Pregnant bellies moving
Baby movements during pregnancy | Pregnancy Birth and Baby
Baby movements during pregnancy | Pregnancy Birth and Baby beginning of content5-minute read
Listen
An exciting landmark of pregnancy is when you first feel the sensation of your baby move. These movements are a sign that your baby is healthy and well.
Every baby is unique, it is important for you to get to know your baby’s individual movement pattern. At any point, if you are concerned about your babies movement pattern, please contact your midwife or doctor immediately. Do not wait until the next day.
When will I feel my baby moving?
You will start to feel your baby moving between 16 and 24 weeks of pregnancy. The location of your placenta will not affect this sensation. It is more common for women having their second or subsequent pregnancies to feel their baby move earlier.
If you have not felt your baby move by 24 weeks, you should contact your doctor or midwife.
What will my baby’s movement feel like?
The type of movement you feel will depend on what your baby is doing and their stage of growth and development. Each baby is different, with some more active than others.
The first sensations you feel may be a fluttering (like 'butterflies in your tummy'), swishing, rolling or tumbling sensation or a tiny kick. These early sensations are often called ‘quickening’. As your pregnancy progresses, the movements will become more distinct, and you will more easily feel their kicks, jabbing and elbowing.
How often should I feel my baby moving?
There is no set number of movements you should feel. As you start to feel your baby's movements more consistently, usually by 24 to 28 weeks of pregnancy, you will get to know what a normal pattern of movement is for you and your baby. You should then consistently feel your baby's movements right up until they are born and even during labour.
You should then consistently feel your baby's movements right up until they are born and even during labour.
Babies tend to move more at certain times of day – they may be more active while you sleep, and sleep while you’re awake. Usually, unborn babies sleep for 20-40 minutes cycles (occasionally up to 90 minutes), and they don’t move when they’re asleep.
Should I track my baby’s movement?
There are no set number of movements a baby should have, so counting kicks or recording on a chart is no longer recommended.
It is important to make time regularly each day to notice your babies’ movements. If you are busy or not paying attention it can be easy to miss this very important signal from your baby. If you are busy or working, it may be helpful to set reminders for yourself to check in with your baby.
Common myths about baby movements
- It is not true that babies move less towards the end of pregnancy.
- Having something to eat or drink does not help stimulate your baby to move.
What should I do if my baby stops moving?
If you haven't felt any movement from your baby by 24 weeks, see your doctor or midwife.
At any stage of your pregnancy, if you are concerned about your baby's movements, contact your midwife or doctor immediately. Do not wait until the next day. A slowing down of movement may be a sign that your baby is unwell.
Your doctor or midwife will invite you into the hospital and check your baby’s heart rate using a CTG Machine. In some instances, you may also have an ultrasound.
What do I do if I have recurring concerns about my baby’s movements?
Remember you are the one who knows your baby’s movements best. It is important that whenever you are concerned about your baby’s movements to contact your doctor or midwife.
Contact your doctor or midwife again even if you have already seen them about your baby’s movements previously.
Speak to a maternal child health nurse
Call Pregnancy, Birth and Baby to speak to a maternal child health nurse on 1800 882 436 or video call. Available 7am to midnight (AET), 7 days a week.
Available 7am to midnight (AET), 7 days a week.
Sources:
Australian Family Physician (Decreased fetal movements: a practical approach in primary care setting), Mater Mother's Hospital (Pregnancy – your baby’s movements and what they mean), Raising Children Network (16 weeks pregnant), Miracle Babies (Your baby’s movements), PSANZ SANDA (Baby's Movements), Red Nose (Decreased fetal movements (DFM)), Centre of Research Excellence in Stillbirth (Movement matters)Learn more here about the development and quality assurance of healthdirect content.
Last reviewed: April 2022
Back To Top
Related pages
- Fetal heart rate monitoring
- Giving birth - early signs of labour
Need more information?
Baby movements during pregnancy | Red Nose Australia
When you're pregnant, you should feel baby move. But what does it means when those movements change, become less frequent, or stop?
But what does it means when those movements change, become less frequent, or stop?
Read more on Red Nose website
Your Baby's Movements - Miracle Babies
This information has been graciously reproduced with permission from Australian and New Zealand Stillbirth Alliance to provide information about what your baby’s movements mean
Read more on Miracle Babies Foundation website
Reducing the risk of stillbirth | Raising Children Network
You can reduce risk of stillbirth by eating well and exercising, sleeping on your side, and seeking immediate medical help if your baby’s movements change.
Read more on raisingchildren.net.au website
How baby learns in the womb - Ngala
From the moment of conception your baby is developing rapidly
Read more on Ngala website
Pregnant women not to trust smartphone heart rate apps
Pregnant women are being urged not to rely on smartphone apps that claim to listen to your baby's heartbeat.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Pregnancy at week 16
At week 16, you might begin to feel your baby moving, while hormonal changes may be affecting your libido.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Premature birth & premature babies | Raising Children Network
This essential guide for parents of premature babies covers gestational age, premature birth risk factors, premature labour and premature development.
Read more on raisingchildren.net.au website
Fetal alcohol spectrum disorder (FASD) | Raising Children Network
Drinking alcohol in pregnancy can cause birth defects and long-term health problems for babies and children. This is fetal alcohol spectrum disorder (FASD).
This is fetal alcohol spectrum disorder (FASD).
Read more on raisingchildren.net.au website
24 weeks pregnant | Raising Children Network
24 weeks pregnant? In this pregnancy week by week guide, find out how your baby is growing, how your body is changing and how to look after yourself.
Read more on raisingchildren.net.au website
7 weeks pregnant: Key points | Parenthub
7 Weeks Pregnant 7 weeks pregnant: Key points ( 2 votes, average: 5
Read more on Parenthub website
Disclaimer
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is not responsible for the content and advertising on the external website you are now entering.
Need further advice or guidance from our maternal child health nurses?
1800 882 436
Video call
- Contact us
- About us
- A-Z topics
- Symptom Checker
- Service Finder
- Linking to us
- Information partners
- Terms of use
- Privacy
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is funded by the Australian Government and operated by Healthdirect Australia.
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is provided on behalf of the Department of Health
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby’s information and advice are developed and managed within a rigorous clinical governance framework. This website is certified by the Health On The Net (HON) foundation, the standard for trustworthy health information.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
This information is for your general information and use only and is not intended to be used as medical advice and should not be used to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any medical condition, nor should it be used for therapeutic purposes.
The information is not a substitute for independent professional advice and should not be used as an alternative to professional health care. If you have a particular medical problem, please consult a healthcare professional.
Except as permitted under the Copyright Act 1968, this publication or any part of it may not be reproduced, altered, adapted, stored and/or distributed in any form or by any means without the prior written permission of Healthdirect Australia.
Support this browser is being discontinued for Pregnancy, Birth and Baby
Support for this browser is being discontinued for this site
- Internet Explorer 11 and lower
We currently support Microsoft Edge, Chrome, Firefox and Safari. For more information, please visit the links below:
For more information, please visit the links below:
- Chrome by Google
- Firefox by Mozilla
- Microsoft Edge
- Safari by Apple
You are welcome to continue browsing this site with this browser. Some features, tools or interaction may not work correctly.
When can you feel baby move? Fetal movement explained.
Feeling your baby kicking is one of the highlights of pregnancy. But when can you feel your baby move, and what does baby movement feel like? The truth is that baby kicks are more like flutters at first, and you may not feel your baby move until halfway through pregnancy. But by the third trimester, your baby will be making some big moves that are impossible to ignore.
When can you feel baby move?
You probably won't feel your baby kick until sometime between 16 and 22 weeks, even though they started moving at 7 or 8 weeks. (You may have witnessed the acrobatics if you've already had an ultrasound. )
)
Veteran moms tend to notice those first subtle kicks, also known as "quickening," earlier than first-time moms because it's easier to distinguish your baby's kicks from other belly rumblings (such as gas) if you've been pregnant before.
Your build may have something to do with when you'll be able to tell a left jab from a hunger pang: Thin women tend to feel movement earlier and more often.
Once you can feel your baby moving, it will probably be a few more weeks until your partner can feel the baby kick.
What does baby movement feel like?
Women have described the early sensation as feeling like popcorn popping, a goldfish swimming around, or butterflies fluttering. You might think those first gentle taps or swishes in your belly are gas, but you'll recognize the difference once you start feeling them more regularly.
Once you've reached your third trimester, you won't be able to ignore your baby's jabs, rolls, and kicks. As they get larger, you may see a pointy elbow or knee moving across your belly or feel a full-on somersault.
Every pregnancy is different, so it's hard to say exactly what you'll feel and when, but here's a rough guide.
Baby movement at 16 to 19 weeks
You'll probably notice faint and fluttery feelings in your womb around this time. If you've been pregnant before, you'll be more familiar with this sensation and quicker to identify your baby's movements.
If this is your first pregnancy, it may take a bit longer before you realize that those gentle bubbling or popping sensations are actually your baby moving! It may be easier to feel your baby when you're sitting quietly or lying down.
Baby movement at 20 to 23 weeks
You may notice gentle kicks and jabs. As the weeks go by, you'll gradually feel stronger and more frequent movements, and you'll come to recognize your baby's unique pattern of activity. If you don't feel your baby moving, tell your doctor or midwife.
You may find that your baby becomes more lively as the day goes on, kicking, squirming, and somersaulting the most in the evening when you're relaxed. Some moms notice their baby moving a lot right after they eat, especially if they have a sugary treat. But studies haven't found a link between what you eat and your baby's activity level.
Some moms notice their baby moving a lot right after they eat, especially if they have a sugary treat. But studies haven't found a link between what you eat and your baby's activity level.
Baby movement at 24 to 28 weeks
Your amniotic sac now contains up to 26 ounces of fluid. This gives your baby plenty of space to move around freely, so you may feel like your little one is doing elaborate acrobatics routines in your womb. Limb movements may feel punchy, while whole-body movements may be smoother. You may even notice your baby jumping at sudden noises, or you may feel repetitive jerking movements when your baby gets hiccups.
Baby movement at 29 to 31 weeks
Your baby is likely to be making smaller, sharper, more definite movements, such as strong kicks and pushes. You may also occasionally feel a shaky movement, like a shiver, as your baby shakes a hand, shoulder, or elbow.
Depending on how your baby is positioned, you may feel the kicks up under your ribs, in the center or side of your belly, or very low in your pelvis. Some women report kicks to their cervix – which feel uncomfortable but are totally normal. Don't worry, no matter how strong your baby's kicks, they're safe inside and won't do any damage.
Some women report kicks to their cervix – which feel uncomfortable but are totally normal. Don't worry, no matter how strong your baby's kicks, they're safe inside and won't do any damage.
Baby movement at 32 to 35 weeks
As your baby grows and has less room to move, you may notice that the type of movement you feel changes, perhaps becoming slower but lasting longer.
Baby movement at 36 to 40 weeks
As you approach your due date, your baby will get larger and won't have enough room for dramatic somersaults. After they move to a head-down position in preparation for birth, you may feel kicks in new places, like underneath your ribs on one side or the other. Your baby's movements may feel slower, but also harder and stronger. Jabs from their arms and kicks from their legs may feel uncomfortable or even painful.
It's normal to notice a change in the types of movement you feel in late pregnancy. But you should still be feeling your baby move right up until and even during labor itself.
How often should I feel my baby kicking?
At first, noticeable kicks will be few and far between. You may feel several movements one day and then none the next. Although your baby is moving and kicking regularly, many of their movements just aren't strong enough for you to feel yet. But those reassuring kicks will become stronger and more regular later in the second trimester or early in the third trimester.
Don't worry if your experience is different from your friends'. Every baby has their own pattern of activity, and as long as your baby's usual activity level doesn't decrease, chances are they're doing just fine.
Do I need to keep track of my baby kicking?
Once you're feeling kicks regularly, pay attention to how often your baby moves, and let your healthcare provider know right away if you ever notice your baby's activity level slow down.
Less movement in the third trimester may signal a problem, and your provider may want you to have a nonstress test, an ultrasound measurement of amniotic fluid, and possibly a biophysical profile to make sure everything is okay. (You may also have these tests as a routine part of your prenatal care if you have a high-risk pregnancy.)
(You may also have these tests as a routine part of your prenatal care if you have a high-risk pregnancy.)
Some providers recommend that in your third trimester, you spend some time each day counting your baby's kicks. There are lots of ways to do this, so ask your provider for specific instructions.
For example, your provider may suggest that you choose a time of day when your baby tends to be active. (Ideally, you'll want to do the counts at roughly the same time each day.) Then sit quietly or lie on your side and time how long it takes to feel 10 distinct movements – kicks, elbow jabs, and whole body movements all count. If you don't feel 10 movements in two hours, call your healthcare provider.
Learn more:
- Pregnancy symptoms you should never ignore
- Sex during pregnancy
advertisement | page continues below
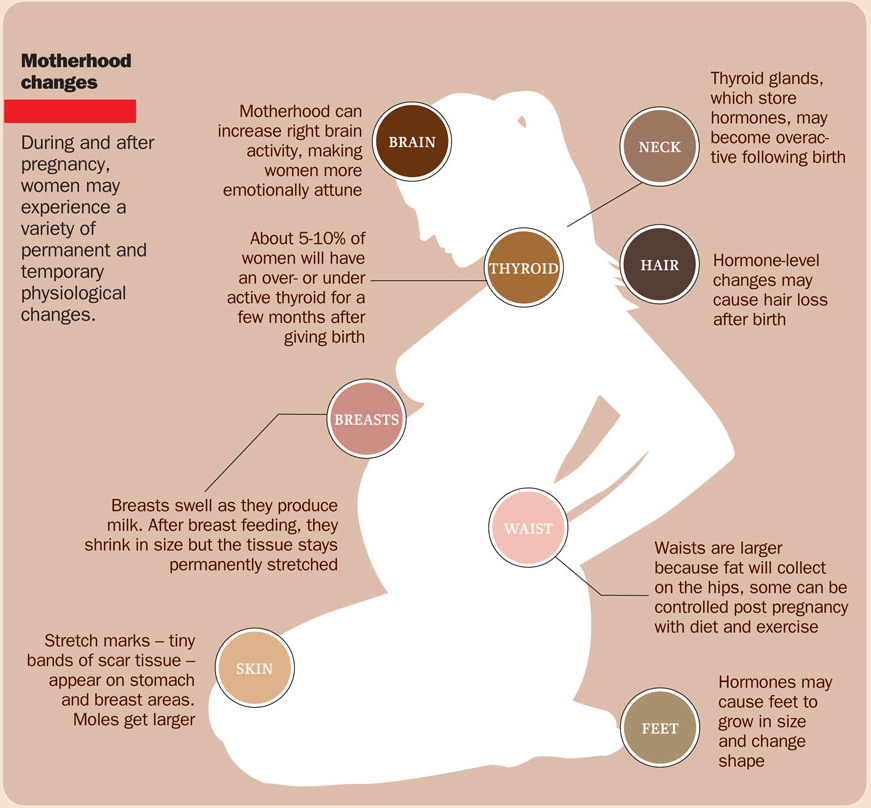
Physiological changes in the body during pregnancy
From the very first days of pregnancy, a woman's body undergoes profound transformations. These transformations are the result of the coordinated work of almost all body systems, as well as the result of the interaction of the mother's body with the child's body. During pregnancy, many internal organs undergo significant restructuring. These changes are adaptive in nature, and, in most cases, are short-lived and completely disappear after childbirth. Consider the changes in the basic systems of the vital activity of a woman's body during pregnancy.
These transformations are the result of the coordinated work of almost all body systems, as well as the result of the interaction of the mother's body with the child's body. During pregnancy, many internal organs undergo significant restructuring. These changes are adaptive in nature, and, in most cases, are short-lived and completely disappear after childbirth. Consider the changes in the basic systems of the vital activity of a woman's body during pregnancy.
The respiratory system during pregnancy works hard. The respiratory rate increases. This is due to an increase in the need of the mother and fetus for oxygen, as well as in the limitation of the respiratory movements of the diaphragm due to an increase in the size of the uterus, which occupies a significant space of the abdominal cavity.
The mother's circulatory system during pregnancy has to pump more blood to ensure an adequate supply of nutrients and oxygen to the fetus. In this regard, during pregnancy, the thickness and strength of the heart muscles increase, the pulse and the amount of blood pumped by the heart in one minute increase. In addition, the volume of circulating blood increases. In some cases, blood pressure increases. The tone of blood vessels during pregnancy decreases, which creates favorable conditions for increased supply of tissues with nutrients and oxygen. During pregnancy, the network of vessels of the uterus, vagina, and mammary glands decreases sharply. On the external genitalia, in the vagina, lower extremities, there is often an expansion of the veins, sometimes the formation of varicose veins. Heart rate decreases in the second half of pregnancy. It is generally accepted that the rise in blood pressure over 120-130 and a decrease to 100 mm Hg. signal the occurrence of pregnancy complications. But it is important to have data on the initial level of blood pressure.
In addition, the volume of circulating blood increases. In some cases, blood pressure increases. The tone of blood vessels during pregnancy decreases, which creates favorable conditions for increased supply of tissues with nutrients and oxygen. During pregnancy, the network of vessels of the uterus, vagina, and mammary glands decreases sharply. On the external genitalia, in the vagina, lower extremities, there is often an expansion of the veins, sometimes the formation of varicose veins. Heart rate decreases in the second half of pregnancy. It is generally accepted that the rise in blood pressure over 120-130 and a decrease to 100 mm Hg. signal the occurrence of pregnancy complications. But it is important to have data on the initial level of blood pressure.
And changes in the blood system. During pregnancy, blood formation increases, the number of red blood cells, hemoglobin, plasma and bcc increases. BCC by the end of pregnancy increases by 30-40%, and erythrocytes by 15-20%. Many healthy pregnant women have a slight leukocytosis. ESR during pregnancy increases to 30-40. Changes occur in the coagulation system that contribute to hemostasis and prevent significant blood loss during childbirth or placental abruption and in the early postpartum period.
Many healthy pregnant women have a slight leukocytosis. ESR during pregnancy increases to 30-40. Changes occur in the coagulation system that contribute to hemostasis and prevent significant blood loss during childbirth or placental abruption and in the early postpartum period.
Kidneys work hard during pregnancy. They secrete decay products of substances from the body of the mother and fetus (the waste products of the fetus pass through the placenta into the mother's blood).
Changes in the digestive system are represented by increased appetite (in most cases), cravings for salty and sour foods. In some cases, there is an aversion to certain foods or dishes that were well tolerated before the onset of pregnancy. Due to the increased tone of the vagus nerve, constipation may occur.
The most significant changes, however, occur in the genitals of pregnant women. These changes prepare the woman's reproductive system for childbirth and breastfeeding.
The uterus of a pregnant woman increases significantly in size. Its mass increases from 50 g - at the beginning of pregnancy to 1200 g - at the end of pregnancy. The volume of the uterine cavity by the end of pregnancy increases by more than 500 times! The blood supply to the uterus is greatly increased. In the walls of the uterus, the number of muscle fibers increases. The cervix is filled with thick mucus that clogs the cavity of the cervical canal. The fallopian tubes and ovaries also increase in size. In one of the ovaries, there is a "corpus luteum of pregnancy" - a place for the synthesis of hormones that support pregnancy. Walls vaginas will loosen and become more elastic. External genitalia (labia minor and major), also increase in size and become more elastic. The tissues of the perineum are loosened. In addition, there is an increase in mobility in the joints of the pelvis and a divergence of the pubic bones. The changes in the genital tract described above are of extremely important physiological significance for childbirth. Loosening the walls, increasing the mobility and elasticity of the genital tract increases their throughput and facilitates the movement of the fetus through them during childbirth.
The changes in the genital tract described above are of extremely important physiological significance for childbirth. Loosening the walls, increasing the mobility and elasticity of the genital tract increases their throughput and facilitates the movement of the fetus through them during childbirth.
Skin in the genital area and in the midline of the abdomen usually becomes darker in color. Sometimes "stretch marks" form on the skin of the lateral parts of the abdomen, which turn into whitish stripes after childbirth.
Mammary glands increase in size, become more elastic, tense. When pressing on the nipple, colostrum (first milk) is released.
Changes in the bone skeleton and muscular system . An increase in the concentration of the hormones relaxin and progesterone in the blood contributes to the leaching of calcium from the skeletal system. This helps to reduce the rigidity of the joints between the bones of the pelvis and increase the elasticity of the pelvic ring. Increasing the elasticity of the pelvis is of great importance in increasing the diameter of the internal bone ring in the first stage of labor and further reducing the resistance of the birth tract to fetal movement in the second stage of labor. Also, calcium, washed out of the mother's skeletal system, is used to build the skeleton of the fetus.
Increasing the elasticity of the pelvis is of great importance in increasing the diameter of the internal bone ring in the first stage of labor and further reducing the resistance of the birth tract to fetal movement in the second stage of labor. Also, calcium, washed out of the mother's skeletal system, is used to build the skeleton of the fetus.
It should be noted that calcium compounds are washed out of all bones of the maternal skeleton (including the bones of the foot and spine). As shown earlier, a woman's weight increases during pregnancy by 10 -12 kg. This additional load against the background of a decrease in bone stiffness can cause foot deformity and the development of flat feet. A shift in the center of gravity of the body of a pregnant woman due to an increase in the weight of the uterus can lead to a change in the curvature of the spine and the appearance of pain in the back and pelvic bones. Therefore, for the prevention of flat feet, pregnant women are advised to wear comfortable shoes with low heels. It is advisable to use insoles that support the arch of the foot. For the prevention of back pain, special physical exercises are recommended that can unload the spine and sacrum, as well as wearing a comfortable bandage. Despite an increase in calcium loss by the bones of the skeleton of a pregnant woman and an increase in their elasticity, structure and bone density (as is the case with osteoporosis in older women).
Changes in the nervous system . In the first months of pregnancy and at the end of it, there is a decrease in the excitability of the cerebral cortex, which reaches its greatest degree by the time of the onset of childbirth. By the same period, the excitability of the receptors of the pregnant uterus increases. At the beginning of pregnancy, there is an increase in the tone of the vagus nerve, in connection with which various phenomena often occur: changes in taste and smell, nausea, increased salivation, etc.
Active endocrine glands there are significant changes that contribute to the proper course of pregnancy and childbirth. Changes in body weight. By the end of pregnancy, a woman's weight increases by about 10-12 kg. This value is distributed as follows: fetus, placenta, membranes and amniotic fluid - approximately 4.0 - 4.5 kg, uterus and mammary glands -1.0 kg, blood - 1.5 kg, intercellular (tissue) fluid - 1 kg , an increase in the mass of adipose tissue of the mother's body - 4 kg.
Changes in body weight. By the end of pregnancy, a woman's weight increases by about 10-12 kg. This value is distributed as follows: fetus, placenta, membranes and amniotic fluid - approximately 4.0 - 4.5 kg, uterus and mammary glands -1.0 kg, blood - 1.5 kg, intercellular (tissue) fluid - 1 kg , an increase in the mass of adipose tissue of the mother's body - 4 kg.
Boy or girl: what do signs say?
- Claudia Hammond
- BBC Fututre
Folk signs say that the sex of the unborn child can be determined by the shape of the belly of a pregnant woman, by hanging a wedding ring mother. But only one of these signs really works.
If a pregnant woman has a neat small belly that protrudes forward and is shaped like a ball, she will give birth to a boy. The belly is large and wide - this is most likely a girl. This is what popular belief says.
Every mother-to-be will tell you how excited her friends and relatives are to offer many ways to determine the sex of her baby.
Even people who barely know each other can't help but make comments and statements, judging by the shape of your belly, you have a boy or a girl - because they have never been wrong. If only it were that easy.
What affects the shape and size of the pregnant belly. The first is the size of the child. Indeed, boys at birth are on average slightly larger than girls, therefore, the belly of the boy's future mother may also be slightly larger. But this difference in weight is so insignificant that it can hardly affect the shape of the abdomen.
Second is the position of the fetus. If the baby is turned backwards along the mother's belly, then the belly will look a little pointed. If the baby's back is closer to the mother's spine, her belly will look flatter.
Image copyright, Thinkstock
Image caption,Is it a brother or a sister?
But just as the position of a child does not depend on whether it is a boy or a girl, so the determination of sex by the shape of the abdomen is a myth.
Skip the podcast and continue
Podkast
SHO TS BULO
Golovna Tizhnya, Yaku explain our magazines
VIPAS
Kinets Podkast
It is good if the form of the abdomen does not give out the gender of the baby, what then will be in relation to other folk ones?
One of them suggests hanging a wedding ring on a thread above the stomach and following which way it will rotate. But how can the fetus influence the movement of things that are outside? So, this is nonsense, as well as sex determination by the food that a woman prefers during pregnancy.
Others say that if a woman is expecting a girl, she is more nauseous in the morning, because she has a double dose of female hormones in her body, which causes nausea. But this is also a myth. Morning sickness is typical for the first 12 weeks of pregnancy, when the embryo is still very small and the level of sex hormones that enter the mother's blood is low.
The only reliable way to find out the sex of the baby is with an ultrasound, amniocentesis (amniotic fluid test), or chorionic biopsy, where a sample of cells is taken from the placenta.
The last two tests are used only when there is a risk of serious illness, which depends on the sex of the child. An ultrasound is the most common way to determine the sex of an heir, however, some hospitals keep parents in the dark.
But there is one sign that allows you to determine the sex quite accurately. For centuries, midwives have joked: if the birth is long and difficult, it's a boy.
Image copyright, Thinkstock
Image caption,Although technology has long been used to accurately determine the sex of a child, parents always listen to folk signs
It turns out that there is more truth in this sign than in others. Irish scientists have a study of 8,000 deliveries in Dublin hospitals from 1997 to 2000.