Pregnant bad heartburn
Indigestion and heartburn in pregnancy
Indigestion, also called heartburn or acid reflux, is common in pregnancy. It can be caused by hormonal changes and the growing baby pressing against your stomach.
You can help ease indigestion and heartburn by making changes to your diet and lifestyle, and there are medicines that are safe to take in pregnancy.
Symptoms of indigestion and heartburn
Symptoms of indigestion and heartburn include:
- a burning sensation or pain in the chest
- feeling full, heavy or bloated
- burping or belching
- feeling or being sick
- bringing up food
Symptoms usually come on soon after eating or drinking, but there can sometimes be a delay between eating and developing indigestion.
You can get symptoms at any point during your pregnancy, but they are more common from 27 weeks onwards.
Things you can do to help with indigestion and heartburn
Changes to your diet and lifestyle may be enough to control your symptoms, particularly if they are mild.
Eat healthily
You're more likely to get indigestion if you're very full.
If you're pregnant, it may be tempting to eat more than you would normally, but this may not be good for you or your baby.
Find out more about a healthy diet in pregnancy and foods to avoid.
Change your eating and drinking habits
You may be able to control your indigestion with changes to your eating habits.
It can help to eat small meals often, rather than larger meals 3 times a day, and to not eat within 3 hours of going to bed at night.
Cutting down on drinks containing caffeine, and foods that are rich, spicy or fatty, can also ease symptoms.
Keep upright
Sit up straight when you eat. This will take the pressure off your stomach. Propping your head and shoulders up when you go to bed can stop stomach acid coming up while you sleep.
Stop smoking
Smoking when pregnant can cause indigestion, and can seriously affect the health of you and your unborn baby.
When you smoke, the chemicals you inhale can contribute to your indigestion. These chemicals can cause the ring of muscle at the lower end of your gullet to relax, which allows stomach acid to come back up more easily. This is known as acid reflux.
Smoking also increases the risk of:
- your baby being born prematurely (before week 37 of your pregnancy)
- your baby being born with a low birthweight
- sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS), or "cot death"
There's lots of help available to stop smoking. Talk to your midwife or call the NHS Smokefree helpline on 0300 123 1044. Find out more about stopping smoking in pregnancy.
Talk to your midwife or call the NHS Smokefree helpline on 0300 123 1044. Find out more about stopping smoking in pregnancy.
Avoid alcohol
Drinking alcohol can cause indigestion. During pregnancy, it can also lead to long-term harm to the baby. It's safest to not drink alcohol at all in pregnancy.
Find out more about alcohol and pregnancy
When to get medical help
See your midwife or GP if you need help managing your symptoms or if changes to your diet and lifestyle do not work. They may recommend medicine to ease your symptoms.
You should also see your midwife or GP if you have any of the following:
- difficulty eating or keeping food down
- weight loss
- stomach pains
Your midwife or GP may ask about your symptoms and examine you by pressing gently on different areas of your chest and stomach to see whether it's painful.
If you're taking prescription medicines
Speak to your GP if you're taking medicine for another condition, such as antidepressants, and you think it may be making your indigestion worse. They may be able to prescribe an alternative medicine.
Never stop taking a prescribed medicine unless you're advised to do so by your GP or another qualified healthcare professional who's responsible for your care.
Medicines for indigestion and heartburn
Medicines for indigestion and heartburn during pregnancy include:
- antacids – to neutralise the acid in your stomach (some are available over the counter from a pharmacist)
- alginates – to relieve indigestion caused by acid reflux by stopping the acid in your stomach coming back up your gullet
You may only need to take antacids and alginates when you start getting symptoms.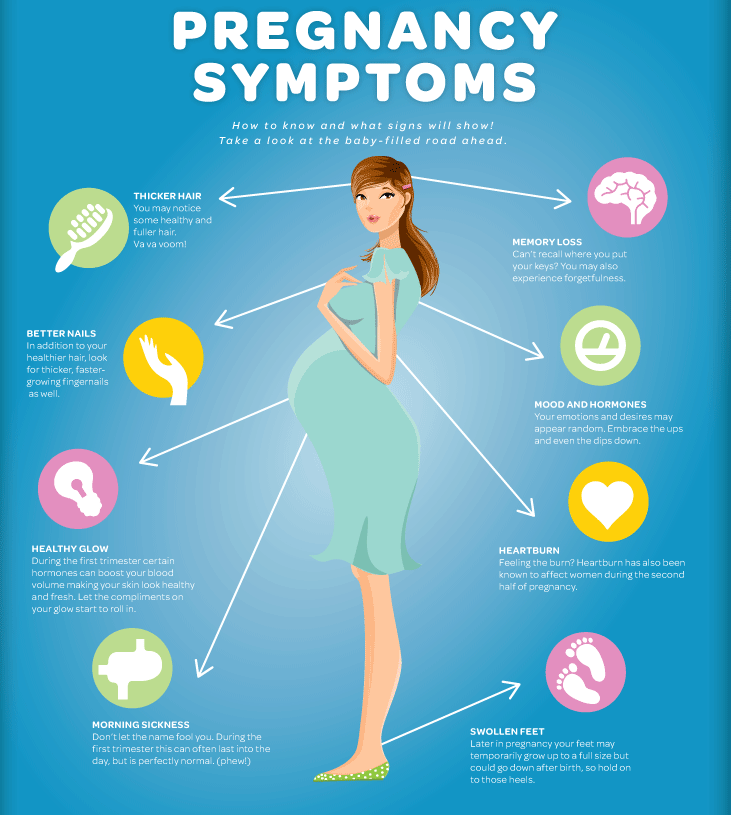 However, your GP may recommend taking them before symptoms come on – for example, before a meal or before bed.
However, your GP may recommend taking them before symptoms come on – for example, before a meal or before bed.
If you're taking iron supplements as well as antacids, do not take them at the same time. Antacids can stop iron from being absorbed by your body.
If antacids and alginates do not improve your symptoms, your GP may prescribe a medicine to reduce the amount of acid in your stomach. 2 that are widely used in pregnancy and not known to be harmful to an unborn baby are:
- ranitidine – a tablet you take twice a day
- omeprazole – a tablet you take once a day
Causes of indigestion in pregnancy
Symptoms of indigestion come when the acid in your stomach irritates your stomach lining or your gullet. This causes pain and a burning feeling.
When you're pregnant, you're more likely to have indigestion because of:
- hormonal changes
- the growing baby pressing on your stomach
- the muscles between your stomach and gullet relaxing, allowing stomach acid to come back up
You may be more likely to get indigestion in pregnancy if:
- you had indigestion before you were pregnant
- you've been pregnant before
- you're in the later stages of pregnancy
Video: Eating well on a budget
In this video, a dietitian gives advice on how to eat healthily on a budget.
Media last reviewed: 13 January 2021
Media review due: 13 January 2024
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) and Heartburn During Pregnancy
Written by WebMD Editorial Contributors
Medically Reviewed by Nivin Todd, MD on August 26, 2022
In this Article
- Symptoms of Heartburn During Pregnancy
- Causes of Heartburn During Pregnancy
- Prevention of Heartburn During Pregnancy
- Treatment of Heartburn During Pregnancy
- Heartburn Medication to Avoid During Pregnancy
More than half of pregnant women get serious heartburn, particularly during their second and third trimesters. Heartburn, also called acid indigestion, is an irritation or burning sensation of the esophagus (the tube that carries food and liquid to your stomach when you swallow). It’s caused by stomach contents that reflux (come back up).
Symptoms of Heartburn During Pregnancy
If you have heartburn while you’re pregnant, you may:
- Feel burning or pain in your chest or throat, especially after you eat
- Have sensations of fullness, heaviness, or bloating
- Burp or belch
- Have a sour or bitter taste in your mouth
- Cough or have sore throat
Causes of Heartburn During Pregnancy
Heartburn in pregnancy may happen because of changing hormone levels, which can affect the muscles of the digestive tract.
Pregnancy hormones can cause your lower esophageal sphincter (the muscular valve between the stomach and esophagus) to relax, allowing stomach acids to flow back up into your esophagus. Also, as your baby grows, your enlarged uterus can crowd the abdomen, pushing stomach acids upward. Although it's rare, gallstones can also cause heartburn during pregnancy.
Prevention of Heartburn During Pregnancy
Some tips that may help you cut down on heartburn during your pregnancy include:
- Eat several small meals each day instead of three large ones.
- Eat slowly.
- Avoid fried, spicy, or rich (fatty) foods or any foods that seem to cause relaxation of the lower esophageal sphincter and increase the risk of heartburn.
- Don’t smoke tobacco or drink alcohol, which can make heartburn symptoms worse.
- Drink less while eating. Drinking large amounts while eating may increase the risk of acid reflux and heartburn.
- Don't lie down directly after eating.

- Keep the head of your bed higher than the foot of your bed. Or place pillows under your shoulders to help prevent stomach acids from rising into your esophagus.
- Wear loose-fitting clothing. Tight-fitting clothes can increase the pressure on your stomach and abdomen.
- Try to avoid constipation.
Treatment of Heartburn During Pregnancy
If your heartburn won’t go away, see your doctor. They may prescribe or recommend OTC medications that are safe to take during pregnancy. Heartburn usually disappears following childbirth.
Medications may include:
Over-the-counter antacids such as calcium carbonate or magnesium hydroxide. These are generally safe to use during pregnancy. You may find that liquid heartburn relievers are more effective in treating heartburn, because they coat the esophagus.
h3 blockers. These medications block chemical signals that produce stomach acid. They include cimetidine (Tagamet) and famotidine (Pepcid, Zantac 360), and they’re available in over the counter and prescription strengths.
Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs). Like h3 blockers, these drugs help cut down on stomach acid. PPIs, which include lansoprazole (Prevacid) and omeprazole (Prilosec), are available over the counter and by prescription.
If you take iron supplements, talk to your doctor before you take a PPI or h3 blocker. These medications can make the supplements less effective.
Heartburn Medication to Avoid During Pregnancy
Talk to your doctor before taking any antacids. Some contain ingredients that may harm you or your baby. Be sure to not to take these medications:
Ranitidine. In 2020, the FDA stopped sales of an h3 blocker called ranitidine (the ingredient in older Zantac products) because it was contaminated with a cancer-causing agent. If you take OTC ranitidine, stop your use. If you have a prescription for ranitidine, talk to your doctor about other options before you stop your medication.
Heartburn / GERD Guide
- Overview & Facts
- Symptoms & Complications
- Diagnosis & Tests
- Treatment & Care
- Living & Managing
How to get rid of heartburn during pregnancy
Boltovsky Vladimir Anatolievich
Pediatrician, Nephrologist
Children's clinic "Mother and Child" Samara
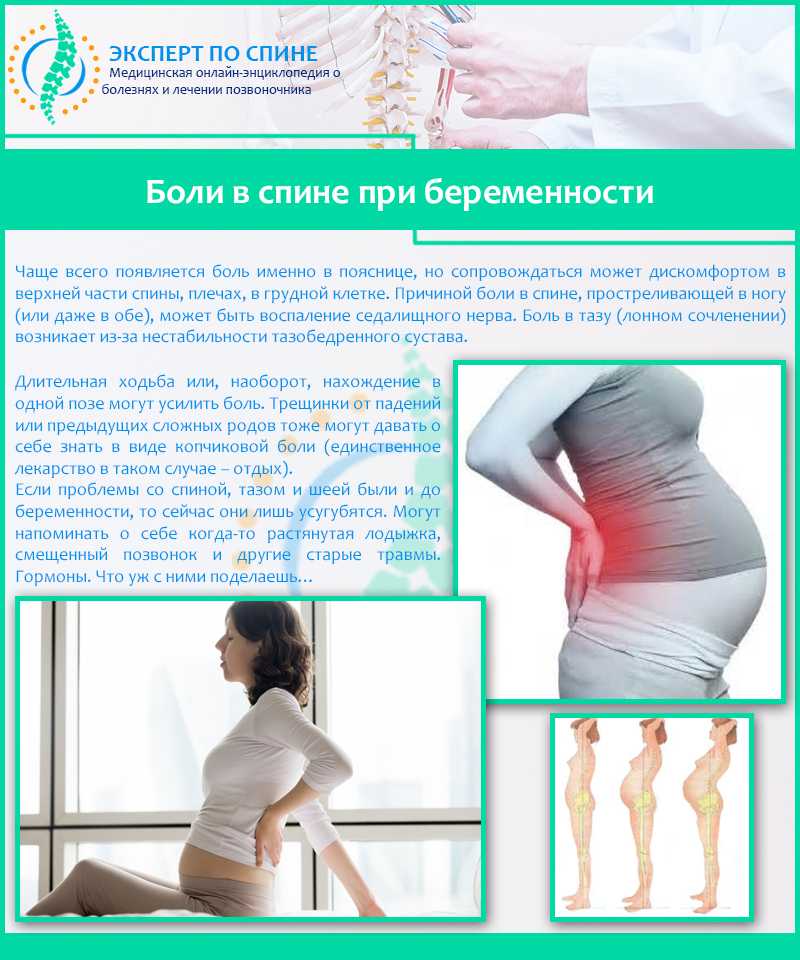
If, after some time after eating, the expectant mother has a feeling of warmth or burning behind the sternum, then this is heartburn.
Not all antacids can be used during pregnancy. For example, preparations containing bismuth nitrate ( Vikalin , etc.), should not be taken by expectant mothers due to the fact that the effect of bismuth on the development of the child is unknown.
Heartburn usually appears after the 20th week of pregnancy and torments the expectant mother until the birth of the child.
what she looks like
If, after some time after eating, the expectant mother has a feeling of warmth or burning behind the sternum, then this is heartburn. And most often these unpleasant sensations occur in the evening. Heartburn usually appears after the 20th week of pregnancy and torments the expectant mother until the birth of the child. According to popular belief, she worries the expectant mother when the baby's hair grows. In fact, heartburn occurs due to the fact that the acidic contents of the stomach are thrown into the lower esophagus. This happens because during pregnancy, the muscular sphincter, located between the esophagus and stomach, relaxes under the influence of the hormone progesterone.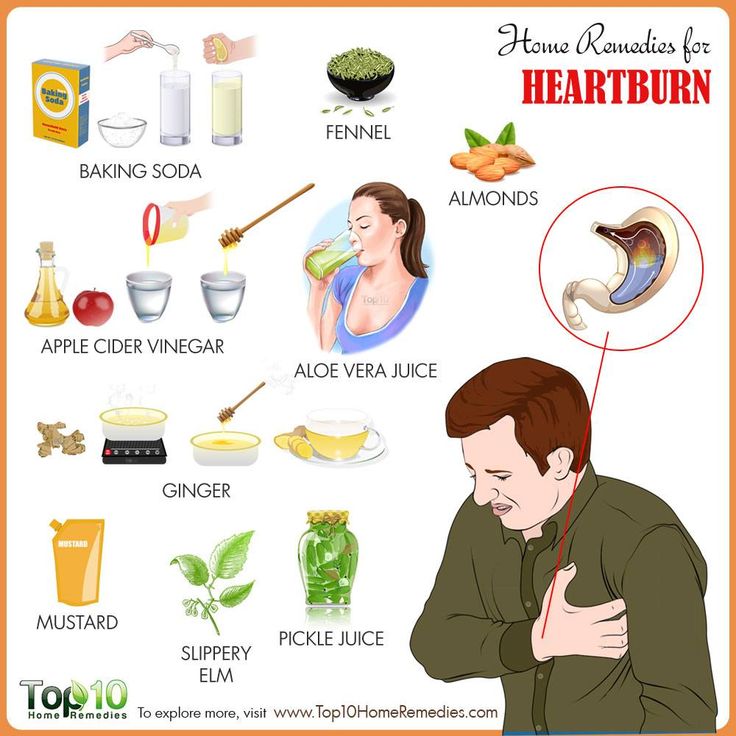 Another cause of heartburn is an enlarged uterus (and it just increases greatly after the 20th week) presses on neighboring organs: the stomach, intestines. As a result, the volume of the stomach decreases and even the usual amount of food leads to its overflow and the reflux of food back into the esophagus.
Another cause of heartburn is an enlarged uterus (and it just increases greatly after the 20th week) presses on neighboring organs: the stomach, intestines. As a result, the volume of the stomach decreases and even the usual amount of food leads to its overflow and the reflux of food back into the esophagus.
what will help
If heartburn occurs infrequently and does not bother you much, then in order to reduce its symptoms, you just need to eat right and change your lifestyle. The simplest thing that helps with heartburn:
- Fractional meals: eat often 5-6 times a day at intervals of 1.5-2 hours and in small portions. Eat slowly, chewing your food thoroughly.
- Healthy food: Avoid fatty and fried foods and chocolate. All these products provoke additional relaxation of the esophageal sphincter.
- Heartburn usually occurs within the first two hours after eating, so do not lie down immediately after eating.
- Sleep with the head of the bed raised by adding another pillow.

simple remedies
The simplest thing that helps with heartburn is some foods. For example, a burning sensation behind the sternum perfectly removes low-fat milk, just a few sips - and heartburn goes away or is significantly reduced. Ice cream works the same way, as well as grapefruit and carrot juices. You can get rid of heartburn by eating nuts (walnuts, hazelnuts, almonds), but they are more likely to prevent heartburn than to eliminate an existing one. And ordinary seeds help someone cope with heartburn. In general, the expectant mother can only choose the right product for herself, but here, as with food in general, one must observe the measure. No need to eat a block of ice cream or a package of seeds every day, drink glasses of juice or endlessly eat nuts. Of course, they will help, but ice cream and nuts are high in fat and calories, and juices in large quantities hit the pancreas and increase sugar levels. A small amount of one of some product will completely cope with an attack of heartburn.
be careful
Some medications, especially antispasmodics (drugs that relieve spasms of the smooth muscles of the internal organs), such as No-shpa , Papaverine , relax the esophageal sphincter and thus contribute to heartburn. Some herbs, such as mint, also work. Tight clothing under the chest (elastic bands, belts), a change in body position (tilts, turns) can also cause heartburn.
In general, every expectant mother can carefully observe herself and identify her personal cause of heartburn, then it will be much easier to deal with it.
old remedy
Baking soda is often used to treat heartburn. It really helps to relieve the unpleasant burning sensation very quickly, but at the same time it does not last long. In addition, when soda interacts with gastric juice, carbon dioxide is formed, which irritates the stomach - as a result, new portions of hydrochloric acid are produced and heartburn resumes. It turns out that a teaspoon of soda in a glass of water instantly relieves heartburn, but in response to taking soda, the next time the heartburn attack will be even stronger.
safe drugs
During pregnancy you can use the so-called antacids (Maalox, Almagel, Rennie, Gaviscon) . They contain salts of magnesium and aluminum, they neutralize the acid of gastric juice, form a protective film on the wall of the stomach, increase the tone of the lower esophageal sphincter. True, sometimes some antacids cause constipation (due to calcium or aluminum salts), and magnesium, on the contrary, has a laxative effect. Therefore, long-term use of these drugs is not worth it. Antacids can absorb other medications, so there should be some time between taking antacids and other medications.
Despite the fact that heartburn is quite unpleasant for the mother, it does not affect the child in any way. Start the fight against heartburn with proper nutrition, and you may not need medication.
Make an appointment
to the doctor - Boltovsky Vladimir Anatolyevich
Children's Clinic "Mother and Child" Samara
Children's First Aid KitChildren's NephrologyFor ChildrenVaccination CalendarComprehensive examination before kindergartenComprehensive examination before schoolNeprologyPediatricsInformation for childrenUrology
By clicking on the send button, I consent to the processing of personal data
why it occurs and how to get rid of it
The prevalence of heartburn increases from the 20th week of pregnancy and covers the vast majority of women by the time of delivery. Usually, the symptom is provoked by the "heavy" food eaten the day before, so it can be repeated many times throughout the day, and one episode of heartburn lasts minutes or even hours. In addition to heartburn itself, there may be belching of air, pain behind the sternum, and swallowing is disturbed 1 .
Usually, the symptom is provoked by the "heavy" food eaten the day before, so it can be repeated many times throughout the day, and one episode of heartburn lasts minutes or even hours. In addition to heartburn itself, there may be belching of air, pain behind the sternum, and swallowing is disturbed 1 .
Causes of heartburn in pregnant women
There are a number of factors that predispose to heartburn during pregnancy. These include2:
episodes of heartburn
before pregnancy
multiple pregnancy
overweight before or
significant weight gain
during pregnancy
The main causes of heartburn in pregnant women are divided into: mechanical (physical) and hormonal 2 .
The mechanical cause of is an increase in the size of the pregnant uterus. The growing uterus displaces and compresses other organs in the abdomen, which increases intra-abdominal pressure. At the same time, the stomach is “squeezed” to the diaphragm, the locking mechanism that separates the esophagus from the stomach is weakened, which predisposes to the development of hiatal hernia. In general, the described mechanisms often lead to acid reflux - the backflow of gastric contents into the esophagus, accompanied by heartburn 2 .
The growing uterus displaces and compresses other organs in the abdomen, which increases intra-abdominal pressure. At the same time, the stomach is “squeezed” to the diaphragm, the locking mechanism that separates the esophagus from the stomach is weakened, which predisposes to the development of hiatal hernia. In general, the described mechanisms often lead to acid reflux - the backflow of gastric contents into the esophagus, accompanied by heartburn 2 .
Hormonal causes include an increase in progesterone production. Progesterone reduces the tone of the smooth muscles of the uterus, protecting the pregnancy from the threat of termination. In the same way, progesterone acts on other smooth muscle organs. Under the influence of hormones during pregnancy, there may be a decrease in the tone of the lower esophageal sphincter and a weakening of intestinal motility, including due to a violation of the sensitivity of intestinal receptors to biologically active substances - serotonin and histamine. As a result, food can linger in the stomach, increasing the likelihood of acid reflux. Due to the weakening of peristalsis, there is also a risk of constipation and changes in the intestinal microflora 2 .
As a result, food can linger in the stomach, increasing the likelihood of acid reflux. Due to the weakening of peristalsis, there is also a risk of constipation and changes in the intestinal microflora 2 .
First trimester
A complaint in pregnant women at an early stage appears due to toxicosis with repeated vomiting, when the esophageal mucosa is constantly irritated by vomit 1 .
First trimester
A complaint in pregnant women at an early stage appears due to toxicosis with repeated vomiting, when the esophageal mucosa is constantly irritated by vomit 1 .
Second and third trimesters
In the second and third trimesters, symptoms may occur due to reduced pressure in the esophagogastric sphincter and functional failure of the upper stomach 1 . Also, in late pregnancy, the factors provoking heartburn may include an increase in intra-abdominal pressure due to an increase in the volume of the uterus and an increase in the level of gastrin in the blood of pregnant women 1 .
Second and third trimesters
In the second and third trimesters, symptoms may occur due to decreased pressure in the esophagogastric sphincter and functional insufficiency of the upper stomach 1 . Also, in late pregnancy, the factors provoking heartburn may include an increase in intra-abdominal pressure due to an increase in the volume of the uterus and an increase in the level of gastrin in the blood of pregnant women 1 .
postpartum period
Unfortunately, heartburn symptoms do not always disappear completely after childbirth: about 20% of women who experience heartburn during pregnancy also experience it in the postpartum period 2 . It is possible that the development of heartburn in the postpartum period may be associated with the lactation period, this relationship has yet to be established. According to the instructions for the medical use of the drug Maalox®, the absorption of combinations of aluminum hydroxide and magnesium salts in the mother is limited, therefore, Maalox® can be used during lactation after consulting a doctor. For occasional heartburn, use 15 ml or 1-2 tablets of Maalox® once . 4-6
According to the instructions for the medical use of the drug Maalox®, the absorption of combinations of aluminum hydroxide and magnesium salts in the mother is limited, therefore, Maalox® can be used during lactation after consulting a doctor. For occasional heartburn, use 15 ml or 1-2 tablets of Maalox® once . 4-6
Unfortunately, the symptoms of heartburn do not always disappear without a trace after childbirth: about 20% of women who experience heartburn during pregnancy also notice it in the postpartum period 2 . It is possible that the development of heartburn in the postpartum period may be associated with the lactation period, this relationship has yet to be established. According to the instructions for the medical use of the drug Maalox®, the absorption of combinations of aluminum hydroxide and magnesium salts in the mother is limited, therefore, Maalox® can be used during lactation after consulting a doctor. For occasional heartburn, use 15 ml or 1-2 tablets of Maalox® once . 4-6
For occasional heartburn, use 15 ml or 1-2 tablets of Maalox® once . 4-6
Symptoms of heartburn in pregnant women
Heartburn is an unpleasant burning sensation, warmth behind the sternum, which can spread to the neck area 3 . The symptom may appear about an hour after eating. Often entails heartburn eating fried, spicy, fatty, sour foods, as well as overeating. Physical activity and changes in body position, such as leaning forward or lying down, may increase heartburn symptoms 3 . In pregnant women, heartburn is often accompanied by belching and difficulty swallowing 1 .
Heartburn is an unpleasant sensation of burning, warmth behind the sternum, which can spread to the neck area 3 . The symptom may appear about an hour after eating. Often entails heartburn eating fried, spicy, fatty, sour foods, as well as overeating. Physical activity and changes in body position, such as leaning forward or lying down, may increase heartburn symptoms 3 . In pregnant women, heartburn is often accompanied by belching and difficulty swallowing 1 .
Physical activity and changes in body position, such as leaning forward or lying down, may increase heartburn symptoms 3 . In pregnant women, heartburn is often accompanied by belching and difficulty swallowing 1 .
Why is heartburn dangerous in pregnant women?
Heartburn that occurs during pregnancy may increase the chance of developing GERD after childbirth. Moreover, the risk of developing the disease is proportional to the number of births. It was noted that in the presence of heartburn in the 1st pregnancy, GERD subsequently develops in 17.7% of women , and two pregnancies with heartburn increase this figure to 36% 2 .
It is important to note that if heartburn occurs during pregnancy, it is imperative to consult a doctor, since other diseases of the digestive system can manifest as heartburn, including a severe pathology of the gestation period - acute fatty liver of pregnant women. In this case, heartburn is short-lived at first, then its intensity and duration increase, accompanied by painful swallowing of not only food, but also liquids. Heartburn in this case is often accompanied by vomiting of the color of "coffee grounds", weakness, lethargy. Such a dangerous condition requires close medical attention and control 1 .
In this case, heartburn is short-lived at first, then its intensity and duration increase, accompanied by painful swallowing of not only food, but also liquids. Heartburn in this case is often accompanied by vomiting of the color of "coffee grounds", weakness, lethargy. Such a dangerous condition requires close medical attention and control 1 .
Heartburn that occurs during pregnancy may increase the chance of developing GERD after childbirth. Moreover, the risk of developing the disease is proportional to the number of births. It has been noted that in the presence of heartburn in the 1st pregnancy, GERD subsequently develops in 17.7% of women , and two pregnancies with heartburn increase this figure to 36% 2 .
It is important to note that if heartburn occurs during pregnancy, it is imperative to consult a doctor, since other diseases of the digestive system can manifest as heartburn, including a severe pathology of the gestation period - acute fatty liver of pregnant women.