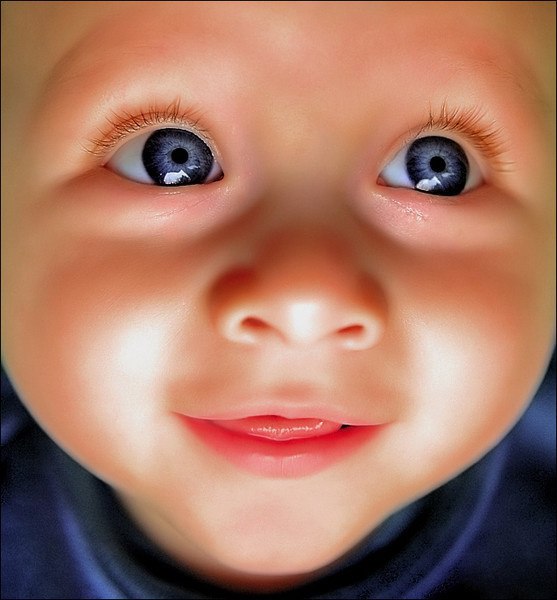
Red puffy eyes on baby
Baby Red Around Eyes: Causes and Treatments
If your sweet baby has redness around their eyes but they haven’t been crying, you’re probably wondering what’s causing it — and how much you should worry.
Let’s look at what could be going on.
Rubbing
Skin around the eyes is probably the most delicate skin of the body. (Yes, this is the first place we’ll notice fine wrinkles later in life for that very reason.) If your child has been rubbing their eyes, the area will easily turn red.
Rubbing — in and of itself — isn’t really cause for concern, unless what’s making your baby rub is more serious. (Do keep in mind that fingers + eyes = recipe for infections.)
But if it’s just a sleepy behavior your newborn’s picked up, you can try hand covers to prevent it, or wait for it to resolve on its own.
Irritants
Irritants are substances that injure the eyes, skin, or airways in some way. You can divide irritants into indoor and outdoor. Indoor irritants include:
- cigarette smoke
- perfumes
- sunscreen
- soaps
Outdoor irritants include:
- smoke
- fumes
- chemical vapors
- chlorine in pool water
- smog
Irritants usually cause localized redness that resolves once your baby is removed from the area where the irritant exists, or the irritant is removed from your home.
Allergies
Allergies happen when our eyes (or another part of our body) react to an allergen. An allergen is usually a harmless substance that triggers an immune response in people who are sensitive to the allergen.
Common allergens include:
- dust mites
- mold
- perfume in cosmetics and lotions
- medications
- foods
- dander from pets
- pollen from trees, plants, grasses, and weeds
- insect venom
If your child has a sensitivity and encounters an allergen, their eyes may produce histamine to fight the allergen. As a result, their eyelids and conjunctiva (the tissue that covers the white part of your eye and the inside of the eyelids) becomes red, swollen, and itchy.
You’ll probably also notice that your child’s eyes are watery with excess tears. A vicious cycle can set in: They rub their eyes to relieve the itching and burning, but the rubbing action irritates their eyes further and the redness increases.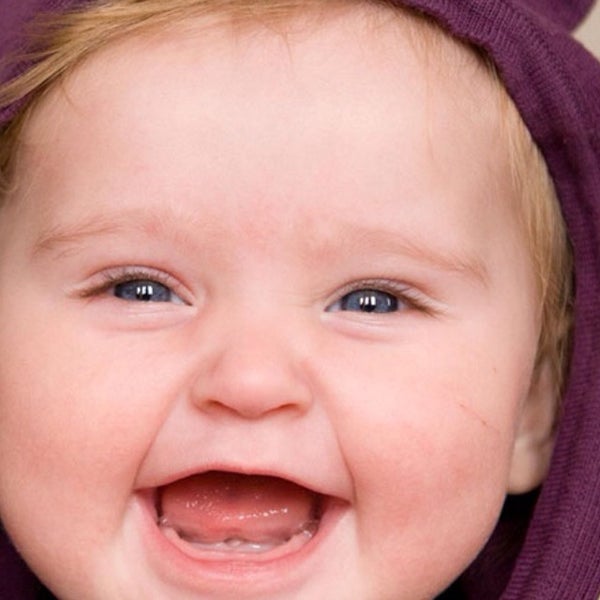
While some of these allergens (like dust mites and pet dander) are around all year long, others are seasonal. If your child is allergic to pollen, you’ll notice their red eyes when pollen counts are high.
Children with eye allergies often have nasal allergies as well. Yes, it’s double the trouble. If you suspect that the redness around your child’s eyes is an allergic reaction, check if they’re sneezing excessively or have a stuffy nose.
Sometimes, if an allergic reaction happens often enough, your child’s mast cells can become oversensitive.
Think of mast cells as your body’s first line of defense against invaders. When mast cells in the eye become oversensitive, they release histamine even if the allergen doesn’t come into direct contact with the eye.
Eye allergies are also called allergic conjunctivitis.
Infections
An eye infection happens when viruses or bacteria enter the eye area. It’s important to know the difference, because bacterial conjunctivitis needs antibiotic treatment.
Viral conjunctivitis
This is also called pink eye, although pink eye can be viral or bacterial. Children with colds commonly develop viral eye infections. Symptoms include:
- red, puffy eyelids
- red in the white part of the eye
- watery eyes
Bacterial conjunctivitis
This is more serious than viral conjunctivitis. You’ll notice the same symptoms as those that you notice in a viral eye infection. Symptoms also include:
- a sticky, yellow discharge from the eye
- eyelashes and eyelids that may get stuck together from the discharge
Newborn conjunctivitis
Redness in the eye area of a newborn can be caused by a blocked tear duct, irritation, or infection. Newborn conjunctivitis can be serious, so talk with your pediatrician right away.
Stye
A stye (also called a hordeolum) is a painful, red bump on the eyelid. A stye happens when a hair follicle, oil gland, or sweat gland becomes infected. Symptoms include:
Symptoms include:
- painful, red bump on the eyelid
- redness on the eyelid
- tenderness and swelling around the eye
Periorbital cellulitis
If the area around your child’s eye is injured or if your child has a sinus infection, they may develop periorbital cellulitis. This is a bacterial infection of the eyelids and skin around them. You’ll notice that your child’s eyelids are very red and swollen.
This is a serious condition and needs immediate treatment.
If your child has redness around their eyes, you can start treatment at home. However, if your child is a newborn or you suspect cellulitis, get immediate medical treatment.
Irritants
If you can, pin down which irritant is affecting your child. Try a different brand of soap, shampoo, and laundry detergent.
Allergies
Eye allergies usually come with a wider range of symptoms that also affect the nasal and airway passages. Keep a journal to track what could be causing the allergic reaction.
Here are some areas to examine:
- What’s on your baby’s daily menu?
- Is the allergic reaction related to the season?
- Does it happen at day care? Or every time you visit a specific family member or friend?
- Is the allergy related to animals?
- Do food allergies, like those to milk, wheat, or eggs, run in your family?
Eye infections
Viral conjunctivitis
Take care of viral conjunctivitis by rinsing the eyes often with warm water. Use a clean cotton ball for each eye. Wash your hands before and after each cleaning.
If you’re nursing, you can try dripping some of your milk into the corner of the eye. Human milk contains many healing properties.
Antibiotics won’t help a viral eye infection. Expect the redness to last between 4 and 7 days.
Bacterial conjunctivitis
A sticky, yellow discharge indicates a bacterial infection. You can use warm water and your milk to keep the area clean and to provide some relief, but you’ll need to talk with a doctor about antibiotic eye drops or eye cream to fight the infection.
Newborn conjunctivitis
Newborns with redness in or around the eye need immediate medical attention.
If the redness is from a blocked tear duct, you can gently massage the opening of the duct and below the lower eyelid to help it open up.
Sometimes, the antimicrobial eye drops that your baby is given right after birth can irritate the eyes. This mild redness should clear up within 24 to 36 hours.
Infection can happen when viruses or bacteria in the birth canal pass from the mother to the baby.
Stye
Use a warm compress three to four times a day to ease discomfort and reduce redness. If you’re nursing, use a few drops of your milk, too.
Take your baby to a pediatrician if you don’t see any improvement despite the home treatments. Take your journal with you so that the doctor can help track any possible causes.
Remember to tell your pediatrician about any milk, egg, or gluten allergies that run in your family.
If your newborn has a bacterial infection, depending on the severity, your pediatrician will prescribe:
- topical treatment, such as eye drops or ointment (most often)
- oral antibiotics (less commonly)
- intravenous antibiotics (very rarely)
If your baby’s tear duct is blocked, your pediatrician can show you how to massage the duct area to help it open.
Tear ducts usually open by themselves. However, if the duct doesn’t open by the time your child reaches age 1, they may need simple surgery.
If your toddler has bacterial conjunctivitis, your pediatrician will prescribe antibiotics.
Any time your little one has something going on, you may worry. But while redness around the eyes may bother you and your baby, it’s usually a simple thing to deal with.
Just be sure to call the doctor if there’s discharge, or if the issue hasn’t gotten better after a few days.
Baby Red Around Eyes: Causes and Treatments
If your sweet baby has redness around their eyes but they haven’t been crying, you’re probably wondering what’s causing it — and how much you should worry.
Let’s look at what could be going on.
Rubbing
Skin around the eyes is probably the most delicate skin of the body. (Yes, this is the first place we’ll notice fine wrinkles later in life for that very reason.) If your child has been rubbing their eyes, the area will easily turn red.
Rubbing — in and of itself — isn’t really cause for concern, unless what’s making your baby rub is more serious. (Do keep in mind that fingers + eyes = recipe for infections.)
But if it’s just a sleepy behavior your newborn’s picked up, you can try hand covers to prevent it, or wait for it to resolve on its own.
Irritants
Irritants are substances that injure the eyes, skin, or airways in some way. You can divide irritants into indoor and outdoor. Indoor irritants include:
- cigarette smoke
- perfumes
- sunscreen
- soaps
Outdoor irritants include:
- smoke
- fumes
- chemical vapors
- chlorine in pool water
- smog
Irritants usually cause localized redness that resolves once your baby is removed from the area where the irritant exists, or the irritant is removed from your home.
Allergies
Allergies happen when our eyes (or another part of our body) react to an allergen. An allergen is usually a harmless substance that triggers an immune response in people who are sensitive to the allergen.
An allergen is usually a harmless substance that triggers an immune response in people who are sensitive to the allergen.
Common allergens include:
- dust mites
- mold
- perfume in cosmetics and lotions
- medications
- foods
- dander from pets
- pollen from trees, plants, grasses, and weeds
- insect venom
If your child has a sensitivity and encounters an allergen, their eyes may produce histamine to fight the allergen. As a result, their eyelids and conjunctiva (the tissue that covers the white part of your eye and the inside of the eyelids) becomes red, swollen, and itchy.
You’ll probably also notice that your child’s eyes are watery with excess tears. A vicious cycle can set in: They rub their eyes to relieve the itching and burning, but the rubbing action irritates their eyes further and the redness increases.
While some of these allergens (like dust mites and pet dander) are around all year long, others are seasonal. If your child is allergic to pollen, you’ll notice their red eyes when pollen counts are high.
If your child is allergic to pollen, you’ll notice their red eyes when pollen counts are high.
Children with eye allergies often have nasal allergies as well. Yes, it’s double the trouble. If you suspect that the redness around your child’s eyes is an allergic reaction, check if they’re sneezing excessively or have a stuffy nose.
Sometimes, if an allergic reaction happens often enough, your child’s mast cells can become oversensitive.
Think of mast cells as your body’s first line of defense against invaders. When mast cells in the eye become oversensitive, they release histamine even if the allergen doesn’t come into direct contact with the eye.
Eye allergies are also called allergic conjunctivitis.
Infections
An eye infection happens when viruses or bacteria enter the eye area. It’s important to know the difference, because bacterial conjunctivitis needs antibiotic treatment.
Viral conjunctivitis
This is also called pink eye, although pink eye can be viral or bacterial. Children with colds commonly develop viral eye infections. Symptoms include:
Children with colds commonly develop viral eye infections. Symptoms include:
- red, puffy eyelids
- red in the white part of the eye
- watery eyes
Bacterial conjunctivitis
This is more serious than viral conjunctivitis. You’ll notice the same symptoms as those that you notice in a viral eye infection. Symptoms also include:
- a sticky, yellow discharge from the eye
- eyelashes and eyelids that may get stuck together from the discharge
Newborn conjunctivitis
Redness in the eye area of a newborn can be caused by a blocked tear duct, irritation, or infection. Newborn conjunctivitis can be serious, so talk with your pediatrician right away.
Stye
A stye (also called a hordeolum) is a painful, red bump on the eyelid. A stye happens when a hair follicle, oil gland, or sweat gland becomes infected. Symptoms include:
- painful, red bump on the eyelid
- redness on the eyelid
- tenderness and swelling around the eye
Periorbital cellulitis
If the area around your child’s eye is injured or if your child has a sinus infection, they may develop periorbital cellulitis. This is a bacterial infection of the eyelids and skin around them. You’ll notice that your child’s eyelids are very red and swollen.
This is a bacterial infection of the eyelids and skin around them. You’ll notice that your child’s eyelids are very red and swollen.
This is a serious condition and needs immediate treatment.
If your child has redness around their eyes, you can start treatment at home. However, if your child is a newborn or you suspect cellulitis, get immediate medical treatment.
Irritants
If you can, pin down which irritant is affecting your child. Try a different brand of soap, shampoo, and laundry detergent.
Allergies
Eye allergies usually come with a wider range of symptoms that also affect the nasal and airway passages. Keep a journal to track what could be causing the allergic reaction.
Here are some areas to examine:
- What’s on your baby’s daily menu?
- Is the allergic reaction related to the season?
- Does it happen at day care? Or every time you visit a specific family member or friend?
- Is the allergy related to animals?
- Do food allergies, like those to milk, wheat, or eggs, run in your family?
Eye infections
Viral conjunctivitis
Take care of viral conjunctivitis by rinsing the eyes often with warm water. Use a clean cotton ball for each eye. Wash your hands before and after each cleaning.
Use a clean cotton ball for each eye. Wash your hands before and after each cleaning.
If you’re nursing, you can try dripping some of your milk into the corner of the eye. Human milk contains many healing properties.
Antibiotics won’t help a viral eye infection. Expect the redness to last between 4 and 7 days.
Bacterial conjunctivitis
A sticky, yellow discharge indicates a bacterial infection. You can use warm water and your milk to keep the area clean and to provide some relief, but you’ll need to talk with a doctor about antibiotic eye drops or eye cream to fight the infection.
Newborn conjunctivitis
Newborns with redness in or around the eye need immediate medical attention.
If the redness is from a blocked tear duct, you can gently massage the opening of the duct and below the lower eyelid to help it open up.
Sometimes, the antimicrobial eye drops that your baby is given right after birth can irritate the eyes. This mild redness should clear up within 24 to 36 hours.
Infection can happen when viruses or bacteria in the birth canal pass from the mother to the baby.
Stye
Use a warm compress three to four times a day to ease discomfort and reduce redness. If you’re nursing, use a few drops of your milk, too.
Take your baby to a pediatrician if you don’t see any improvement despite the home treatments. Take your journal with you so that the doctor can help track any possible causes.
Remember to tell your pediatrician about any milk, egg, or gluten allergies that run in your family.
If your newborn has a bacterial infection, depending on the severity, your pediatrician will prescribe:
- topical treatment, such as eye drops or ointment (most often)
- oral antibiotics (less commonly)
- intravenous antibiotics (very rarely)
If your baby’s tear duct is blocked, your pediatrician can show you how to massage the duct area to help it open.
Tear ducts usually open by themselves. However, if the duct doesn’t open by the time your child reaches age 1, they may need simple surgery.
If your toddler has bacterial conjunctivitis, your pediatrician will prescribe antibiotics.
Any time your little one has something going on, you may worry. But while redness around the eyes may bother you and your baby, it’s usually a simple thing to deal with.
Just be sure to call the doctor if there’s discharge, or if the issue hasn’t gotten better after a few days.
Redness of the eyes in children
Fantasy Ophthalmologists are doctors of evidence-based medicine, treat according to modern protocols, prescribe only effective treatment. We solve specific problems without redirecting to specialized centers. In our clinic, we have all the possibilities for the conservative treatment of eye diseases in children. Our specialists diagnose and treat all pathologies, including complex and rare ones.
Make an appointment via WhatsApp
Prices Doctors
The first children's clinic of evidence-based medicine in Moscow
No unnecessary examinations and drugs! We will prescribe only what has proven effective and will help your child.
Treatment according to world standards
We treat children with the same quality as in the best medical centers in the world.
The best team of doctors in Fantasy!
Pediatricians and subspecialists Fantasy - highly experienced doctors, members of professional societies. Doctors constantly improve their qualifications, undergo internships abroad.
Ultimate safety of treatment
We have made children's medicine safe! All our staff work according to the most stringent international standards JCI
We have fun, like visiting best friends
Game room, cheerful animator, gifts after the reception. We try to make friends with the child and do everything to make the little patient feel comfortable with us.
You can make an appointment by calling or by filling out the form on the site
Other services under Pediatric Ophthalmology
- Consultation of a pediatric ophthalmologist (oculist)
- Children's glasses frames
Frequent calls
- Lacrimation in children
- Astigmatism in children
- Conjunctivitis in children: diagnosis and treatment
- Farsightedness in children: diagnosis and treatment
- Myopia in children: diagnosis and treatment
- Strabismus in children: diagnosis and treatment
- Peeling eyelids in a child: causes and treatment
- Selection of lenses for children
- Children's vision test
- Choosing glasses for a child
- Measurement of intraocular pressure (IOP) with the Icare device for a child
- Removal of a chalazion in children
- Schirmer's test
- Lazy eye (amblyopia)
Rare eye diseases in children
- Aniridia in a child
- Retinitis pigmentosa in a child
- Best's dystrophy in a child
- Ophthalmology for children with albinism
- Achromatopsia in a child
- Chronic progressive external ophthalmoplegia in a child
- Ophthalmology for children with Down syndrome
Online payment
Documents online
Online services
ophthalmology0001
There are many reasons for reddening of the eyes, and even though redness looks the same on the outside, the cause in each case is far from the same. It can be dust, sand, wind, fatigue or allergies, or it can be a formidable uveitis, which, if left unattended, can have serious consequences.
It can be dust, sand, wind, fatigue or allergies, or it can be a formidable uveitis, which, if left unattended, can have serious consequences.
Let's take a closer look. And what to do if your child has reddened eyes?
1. A common cause may be a banal irritation of the mucous membrane of the eyes associated with overwork, overstrain or eye fatigue. Long-term visual stress in the form of computer games, TV, playing with small objects, and even too much reading can cause redness of the eyes. The advice in these cases is simple and clear - distribute visual loads in the proportion of 50 to 50: two hours of classes, two hours of walking or outdoor games. That rare case when it goes away on its own.
2. If a foreign body (sand, dust, speck) enters, it can cause redness of the eye, it is necessary to rinse the eye with plain water or saline solution and apply antiseptic eye drops. You can wash your eyes with a decoction of chamomile or a solution of furacilin. If, after the manipulations, the redness in the eyes does not go away and the child complains about the eyes, we recommend that you contact an ophthalmologist.
If, after the manipulations, the redness in the eyes does not go away and the child complains about the eyes, we recommend that you contact an ophthalmologist.
3. K conjunctivitis . This disease in children is not the same as in adults. If a child becomes ill with conjunctivitis at a very early age, then he may experience a violation of sleep and appetite, he will become capricious and even stop playing with his favorite toys. Older children themselves may complain that their eyes itch, something interferes, they will rub their eyes.
The main signs of conjunctivitis in a child:
- in the morning the eyelids are glued together and a yellow crust forms on them;
- the child reacts too strongly to light;
- purulent, mucous discharge appears from the eye, there may be edematous eyelids;
- the whites of the eyes are red, the mucous membrane of the eyes (conjunctiva) may be edematous;
- there are complaints of discomfort in the eyes, "sand feeling" in the eyes.

Conjunctivitis can be caused by a viral, bacterial, protozoan or allergic reaction. Depending on the type of conjunctivitis, certain features of the course of the disease will be observed.
When virus becomes the cause of red eyes, redness usually occurs after a runny nose or cough, fever, conjunctivitis occurs against the background of SARS. Although the child may wake up with eyes stuck together, during the day the discharge from the eyes is slight and mucus-watery. Often children complain of a burning sensation in their eyes or describe a feeling of "sand in their eyes". Symptoms disappear during the treatment of a common disease, however, if the problem drags on, you need to go to an ophthalmologist. Treatment of conjunctivitis can only be prescribed by a specialist!
In case of bacterial conjunctivitis the eyeball looks red, the child is worried about irritation and thick discharge of white, yellow or green color. Moreover, the eyes turn sour not only in the morning, but also constantly during the day, this feature is a clear sign of the presence of a bacterial infection. Here the improvisation of parents is dangerous. Urgently to the ophthalmologist!
Moreover, the eyes turn sour not only in the morning, but also constantly during the day, this feature is a clear sign of the presence of a bacterial infection. Here the improvisation of parents is dangerous. Urgently to the ophthalmologist!
Allergic conjunctivitis is an unusual inflammatory reaction of the mucous membrane of the eye to common exposures that does not cause reactions in most people. Allergic conjunctivitis is often combined with allergic rhinitis, bronchial asthma, dermatitis. Throughout our lives, we come into contact with various microorganisms, particles of various origins, and chemical compounds. But if for most people these satellites remain invisible, then allergy sufferers very quickly feel their presence. Allergic conjunctivitis can begin in an acute form with unbearable itching of the eyelids, burning under the eyelids, photophobia, lacrimation with severe swelling and redness of the conjunctiva. But more often it is chronic, causing anxiety for many years. Depending on the allergens, its symptoms can be seasonal or year-round. Seasonal allergic conjunctivitis is caused by sensitivity to pollen from grasses, trees, weeds, or molds. House dust, animal dander, household chemicals, perfumes, contact lenses, medications, foods with preservatives or chemical additives, long-term unmaintained air conditioning at home or in a car are common causes of year-round conjunctivitis.
Depending on the allergens, its symptoms can be seasonal or year-round. Seasonal allergic conjunctivitis is caused by sensitivity to pollen from grasses, trees, weeds, or molds. House dust, animal dander, household chemicals, perfumes, contact lenses, medications, foods with preservatives or chemical additives, long-term unmaintained air conditioning at home or in a car are common causes of year-round conjunctivitis.
What to do?
Before starting eye allergy treatment, it is worth contacting an allergist to determine the allergen. If the cause is known, you need to remove contact with the allergen as soon as possible. Complete elimination of the action of allergens, if possible, is the most effective method of preventing an allergic reaction, and is also the first step in the treatment of an already unfolding picture of the disease. Taking antihistamines systemically and locally, in the form of eye drops, will reduce the intensity of allergy manifestations.
Attention!
In most cases, allergic conjunctivitis does not cause complications, but during the treatment of this disease, it is necessary to strictly adhere to eye hygiene, have a personal towel, hygiene items, wipe your eyes very carefully, use a new cotton pad for each eye. It is advisable to wash and instill in both eyes at once, even if the problem is in one eye. In most cases, the disease starts in one eye and spreads to the other.
Do not cover your eyes under any circumstances!
Heat and humidity are favorable conditions for the spread of infection.
4. If you notice redness and thickening of the edge of the eyelid in your child, accumulation of crusts, scales at the roots of the eyelashes, this may be a consequence of blepharitis . Today, blepharitis in children is a common disease. This is inflammation of the edges of the eyelids, associated with a too thin layer of skin and fiber in this place, due to looseness of the tissues and the complete absence of fat. There is a dysfunction of the meibomian glands located in the thickness of the eyelids. The causes of blepharitis in children can be: Staphylococcus aureus, demodectic mite, which enters the eyelash bulbs when the child comes in contact with birds, down and feather pillows, as well as chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, diabetes, various types of allergies, focal foci of infection - tonsillitis and caries. Often blepharitis occurs with uncorrected farsightedness, helminthic invasion and a banal violation of hygiene.
There is a dysfunction of the meibomian glands located in the thickness of the eyelids. The causes of blepharitis in children can be: Staphylococcus aureus, demodectic mite, which enters the eyelash bulbs when the child comes in contact with birds, down and feather pillows, as well as chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, diabetes, various types of allergies, focal foci of infection - tonsillitis and caries. Often blepharitis occurs with uncorrected farsightedness, helminthic invasion and a banal violation of hygiene.
What should parents do?
First, teach your child to follow the basic rules of hygiene. Secondly, to introduce him to a healthy lifestyle from an early age. Thirdly, treat any internal diseases in time. Visit your dentist regularly. Local ophthalmic treatment is prescribed only by a doctor!
5. Local redness of the eyelid may indicate stye – inflammation of the eyelash hair follicle or sebaceous gland. A small swelling forms on the edge of the eyelid, which increases in size and turns red. The eyelid is very swollen, which leads to a narrowing of the eye lumen. Barley can form on one or both eyes at once. Usually on the fourth or fifth day, the purulent chamber is opened, after which pus begins to flow out of it. After that, the child's well-being improves markedly.
The eyelid is very swollen, which leads to a narrowing of the eye lumen. Barley can form on one or both eyes at once. Usually on the fourth or fifth day, the purulent chamber is opened, after which pus begins to flow out of it. After that, the child's well-being improves markedly.
Important!
Do not squeeze or pierce the abscess! When the abscess is formed, thermal procedures are contraindicated. Otherwise, there is a risk of various complications (abscess, meningitis, etc.). It is also important to ensure that the baby does not rub his eyes with his hands so that the infection does not get to other areas of the skin. It is better not to self-medicate, show the child to the doctor.
6 . Chalazion in Greek means "hailstone" and is a chronic inflammation of the cartilage of the eyelid around the meibomian gland, in which there was a blockage of the excretory duct and, as a result, stagnation of the secret. It is quite difficult to get rid of such a disease of the century in a child. With a sluggish process, the baby is helped by therapeutic methods of treatment: local anti-inflammatory therapy, physiotherapy, the treatment will be long and you need to be patient. In more acute periods, it is impossible to do without surgery. Symptoms of a chalazion are swelling of the edge of the eyelid, over time, an elastic, painless formation the size of a large pea is felt. The main factors influencing the appearance of a chalazion are considered frequent colds, a weak immune system, and diabetes mellitus. Sometimes chalazion occurs due to problems with the digestive tract - dysbacteriosis.
With a sluggish process, the baby is helped by therapeutic methods of treatment: local anti-inflammatory therapy, physiotherapy, the treatment will be long and you need to be patient. In more acute periods, it is impossible to do without surgery. Symptoms of a chalazion are swelling of the edge of the eyelid, over time, an elastic, painless formation the size of a large pea is felt. The main factors influencing the appearance of a chalazion are considered frequent colds, a weak immune system, and diabetes mellitus. Sometimes chalazion occurs due to problems with the digestive tract - dysbacteriosis.
Experts believe that blockage of the meibomian glands of the eyelid in children is often caused by functional and anatomical imperfections, i.e. narrow outlet ducts, weak smooth muscle cells that squeeze the secret, or insufficiently high levels of the protective protein secretory tear immunoglobulin.
7. Uveitis – inflammation of the choroid of the eye of an inflammatory nature. The main properties of the choroid are accommodation - the ability of our eyes to see clearly at different distances, and nutrition of the retina.
The main properties of the choroid are accommodation - the ability of our eyes to see clearly at different distances, and nutrition of the retina.
Uveitis in children requires urgent treatment! The causes of inflammation of the choroid can be very different: infections, metabolic disorders, diabetes mellitus, tuberculosis, immune suppression, autoimmune processes, etc. Uveitis can be a secondary disease, while the focus of inflammation is located elsewhere, and the infection spreads through the bloodstream with angina, meningitis, sinusitis, septic endocarditis. Also, uveitis can occur against the background of an exacerbation of allergies, and in some cases - after a penetrating eye injury. Very rarely, despite a thorough examination, it is not possible to determine the cause of uveitis. With uveitis in children, the symptoms and complications are basically the same as in adults. However, the symptoms are more pronounced. The younger the child, the more difficult it is to diagnose uveitis on time, in the early stages. With anterior uveitis, redness of the eyes appears, which adults can pay attention to; visual acuity decreases, photosensitivity increases, tearing. With posterior uveitis, the main symptoms are: decreased visual acuity and vision distortion, the appearance of spots before the eyes. Diagnosis is difficult, because if the process has affected one eye, and the second one sees well, then the child will not complain. The main signal symptom of the presence of the disease - pain - may be absent.
With anterior uveitis, redness of the eyes appears, which adults can pay attention to; visual acuity decreases, photosensitivity increases, tearing. With posterior uveitis, the main symptoms are: decreased visual acuity and vision distortion, the appearance of spots before the eyes. Diagnosis is difficult, because if the process has affected one eye, and the second one sees well, then the child will not complain. The main signal symptom of the presence of the disease - pain - may be absent.
Without proper treatment, retinal detachment may occur over time. If treatment does not occur, the inflammatory process can affect the other healthy eye. The later treatment of uveitis is started, the more serious the damage to the finest structures of the eye, which can lead to loss of vision.
Strongest advice: for reddening of the eye that does not go away one or two days and is not accompanied by pain, visit an ophthalmologist immediately !
8. In infants, a possible cause of reddening of the eyes may be dacryocystitis , in other words, inflammation of the lacrimal sac. The main signs of this disease are mucopurulent discharge from the eye, a slight swelling in the inner corner of the eye, and tearing. Distinctive symptoms of dacryocystitis are mucopurulent discharge, when pressed on the zone of the lacrimal openings. Most often, this problem is associated with obstruction of the lacrimal canal. During the intrauterine development of the child, the lacrimal canal is closed, a special gelatinous film blocks the ingress of amniotic fluid. At the moment when the child takes his first breath and starts to scream, this film bursts. If this does not happen, tears gradually accumulate in the lacrimal sac, stagnation occurs, and a breeding ground for pathogenic microorganisms appears, which cause inflammation. Most likely, at first you are recommended to do a special massage aimed at helping to break this film, in parallel with the instillation of antiseptic drops.
In infants, a possible cause of reddening of the eyes may be dacryocystitis , in other words, inflammation of the lacrimal sac. The main signs of this disease are mucopurulent discharge from the eye, a slight swelling in the inner corner of the eye, and tearing. Distinctive symptoms of dacryocystitis are mucopurulent discharge, when pressed on the zone of the lacrimal openings. Most often, this problem is associated with obstruction of the lacrimal canal. During the intrauterine development of the child, the lacrimal canal is closed, a special gelatinous film blocks the ingress of amniotic fluid. At the moment when the child takes his first breath and starts to scream, this film bursts. If this does not happen, tears gradually accumulate in the lacrimal sac, stagnation occurs, and a breeding ground for pathogenic microorganisms appears, which cause inflammation. Most likely, at first you are recommended to do a special massage aimed at helping to break this film, in parallel with the instillation of antiseptic drops.