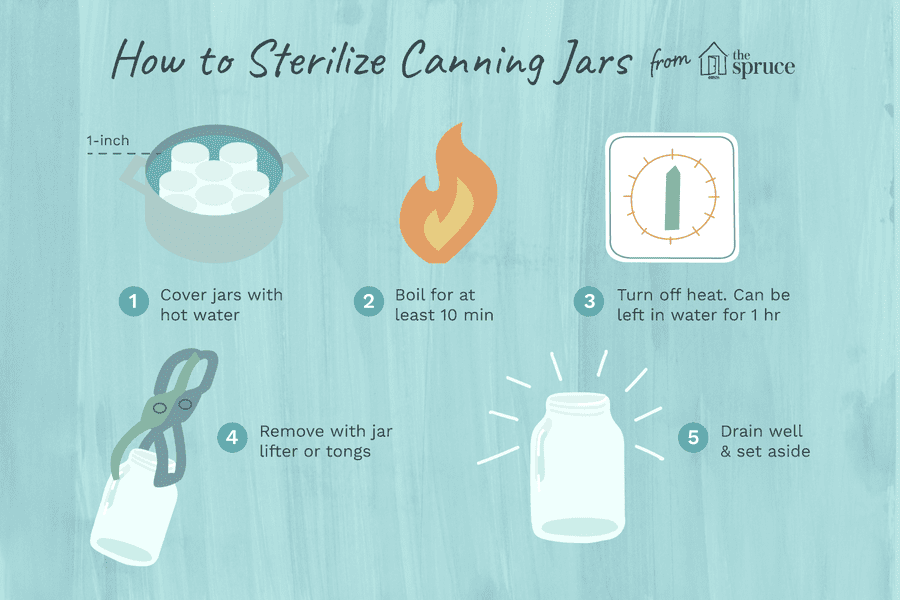
Signs of milk intolerance in infants
What should I do if I think my baby is allergic or intolerant to cows' milk?
If you think your baby is having a reaction to cows' milk, see your GP to discuss your concerns.
They will be able to assess if your baby's symptoms may be caused by a cows' milk allergy or something else. Make sure you get medical advice before taking cows' milk out of your child's diet as it contains important nutrients.
Cows' milk allergy in babies
Cows' milk allergy (CMA), also called cows' milk protein allergy, is one of the most common childhood food allergies. It is estimated to affect around 7% of babies under 1, though most children grow out of it by the age of 5.
CMA typically develops when cows' milk is first introduced into your baby's diet either in formula or when your baby starts eating solids.
More rarely, it can affect babies who are exclusively breastfed because of cows' milk from the mother's diet passing to the baby through breast milk.
There are 2 main types of CMA:
- immediate CMA – where symptoms typically begin within minutes of having cows' milk
- delayed CMA – where symptoms typically begin several hours, or even days, after having cows' milk
Symptoms of cows' milk allergy
Cows' milk allergy can cause a wide range of symptoms, including:
- skin reactions – such as a red itchy rash or swelling of the lips, face and around the eyes
- digestive problems – such as stomach ache, vomiting, colic, diarrhoea or constipation
- hay fever-like symptoms – such as a runny or blocked nose
- eczema that does not improve with treatment
Occasionally CMA can cause severe allergic symptoms that come on suddenly, such as swelling in the mouth or throat, wheezing, cough, shortness of breath, and difficult, noisy breathing.
A severe allergic reaction, or anaphylaxis, is a medical emergency – call 999 or go immediately to your local hospital A&E department.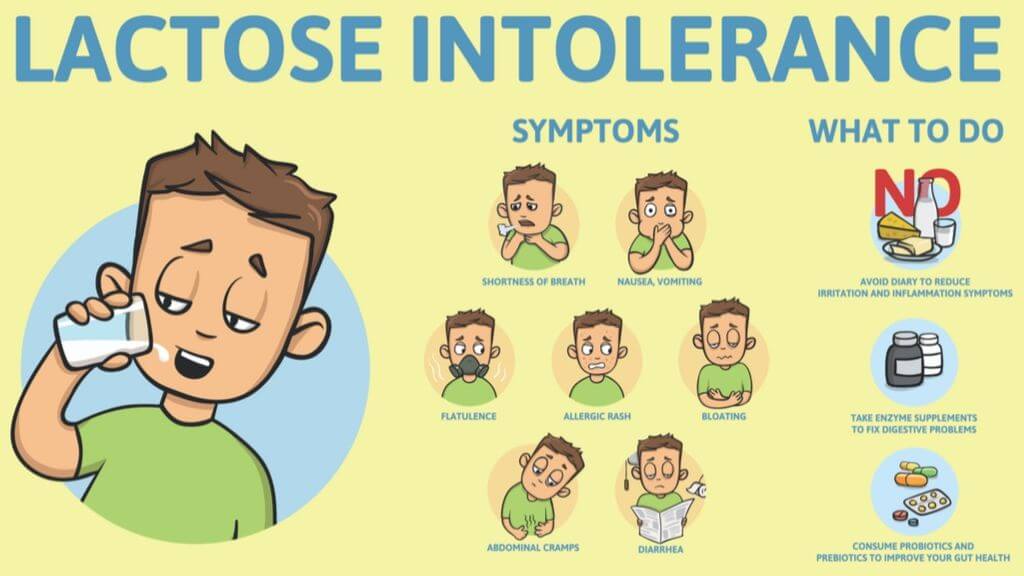
Treatment for CMA
If your baby is diagnosed with CMA, you'll be offered advice by your GP or an allergy specialist on how to manage their allergy. You may also be referred to a dietitian.
Treatment involves removing all cows' milk from your child's diet for a period of time.
If your baby is formula-fed, your GP can prescribe special infant formula.
Do not give your child any other type of milk without first getting medical advice.
If your baby is exclusively breastfed, the mother will be advised to avoid all cows' milk products.
Your child should be assessed every 6 to 12 months to see if they have grown out of their allergy.
Read more about cows' milk allergy.
Could it be lactose intolerance?
Lactose intolerance is another type of reaction to milk, when the body cannot digest lactose, a natural sugar found in milk. However, this is not an allergy.
Lactose intolerance can be temporary – for example, it can come on for a few days or weeks after a tummy bug.
Symptoms of lactose intolerance include:
- diarrhoea
- vomiting
- stomach rumbling and pains
- wind
Treatment for lactose intolerance
Treatment depends on the extent of your child's intolerance. Some children with lactose intolerance may be able to have small amounts of dairy products without having symptoms.
Your child may be referred to a dietitian for specialist advice.
Read more about treatment for lactose intolerance in children.
Further information:
- Colic
- Food allergies in babies and children
- Reflux in babies
- How can I tell if my baby is seriously ill?
- When should I start giving my baby solids?
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE): food allergy in children
Page last reviewed: 12 July 2019
Next review due: 12 July 2022
Milk Allergy in Infants (for Parents)
What Is a Milk Allergy?
When a baby is allergic to milk, it means that his or her immune system, which normally fights infections, overreacts to proteins in cow's milk. Every time the child has milk, the body thinks these proteins are harmful invaders and works hard to fight them. This causes an allergic reaction in which the body releases chemicals like
Every time the child has milk, the body thinks these proteins are harmful invaders and works hard to fight them. This causes an allergic reaction in which the body releases chemicals like
histamine.
Cow's milk is in most baby formulas. Babies with a milk allergy often show their first symptoms days to weeks after they first get cow milk-based formula. Breastfed infants have a lower risk of having a milk allergy than formula-fed babies.
People of any age can have a milk allergy, but it's more common in young children. Many kids outgrow it, but some don't.
If your baby has a milk allergy, keep two epinephrine auto-injectors on hand in case of a severe reaction (called anaphylaxis). An epinephrine auto-injector is an easy-to-use prescription medicine that comes in a container about the size of a large pen. Your doctor will show you how to use it.
What Are the Signs & Symptoms of a Milk Allergy?
In children who show symptoms shortly after they have milk, an allergic reaction can cause:
- wheezing
- trouble breathing
- coughing
- hoarseness
- throat tightness
- stomach upset
- vomiting
- diarrhea
- itchy, watery, or swollen eyes
- hives
- swelling
- a drop in blood pressure causing lightheadedness or loss of consciousness
The severity of allergic reactions to milk can vary. The same child can react differently with each exposure. This means that even though one reaction was mild, the next could be more severe and even life-threatening.
The same child can react differently with each exposure. This means that even though one reaction was mild, the next could be more severe and even life-threatening.
Children also can have:
- an intolerance to milk in which symptoms — such as loose stools, blood in the stool, refusal to eat, or irritability or colic — appear hours to days later
- lactose intolerance, which is when the body has trouble digesting milk
If you're not sure if your child has an intolerance versus an allergy, talk to your doctor.
If Your Child Has an Allergic Reaction
If your child has symptoms of an allergic reaction, follow the food allergy action plan your doctor gave you.
If your child has symptoms of a serious reaction (like swelling of the mouth or throat or difficulty breathing, or symptoms involving two different parts of the body, like hives with vomiting):
- Give the epinephrine auto-injector right away. Every second counts in an allergic reaction.

- Then, call 911 or take your child to the emergency room. Your child needs to be under medical supervision because, even if the worst seems to have passed, a second wave of serious symptoms can happen.
How Is a Milk Allergy Diagnosed?
If you think your infant is allergic to milk, call your baby's doctor. He or she will ask you questions and talk to you about what's going on. After the doctor examines your baby, some stool tests and blood tests might be ordered. The doctor may refer you to an allergist (a doctor who specializes in treating allergies).
The allergist might do skin testing. In skin testing, the doctor or nurse will place a tiny bit of milk protein on the skin, then make a small scratch on the skin. If your child reacts to the allergen, the skin will swell a little in that area like an insect bite.
If the allergist finds that your baby is at risk for a serious allergic reaction, epinephrine auto-injectors will be prescribed.
Avoiding a Milk Allergy Reaction
If You're Breastfeeding
If your breastfed infant has a milk allergy, talk to the allergist before changing your diet.
If You're Formula Feeding
If you're formula feeding, your doctor may advise you to switch to an extensively hydrolyzed formula or an amino acid-based formula in which the proteins are broken down into particles so that the formula is less likely to trigger an allergic reaction.
You also might see "partially hydrolyzed" formulas, but these aren't truly hypoallergenic and can lead to a significant allergic reaction.
If you're concerned about a milk allergy, it's always best to talk with your child's doctor and work together to choose a formula that's safe for your baby.
Do not try to make your own formula. Commercial formulas are approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and created through a very specialized process that cannot be duplicated at home. Other types of milk that might be safe for an older child with a milk allergy are not safe for infants.
Other types of milk that might be safe for an older child with a milk allergy are not safe for infants.
If you have any questions or concerns, talk with your child's doctor.
Lactose insufficiency - articles from the specialists of the clinic "Mother and Child"
what it is
The main food of babies is milk (breast or formula). It contains many different nutrients (proteins, fats, carbohydrates), which, with the help of special digestive enzymes, are broken down into simple components and digested. But in young children, the gastrointestinal tract is still immature, there are few enzymes in it, others are not at all or they are not yet working at full capacity. When the baby grows up, there will be more enzymes, the digestive system will mature, but for now there may be various problems with it.
All milk (women's, cow's, goat's, artificial mixtures) and dairy products contain the carbohydrate lactose, also called "milk sugar". In order for lactose to be absorbed, the lactase enzyme must break it down, but if the child has little or no lactase enzyme, then lactose is not broken down and remains in the intestine. As a result, there is always a large amount of milk sugar in the intestines, which begins to ferment, and where there is fermentation, conditionally pathogenic flora actively reproduces. What we feel during fermentation: intestinal motility increases (it rumbles), plus gas formation increases (the stomach swells). But in an adult, this is usually a one-time situation due to some inaccuracies in nutrition, and it quickly passes. But in babies, everything is different, especially since they lack the enzyme not once, but constantly. What it looks like: The milk sugar lactose retains water, hence loose stools. In the child’s stomach, “rumbles and boils”, colic begins, the stool becomes frothy, greens, mucus and even blood may appear in it. If at first the stool was liquid, then constipation appears, and all this changes in a circle: yesterday there was diarrhea, today and tomorrow there is no stool at all, the day after tomorrow it is liquid again.
In order for lactose to be absorbed, the lactase enzyme must break it down, but if the child has little or no lactase enzyme, then lactose is not broken down and remains in the intestine. As a result, there is always a large amount of milk sugar in the intestines, which begins to ferment, and where there is fermentation, conditionally pathogenic flora actively reproduces. What we feel during fermentation: intestinal motility increases (it rumbles), plus gas formation increases (the stomach swells). But in an adult, this is usually a one-time situation due to some inaccuracies in nutrition, and it quickly passes. But in babies, everything is different, especially since they lack the enzyme not once, but constantly. What it looks like: The milk sugar lactose retains water, hence loose stools. In the child’s stomach, “rumbles and boils”, colic begins, the stool becomes frothy, greens, mucus and even blood may appear in it. If at first the stool was liquid, then constipation appears, and all this changes in a circle: yesterday there was diarrhea, today and tomorrow there is no stool at all, the day after tomorrow it is liquid again. And the most unpleasant thing is endless colic and endless crying, there is no rest for both the parents themselves and the baby. Mom at some point notices that the baby is crying just after feeding, and then a variety of advice falls upon her. “Your milk is bad, better give the mixture,” says the beloved mother-in-law. “Only breasts and nothing else!” - advise breastfeeding gurus. As a result, the mother tries one thing or the other, but neither breast milk nor artificial mixture gives relief to the child. Colic, crying and problems with the stomach and stool continue. The parents are in a panic because they don't understand what is going on. In fact, this is a typical picture of bright lactase deficiency (LN), or insufficient production of the lactase enzyme.
And the most unpleasant thing is endless colic and endless crying, there is no rest for both the parents themselves and the baby. Mom at some point notices that the baby is crying just after feeding, and then a variety of advice falls upon her. “Your milk is bad, better give the mixture,” says the beloved mother-in-law. “Only breasts and nothing else!” - advise breastfeeding gurus. As a result, the mother tries one thing or the other, but neither breast milk nor artificial mixture gives relief to the child. Colic, crying and problems with the stomach and stool continue. The parents are in a panic because they don't understand what is going on. In fact, this is a typical picture of bright lactase deficiency (LN), or insufficient production of the lactase enzyme.
various reasons
There are several types of lactase deficiency, and it is with them that confusion arises.
Congenital lactase deficiency is a genetic and very rare disease (one case in several thousand newborns), it is difficult to confuse it with something, since it is very difficult. The diagnosis is made in the maternity hospital or in the first days after birth, the child does not have lactase at all, he quickly loses weight, he is immediately started to be fed intravenously or through a tube. Some experts (but not doctors) on breastfeeding read once that congenital lactase deficiency is an extremely rare disease, and that’s all - they further began to assure young mothers: “In fact, LN is extremely rare, you don’t have it, you don’t need to listen to doctors ", etc. Yes, congenital LN is a rare disease, but the key word here is "congenital", and there are other types of lactase deficiency.
The diagnosis is made in the maternity hospital or in the first days after birth, the child does not have lactase at all, he quickly loses weight, he is immediately started to be fed intravenously or through a tube. Some experts (but not doctors) on breastfeeding read once that congenital lactase deficiency is an extremely rare disease, and that’s all - they further began to assure young mothers: “In fact, LN is extremely rare, you don’t have it, you don’t need to listen to doctors ", etc. Yes, congenital LN is a rare disease, but the key word here is "congenital", and there are other types of lactase deficiency.
Transient lactase deficiency in infants . And this is exactly the condition that occurs very often. The baby was born, and so far he still has little lactase enzyme, plus little normal intestinal microflora. Hence the colic, and loose stools, and mucus, and greenery, and crying, and the nerves of the parents. After a while, the child's digestive system will fully mature, all enzymes will begin to work actively, the intestines will be populated with what is needed, and "lactase deficiency" will disappear. Therefore, such a LN is called "transient", that is, temporary, or passing. It passes for someone a month after birth, for someone longer - after six to seven months, and there are children in whom lactase deficiency completely disappears only by the year.
Therefore, such a LN is called "transient", that is, temporary, or passing. It passes for someone a month after birth, for someone longer - after six to seven months, and there are children in whom lactase deficiency completely disappears only by the year.
Secondary lactase deficiency. This condition appears if a person has had some kind of intestinal infection, and it does not matter whether it is an adult or a baby. For some time after the illness, the child does not tolerate milk (any), and then with proper nutrition and sometimes even without treatment, everything quickly passes.
Lactase deficiency in adults. There are people in whom the lactase enzyme begins to be lacking only in adulthood, this happens for various reasons: for some, lactase ceases to be produced in the right amount after some kind of illness, for other people, the activity of this enzyme simply fades over time by itself. yourself. As a result, at some age, a person begins to tolerate milk and dairy products poorly, although before that everything was fine. The symptoms are the same as in babies: he drank milk and after that the stomach rumbles, boils, and the stool is liquid. Sooner or later, a person realizes that milk is not his product, and simply stops drinking it in its pure form.
The symptoms are the same as in babies: he drank milk and after that the stomach rumbles, boils, and the stool is liquid. Sooner or later, a person realizes that milk is not his product, and simply stops drinking it in its pure form.
what to do
If there is transient lactase deficiency, then what to do with it? First you need to understand if it exists at all. Why does the child have problems with the stomach, stool, why does he cry all the time? Is it neurology, common colic, errors in the mother's diet, an inappropriate mixture (if the baby is bottle-fed), improper breastfeeding technique, lactase deficiency, or a reaction to the weather? It can be difficult to figure it out right away, but if the tests show that there is lactase deficiency, then it is most likely in it. Now what to do next - treat it, wait for the enzymes to mature, or something else? Firstly, everything here will depend on how much the enzyme is lacking and, therefore, on how much LN worries the child and parents. Some children lack the enzyme quite a bit, so their colic is mild and children cry quite normally. Plus, the violation of the stool is also not very bright: there are a couple of times a slightly liquefied stool, but that's all. In other children, the lack of lactase is more pronounced, the child does not cry, but simply yells after each feeding, if at first he gained weight well, then after two months the increase is minimal, problems with stools begin in parallel (day - constipation, day - diarrhea), stool sometimes green, sometimes with mucus. Atopic dermatitis appears on the skin (the skin is the first to react to problems with the gastrointestinal tract). Parents have no rest day or night: the baby cries - he is fed - he cries again, they try to calm him down in other ways. But nothing helps. Mom and dad are in a panic, and no one has the strength anymore.
Some children lack the enzyme quite a bit, so their colic is mild and children cry quite normally. Plus, the violation of the stool is also not very bright: there are a couple of times a slightly liquefied stool, but that's all. In other children, the lack of lactase is more pronounced, the child does not cry, but simply yells after each feeding, if at first he gained weight well, then after two months the increase is minimal, problems with stools begin in parallel (day - constipation, day - diarrhea), stool sometimes green, sometimes with mucus. Atopic dermatitis appears on the skin (the skin is the first to react to problems with the gastrointestinal tract). Parents have no rest day or night: the baby cries - he is fed - he cries again, they try to calm him down in other ways. But nothing helps. Mom and dad are in a panic, and no one has the strength anymore.
If parents see that the child may have signs of lactase deficiency, that he needs help, first of all, you need to look for a good doctor. Only an experienced pediatrician will be able to figure out why the baby has colic or green stools, what the numbers in the tests say, and what is the norm for one baby and the pathology for another. And of course, it is not necessary to cancel breastfeeding and immediately prescribe lactose-free or low-lactose artificial mixtures (even as a supplement). By itself, milk sugar lactose is very necessary for a child, when lactose is broken down, its components (glucose and galactose) go to the development of the brain, retina, for the life of normal intestinal microflora. So do not completely eliminate this sugar, you need to help it break down. With a strongly pronounced LN, the missing enzyme is given before each feeding (it has long been learned to produce and it is sold in pharmacies), with a dim clinic, its dose can be reduced. And it is also possible that there is lactase deficiency (even according to tests), but it does not need to be treated, there are almost no symptoms.
Only an experienced pediatrician will be able to figure out why the baby has colic or green stools, what the numbers in the tests say, and what is the norm for one baby and the pathology for another. And of course, it is not necessary to cancel breastfeeding and immediately prescribe lactose-free or low-lactose artificial mixtures (even as a supplement). By itself, milk sugar lactose is very necessary for a child, when lactose is broken down, its components (glucose and galactose) go to the development of the brain, retina, for the life of normal intestinal microflora. So do not completely eliminate this sugar, you need to help it break down. With a strongly pronounced LN, the missing enzyme is given before each feeding (it has long been learned to produce and it is sold in pharmacies), with a dim clinic, its dose can be reduced. And it is also possible that there is lactase deficiency (even according to tests), but it does not need to be treated, there are almost no symptoms.
But what cannot be done is to listen to non-specialists who deny either lactase deficiency itself or its treatment. They see the cause of all problems with the child's stomach and stool either in the wrong technique of breastfeeding, or partially admit that there is immaturity of the enzyme, but this is natural and will pass by itself. Yes, for some, LN is expressed easily and will pass quickly, but what about those parents whose child yells day and night, covered with a crust from atopic dermatitis and stopped gaining weight? Wait for the time to come and the enzymes to mature? Alas, with pronounced lactase deficiency (even if transient), enterocytes (intestinal cells) often suffer, so it is simply necessary to help such a child.
They see the cause of all problems with the child's stomach and stool either in the wrong technique of breastfeeding, or partially admit that there is immaturity of the enzyme, but this is natural and will pass by itself. Yes, for some, LN is expressed easily and will pass quickly, but what about those parents whose child yells day and night, covered with a crust from atopic dermatitis and stopped gaining weight? Wait for the time to come and the enzymes to mature? Alas, with pronounced lactase deficiency (even if transient), enterocytes (intestinal cells) often suffer, so it is simply necessary to help such a child.
If you see that your baby has signs of lactase deficiency, look for a doctor who is committed to maintaining breastfeeding and has extensive experience. He will definitely help to find out why the baby is crying, why he has a stomach ache or has problems with stool. And then the life of the parents and the child will return to normal.
"Transient" (temporary) lactase deficiency in someone passes a month after birth, in someone longer - after six to seven months, and there are children in whom lactase deficiency completely disappears only by the age of one
If the tests show that there is a lactase deficiency, then the matter is most likely in it.
Milk sugar lactose is very necessary for a child: when lactose is broken down, its components (glucose and galactose) go to the development of the brain, retina, for the life of normal intestinal microflora
Parent's note
1. In infants, transient (temporary) lactase deficiency is most common.
2. Symptoms of lactase deficiency usually appear some time after birth. These are colic, frequent crying, increased gas formation, stool - either constipation or diarrhea (over time it becomes frothy, greens, mucus and even blood may appear in it).
3. The simplest study that can reveal lactase deficiency is the analysis of feces for carbohydrates.
4. It is usually not necessary to cancel breastfeeding or partially replace it with lactose-free or low-lactose formulas. You can give the missing enzyme from the outside.
Lactase deficiency in infants: symptoms and diagnosis
Signs of lactase deficiency in infants should be known to parents, because this will allow them to suspect this condition in a timely manner, identify its cause and improve the condition of the baby.
Signs of lactose intolerance
Signs of lactase deficiency in a child are diverse. This is a stool with a large water spot and a sour smell, bloating, rumbling, abdominal pain (colic). One of the most common symptoms that worries parents is frequent loose stools in a baby. It is watery, frothy and has a sour smell. It should be remembered that the younger the child, the more frequent his stool, and this is completely normal. So if the baby is developing well and feels good, and his feces are normal, you should not think that these are signs of lactose intolerance in newborns.
Sometimes lactase deficiency in newborns is accompanied by poor weight gain and growth. This is due to the fact that the carbohydrates necessary for the child do not enter the body, and the baby may lack nutrients.
If the baby quickly grew out of the recently purchased sliders and sleepsuits, and his cheeks and handles are rounded and plump, you should not suspect lactase deficiency in the child.
Intestinal colic may be present in children with lactose intolerance. After eating, the child will experience bloating, anxiety, crying. These signs usually appear on the 3-6th week of a baby's life. This is probably due to an increase in milk consumption by an older baby.
The mechanism of such manifestations of lactose intolerance as intestinal colic, bloating and rumbling is as follows. Carbohydrates that are not digested due to the absence or lack of the lactase enzyme continue their movement through the intestines. In the colon, they are exposed to intestinal microflora, resulting in the formation of an excess of gases (hydrogen, methane, carbon dioxide). Gas stretches the walls of the intestines, causing bloating, pain and increased intestinal peristalsis. Violation of the normal chemical composition of intestinal contents can lead to disturbances in the composition of the intestinal microflora.
When should you not think about lactase deficiency?
Quite often in recent years, when there are problems with digestion, children are diagnosed with lactose intolerance. However, this is not always true. As mentioned above, the frequency of stool in infants is individual. Frequent or rare stools are not in themselves a sign of lactase deficiency in a child. The symptoms of this pathology are multiple.
However, this is not always true. As mentioned above, the frequency of stool in infants is individual. Frequent or rare stools are not in themselves a sign of lactase deficiency in a child. The symptoms of this pathology are multiple.
Important!
Sometimes regurgitation is taken as a sign of lactose intolerance by parents. But even if regurgitation is frequent and plentiful, it is unlikely that this is lactase deficiency - the symptoms in children with this pathology are associated with the work of the intestines, and not the esophagus or stomach.
How to identify lactose intolerance
The diagnosis of lactose intolerance usually begins with an organoleptic evaluation of feces. Unformed, watery, frothy yellow or green feces with a sour smell testify in favor of this pathology. In a chemical study, the reaction of feces is acidic (pH less than 5.5).
Another research method is to determine the content of carbohydrates in feces. Exceeding their value by 0. 25% is typical for lactase deficiency. Despite the widespread use, this method is not the most accurate, since it does not allow you to determine which carbohydrates are present in the feces.
25% is typical for lactase deficiency. Despite the widespread use, this method is not the most accurate, since it does not allow you to determine which carbohydrates are present in the feces.
Important!
Whenever lactose intolerance is suspected, a specialist should be consulted. He will prescribe examinations that will allow you to say if the child has lactose intolerance, or if the symptoms are not associated with this condition.
Other methods are used in difficult cases. For example, a specific breath test based on determining the concentration of hydrogen in exhaled air after a load of lactose. The advantage of this method is its simplicity, the disadvantage is the possibility of false positive results and the impossibility of determining the degree of lactase deficiency.
Lactose curve - another test for lactose intolerance. Normally, lactose, under the action of the lactase enzyme, breaks down into simpler sugars, in particular, glucose. Subsequently, glucose is absorbed through the intestinal wall and enters the bloodstream.