Signs of pregnancy during ovulation
Early Pregnancy Symptoms at 4 Days Post Ovulation
Early Pregnancy Symptoms at 4 Days Post Ovulation- Health Conditions
- Featured
- Breast Cancer
- IBD
- Migraine
- Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
- Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Type 2 Diabetes
- Articles
- Acid Reflux
- ADHD
- Allergies
- Alzheimer's & Dementia
- Bipolar Disorder
- Cancer
- Crohn's Disease
- Chronic Pain
- Cold & Flu
- COPD
- Depression
- Fibromyalgia
- Heart Disease
- High Cholesterol
- HIV
- Hypertension
- IPF
- Osteoarthritis
- Psoriasis
- Skin Disorders and Care
- STDs
- Featured
- Discover
- Wellness Topics
- Nutrition
- Fitness
- Skin Care
- Sexual Health
- Women's Health
- Mental Well-Being
- Sleep
- Product Reviews
- Vitamins & Supplements
- Sleep
- Mental Health
- Nutrition
- At-Home Testing
- CBD
- Men’s Health
- Original Series
- Fresh Food Fast
- Diagnosis Diaries
- You’re Not Alone
- Present Tense
- Video Series
- Youth in Focus
- Healthy Harvest
- No More Silence
- Future of Health
- Wellness Topics
- Plan
- Health Challenges
- Mindful Eating
- Sugar Savvy
- Move Your Body
- Gut Health
- Mood Foods
- Align Your Spine
- Find Care
- Primary Care
- Mental Health
- OB-GYN
- Dermatologists
- Neurologists
- Cardiologists
- Orthopedists
- Lifestyle Quizzes
- Weight Management
- Am I Depressed? A Quiz for Teens
- Are You a Workaholic?
- How Well Do You Sleep?
- Tools & Resources
- Health News
- Find a Diet
- Find Healthy Snacks
- Drugs A-Z
- Health A-Z
- Health Challenges
- Connect
- Breast Cancer
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease
- Psoriatic Arthritis
- Migraine
- Multiple Sclerosis
- Psoriasis
Medically reviewed by Debra Rose Wilson, Ph. D., MSN, R.N., IBCLC, AHN-BC, CHT — By Madison Manske on July 29, 2020
If you are trying to conceive, it may be hard to wait until you take a pregnancy test to see if you’re pregnant. In fact, you may wonder about some of the things you’re feeling shortly after ovulation — could they be pregnancy symptoms?
While taking a home pregnancy test a day after your missed period — or even a few days after that — is the best way to determine if you’re pregnant, some women may wonder about symptoms as early as 4 DPO, otherwise known as 4 days past ovulation.
In reality, your symptoms aren’t likely to start until around the time of your missed period (about 14 DPO). But anecdotal evidence suggests it’s possible to have signs earlier. Let’s take a closer look.
4 DPO is a very early stage in your cycle’s luteal phase, or time after an egg is released. If the egg released during ovulation is fertilized, it’s an early step toward becoming pregnant.
If the egg was fertilized by a sperm cell when you ovulated, the fertilized egg will transform into a zygote. Eventually, the zygote will travel down the fallopian tubes, making its way to becoming a morula or a blastocyst. This is the beginning stage for an embryo. When an embryo implants in your uterine lining, you’re considered pregnant.
Eventually, the zygote will travel down the fallopian tubes, making its way to becoming a morula or a blastocyst. This is the beginning stage for an embryo. When an embryo implants in your uterine lining, you’re considered pregnant.
But all this takes time. At 4 DPO, fertilization, if it occurred, has only just occurred, and the fertilized egg is just starting its journey toward the uterus.
It’s normal for women to have a heightened awareness of any bodily changes when they’re actively trying to conceive. Some women may experience symptoms this early on, but don’t worry if you aren’t exactly feeling pregnant at 4 DPO — because technically, you’re not.
Some women may start to experience mild symptoms at 4 DPO but it’s more likely that you’ll need to wait a few weeks.
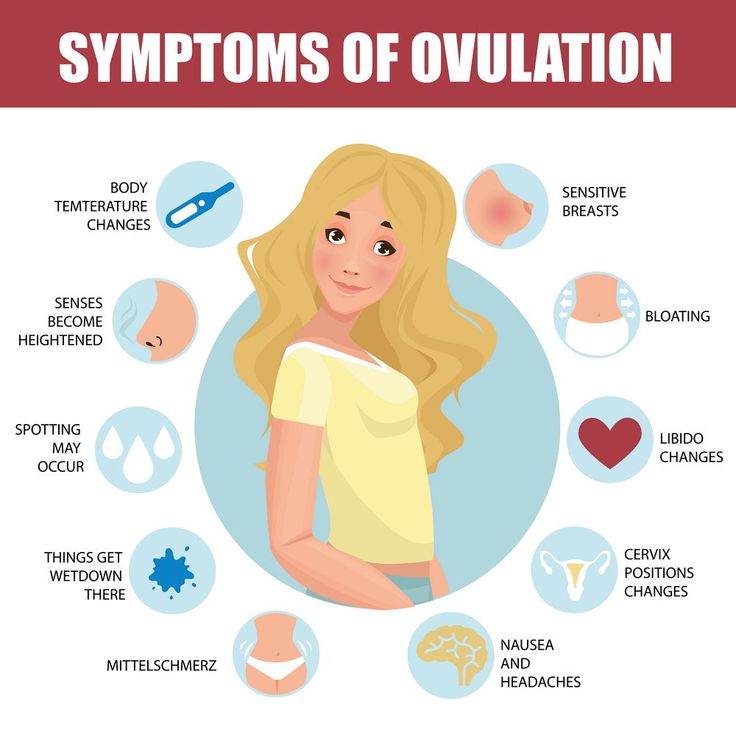
The earliest symptoms of pregnancy you may start to notice include:
- Cramps. The earlier days of pregnancy may include abdominal cramping. However, this is also a sign that you may be starting your menstrual period.

- Spotting. This may be implantation bleeding and typically happens around 6 to 12 days after the egg gets fertilized. (The egg needs time to travel to the uterus before it can implant.) You may want to talk to your doctor if you begin spotting at 4 DPO since it’s not likely caused by implantation bleeding.
- Nausea. This is a common sign in pregnancy and is caused by rising hormone levels. At 4 DPO, you may not experience nausea quite yet.
- Tender breasts. Your breasts may become sensitive due to hormonal changes. This is also a sign that you may be starting your menstrual period.
A missed period is the most telltale sign of pregnancy, but if you’re 4 DPO, you likely have around 9 to 12 days before you’ll experience this sign.
Other symptoms that you may experience within the first trimester of pregnancy include:
- fatigue
- bloating
- food cravings
- mood swings
- headaches
- constipation
- nasal congestion
It’s important to pay close attention to your body as it changes. Talk to your doctor if you have any questions or concerns about early pregnancy symptoms.
Talk to your doctor if you have any questions or concerns about early pregnancy symptoms.
If you’re trying to conceive, it’s normal to be antsy for results! The most accurate and reliable results will show up best from the first day of your missed period — likely around 13 to 15 DPO. It may be best to wait at least three weeks after conceiving before taking a test if you don’t have regular menstrual periods.
Some pregnancy tests may have instructions specific to the test you take. Check the packaging on the test before taking it.
Can I be pregnant and test negative?
If your test comes back negative and you still think you’re pregnant, it’s certainly possible! You may have taken the test too early and need to produce more pregnancy hormones first.
You can talk to your doctor, who may recommend taking a blood test for the earliest and most accurate results.
False positives are rare. Positive pregnancy tests rarely indicate something other than pregnancy, including:
- a problem in the ovaries
- menopause
- medication containing the hormone hCG
While it’s unlikely for signs of pregnancy to show at 4 DPO, some women report symptoms.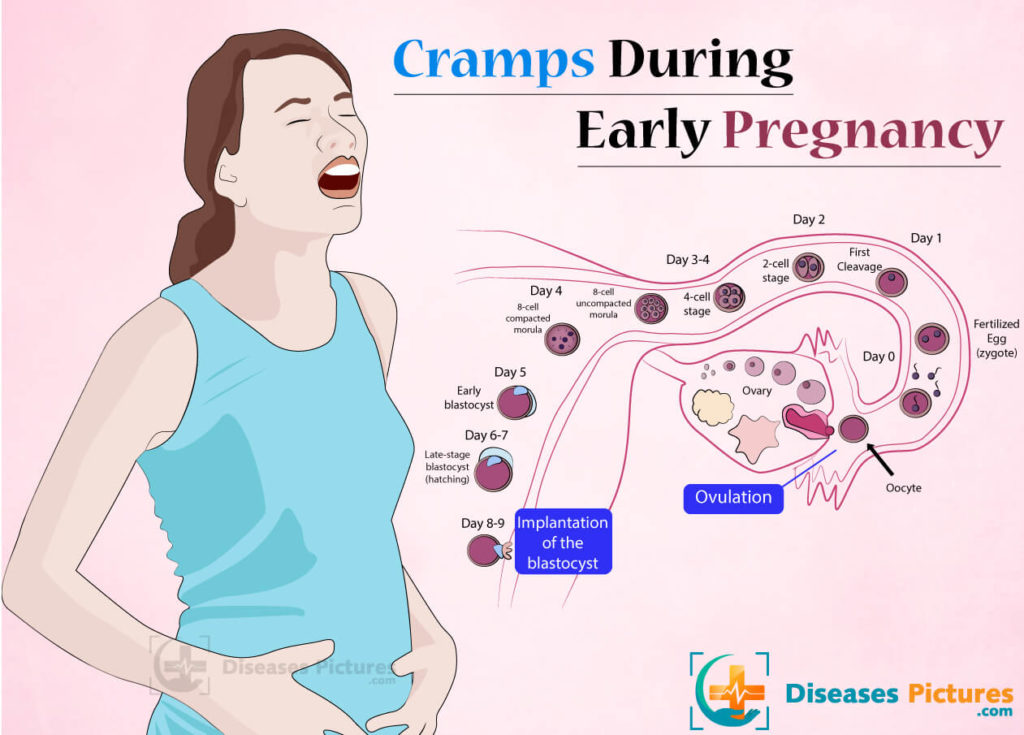
Talk to your doctor if you’re concerned about your pregnancy or have questions about conception.
Last medically reviewed on July 29, 2020
- Parenthood
- Becoming a Parent
- Getting Pregnant
How we reviewed this article:
Healthline has strict sourcing guidelines and relies on peer-reviewed studies, academic research institutions, and medical associations. We avoid using tertiary references. You can learn more about how we ensure our content is accurate and current by reading our editorial policy.
- Foxcroft K. (2013). Development and validation of a pregnancy symptoms inventory.
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3599678/ - Harville EW. (2003). Vaginal bleeding in very early pregnancy.
academic.oup.com/humrep/article/18/9/1944/708284 - Stages of pregnancy. (n.d.).
womenshealth.gov/pregnancy/youre-pregnant-now-what/stages-pregnancy - What are common signs of pregnancy? (n.
 d.).
d.).
nichd.nih.gov/health/topics/pregnancy/conditioninfo/signs
Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information becomes available.
Current Version
Jul 29, 2020
Written By
Madison Manske
Edited By
Jessica Jondle
Medically Reviewed By
Debra Rose Wilson, PhD, MSN, RN, IBCLC, AHN-BC, CHT
Copy Edited By
Lissa Poirot
Share this article
Medically reviewed by Debra Rose Wilson, Ph.D., MSN, R.N., IBCLC, AHN-BC, CHT — By Madison Manske on July 29, 2020
related stories
8 DPO: The Early Pregnancy Symptoms
What to Expect at 14 DPO
Early Pregnancy Symptoms
Cramps but No Period: 7 Early Pregnancy Symptoms
Can I Tell If I’m Pregnant Before I Miss My Period?
Read this next
8 DPO: The Early Pregnancy Symptoms
Medically reviewed by Kimberly Dishman, MSN, WHNP-BC, RNC-OB
If you miss your period, you might wonder if you’re pregnant.
 Some women have symptoms of pregnancy as early as eight days past ovulation (8 DPO). We…
Some women have symptoms of pregnancy as early as eight days past ovulation (8 DPO). We…READ MORE
What to Expect at 14 DPO
Medically reviewed by Fernando Mariz, MD
We’ll tell you about what symptoms you might encounter at 14 DPO, or 14 days post ovulation, that could mean you’re pregnant.
READ MORE
Early Pregnancy Symptoms
Medically reviewed by Valinda Riggins Nwadike, MD, MPH
What are the telltale early symptoms of pregnancy? Every person is different, but here are a few top signs.
READ MORE
Cramps but No Period: 7 Early Pregnancy Symptoms
Medically reviewed by Kimberly Dishman, MSN, WHNP-BC, RNC-OB
If you're experiencing cramping but don't get your period, you might be pregnant. Here are seven common early pregnancy symptoms.
READ MORE
Can I Tell If I’m Pregnant Before I Miss My Period?
Medically reviewed by Debra Sullivan, Ph.D., MSN, R.N., CNE, COI
While some women do experience pregnancy symptoms earlier than others, the only way to confirm a pregnancy is with a test. Here's what you need to…
READ MORE
What Are the Symptoms of Hyperovulation?
Hyperovulation has few symptoms, if any. It's typically diagnosed after an individual develops multiple pregnancies at once.
READ MORE
Pregnancy Friendly Recipe: Creamy White Chicken Chili with Greek Yogurt
This pregnancy-friendly spin on traditional chili is packed with the nutrients your body needs when you're expecting.
READ MORE
What You Should Know About Consuming Turmeric During Pregnancy
Consuming turmeric in pregnancy is a debated subject.
 We'll tell you if it's safe.
We'll tell you if it's safe.READ MORE
Pregnancy-Friendly Recipe: Herby Gruyère Frittata with Asparagus and Sweet Potatoes
Medically reviewed by Kathy W. Warwick, R.D., CDE
So easy and delicious. This frittata is high in protein and rich in essential nutrients your body needs to support a growing baby. Bonus: You can…
READ MORE
The Best Stretch Mark Creams and Belly Oils for Pregnancy in 2023
Stretch marks are easier to prevent than erase. If you're seeking a preventive, we've gathered a few of the best stretch mark creams for pregnancy.
READ MORE
What to expect in the 2-week wait
For couples trying to get pregnant, the days following ovulation mark the infamously difficult 2-week wait.
However, knowing what is happening in the body, as well as the typical pregnancy symptoms that occur on different days past ovulation (DPO), can make the wait a little easier.
Many women wonder if every twinge and ache could be a sign of pregnancy. However, the early symptoms of pregnancy are often similar to the symptoms of an impending period. Some, like muscle aches and pains, are also a part of everyday life.
It is not possible to know for sure if a woman is pregnant until a pregnancy test confirms it. Also, pregnancy symptoms, and when they occur, vary significantly between individuals.
In this article, we look at what is happening in the body around the time of ovulation, and what early signs women might notice in the early DPO.
Share on PinterestEarly pregnancy symptoms can be similar to PMS symptoms.While some women experience many early pregnancy symptoms, others experience few or no symptoms at all.
Also, early pregnancy symptoms can be very similar to the symptoms experienced around the time of ovulation, during PMS, and by those taking fertility medications.
This is why DPO symptoms are not a reliable measure of whether or not a woman has become pregnant. Women should talk with a doctor about their specific symptoms.
Women should talk with a doctor about their specific symptoms.
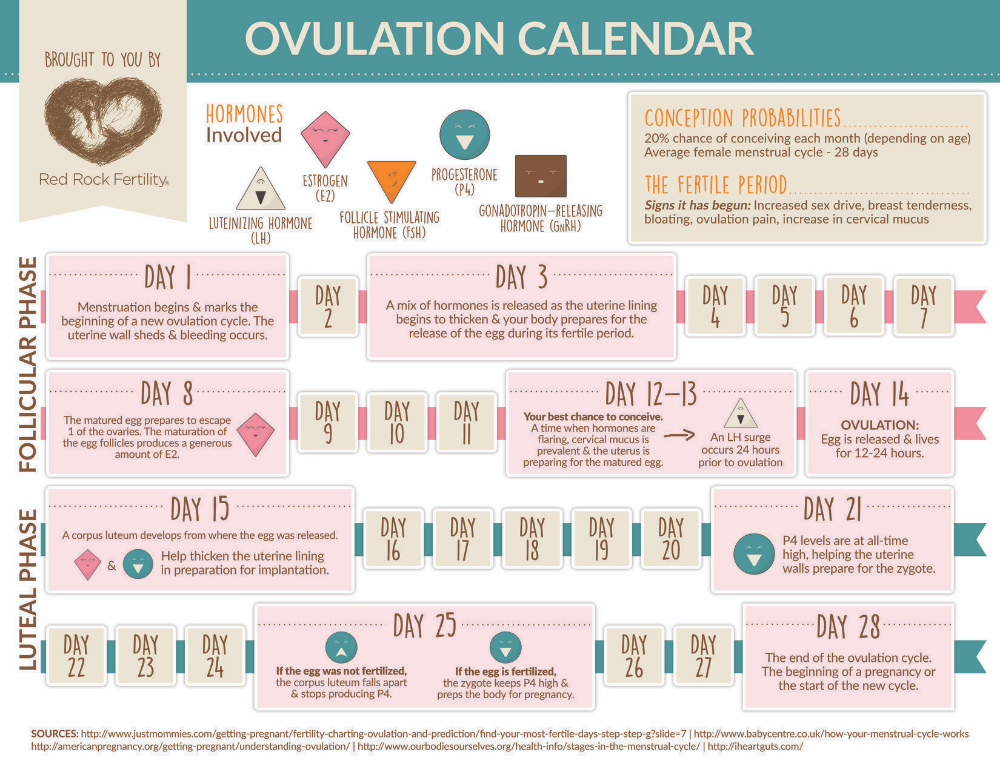
Days 0–7 past ovulation
Ovulation is the moment an ovary releases an egg.
As soon as an ovary releases an egg, the luteal phase of the menstrual cycle begins. The luteal phase ends with a menstrual period unless pregnancy occurs.
Women will not experience any pregnancy symptoms during the earliest part of the luteal phase. This is because pregnancy does not occur until the fertilized egg implants into the wall of the uterus.
During the luteal phase, the body produces more progesterone, which is a hormone that helps sustain an early pregnancy. The levels of progesterone peak at 6–8 days after ovulation, even when a woman does not become pregnant.
Progesterone levels can affect a woman’s mood and body — this means that after a week or so, they may experience similar symptoms in early pregnancy as they do before a period.
When a fertilized egg reaches the uterus, it implants itself into the wall of the uterus.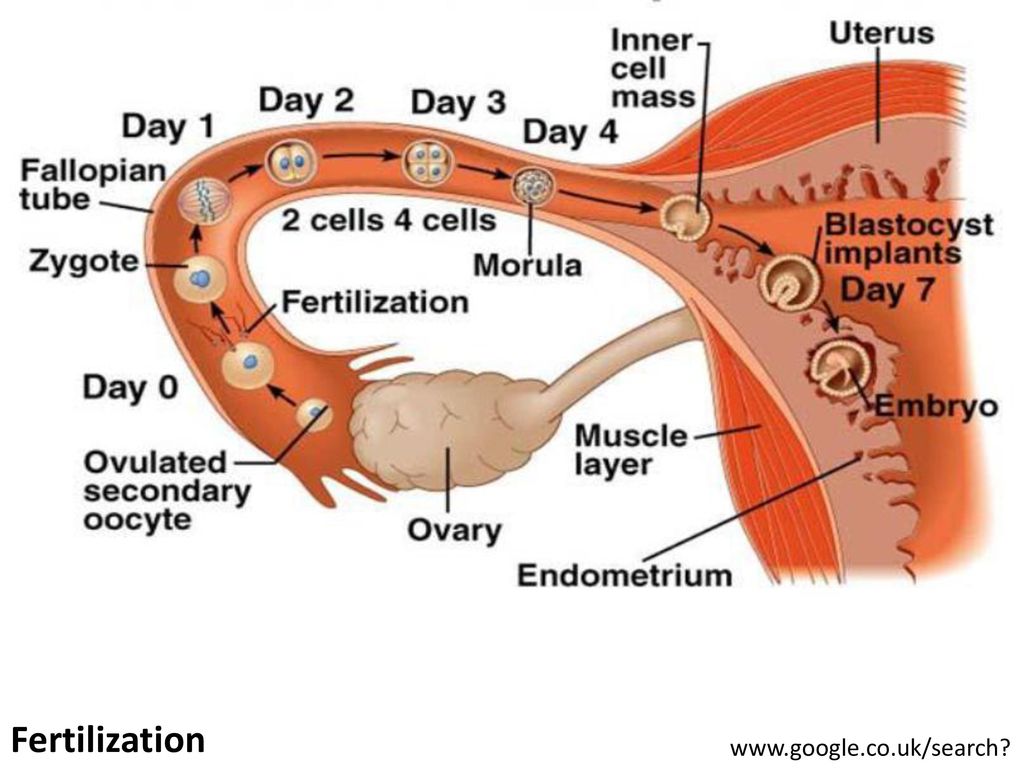 This is called implantation and marks the start of pregnancy. Implantation typically happens 6–12 days after fertilization.
This is called implantation and marks the start of pregnancy. Implantation typically happens 6–12 days after fertilization.
This is the time when women may begin to experience pregnancy symptoms, including:
- breast tenderness
- bloating
- food cravings
- increased nipple sensitivity
- headaches and muscle aches
However, these symptoms may also occur in those who are not pregnant. This is because of the increased levels of progesterone that are present during the last stages of the menstrual cycle.
Days 7–10 past ovulation
When the fertilized egg implants itself in the uterus, around one-third of women will notice light bleeding or spotting, which is called implantation bleeding.
This spotting typically lasts only a day or two and is very light in flow. Implantation bleeding is one of the earliest signs of pregnancy since it happens around the time the woman becomes pregnant.
However, even when a woman notices bleeding around the time of implantation, they may still not get a positive pregnancy test. They may have a very early miscarriage called a chemical pregnancy, or the bleeding might be due to something else.
They may have a very early miscarriage called a chemical pregnancy, or the bleeding might be due to something else.
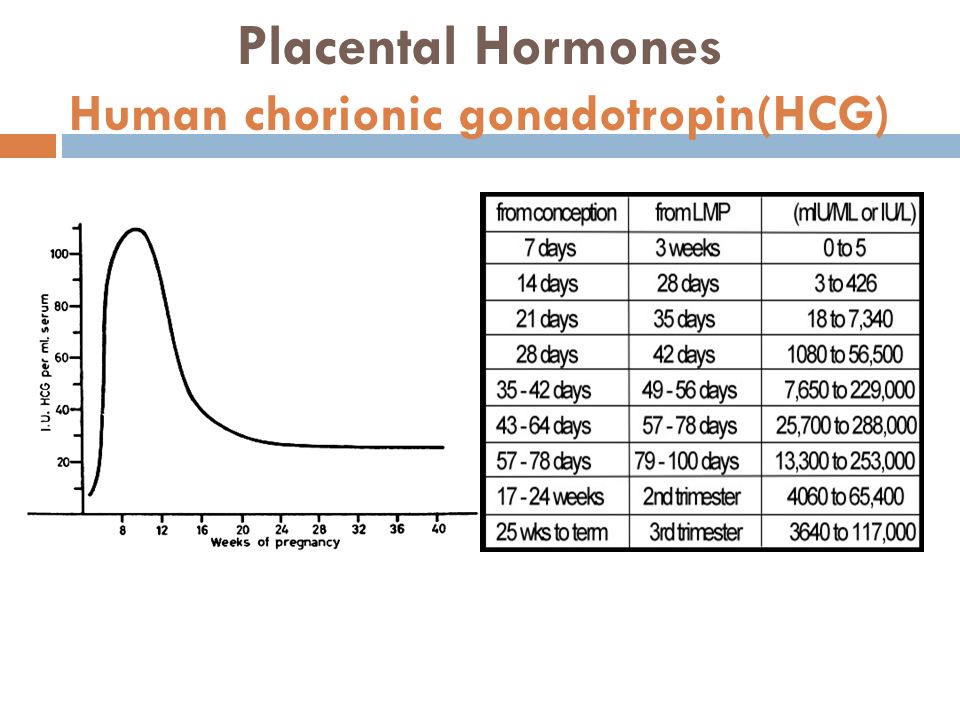
At implantation, the body begins producing a pregnancy hormone called human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG). Known as the pregnancy hormone, hCG — along with progesterone and estrogen — is responsible for early pregnancy symptoms. It is also the hormone that pregnancy tests identify.
However, it can take several days for hCG to reach to a detectable level, so pregnancy tests may not pick up the hormone, and symptoms may not develop immediately.
Days 11–14 past ovulation
A few days after implantation, hCG levels may be high enough to cause early pregnancy symptoms. However, this is also the phase of the menstrual cycle when a woman is most likely to experience symptoms that mean they are about to get their period.
Women who are aware of how their body behaves each month might be better able to identify whether their symptoms are due to pregnancy or regular menstruation.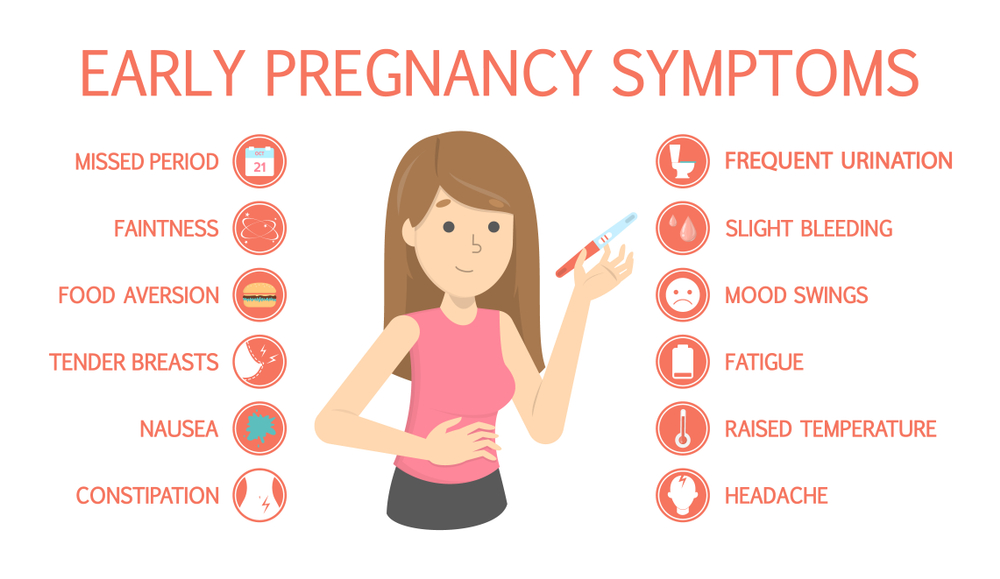
Some other symptoms of early pregnancy include:
- darkening in the color of the nipples
- fatigue
- food cravings or increased hunger
- increased need to use the bathroom
- gastrointestinal changes, such as cramping or diarrhea
By the time a woman has experienced several early pregnancy symptoms, it is possible that the hCG levels are high enough that a pregnancy test can indicate a pregnancy. However, hCG levels vary, so this is not always the case.
Share on PinterestNausea is a common symptom of early pregnancy.
As pregnancy progresses and hCG levels rise even more, many women begin experiencing more symptoms.
Some of the most common include:
- dizziness or lightheadedness due to hormonal shifts and changes in the blood pressure and heart rate
- nausea, especially when hungry
- vomiting
- strong aversions to certain foods or smells
- changes in the sense of smell
- fatigue
- bloating and water retention
Whether a woman is trying to get pregnant or trying to avoid a pregnancy, the 2-week wait can be frustrating.
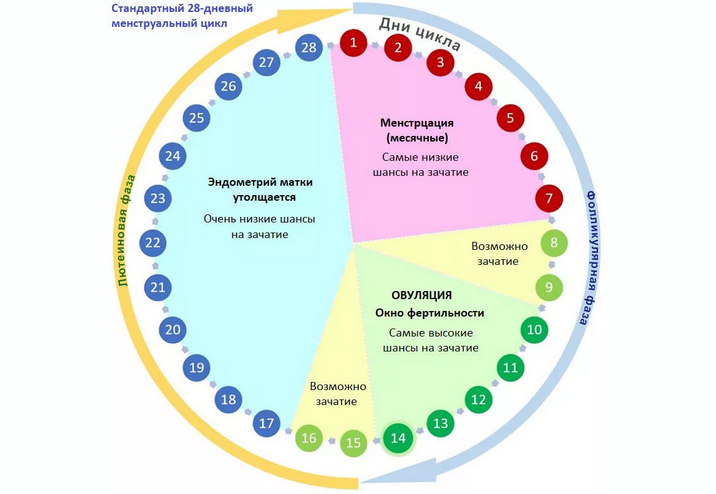
Some women track their ovulation by looking out for physical symptoms or using ovulation tests. It is important to note that the only way to detect ovulation is through medical testing.
However, home ovulation tests can be misleading, particularly if a woman has a condition that affects ovulation.
No symptom alone can confirm early pregnancy, and many women experience no early pregnancy symptoms at all. The only way to establish a pregnancy is by taking a pregnancy test.
Signs of ovulation | Clinic MEdel
OVULATION (from lat. ovum - egg) - release of a mature egg capable of fertilization from the ovarian follicle into the abdominal cavity; stage of the menstrual cycle (ovarian cycle). Ovulation in women of childbearing age occurs periodically (every 21-35 days). The frequency of ovulation is regulated by neurohumoral mechanisms, mainly gonadotropic hormones of the anterior pituitary gland and ovarian follicular hormone. Ovulation contributes to the accumulation of follicular fluid and thinning of the ovarian tissue located above the protruding pole of the follicle. The rhythm of ovulation , which is constant for every woman, undergoes changes within 3 months after an abortion, within a year after childbirth, and also after 40 years, when the body is preparing for the premenopausal period. Stops ovulation with the onset of pregnancy and after the extinction of menstrual function. Setting a deadline ovulation is important when choosing the most effective time for fertilization, artificial insemination and in vitro fertilization.
Ovulation contributes to the accumulation of follicular fluid and thinning of the ovarian tissue located above the protruding pole of the follicle. The rhythm of ovulation , which is constant for every woman, undergoes changes within 3 months after an abortion, within a year after childbirth, and also after 40 years, when the body is preparing for the premenopausal period. Stops ovulation with the onset of pregnancy and after the extinction of menstrual function. Setting a deadline ovulation is important when choosing the most effective time for fertilization, artificial insemination and in vitro fertilization.
Signs of ovulation
Subjective signs of ovulation may be short-term pain in the lower abdomen. objective signs of ovulation are an increase in mucous discharge from the vagina and a decrease in rectal (basal) temperature on the day of ovulation with an increase in it the next day, an increase in the content of progesterone in the blood plasma, etc.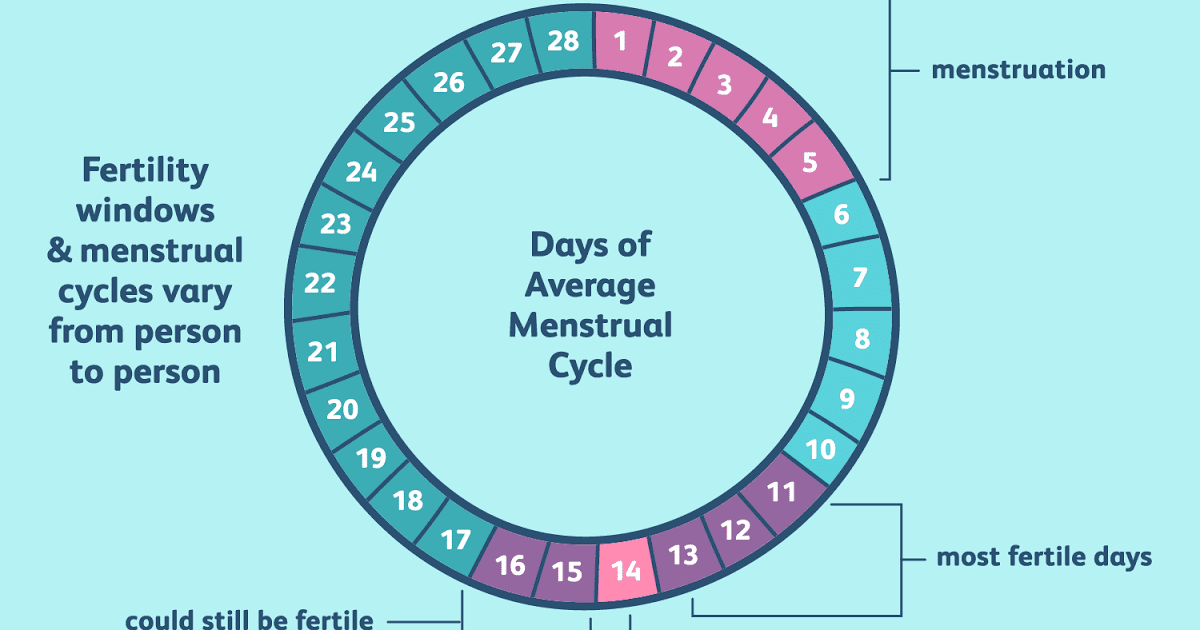 Violation of ovulation is due to dysfunction of the hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian system and can be caused by inflammation of the genitals, dysfunction of the adrenal cortex or thyroid gland, systemic diseases, tumors of the pituitary and hypothalamus , stressful situations. Lack of ovulation at childbearing age (anovulation) is manifested by a violation of the rhythm of menstruation by the type of oligomenorrhea (menstruation lasting 1-2 days), amenorrhea, dysfunctional uterine bleeding. Absence ovulation (anovulation) is always the cause of a woman's infertility. Methods for restoring ovulation are determined by the cause that caused anovulation, and require an appointment with a gynecologist and special treatment.
Violation of ovulation is due to dysfunction of the hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian system and can be caused by inflammation of the genitals, dysfunction of the adrenal cortex or thyroid gland, systemic diseases, tumors of the pituitary and hypothalamus , stressful situations. Lack of ovulation at childbearing age (anovulation) is manifested by a violation of the rhythm of menstruation by the type of oligomenorrhea (menstruation lasting 1-2 days), amenorrhea, dysfunctional uterine bleeding. Absence ovulation (anovulation) is always the cause of a woman's infertility. Methods for restoring ovulation are determined by the cause that caused anovulation, and require an appointment with a gynecologist and special treatment.
Some women experience peak sexual arousal on days 90,003 of ovulation 90,004. However, the use of a physiological method of contraception against pregnancy, based on sexual abstinence during ovulation , is especially difficult for young spouses, whose frequency of sexual intercourse reaches a fairly high level. In addition, with strong love excitement and nervous stress, additional ovulation can occur (especially with episodic, irregular intercourse), and then not one, but two eggs mature in one menstrual cycle. This should be remembered when choosing one or another method of contraception.
In addition, with strong love excitement and nervous stress, additional ovulation can occur (especially with episodic, irregular intercourse), and then not one, but two eggs mature in one menstrual cycle. This should be remembered when choosing one or another method of contraception.
As soon as every healthy girl at the age of 11-15 begins to menstruate, which is an indicator of her body's readiness for childbearing, then there are problems associated with counting the days of the menstrual cycle and the legitimate question why menstruation does not occur, or vice versa, why the long-awaited pregnancy does not occur. . This makes a woman think and wait all the time, be in the dark about what happens to her every month. And so every month for decades.
Length of menstruation and cycle
Ideal menstruation lasts 3-5 days and repeats every 28 days. However, for some women, this cycle takes 19 days or even less, while for others it lasts from 35 to 45 days, which is a feature of their body, and not a violation of menstrual function.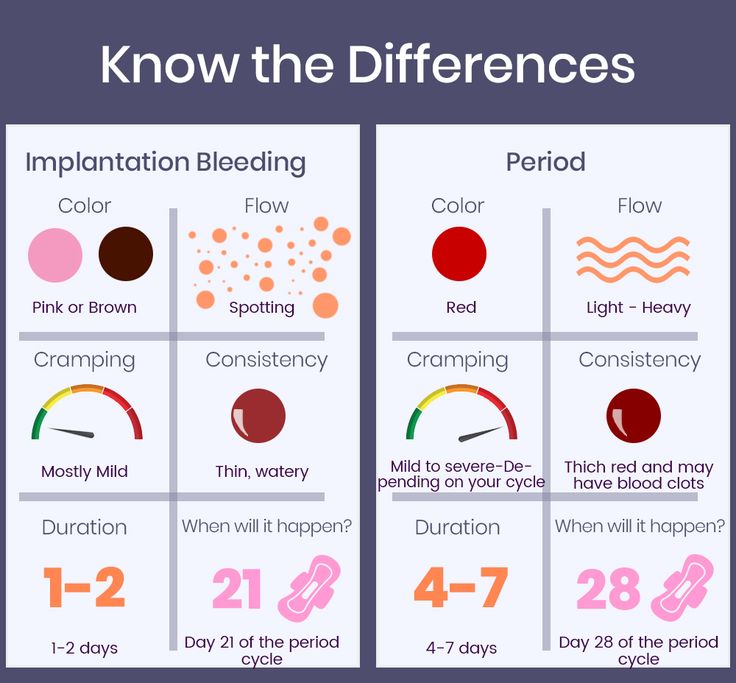 The duration of menstruation also, depending on the organism, can vary within a week. All this should not cause alarm in a woman, but a delay of more than two months, called opsometry or more than six months - amenorrhea, should alert the woman and make sure to find out the cause with a gynecologist.
The duration of menstruation also, depending on the organism, can vary within a week. All this should not cause alarm in a woman, but a delay of more than two months, called opsometry or more than six months - amenorrhea, should alert the woman and make sure to find out the cause with a gynecologist.
Length of menstrual cycle
The menstrual cycle is a complex physiological process that continues in women up to 45-55 years. It is regulated by the so-called sex centers located in the middle part of the diencephalon - the hypothalamus. The changes that occur during the menstrual cycle are most pronounced in the uterus and ovaries. In the ovary, under the influence of hormones produced by the ovarian follicles, partly by the adrenal cortex and testes, the main follicle, which contains the egg, grows and matures. The mature follicle ruptures and the egg, together with the follicular fluid, enters the abdominal cavity, and then into the fallopian tube. The process of rupture of the follicle and the release of a mature (suitable for fertilization) egg from its cavity is called ovulation , which, with a 28-day cycle, occurs most often between the 13th and 15th days.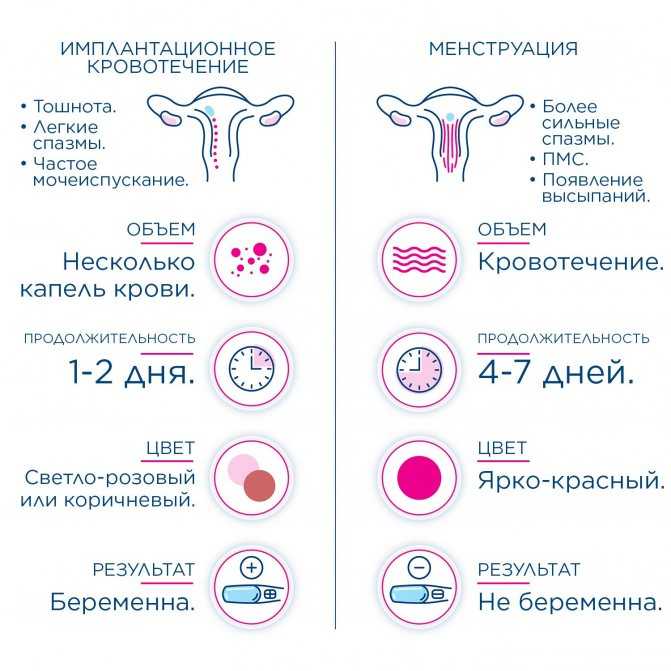
Corpus luteum, estrogen, progesterone
A corpus luteum forms at the site of the ruptured follicle. These morphological changes in the ovary are accompanied by the release of sex steroid hormones - estrogens and progesterone. Estrogens are secreted by the maturing follicle, and progesterone by the corpus luteum.
The release of estrogen has two maxima - during ovulation and during the period of maximum activity of the corpus luteum. So, for example, if the normal estrogen content is about 10 µg/l, then during ovulation it is about 50 µg/l, and during pregnancy, especially towards the end of it, the estrogen content in the blood increases to 70-80 µg/l per due to a sharp increase in the biosynthesis of estrogens in the placenta.
Together with progesterone, estrogens promote the implantation (introduction) of a fertilized egg, maintain pregnancy and promote childbirth. Estrogens play an important role in the regulation of many biochemical processes, are involved in carbohydrate metabolism, lipid distribution, stimulate the synthesis of amino acids, nucleic acids and proteins. Estrogens contribute to the deposition of calcium in bone tissue, delay the release of sodium, potassium, phosphorus and water from the body, that is, increase their concentration both in the blood and in electrolytes (urine, saliva, nasal secretions, tears) of the body.
Estrogens contribute to the deposition of calcium in bone tissue, delay the release of sodium, potassium, phosphorus and water from the body, that is, increase their concentration both in the blood and in electrolytes (urine, saliva, nasal secretions, tears) of the body.
The secretion of estrogens is controlled by the anterior pituitary gland and its genadotropic hormones: follicle-stimulating (FSH) and luteinizing (LH).
Under the influence of estrogens in the first phase of the menstrual cycle, called folliculin, regeneration occurs in the uterus, that is, the restoration and growth of its mucous membrane - the endometrium, the growth of glands that stretch in length and become convoluted. The mucous membrane of the uterus thickens 4-5 times. In the glands of the cervix, the secretion of mucous secretion increases, the cervical canal expands, and becomes easily passable for spermatozoa. In the mammary glands, the epithelium grows inside the milk ducts.
In the second phase, called luteal (from the Latin word luteus - yellow), under the influence of progesterone, the intensity of metabolic processes in the body decreases.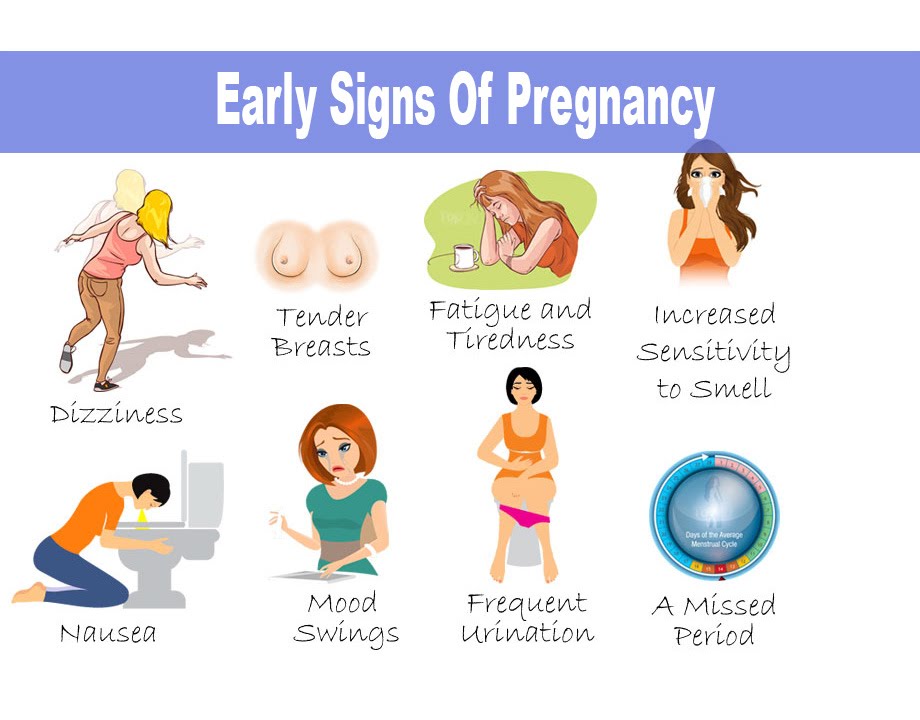 The growth of the mucous membrane of the body of the uterus stops, it becomes loose, edematous, a secret appears in the glands, which creates favorable conditions for attaching a fertilized egg to the mucous membrane and developing the embryo. The glands stop secreting mucus, the cervical canal closes. In the mammary glands, from the overgrown epithelium of the end sections of the milk ducts, alveoli arise, capable of producing and secreting milk.
The growth of the mucous membrane of the body of the uterus stops, it becomes loose, edematous, a secret appears in the glands, which creates favorable conditions for attaching a fertilized egg to the mucous membrane and developing the embryo. The glands stop secreting mucus, the cervical canal closes. In the mammary glands, from the overgrown epithelium of the end sections of the milk ducts, alveoli arise, capable of producing and secreting milk.
If pregnancy does not occur, the corpus luteum dies, the functional layer of the endometrium is rejected, and menstruation occurs. Monthly bleeding varies from three to seven days, the amount of blood lost is from 40 to 150 g.
It should be noted that different women have a noticeable difference in the timing of ovulation . And even for the same woman, the exact timing of the onset fluctuates in different months. In some women, cycles are characterized by exceptional irregularity. In other cases, cycles may be longer or shorter than the average - 14 days. In rare cases, it happens that in women with a very short cycle ovulation occurs around the end of the period of menstrual bleeding, but still, in most cases, ovulation occurs quite regularly.
In rare cases, it happens that in women with a very short cycle ovulation occurs around the end of the period of menstrual bleeding, but still, in most cases, ovulation occurs quite regularly.
If, for one reason or another, ovulation does not occur , the endometrial layer in the uterus is thrown out during menstruation. If the fusion of the egg and sperm has occurred, then the cytoplasm of the egg begins to vibrate very strongly, as if the egg is experiencing an orgasm. Sperm penetration is the final stages of egg maturation. All that remains of a spermatozoon is its nucleus, where 23 chromosomes are densely packed (half the set of a normal cell). The sperm nucleus is now rapidly approaching the egg nucleus, which also contains 23 chromosomes. The two cores are slowly touching. Their shells dissolve and they merge, as a result of which they are divided into pairs and form 46 chromosomes. Of the 23 chromosomes of the sperm, 22 are completely analogous to the chromosomes of the egg. They determine all the physical characteristics of a person except gender. In the remaining pair from the egg there is always an X chromosome, and from the sperm there can be an X or Y chromosome. Thus, if there are 2 XX chromosomes in this set, then a girl will be born, if XY, then a boy.
They determine all the physical characteristics of a person except gender. In the remaining pair from the egg there is always an X chromosome, and from the sperm there can be an X or Y chromosome. Thus, if there are 2 XX chromosomes in this set, then a girl will be born, if XY, then a boy.
Studies conducted at the National Institute of Environmental Medical Problems (North Carolina) showed that the time of conception in relation to the time of onset of ovulation depends not only on the actual conception of a child, but also on its gender.
The probability of conception is maximum on day of ovulation and is estimated at about 33%. A high probability is also noted on the day before ovulation - 31%, two days before it - 27%. Five days before ovulation the probability of conception is estimated to be 10% four days before ovulation - 14% and three days - 16%. Six days before ovulation and the day after ovulation, the probability of conception during sexual intercourse is very small.
Considering that the average “lifespan” of spermatozoa is 2-3 days (in rare cases it reaches 5-7 days), and the female egg remains viable for about 12-24 hours, then the maximum duration of the “dangerous” period is 6- 9days and the “dangerous” period corresponds to the phase of slow rise (6-7 days) and rapid decline (1-2 days) before and after the day of ovulation , respectively. Ovulation , as noted above, divides the menstrual cycle into two phases: the follicle maturation phase, which, with an average cycle duration of 10-16 days, and the luteal phase (corpus luteum phase), which is stable, independent of the duration of the menstrual cycle and is 12-16 days. The phase of the corpus luteum is referred to as the period of absolute infertility, it begins 1-2 days after ovulation and ends with the onset of a new menstruation.
The first signs of fertilization after ovulation in women. Tips NMK
Our ancestors determined the onset of pregnancy using folk signs. An accurate diagnosis of the success of conception appeared only in the early 60s of the last century. The author of the now popular rapid test that measures the level of hCG in the urine, was the German scientist Sondek. And what signs of pregnancy will allow the expectant mother to guess about the birth of a new life without diagnosis?
An accurate diagnosis of the success of conception appeared only in the early 60s of the last century. The author of the now popular rapid test that measures the level of hCG in the urine, was the German scientist Sondek. And what signs of pregnancy will allow the expectant mother to guess about the birth of a new life without diagnosis?
A bit of theory
Ovulation is the moment when the egg leaves the corpus luteum, ready to meet the sperm. This date occurs approximately in the middle of the cycle, 4-7 days after the end of menstruation.
If the woman's reproductive system is functioning normally, unprotected intercourse during ovulation leads to conception. The event can take place a few days before the expected date: the activity and viability of spermatozoa persists for three days.
The connection between the sperm and the egg takes place inside the woman's fallopian tubes. It leads to the appearance of a special element - a zygote. From this point on, the woman can be considered pregnant.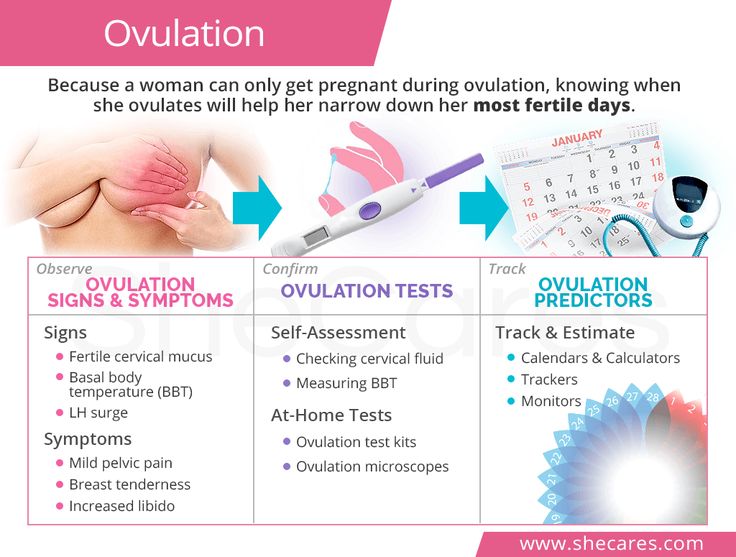
The resulting zygote actively divides, creating cells of the future embryo. The fifth day is considered the date of its transformation into a blastocyte. If at first the embryo floats in the fallopian tubes, now it is trying to gain a foothold in the endometrium of the uterus. When this moment comes, the woman's hormonal background changes, and she feels the first symptoms.
The stages of in vitro fertilization in our center are almost exactly the same, only the zygote is formed in the laboratory, under the supervision of specialists. The formed embryos are implanted into the uterine cavity, and after a few days the success of the procedure is determined.
The sooner a woman finds out about pregnancy, the better: any disturbances in the functioning of the body, improper regimen, stress can negatively affect the development of the baby.
First signs
Immediately after the end of ovulation, it is impossible to assess the success of conception. At this moment, the attachment of the embryo to the uterine cavity has not yet occurred, and the hormonal background of the woman is still stable.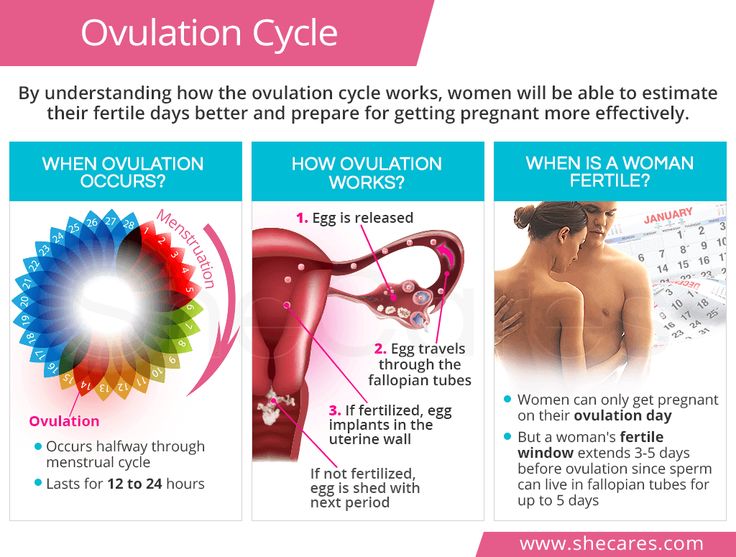 Sometimes pregnancy may not occur:
Sometimes pregnancy may not occur:
- if there was no ovulation;
- the egg was not viable;
- there is a discrepancy between the immune systems of the spouses.
If the process was successful, the following symptoms may occur.
Lower abdominal pain
Most expectant mothers experience discomfort in the lower abdomen, reminiscent of menstrual pain. Such spasms are not a signal of the growth of the uterus, the period is still too short. They are a kind of reaction of the body to the successful implementation of conception.
Our experts recommend that women who decide on IVF should carefully monitor their own feelings. Cramps in the lower abdomen should last no longer than 14 days. If they do not disappear, discomfort may indicate an ectopic pregnancy. An urgent visit to a personal doctor is required!
Gastrointestinal disorders
Hormonal changes affect the productivity of all systems and organs of the expectant mother.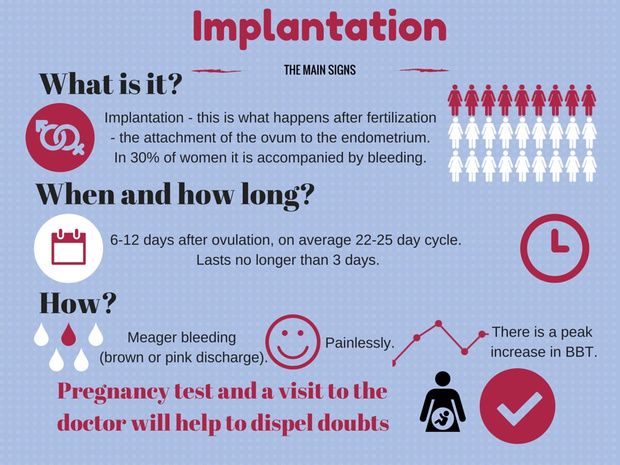 After the embryo attaches to the uterus, stool disorder, heartburn, nausea and vomiting may occur.
After the embryo attaches to the uterus, stool disorder, heartburn, nausea and vomiting may occur.
Taste preferences change, and habitual products cause rejection. Such phenomena can be a symptom of pregnancy if they began 7-10 days after unprotected intimate contact.
Changes in mood
Their cause is the same hormones. A woman can suddenly become whiny, compassionate, overly emotional. It should be understood that this is only a temporary state caused by the restructuring of the body, and treat it with understanding. Pregnancy planning is a process that requires maximum patience and composure. Psychological stress in expectant mothers is often already at the limit, and the changes that occur with the body are beyond their control.
Breast tenderness
The phenomenon is observed in 90% of cases. A couple of days before the expected date of menstruation, the breast grows and becomes more rounded. The nipples darken, and their width increases. As a result, the woman feels tension and soreness in the chest area.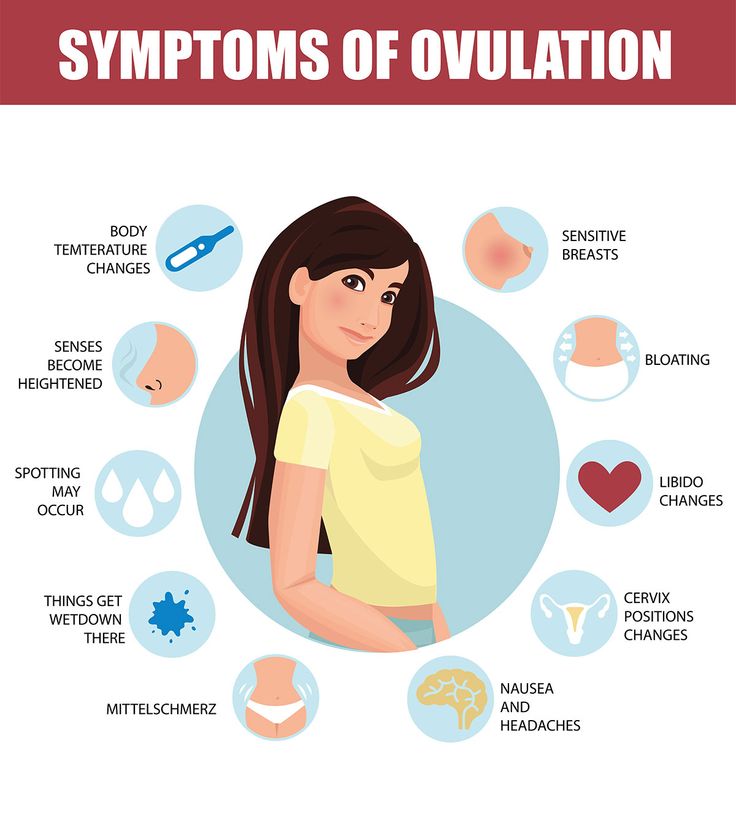 This is a symptom that the body is preparing for future feeding.
This is a symptom that the body is preparing for future feeding.
Signs of cystitis
Changes in the hormonal background reduces the woman's immunity. As a result, there are various ailments caused by the penetration of pathogenic flora. The beginning of pregnancy is often accompanied by frequent urge to urinate and discomfort, reminiscent of the symptoms of cystitis. It can continue until delivery.
Basal body temperature
If you are planning to conceive, make it a rule to keep a basal body temperature chart. Its value rises during ovulation, and then returns to normal. The temperature is stable at around 37, and is it growing? Congratulations, this is one of the symptoms of a successful conception! If the indicator has not changed, but there are other signs, a miscarriage is possible.
If you notice one of the symptoms, perform a pharmacy rapid pregnancy test. The optimal period is at least 10 days after intercourse. However, express diagnostics cannot be considered 100% reliable.