intense.
- All other pain symptoms in the region of the rectus muscles need to be monitored by a doctor, in this sense it is better to play it safe and minimize the risk of possible complications.
Why groin muscles hurt during pregnancy
A pain symptom in the groin area in pregnant women can be triggered by various factors, the diagnosis of which is rather difficult. The fact is that the groin area is not considered a separate anatomical unit, rather it is a zone of connection between the hips and the articulation of the abdominal cavity. A large number of different muscles are attached to the groin, which are called adductor muscles, they are responsible for the movement of the hips and their attachment to the pelvis. Also in the inguinal zone there is a canal that includes one of the largest arteries of the body - the femoral vessels, there is also an important element - the round ligament of the uterus, which is subject to severe stretching during pregnancy.
Usually, groin pain is well known to athletes and those who undergo intense physical exertion, but the groin muscles also hurt during pregnancy.
What causes pain in the groin muscles in a pregnant woman?
- Physiological stretching of the round ligament that supports the uterus.

- Varicose veins.
- Infectious inflammatory diseases of the organs located in the pelvic region. Inflammation causes an increase in the lymphatic inguinal nodes, pain.
- Adnexitis, inflammation of the appendages, ovaries.
- Calcium deficiency associated with its increased consumption during pregnancy.
- Back pain radiating to the groin may not be related to muscle tissue, but felt like pain in the muscles. This happens with urolithiasis, its exacerbation, renal colic.
- Pain in the inguinal region can be provoked by constipation - both a physiological, hormonal factor, and caused by the psycho-emotional state of a pregnant woman (neurotic spastic constipation).
- Inguinal hernia.
- Varicose veins of the great vein of the leg, located under the skin in the inguinal region.
- Injury, bruised groin.
- Symphysitis in the second half of gestation (softening, stretching of the bones of the pubic joint).

- Excessive strain on the muscles of the thighs during stretching exercises for pregnant women.
If your back muscles hurt during pregnancy
About 70-75% of pregnant women experience pain of a different nature in the back, lower back.
Why do back muscles hurt during pregnancy?
- Physiologically acceptable hormonal changes, relaxin secretion, resulting in the expansion and relaxation of the pelvic bones, intervertebral ligaments. At the same time, the muscles still try to perform a “corset” function, but are subject to increased stress, are in hypertonicity. Such pain subsides after the 20-22nd week, when the body is already prepared and the production of relaxin decreases.
- Displacement of the main center of gravity due to an increase in the body weight of the expectant mother. The center is significantly shifted forward, respectively, all the muscles of the back are tensed with double strength. Sometimes the woman herself exacerbates the pain symptom, because she does not follow her posture, her back bends forward too much after her stomach.

- The pressure of the growing, growing uterus on the nerve endings of the spinal column is also squeezed and blood vessels, blood flow and nutrition of the tissues surrounding the spinal discs are disturbed. Such shooting, strong, but short-term pains in the lumbosacral zone of the back are especially characteristic.
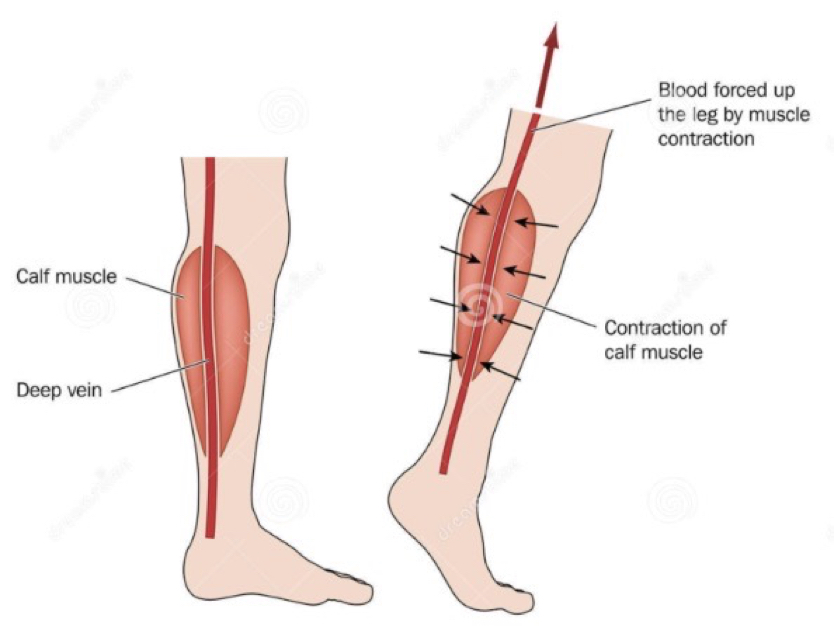
- A significant increase in body weight of a pregnant woman provokes varicose veins, disrupts the venous outflow of blood in the pelvic area, legs and lower back hurt.
- Incorrectly selected shoes, especially high heels, which are not useful in principle, as they provoke an unphysiological gait,
Calf cramps during pregnancy: causes and remedies
- Home
- Useful information
- Calf cramps in pregnancy: causes and remedies
Contents
- Introduction
- Why does it occur
- Removal methods
- Conclusion
Calf cramps in pregnant women
Cramps often accompany even quite healthy women during pregnancy. Especially often they occur at night, preventing the expectant mother from having a good rest.
Why it occurs
A cramp is a condition of the calf muscles that is susceptible to involuntary contraction, accompanied by severe pain. Spasm can be caused by several factors, such as:
- lack of vitamins and microelements, especially magnesium, resulting from their increasing needs;
- malnutrition that does not allow to meet the needs of the body of the pregnant woman and the fetus;
- overdose of diuretics, which are often used during pregnancy to relieve swelling;
- varicose veins, which often occurs in pregnant women, especially in the second half of the period of fetal development, due to increased stress on the lower limbs and impaired blood supply to the muscles.

To prevent the occurrence, pregnant women should avoid excessive exercise, and, going to bed, avoid stretching, which can contribute to spasm of the calf muscles. If convulsive spasms have become your constant companions during pregnancy, you should consult a doctor. Depending on the clinical picture, he will prescribe a complex of trace elements that will ensure the normal functioning of the fetus, or he will recommend a consultation with a phlebologist.
Ways to relieve
To get rid of spasm and pain in the calf muscle, a pregnant woman can use one of the simple methods:
- Stand with your feet (barefoot) on a warm floor and stand for a while. Just half a minute in a stationary position will get rid of this unpleasant manifestation.
- Smoothly and slowly pull the toes towards you. Repeat the reception several times until the pain subsides. After the spasm is relieved, you can warm the muscle with a heating pad, but avoid contact with the varicose vein.
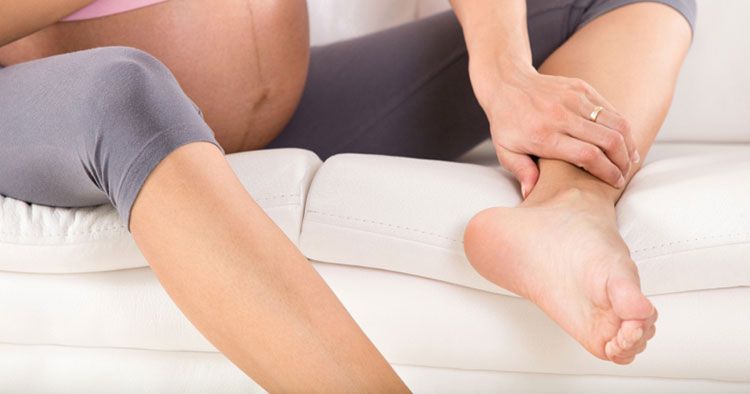
- Use massage techniques without touching the veins affected by varicose veins. After relief, lie down with your legs elevated, which will cause the outflow of blood.
But a pregnant woman should remember that a cramp indicates certain disorders in the body. And they must be taken seriously. In particular, the consultation of a phlebologist is required. You can get professional help at the "First Phlebological Center". Of course, the possibilities of treating venous pathologies during pregnancy are limited, but here they will advise you on how to prevent their development, help you choose compression stockings, and after childbirth, completely overcome the disease.
The results of our patients
Specialists
-
Read more Sign up
Lobanov Viktor Nikolaevich
Head of the clinic. Surgeon-phlebologist, doctor of ultrasound diagnostics
-
Read more Sign up
Bogachev Vadim Yurievich
Surgeon-phlebologist, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor
Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor, laureate of the Prize of the Government of the Russian Federation in the field of science and technology.