Signs leading up to a miscarriage
Warning signs, treatments, and prevention
A miscarriage is defined as the spontaneous loss of a fetus before it is viable, which in the United States is the 20th week of pregnancy. The medical term for miscarriage is “spontaneous abortion.”
Miscarriage is one of the most common complications associated with early pregnancy. Sadly, around one-quarter of all pregnancies result in miscarriage.
Most miscarriages occur during the first few months of pregnancy. An estimated 85 percent of miscarriages happen before week 12. A woman may have a miscarriage before she knows she is pregnant.
Although miscarriage is relatively common, it can be an extremely traumatic and devastating experience.
The main sign of miscarriage is vaginal spotting or bleeding, which can vary from slight brownish discharge to very heavy bleeding.
Other symptoms include:
- cramping and pain in the abdomen
- mild to severe back pain
- weight loss
- fluid discharge from the vagina
- tissue or clotted discharge from the vagina
- feeling faint or light-headed
- contractions
If you are pregnant and experience any of these symptoms, contact your doctor, midwife, or antenatal clinic immediately.
Ectopic pregnancy and miscarriage
An ectopic pregnancy is when the fertilized egg settles and grows outside the inner lining of the uterus, instead of inside.
Around 1–2 percent of all pregnancies are ectopic. If left untreated, they can be fatal because of internal bleeding, and the risk of losing the baby is increased.
Symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy are:
Shoulder tip pain – where the shoulder ends and the arm begins; this is more evident when the woman is lying down; also:
- severe abdominal pain
- feeling light-headed
- dizziness
There are a variety of terms that doctors use when discussing miscarriage, these include:
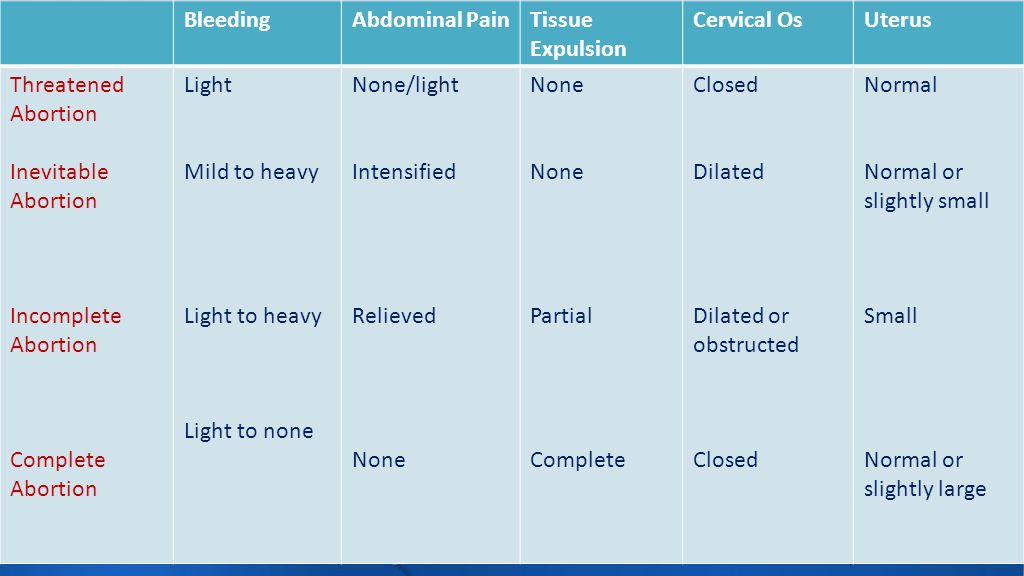
Threatened miscarriage: Some bleeding in early pregnancy with lower backache. Cervix stays closed. In this case, the pregnancy continues.
Inevitable or incomplete miscarriage: Abdominal or back pain, bleeding, and an open cervix. If the cervix is open, the miscarriage is considered inevitable.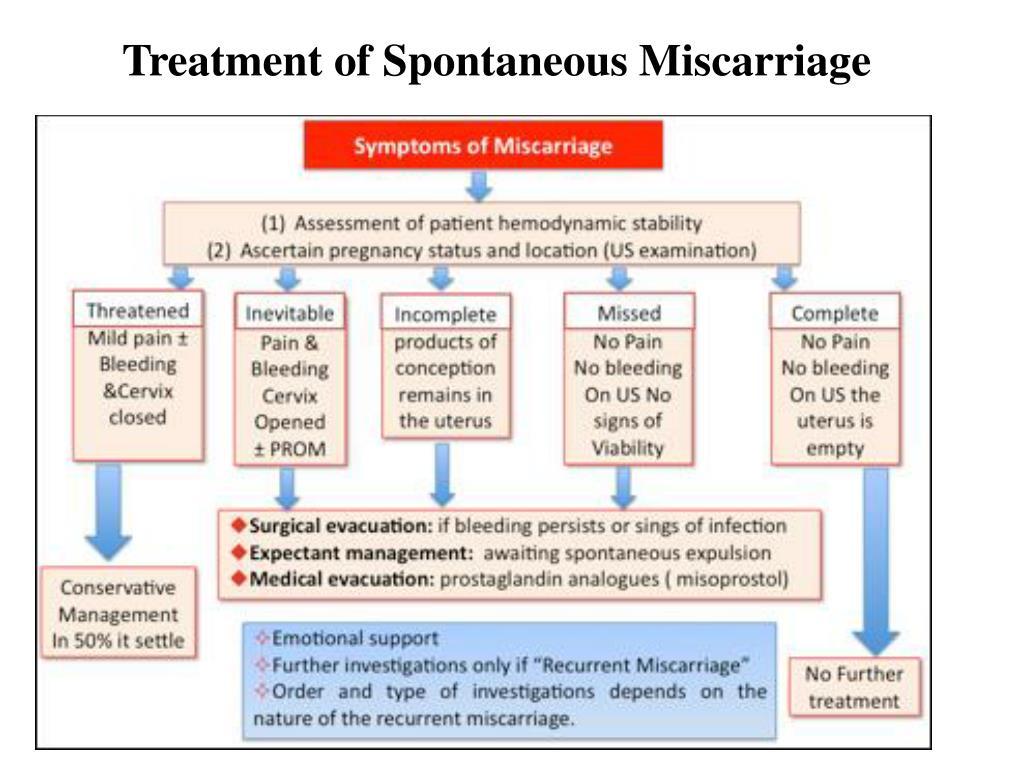
Complete miscarriage: The embryo empties out of the uterus. Bleeding and pain subside quickly.
Missed miscarriage: The embryo has died, but there are no other symptoms, such as bleeding or pain.
Recurrent miscarriage: This is defined as three or more miscarriages during the first trimester.
The aim of treatment following or during a miscarriage is to prevent hemorrhaging (bleeding) and infection. Normally, the body expels the fetal tissue on its own, especially earlier in the pregnancy. However, if it does not, a doctor may perform a dilation and curettage (D and C).
During a D and C, a doctor opens the cervix and inserts a thin instrument into the uterus to remove tissue. After the procedure, drugs may be prescribed to control bleeding.
Miscarriage can happen for a range of reasons.
Placental problems: If the placenta develops abnormally, blood supply from the mother to the baby is interrupted.
Chromosome problems: Sometimes, a fetus can receive the wrong number of chromosomes, causing abnormal development of the fetus. Miscarriages that occur during the first trimester are mainly related to chromosomal abnormalities in the baby.
Womb structure abnormalities: Abnormally shaped wombs and the development of fibroids (non-cancerous growths) in the womb can put a developing fetus at risk.
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS): This occurs when the ovaries are too big, causing a hormonal imbalance.
Weakened cervix: The cervix is the neck of the womb. When the muscles of the cervix are weak, they can open up too early during pregnancy, resulting in miscarriage.
Lifestyle factors: Habits such as smoking, drinking alcohol, or using illegal drugs can lead to miscarriage.
Underlying health conditions
Share on PinterestPre-existing kidney conditions can increase the risk of miscarriage.
Underlying health conditions among pregnant woman that are associated with miscarriage include:
- high blood pressure
- coeliac disease
- diabetes
- kidney disease
- lupus
- thyroid gland problems
- HIV
- malaria
- rubella
- chlamydia
- syphilis
- gonorrhea
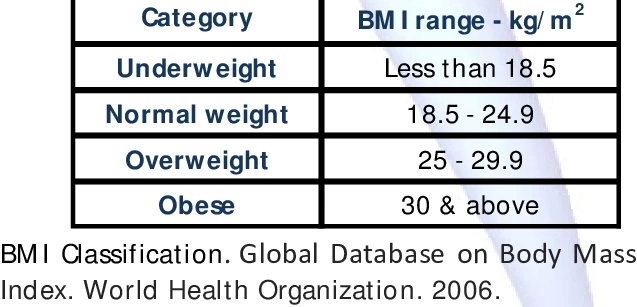
Being overweight or underweight
Obesity is known to increase the risk of first and subsequent miscarriages.
Women with a low body mass index before they become pregnant are also at a heightened risk of miscarriage. Research published in the International Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology reported that underweight women were 72 percent more likely to suffer a miscarriage during their first 3 months of pregnancy, compared with women whose weight was healthy.
Be aware of current medications
It is crucial to check with a doctor which medications are safe to take during pregnancy. Medicines that should be avoided (if possible) while pregnant include:
- retinoids
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- methotrexate
- misoprostol
- antidepressants
Limit caffeine
A meta-analysis published in the European Journal of Epidemiology combined data from 60 studies and concluded:
“Greater caffeine intake is associated with an increase in spontaneous abortion, stillbirth, low birth weight, and SGA, but not preterm delivery. ”
”
The World Health Organization (WHO) advises that women who consume more than 300 milligrams (mg) of caffeine per day should reduce their intake.
Miscarriage myths
There are many misconceptions regarding miscarriage. Many people believe that having sex and/or exercising can result in miscarriage, but there is no evidence to suggest this. However, some types of exercise would not be suitable for a woman who is 8 months pregnant. If you are pregnant, ask your doctor which exercises are appropriate.
In many cases, a miscarriage has no apparent cause.
The tests used to diagnose miscarriage are:
Ultrasound scans: Transvaginal ultrasounds involve placing a small probe into the vagina to check for the heartbeat of the fetus. Some women may choose to undergo an external abdominal ultrasound instead to avoid discomfort.
Blood tests: These are useful because they can determine if levels of beta-human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) and progesterone are normal – both of these hormones are associated with a healthy pregnancy.
Pelvic exams: These determine whether the cervix has thinned out or opened.
A few simple lifestyle changes can reduce the risk of miscarriage:
- Avoid smoking, drinking alcohol, and using illicit drugs during pregnancy.
- Eat a healthful diet.
- Maintain a healthy weight before and during pregnancy.
- Be careful to avoid certain infections, such as German measles (rubella).
Read the article in Spanish.
What does a miscarriage look like? Symptoms and seeking help
Miscarriage, or pregnancy loss, can look and feel different for each person. Common symptoms include bleeding and cramping.
It is important to note that bleeding is common during pregnancy — especially in early pregnancy. It does not necessarily mean that anything is wrong.
The only way to accurately identify a pregnancy loss is to test pregnancy hormone levels and have an ultrasound of the uterus.
Read on to learn more about what pregnancy loss can look and feel like.
According to a 2016 study, not all pregnancy losses involve bleeding. Overall, they do not follow a single pattern. This is why it is crucial to seek medical care for bleeding and any unusual symptoms during pregnancy.
Pregnancy loss during the first trimester may involve:
- heavy bleeding
- bleeding that starts light and gets heavier
- passing blood clots or tissue
- cramping, which may come in waves
- a gush of fluid from the vagina
If a person takes a pregnancy test after experiencing a pregnancy loss during the first trimester, the result may be negative, or the test may have a positive line that gets fainter.
Experiencing pregnancy loss later in the first trimester and beyond will involve passing more tissue.
Second-trimester pregnancy loss can also cause intense cramping and sometimes even contractions.
In addition to bleeding and cramping, some people may notice larger blood clots.
According to a 2019 meta-analysis, one-quarter of pregnant women experience bleeding during the first trimester. Another study from 2016 puts that percentage higher, at closer to 20–40%.
Another study from 2016 puts that percentage higher, at closer to 20–40%.
A large-scale 2010 study found that about 12% of pregnant women experienced pregnancy loss, and about two-thirds of that group reported bleeding during their pregnancy.
Some differences between bleeding due to a pregnancy loss and other types of bleeding during pregnancy include:
- Amount of blood: Heavy bleeding is more likely to signal a pregnancy loss.
- Bleeding pattern: Bleeding that gets progressively heavier may indicate a pregnancy loss.
- Pain: Cramping, especially when it occurs in a clear pattern, is more likely to signal a pregnancy loss.
- Passing tissue: Some — not all — people who experience a pregnancy loss pass large blood clots or tissue.
For people who do experience bleeding during a pregnancy loss, the duration tends to depend on how far the pregnancy has progressed.
Pregnancy losses that occur in the first weeks of pregnancy tend to cause bleeding that lasts a few days. Those that occur later may cause bleeding that lasts for as long as 4 weeks.
Those that occur later may cause bleeding that lasts for as long as 4 weeks.
Sometimes, the bleeding stops and starts again. Over time, it should get lighter.
A very early pregnancy loss is sometimes called a chemical pregnancy. These pregnancies are lost shortly after the embryo implants, usually within a few days or weeks.
A chemical pregnancy may be detectable by a pregnancy test, but it would likely not be seen on an ultrasound.
In many cases, early pregnancy losses can happen before a person knows they are pregnant.
In fact, around 80% of early pregnancy losses occur in the first trimester, or in weeks 0–13. The end of these early pregnancies may be mistaken for a period because the symptoms are similar.
For example, both a period and an early pregnancy loss can involve bleeding and cramping. Pregnancy tissue that passes out of the vagina may look like typical blood clots that occur during a period.
It is possible that a person will not realize they have missed a period.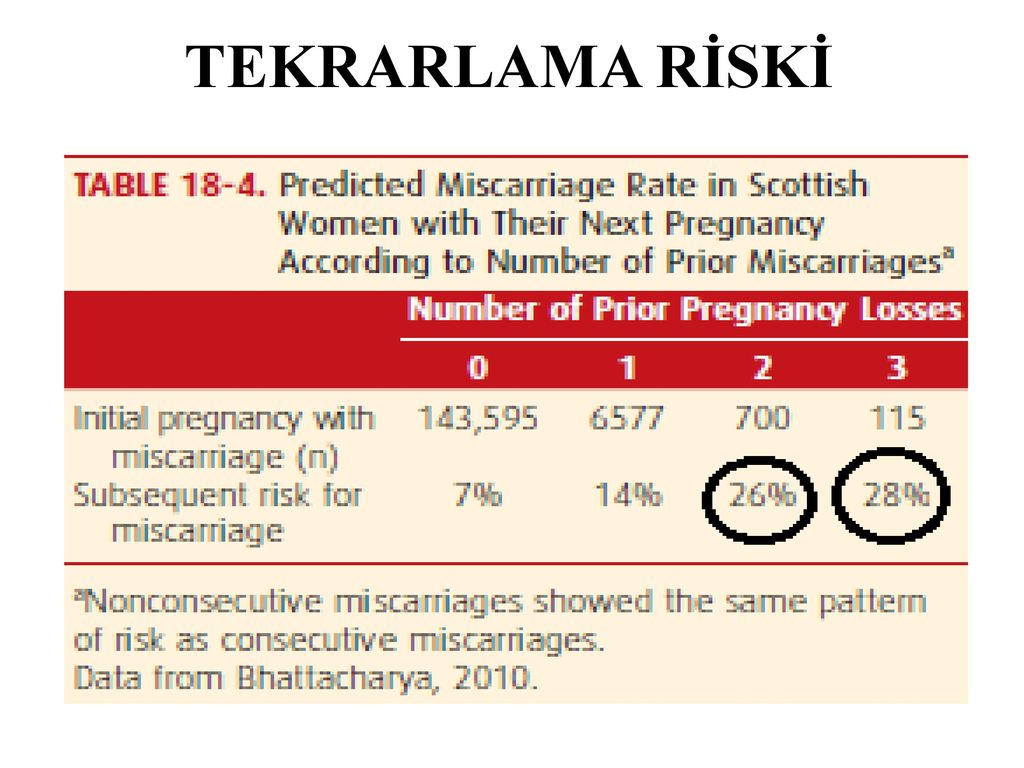 Instead, they may mistake the symptoms of a pregnancy loss for those of a menstrual period.
Instead, they may mistake the symptoms of a pregnancy loss for those of a menstrual period.
Pregnancy losses and periods can both cause:
- vaginal bleeding
- passing blood clots or tissue
- abdominal pain
However, a pregnancy loss will often cause additional symptoms that set it apart from a period, especially if the pregnancy loss occurs several weeks into the pregnancy. These symptoms include:
- larger clots or pregnancy loss tissue
- more clots than typical periods
- lower abdominal cramping
- back pain
- passing a significant amount of clear or pinkish fluid
- sudden heavy bleeding, or heavier bleeding than a typical period
- longer bleeding
- sudden easing of some early pregnancy symptoms, such as nausea and breast tenderness
It is important to remember that bleeding during the first weeks of a pregnancy is not uncommon, and it is not always a sign of pregnancy loss or a problem with a pregnancy.
However, if a person experiences other symptoms of pregnancy loss, they should seek care from a doctor.
A “missed miscarriage” refers to a delay between the loss of the pregnancy and any bleeding or passing of tissue.
During a missed miscarriage, an embryo dies but does not leave the uterus for several weeks. In fact, a pregnant person may not realize the pregnancy has ended until an ultrasound finds no heartbeat.
When the embryo does leave the uterus, the blood, tissue, and clots may be dark brown. The tissue has had time to deteriorate, so bright red blood or heavy bleeding may not occur. The bleeding may last several days to several weeks.
A doctor may prescribe medication to help the person who has had the pregnancy loss bleed and pass the tissue. Surgery may also be necessary.
It is not possible for healthcare professionals to stop a pregnancy loss once it starts.
Call a doctor and schedule an appointment within 24 hours if any of the following occur:
- vaginal bleeding
- a fever
- intense pain or cramping
- bleeding that stops and starts again
- any other changes in the pattern of bleeding, even if a doctor has already addressed the cause
- bleeding that lasts for longer than 7 days, even if a doctor has already confirmed pregnancy loss
Pregnant people should receive emergency medical attention if they:
- experience heavy bleeding during the second trimester and cannot reach their doctor
- bleed heavily enough to soak through more than one pad per hour for more than 2 hours
- feel faint, lightheaded, or confused
- experience contractions, amniotic fluid leakage, the water breaking, or other signs of premature labor
Most pregnancy losses pass on their own.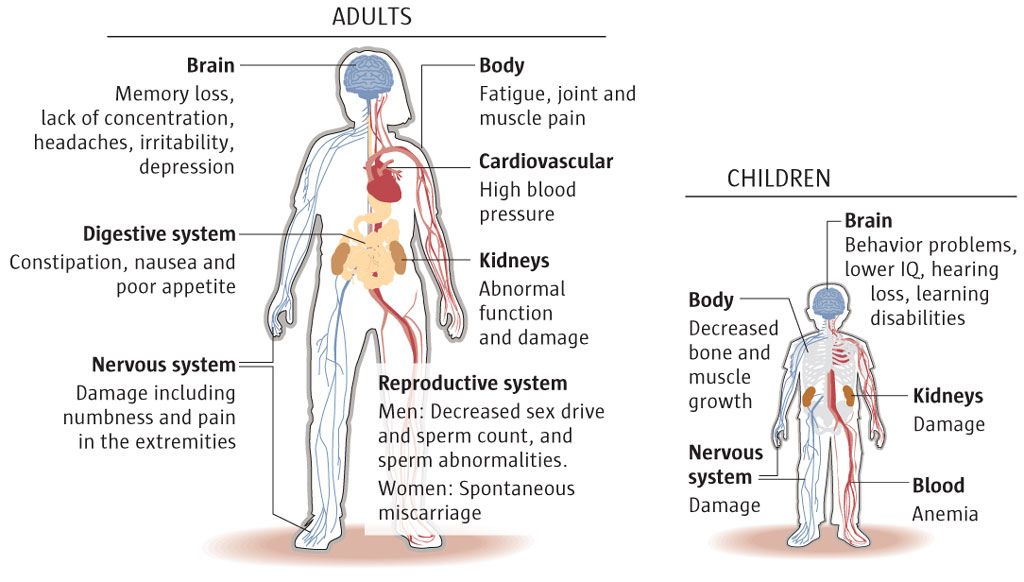
In some cases, the fetus dies without causing any bleeding. When this happens, the person carrying the fetus may want to wait for the pregnancy to pass on its own or want it to be over as quickly as possible.
If a person wants to expedite a pregnancy loss, a doctor can supply medication that helps with passing the pregnancy at home. This approach is safest during early pregnancy.
A healthcare professional can also perform surgery to remove the remains of the embryo or fetus.
Sometimes a pregnancy loss is incomplete, leaving behind tissue that can lead to infection or other health problems. When this happens, a doctor may recommend medication or surgery.
Doctors used to advise couples to wait 1 month, or sometimes much longer, before trying to conceive again after a pregnancy loss.
However, research now shows that there is no medical justification for this recommendation. If a couple feels ready, it is safe to begin trying to conceive again right away.
A 2017 study indicates that fertility may even be slightly higher immediately following a pregnancy loss.
Sometimes, however, it takes a while for a menstruating person’s cycle to resume following a pregnancy loss.
This can make it difficult to time sexual intercourse for conception and to accurately date a pregnancy — especially if a person becomes pregnant before the first menstrual period after a pregnancy loss.
To improve accuracy, it can be helpful to:
- monitor basal body temperature
- use ovulation tests
- try other ways to predict fertility
Early pregnancy losses can sometimes result from chromosomal irregularities. This means that the developing embryo or fetus has an irregular number of chromosomes.
These irregularities usually occur at random, meaning they are unlikely to reoccur. In other words, experiencing one pregnancy loss does not increase the likelihood of experiencing another.
A 2017 study finds that 15. 7% of women with a previous pregnancy loss had another during the 2-year study period.
7% of women with a previous pregnancy loss had another during the 2-year study period.
Meanwhile, a 2016 study finds that women were more likely to become pregnant in the 3 months following a pregnancy loss.
Many people become pregnant again shortly after a pregnancy loss, and a smaller number experience multiple losses in a row.
The risk of repeat pregnancy losses increases with age, according to a 2019 study. The risk is also higher among people with a history of:
- preterm labor
- gestational diabetes
- stillbirth
- cesarean delivery
A 2017 study found that 15.7% of participants whose most recent pregnancy ended in a pregnancy loss went on to have a second pregnancy loss.
A 2018 study focused on women who had three or more pregnancy losses. This study found that 64.5% of those women had a live birth within 5 years. Some of these participants may have received fertility treatments.
Pregnancy loss is one of the less common causes of bleeding during pregnancy, especially when the bleeding occurs early on.
But bleeding in early pregnancy is not always a sign of pregnancy loss.
Some other signs of pregnancy loss include cramping and passing blood clots or tissue.
Only a healthcare professional can accurately identify a pregnancy loss. For this reason, it is important to consult a doctor or nurse midwife about any bleeding during pregnancy.
What does an early miscarriage look like?
Bleeding is common in the early weeks of pregnancy. That is why bleeding alone should not be seen as an indication of an early pregnancy loss.
In addition to bleeding, an early pregnancy loss may cause a person to experience:
- a gush of clear or pale pink fluid from the vagina
- passing blood clots or tissue
- a sudden decrease in pregnancy symptoms (such as nausea and morning sickness)
- a negative result on a pregnancy test, or a positive sign that is very faint
How do I know if I’m miscarrying?
The signs and symptoms of a pregnancy loss will remain largely the same, no matter the week. But the further along a person is, the greater the amount of tissue loss during the miscarriage.
But the further along a person is, the greater the amount of tissue loss during the miscarriage.
Symptoms of pregnancy loss include:
- sudden bleeding, sometimes heavy
- a gush of clear or pink fluid from the vagina
- mild to severe back pain and abdominal cramping
- contraction-like pain
What does miscarriage tissue look like?
The clots and tissue passed during a pregnancy loss may look like typical period clots, or they may be larger.
Pregnancy loss tissue includes:
- the fetus or embryo
- gestational sac
- placenta
When a pregnancy is more advanced (after 6 to 8 weeks), the gestational sac may be noticeable. Before that, it may be too small to see.
The tissue passed during a pregnancy loss may be:
- brown
- black
- dark red
- bright red or pink
- white or gray, in some cases
If the pregnancy began to deteriorate before the start of bleeding, the clots may be smaller and darker.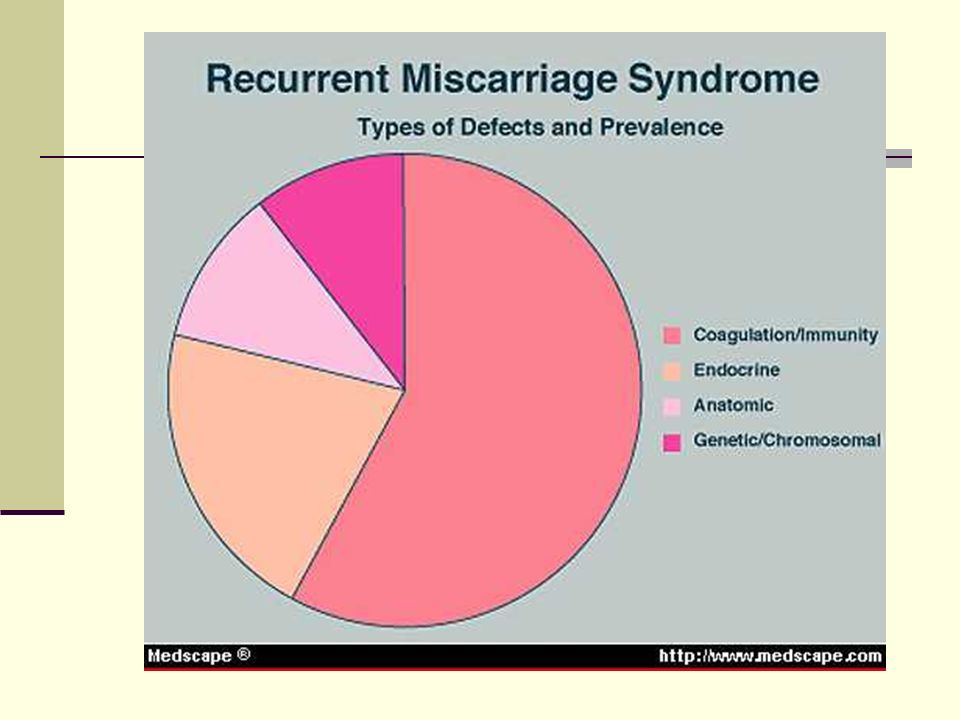 This is common with a missed miscarriage.
This is common with a missed miscarriage.
What does miscarriage tissue vs. a blood clot look like?
It is not always easy to tell the difference between pregnancy loss tissue and a blood clot. Both may look like typical period clots, though it is not uncommon for them to be larger than normal.
Actual pregnancy tissue may not be discernible until after the eighth week. Then, the tissue may look like pink, white, or gray tissue. A person may also be able to see a fluid-filled sac in the passed tissue.
Miscarriage due to missed pregnancy
What is a miscarriage?
According to medical statistics, miscarriage is the most common complication during pregnancy. About 10-20% of all recorded pregnancies end in miscarriage. Miscarriage is a sporadic, sudden, termination of pregnancy, which is accompanied by complete or partial emptying of the uterus.
Missed pregnancy loss (MP) can be seen on ultrasound. It consists in confirming the non-viability of the fetus without bleeding. The ST can end in a miscarriage, when the body gets rid of the dead fetus on its own, or in a medical abortion, when medical or surgical manipulations are used to clean the uterine cavity.
The ST can end in a miscarriage, when the body gets rid of the dead fetus on its own, or in a medical abortion, when medical or surgical manipulations are used to clean the uterine cavity.
Causes of miscarriage and miscarriage
80% of miscarriages occur in the first trimester before 12 weeks. In 50% of cases, this occurs due to genetic defects in the fetus. The threat of miscarriage due to chromosomal abnormalities decreases with the course of pregnancy: by 20 weeks it is 10-20% versus 41-50% in the first trimester. The main cause of genetically determined early miscarriages are autonomous trisomies - when three homologous chromosomes are present in the cells instead of two. Such defects occur at the time of conception and are not subject to correction. They lead to miscarriage or to the development of severe genetic diseases. In addition to genetics, immunological, endocrine and infectious causes are distinguished.
In the second trimester, various diseases and disorders in the mother's body become the main cause of miscarriage.
There is a list of factors that can trigger early pregnancy loss:
-
woman's age. At the age of 20-30 years, the risk of spontaneous miscarriage is 9-17%, at 35-40 years old - 20%, at 40-45 - 40%;
-
alcohol abuse;
-
abuse of caffeine;
-
smoking;
-
drug use;
-
chronic diseases of the mother;
-
maternal infections;
-
use of medications incompatible with pregnancy;
-
history of spontaneous abortion. The risk of subsequent pregnancy loss in women with one miscarriage in history is 18-20%, with two - 30%, with three - 43%.
Symptoms and signs of miscarriage
You can suspect a miscarriage by sudden spotting and sharp pain in the lower abdomen. If these symptoms appear, seek immediate medical attention. The doctor must conduct an ultrasound diagnosis. Transvaginal scanning (TVS) is considered the gold standard for diagnostics - when the sensor is inserted into the uterus through the vagina. If TVS is not available, a transabdominal scan can be applied - through the anterior abdominal wall.
If TVS is not available, a transabdominal scan can be applied - through the anterior abdominal wall.
Missed pregnancy may be asymptomatic and not manifest until the next scheduled ultrasound.
How does a miscarriage occur?
The miscarriage process has four stages. This does not happen overnight and lasts from several hours to several days.
The first stage - the threat of miscarriage. Among the symptoms: pulling pains in the lower abdomen, scanty blood discharge, increased uterine tone. The process of detachment of the placenta from the place of attachment in the uterus begins. The internal os is closed. The main thing is to seek help in time, then with proper therapy if there is a chance to stop the miscarriage and save the pregnancy.
The second stage - the beginning of a miscarriage. Strong discharge, the cervical canal is ajar, the doctor diagnoses the final detachment of the placenta.
The third stage is a miscarriage in progress. You can feel the regular contractions of the uterus, the outcome of the fetus, placenta and uterine contents, profuse blood discharge has begun.
You can feel the regular contractions of the uterus, the outcome of the fetus, placenta and uterine contents, profuse blood discharge has begun.
The last fourth stage is a complete miscarriage. The pregnancy is interrupted, the uterine cavity does not contain the fetus and products of conception.
How to determine the ST?
It should be remembered that a miscarriage can be diagnosed only during an ultrasound examination. Home tests will not give reliable results. Ultrasound will show the presence or absence of a heartbeat in the fetus.
Treatment of miscarriage and miscarriage
Due to the fact that the vast majority of spontaneously terminated pregnancies are due to genetic abnormalities (non-viability) of the fetus, then, speaking about the treatment of miscarriage, it is worth talking about ensuring complete and safe cleansing of the uterus, preventing infection and preventing bruising. With the help of an ultrasound examination, the doctor will check whether the uterus has completely cleared. If yes, then no additional treatment is required. In the event of an incomplete miscarriage or STD, the patient will be indicated for surgical or medical cleaning. If the miscarriage is only in a state of threat, the treatment tactics will be aimed at blocking uterine contractions and stopping the development of a miscarriage. If you need treatment for a missed pregnancy in Moscow, contact our specialists.
If yes, then no additional treatment is required. In the event of an incomplete miscarriage or STD, the patient will be indicated for surgical or medical cleaning. If the miscarriage is only in a state of threat, the treatment tactics will be aimed at blocking uterine contractions and stopping the development of a miscarriage. If you need treatment for a missed pregnancy in Moscow, contact our specialists.
miscarriage, symptoms - Health Clinic 365 G. Yekaterinburg
Causes of miscarriage
Questions to the doctor about miscarriages
Diagnostics of miscarriage
Treatment and prevention of miscarriage
Pereti - this is a spontaneous termination of pregnancy at the period of 20 weeks. According to statistics, 10 to 20% of all pregnancies end in miscarriage. However, the real numbers could be much higher, as a large number of miscarriages happen very early, and women are not even aware of their pregnancy. Most miscarriages happen due to abnormal development of the fetus.
Miscarriage is quite common, but this fact does not make things any easier. It is always difficult to cope with the realization that there was a pregnancy, but no child. Try to deal with the situation psychologically and understand what could be causing the miscarriage, what increases the risk of it, and what type of treatment might be needed.
Symptoms of miscarriage .
Most miscarriages occur before 12 weeks. Signs and symptoms of a miscarriage include:
- Vaginal bleeding or spotting (although quite common in early pregnancy)
- Pain or cramps in the abdomen or lower back
- Fluid vaginal discharge or tissue fragments
It is important to consider the fact that in early pregnancy, spotting or vaginal bleeding is quite common. In most cases, women who experience light bleeding during the first three months have an uneventful pregnancy thereafter. In some cases, even with heavy bleeding, the pregnancy does not end in a miscarriage.