Possible sign of miscarriage
Miscarriage Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis, and Treatment
Written by WebMD Editorial Contributors
In this Article
- What Is a Miscarriage?
- Miscarriage Symptoms
- Miscarriage Causes and Risk Factors
- Miscarriage Types
- Miscarriage Diagnosis
- Miscarriage Treatments
- Symptoms Following a Miscarriage
- Pregnancy Following a Miscarriage
- When to Try to Conceive After a Miscarriage
- Miscarriage Prevention
What Is a Miscarriage?
A miscarriage is the loss of a baby before the 20th week of pregnancy. The medical term for a miscarriage is spontaneous abortion. But it isn’t an abortion in the common meaning of the term.
As many as 50% of all pregnancies end in miscarriage -- most often before a woman misses a menstrual period or even knows they’re pregnant. About 15%-25% of recognized pregnancies will end in a miscarriage.
More than 80% of miscarriages happen within the first 3 months of pregnancy. Miscarriages are less likely to happen after 20 weeks. When they do, doctors call them late miscarriages.
Miscarriage Symptoms
Symptoms of a miscarriage include:
- Bleeding that goes from light to heavy
- Severe cramps
- Belly pain
- Weakness
- Worsening or severe back pain
- Fever with any of these symptoms
- Weight loss
- White-pink mucus
- Contractions
- Tissue that looks like blood clots passing from your vagina
- Fewer signs of pregnancy
If you have these symptoms, contact your doctor right away. They’ll tell you whether to come to the office or go to the emergency room.
Miscarriage Causes and Risk Factors
Most miscarriages happen when the unborn baby has fatal genetic problems. Usually, these problems are not related to the mother.
Usually, these problems are not related to the mother.
Other problems that can increase the risk of miscarriage include:
- Infection
- Medical conditions in the mother, such as diabetes or thyroid disease
- Hormone problems
- Immune system responses
- Physical problems in the mother
- Uterine abnormalities
- Smoking
- Drinking alcohol
- Using street drugs
- Exposure to radiation or toxic substances
A woman has a higher risk of miscarriage if they:
- Are over age 35
- Have certain diseases, such as diabetes or thyroid problems
- Have had three or more miscarriages
Cervical insufficiency. A miscarriage sometimes happens when the mother has a weakness of the cervix. Doctors call this a cervical insufficiency. It means the cervix can’t hold the pregnancy. This type of miscarriage usually happens in the second trimester.
Doctors call this a cervical insufficiency. It means the cervix can’t hold the pregnancy. This type of miscarriage usually happens in the second trimester.
There are usually few symptoms before a miscarriage caused by cervical insufficiency. You may feel sudden pressure, your water might break, and tissue from the baby and placenta could leave your body without much pain. Doctors usually treat an insufficient cervix with a "circling" stitch in the next pregnancy, usually around 12 weeks. The stitch holds your cervix closed until the doctor removes it around the time of delivery. If you never had a miscarriage but your doctor finds that you have cervical insufficiency they might add the stitch to prevent a miscarriage.
Miscarriage Types
There are different kinds of miscarriages, including:
Threatened miscarriage. You’re bleeding and there’s the threat of a miscarriage, but your cervix hasn’t dilated. Your pregnancy will likely continue without any problems.
Inevitable miscarriage. You’re bleeding and cramping. Your cervix is dilated. A miscarriage is likely.
Incomplete miscarriage. Some tissue from the baby or the placenta leaves your body, but some stays in your uterus.
Complete miscarriage. All the pregnancy tissues leave your body. This type of miscarriage usually happens before the 12th week of pregnancy.
Missed miscarriage. The embryo dies or was never formed, but the tissues stay in your uterus.
Recurrent miscarriage (RM). You lose three or more pregnancies in a row during the first trimester. This type of miscarriage only affects about 1% of couples trying to have a baby.
Miscarriage Diagnosis
To check whether you've had a miscarriage, your doctor will do:
- A pelvic exam. They’ll check to see if your cervix has started to dilate.
- An ultrasound test. This test uses sound waves to check for a baby’s heartbeat.
 If the results aren’t clear, you may go back for another test in a week.
If the results aren’t clear, you may go back for another test in a week. - Blood tests. The doctor uses them to look for pregnancy hormones in your blood and compare it to past levels. They may also test you for anemia if you’ve been bleeding a lot.
- Tissue tests. If tissue left your body, the doctor may send it to a lab to confirm that you had a miscarriage. It can also help make sure there wasn’t another cause for your symptoms.
- Chromosome tests. If you’ve had two or more miscarriages, the doctor might do these tests to see if you or your partner’s genes are the cause.
Miscarriage Treatments
If the miscarriage is complete and your uterus is empty, you probably won’t need further treatment.
Sometimes all the tissue doesn’t come out. If that happens, your doctor might do a dilation and curettage (D&C) procedure. They’ll dilate your cervix and gently remove any remaining tissue. There are also medications you can take that cause any tissue left in your uterus to leave your body. This may be a better option if you want to avoid surgery.
There are also medications you can take that cause any tissue left in your uterus to leave your body. This may be a better option if you want to avoid surgery.
If it’s later in the pregnancy and the fetus has died in the womb, the doctor will induce labor and delivery.
When the bleeding stops, you should be able to go back to your normal activities. If your cervix dilated on its own but you’re still pregnant, you could have a condition known as incompetent cervix. Your doctor might do a procedure to close it called cerclage.
If your blood type is Rh negative, the doctor may give you a blood product called Rh immune globulin (Rhogam). This prevents you from developing antibodies that could harm your baby or any future pregnancies.
You may get blood tests, genetic tests, or medication if you’ve had more than two miscarriages in a row (recurrent miscarriage). To diagnose this condition, your doctor might use tests like:
- Pelvic ultrasound
- Hysterosalpingogram, An X-ray of the uterus and fallopian tubes
- Hysteroscopy.
 The doctor uses a thin, telescope-like device inserted through your vagina and cervix to look inside your uterus
The doctor uses a thin, telescope-like device inserted through your vagina and cervix to look inside your uterus
If you've had two miscarriages in a row, use a form of birth control and talk to your doctor about tests to find the cause
Symptoms Following a Miscarriage
Bleeding and mild discomfort are common symptoms after a miscarriage. If you have heavy bleeding with fever, chills, or pain, contact your doctor right away. These may be signs of an infection.
Besides the physical effects, you may also feel a range of emotions, from sadness and guilt to grief and worry about future pregnancies. What you’re feeling is normal. Let yourself grieve.
If you’re up to it, talk to people in your life who are supportive like your partner, a friend, or family member. You can also talk to a professional mental health counselor. Pregnancy loss support groups may also be a valuable resource to you and your partner. Ask your doctor for more information about these resources. And remember that everyone heals at a different pace and in different ways.
And remember that everyone heals at a different pace and in different ways.
Pregnancy Following a Miscarriage
You can get pregnant after a miscarriage. At least 85% of women who have one go on to have normal pregnancies and births. Having a miscarriage doesn’t mean you have a fertility problem. On the other hand, about 1%-2% of women may have repeated miscarriages (three or more). Some researchers believe this is related to an autoimmune response.
If you've had two miscarriages in a row, you should stop trying to conceive, use a form of birth control, and ask your doctor to do tests to figure out what’s causing the miscarriages.
When to Try to Conceive After a Miscarriage
Discuss the timing of your next pregnancy with your doctor. Some experts say you should wait a certain amount of time (from one menstrual cycle to 3 months) before you try again. While this is not a widespread practice, to prevent another miscarriage the doctor may suggest treatment with progesterone, a hormone that helps the embryo implant and supports early pregnancy in your uterus.
Taking time to heal both physically and emotionally after a miscarriage is important. Above all, don't blame yourself. Counseling is available to help you handle your loss.
Miscarriage Prevention
Most miscarriages happen because there’s a problem with the pregnancy. You can’t prevent them. If your doctor does testing and finds a problem, treatment options may be available.
If you have an illness, treating it can improve your chances for a successful pregnancy. One step you can take is to get as healthy as you can before you try to have a baby:
- Get regular exercise.
- Eat a healthy, well-balanced diet.
- Maintain a healthy weight.
- Avoid infections.
- Don’t smoke, drink alcohol, or take illegal drugs.
- Cut back on caffeine.
Health & Pregnancy Guide
- Getting Pregnant
- First Trimester
- Second Trimester
- Third Trimester
- Labor and Delivery
- Pregnancy Complications
- All Guide Topics
Symptoms, Types, Causes, and Support
Miscarriages: Symptoms, Types, Causes, and SupportMedically reviewed by Deborah Weatherspoon, Ph. D., MSN — By Jacquelyn Cafasso on May 1, 2019
D., MSN — By Jacquelyn Cafasso on May 1, 2019
What is a miscarriage?
A miscarriage, or spontaneous abortion, is an event that results in the loss of a fetus before 20 weeks of pregnancy. It typically happens during the first trimester, or first three months, of the pregnancy.
Miscarriages can happen for a variety of medical reasons, many of which aren’t within a person’s control. But knowing the risk factors, signs, and causes can help you to better understand the event and get any support or treatment you may need.
Miscarriage signs
The symptoms of a miscarriage vary, depending on your stage of pregnancy. In some cases, it happens so quickly that you may not even know you’re pregnant before you miscarry.
Here are some of the symptoms of a miscarriage:
- heavy spotting
- vaginal bleeding
- discharge of tissue or fluid from your vagina
- severe abdominal pain or cramping
- mild to severe back pain
Call your doctor right away if you experience any of these symptoms during your pregnancy. It’s also possible to have these symptoms without experiencing a miscarriage. But your doctor will want to conduct tests to make sure that everything is fine.
It’s also possible to have these symptoms without experiencing a miscarriage. But your doctor will want to conduct tests to make sure that everything is fine.
Miscarriage causes
While there are some things that increase the risk of miscarriage, generally it isn’t a result of something that you did or didn’t do. If you’re having difficulty maintaining pregnancy, your doctor may check for some known causes of miscarriage.
During pregnancy, your body supplies hormones and nutrients to your developing fetus. This helps your fetus grow. Most first trimester miscarriages happen because the fetus doesn’t develop normally. There are different factors that can cause this.
Genetic or chromosome issues
Chromosomes hold genes. In a developing fetus, one set of chromosomes is contributed by the mother and another by the father.
Examples of these chromosome abnormalities include:
- Intrauterine fetal demise: The embryo forms but stops developing before you see or feel symptoms of pregnancy loss.

- Blighted ovum: No embryo forms at all.
- Molar pregnancy: Both sets of chromosomes come from the father, no fetal development occurs.
- Partial molar pregnancy: The mother’s chromosomes remain, but the father has also provided two sets of chromosomes.
Errors can also occur randomly when the cells of the embryo divide, or due to a damaged egg or sperm cell. Problems with the placenta can also lead to a miscarriage.
Underlying conditions and lifestyle habits
Various underlying health conditions and lifestyle habits may also interfere with the development of a fetus. Exercise and sexual intercourse do not cause miscarriages. Working won’t affect the fetus either, unless you’re exposed to harmful chemicals or radiation.
Conditions that can interfere with fetus development include:
- poor diet, or malnutrition
- drug and alcohol use
- advanced maternal age
- untreated thyroid disease
- issues with hormones
- uncontrolled diabetes
- infections
- trauma
- obesity
- problems with the cervix
- abnormally shaped uterus
- severe high blood pressure
- food poisoning
- certain medications
Always check with your doctor before taking any medications to be sure a drug is safe to use during pregnancy.
Miscarriage or period?
Many times, a miscarriage can happen before you even know that you’re pregnant. Additionally, as with your menstrual period, some of the symptoms of a miscarriage involve bleeding and cramping.
So how can you tell if you’re having a period or a miscarriage?
When trying to distinguish between a period and a miscarriage, there are several factors to consider:
- Symptoms: Severe or worsening back or abdominal pain as well as passing fluids and large clots could indicate a miscarriage.
- Time: A miscarriage very early in pregnancy can be mistaken for a period. However, this is less likely after eight weeks into a pregnancy.
- Duration of symptoms: The symptoms of a miscarriage typically get worse and last longer than a period.
If you’re experiencing heavy bleeding or believe that you’re having a miscarriage, you should contact your doctor. Read on to learn more about distinguishing between a period and a miscarriage.![]()
Miscarriage rate by week
Most miscarriages happen within the first trimester (first 12 weeks) of pregnancy. The earliest weeks of pregnancy are when a woman is at the highest risk of a miscarriage. However, once pregnancy reaches 6 weeks, this risk drops.
From weeks 13 to 20 of pregnancy, the risk of miscarriage drops further. However, it’s important to keep in mind that miscarriage risk doesn’t change much after this, as complications can arise at any point in a pregnancy. Discover further details about miscarriage rate by week.
Miscarriage statistics
The early loss of a pregnancy is common. According to the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG), it occurs in 10 percent of known pregnancies.
Sometimes the cause of a miscarriage will remain unknown. However, the Mayo Clinic estimates that about 50 percent of miscarriages are due to chromosome issues.
The risk of miscarriage definitely increases with age.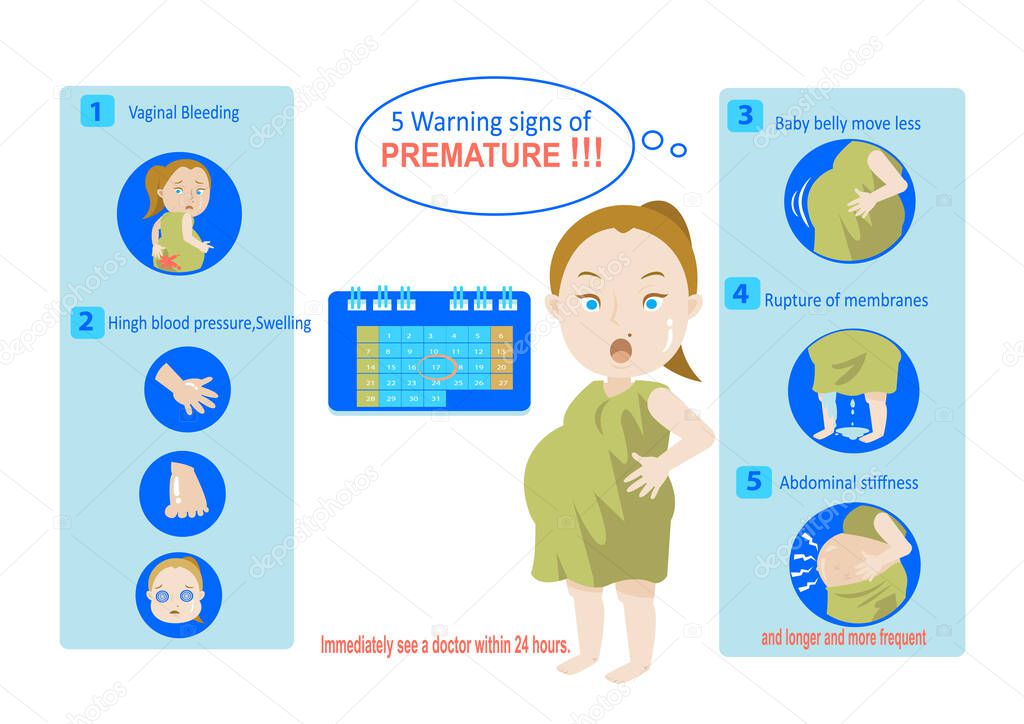 According to the Mayo Clinic, the risk of miscarriage is 20 percent at age 35. It increased to 40 percent at age 40 and rises further to 80 percent at age 45.
According to the Mayo Clinic, the risk of miscarriage is 20 percent at age 35. It increased to 40 percent at age 40 and rises further to 80 percent at age 45.
A miscarriage doesn’t mean that you won’t go on to have a baby. According to the Cleveland Clinic, 87 percent of women who have had a miscarriage will go on to carry a baby to full term. Approximately only 1 percent of women have three or more miscarriages.
Miscarriage risk
Most miscarriages are due to natural and unpreventable causes. However, certain risk factors can increase your chances of having a miscarriage. These include:
- body trauma
- exposure to harmful chemicals or radiation
- drug use
- alcohol abuse
- excessive caffeine consumption
- smoking
- two or more consecutive miscarriages
- being underweight or overweight
- chronic, uncontrolled conditions, like diabetes
- problems with the uterus or cervix
Being older can also affect your risk for miscarriage. Women who are over 35 years old have a higher risk of miscarriage than women who are younger. This risk only increases in the following years.
Women who are over 35 years old have a higher risk of miscarriage than women who are younger. This risk only increases in the following years.
Having one miscarriage doesn’t increase your risk for having other miscarriages. In fact, most women will go on to carry a baby full term. Repeated miscarriages are actually quite rare.
Miscarriage types
There are many different types of miscarriage. Depending on your symptoms and the stage of your pregnancy, your doctor will diagnose your condition as one of the following:
- Complete miscarriage: All pregnancy tissues have been expelled from your body.
- Incomplete miscarriage: You’ve passed some tissue or placental material, but some still remains in your body.
- Missed miscarriage: The embryo dies without your knowledge, and you don’t deliver it.
- Threatened miscarriage: Bleeding and cramps point to a possible upcoming miscarriage.
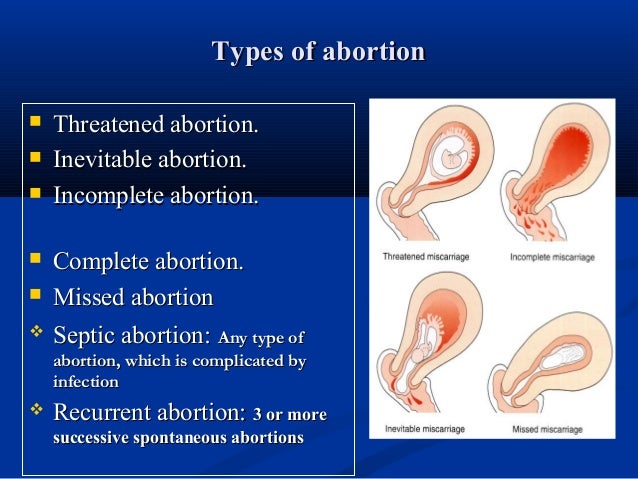
- Inevitable miscarriage: The presence of bleeding, cramping, and cervical dilation indicates that a miscarriage is inevitable.
- Septic miscarriage: An infection has occurred within your uterus.
Miscarriage prevention
Not all miscarriages can be prevented. However, you can take steps to help maintain a healthy pregnancy. Here are a few recommendations:
- Get regular prenatal care throughout your pregnancy.
- Avoid alcohol, drugs, and smoking while pregnant.
- Maintain a healthy weight before and during pregnancy.
- Avoid infections. Wash your hands thoroughly, and stay away from people who are already sick.
- Limit the amount of caffeine to no more than 200 milligrams per day.
- Take prenatal vitamins to help ensure that you and your developing fetus get enough nutrients.
- Eat a healthy, well-balanced diet with lots of fruits and vegetables.
Remember that having a miscarriage doesn’t mean you won’t conceive again in the future. Most women who miscarry have healthy pregnancies later. Get additional information about ways to prevent miscarriage.
Most women who miscarry have healthy pregnancies later. Get additional information about ways to prevent miscarriage.
Miscarriage with twins
Twins typically happen when two eggs are fertilized instead of one. They can also happen when one fertilized egg splits into two separate embryos.
Naturally, there are additional considerations when a woman is pregnant with twins. Having multiple babies in the womb can affect growth and development. Women who are pregnant with twins or other multiples may be more likely to have complications such as preterm birth, preeclampsia, or miscarriage.
Additionally, a type of miscarriage called vanishing twin syndrome can affect some who are pregnant with twins. Vanishing twin syndrome occurs when only one fetus can be detected in a woman who was previously determined to be pregnant with twins.
In many cases, the vanished twin is reabsorbed into the placenta. Sometimes this happens so early in the pregnancy that you didn’t even know you were pregnant with twins. Find out more about the phenomena of vanishing twin syndrome.
Find out more about the phenomena of vanishing twin syndrome.
Miscarriage treatment
The treatment that you receive for a miscarriage can depend on the type of miscarriage that you’ve had. If there’s no pregnancy tissue left in your body (complete miscarriage), no treatment is required.
If there’s still some tissue present in your body, there are a few different treatment options:
- expectant management, which is where you wait for the remaining tissue to pass naturally out of your body
- medical management, which involves taking medications to help you pass the rest of the remaining tissue
- surgical management, which involves having any remaining tissue surgically removed
The risk of complications from any of these treatment options is very small, so you can work with your doctor to determine which one is best for you.
Physical recovery
Your body’s recovery will depend on how far along your pregnancy was before the miscarriage. After a miscarriage, you might experience symptoms such as spotting and abdominal discomfort.
After a miscarriage, you might experience symptoms such as spotting and abdominal discomfort.
While pregnancy hormones might last in the blood for a couple months after a miscarriage, you should start having normal periods again in four to six weeks. Avoid having sex or using tampons for at least two weeks after having a miscarriage.
Support after a miscarriage
It’s normal to experience a wide range of emotions after a miscarriage. You may also experience symptoms such as trouble sleeping, low energy, and frequent crying.
Take your time to grieve for your loss, and ask for support when you need it. You may also want to consider the following:
- Reach out for help if you’re overwhelmed. Your family and friends may not understand how you’re feeling, so let them know how they can help.
- Store any baby memorabilia, maternity clothing, and baby items until you’re ready to see them again.
- Engage in a symbolic gesture that may help with remembrance.
 Some women plant a tree or wear a special piece of jewelry.
Some women plant a tree or wear a special piece of jewelry. - Seek counseling from a therapist. Grief counselors can help you cope with feelings of depression, loss, or guilt.
- Join an in-person or online support group to talk with others who have been through the same situation.
Getting pregnant again
Following a miscarriage, it’s a good idea to wait until you’re both physically and emotionally ready before trying to conceive again. You may want to ask your doctor for guidance or to help you develop a conception plan before you try to get pregnant again.
A miscarriage is typically only a one-time occurrence. However, if you’ve had two or more consecutive miscarriages, your doctor will recommend testing to detect what may have caused your previous miscarriages. These may include:
- blood tests to detect hormone imbalances
- chromosome tests, using blood or tissue samples
- pelvic and uterine exams
- ultrasounds
Read this article in Spanish.
Last medically reviewed on May 2, 2019
- Parenthood
- Pregnancy
How we reviewed this article:
Healthline has strict sourcing guidelines and relies on peer-reviewed studies, academic research institutions, and medical associations. We avoid using tertiary references. You can learn more about how we ensure our content is accurate and current by reading our editorial policy.
- Being pregnant with twins, triplets, and other multiples. (2017).
marchofdimes.org/complications/being-pregnant-with-twins-triplets-and-other-multiples.aspx - Cohain JS, et al. (2017). Spontaneous first trimester miscarriage rates per woman among parous women with 1 or more pregnancies of 24 weeks or more. DOI:
10.1186/s12884-017-1620-1 - Early pregnancy loss. (2015).
acog.org/Patients/FAQs/Early-Pregnancy-Loss - Magnus MC, et al. (2019). Role of maternal age and pregnancy history in risk of miscarriage: Prospective register based study.
 DOI:
DOI:
10.1136/bmj.l869 - Mayo Clinic Staff. (2016). Miscarriage.
mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/pregnancy-loss-miscarriage/symptoms-causes/syc-20354298 - Mayo Clinic Staff. (2019). Pregnancy after miscarriage: What you need to know.
mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/getting-pregnant/in-depth/pregnancy-after-miscarriage/art-20044134 - Miscarriage. (2012).
my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/9688-miscarriage - Miscarriage. (2017).
marchofdimes.org/complications/miscarriage.aspx - Miscarriage. (2018).
nhs.uk/conditions/miscarriage/
Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information becomes available.
Current Version
May 2, 2019
Edited By
Suan Pineda
Medically Reviewed By
Deborah Weatherspoon, Ph.D., MSN
Share this article
Medically reviewed by Deborah Weatherspoon, Ph. D., MSN — By Jacquelyn Cafasso on May 1, 2019
D., MSN — By Jacquelyn Cafasso on May 1, 2019
related stories
Pain, Bleeding, and Discharge: When Should You Worry?
Is There a Link Between Endometriosis and Miscarriage?
How Long Does a Miscarriage Last?
What You Should Know About Blighted Ovum, Miscarriage, and Future Pregnancies
What I’ve Learned from Counseling Couples Through Miscarriage
Read this next
Pain, Bleeding, and Discharge: When Should You Worry?
Medically reviewed by Debra Rose Wilson, Ph.D., MSN, R.N., IBCLC, AHN-BC, CHT
During the second trimester, pain, bleeding, and vaginal discharge are normal symptoms. In some cases, however, these symptoms may be a sign of a…
READ MORE
Is There a Link Between Endometriosis and Miscarriage?
Medically reviewed by Valinda Riggins Nwadike, MD, MPH
Does endometriosis increase your risk for miscarriage? We explain the connection.
READ MORE
How Long Does a Miscarriage Last?
Medically reviewed by Holly Ernst, PA-C
The loss of a pregnancy before 20 weeks is considered a miscarriage. The length of time a miscarriage lasts varies from woman to woman, as do the risk…
READ MORE
What You Should Know About Blighted Ovum, Miscarriage, and Future Pregnancies
Medically reviewed by Debra Rose Wilson, Ph.D., MSN, R.N., IBCLC, AHN-BC, CHT
A blighted ovum eventually leads to miscarriage, but women can have future healthy pregnancies. Here's how blighted ovum is diagnosed and why it…
READ MORE
What I’ve Learned from Counseling Couples Through Miscarriage
Most women tell me it doesn’t get better, but it does get easier.
READ MORE
Can Taking Prometrium Vaginally Prevent Miscarriage?
Medically reviewed by Debra Sullivan, Ph.
 D., MSN, R.N., CNE, COI
D., MSN, R.N., CNE, COIProgesterone is known as the “pregnancy hormone.” Without enough progesterone, a woman’s body can’t continue to grow a fertilized egg. If you’ve…
READ MORE
11 Books That Shine a Light on Infertility
These books about infertility offer guidance, information, compassion, and real stories of what it's like to live with infertility.
READ MORE
Threatened Abortion (Threatened Miscarriage)
Threatened abortion refers to vaginal bleeding during the first 20 weeks of pregnancy. Learn about its symptoms, risk factors, and diagnosis.
READ MORE
Identifying and Treating a Missed Abortion
A missed abortion is another term for a missed miscarriage or a silent miscarriage. We’ll explore symptoms, causes, and treatment options.
READ MORE
A Breakdown of Miscarriage Rates by Week
Medically reviewed by Holly Ernst, PA-C
A miscarriage is the early loss of a pregnancy before the 20th week of pregnancy. Unfortunately, miscarriages are common in the first trimester. The…
READ MORE
Causes and symptoms of miscarriage in early pregnancy
A woman treats the news of her own pregnancy with particular trepidation. A new life begins to develop inside it, which will soon be born and become the main reason for its existence for the coming years. However, early miscarriage is able to cross out unrealizable dreams and postpone successful delivery for an indefinite period. When the expulsion of the fetus occurs before 12 weeks of its development in the womb, every fifth woman does not yet know about the upcoming motherhood. This does not make the process of loss any less emotionally and physically painful. But after learning about a failed pregnancy and turning to a doctor, a woman can determine causes of miscarriage to prevent a similar situation in the future.
But after learning about a failed pregnancy and turning to a doctor, a woman can determine causes of miscarriage to prevent a similar situation in the future.
Early miscarriage - how does the anomaly proceed
What does science define by the term "miscarriage"? From the point of view of gynecology, this is the process of spontaneous termination of pregnancy up to 22 weeks, when the weight parameters of the embryo do not exceed 0.5 kg. If a baby developing in the womb weighs 500 grams, then doctors can save him and give a premature baby the opportunity for a happy life. If the weight is less than this indicator, then the struggle for the life of the born baby is meaningless. As mentioned above, early miscarriage is often not felt by the woman. All she notices is a slight delay in the menstrual cycle and increased bleeding during the onset of menstruation, accompanied by severe pain.
Discomfort and painful symptoms can be soothed by taking painkillers and nettle infusion. However, in some cases they are powerless, so going to the doctor is the only right decision in this situation. Analyzing causes of miscarriage , you will surely remember how a copious blood clot came out of you along with menstruation. It was he who became the main symptom of spontaneous expulsion of the fetus by the body.
However, in some cases they are powerless, so going to the doctor is the only right decision in this situation. Analyzing causes of miscarriage , you will surely remember how a copious blood clot came out of you along with menstruation. It was he who became the main symptom of spontaneous expulsion of the fetus by the body.
When a clot breaks, it is important to see a doctor immediately. After the examination, the specialist will tell you if there are any remains of the fetus inside you. In this case, early miscarriage requires cleaning of the uterus to remove traces of embryonic decay from it and prevent subsequent development of infection.
In case of a miscarriage before 12 weeks, the woman's body seems to give a signal that it is not ready for a full-fledged pregnancy. Or that the parents have health problems that need to be addressed. Consult a doctor to find out the causes of the pathology. The specialist will conduct an examination, prescribe a set of preventive, therapeutic and supportive procedures, after which it will be possible to start talking about pregnancy and childbirth again.
Such different causes of miscarriage – let's get acquainted with provocateurs
Among the most common causes of miscarriage, problems of various etiologies can be noted. Among them:
- Genetic failures - in the presence of a mutating element in the parental chromosomes, the fetus is expelled from the uterus as incapacitated and contrary to the principles of natural selection of the organism. Various factors can influence the manifestation and development of pathology, it is not always possible to determine them exactly.
- Hormonal imbalance - the cause of miscarriage may be insufficient production of the hormone progesterone, or the predominance of male hormones in the female body. At the stage of preparation for pregnancy, such an anomaly is easily eliminated by the use of hormone therapy. Such measures help to avoid spontaneous abortion at an early stage.
- Rh-conflict of parents - with a negative Rh factor of the mother's blood, the same indicator of the father plays a very important role.
 With opposite values early miscarriage is quite possible. If the fetus has a positive Rh factor, then the mother's body seeks to get rid of the foreign body, trying to expel the embryo by any available means. With early diagnosis of an anomaly, the doctor uses progesterone to protect the fetus, which prevents the expulsion of the fetus. If both parents are negative for the Rh factor, then the conflict can be avoided.
With opposite values early miscarriage is quite possible. If the fetus has a positive Rh factor, then the mother's body seeks to get rid of the foreign body, trying to expel the embryo by any available means. With early diagnosis of an anomaly, the doctor uses progesterone to protect the fetus, which prevents the expulsion of the fetus. If both parents are negative for the Rh factor, then the conflict can be avoided. - Infectious diseases are a negative factor that can cause harm to the fetus and the body of the expectant mother of various strengths. In the case of genital infections, it is better to get rid of them before the moment of conception, otherwise infection of the embryo is inevitable. It could become cause of miscarriage early pregnancy . Inflammatory processes in the body of a woman are also taken into account. An increase in temperature in response to the harmful effects of the disease is often accompanied by a general intoxication of the body.
 This takes away the strength of the fetus, so the body easily gives up the embryo without keeping it in the uterus.
This takes away the strength of the fetus, so the body easily gives up the embryo without keeping it in the uterus. - Abortion is a rather complicated operation in terms of the strength of the subsequent impact on the female body. Unprofessional disposal of the fetus can become cause a miscarriage in the future, and also lead the woman to a complete loss of reproductive function. It is impossible to correct the situation, therefore, doctors, as a rule, communicate for a long time with a woman who has decided to have an abortion in order to convince her to carry out her plans.
- Medicines and medicines - the first trimester of pregnancy is famous for the fact that during this period it is strictly forbidden to take any medicines and drugs. Since vital organs are laid in the embryo, the funds can provoke an anomaly in the development of the child. Also during pregnancy, herbs are prohibited: nettle, tansy, St. John's wort, parsley. Their intake can cause miscarriage and loss of the embryo by the mother's body.

- Mechanical injuries - during pregnancy it is very important to protect yourself from serious physical exertion and possible mechanical damage. From the first days, fitness and other types of physical activity in non-specialized groups are prohibited. In order not to provoke an early miscarriage , it is better to enroll in specialized sports groups for pregnant women, where the load is accurately calculated and only exercises that are harmless to the health of the mother and child are used. You can not lift weights, overexert yourself, be subjected to falls, bumps and unsuccessful loads. Even if the mother is full of health and strength, during pregnancy it is better to beware of careless actions.
- Other factors - unfavorable environment, harmful working conditions, unbalanced diet.
There are also causes of miscarriage based on stress, depression, nervous mood of the future mother. Even at the stage of pregnancy planning, parents should change the usual rhythm of life in order to exclude all negative factors from it. This truth is especially true for women. In order not to provoke an early miscarriage , she must get rid of bad habits, addiction to coffee, alcohol, smoking. She needs to rest more, get enough sleep, eat right and rationally, walk more and breathe fresh air.
This truth is especially true for women. In order not to provoke an early miscarriage , she must get rid of bad habits, addiction to coffee, alcohol, smoking. She needs to rest more, get enough sleep, eat right and rationally, walk more and breathe fresh air.
Symptoms of a miscarriage - how to determine the termination of pregnancy
The most pronounced signs of spontaneous abortion are pain in the lower abdomen and in the lumbar region, as well as bleeding. Pain symptoms are often spasmodic in nature. They arise suddenly, slowly step aside and after a certain period they roll again. Bloody discharge from the vagina or unstoppable bleeding requires the immediate call of an ambulance team. When observing such signs, there is a high probability of miscarriage in the early stages , so the hospitalization of the expectant mother in such conditions is necessary.
If we compare abundant bleeding and spotting manifestations, then the latter give more chances for the preservation of the fetus. However, it is not worth delaying the call of the doctor in both cases. The consequences can be very serious. If abundant blood flow is accompanied by the presence of clots and pieces of mucous in the fluid, then this indicates a miscarriage that has already occurred.
However, it is not worth delaying the call of the doctor in both cases. The consequences can be very serious. If abundant blood flow is accompanied by the presence of clots and pieces of mucous in the fluid, then this indicates a miscarriage that has already occurred.
Often a possible harbinger of termination of pregnancy is a diagnosis made by an obstetrician-gynecologist, indicating a high tone of the uterus. So that the cause of miscarriage does not provoke it, the future woman in labor is advised to remain calm, not to be nervous, not to overwork.
In general, the presence of many of the symptoms listed above is not a panacea for abortion. With timely treatment of a woman to a doctor, further gestation is possible. The only thing that will have to be faced in this case is the careful care of the attending staff of the gynecological consultation.
Treatment of early miscarriage
Bed rest is the main rule for the normal course of pregnancy when there are threats to it. The doctor, excluding any causes of miscarriage , recommends that the future woman in labor lead a measured and calm lifestyle, take care of herself and her own nerves, eat well and give herself little joys, raising her spirits and tuning in to positive. If the threat of losing the child is strong, then the specialist may completely prohibit getting out of bed once again. In this case, ideal conditions can only be achieved in a hospital, which is why pregnant women with a burdened history are often placed in the prenatal ward for preservation.
The doctor, excluding any causes of miscarriage , recommends that the future woman in labor lead a measured and calm lifestyle, take care of herself and her own nerves, eat well and give herself little joys, raising her spirits and tuning in to positive. If the threat of losing the child is strong, then the specialist may completely prohibit getting out of bed once again. In this case, ideal conditions can only be achieved in a hospital, which is why pregnant women with a burdened history are often placed in the prenatal ward for preservation.
Psychologists say that the psycho-emotional background of the expectant mother plays one of the leading roles in the process of preparing for childbirth. In order not to provoke a miscarriage at an early stage and at a later period, a woman needs to think about the good and pleasant. It is useful to read your favorite books, listen to soothing music, breathe measuredly and calmly. To prevent you from having the slightest chance of being upset, your doctor may prescribe valerian or motherwort. For pregnant women, they are absolutely harmless. Expectant mothers are encouraged to think positive. About how the baby will be born, what name the parents will give him, how beautiful and strong he will become as he grows up.
For pregnant women, they are absolutely harmless. Expectant mothers are encouraged to think positive. About how the baby will be born, what name the parents will give him, how beautiful and strong he will become as he grows up.
If the causes of miscarriage are more significant, then the doctor may prescribe hormonal agents that normalize the general background of pregnancy. Medications with a high content of progesterone, anti-hyperandrogenism drugs and reducing the risk of Rhesus conflict pills may be prescribed. If the threat of miscarriage is high, then cervical closure may be used. The sutures are applied under anesthesia, so the procedure is not painful.
Some women have to be under the strict supervision of specialists for the entire period of pregnancy. It happens when possible early miscarriage and later. At the same time, the future woman in labor can be placed in the hospital once, and can also be there on a permanent basis. The reward for strict adherence to the doctor's recommendations is a full-fledged process of pregnancy development and childbirth in due time. A healthy baby who was born can more than compensate for all the inconvenience and discomfort experienced by the parents.
The reward for strict adherence to the doctor's recommendations is a full-fledged process of pregnancy development and childbirth in due time. A healthy baby who was born can more than compensate for all the inconvenience and discomfort experienced by the parents.
In order to prevent miscarriage, it is recommended that both parents take a balanced approach to the decision to become pregnant. It is necessary to prepare for conception in advance, undergo all the necessary examinations, pass the recommended tests. This will eliminate the maximum causes of miscarriage and reduce the risk of developing a negative scenario during pregnancy. At least six months before the date of the intended conception, it is necessary to change the usual way of life of the parents. It is necessary to eliminate bad habits, give up alcohol, smoking, and the use of harmful products.
What are the possible consequences of an early miscarriage
If a miscarriage occurs early in the course of pregnancy, then serious consequences are extremely rare.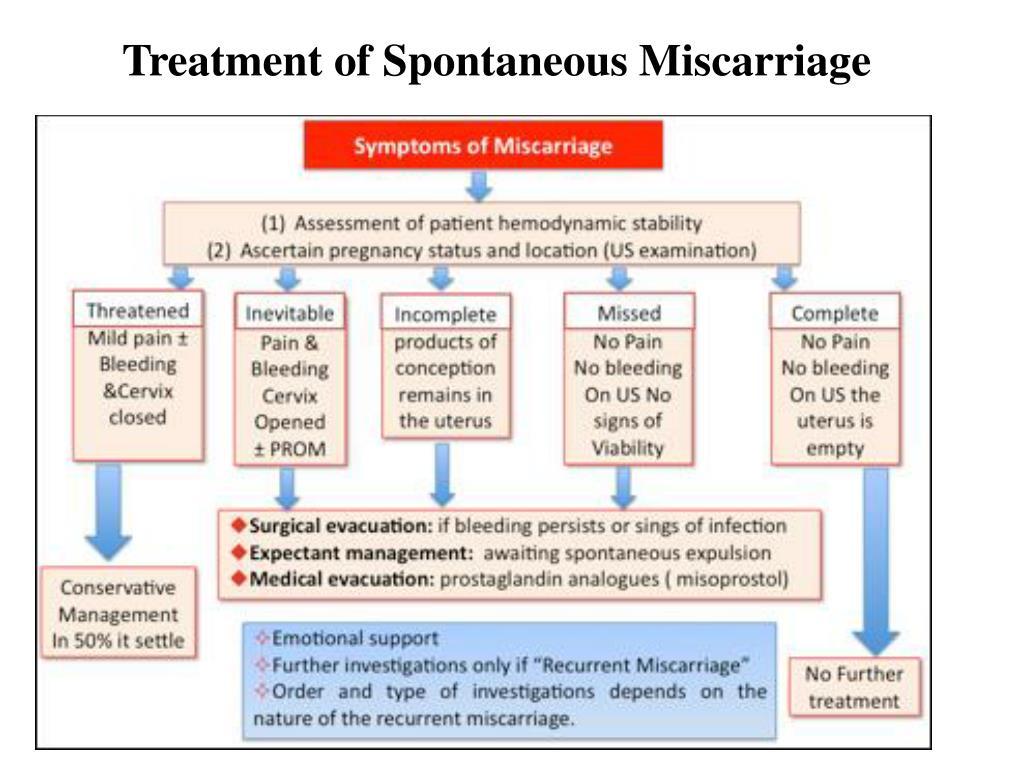 They can be caused by self-termination of pregnancy with the help of drugs and artisanal traditional medicine recipes. An urgent consultation with a gynecologist is necessary when a blood clot comes out of the vagina, indicating a miscarriage. It is better to clean the uterus in time than to expose it to the risk of developing sepsis and blood poisoning.
They can be caused by self-termination of pregnancy with the help of drugs and artisanal traditional medicine recipes. An urgent consultation with a gynecologist is necessary when a blood clot comes out of the vagina, indicating a miscarriage. It is better to clean the uterus in time than to expose it to the risk of developing sepsis and blood poisoning.
Causes of miscarriage
Questions to the doctor about miscarriages
Diagnostics of miscarriage
Treatment and prevention of miscarriage
Patterns - a spontaneous termination of pregnancy in a period of up to 20 weeks. According to statistics, 10 to 20% of all pregnancies end in miscarriage. However, the real numbers could be much higher, as a large number of miscarriages happen very early, and women are not even aware of their pregnancy. Most miscarriages happen due to abnormal development of the fetus.
Miscarriage is quite common, but this fact does not make things any easier. It is always difficult to cope with the realization that there was a pregnancy, but no child. Try to deal with the situation psychologically and understand what could be causing the miscarriage, what increases the risk of it, and what type of treatment might be needed.
It is always difficult to cope with the realization that there was a pregnancy, but no child. Try to deal with the situation psychologically and understand what could be causing the miscarriage, what increases the risk of it, and what type of treatment might be needed.
Symptoms of miscarriage .
Most miscarriages occur before 12 weeks. Signs and symptoms of a miscarriage include:
- Vaginal bleeding or spotting (although quite common in early pregnancy)
- Pain or cramps in the abdomen or lower back
- Fluid vaginal discharge or tissue fragments
It is important to consider the fact that in early pregnancy, spotting or vaginal bleeding is quite common. In most cases, women who experience light bleeding during the first three months have an uneventful pregnancy thereafter. In some cases, even with heavy bleeding, the pregnancy does not end in a miscarriage.
Some women who have a miscarriage develop an infection in the uterus.