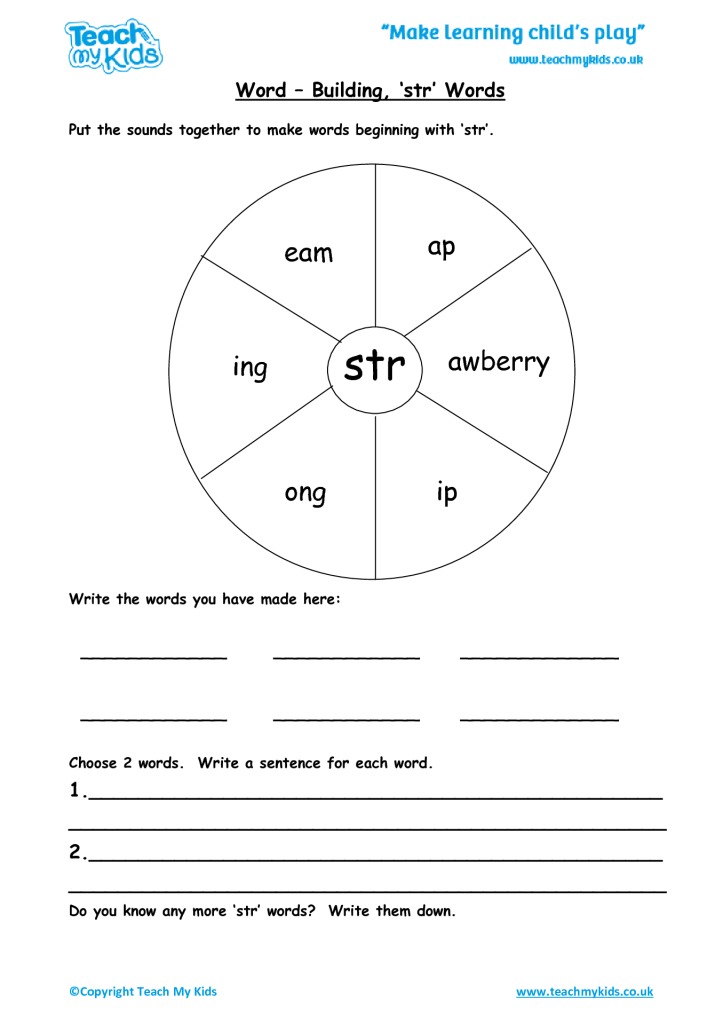
Pregnant during breastfeeding
Breastfeeding while pregnant | Pregnancy Birth and Baby
beginning of content4-minute read
Listen
You can carry on breastfeeding while you’re pregnant with your next child, without causing any harm to your toddler or your unborn baby. Here’s what you need to know if you decide to breastfeed while pregnant.
Is it safe to breastfeed while pregnant?
You might choose to breastfeed through your next pregnancy for several reasons. For example, you might unexpectedly fall pregnant while your first baby is still young (it is possible to fall pregnant while breastfeeding, even if your periods haven’t come back). Or you might not be ready to wean your toddler yet (weaning usually happens any time between birth and age 3).
Whatever the reason, it is usually perfectly safe to breastfeed while pregnant. Your body will carry on producing enough milk to nourish your older child, while your unborn baby will get all the nutrients they need from your body.
Breastfeeding does trigger mild contractions. These are safe in uncomplicated pregnancies, but if you are at risk of preterm labour — for example, if you are expecting twins or more, or if you have had a miscarriage or preterm birth in the past — then seek advice from your doctor or midwife.
Looking after your first child
Your breastmilk will still provide your first child with the nutrients they need. However, you are likely to produce less milk as your pregnancy progresses. Also, the content of your milk will change as you start to produce colostrum, and it might taste different. These changes might lead your older child to wean themselves at some point during your pregnancy. This often happens around the 5-month mark.
Colostrum is a natural laxative, so your older child’s poo might be more liquid than normal. This is nothing to worry about.
This is nothing to worry about.
If your older child is less than 1 year of age when you fall pregnant, keep a close watch to make sure they’re putting on enough weight after your milk changes. You may need to introduce extra feeds if they are still relying on breastmilk for their nutrition. Talk to your maternal child health nurse for advice.
How to look after yourself
Breastfeeding while pregnant can make your breasts sore and your nipples tender. You might find you are even more tired or experience worse morning sickness than you normally would during pregnancy.
These side effects are due to your pregnancy hormones. They may clear up after the first trimester, but for some women they last the entire pregnancy. It can help if you make sure your older child is attached well, or change your position while breastfeeding.
You can look after yourself by eating well, making sure you are well hydrated, and getting plenty of rest. You don’t need to take lots of vitamin or mineral supplements — your body will adjust to making breastmilk and nourishing your unborn baby at the same time.
After the baby is born
You can keep feeding your older child after the baby is born. This is called tandem feeding. Your newborn will still get all the colostrum they need. You don’t have to limit your older child to one side.
There are different ways of tandem feeding. You could feed both children at the same time (you might need some cushions to prop you up or you might find it easier lying down). Or you could feed the newborn first and then your older child.
You might find your older child wants to feed all the time because you have a lot of milk. If you like, you can limit their feeds. You might also find that your newborn has trouble coping with your let down reflex because you are producing so much milk. You could try feeding your older child first then attaching the newborn to the other breast after the milk has started to flow.
How to wean your older child
If you decide to wean your older child, it’s a good idea to do this while you’re still pregnant so they don’t have to cope with so many adjustments after the baby is born.
If you would like to encourage your older child to wean while you are pregnant, you could try weaning them slowly by delaying feeds or encouraging shorter feeds. If your child is old enough, explain to them that your breasts feel sore.
For more tips, see weaning.
More information
Call Pregnancy, Birth and Baby on 1800 882 436 to speak to a maternal child health nurse for advice and support.
Sources:
American Pregnancy Association (Breastfeeding while pregnant), Australian Breastfeeding Association (Breastfeeding through pregnancy and beyond)Learn more here about the development and quality assurance of healthdirect content.
Last reviewed: November 2020
Back To Top
Related pages
- Weaning
- Breastfeeding your baby
This information is for your general information and use only and is not intended to be used as medical advice and should not be used to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any medical condition, nor should it be used for therapeutic purposes.
The information is not a substitute for independent professional advice and should not be used as an alternative to professional health care. If you have a particular medical problem, please consult a healthcare professional.
Except as permitted under the Copyright Act 1968, this publication or any part of it may not be reproduced, altered, adapted, stored and/or distributed in any form or by any means without the prior written permission of Healthdirect Australia.
Support this browser is being discontinued for Pregnancy, Birth and Baby
Support for this browser is being discontinued for this site
- Internet Explorer 11 and lower
We currently support Microsoft Edge, Chrome, Firefox and Safari. For more information, please visit the links below:
- Chrome by Google
- Firefox by Mozilla
- Microsoft Edge
- Safari by Apple
You are welcome to continue browsing this site with this browser. Some features, tools or interaction may not work correctly.
Some features, tools or interaction may not work correctly.
Can you Get Pregnant While Breastfeeding?
The simple answer is yes, but it’s a little bit more complicated than that. In this post, we’ll unpack fertility while nursing, the chances of getting pregnant while breastfeeding, and how tracking your temperature holds the key to your fertility. Get comfy, grab a coffee, and join us as we answer ‘can you get pregnant while breastfeeding?’
This article is also available in Spanish.
How soon can you get pregnant after giving birth while breastfeeding?
If you’re not breastfeeding, you can get pregnant again as soon as three weeks after giving birth. However, a review of studies in 2011 found that most women did not ovulate until six weeks after giving birth, this is different if you choose to breastfeed. If you are exclusively breastfeeding (i.e. feeding your baby only breast milk) this can work as a method of birth control for up to six months after giving birth.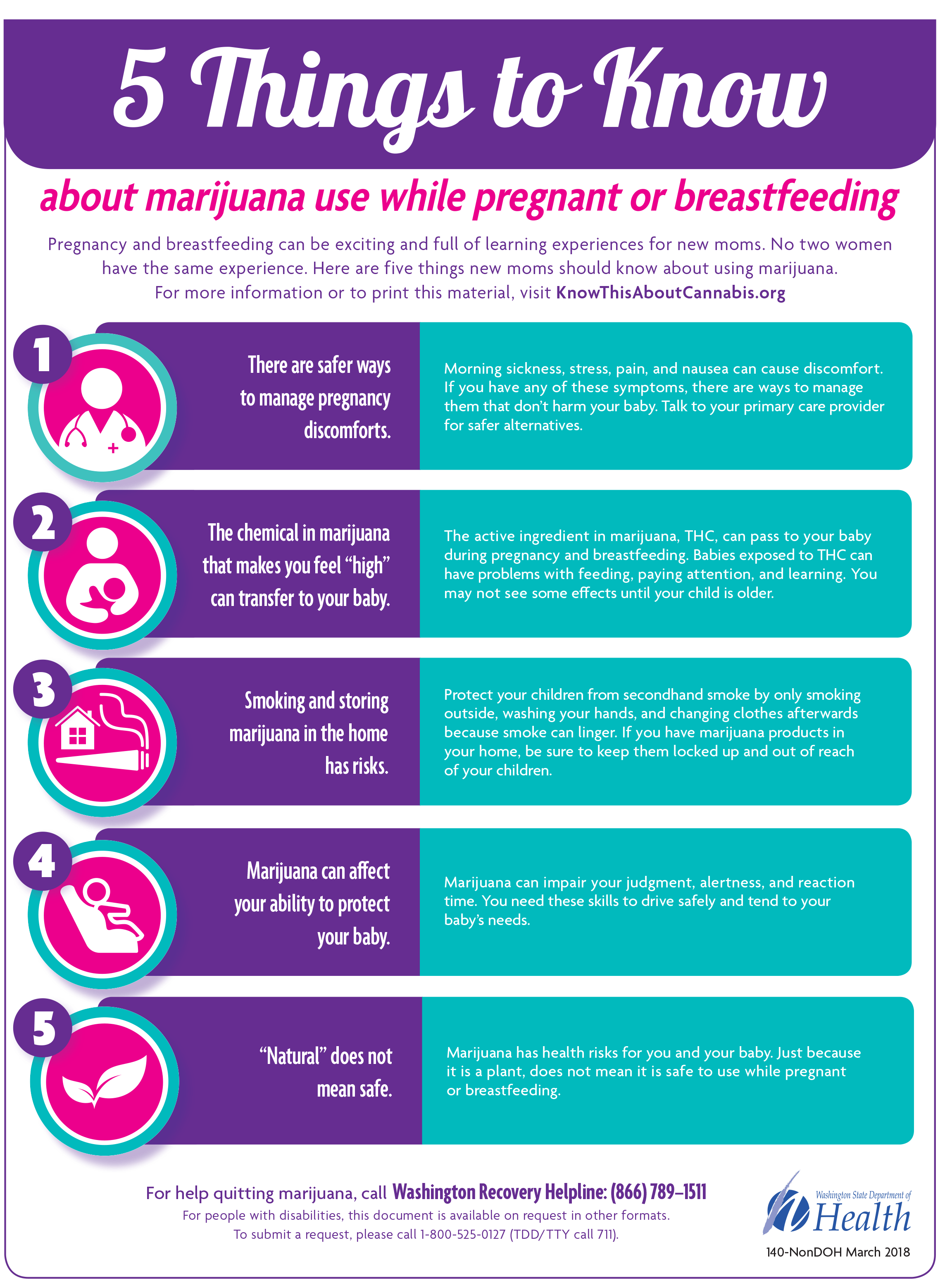
Unfortunately, it’s difficult to know when that first ovulation is going to arrive - you might not know it’s happened until you get your first period after pregnancy, by which point you’ve already been fertile. There are a couple of options available to help you detect ovulation. LH tests can detect a surge in hormones before ovulation, while taking your basal body temperature can confirm ovulation has happened.
Do I ovulate while breastfeeding?
You’re extremely unlikely to ovulate in the first weeks after giving birth, and if you are only feeding your baby breast milk then ovulation is likely to be delayed further. Of course, if you’re not ovulating, then you can’t get pregnant. However, since the signs of ovulation are extremely subtle, you likely won’t be able to tell when it’s coming and prepare for it.
You should get the opportunity to get contraceptive counseling with your doctor both before and after the birth of your baby. This is a good time to consider your birth control options and ask questions as you might want to try a different method of birth control than what you’ve used previously.
Chances of getting pregnant while breastfeeding
If used perfectly, breastfeeding as a birth control can be as much as 98% effective. This means you are only giving your baby breast milk, and only for the first six months. After this time the chances of becoming pregnant will increase. Of course, this varies from woman to woman, and while for some it might take a longer time for ovulation to resume, once it does there is a risk you might get pregnant.
If we look at birth control effectiveness, and take couples who have regular sex without using any protection there is an 85% chance they will fall pregnant within a year. Again, if you are breastfeeding exclusively, then ovulation is likely to be halted for the first months after giving birth and you can rely on breastfeeding as contraception during this time.
Pregnant while breastfeeding symptoms
The symptoms of early pregnancy can be hard to detect at the best of times, but if you’re looking after a little one and you’re having irregular cycles, it might be extra hard to detect a pregnancy. However, some symptoms of becoming pregnant while breastfeeding include:
However, some symptoms of becoming pregnant while breastfeeding include:
- Missed/late period
- Tiredness
- Nausea
- Sore breasts
The symptoms of early pregnancy are also very similar to those of PMS, so it can be a little confusing - especially if you have been experiencing irregular cycles after giving birth. If you’re in doubt, take a pregnancy test and consult with your doctor if you still have concerns.
Birth control and breastfeeding
You can use both hormonal and non-hormonal birth control while breastfeeding. However, for the first three weeks after giving birth you should avoid birth control containing the hormone estrogen. You might want to try a non-hormonal birth control method post-pregnancy - or if the pill has always worked for you, you might reach for the packet again. Either way, it’s a good time to have a discussion about the available methods with a healthcare professional.
Using Natural Cycles while breastfeeding
Natural Cycles is an FDA Cleared app and thermometer that helps you understand your own personal fertile window. Natural Cycles has three modes that adapt to your unique fertility journey: NC° Birth Control, NC° Plan Pregnancy and NC° Follow Pregnancy.
Natural Cycles has three modes that adapt to your unique fertility journey: NC° Birth Control, NC° Plan Pregnancy and NC° Follow Pregnancy.
Regardless of whether or not you choose to breastfeed, we recommend you start using Natural Cycles once you get your first period after giving birth. You can use Natural Cycles earlier, but keep in mind that until your first ovulation has been detected, NC° Birth Control will give you only red days.
We hope you’ve learned lots about breastfeeding, preventing pregnancy, and when you’re likely to ovulate again after giving birth. There’s lots more to learn about your body and whether you’re looking to plan or prevent pregnancy, Natural Cycles is a great tool that gives you personal insights into your own cycle. Are you ready to take control of your fertility?
Breastfeeding pregnancy: first signs
0-6 months
Article
0 reviews
Is it possible to get pregnant during lactation? There is an opinion that this is impossible. However, in practice, such cases are not uncommon. How to recognize the first signs of pregnancy while breastfeeding and what are the risks? More on this later in the article.
However, in practice, such cases are not uncommon. How to recognize the first signs of pregnancy while breastfeeding and what are the risks? More on this later in the article.
4 min. for reading Feb. 17, 2022
What happens in the body of a breastfeeding woman
Immediately after the birth of a child, the amount of a special hormone, oxytocin, increases in a woman's body. It causes the uterus to contract after childbirth and is also responsible for the production of breast milk. The more often you breastfeed your baby, the higher the concentration of oxytocin in the blood. Interestingly, the same hormone is a provocateur of lactational amenorrhea. In other words, it is he who is to blame for the absence of menstruation.
It is generally accepted that as long as you are breastfeeding your baby and there are no periods, it is impossible to get pregnant. After all, there is no menstruation, no ovulation. No ovulation - no egg ready for fertilization. Everything is logical. In some women, amenorrhea can last a year or two, and in some - a month. And to understand when it ended is extremely difficult. The main sign of the restoration of fertility (ability to reproduce) is menstruation. But menstruation begins two weeks after ovulation. Therefore, a sexually active nursing mother can become pregnant again at any time, without even knowing it.
No ovulation - no egg ready for fertilization. Everything is logical. In some women, amenorrhea can last a year or two, and in some - a month. And to understand when it ended is extremely difficult. The main sign of the restoration of fertility (ability to reproduce) is menstruation. But menstruation begins two weeks after ovulation. Therefore, a sexually active nursing mother can become pregnant again at any time, without even knowing it.
In addition to oxytocin, the amount of prolactin in the body of a nursing woman also increases. It blocks the growth of follicles and ovulation, but there is no guarantee that the follicle will not start growing. Therefore, it is also impossible to exclude the possibility of fertilization during this period.
Pregnancy while breastfeeding: how it is possible
Unplanned fertilization during lactation can occur, doctors say. The fact is that during breastfeeding, fertility decreases, but does not freeze completely. And if a woman is breastfeeding her baby on schedule rather than on demand, or if she alternates between breastfeeding and formula, the chances of getting pregnant again are quite high.
Longer intervals between feedings or complete weaning of the baby from the breast reduces the level of oxytocin and prolactin in the blood. This, in turn, starts the process of follicle growth and ovulation, the resumption of the menstrual cycle. If you are not planning a second child in the first year after the birth of the first, consider contraception.
Symptoms of pregnancy while breastfeeding
How to determine pregnancy during lactation? It's not easy enough. Breastfeeding mothers often simply do not notice the classic signs of the birth of a new life in the womb, attributing them to the natural postpartum state of the body. Indeed, insomnia, anxiety, excessive fatigue, nausea and back pain are quite typical phenomena for a woman who has recently given birth. And the most obvious symptom of pregnancy - the absence of menstruation - is completely written off, since they are not there anyway. How do you know if you are pregnant or not?
See also: The second child in the family
The first signs of pregnancy during breastfeeding may be:
- You are more tired than usual and constantly want to sleep.

This symptom can be attributed to sleep deprivation at night and baby care, which takes all your strength. However, if you notice that you are getting tired more than usual and in the morning you feel completely overwhelmed, even if the baby did not wake up at night, buy a pregnancy test.
- Often run to the toilet
This may be due to cystitis or kidney disease, or it may be one of the symptoms of a new pregnancy. Our body is designed in this way: as soon as a new life is born in the womb, the body increases blood flow to provide the unborn baby with all the necessary substances. This in turn causes the kidneys to produce more urine. Do you often go to the toilet? Make an appointment with a gynecologist and buy a pregnancy test.
- You feel pain in your chest
This may be due not only to stagnation of milk, but also to a new pregnancy. Changes in the amount of estrogen and progesterone cause those very painful sensations in the mammary glands. Are you seeing this symptom in yourself? Buy a test.
Are you seeing this symptom in yourself? Buy a test.
- You feel sick in the morning.
Anything can make you feel sick, including an increase in the concentration of hCG in the blood. This hormone increases during pregnancy. Take blood tests and take a pregnancy test. It will respond to changes in the composition of urine, even during lactation.
- The baby refuses to breastfeed.
When a new pregnancy occurs, the hormonal background changes. Because of this, the taste of breast milk changes, its consistency thickens and it becomes smaller. Therefore, your baby may refuse to take the breast, will be naughty and constantly demand to eat.
Pregnancy during lactation: pros and cons
Another baby in the family is a joy. You should be aware of the possible risks and positive aspects that a new pregnancy promises.
It is much easier to bring up children who are the same age as children with a difference in age of several years. They have a common daily routine, common interests and toys for two. It will be easier for you to adjust.
They have a common daily routine, common interests and toys for two. It will be easier for you to adjust.
Possible risks:
- A woman's body needs at least 2 years to fully recover after childbirth. A new child may simply not have enough resources for growth and development.
- If the delivery was by caesarean section, the uterus may not be ready. There is a risk of fetal death and irreversible consequences for the woman's health.
- Breastfeeding causes uterine contractions, which can cause miscarriage.
Keeping an unplanned pregnancy or not is entirely up to you. If the first pregnancy and first birth went without complications, it is quite possible to bear a healthy child.
Related Articles:
Sex During Pregnancy
Latest Reviews
Average Customer Rating
0 customer ratings
Snapshot of community ratings
- 5 0
- four 0
- 3 0
- 2 0
- one 0
Breastfeeding during pregnancy
There is a statistic that says that half of the women in the world become pregnant while breastfeeding their previous baby. And before each of them the question arises - whether to continue feeding, and how it will affect both children?
And before each of them the question arises - whether to continue feeding, and how it will affect both children?
Lactose-free milk Valio Eila UHT, enriched with vitamin D, 1.5%, 1 l More
Cottage cheese Valio "Soft", 4.5%, 180 g Read more
There is no clear answer about the advisability of continuing breastfeeding during pregnancy. It all depends on the health of the woman and the child, as well as the course of the waiting period for a new baby. The woman makes the decision herself, but after a mandatory consultation with the supervising doctor. The thing is that pregnancy, childbirth and feeding is a stressful period for the body of any woman. It has been proven that a young mother needs at least 2 years to fully recover. Having realized this information, it is easy to guess that a new pregnancy, when the first child is still quite a baby, is a tough situation for the body, almost an emergency. Mom's, not yet recovered, resources should now be enough for three. However, it is not uncommon for a woman to cope with an increased load, so the situation is not considered critical. Rather difficult.
Mom's, not yet recovered, resources should now be enough for three. However, it is not uncommon for a woman to cope with an increased load, so the situation is not considered critical. Rather difficult.
If, after discussing all the nuances with your gynecologist, you decide that feeding is not worth interrupting, make sure that your diet is as balanced and complete as possible. Take extra vitamins. During breastfeeding and bearing a baby, calcium, magnesium, iron, folic acid, and phosphorus are especially actively consumed. These elements must be supplied to the body of a young mother in sufficient quantities. Remember how important the presence of protein foods in your menu, because protein is the main building material for the fetus. Its main source is meat and dairy products. There is also a lot of protein in nuts and legumes. However, when adding them to the menu, remember that nuts are strong allergens, and legumes can cause gas in the baby.
You will not be able to feed during the entire period of pregnancy.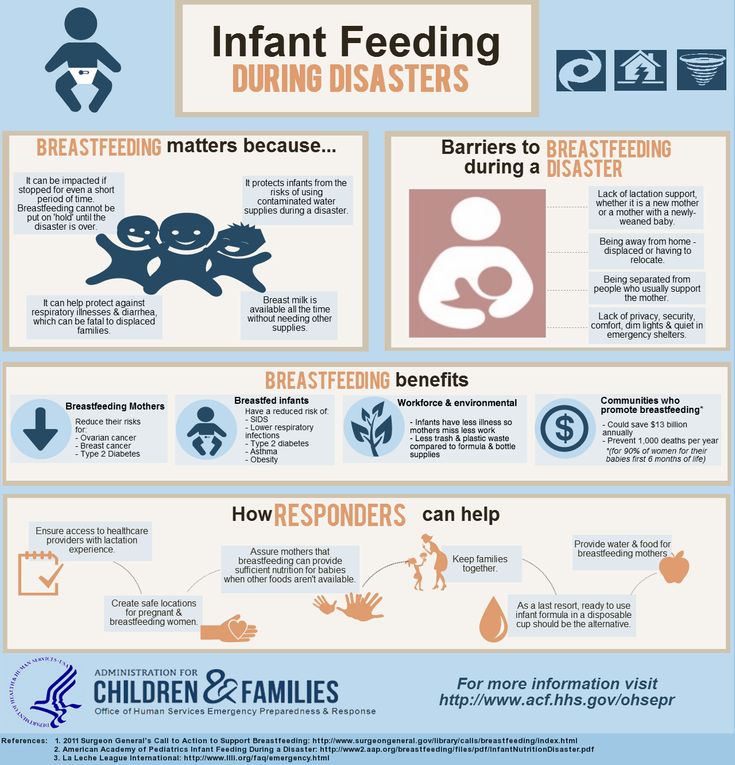 In obstetrics, there is a so-called "gold standard" - feeding stops no later than the 20th week. If there is a threat of miscarriage or other complications (for example, a decrease in hemoglobin levels or significant toxicosis), the process will have to be curtailed earlier. Sometimes the baby himself refuses the breast. In the mother's body, hormonal changes begin to occur that change the taste of milk. It becomes less tasty for the baby. Often a woman refuses to feed, because, naturally, her nipples become noticeably more sensitive and feeding begins to be accompanied by pain.
In obstetrics, there is a so-called "gold standard" - feeding stops no later than the 20th week. If there is a threat of miscarriage or other complications (for example, a decrease in hemoglobin levels or significant toxicosis), the process will have to be curtailed earlier. Sometimes the baby himself refuses the breast. In the mother's body, hormonal changes begin to occur that change the taste of milk. It becomes less tasty for the baby. Often a woman refuses to feed, because, naturally, her nipples become noticeably more sensitive and feeding begins to be accompanied by pain.
#PROMO_BLOCK#
Weaning crumbs from the breast due to a new pregnancy, of course, is an undesirable phenomenon. In some situations, to the extreme. It is very important to continue breastfeeding for at least 6 months for babies born prematurely, treated with antibiotics, retarded, prone to allergies or have gastrointestinal pathologies.
It is better, of course, to plan a new pregnancy, taking into account all the nuances of your health and the health of a little person. Have time to recover after such a resource-intensive period for the body. And be healthy!
Have time to recover after such a resource-intensive period for the body. And be healthy!
3.48 23
FoodShare:
Author: Reetta Tikanmäki
Palm oil in baby food
Infant milk formulas are made from cow's milk. However, in terms of fat composition, it differs significantly from that of the mother.
Read
Author: Ivargizova Oksana
How to choose milk formula for a baby
Breast milk is the best food for a newborn baby.