Premature survival rate by week
Premature birth statistics | Tommy's
Tommy's PregnancyHub
A preterm birth is one that happens before 37 weeks of pregnancy. Globally, more than 1 in 10 pregnancies will end in preterm birth.
A preterm birth is one that happens before 37 completed weeks of pregnancy.
The World Health Organisation gives the following definitions for the different stages of preterm birth:
- Extremely preterm: before 28 weeks
- Very preterm: from 28 to 31 weeks
- Moderate to late preterm: from 32 to 37 weeks.
General UK premature birth statistics
- Around 8% of births in the UK are preterm. That is around 60,000 babies each year.
- This is higher than many countries in Europe and higher than Cuba and Iran
Of the births that were preterm in the UK:
- 5% were extremely preterm (before 28 weeks)
- 11% were very preterm (between 28 and 32 weeks)
- 85% were moderately preterm (between 32 and 37 weeks).
In 2019, live births where gestational age was under 24 weeks increased to 0.15% compared with 0.13% in 2018 and 0.11% in 2010.
Chances of survival following preterm birth
Medical advances mean that we are getting better at treating preterm babies but the chances of survival still depend on gestational age (week of pregnancy) at time of birth.
- Less than 22 weeks is close to zero chance of survival
- 22 weeks is around 10%
- 24 weeks is around 60%
- 27 weeks is around 89%
- 31 weeks is around 95%
- 34 weeks is equivalent to a baby born at full term.
Preterm birth and neonatal death
Complications arising from premature birth is the leading cause of neonatal death (death in the first few weeks after birth) in the UK.
Preterm birth and multiple pregnancies
Having more than one baby is a risk factor for preterm birth. On average, most singleton pregnancies last 39 weeks, twin pregnancies 37 weeks and triplets 33 weeks.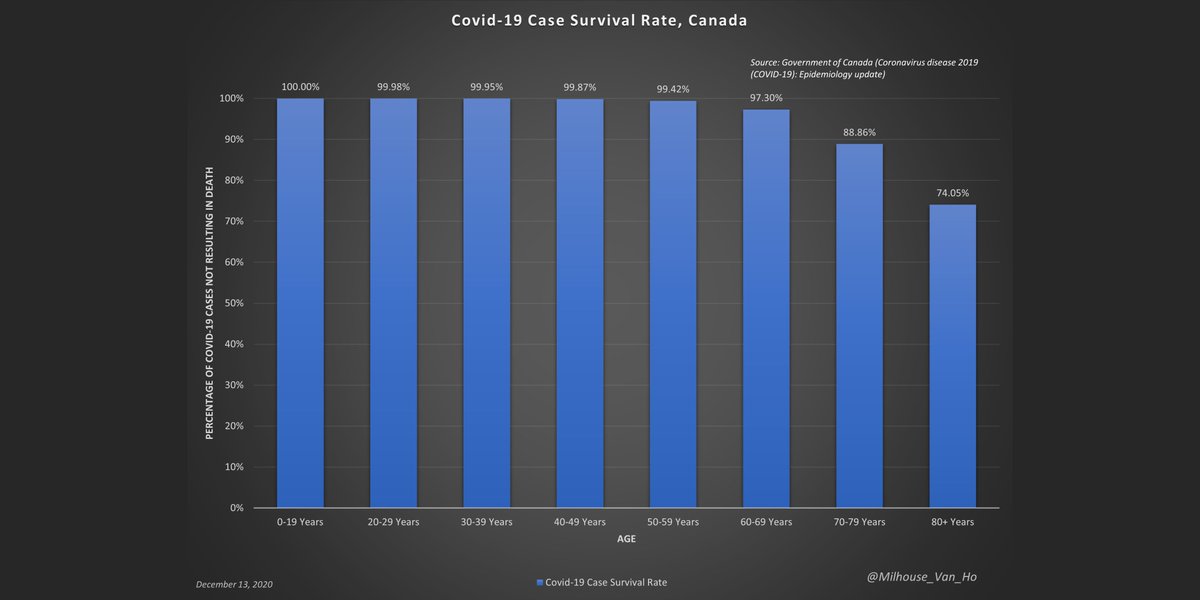
- Risk of prematurity with singleton pregnancy: 7%
- Risk of prematurity with multiple pregnancy: 57%
Risk of disability in preterm children
Generally, the earlier the birth, the higher the risk of problems. However these are only statistics and cannot predict how an individual child will do; some extremely premature babies do very well and develop into healthy children.
- 1 in 10 of all premature babies will have a permanent disability such as lung disease, cerebral palsy, blindness or deafness.
- 1 in 2 of premature babies born before 26 weeks of gestation will have some sort of disability (this includes mild disability such as requiring glasses).
In one study of 241 children born before 26 weeks' gestation the following was found:
- 22% severe disability (eg cerebral palsy + not walking, low cognitive scores, blindness, profound deafness)
- 24% moderate disability (eg cerebral palsy + walking, IQ/cognitive scores in the special needs range, lesser degree of visual or hearing impairment)
- 34% mild disability (defined as low IQ/cognitive score, squint, requiring glasses)
- 20% no problems.
Preterm birth by ethnicity
The risk of preterm birth is highest for Black Caribbean women and lowest for White British and White Other.
- Bangladeshi: 8%
- Indian: 7%
- Pakistani:7%
- Black African: 8%
- Black Caribbean: 10%
- White British: 7%
- White Other: 6%
Causes of preterm birth
In some cases a cause of preterm birth can be shown but more often it is unknown or unclear.
In 1 in 4 preterm births, the birth is planned (induced labour or c-section) to save the life of mother or baby from pregnancy complications such as pre-eclampsia, fetal growth restriction, waters breaking early (PPROM) or infection
Preventing premature birth
Too often health professionals are not able to tell women why they have had a premature birth. This area of research is underfunded, with many taking an unhelpful (and unique to pregnancy) approach of ‘It was not meant to be’.
Research into why premature birth happens is the only way we can save lives and prevent future loss. Tommy's funds more than £400k of research into premature birth every year. We are focused on predicting early which women will have a premature birth and treating them to prevent it happening.
Tommy's funds more than £400k of research into premature birth every year. We are focused on predicting early which women will have a premature birth and treating them to prevent it happening.
Read about our research into prematurity here.
Back to top
Premature Baby Survival Rates
So, your little one couldn’t wait to join you in the big, big world and has decided to make a grand entrance! If your baby is premature, or “preterm,” they’re in good company — about 1 in 10 babies are born prematurely in the United States.
A premature birth is one that happens at least three weeks before your estimated 40-week due date — so, before the 37th week of pregnancy. That said, “premature” is a range.
Premature birth ranges are called:
- extremely preterm (before 28 weeks)
- very preterm (28 to 32 weeks)
- moderate preterm (32 to 34 weeks)
- late preterm (34 to 37 weeks)
You may also hear the term “periviable birth,” which refers to delivery between 20 and 26 weeks, according to the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists.
How early your baby is born makes a difference in what kind of interventions they might need. The more premature a little one is, the higher the chance of some complications. Each gestational week makes a difference in survival rate, when it comes to premature babies.
Doctor’s don’t always know why a baby is born premature, and they can’t always prevent it. What’s more, the research on preemie survival rates is extremely broad.
Outcomes vary widely based on country, maternal factors, and baby’s birth weight. But rest assured, the survival rate for babies born extremely preterm without neurodevelopmental problems has been improving since 2000.
A baby born between 20 and 26 weeks is a considered to be periviable, or born during the window when a fetus has a chance of surviving outside the womb. These babies are called “micro-preemies.”
A baby born before 24 weeks has less than a 50 percent chance at survival, say the experts at University of Utah Health.
However, according to this 2016 analysis of more than 8,300 deliveries in the United States, babies born at 24 weeks had a 68 percent chance of survival. A 2016 cohort study of more than 6,000 births found a survival rate of 60 percent. (Utah Health notes a 60 to 70 percent survival rate for this gestational age.)
With an extremely premature birth, you and your baby may face some rough times (and choices) together. Fortunately, advances in medicine means even the tiniest babies can likely get bigger and stronger in neonatal intensive care units (NICU).
About 40 percent of babies born at 24 weeks will have health problems, says the Irish Neonatal Health Alliance. Some of these complications may happen right away, or others that appear later in life.
Risks for a baby born this early include complications regarding:
Skin and warmth
Your tiny one will need to go into an incubator (like a portable womb) right away to keep them warm. Babies born this early have not yet had the chance to develop brown fat — the kind just under the skin that keeps them toasty.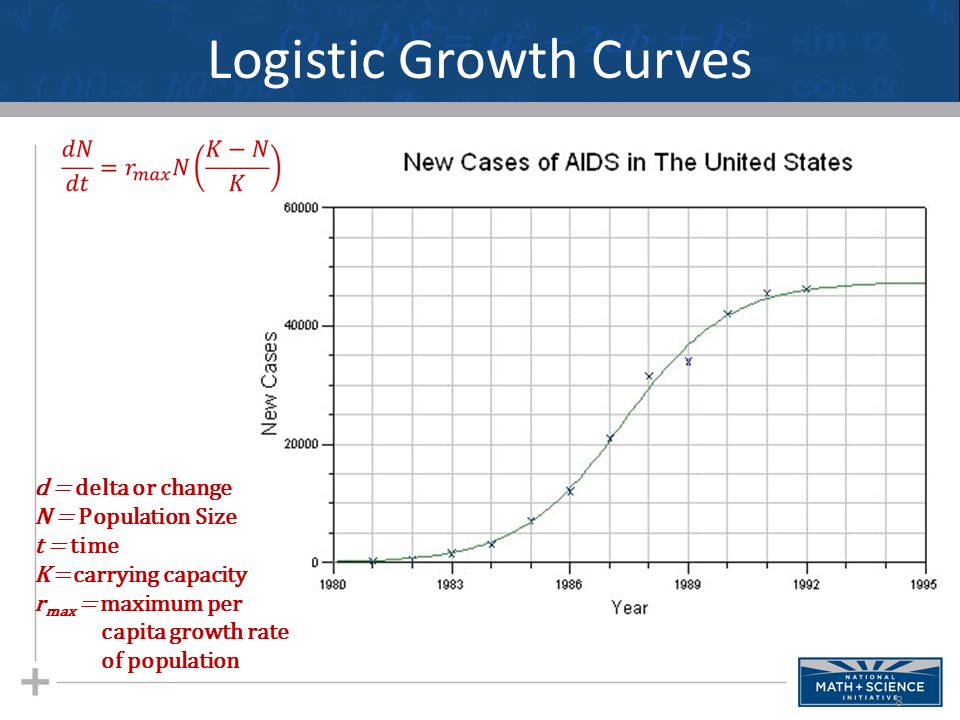 Their skin will also be extremely thin and delicate.
Their skin will also be extremely thin and delicate.
Breathing
A baby’s lower lungs and airways are only just beginning to develop around 24 weeks. A baby born at this time will need help to breathe. This might mean little tubes going into their nose, as they grow in the incubator.
Eyesight
At about 24 weeks in the womb, a baby’s eyes are still closed. Their eyelids and eyes are not yet developed enough to open them. Your baby will need to have soft cotton or gauze taped over their eyes to protect them from the light as their sight continues to develop.
In some cases, a baby’s eyes might not grow as they should, which could lead to vision problems or even blindness.
Hearing
Amazingly, an extremely premature baby already has fully formed ears. Your baby can start to hear you at about 18 weeks gestation! However, your little one’s eardrums are still very delicate and sensitive at 24 weeks. Some babies born this early may have problems hearing or experience deafness.
Some extremely premature babies may have issues that affect the brain and nervous system as they get older. Some of these are serious. Complications include cerebral palsy, learning problems, and behavioral issues.
If your baby is born at 26 weeks, they’re still considered “extremely preterm.” But a lot can improve for a developing baby in just a couple of weeks of gestation time, increasing chances of survival.
Babies born at 26 weeks were found to have a survival rate of 89 percent in the 2016 analysis and 86 percent in the 2016 cohort study.
A big difference contributing to the jump in survival rate at 26 weeks versus 24 weeks is your baby’s lung development. By about 26 weeks of gestational age, a baby’s lower lungs have grown and developed little air sacs called alveoli.
Your baby will still be too little to breathe on their own, but their lungs will be more developed and stronger. Your little one will still need to be in an incubator for warmth with breathing tubes to help bathe them in life-giving oxygen.
About 20 percent of babies born at 26 weeks may still have some health problems as they age. These might include issues with:
- seeing
- hearing
- learning
- understanding
- behavior
- social skills
Babies born at 26 weeks may also develop heart problems.
A baby born after 28 weeks is considered “very preterm” but has a big head start compared to babies born just 2 to 4 weeks earlier. This is because their vital organs — like the heart and lungs — are much more developed.
According to the University of Utah Health, the survival rate for your baby is 80 to 90 percent at 28 weeks. Some clinical studies have even more promising data, showing survival rates of 94 percent and 98 percent at this age.
Only 10 percent of babies born at 28 weeks risk long-term complications. These can include:
- breathing problems
- infections
- digestive problems
- blood problems
- kidney problems
- brain and nervous system problems like seizures
What a difference a few womb weeks make! Babies born between 30 and 32 weeks, while still considered preterm, have at least a 99 percent chance of survival. They also have very low risk of health and development complications later on.
They also have very low risk of health and development complications later on.
If your baby is born at 34 to 36 weeks they are in a new category called “late preterm.” This is the most common kind of premature baby. It’s also the one with the least risks because your baby has more time to grow and develop inside you.
In fact — good news — a preemie baby born at 34 to 36 weeks has nearly a 100 percent chance at survival and the same chances at long-term health as a baby who was born full-term.
Still, your 34- to 36-week-old baby might be smaller and a bit more delicate than a 40-week or full-term baby. Your doctor may recommend that they stay in an incubator at the hospital for a week or two, so they can rest and get a bit bigger before going home.
If your baby is born prematurely, there are several things that affect their survival rate and how healthy they’ll be as they age. A week or two more in the womb can make a big difference for your baby.
Medical advances in caring for premature babies means better outcomes, and more peace of mind for parents. While every week in the womb will give you more assurance, know that chances for your preemie’s survival are increasing every year.
While every week in the womb will give you more assurance, know that chances for your preemie’s survival are increasing every year.
Premature birth - Juno
Premature birth: content of the article
What is preterm birth
The birth of a baby weighing more than 0.5 kg from 22 to 37 weeks is considered early. According to statistics, 15 million babies are born prematurely around the world.
In our country, until 2012, babies were registered who were born at 28 weeks, and all those born earlier - a week later. The development of obstetrics made it possible to nurse critically premature babies and increased their survival statistics.
Who is at risk
Any pregnant woman can give birth prematurely. Some expectant mothers have a higher chance of preterm birth. The risk zone includes pregnant women:
- under 17 and over 35;
- have more than one fetus;
- have structural features of the uterus or its cervix;
- use harmful substances - drugs, alcohol, smoke;
- have heavy physical activity;
- have a history of preterm birth;
- work in hazardous production;
- are subjected to sexual, emotional abuse, stress, mental stress.

At risk are expectant mothers who are not registered during the gestation period or ignore ultrasound, screenings, laboratory tests.
The threat of early preterm birth is more common with diagnoses: diabetes mellitus, anemia, hypertension, genitourinary infections, hypothyroidism, problems with weight before conception (deficiency or obesity), thrombophilia, vaginal bleeding. There is also a risk when conceiving through IVF, with congenital malformations of the fetus.
If a woman has previously given birth to a child ahead of schedule, the chances of premature birth remain in subsequent pregnancies. The same applies to the weight of the crumbs: if the firstborn was born with a lack of body weight, then his brother or sister may be underweight.
Risk factors
Doctors point to a number of factors that take place long before the conception of a child. These include:
- Gynecological diseases suffered in childhood or adolescence;
- Early initiation of intimate life;
- Hereditary factor;
- Pathologies of previous pregnancy: preeclampsia, fetoplacental insufficiency, premature birth;
- Excessive uterine distension in multiple pregnancies, polyhydramnios;
- Threat of early miscarriage.

Another risk factor is surgery or trauma to the abdominal organs during the gestation period.
Risk of preterm birth at different terms
The birth of a child prematurely has many negative consequences for him. It depends on the trimester in which the pregnancy ended.
The most severe consequence is the death of the infant. With early preterm birth in the period of 22-24 weeks, the threat is the highest - up to 80% of babies die. This occurs against the background of intracranial hemorrhage of 3-4 degrees, cardiopulmonary insufficiency, intrauterine infection of the fetus.
Among those born in the period of 25 - 26 weeks, 40% of babies die, in 27 - 28 - about 20%, in 29 - 32 - no more than 10%, and in 33 - 34 - 2% of newborns are at risk.
Modern medicine is able to provide care for a premature baby and save his life. But no one can guarantee a full healthy life. Such a child can subsequently be given disappointing diagnoses: cerebral palsy, mental retardation, retinopathy of prematurity. He may suffer all his life from problems with the digestive and respiratory systems, impaired vision, hearing, delayed mental and physical development. Diagnosis implies disability.
He may suffer all his life from problems with the digestive and respiratory systems, impaired vision, hearing, delayed mental and physical development. Diagnosis implies disability.
For a woman in labor, preterm labor is usually not dangerous. Without concomitant pathologies, the mother's body does not care how long the child is born. There are only psychological problems: stress, fear and worries about the baby. It is better for a mother to tune in that her child, in case of severe prematurity, will be taken to the intensive care unit for nursing, so she will not see him immediately.
A newly minted mother needs rehabilitation. Therapy is prescribed, depending on the cause of the pathology: a complex of vitamins, antioxidants, hormones.
Why preterm birth is dangerous
Infants are immature: their body is covered with a large amount of cheese-like lubricant, there is a deficiency of subcutaneous fatty tissue, few hairs on the head and fluff on the body, cartilage on the ears and nose are soft, the nails do not go beyond the fingertips, the navel is located closer to the pubis.
Babies are underweight. Depending on the weight of the crumbs, 4 degrees of prematurity are distinguished: at the 1st degree, the baby weighs from 2500 to 2001 g, the 2nd - from 2000 to 1500 g, the 3rd - from 1500 to 1001 g, the 4th - 1000 g and below .
The development of the genital organs has not been completed: the testicles in boys are not lowered into the scrotum, and in girls the large labia do not cover the small and clitoris.
Children have immature lungs. They cannot breathe adequately - often they need help. The cry is weak. There are also problems with digestion. The body cannot absorb all the components from mother's milk.
Extrauterine life for children becomes a strong stress. It's hard to deal with him. They poorly resist infections, quickly lose heat, thermoregulation is impaired. They are subject to hemorrhages against the background of fragile vessels. Especially dangerous are hemorrhages in the cervical spinal cord and ventricles of the brain.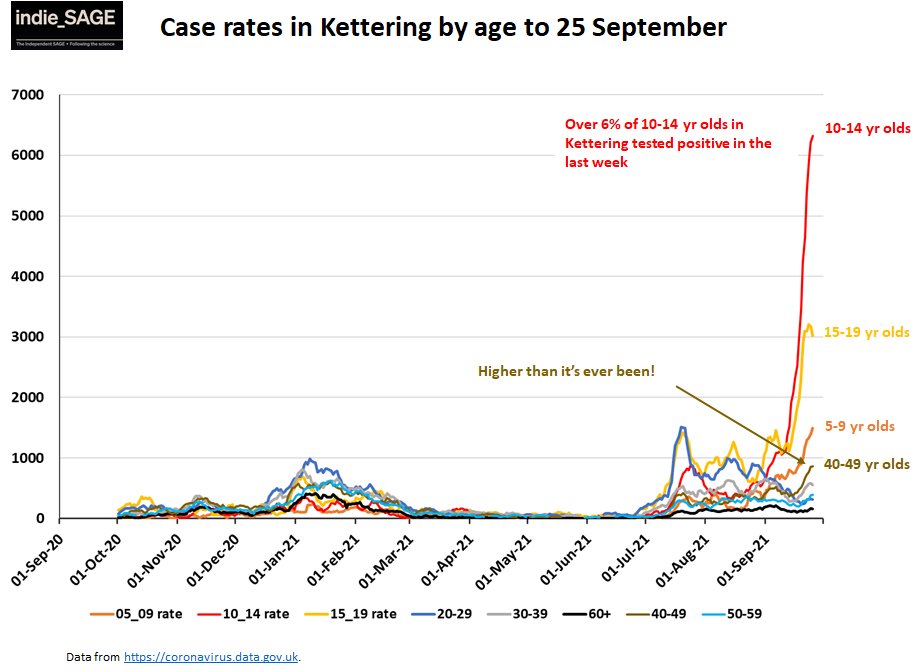
Among the complications of preterm birth are intracranial hemorrhages, asphyxia, intrauterine growth retardation.
Types of preterm birth
Several classifications have been adopted. Let's consider them.
- By term: critically early - up to 28 weeks, significantly early - from 28 to 32 weeks, moderately early or late - from 32 to 37 weeks;
- By the mechanism of attack: induced and spontaneous. Induced cause artificially for medical reasons. Occurs in 40% of cases. Spontaneous in 60% of cases begin with contractions, in 40% - with a rupture of the membranes;
- By the nature of the course: spontaneous, with regular labor activity, without it and artificially provoked. In 80% of cases, preterm labor begins spontaneously. At the same time, the fetal bladder can be intact - and then the contractions are regular, growing. Or amniotic fluid may pour out, labor activity is chaotic. For medical reasons, early delivery can be artificially induced.
 For example, in case of danger to the life of the mother, intrauterine death of the fetus, or defects that are incompatible with life;
For example, in case of danger to the life of the mother, intrauterine death of the fetus, or defects that are incompatible with life; - According to symptoms: threatening, incipient and incipient. With threatening early premature birth, the lower abdomen and lower back hurt, the tone rises. Her neck remains unchanged, the external os is closed. When the process begins, pains appear in the lower abdomen. Regular contractions may begin. The neck is flattened or shortened. The main symptom of the onset of preterm labor is regular labor activity. The cervix opens by 2 - 3 cm, it happens quickly.
In 40% of women in labor, water breaks, 35% gave birth quickly and quickly. The active phase lasts less than when the baby appears on time. The contractions are monotonous, long and painful, the pauses between them are small.
Causes of preterm birth
Doctors indicate the main causes of the pathology:
- Early activity of the fetal endocrine system;
- Infections and inflammatory processes - ureaplasmosis, mycoplasmosis, pyelonephritis, bacterial vaginosis.
 They stimulate the production of prostaglandins. Hormones affect the uterine muscles - cause contractions and premature birth;
They stimulate the production of prostaglandins. Hormones affect the uterine muscles - cause contractions and premature birth; - Placental bleeding. They occur with incorrect presentation or detachment. The situation is serious, there is a threat to the life of the mother. Therefore, with presentation, hospitalization is indicated;
- Neck weakness. In 20% of cases, it leads to preterm birth. This also includes such factors: the interval between the current and previous gestation is less than 2 years, the woman is expecting 4 children or more;
- Isthmic-cervical insufficiency. The cervix opens itself - a miscarriage or premature birth occurs. It is possible to open mechanically - when scraping after a miscarriage, IVF, abortion;
- Pathologies on the part of the baby - intrauterine infection, malformations of internal organs.
Chronic ailments, dental problems, angina, health status during gestation, genetic factors are all common reasons for early delivery. Sometimes it is impossible to determine. Although this is important for the development of effective means of preventing pathology.
Sometimes it is impossible to determine. Although this is important for the development of effective means of preventing pathology.
Symptoms of preterm labor
We list the signs by which you may suspect that the baby is in a hurry to be born ahead of time.
Spasms over the pubis. They are similar to pain during menstruation.
Pain, pressure and discomfort in the genitals, thighs, pelvis. There is a dull pain in the lumbar region.
Feeling of pressure, pressure in the back.
Diarrhea, spasms and pain in the intestines.
Vaginal discharge - they get worse. May be watery, pink, brown, bloody.
Contractions of varying intensity. Touch your stomach with your fingertips - you will feel the contraction and relaxation of the uterus. Counted more than 4 contractions in 60 minutes? Call an ambulance - you need an urgent examination by an obstetrician.
The following symptoms are also dangerous: sudden blurred vision, flashes and “flies” before the eyes, incessant migraine, swelling of the face or hands, temperature of 38º C and above, painful urination, abdominal trauma, decreased fetal activity in the 3rd trimester (less than 10 movements in 12 hours).
Any of the above symptoms indicate the risk of preterm birth. Seek medical attention.
Diagnosis of preterm birth
Includes several stages.
Transvaginal ultrasound. The length of the cervix is measured, fetal fibronectin is determined - a kind of "biological glue" that binds the fetal sac to the uterine mucosa.
Gynecological examination. Allows you to assess the degree of opening of the neck, its length.
Rapid test for the determination of phosphorylated protein-1. The test determines the possibility of preterm birth. In the future, this helps prevent iatrogenic complications.
When diagnosing, 2 parameters are evaluated:
- Regularity of contractions;
- Neck changes - shortening and smoothing. informative method. For example, with a neck length of 3 cm, the risk of preterm birth in the next week is 1%. The patient is not admitted to the hospital, there is no danger to her and the fetus.

Differential diagnosis
Its goal is to correctly diagnose. The early birth of a baby is accompanied by cramps in the lower abdomen, diarrhea, pain in the lumbar region. These same symptoms are characteristic of other conditions: appendicitis, colitis, cystitis, pyelonephritis.
When complaining of pain in the lower abdomen, the patient is examined for the consistency of the scar after the previous cesarean section, for example. When the temperature rises, flu, sore throat, viral infection are excluded.
Diagnosis
Preterm birth is stated based on the clinical picture. Doctors are guided by such markers.
The first is the length of the neck - less than 2 - 2.5 cm.
The second is the determination of phosphorylated protein-1.
The third is the regularity of contractions. There should be at least 4 in 20 minutes.
Fourth - neck changes in dynamics.
Fifth - assessment of the degree of maturity of the neck. Determined by the level of PSIFR-1 in the cervical canal.
Determined by the level of PSIFR-1 in the cervical canal.
Usually the process begins rapidly, suddenly and intensely.
Treatment for preterm birth
The goal is to reduce the tone of the myometrium, reduce uterine contractions. This is achieved by blocking oxytocin receptors - it is the hormone oxytocin that triggers the birth process.
Such antagonists of oxytocin receptors are tocolytics. One of the modern representatives of this group of drugs is atosiban.
The remedy is effective, but has contraindications. It is forbidden to treat pregnant women for less than 24 and more than 33 weeks, with uterine bleeding, growth retardation, distress or fetal death, severe preeclampsia, with rupture of the fetal membrane after 30 weeks, placenta previa or its detachment.
5 stages of preterm labor
The first stage is forecasting their onset. Depends on the situation: the process is starting, has begun, or it is a threat.
Stage two - prevention of respiratory distress syndrome in a child. Doctors stimulate the maturation of the lungs. Apply funds from the group of glucocorticoids.
Stage three - prolongation of pregnancy. Doctors try to delay preterm labor by giving the baby's lungs and placenta time to mature. For this, tocolytics are used - they inhibit the contractile activity of the uterus. Usually prophylaxis is carried out - tocolysis is carried out before contractions. When started, therapy is ineffective. The duration of treatment is a maximum of 48 hours.
Stage four - preparation for the birth of a premature baby. The woman in labor is transferred to a higher-level hospital. The physiology of preterm labor does not differ from the birth of a child at term. But close attention is required from doctors to minimize complications for mom and baby.
The fifth stage is the prevention of infections and their complications. At risk are women in labor whose waters have broken. If the patient gives birth before 34 weeks, she can be pierced with a course of dexamethasone. It accelerates the maturation of the placenta and internal organs of the baby, reduces the risk of complications.
If the patient gives birth before 34 weeks, she can be pierced with a course of dexamethasone. It accelerates the maturation of the placenta and internal organs of the baby, reduces the risk of complications.
OB sequence
When registering a patient with preterm birth, the doctor gets acquainted with the exchange card, studies the general, gynecological and infectious anamnesis, and the results of examinations. Clarifies complaints and evaluates the condition of the woman in labor. He examines her, measures the pulse and respiration rate, temperature, pressure, abdominal circumference and the height of the uterus.
Clarifies data on the fetus: movements, measures heart rate by auscultation - listening to the heart through the mother's stomach through the device. To assess the condition of the crumbs, the doctor performs cardiotocography. The device records the heart rate.
Ultrasound is performed to assess the condition of the child and mother's organs.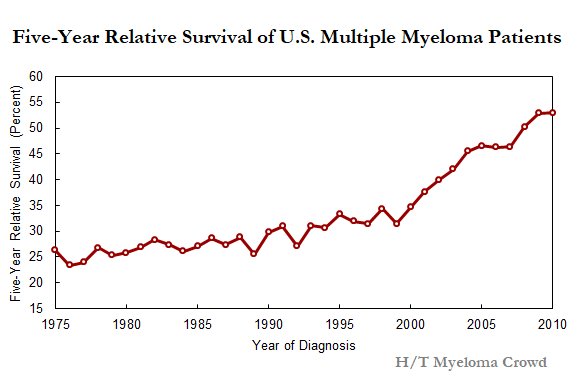
A gynecological examination is carried out: with intact membranes - external, with their rupture - internal. This is necessary to determine the position and position of the child, to assess the degree of disclosure.
Conduct a laboratory examination. They take a smear from the vagina: culture for β-hemolytic streptococcus, bacteriological culture, take blood and urine for a general analysis.
According to the results of the examination, the obstetrician confirms or refutes preterm birth, their stage.
The expectant mother is informed about her condition, forecasts for the child. At the slightest opportunity, they try to prolong the pregnancy. If the child is ready to be born in the near future, the doctor determines the tactics of assistance, coordinates the issue of anesthesia with the woman in labor.
In the absence of indications for a caesarean section, they give birth naturally. This is the best way - it is less traumatic for the baby. A gentle approach is what a weak newborn needs.
A gentle approach is what a weak newborn needs.
Preterm birth care policy
The woman in labor is provided with continuous psychological support. Describe the current obstetric situation.
With head presentation, they give birth naturally.
With pelvic - take into account clinical indications. Caesarean section is not the only effective method in this case. The operation does not improve the prognosis for a premature baby, but it puts an additional burden on the mother's body: it increases infection, morbidity, and complications.
With foot presentation, only a caesarean section is done.
Anesthesia is carefully selected. Avoid opiates - they depress the respiratory center, which is dangerous for premature babies.
At the birth of a baby before 34 weeks, vacuum aspiration is prohibited. It increases the risk of neonatal morbidity. Dosed episiotomy, exit forceps for the birth of the head and epidural anesthesia are performed.
The umbilical cord is clamped at least 1 minute after the baby is born. This tactic reduces the frequency of intraventricular hemorrhage in preterm pregnancies up to 37 weeks of gestation.
Control the state of the crumbs. CTG is done every hour for 40 minutes, auscultation - periodically.
General recommendations for prevention
You need to think about it from the first trimester. If you want to inform the baby, follow the advice of gynecologists.
- Take care of yourself. Rest, avoid nervous overload. Sleep at least 7 hours;
- Eat well. Eat foods rich in vitamins, exclude fast food, fatty, fried, spicy and salty foods from the diet. Give up coffee and strong tea;
- Observe the drinking regimen. Try not to feel thirsty - drink water every 2 hours. If you don't want to - don't force yourself;
- Avoid physical activity. Active training, hard work, general cleaning alone are taboo for a pregnant woman.
 Try not to go outside on ice - you may fall, you will strain your muscles - this can increase your tone and provoke premature birth;
Try not to go outside on ice - you may fall, you will strain your muscles - this can increase your tone and provoke premature birth; - Maintain personal hygiene. Wash your face after a bowel movement. Always wash and dry from front to back. This way you will not bring bacteria from the intestine into the vagina. Infections are provocateurs of premature birth;
- Lead a healthy lifestyle. Alcohol and cigarettes are taboo. Smoking pregnant women are predisposed to preterm labor. If you take medications on a regular basis, tell your gynecologist about it. Walk outdoors. Cancel active workouts in favor of leisurely walks in the park;
- Register at the antenatal clinic in the first trimester - at 6 ‒ 8 weeks. Visit a gynecologist, listen to him, take tests, undergo ultrasound, screenings;
- Be careful with sex. In the first trimester, it is better to limit or abstain from it as much as possible - the embryo must be fixed. With placenta previa and other pathologies, the gynecologist may forbid you to have intimate contacts - listen to him;
- Learn to understand your body.
 In the 2nd trimester, start listening to the baby: his movements, activity. Fix any changes, strange and unpleasant sensations - and talk about them to the doctor. In case of acute pain, contractions, spasms, blood, urgently call an ambulance - this may be a premature birth;
In the 2nd trimester, start listening to the baby: his movements, activity. Fix any changes, strange and unpleasant sensations - and talk about them to the doctor. In case of acute pain, contractions, spasms, blood, urgently call an ambulance - this may be a premature birth; - Maintain bed rest. A gynecologist can advise you to rest. For example, with increased uterine contractions, tone;
- Rest every hour. Sit in a chair, lift your legs up. This will relax the muscles, eliminate swelling;
- Be aware of the signs of preterm labor. In case of their threat, you will not miss a moment and consult a doctor. Perhaps the process can be stopped with the help of drugs. Treatment minimizes complications in the premature baby.
Preterm birth prevention
It is divided into 2 stages: before conception and after.
Preventive measures before conception
It is advisable to carry them out to mothers from the risk zone. The gynecologist limits intrauterine manipulations, such as curettage. During IVF, the number of embryos for transfer is regulated taking into account the age of the expectant mother and her health. Inform about the possibility of premature birth at conception through reproductive technologies.
The gynecologist limits intrauterine manipulations, such as curettage. During IVF, the number of embryos for transfer is regulated taking into account the age of the expectant mother and her health. Inform about the possibility of premature birth at conception through reproductive technologies.
Hydration is shown - enhanced drinking regimen. It improves fetoplacental blood flow and reduces the risk of preterm birth.
Eliminate infections. It is advisable to do this at the planning stage, since antibiotic treatment during gestation harms the fetus.
It is recommended to postpone the conception of a child soon after the birth of an older brother or sister. Mommy's body needs to recover from the previous pregnancy. It takes him at least 2 years to do this. During this time, the uterus will return to its previous state, strength, vitamin reserves and body reserves will be restored.
Vitamin complexes are prescribed for predisposition to preterm birth for planning and expectant mothers. Protein-rich dietary supplements are helpful. They strengthen the immune system, improve blood circulation, protect the pregnant woman from infections - and hence the child.
Protein-rich dietary supplements are helpful. They strengthen the immune system, improve blood circulation, protect the pregnant woman from infections - and hence the child.
Secondary prevention of early delivery
With the threat of premature birth, the condition of the pregnant woman is monitored at critical periods: from 2 to 12 and from 18 to 22 weeks. During these periods, it is better to stay in the hospital of the perinatal center. Doctors prescribe drugs to maintain and prolong pregnancy.
Therapy is selected on an individual basis.
With a short neck from 1 to 2.5 cm, progesterone suppositories are prescribed vaginally. The hormone is also shown in previous preterm births. This tactic reduces their risk by 35%. This is a natural hormone. It is efficient and safe. It is prescribed in the first trimester. Synthetic hormone is harmful: it can provoke gestational diabetes.
If there is a threat of early birth of the crumbs, sutures are placed on the neck. The expectant mother is out of the risk zone in this situation, stitches may not be applied.
The expectant mother is out of the risk zone in this situation, stitches may not be applied.
Another option is to install a pessary on the neck.
These methods reduce the statistics of premature births. But the mortality rate of newborns is not affected.
When carrying twins, circular or U-shaped sutures can be applied. In most cases, such tactics with a short neck in multiple pregnancies can provoke preterm labor. Vaginal progesterone is not prescribed.
For infections (for example, bacteriuria, gonococcus, syphilis, β-hemolytic streptococcus, bacterial vaginosis, chlamydia), antibiotic prophylaxis is prescribed. Depending on the diagnosis, penicillin, ampicillin, metronidazole, erythromycin, ceftriaxone, josamycin may be prescribed.
Terminals
Premature birth is one of the fears of many expectant mothers. Nobody is immune from this. But you can minimize the risks. Follow the recommendations of the gynecologist, take care of yourself, listen to your body, do not refuse to stay in the perinatal center.
Don't think bad. Modern medicine successfully nurses premature babies, reduces the risks of complications and consequences.
"His organs and systems are not ready" Why in Russia they are trying to save children who have almost no chance to survive and be healthy: Society: Russia: Lenta.ru
In Russia, it was proposed to register only from the seventh day babies who were born very early (less than 22 weeks) and with extremely low birth weight (less than 500 grams). This happened after a series of criminal cases that the Investigative Committee initiated against obstetricians. So, neonatologist Elina Sushkevich from Kaliningrad was accused of killing a 22-week-old boy. Why are they trying to save 500-gram children in Russia at all today, what are their chances of surviving and whether they can grow up healthy - Lenta.ru learned from the doctor of medical sciences, head of the scientific department of neonatology and pathology of young children at the Research Clinical Institute of Pediatrics named after Yu. E. Veltishchev Elena Keshishyan.
E. Veltishchev Elena Keshishyan.
***
Lenta.ru: Now the minimum criteria for saving premature babies are 22-23 weeks and 500 grams of weight. Why?
Elena Keshishyan : In order to understand the limits of possibilities both in technical terms (creating an environment close to intrauterine) and in terms of the maturity of the child's brain, which is capable of developing out of utero, attempts were made in the world to give birth to premature babies of different ages. The greatest successes in this were achieved by the Japanese. They tried out babies born at 20 weeks. That is, the approximate gestational age was five months. The Japanese succeeded, but in isolated cases. And they saw that in children born at this age there is no differentiation of the brain, division into gray and white matter. Roughly speaking, this process determines the ability to think, to feel. This is called higher nervous activity. It is this ability that distinguishes man from animals.
Therefore, guided by research data and on the basis of a humanistic idea, the World Health Organization has set this limit for human live birth - 23 weeks, which corresponds to approximately 500 grams of weight. This is the minimum age at which the brain can differentiate into gray and white matter. And, accordingly, there is hope that it will already be a human person with mental abilities.
Countries with technological capabilities, including Russia, have agreed that those born at this gestational age can legally be considered human. That is, they have all human rights, including medical care.
Since 2012, Russia has switched to the WHO criteria for nursing premature babies. How many of these children have been saved during this time?
As a percentage of all those born, this is minuscule. I don't have exact numbers. But I want to say that the body of children born almost half prematurely is very immature. And their survival rate, conditionally, is one in a hundred. Still, 22-23 weeks is not childbirth in the full sense. From the point of view of nature, this is a miscarriage, this is a critical situation that may be associated with the health of the mother or the sick child herself. Therefore, the readiness for independent existence in such fruits is close to zero. Even if we assume that the maximum efforts of doctors are thrown to save the child, all the necessary equipment is connected, the chance that he will get out is very small. In such an infant, the kidneys, gastrointestinal tract, heart and other organs may not work. This is a very, very complex, jewelry work of doctors.
Still, 22-23 weeks is not childbirth in the full sense. From the point of view of nature, this is a miscarriage, this is a critical situation that may be associated with the health of the mother or the sick child herself. Therefore, the readiness for independent existence in such fruits is close to zero. Even if we assume that the maximum efforts of doctors are thrown to save the child, all the necessary equipment is connected, the chance that he will get out is very small. In such an infant, the kidneys, gastrointestinal tract, heart and other organs may not work. This is a very, very complex, jewelry work of doctors.
One of the world's smallest surviving premature babies. Amilya Taylor was born in 2006 in Miami, USA. She spent only 22 weeks in the womb and was born with a weight of 284 grams and a height of 24 centimeters.
Photo: Baptist Health South Florida / Reuters
And dear?
Of course. A day in a well-equipped neonatal intensive care unit costs several thousand dollars. And to leave such a child, months are needed. But I want to emphasize that the number of survivors in this period is minimal. And it is minimal in almost all countries where the WHO criteria apply.
And to leave such a child, months are needed. But I want to emphasize that the number of survivors in this period is minimal. And it is minimal in almost all countries where the WHO criteria apply.
If these children are not viable, cost too much, then why were these criteria established?
The medical task here is not at all to save all the children who are born within five months. It is clear that there is not a single person who does not understand that this child is at risk of being blind, deaf and immobilized. The task of medicine in this situation is to acquire knowledge and experience.
Obstetricians learn how to prolong pregnancy as much as possible. There is a whole range of activities: prenatal diagnosis of genetic chromosomal diseases, various fetal malformations, identification of risk groups among pregnant women, their special monitoring, prenatal logistics and routing. They also hone the ability to properly take birth at this time. This must be done as carefully as possible and do not forget about the "golden hour". It is necessary to have time to give the child, without waiting until his condition worsens, what he could not get from his mother. That is, even if the child screamed, you need to understand that soon he will stop doing this and will not be able to breathe. The "golden hour" essentially determines whether or not there will be damage to brain cells. This means whether or not a child will have a full life.
It is necessary to have time to give the child, without waiting until his condition worsens, what he could not get from his mother. That is, even if the child screamed, you need to understand that soon he will stop doing this and will not be able to breathe. The "golden hour" essentially determines whether or not there will be damage to brain cells. This means whether or not a child will have a full life.
And the qualifications of resuscitators working with such children are growing today. All this led to an important point: the quality of nursing of children born a little later, at 26-28 weeks, has become much better. I see these babies regularly. And I can say that over time, many of them are no different from their peers.
And before?
About 30 years ago, about six or seven out of ten children would become severely disabled. And today I had three 26-week-old babies at my appointment. And everyone is developing quite well, there is a slight backlog, but they will catch up.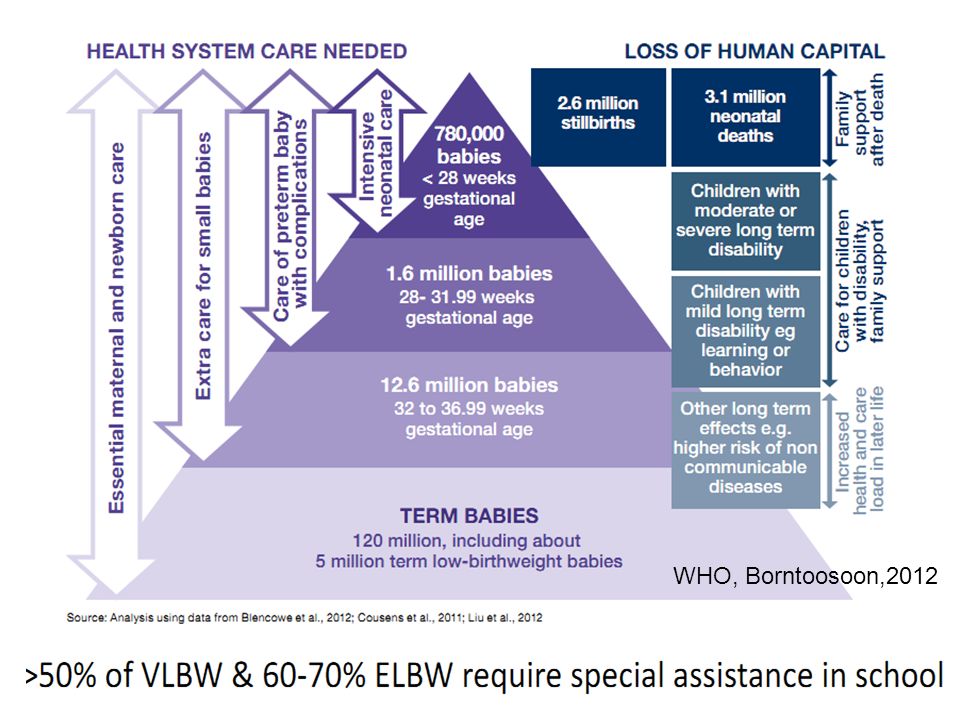 These children no longer have those possible malformations that, unfortunately, would have necessarily arisen in past years.
These children no longer have those possible malformations that, unfortunately, would have necessarily arisen in past years.
And this became possible thanks to the experience, the accumulation of knowledge about how such babies develop. There are no small things. This applies to everything - how to evaluate the heartbeat, how to interpret blood tests, and so on. Caring for a premature baby, both in the neonatal period and later, in the first or second year of life, is not the same as managing a normal, full-term baby. But knowledge allows timely adjustment of development, without even waiting for problems.
Photo: Science Photo Library / East News
It is important to understand that a premature baby is not a reduced copy of a normal one. This is a child who is forced to adapt to extrauterine life, when physiologically he should not do this. Its organs and systems are not prepared to function in the new conditions.
"This is painful love at the level of deep depression"
What do such children most often suffer from?
One of the typical pathologies is retinopathy of prematurity. In children, the mechanism that protects the eye from light has not yet matured. And they experience a real shock, suddenly falling into our bright world. Photons of light and the flow of oxygen begin to act on the retina, its vessels begin to grow rapidly, penetrate all the media of the eye, and, ultimately, exfoliate the retina, leading to total blindness. Earlier, even when I was just starting to work, although we knew about such a disease as retinopathy of prematurity, there were few children born and surviving at gestational ages of less than 30 weeks. Therefore, no one knew how to treat this disease. It's scary to remember, but premature babies were in wards with round-the-clock lighting. The light was needed so that doctors and nurses could observe the baby's condition and notice changes in time. At that time, six out of ten children whose birth weight was less than a kilogram went blind. Just then, the borders were opened in Russia, and we were amazed that in Europe, a maximum of two out of ten newborns had blindness.
In children, the mechanism that protects the eye from light has not yet matured. And they experience a real shock, suddenly falling into our bright world. Photons of light and the flow of oxygen begin to act on the retina, its vessels begin to grow rapidly, penetrate all the media of the eye, and, ultimately, exfoliate the retina, leading to total blindness. Earlier, even when I was just starting to work, although we knew about such a disease as retinopathy of prematurity, there were few children born and surviving at gestational ages of less than 30 weeks. Therefore, no one knew how to treat this disease. It's scary to remember, but premature babies were in wards with round-the-clock lighting. The light was needed so that doctors and nurses could observe the baby's condition and notice changes in time. At that time, six out of ten children whose birth weight was less than a kilogram went blind. Just then, the borders were opened in Russia, and we were amazed that in Europe, a maximum of two out of ten newborns had blindness.
But we started learning very quickly. Now in perinatal centers in all intensive care units for premature babies - twilight. The cuveuses are completely covered with dark blankets. The staff does not need to watch the baby all the time - all readings are automatically recorded by special devices. In good ICUs, nurses who approach babies have headlights. This is to avoid disturbing other children. In many intensive care units, a large “ear” hangs. If the decibel level in the room begins to exceed the allowable limit, the device lights up red.
After the birth of the child, every week they begin to look at the eyes with a special method. If there is proliferation of blood vessels, laser coagulation of the retina is performed. There are specialists in such operations in almost every major city.
Approximately 400-600 babies pass through me every year, born at 26-28 weeks. Over the past few years, not a single blind person has been among them. Although earlier in hospitals for such newborns it was necessary to open entire departments.
Is there any data on how many premature babies later became healthy?
Now, among premature babies born at five or six months (25-26 weeks of pregnancy), 25-30 percent become disabled. The same is true in developed countries. And even 20-30 years ago there were 75-80 percent of them.
The risks for these children are still very high. They require long-term observation and treatment. But still today they have incommensurably or better chances than before.
Photo: East News
Do unfortunate parents regret insisting on resuscitation at all costs?
As a doctor, no one has ever told me this. Naturally, the families had very different hopes for childbirth. In the doctor's office they cry, but they don't moan. These children are madly loved. But this is painful love at the level of deep depression. Probably, some of these mothers may think at night what would happen if they knew in advance how everything would turn out. Perhaps they voice this to their mothers, husbands, girlfriends .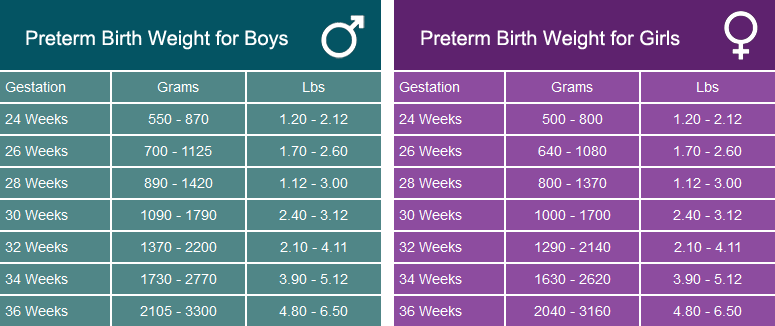 .. But not to doctors. This is where people prefer to stay.
.. But not to doctors. This is where people prefer to stay.
When a child is one or two years old, from a moral point of view, the situation is more difficult than in three days. Newborns are all wonderful bags, it is only then that children begin to differ from each other. These families have a very specific and difficult life. When a child lies at home, does not move, does not swallow, never looks at you, does not speak - this is very difficult. And parents need to be helped to turn their life into at least a relatively social one, not to make them outcasts.
What family support can I expect now?
When Russia switched to WHO standards, doctors began to say that if we started caring for such children, there would be a high incidence of cerebral palsy, mental retardation and other pathologies leading to severe disability. Without the development of a specialized service that will help such children, we will inflict enormous damage on a society that will not accept such an increase in the number of people with disabilities.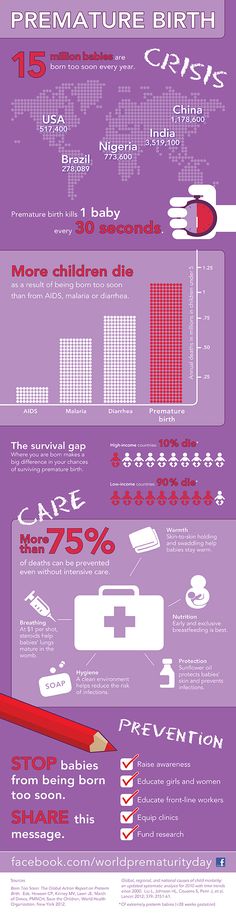 Then a follow-up system for premature babies began to develop, which leads them up to three years. Because in the usual polyclinic network there are not always doctors who understand how a child born with low or extremely low body weight grows and develops. In parallel with this, the system of medical rehabilitation is developing quite rapidly.
Then a follow-up system for premature babies began to develop, which leads them up to three years. Because in the usual polyclinic network there are not always doctors who understand how a child born with low or extremely low body weight grows and develops. In parallel with this, the system of medical rehabilitation is developing quite rapidly.
The worst situation is with the social service. Help for these children is minimal. Few people explain to families how to care for such a child, how to develop him, how to maintain motor skills. If in large cities at least some minuscule can be achieved, then what can we say about the province? All this turns one of the parents out of social life. There are no places where it would be possible to transfer such a child at least for a week, a month, so that the parents could have a little rest. Since the state has taken such a step, since we have legally recognized a 500-gram fetus as a person, then they themselves also need to act humanly in the future with his family.
Is there a support system in other countries?
I know that in Europe and in the USA it is built very well. The emphasis is not on medical rehabilitation, but on social rehabilitation. They have social workers who come and relieve these families of a significant part of their worries. Somewhere there are social centers where a child can be taken to a kindergarten. Moreover, they are zoned - parents do not need to go to the other end of the city.
Photo: Alexander Kondratyuk / RIA Novosti
“Even if it is clear that a child has pathologies that are incompatible with life, they must be saved to the last”
You say that some time ago, 1kg premature babies were also considered “non-residents”, but now they are quite promising. Is it possible that in 30-40 years the same can be said about 500-gram ones?
Indeed, even 30-40 years ago, when it was not possible to maintain breathing, children born before seven months of age survived very rarely.
Then, when some first mechanisms appeared, the bar was raised until the 28th week of pregnancy, which is about six months. But technological progress is always moving forward, and this has allowed us to further gradually reduce the age of survival. We can now at least partially simulate intrauterine conditions. For example, when a child is not born on time, he does not yet have a substance in his lungs, thanks to which he can breathe - surfactants. They can be introduced immediately at birth, start artificial ventilation of the lungs and thereby support gas exchange. It also became possible to give nutritional subsidies not through the gastrointestinal tract, but through a vein with special substances that are already ready for inclusion in metabolism. There are many other adaptations: the creation of a thermal regime, humidity close to intrauterine.
But technological progress is always moving forward, and this has allowed us to further gradually reduce the age of survival. We can now at least partially simulate intrauterine conditions. For example, when a child is not born on time, he does not yet have a substance in his lungs, thanks to which he can breathe - surfactants. They can be introduced immediately at birth, start artificial ventilation of the lungs and thereby support gas exchange. It also became possible to give nutritional subsidies not through the gastrointestinal tract, but through a vein with special substances that are already ready for inclusion in metabolism. There are many other adaptations: the creation of a thermal regime, humidity close to intrauterine.
Technologically, the frontier could move indefinitely. If desired, you can simulate a situation where a woman is not needed at all to bear a child. But I have already said that scientists have established that the age of 22-23 weeks is the minimum period at which the cells of the cerebral cortex can develop postnatally.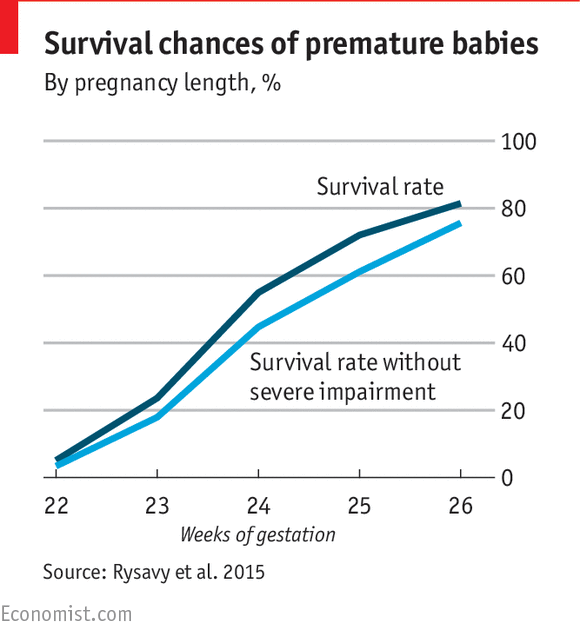 Still, the main criterion for the normal development of a child is not technological achievements, but the capabilities of the brain.
Still, the main criterion for the normal development of a child is not technological achievements, but the capabilities of the brain.
Is it true that they try to save all 500-gram children only in Russia and Turkey, and in other countries - only if the child has high chances for a normal life?
This is not true. In all countries where the WHO concept has been adopted, these children are subject to mandatory medical care. But there are nuances. If the baby was born between the 23rd and 25th weeks, parents can refuse resuscitation. To do this, in many countries there is a legal standard, reminiscent of the law on euthanasia.
There is a special service in perinatal centers. When it becomes clear that preterm labor has begun, representatives approach relatives - the father and, if possible, the mother. “We assume that a baby will be born with such and such parameters. In this case, there are such and such development risks ... You have the right to choose either full resuscitation or palliative care. And depending on what the parents decide, the doctors act.
And depending on what the parents decide, the doctors act.
Photo: Sergey Pyatakov / RIA Novosti
In Russia, you can also choose a palliative today, right?
This is not prescribed by law. Today, even if it is clear that a child has pathologies incompatible with life, they must be saved to the last. It happens that parents can sign a paper on their own that they would not like resuscitation, but this has no legal force. Parents can say, “Look, he is breathing, breathing. He opened his eyes. Let's revive him now!" And we lost time, which in this case is very important. This child initially has little chance, but it has become even less. And a situation may arise when parents accuse the doctors that their child was not specially treated, “talking teeth”.
The medical community is very concerned about this ambiguous position of doctors. And we have a number of proposals to solve the problem of their protection.
What exactly is offered?
Legislative initiative to allow parents to independently decide whether resuscitation care is appropriate for a child born between the 23rd and 25th weeks.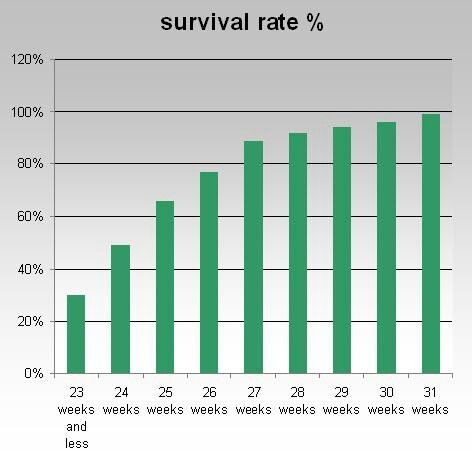 Naturally, all this should be discussed. It is necessary to involve the public in the discussion: these are lawyers, doctors, patient communities, representatives of religious denominations.
Naturally, all this should be discussed. It is necessary to involve the public in the discussion: these are lawyers, doctors, patient communities, representatives of religious denominations.
The Ministry of Health has now prepared new criteria for newborns born too early. In particular, it is proposed not to register such a child until he has lived seven days. Maybe this will fix the situation, protect doctors from murder charges?
There are a lot of pitfalls here. In Russia, there was a similar law on kilogram children. They were assisted from birth, but until the age of seven days the child was considered a fetus. If he died, then his mortality already went into other criteria, it was not considered the death of a newborn.
There are not many children born with extremely low rates, they simply cannot influence the demographic structure in any way. But if there is such a situation that you can not register for up to seven days, it seems to me that even more claims may arise against doctors regarding the failure to provide assistance.
These are very difficult questions. On the one hand, parents can say: you did not save the child. And others, on the contrary, will say: why are you torturing him in vain? And imagine a resuscitator who may be faced with an ethical choice: he has only one ventilator in the hospital, and a 23-week-old baby has been on it for the 40th day. And then a 32-week-old is born in the hospital. He needs help, hold him for three days on the device, and then the baby will cope on his own. In the first case, there will certainly be a disabled person. And in the second - almost healthy. And what should a doctor do?
Are you speaking theoretically now or do such situations occur?
We cannot have this in federal centers. We have enough equipment. I just illustrated with an example that the issue of nursing such children is the most difficult, all aspects are in common in it - from medical to ethical and religious.
Photo: Sergey Krasnoukhov / RIA Novosti
“The issue of infant mortality has always been political”
The issue of infant mortality has recently become political. Perhaps that is why patient scandals associated with maternity hospitals are developing so sharply?
Perhaps that is why patient scandals associated with maternity hospitals are developing so sharply?
The issue of infant mortality has always been political. This is a socially significant parameter that determines the position of the country in terms of development. In our country as a whole, infant mortality has significantly decreased over ten years. However, in the last two years the rate of decline has slowed down. Our government says it's bad. From the point of view of doctors, this is not entirely true. There are objective reasons that cannot be overcome with a swoop.
The primary decrease in mortality occurred due to the high-quality saturation of hospitals with equipment, due to the construction of perinatal centers. This gave immediate results. And now these figures have reached a plateau. Another thing is that a plateau, for example, in Kaliningrad, St. Petersburg, is one thing. There mortality rates are at the European level. That is very low. And there are regions where mortality is high - the Altai Territory, the Jewish Autonomous Region, Magadan. There is a lack of doctors, a lack of equipment, very long distances, routing difficulties. And it's very difficult to do anything about it.
There is a lack of doctors, a lack of equipment, very long distances, routing difficulties. And it's very difficult to do anything about it.
We are not compact Switzerland. We have a huge country with difficult geographical conditions. There are regions where we cannot even deliver a woman by helicopter. At one time I spent a lot of time in Chukotka, watching the obstetric service. Often, if a premature baby is born there, you will not help him in any way.
There are no good hospitals there?
Everything is there, but in one city - in Anadyr. And if a woman gave birth in another place, then often she can be cut off from the world. There are periods when even planes do not fly: a snowstorm, something else. And with routing too you will not guess. Because when you are expecting your first child, you are not going to give birth at 24 weeks. This is if the situation with childbirth repeats, then you can plan something, come closer to specialized care at the “dangerous” time . ..
..
Is it true that there have been more premature births lately?
No, their number is stable. This is approximately 7-10 percent of all newborns. Significantly increased their survival rate.
One of the most "inciting" topics on parenting Internet forums is that children who are "culled out" by nature have a bad effect on the quality of the gene pool. Is there any reason to think so?
In order for the “survivors” to influence the population, there must be a lot of them in percentage terms. For example, there are very few 26-week-olds - no more than two percent of all births. It can't affect anything in any way.
I know that at one time they discussed: what will happen if my child marries in the future someone who was once premature, will the gene pool suffer? Firstly, I can say that, as for children born after the 30th week, they are completely healthy, adapted and no different from others. They themselves give birth to beautiful healthy children, we have already seen many generations.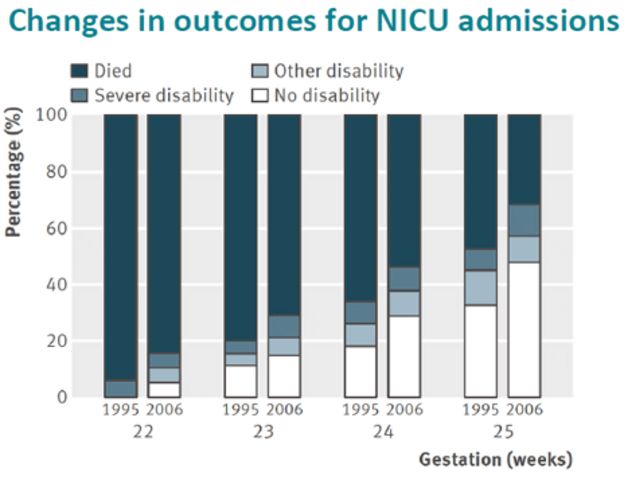


:strip_icc():format(webp)/kly-media-production/medias/2785562/original/028627600_1556001360-shutterstock_1019963743.jpg)









