Periods post pregnancy
Will my period change after pregnancy? | Your Pregnancy Matters
×
What can we help you find?Refine your search: Find a Doctor Search Conditions & Treatments Find a Location
Appointment New Patient Appointment
or Call214-645-8300
MedBlog
Your Pregnancy Matters
October 12, 2021
Your Pregnancy Matters
Shivani Patel, M. D. Obstetrics and Gynecology
Many new moms are surprised by how much they bleed after having a baby. For two to three weeks after a vaginal or cesarean section (C-section) delivery, they experience what looks like a heavy period. This is called lochia, a mix of blood and uterine tissue the body doesn’t need after pregnancy.
Like a period, it typically starts heavy and becomes lighter over time, eventually ending with some spotting. The color will transition from dark red to brownish-pink to off-white. However, you are not ovulating regularly yet – releasing eggs from your ovaries – so lochia isn’t a true menstrual period.
Cramping further blurs the line between lochia and menstrual bleeding. Your uterus expands several times its size to keep up with the growth of your baby; after birth, it shrinks back down. The muscle contractions from this process feel similar to period cramps.
Caring for a newborn will consume most of your attention, but be sure to monitor the amount of blood you’re losing during the first few weeks after delivery. Up to 5% of patients experience uncontrolled bleeding, or postpartum hemorrhage, a condition accompanied by symptoms such as low blood pressure, pale skin, and nausea.
If your blood loss seems excessive, see your provider right away. After lochia ends, the timing, flow, and duration of every woman’s period varies, but enough similarities exist to answer common questions about postpartum menstruation.
When should I expect my first period after pregnancy?
Your first period can come anytime between two and 12 weeks after delivery. For most women, it happens between six and 12 weeks.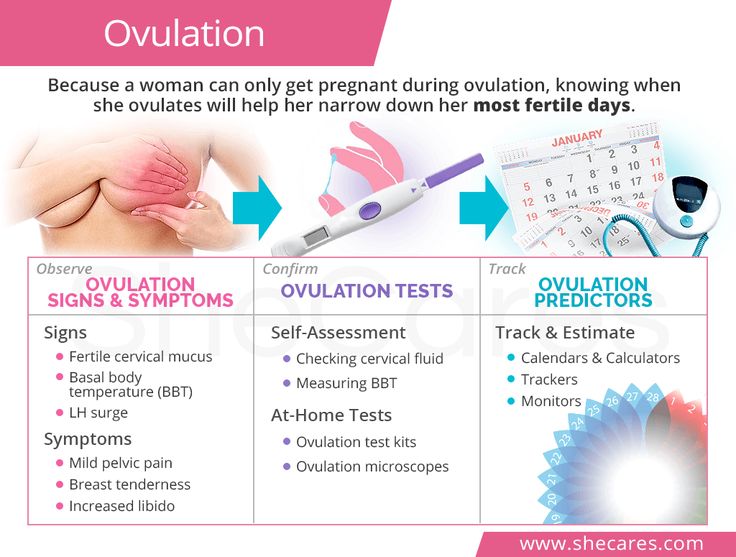
If you exclusively breastfeed, your period will likely be delayed until you give your baby solid food and other forms of milk. As your levels of prolactin – the hormone that helps your body produce milk – increase, your levels of estrogen and progesterone decrease. These hormones help regulate your period; lower levels reduce the likelihood of ovulation and menstruation.
While you are experiencing lochia, your flow will act like a typical period: starting heavier, then gradually getting lighter. However, if the amount of blood increases after a few lighter days, consider slowing down your activity level for a few days so your body can rest and heal from childbirth.
Related reading: The ‘fourth trimester’: Why women need health care after delivery
Will my period look or feel different?
Most women can expect their first couple of periods after giving birth to be heavier than those they experienced before pregnancy. Menstrual blood should look like you expect: a bright red that fades into a darker, brownish red. You may see small clots the first time but should not see large clots (the size of a plum or golf ball). If you do, alert your provider.
You may see small clots the first time but should not see large clots (the size of a plum or golf ball). If you do, alert your provider.
Some research has shown that C-section scarring can increase period pain as well as flow. In general, postpartum period symptoms will be similar to pre-pregnancy symptoms, so if you used to have cramps, they likely will resume. However, some patients say their period pain improves after pregnancy.
Related reading: What’s going on with my uterus? 3 conditions related to pelvic pain and bleeding
How regular will my menstrual cycle be?
Your period can take up to a year to become regular, no matter how consistent it was before pregnancy. To develop, grow, and deliver a baby, your body experiences several hormonal changes, and it needs time to return to normal.
Breastfeeding moms are even more likely to have an irregular menstrual cycle. When you breastfeed, you have lower levels of estrogen in your body – a hormone that fluctuates with your period. Without normal estrogen fluctuation, you won’t have normal periods.
Without normal estrogen fluctuation, you won’t have normal periods.
Whether or not you breastfeed, don’t be alarmed if your second period is late – unless you’ve recently had unprotected sex.
You may associate post-traumatic stress disorder with survivors of assault, war, or natural disasters. But as maternal-fetal specialist Dr. Shivani Patel will tell you, symptoms of PTSD can weigh heavy on moms who had complex pregnancies. She knows from personal experience.
Learn more
Preventing postpartum pregnancy
If you have sex without a reliable form of birth control, you can get pregnant – even in the first few weeks after giving birth. The majority of pregnancies that occur less than a year after a previous birth are unplanned.
You will start ovulating between delivery and your first period – up to six weeks after birth, which is typically the same amount of time we recommend you wait to have sex.
Related reading: Birth control after childbirth: Long-term options for new moms
Research-based recommendations suggest spacing pregnancies by at least 12 to 18 months. Postpartum pregnancy can prevent your body from fully healing from childbirth and put your baby at risk of premature birth and infant mortality. A CDC study also found that a shorter time period between births is linked to autism spectrum disorder.
Risks vary based on your age. So, if you want to get pregnant again soon after giving birth, work with your doctor to develop a safe plan that is specific to your situation.
Postpartum bleeding can be confusing. We’re here to provide clarity. To visit with an Ob/Gyn, call 214-645-8300 or request an appointment online.
More in: Your Pregnancy Matters
Your Pregnancy Matters
- Robyn Horsager-Boehrer, M.
 D.
D.
December 20, 2022
Your Pregnancy Matters
- Robyn Horsager-Boehrer, M.D.
December 13, 2022
Pediatrics; Your Pregnancy Matters
- Jessica Morse, M.
 D.
D.
December 6, 2022
Your Pregnancy Matters
- Shivani Patel, M.D.
November 22, 2022
Your Pregnancy Matters
- Robyn Horsager-Boehrer, M.D.
November 15, 2022
Your Pregnancy Matters
- Robyn Horsager-Boehrer, M.
 D.
D.
November 7, 2022
Mental Health; Your Pregnancy Matters
- Robyn Horsager-Boehrer, M.D.
October 11, 2022
Prevention; Your Pregnancy Matters
- Robyn Horsager-Boehrer, M.
 D.
D.
October 4, 2022
Mental Health; Your Pregnancy Matters
- Meitra Doty, M.D.
September 27, 2022
More Articles
Periods after pregnancy | Pregnancy Birth and Baby
Periods after pregnancy | Pregnancy Birth and Baby beginning of content5-minute read
Listen
Why do periods stop during pregnancy?
Each month, your body goes through a cycle of changes to prepare for a potential pregnancy.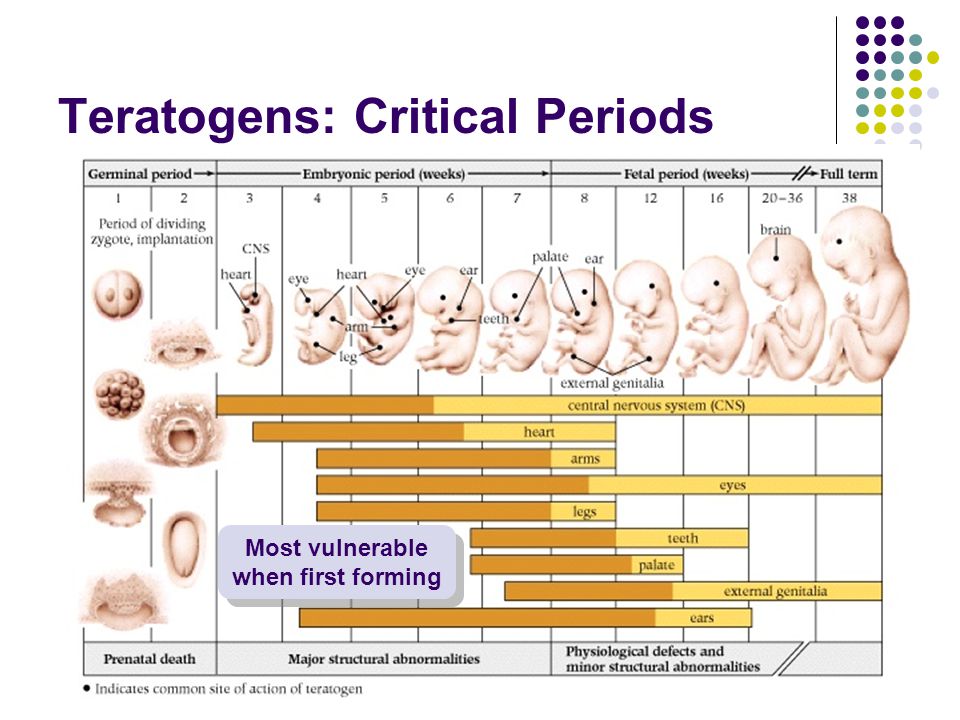 One of your ovaries releases an egg, hormones prepare the vagina and cervix to support possible sperm, and your uterus thickens to nurture a possible baby. If you don’t become pregnant, on day 28 (on average) the cycle ends and the lining of your uterus sheds — this blood is your period. If you have sex during a cycle and your egg meets a sperm, you can become pregnant. Throughout your pregnancy, your body retains the lining of your uterus, which is why you stop getting your period during this time.
One of your ovaries releases an egg, hormones prepare the vagina and cervix to support possible sperm, and your uterus thickens to nurture a possible baby. If you don’t become pregnant, on day 28 (on average) the cycle ends and the lining of your uterus sheds — this blood is your period. If you have sex during a cycle and your egg meets a sperm, you can become pregnant. Throughout your pregnancy, your body retains the lining of your uterus, which is why you stop getting your period during this time.
Can I bleed during pregnancy?
Even though your periods stop, you can still experience bleeding during pregnancy. This happens in almost 1 in 4 women for different reasons. Many women who bleed during pregnancy go on to deliver a healthy baby. However, you should immediately contact your doctor or midwife if you notice bleeding from your vagina at any time during your pregnancy.
In the first 12 weeks of pregnancy, the fertilised egg planting itself in your womb may cause bleeding.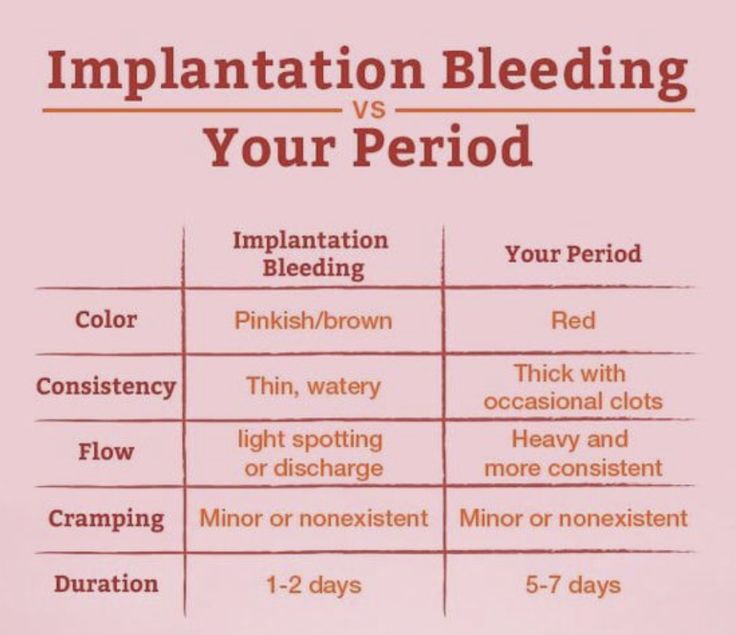 This is known as implantation bleeding. It normally only lasts for a few days. However, bleeding during early pregnancy could signal that the fertilised egg has planted itself outside the uterus — this is called an ectopic pregnancy. It could also signal a miscarriage.
This is known as implantation bleeding. It normally only lasts for a few days. However, bleeding during early pregnancy could signal that the fertilised egg has planted itself outside the uterus — this is called an ectopic pregnancy. It could also signal a miscarriage.
In the later stages of pregnancy, vaginal bleeding can have many different causes.
What can I expect after the birth?
In the first few days after birth, it’s normal to have some period-like bleeding as your uterus contracts back to the size it was before pregnancy. Bleeding immediately after birth can be fairly heavy. It can also be bright red for the first couple of days, but gradually becomes a brownish colour before it stops after about 2 months. Bleeding might be heavier in the morning when you get up, after breastfeeding or after exercise.
Uncontrolled heavy bleeding after birth, called a postpartum haemorrhage, can be a serious concern.
If you've given birth more than 24 hours ago, contact your doctor or midwife immediately if you notice:
- blood that soaks more than one pad every 1 to 2 hours
- a sudden increase in blood or large clots
- blood which suddenly turns bright red in colour
- dizziness, weakness or trouble breathing
- anything else that seems unusual about your post-birth bleeding
When will my period return?
After birth, your periods will return at your body’s own pace. If you bottle feed your baby, you’ll tend to resume regular ovulation and your period sooner than if you exclusively breastfeed. If you choose to breastfeed exclusively, your first period may not return for several months — sometimes, it might not even return for 1 to 2 years if you keep breastfeeding. If you choose to bottle feeding or partially breastfeed your baby, your periods may return as soon as 3 weeks after childbirth.
If you bottle feed your baby, you’ll tend to resume regular ovulation and your period sooner than if you exclusively breastfeed. If you choose to breastfeed exclusively, your first period may not return for several months — sometimes, it might not even return for 1 to 2 years if you keep breastfeeding. If you choose to bottle feeding or partially breastfeed your baby, your periods may return as soon as 3 weeks after childbirth.
Does breastfeeding affect my periods?
Not having your period while you're breastfeeding is known as lactational amenorrhea. How long it lasts depends on how often you breastfeed and when you introduce other food into your baby’s diet.
It’s hard to predict when your period will return after you give birth — and how you feed your baby is only one factor that influences this. However, once your body begins releasing eggs again, you can get pregnant even before you actually have your first period after giving birth. There are several safe contraception options you can consider while breastfeeding, but speak to your doctor for advice before resuming sexual activity.
Will a period affect the taste of my breastmilk?
Ovulation and menstruation mean hormonal changes are occurring in your body. These may affect both your breastmilk’s taste and supply. If you notice that your baby fusses at your breast when you have your period, it might just be a sign that it tastes different.
When is it OK to use tampons again after pregnancy?
It's best not to use tampons until after you attend the medical check that occurs 6 weeks after you give birth. If your normal periods return before this, use a sanitary pad until your doctor gives you advice.
Speak to a maternal child health nurse
Call Pregnancy, Birth and Baby to speak to a maternal child health nurse on 1800 882 436 or video call. Available 7am to midnight (AET), 7 days a week.
Sources:
Royal Women's Hospital Melbourne (About periods), Health Department Victoria (Bleeding in early pregnancy fact sheet), The Royal Women's Hospital (Bleeding in early pregnancy), The Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists (The first few weeks following birth), Mater Mother’s Hospital (After birth – care of the new mother), Fertility and Sterility (The resumption of ovulation and menstruation in a well-nourished population of women breastfeeding for an extended period of time), Queensland Clinical Guidelines (Bleeding after birth), The Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists (Management of Postpartum Haemorrhage (PPH)), Australian Breastfeeding Association (The Lactational Amenorrhea Method (LAM) for postpartum contraception), National Health and Medical Research Council (Infant Feeding Guidelines)Learn more here about the development and quality assurance of healthdirect content.
Last reviewed: July 2020
Back To Top
Related pages
- Sex after having a baby
- Mum's first few days after giving birth
- Ovulation signs
- Bleeding during pregnancy
Need more information?
Menstrual cycle: normal - MyDr.com.au
All you need to know about periods, including what's normal and what's not. Plus, see what happens inside your body during the different phases of a normal menstrual cycle.
Read more on myDr website
About the menstrual cycle | Jean Hailes
Learn all about the menstrual cycle, what happens during a cycle, how long a menstrual cycle usually is and when you should seek help.
Read more on Jean Hailes for Women's Health website
What will happen if I get coronavirus? - MyDr.com.au
Dr Norman Swan explains what will likely happen if you get COVID-19.
Read more on myDr website
Period Problems | Family Planning NSW
There are a variety of problems that can occur with the menstrual cycle. Some of the common problems are covered briefly below but it is best to discuss any specific period problems with your local doctor or Family Planning clinic.
Read more on Family Planning NSW website
Heavy Menstrual Bleeding
Read more on RANZCOG - Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists website
Understanding ovulation and the fertile window
When you want to have a baby you can improve your chance of getting pregnant if you know about ovulation and the ‘fertile window’ in the menstrual cycle.
Read more on Your Fertility website
Polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) - Better Health Channel
Polycystic ovarian syndrome is a hormonal condition associated with irregular menstrual cycles, excess hair growth, acne, reduced fertility, and increased risk of diabetes and mood changes.
Read more on Better Health Channel website
Early signs of pregnancy
For women who have a regular menstrual cycle, the earliest and most reliable sign of pregnancy is a missed period. Read about some of the other early pregnancy signs and symptoms.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Periods | Family Planning NSW
Family Planning NSW provides reproductive and sexual health services, including information and health promotion activities, as well as education and training.![]()
Read more on Family Planning NSW website
Pregnancy - week by week - Better Health Channel
Pregnancy is counted as 40 weeks, starting from the first day of the mother's last menstrual period.
Read more on Better Health Channel website
Disclaimer
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is not responsible for the content and advertising on the external website you are now entering.
OKNeed further advice or guidance from our maternal child health nurses?
1800 882 436
Video call
- Contact us
- About us
- A-Z topics
- Symptom Checker
- Service Finder
- Linking to us
- Information partners
- Terms of use
- Privacy
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is funded by the Australian Government and operated by Healthdirect Australia.
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is provided on behalf of the Department of Health
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby’s information and advice are developed and managed within a rigorous clinical governance framework. This website is certified by the Health On The Net (HON) foundation, the standard for trustworthy health information.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
This information is for your general information and use only and is not intended to be used as medical advice and should not be used to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any medical condition, nor should it be used for therapeutic purposes.
The information is not a substitute for independent professional advice and should not be used as an alternative to professional health care. If you have a particular medical problem, please consult a healthcare professional.
Except as permitted under the Copyright Act 1968, this publication or any part of it may not be reproduced, altered, adapted, stored and/or distributed in any form or by any means without the prior written permission of Healthdirect Australia.
Support this browser is being discontinued for Pregnancy, Birth and Baby
Support for this browser is being discontinued for this site
- Internet Explorer 11 and lower
We currently support Microsoft Edge, Chrome, Firefox and Safari. For more information, please visit the links below:
- Chrome by Google
- Firefox by Mozilla
- Microsoft Edge
- Safari by Apple
You are welcome to continue browsing this site with this browser. Some features, tools or interaction may not work correctly.
Recovery of the female body after childbirth
What happens to the female body after childbirth? How to quickly recover after childbirth? These questions concern all mothers.
9 months of pregnancy behind and after childbirth you have to take care not only of the baby, but also take care of your own health. And there is a lot of “work” here - while the hormonal background is being restored, it is necessary to maintain normal bowel function, take care of the stitches after childbirth, if there were any, and establish breastfeeding. Where to begin? nine0003
And there is a lot of “work” here - while the hormonal background is being restored, it is necessary to maintain normal bowel function, take care of the stitches after childbirth, if there were any, and establish breastfeeding. Where to begin? nine0003
Recovery after childbirth is an important process that affects the further state of health. Complications may appear in the first hours after childbirth - bleeding, fever, changes in blood pressure, etc.
The postpartum period consists of 2 periods - early and late. The early one lasts 2 hours after the birth and takes place under the supervision of the staff of the maternity hospital. Late lasts approximately 6-8 weeks, during which there is a restoration of all organs and systems that were involved during pregnancy and childbirth. Full recovery from childbirth can take up to two years. Especially if the baby was born by caesarean section. Some changes are irreversible, but outwardly they are invisible (except for stretch marks), they can be determined by gynecologists during an examination of the genital organs (the shape of the cervix and external os changes, the size of the uterus and vagina changes). nine0003
nine0003
Reproductive system
After childbirth, the uterus is enlarged, and as the body recovers, it shrinks in size. Depending on the variant of delivery and feeding, this process can take place at different speeds. If the birth went naturally and the mother is breastfeeding the baby, the uterus will quickly return to its normal size. The contraction of the muscles of the uterus is stimulated by the hormone oxytocin, which is released during sucking movements. The process of feeding may be accompanied by pain of varying intensity in the lower abdomen, possibly a slight increase in blood secretions. But discomfort will be felt only at first. nine0003
Immediately after the birth of the baby, the weight of the uterus reaches about 1 kilogram. And after 2 months, during which it is actively reduced in size, the weight of the uterus is about 50 grams
40 days after birth
After childbirth, blood discharge begins - lochia. They last approximately 4-6 weeks. You should not be afraid - this is not a sign that something is wrong with the body. On the contrary, this is a consequence of the gradual healing of the wound surface on the walls of the uterus, which was formed after childbirth. During the entire period of recovery, the nature of lochia changes. Discharges from moderate blood flow to bloody scanty and then become mucous with streaks of blood. nine0003
They last approximately 4-6 weeks. You should not be afraid - this is not a sign that something is wrong with the body. On the contrary, this is a consequence of the gradual healing of the wound surface on the walls of the uterus, which was formed after childbirth. During the entire period of recovery, the nature of lochia changes. Discharges from moderate blood flow to bloody scanty and then become mucous with streaks of blood. nine0003
During this time, avoid using tampons and shower regularly to prevent infection in the genital tract.
A young mother must watch her discharge. Warning signs are too much bleeding, a sudden increase in discharge, a sharp unpleasant odor, a change in color, too large blood clots, cheesy or purulent discharge. If at least one of these signs is observed, it is urgent to see a gynecologist. nine0003
Even during pregnancy, doctors recommend doing Kegel exercises. The same exercises help to quickly restore the tone of the muscles of the vagina after childbirth.
Hormonal background
The level of hormones changes even during pregnancy. They are headed by progesterone, estrogen and HCH (human chorionic gonadotropin), as well as prolactin and oxytocin. After childbirth, the hormone prolactin is responsible for the start of breastfeeding. The level of prolactin gradually rises during pregnancy, and by the onset of childbirth, it reaches the required level for the initiation of breastfeeding. Oxytocin is responsible for emptying the mammary glands. nine0003
Hormonal imbalance after childbirth is common. Basically, things will stabilize for some time without outside interference. But if a few months after the birth, the hormonal background has not returned to normal, you should contact a gynecologist-endocrinologist to tell him how to restore it. As a rule, hormonal preparations are prescribed in such cases. They are selected individually for each girl.
Signs of hormonal imbalance
-
excessive sweating;
-
depression, irritability, apathy;
-
fatigue;
-
decreased libido;
-
active hair loss/excessive hair growth;
-
sudden change in weight.
Urinary system
On the first day after childbirth, there may be a problem with urination. The reason that the mother cannot urinate may be the pressure of the fetal head on the bladder during childbirth, which leads to swelling, or a spasm of the sphincter of the bladder. You can induce urination with the help of a reflex from the sound of pouring water, in extreme cases, a catheter or diuretics are used for this.
There is also the opposite problem - urinary incontinence. It usually occurs in those who give birth not for the first time. This is due to the weakening and stretching of the pelvic floor muscles. The problem with incontinence may go away on its own after a few days. But to improve muscle tone, it is recommended to do Kegel exercises. nine0003
Digestive system
The first stool after childbirth comes in 2-3 days. This is due to the fact that an enema is done before childbirth. Doctors in the maternity hospital ensure that the emptying of the intestines in women in labor occurs regularly, if necessary, special stimulating suppositories (for example, glycerin ones) are issued. With proper nutrition, bowel function is usually restored fairly quickly. After a caesarean section, it can take up to several weeks to restore gastrointestinal motility. Also at this time, liver function is normalized, which is reflected in the normalization of biochemical blood tests. nine0003
With proper nutrition, bowel function is usually restored fairly quickly. After a caesarean section, it can take up to several weeks to restore gastrointestinal motility. Also at this time, liver function is normalized, which is reflected in the normalization of biochemical blood tests. nine0003
Nervous system
After childbirth, the mother's nervous system encounters new unusual sensations. Depending on life circumstances, stimuli are different. Those who have a first child are worried about how they will take care of the baby, the awareness of motherhood comes and a huge responsibility piles up. For those who already have children, there are also enough reasons for concern - how older children will react to a new family member, how to do everything in time, when to relax ...
The process of giving birth, inevitably accompanied by pain and strong emotions, is always stressful for a new mother. It is not surprising that in the postpartum period, many mothers are on the verge of a breakdown, and someone can not stand it and breaks down. Relatives, especially the husband, can help in this situation. As well as psychological consultations, which can be obtained free of charge at the antenatal clinic or at the maternity hospital.
Relatives, especially the husband, can help in this situation. As well as psychological consultations, which can be obtained free of charge at the antenatal clinic or at the maternity hospital.
Stitches after childbirth
Depending on the circumstances, doctors apply different sutures to tears or incisions: absorbable, non-absorbable and metal staples. The first, as the name implies, resolves on its own after 5-7 days and does not entail further medical intervention, and the remaining two require subsequent removal after 3-6 days. nine0003
Cervical sutures are easy to care for, just normal hygiene as described below is sufficient. The nurses begin to process the stitches in the maternity hospital with brilliant green or potassium permanganate, and then, after they are removed or resorbed, the mother herself monitors healing at home. For the speedy healing of stitches, it is also useful to take air baths.
If there are stitches, do not sit for several days, or sit in a certain position with support on the side where there are no stitches. Although this is unusual, some mothers will have to lie down, reclining or standing for some time. nine0003
Although this is unusual, some mothers will have to lie down, reclining or standing for some time. nine0003
How to recover quickly after childbirth
Every mother wants to get her body back to normal as soon as possible. Hurrying up and turning a blind eye to suspicious phenomena is not the best way out, since subsequently these tricks can greatly affect health in the future, even years later. Restoration of strength after childbirth goes on for everyone in their own individual rhythm, the main thing is to tune in to success and think positively. All the difficulties associated with childbirth are quickly forgotten, and attention is switched to the care and upbringing of the child. The effectiveness of recovery is influenced by proper nutrition, intimate hygiene, time for rest, Kegel exercises, help from loved ones and a positive attitude. nine0003
How to start recovery?
It is better to consult a doctor on this issue, so as not to harm your health, trying to rush the body. The first consultation with the doctor who conducted the pregnancy is indicated 10 days after the birth. In the first days after childbirth, strict diets should be refrained from, as well as strength physical exercises. At this time, it is better to rest enough, establish breastfeeding and lead an active lifestyle.
The first consultation with the doctor who conducted the pregnancy is indicated 10 days after the birth. In the first days after childbirth, strict diets should be refrained from, as well as strength physical exercises. At this time, it is better to rest enough, establish breastfeeding and lead an active lifestyle.
Postpartum hygiene
Congratulations! You have become a mother!
The postpartum period is no less important and responsible stage in the life of a family than pregnancy.
The postpartum period lasts 6-8 weeks (begins after the birth of the placenta and ends when the organs and systems that have changed during pregnancy return to their original state).
In the process of healing the inner surface of the uterus, postpartum discharge appears - lochia, which is a wound secret. Their character during the postpartum period changes: in the first days, lochia has a bloody character; from the 4th day, their color changes to reddish-brown; by the 10th day they become light, liquid, without blood, and after 3 weeks there is practically no discharge. There may be discomfort due to uterine contractions. To relieve discomfort, bend forward and gently massage your belly. If discomfort in the uterine area occurs during feeding, try choosing a different position. It is convenient to feed lying on your side. The stomach may ache for another reason. It hurts the abdominal muscles that were actively involved during childbirth, try to relax or do a light massage. nine0125 In most non-nursing women, menstruation occurs on the 6-8th week after childbirth, more often it comes without the release of an egg from the ovary. However, ovulation and pregnancy may occur during the first months after childbirth. In lactating women, the time of the onset of the first menstruation after childbirth can be delayed for many months.
There may be discomfort due to uterine contractions. To relieve discomfort, bend forward and gently massage your belly. If discomfort in the uterine area occurs during feeding, try choosing a different position. It is convenient to feed lying on your side. The stomach may ache for another reason. It hurts the abdominal muscles that were actively involved during childbirth, try to relax or do a light massage. nine0125 In most non-nursing women, menstruation occurs on the 6-8th week after childbirth, more often it comes without the release of an egg from the ovary. However, ovulation and pregnancy may occur during the first months after childbirth. In lactating women, the time of the onset of the first menstruation after childbirth can be delayed for many months.
The normal postpartum period is characterized by a good general condition of the woman, normal temperature, sufficient lactation. For the prevention of infectious complications, strict adherence to sanitary and epidemiological requirements and personal hygiene rules is important.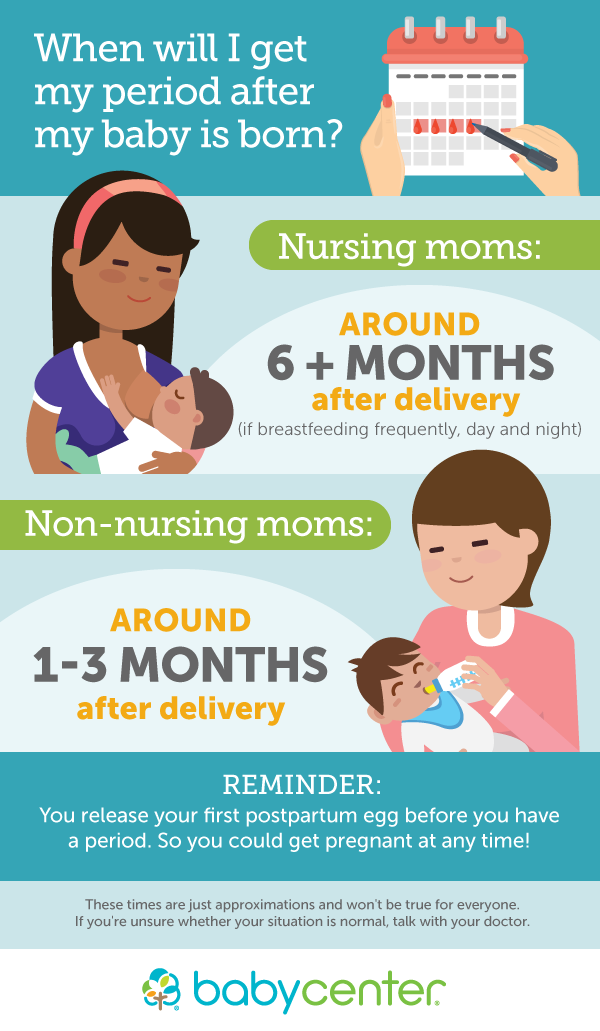 nine0003
nine0003
POSTPARTUM HYGIENE
The strictest cleanliness is essential.
- The mother should take a shower twice a day (in the morning and in the evening), then wash the mammary gland with soap and brush her teeth.
- Particular attention should be paid to the cleanliness of hands. Nails should be cut short, hands should be washed more often with soap and be sure before each feeding of the child (if the hands are dirty, you can infect the child, infect the nipples). nine0050
- Among the hygienic measures of particular importance in the postpartum period is the maintenance of cleanliness of the external genitalia and the surrounding skin.
- Should be washed with warm water and soap (liquid with a dispenser, because microbes feel great on lumps) with a fluid stream, washing the genitals should be from front to back (from the pubis to the anus) after each visit to the toilet at least 4-5 times a day (you need to go to the toilet exactly at such a frequency that the filled bladder does not interfere with uterine contraction).
 nine0125 Wash hands cleanly before washing.
nine0125 Wash hands cleanly before washing. - Keep the pads clean, change them every 3-4 hours regardless of fullness. Remove pads from front to back to prevent microorganisms from entering the vagina from the anus. If there are seams on the perineum, they should be washed thoroughly enough - you can simply direct a jet of water at it. After washing, you need to dry the perineum and the seam area by blotting the towel from front to back. nine0050
- Do not take a bath for the first 6 weeks after giving birth. This is due to the fact that the entrance to the vagina is not yet closed enough and pathogenic microbes can penetrate into it along with water. It is clear that at this time you can not swim in the pool, river, lake, sea.
- The use of tight underwear is strictly excluded, as it puts significant pressure on the perineum, which disrupts blood circulation, preventing healing.
- If there are stitches on the perineum, a woman should not sit down for 7-14 days (depending on the degree of damage).
 At the same time, you can sit on the toilet already on the first day after childbirth. By the way, about the toilet. Many women are afraid of severe pain and try to skip bowel movements, as a result, the load on the muscles of the perineum increases and the pain intensifies. nine0050
At the same time, you can sit on the toilet already on the first day after childbirth. By the way, about the toilet. Many women are afraid of severe pain and try to skip bowel movements, as a result, the load on the muscles of the perineum increases and the pain intensifies. nine0050
To avoid constipation after childbirth, do not eat foods that have a fixative effect. If the problem of constipation is not new to you, drink a tablespoon of vegetable oil before each meal. The stool will be soft and will not affect the healing process of the stitches.
- Underwear and bed linen must be cotton. We change underwear daily, bedding - at least once every three to five days.
- Stitches after caesarean section do not require special care. After the stitches and bandage are removed, you can take a shower. Do not scrub the seam area with a washcloth. With painful sensations in the anterior abdominal wall, a postpartum or postoperative bandage, which must be worn for 4 months, will help to cope.
 Young mothers are often interested in: will the seams come apart if you carry a baby in your arms? For the first 2-3 months after surgery, it is recommended to lift no more than your child's weight. nine0050
Young mothers are often interested in: will the seams come apart if you carry a baby in your arms? For the first 2-3 months after surgery, it is recommended to lift no more than your child's weight. nine0050
It happens that redness, irritation, bloody or purulent discharge occurs at the suture site. This indicates suppuration or divergence of the seams. Then you should immediately consult a doctor in a antenatal clinic.
Sexual activity after childbirth can be resumed after 6-8 weeks. By this time, the woman's body is already completely back to normal. Your doctor will advise you on contraceptives.
To fully recover from childbirth, at least two years must pass before the next pregnancy. nine0003
BREASTFEEDING
Feeding the baby should not go by the clock, but on demand, incl. at night time. At one feeding, put the baby on one breast so that he suckles for a long time and receives later milk, which contains brain and intelligence development factors, growth factors and immunoglobulins. Later, the milk comes in droplets like colostrum, the child sucks it intermittently. Sometimes the mother at this moment thinks that the child is indulging and tearing him off the breast. You don't need to do this. Let him let her go. nine0125 Breast milk is the best food for a baby!
Later, the milk comes in droplets like colostrum, the child sucks it intermittently. Sometimes the mother at this moment thinks that the child is indulging and tearing him off the breast. You don't need to do this. Let him let her go. nine0125 Breast milk is the best food for a baby!
- After the baby has had enough, the mother should carefully feel the mammary gland. If the breast is soft and there is no soreness and seals anywhere, then pumping is not necessary. If necessary, you can wash the mammary glands with warm water after feeding, starting from the nipple and ending with the armpit, and dry with a clean towel.
Very useful for breasts after childbirth and air baths, which are best taken after feeding, to give the breast the opportunity to rest, "breathe". The duration of such an air bath may not exceed 15-20 minutes, but the benefits of it are enormous. nine0003
- The nipple should be carefully inspected daily, the surface of which should not be cracked, and as a preventive measure, leave a drop of milk on the nipple and let it dry in the open air.

Only breast milk should be used as the main and only product for feeding a newborn. The use of nipples, horns and "pacifiers" is unacceptable, as this leads to a weakening of sucking in newborns and, accordingly, to incomplete emptying of the mammary gland, a decrease in prolactin production. nine0125 Are you worried about the question - do I have enough milk?
To resolve this issue, you need to observe the child, if he urinates more than 6 times a day, then he receives a sufficient amount of milk. The reason for the decrease in the amount of milk can be:
- rare feeding break (3 or more hours)
- if you do not feed at night
- short feedings or by the hour
To increase the amount of milk, you need to rearrange the feeding regimen, feed often and for as long as you want child. Try to feed with one breast so that the baby sucks out milk later, you can strain the empty breast for 10 minutes, thereby increasing the flow of milk. It is necessary to improve the mother's nutrition or use herbal teas to increase lactation. nine0003
nine0003
NUTRITION
Nutrition of a nursing mother should be high in calories (3200 kcal), balanced with the proper amount of proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins and microelements. This diet will be dominated by lactic acid, protein foods, fresh fruits and vegetables. Food should be rich in vitamins and minerals. Spicy, fatty, fried, smoked foods, canned food, sausages, alcohol and potential allergens for the child (chocolate, citrus fruits, coffee) should be excluded from the diet. nine0125 The food of the puerperal should be 5-6 times a day. It is necessary to distribute products in the daily menu in such a way that those that are rich in protein and are much more difficult to digest in the gastrointestinal tract (meat, fish, cereals) would be used during the first half of the day, and in the second half it is advisable to give preference to milk. - vegetable food.
Conditions requiring special attention
Unfortunately, the first month after childbirth does not always go smoothly. Situations may arise, when medical attention is needed . Monitor your well-being, regularly measure your body temperature, as fever is most often the first sign of complications in the postpartum period.
Situations may arise, when medical attention is needed . Monitor your well-being, regularly measure your body temperature, as fever is most often the first sign of complications in the postpartum period.
All complications of the postpartum period can be divided into several groups:
1. Complications from the uterus.
Subinvolution of the uterus - a decrease in the rate of contraction of the uterus, due to a delay in the uterus of postpartum discharge. The disease often occurs 5-7 days after childbirth, due to the closure of the cervical canal with a blood clot or a piece of membranes, as well as the inflection of the uterus due to relaxation of the ligamentous apparatus. nine0125 Infection of the contents of the uterus can lead to inflammation of the uterine mucosa - endometritis. Predisposing factors for the occurrence of endometritis are difficult childbirth, violations of the separation of the placenta during childbirth, infections of the genital tract during pregnancy, impaired immunity, abortion. Symptoms of the disease are: fever, unpleasant odor in lochia, aching pain in the lower abdomen. If these symptoms appear, you should consult an obstetrician-gynecologist at the place of residence. To clarify the diagnosis, an ultrasound examination is performed and, if necessary, surgery, during which the contents are removed from the uterine cavity (washing or curettage of the uterus). After surgery, antibiotics must be prescribed. nine0003
Symptoms of the disease are: fever, unpleasant odor in lochia, aching pain in the lower abdomen. If these symptoms appear, you should consult an obstetrician-gynecologist at the place of residence. To clarify the diagnosis, an ultrasound examination is performed and, if necessary, surgery, during which the contents are removed from the uterine cavity (washing or curettage of the uterus). After surgery, antibiotics must be prescribed. nine0003
2. Breast complications.
Laktostasis - stagnation of milk in the mammary gland. At the same time, the chest swells and becomes painful, foci of seals appear, a short-term rise in body temperature is possible. In itself, lactostasis is not a disease, requiring only gentle pumping of the breast, restriction of fluid intake, and frequent feeding of painful breasts. However, when an infection joins, it turns into lactational mastitis, requiring immediate medical attention , antibiotic therapy, and sometimes surgery. The question of the possibility of breastfeeding with mastitis is decided individually, depending on the stage of the disease.
The question of the possibility of breastfeeding with mastitis is decided individually, depending on the stage of the disease.
Another complication of the chest is the appearance of cracks in the nipples. The main reason for their appearance is improper attachment of the baby to the breast, when the baby captures only the nipple, and not the entire areola. Such a seizure is very painful for the mother - and this is the main danger signal. Breastfeeding doesn't have to be painful. Good advisory and practical help for lactostasis and cracked nipples is provided by breastfeeding consultants. Treatment of cracks consists in treating the nipple with wound healing drugs. nine0125 Hypogalactia - insufficient milk production. In order to increase the amount of milk, a mother needs to increase the frequency of feedings, not skip night feedings, offer her baby both breasts in one feeding, drink more, eat well and sleep a lot.
3. Complications from the tissues of the cervix, vagina and skin.
Inflamed wounds of these tissues are called postpartum ulcers. When an infection is attached, these wounds swell, become covered with a purulent coating, and their edges are painful. For the purpose of treatment, they are treated with various antiseptics, sometimes they require surgical treatment. nine0003
4. Complications of the venous system.
Hemorrhoids (varicose veins of the rectum) also cause pain. When infringed, they increase, become swollen, tense and painful. Thorough hygiene helps to reduce pain (shower after each visit to the toilet), applying ice to the perineum. Certain medications can be used as prescribed by a doctor.
Thrombophlebitis is a disease of the veins characterized by inflammation of the venous wall and thrombosis of the vein. After childbirth, thrombophlebitis of the pelvic veins most often occurs. Usually this disease occurs in the third week after childbirth. In terms of symptoms, it is very similar to endometritis, but requires a different treatment.