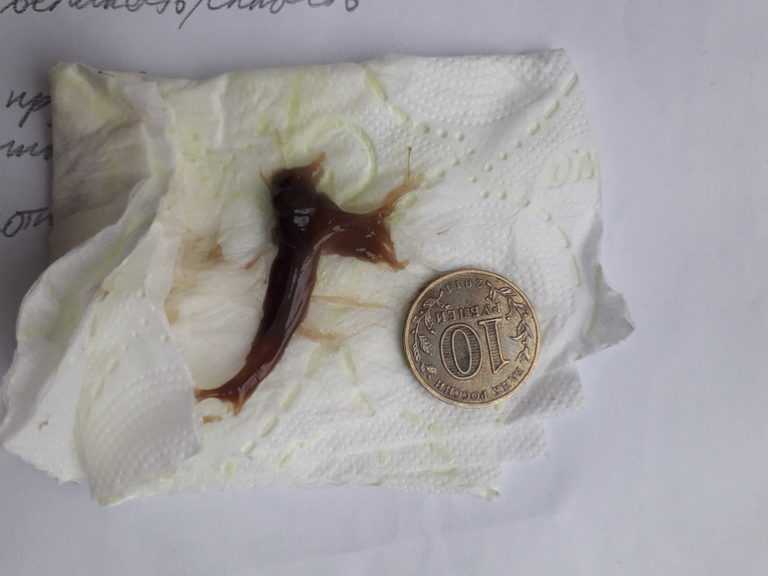
Passing clots after miscarriage
Miscarriage - Better Health Channel
What is a miscarriage?
A miscarriage is defined as the loss of a pregnancy before 20 weeks gestation. Miscarriage happens when a pregnancy stops growing. Eventually, the pregnancy tissue will pass out of the body. Some women will feel crampy, period-like pain and in most cases there will be vaginal bleeding.
Most spontaneous miscarriages (75 to 80 per cent) occur in the first 12 weeks of pregnancy. It is estimated that 1 in 4 pregnancies end in miscarriage. Many miscarriages are unreported or go unrecognised because they occur very early in the pregnancy.
Causes of a miscarriage
A miscarriage usually occurs because the pregnancy is not developing properly. The development of a baby from a female and a male cell is a very complicated process. If something goes wrong with the process, the pregnancy will stop developing. Miscarriages are more common in older women than younger women, largely because chromosomal abnormalities are more common with increasing age.
Another cause of miscarriage may be that the developing pregnancy did not embed itself properly into the lining of the uterus (womb). The natural reaction of the uterus is to expel the non-viable pregnancy.
Symptoms of a miscarriage
Pain and bleeding in early pregnancy can mean that you are having a miscarriage, but not always. Bleeding is very common in early pregnancy, affecting about one in four women, many of whom will go on to have a healthy baby. Early bleeding that does not lead to miscarriage will not have caused your baby any harm.
If the bleeding is being caused by a miscarriage, there is no treatment or therapy that can stop the miscarriage from occurring. However, it is still very important that you see a health professional.
Treatment for a miscarriage
Nothing can be done to stop a miscarriage once it has begun. Treatment is aimed at avoiding heavy bleeding and infection. It is also aimed at looking after you, physically and emotionally.
You may need to wait a short period of time before treatments begin. If you experience heavy bleeding with clots and crampy pain in that time, it is likely that you are passing the pregnancy tissue. The bleeding, clots and pain will usually settle when most of the pregnancy tissue has been passed.
Sometimes, the bleeding will continue to be heavy and you may need further treatment. If you think you are having, or have had, a miscarriage, you should see a doctor or go to an emergency department.
You should go to your nearest emergency department if you have:
- increased bleeding – for instance, soaking 2 pads per hour or passing golf ball-sized clots
- severe abdominal pain or shoulder pain
- fever or chills
- dizziness or fainting
- vaginal discharge that smells unpleasant
- diarrhoea or pain when you open your bowels.
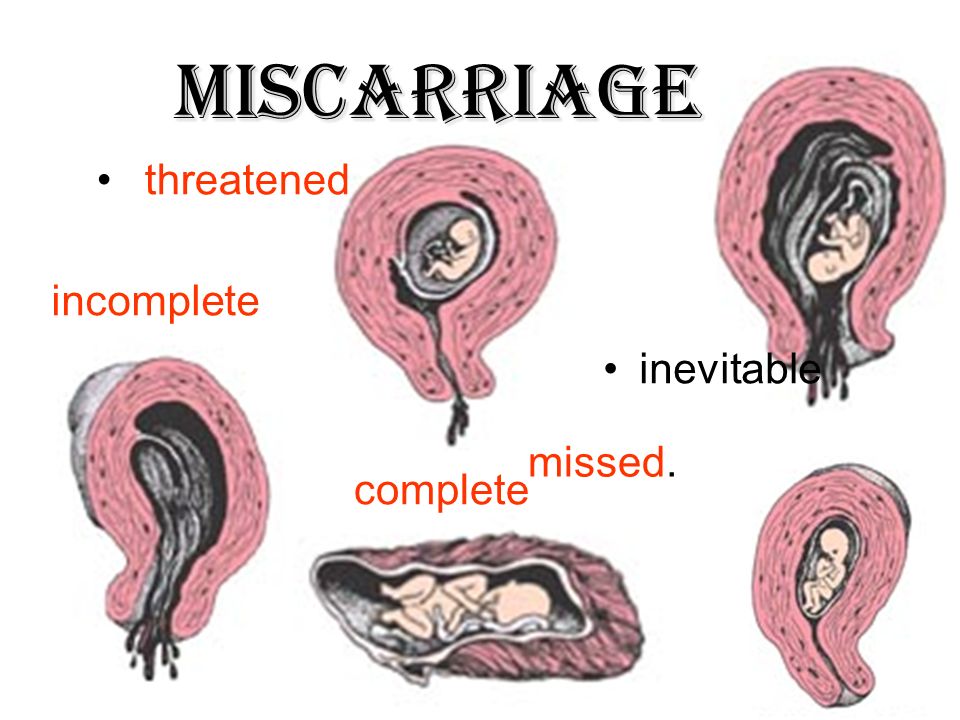
Types of miscarriage
The types of miscarriage that can occur include:
- Missed miscarriage (also known as a missed abortion) – occurs when the pregnancy has failed, although there has not been any bleeding or other signs.
 Occasionally, the aborted pregnancy may remain in the uterus for weeks or even months until bleeding commences. Missed miscarriage is suspected when pregnancy symptoms disappear and the uterus stops growing. It is diagnosed by an ultrasound examination.
Occasionally, the aborted pregnancy may remain in the uterus for weeks or even months until bleeding commences. Missed miscarriage is suspected when pregnancy symptoms disappear and the uterus stops growing. It is diagnosed by an ultrasound examination. - Blighted ovum – this occurs when a pregnancy sac is formed, but there is no developing baby within the sac. This is diagnosed by ultrasound, usually after some bleeding.
- Ectopic pregnancy – this occurs when the developing pregnancy implants in the fallopian tubes rather than in the uterus. One to two per cent of all pregnancies are ectopic and without treatment, an ectopic pregnancy can seriously impact on your health and fertility.
Reactions to miscarriage
There is no ‘right way’ to feel after a miscarriage. A range of feelings is normal, and they often linger for some time after the miscarriage. Reactions may include feelings of:
- emptiness
- anger and disbelief
- disappointment
- sadness and a sense of isolation.

Some degree of grief is very common, even if the pregnancy wasn’t planned. Partners may react quite differently, just as people can respond differently to a continuing pregnancy. Try to take it a day at a time and acknowledge your feelings and reactions as they arise.
In addition to the grief you may feel, your body will be undergoing many hormonal changes, which may make you feel very emotional. Family or close friends can be a great source of support at these times. Alternatively, you may choose to seek professional support.
Don’t blame yourself for a miscarriage
Pathology tests are sometimes performed after a miscarriage, but usually, no cause can be identified. This can add to feelings of distress and disbelief, and may lead to feelings of guilt. However, doctors agree that a miscarriage is rarely caused by anything the mother did – or didn’t – do (for example, drank a glass of wine, ate a particular food, had sex or did not rest enough). In the majority of cases, the next pregnancy proceeds to full term.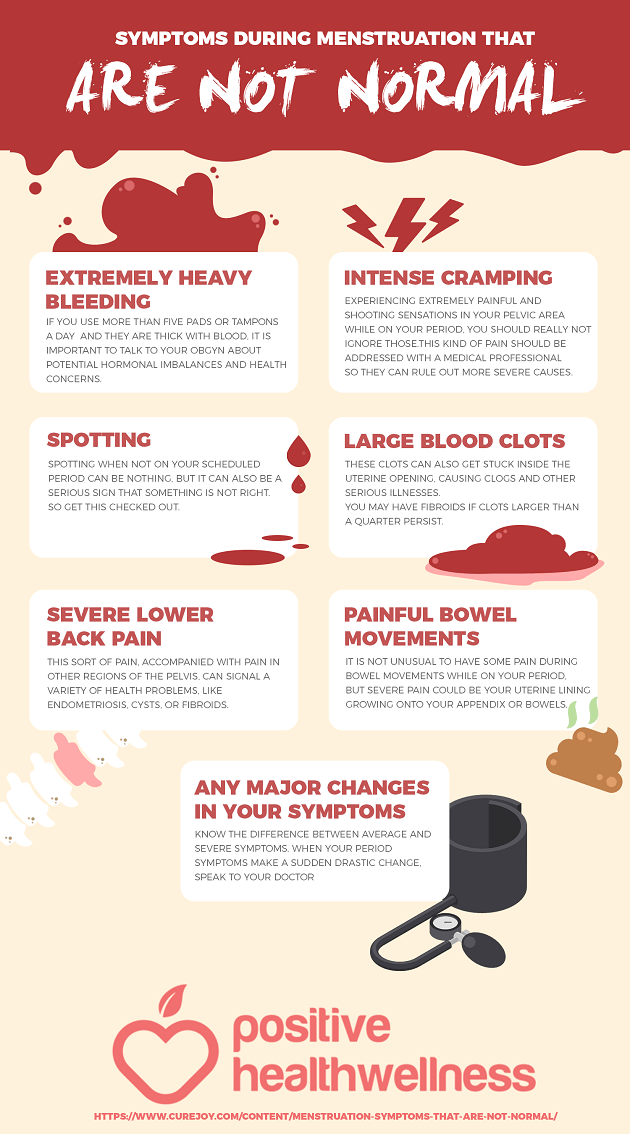
After a miscarriage
Often, some of the pregnancy tissue remains in the uterus after a miscarriage. If it is not removed by scraping the uterus with a curette (a spoon-shaped instrument), you may bleed for a long time or develop an infection. Unless all the pregnancy tissue has been passed, your doctor will usually recommend that a curette (also called a ‘D&C’ – dilation and curettage) be performed. This is done under a light general anaesthetic and you can usually go home later the same day. A sample of tissue is usually sent for pathology tests.
After the curette
Most women bleed for 5 to 10 days following a curette. Contact your doctor if you experience:
- prolonged or heavy bleeding
- blood clots or strong abdominal pain
- changes in your vaginal discharge
- fever or flu-like symptoms.
Your next period after a miscarriage
Your ovaries will usually produce an egg about 2 weeks after your miscarriage. Your first period should occur within 4 to 6 weeks. You should have a check-up with your doctor 6 weeks after your miscarriage to make sure there are no problems and to ensure your uterus has returned to normal size. You can also ask any questions about your miscarriage at this time, including the results of any pathology tests.
You should have a check-up with your doctor 6 weeks after your miscarriage to make sure there are no problems and to ensure your uterus has returned to normal size. You can also ask any questions about your miscarriage at this time, including the results of any pathology tests.
The effect of miscarriage on future pregnancies
Most of the problems that cause miscarriage happen by chance and are not likely to happen again. One miscarriage does not significantly increase the risk of the same thing happening with your next pregnancy, as long as no specific cause has been found. Testing is not usually offered to women who have miscarried once or twice because it is very unlikely that anything would be found.
However, women who have had 3 consecutive miscarriages are at risk of miscarrying again. If you fall into this category, you can attend the Recurrent Miscarriage ClinicExternal Link at The Royal Women’s Hospital for further investigations, counselling and management of future pregnancies.
Trying for another pregnancy after miscarriage
There is no right time to try for another pregnancy. Some people decide they need time to adjust to their loss, while others want to try again right away. It is usually suggested you wait until after your next period before trying again. As it is possible to become pregnant again straight away, it is important to use contraception until you are ready to try again.
If you are Rh (Rhesus) negative
If you have an Rh negative blood group, you will require an injection of anti-D immunoglobulin following a miscarriage. This will prevent problems with the Rh factor in future pregnancies. Your doctor will discuss this with you further.
Preparing for another pregnancy after a miscarriage
Although the common reasons for miscarriage cannot be prevented, you can improve your chances for long-term fertility and a successful pregnancy by:
- stopping smoking
- taking regular exercise and having a balanced diet
- reducing stress
- maintaining your weight within recommended limits.

Take folic acid
It is recommended that all women planning a pregnancy take folic acid as it helps promote the normal development of a baby’s nervous system. You will need to take 0.5 mg per day for one month prior to pregnancy and up to 12 weeks gestation.
Where to get help
- In an emergency, call 000 for an ambulance
- Your GP (doctor)
- The Royal Women’s HospitalExternal Link Tel. (03) 8345 2000
- Miscarriage AustraliaExternal Link are researchers and clinicians who aim to help all affected by miscarriage.
- Recurrent Miscarriage ClinicExternal Link, The Royal Women’s Hospital Tel. (03) 8345 2000
- Stillbirth and Neonatal Death Support (SANDS)External Link Tel. (03) 9899 0218
Miscarriage - Better Health Channel
What is a miscarriage?
A miscarriage is defined as the loss of a pregnancy before 20 weeks gestation. Miscarriage happens when a pregnancy stops growing. Eventually, the pregnancy tissue will pass out of the body.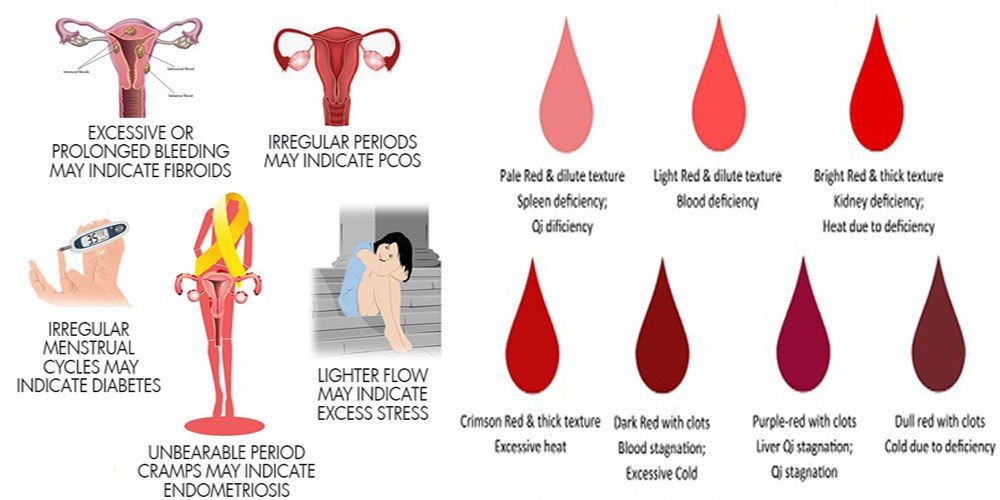 Some women will feel crampy, period-like pain and in most cases there will be vaginal bleeding.
Some women will feel crampy, period-like pain and in most cases there will be vaginal bleeding.
Most spontaneous miscarriages (75 to 80 per cent) occur in the first 12 weeks of pregnancy. It is estimated that 1 in 4 pregnancies end in miscarriage. Many miscarriages are unreported or go unrecognised because they occur very early in the pregnancy.
Causes of a miscarriage
A miscarriage usually occurs because the pregnancy is not developing properly. The development of a baby from a female and a male cell is a very complicated process. If something goes wrong with the process, the pregnancy will stop developing. Miscarriages are more common in older women than younger women, largely because chromosomal abnormalities are more common with increasing age.
Another cause of miscarriage may be that the developing pregnancy did not embed itself properly into the lining of the uterus (womb). The natural reaction of the uterus is to expel the non-viable pregnancy.
Symptoms of a miscarriage
Pain and bleeding in early pregnancy can mean that you are having a miscarriage, but not always. Bleeding is very common in early pregnancy, affecting about one in four women, many of whom will go on to have a healthy baby. Early bleeding that does not lead to miscarriage will not have caused your baby any harm.
If the bleeding is being caused by a miscarriage, there is no treatment or therapy that can stop the miscarriage from occurring. However, it is still very important that you see a health professional.
Treatment for a miscarriage
Nothing can be done to stop a miscarriage once it has begun. Treatment is aimed at avoiding heavy bleeding and infection. It is also aimed at looking after you, physically and emotionally.
You may need to wait a short period of time before treatments begin. If you experience heavy bleeding with clots and crampy pain in that time, it is likely that you are passing the pregnancy tissue. The bleeding, clots and pain will usually settle when most of the pregnancy tissue has been passed.
Sometimes, the bleeding will continue to be heavy and you may need further treatment. If you think you are having, or have had, a miscarriage, you should see a doctor or go to an emergency department.
You should go to your nearest emergency department if you have:
- increased bleeding – for instance, soaking 2 pads per hour or passing golf ball-sized clots
- severe abdominal pain or shoulder pain
- fever or chills
- dizziness or fainting
- vaginal discharge that smells unpleasant
- diarrhoea or pain when you open your bowels.
Types of miscarriage
The types of miscarriage that can occur include:
- Missed miscarriage (also known as a missed abortion) – occurs when the pregnancy has failed, although there has not been any bleeding or other signs. Occasionally, the aborted pregnancy may remain in the uterus for weeks or even months until bleeding commences. Missed miscarriage is suspected when pregnancy symptoms disappear and the uterus stops growing. It is diagnosed by an ultrasound examination.
- Blighted ovum – this occurs when a pregnancy sac is formed, but there is no developing baby within the sac. This is diagnosed by ultrasound, usually after some bleeding.
- Ectopic pregnancy – this occurs when the developing pregnancy implants in the fallopian tubes rather than in the uterus. One to two per cent of all pregnancies are ectopic and without treatment, an ectopic pregnancy can seriously impact on your health and fertility.
Reactions to miscarriage
There is no ‘right way’ to feel after a miscarriage. A range of feelings is normal, and they often linger for some time after the miscarriage. Reactions may include feelings of:
- emptiness
- anger and disbelief
- disappointment
- sadness and a sense of isolation.
Some degree of grief is very common, even if the pregnancy wasn’t planned. Partners may react quite differently, just as people can respond differently to a continuing pregnancy. Try to take it a day at a time and acknowledge your feelings and reactions as they arise.
In addition to the grief you may feel, your body will be undergoing many hormonal changes, which may make you feel very emotional. Family or close friends can be a great source of support at these times. Alternatively, you may choose to seek professional support.
Don’t blame yourself for a miscarriage
Pathology tests are sometimes performed after a miscarriage, but usually, no cause can be identified. This can add to feelings of distress and disbelief, and may lead to feelings of guilt. However, doctors agree that a miscarriage is rarely caused by anything the mother did – or didn’t – do (for example, drank a glass of wine, ate a particular food, had sex or did not rest enough). In the majority of cases, the next pregnancy proceeds to full term.
After a miscarriage
Often, some of the pregnancy tissue remains in the uterus after a miscarriage. If it is not removed by scraping the uterus with a curette (a spoon-shaped instrument), you may bleed for a long time or develop an infection. Unless all the pregnancy tissue has been passed, your doctor will usually recommend that a curette (also called a ‘D&C’ – dilation and curettage) be performed. This is done under a light general anaesthetic and you can usually go home later the same day. A sample of tissue is usually sent for pathology tests.
After the curette
Most women bleed for 5 to 10 days following a curette. Contact your doctor if you experience:
- prolonged or heavy bleeding
- blood clots or strong abdominal pain
- changes in your vaginal discharge
- fever or flu-like symptoms.
Your next period after a miscarriage
Your ovaries will usually produce an egg about 2 weeks after your miscarriage. Your first period should occur within 4 to 6 weeks. You should have a check-up with your doctor 6 weeks after your miscarriage to make sure there are no problems and to ensure your uterus has returned to normal size. You can also ask any questions about your miscarriage at this time, including the results of any pathology tests.
The effect of miscarriage on future pregnancies
Most of the problems that cause miscarriage happen by chance and are not likely to happen again. One miscarriage does not significantly increase the risk of the same thing happening with your next pregnancy, as long as no specific cause has been found. Testing is not usually offered to women who have miscarried once or twice because it is very unlikely that anything would be found.
However, women who have had 3 consecutive miscarriages are at risk of miscarrying again. If you fall into this category, you can attend the Recurrent Miscarriage ClinicExternal Link at The Royal Women’s Hospital for further investigations, counselling and management of future pregnancies.
Trying for another pregnancy after miscarriage
There is no right time to try for another pregnancy. Some people decide they need time to adjust to their loss, while others want to try again right away. It is usually suggested you wait until after your next period before trying again. As it is possible to become pregnant again straight away, it is important to use contraception until you are ready to try again.
As it is possible to become pregnant again straight away, it is important to use contraception until you are ready to try again.
If you are Rh (Rhesus) negative
If you have an Rh negative blood group, you will require an injection of anti-D immunoglobulin following a miscarriage. This will prevent problems with the Rh factor in future pregnancies. Your doctor will discuss this with you further.
Preparing for another pregnancy after a miscarriage
Although the common reasons for miscarriage cannot be prevented, you can improve your chances for long-term fertility and a successful pregnancy by:
- stopping smoking
- taking regular exercise and having a balanced diet
- reducing stress
- maintaining your weight within recommended limits.
Take folic acid
It is recommended that all women planning a pregnancy take folic acid as it helps promote the normal development of a baby’s nervous system. You will need to take 0. 5 mg per day for one month prior to pregnancy and up to 12 weeks gestation.
5 mg per day for one month prior to pregnancy and up to 12 weeks gestation.
Where to get help
- In an emergency, call 000 for an ambulance
- Your GP (doctor)
- The Royal Women’s HospitalExternal Link Tel. (03) 8345 2000
- Miscarriage AustraliaExternal Link are researchers and clinicians who aim to help all affected by miscarriage.
- Recurrent Miscarriage ClinicExternal Link, The Royal Women’s Hospital Tel. (03) 8345 2000
- Stillbirth and Neonatal Death Support (SANDS)External Link Tel. (03) 9899 0218
What to do after a miscarriage
If a woman has a miscarriage, it is important to take competent measures to restore health. This will help to cope mentally and prepare the ground for a new pregnancy. According to medical statistics, 15-20% of pregnancies end in spontaneous termination for various reasons. The symptoms of what happened rarely go unnoticed, which makes it possible to diagnose the pathology in time, consult a gynecologist, undergo adequate treatment and plan the birth of a child for the future.
Specialists classify spontaneous abortion into two categories:
1. Termination of biochemical pregnancy - the embryo leaves the uterine cavity in the first or third weeks after conception. A woman during this period most often does not suspect that she is carrying a child. Pregnancy becomes known only when testing for the content of hCG in the urine and blood. The blood that has left the body is usually perceived as menstruation, which, for unknown reasons, began outside the scheduled time. Units who carefully monitor their health go to the doctor.
2. Spontaneous abortion or miscarriage in early pregnancy - up to 22 weeks, when the weight of the embryo does not reach 0.4 kg.
Medical therapy
Any method is useful to maintain pregnancy. A qualified doctor develops an individual treatment protocol based on the available diagnostic data. Drugs used may include:
- sedatives;
- restorative therapy;
- hormone stabilizing drugs;
- uterine antispasmodics;
- vitamin and mineral supplements.

The specialist eliminates the threat of miscarriage in the early stages, tells how to prevent a relapse. In the later stages, the cervix is fixed with a special suturing (usually for a period of 16-25 weeks, if there is an ICI).
If an attempt to stop a spontaneous abortion fails, the following treatment tactics are used:
- Waiting – an organism freed from an embryo does not require specialized treatment.
- Drug therapy - the patient is prescribed drugs that complete the removal of foreign tissues from the body. By causing severe spasms of the muscular walls of the uterus, the tablets provoke the expulsion of residues from the cavity.
- Surgery - is used in case of complications or inconvenient for the independent exit of the fetus, the bending of the uterus.
Curettage
Having symptoms of a miscarriage in early pregnancy and faced with the need for a curettage (gynecological cleaning), a woman worries about the state of her reproductive system. It is not worth doing this, the operation takes place in a gentle mode, with maximum delicacy in relation to the patient's childbearing ability. Curettage is performed when there is a risk of incomplete exit of the embryo from the uterine cavity and the development of infection in the pelvic organs due to the elements remaining in it. Ignoring the procedure can lead to blood poisoning and the formation of a pathology that prevents re-conception.
It is not worth doing this, the operation takes place in a gentle mode, with maximum delicacy in relation to the patient's childbearing ability. Curettage is performed when there is a risk of incomplete exit of the embryo from the uterine cavity and the development of infection in the pelvic organs due to the elements remaining in it. Ignoring the procedure can lead to blood poisoning and the formation of a pathology that prevents re-conception.
Vacuum aspiration, however, is performed more frequently, which is more gentle. The complex application of the method with hysteroscopy allows you to carefully examine the internal contents of the uterus in order to prevent poorly cleaned areas on the mucous membrane.
Preparation for gynecological cleaning (curettage)
Gynecological cleaning is performed for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes for various indications :
- after childbirth;
- in missed pregnancy, miscarriages;
- for menstrual irregularities;
- for accurate diagnosis of gynecological disorders.
Curettage is recommended a few days before the onset of menstruation. In this case, blood loss decreases and a favorable prognosis is given for rapid tissue recovery. The operation requires a preliminary examination, testing. This is :
- complete blood count;
- blood coagulation tests;
- smear for examination of the bacteriological environment;
- STI testing.
Before curettage, you stop taking any medications, dietary supplements that have not been discussed with a specialist. Even plant components that can affect blood clotting and provoke blood loss during surgery can be dangerous. Your healthcare provider should be made aware of the medications you are taking so that they know what risks may arise.
Rules for preparing for the procedure:
- refrain from sexual intercourse three days before the operation;
- avoid the use of intimate hygiene products (gels, creams, ointments, liquids), suppositories, tablets and vaginal sprays;
- Do not douche;
- Do not eat or drink 10 hours before surgery.
 This is necessary for high-quality anesthesia.
This is necessary for high-quality anesthesia.
Cleaning
Curettage is carried out in a hospital, the woman is placed on the gynecological chair of the operating room. The doctor removes the upper layer of the mucous lining the uterine cavity from the inside. The exclusion of pain involves anesthesia. If there were signs of miscarriage in the early stages of pregnancy or at a later period, after which it spontaneously terminated, the dilated cervix allows for curettage without anesthesia. For anesthesia, intravenous administration of the drug is used, selected individually, taking into account the characteristics of the patient's body. A few seconds after the injection, the woman falls into a shallow sleep, the discomfort disappears, which makes the doctor's actions painless.
A dilator inserted into the cervix straightens the walls of the organ, facilitating access to the internal cavity. Holding the neck, the specialist inserts a rounded probe with a small diameter, after which he replaces it with a more voluminous analogue. A special video camera attached to the end of the probe allows for hysteroscopy - examination of the cavity before curettage. Cleaning is done with a curette, shaped like a small spoon on a long handle. Carefully collected tissues are stored in a specialized sterile tube, which is later sent to the laboratory for histological examination.
A special video camera attached to the end of the probe allows for hysteroscopy - examination of the cavity before curettage. Cleaning is done with a curette, shaped like a small spoon on a long handle. Carefully collected tissues are stored in a specialized sterile tube, which is later sent to the laboratory for histological examination.
The procedure rarely takes more than one hour, usually 20 minutes is enough for the doctor. Together with the cavity, the cervical canal is cleaned. Manipulations are called RDV - separate diagnostic curettage. Collected samples are placed separately. Histology is used to identify the structure of tissues in order to exclude the presence of atypical cells in them, indicating cancerous lesions, precancerous conditions. The study is carried out within two weeks, after receiving the results, the woman revisits the gynecologist for a follow-up examination.
Curettage is often carried out for diagnostic purposes to determine the symptoms of pathological conditions in the functioning of the organs of the reproductive system.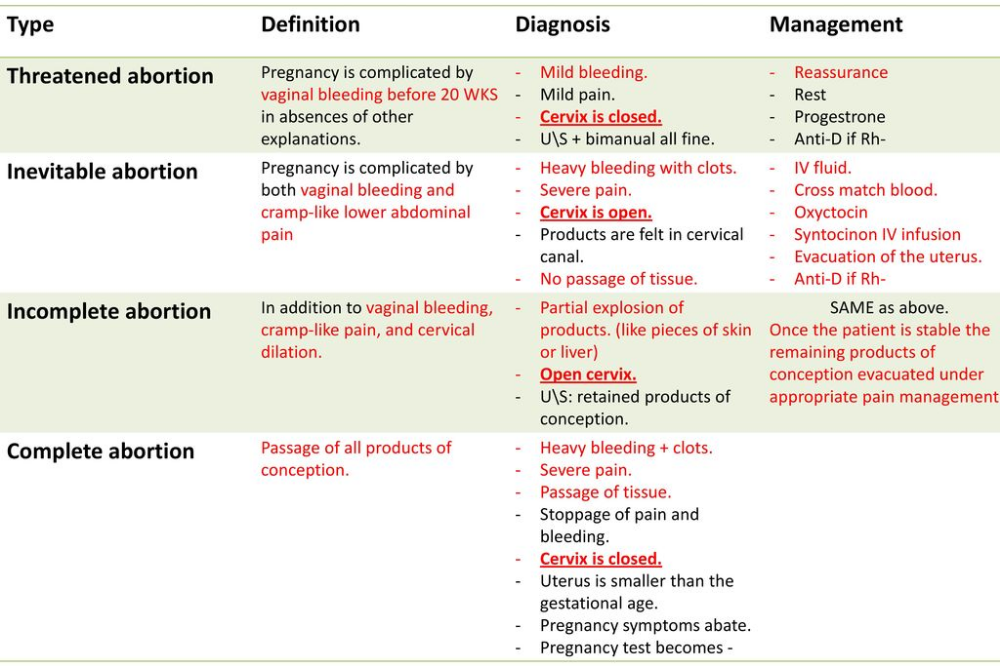 These can be:
These can be:
- irregular cycle;
- voluminous discharge and painful menstruation;
- bleeding during menopause;
- difficulties in conceiving in the absence of visible causes of pathology;
- suggestion of developing uterine cancer.
Possible complications
Complications can occur, as after any surgical intervention. A serious consequence is the discovery of uterine bleeding. In order to prevent it, oxytocin is used - injections stimulate the cessation of abnormal blood flow. Oxytocin will help if the bleeding is due to insufficient contraction of the uterus. In violation of blood clotting, it is ineffective.
Another complication of is hematometra, when blood clots accumulate in the uterine cavity, which can cause an inflammatory process in the tissues. It is caused by a spasm of the cervix that occurred immediately after cleaning, which interferes with the evacuation of blood. Experts recommend the use of antispasmodics that relax the muscles of the organ and contribute to the normal outflow of blood. A woman should be alerted by pulling pains in the lower abdomen and a sharp cessation of discharge.
Experts recommend the use of antispasmodics that relax the muscles of the organ and contribute to the normal outflow of blood. A woman should be alerted by pulling pains in the lower abdomen and a sharp cessation of discharge.
After cleansing, endometritis may occur when inflammation affects the lining of the uterus. A measure of therapy for a dangerous diagnosis is a course of antibiotics. Pain in the abdomen and a sharp increase in body temperature testify to the pathology. Any dangerous change in condition should be reported to the doctor immediately. In this case, countermeasures will be taken in a timely manner, which will eliminate the risks of developing more formidable complications.
How to behave after a miscarriage
A miscarriage that has occurred requires a certain tactic of behavior. Among the measures recommended by doctors:
- It is advisable to postpone a new pregnancy attempt for 3-6 months . Otherwise, the risk of repeating the undesirable development of events is high.
 If pregnancy occurs before the expiration date, there is no need to panic. The main thing is the supervision of a specialist.
If pregnancy occurs before the expiration date, there is no need to panic. The main thing is the supervision of a specialist. - If you are waiting for , ask for advice on effective contraception.
- Follow your doctor's advice .
- Pass the necessary examinations , take tests.
Ask about the effect of the drugs you take on the fetus if you become pregnant during therapy. Find out after what period of time you can fearlessly try to conceive a child.
How to detect genetic pathologies during repeated pregnancy
If a miscarriage of the first pregnancy occurs due to a genetic factor, it is especially scary to decide on a second one. But you should not be afraid of this, with a well-designed therapy, the chances of success are more than great. Diagnostic procedures today are highly accurate and allow you to identify pathology in the early stages. Examination in this case is mandatory, as well as the following:
- who are over 35;
- has screening changes;
- who had markers of chromosomal pathologies and malformations of the embryo;
- who already have children with chromosomal abnormalities.
Ultrasound diagnostics can detect malformations in 80-85% of cases. However, the technology is not impeccably reliable, as it misses pathologies in 20% of situations. Biochemical screening, invasive examinations have valid data. The latest version of the study allows you to identify up to 99% anomalies.
When planning a new pregnancy, it is imperative to visit a geneticist. Screening diagnostics for the detection of abnormal genes will help eliminate the risks of possible pathologies, the factor of heredity and genetic failure during conception. Sometimes the threat of miscarriage in the early stages exists in almost healthy carriers. The examination will allow you to find out about the anomaly in advance and undergo treatment.
What is a miscarriage like
A miscarriage that occurs is complete when all parts of the embryo come out of the uterine cavity together with membranes and amniotic fluid. If parts of the fetus remain in the uterus, they speak of an incomplete miscarriage, which occurs more often in the early stages of pregnancy.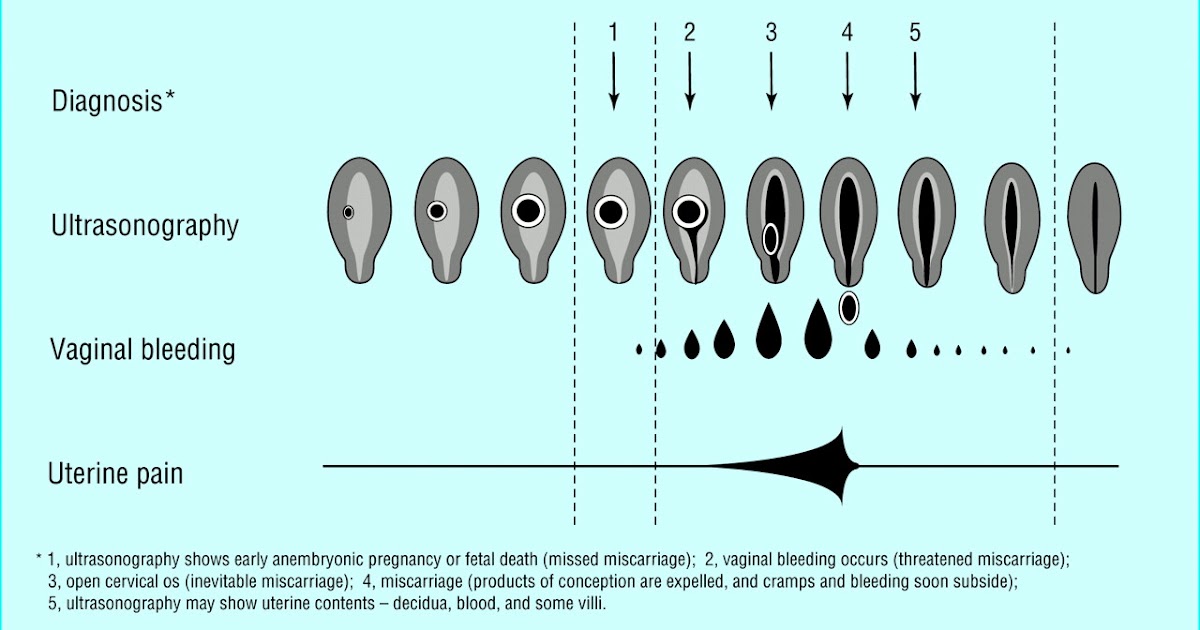 To neutralize the negative consequences, to prevent the development of an infectious process in the tissues, the product of conception is evacuated from the uterine cavity by the methods of medical interruption, gynecological curettage, and vacuum aspiration. Therapy may include the use of drugs aimed at contracting the uterus and pushing the contents out. The control method of diagnosis is considered to be ultrasound.
To neutralize the negative consequences, to prevent the development of an infectious process in the tissues, the product of conception is evacuated from the uterine cavity by the methods of medical interruption, gynecological curettage, and vacuum aspiration. Therapy may include the use of drugs aimed at contracting the uterus and pushing the contents out. The control method of diagnosis is considered to be ultrasound.
Why the body rejects the embryo
The causes of miscarriage often lie in the presence of chromosomal abnormalities in the fetus. Among the factors that provoke rejection of embryos are also:
- Heredity and genetic failure at the stage of fertilization of the egg by the sperm.
- A non-viable fetus may appear as a result of various risk factors - environmental conditions, occupational hazards, viral illness of parents. It is impossible to neutralize these factors. The only way out of the situation is to reduce the likelihood of their manifestation by protecting the expectant mother from dangers during gestation.
- Hormonal imbalance caused by disruption of the endocrine system. The situation can be affected by an insufficient amount of progesterone in the mother's body or an excess of testosterone. With early detection of a failure of the hormonal system, a woman undergoes specially organized therapy before pregnancy.
- The presence of tumors , neoplasms in the pelvic organs.
- Isthmic-cervical insufficiency when the isthmus and cervix dilate prematurely, unable to cope with the increasing pressure caused by the growing fetus in the body.
- There is a risk of miscarriage in the presence of anomalies in the work of the cardiovascular and renal systems.
- Drug addiction , alcohol addiction, substance abuse of mother and father.
- Depressive conditions , stress, nervous stress of a pregnant woman.
- Mechanical stress , blows, bruises, excessive physical labor of the future woman in labor.
- X-ray examination - radiation can cause miscarriage.
- Drug use . In the first trimester, you can not use potent medicinal formulas. Drugs can cause the development of defects in the embryo. Some decoctions of herbs are also contraindicated - parsley, tansy, cornflower, nettle, St. John's wort. It is forbidden to self-medicate. Each drug is agreed with the attending physician.
- Infectious and viral process in the body. Any sexually transmitted infection can provoke a miscarriage, which must be cured before pregnancy, otherwise there is a high risk of infection of the fetus in the womb. A great threat of miscarriage in the early stages exists due to viral infections and inflammation of the internal organs. A dangerous symptom is the high temperature of the mother, accompanied by intoxication of the body. At the stage of pregnancy planning, it is important to stop chronic diseases.
- History of abortion , unsuccessful surgery, unprofessionalism of the doctor and unfortunate circumstances.
- Immunological factors .
The list of causes of miscarriage in the early stages of pregnancy and in the later period may be more extensive, in each case, doctors identify the pathology individually.
Isthmic-cervical insufficiency (ICI)
One of the most common causes of spontaneous miscarriage during pregnancy is CSI - dilatation of the cervix and isthmus of the uterus as a result of increasing pressure from the growing fetus. Pre-pregnancy manipulations with the uterus (cervical dilation due to abortion, childbirth or curettage) affect the condition of the muscle ring. Damaged areas are tightened by scar tissue that does not have elasticity, is not amenable to stretching and contraction. ICI also has a functional nature when there is a hormonal imbalance.
ICI occurs in the period from the 11th to the 27th week after conception, when the embryo begins to produce androgens in the mother's body with the launch of the adrenal glands. Taking into account the mother's hormones, their indicator can be exceeded - this softens the cervix, opens and shortens it. Harmful bacteria and microorganisms penetrate into the formed channel, infecting the fetal egg. The initial stages of ICI do not have obvious symptoms, since they do not entail the tone of the uterine muscles. With the loss of strength of the membranes, amniotic fluid pours out. There are no pain sensations.
If a woman has had a miscarriage that started with amniotic fluid, she should report it to her doctor when monitoring a subsequent pregnancy.
Treatment of isthmic-cervical insufficiency
Endocrine disorders are corrected by prescribing hormonal drugs. An assessment of the condition of the uterus is carried out by a doctor a couple of weeks after the start of taking medications. They say about positive dynamics when the opening is suspended and no further expansion of the neck is observed. In the absence of the planned effect, surgical intervention is prescribed. Similar measures are used for the traumatic nature of the neck deformity. You should not be afraid of the operation, the doctor acts delicately, without causing additional injuries to the patient, without causing discomfort to the baby growing in the womb. The procedure is most effective in the early stages of pregnancy. Suturing can significantly reduce the risk of infection of the embryo through the lower edge of the cavity.
Surgical intervention takes place in a hospital. Before the operation, the pregnant woman is examined. After the procedure, the vagina is sanitized, for which the suturing site is treated with chlorhexidine and furatsilin for three days. The patient needs to undergo a weekly follow-up examination with the attending physician, where he assesses the situation, making adjustments to the therapeutic protocol if necessary. The sutures are removed at the 38th week of pregnancy. During this time, the neck matures, preparing the birth canal for the passage of the fetus. Many women in labor worry that they will need a caesarean section if they have stitches, but this is not true. In most cases, women give birth on their own.
Immediate action is recommended if the amniotic sac prolapses (falls out) into the cervix between 16 and 24 weeks. The suturing of the neck obliges the woman to observe bed rest, strictly follow the daily routine, avoid physical exertion, and do not skip taking medications. In rare cases, complications occur. Among them, the eruption of sutures through the tissues, provoked by the frequent tension of the muscles of the uterus. To prevent tone, tocolytics are prescribed - medicines to prevent premature birth. The expectant mother should be prepared for frequent examinations and smears, which may be caused by the likelihood of accumulation of pathological microflora on the suture threads.
It is also important to conduct psychological therapy, where a woman is taught relaxation techniques. The behavior of the future mother is a decisive factor in the successful bearing of the fetus in case of pregnancy complications. Panic and fuss create an unfavorable prognosis in stabilizing the situation. If a spontaneous abortion occurred for reasons of ICI, when you can get pregnant after a miscarriage, the doctor will say. Ideally, the period should be at least two years. The specialist must also take measures to prevent a repeated situation of losing a child.
In addition to the suture, ICI correction is also carried out using an obstetric pessary. An alternative method is the imposition of a special ring of hypoallergenic materials on the cervix. Silicone is the most commonly used. The ring creates additional support, preventing the opening of the neck.
Uterine hypertonicity - risk prevention
Uterine contractions before natural delivery is called hypertonicity. The condition is not an independent disease, it signals a malfunction in the body, often manifesting itself in the early stages of pregnancy. The causes of the pathological phenomenon are:
- Hormonal disorders caused by insufficient function of the placenta, ovaries, problems with the adrenal glands causing imbalance.
- Genital infantilism organ defects.
- Neoplasms , tumors in the uterus that are not necessarily malignant (eg, fibroids).
- During pregnancy infectious processes, viral diseases.
- CCI - opening of the cervix under increasing pressure created by the growing embryo.
- Immunological problems .
- Chronic diseases of the body (cardiovascular disorders, renal insufficiency).
- Past miscarriages early pregnancy, symptoms of which may recur, induced abortions.
In addition to physiological causes, psychological factors are of no small importance. A woman who is in a depressed state can provoke hypertonicity in herself.
You can feel the tension of the muscles of the uterus on your own, without the help of a specialist. This is evidenced by the heaviness that appears in the lower abdomen, pulling pains in the lumbar region. Symptoms are similar to painful menstruation. Arising in the first trimester, the condition provokes spontaneous abortion, missed pregnancy, death of the fetal egg. In the subsequent period, premature birth due to hypertonicity is likely.
Why does the tension of the walls of the uterus cause irreversible consequences? The reason is the disturbed blood supply to the placental tissues, the occurrence of hypoxia of the embryo and the slowdown in the development of the emerging child. Following the contraction of the muscles of the uterus, the placenta does not contract, which causes its detachment and provoking the release of the fetal bladder.
Hypertonicity is diagnosed during a scheduled visit to a specialist. Stabilization of the situation requires the appointment of sedative drugs and antispasmodics. A strengthening effect is provided by therapy with the inclusion of vitamin B6, magnesium. In most cases, the measures taken are sufficient to neutralize the risks. Self-treatment, which can cause irreversible consequences, is strictly prohibited. With hypertonicity, the main rule for a pregnant woman is calmness and lack of physical activity. Some women who have had a successful delivery say they "didn't get up" during their entire pregnancy. With hypertonicity, sexual intercourse is also excluded.
If the threat cannot be neutralized, hospitalization is recommended. It is especially dangerous when severe cramping pain is complemented by spotting. Lie down "for preservation" is an adequate measure in the struggle for the birth of a healthy and strong baby. In the hospital walls, a pregnant woman is prescribed a vaginal examination, ultrasound. If necessary, a woman takes urine and blood tests, checks the hormonal background, and is examined for the presence of STIs.
At the onset of labor activity before the 34th week, the condition is tried to be stabilized with tocolytics. The most dangerous period is from the 25th to the 28th week, when the woman is recommended the maximum possible bed rest. After that, the fetus has every chance of survival. In order to quickly form the pulmonary system of the embryo, allowing it to survive with an early birth, hormones are prescribed.
Having an unfavorable prognosis for miscarriage and the threat of miscarriage, it is necessary to take up prevention at the stage of conception planning.
Stages of spontaneous termination of pregnancy
There are certain signs that attract attention and divide the course of a miscarriage into specific stages:
Symptoms of miscarriage - how not to miss the threat
If there is a threat of miscarriage in the early stages, the following symptoms may occur: The pain may be monotonous or come in waves.
A woman who does not know how an early miscarriage occurs should listen to her inner state.
Should alert:
- spasmodic pain impulses;
- Drawing pain in the lumbar region.
In the later stages, the above symptoms are added:
- liquid discharge from the vagina, which may indicate damage to the amniotic sac;
- pain when urinating;
- internal bleeding, which warns of a deterioration in the general condition, fainting, dizziness, pallor of the skin.
All this is an indication for emergency hospitalization of a pregnant woman.
The beginning of an abortion is characterized by more pronounced symptoms of a miscarriage - contraction-like pain, severe dizziness, loss of strength. Instead of smearing discharges, clot-like ones appear, abundantly manifested during movement. Pregnancy can be saved if the area of detachment of the fetal egg is small and the fetal heartbeat is determined.
The third stage is useless for saving the fetus. There is girdle pain in the lower back and abdomen. Together with abundant blood loss, a fetal egg comes out of the uterus. Incomplete miscarriage requires curettage of the uterine cavity if parts of the embryo or membranes of the fetal egg remain in it, otherwise there is a high risk of complications that will endanger the life of the mother.
In rare cases, complications and serious health consequences can occur after a spontaneous abortion. But in the majority of situations, the body independently copes with what happened, expelling the parts remaining in the uterine cavity with a natural contraction of the muscles. An early spontaneous miscarriage does not always occur, a dangerous condition can also occur in the later stages. Some women try to provoke the release of the fetus with decoctions of herbs and medications. This is fraught with complications, including sepsis, dysfunction of the reproductive organs, after which pregnancy becomes impossible.
Methods of diagnosis
The symptoms of a threatened miscarriage at an early stage will be determined by a doctor during a visit to the antenatal clinic. The specialist will check the size of the uterus, determine the tone of its muscles, the condition of the cervix, and examine the discharge from the genital organs. A reliable method to identify the existing threat is transvaginal ultrasound diagnostics. The doctor draws attention to segmental muscle contractions of the uterus, detachment of the fetal egg. Genetic testing will help analyze the likely causes of a miscarriage. The patient's history is carefully collected.
Planning a new pregnancy
The medical community is unanimous in the issue of planning a new pregnancy after a spontaneous abortion. Conception is not recommended for at least 3-6 months. During this period, the woman's body will recover and gain strength to carry the fetus. Observation by a doctor, harmonization of hormonal levels, examination of parents to identify possible pathologies are important. In order not to become pregnant in the first months, it is recommended to use contraceptive methods prescribed by your doctor.
Examination after a miscarriage includes blood and urine tests, examination of the microflora of the vagina with a smear, detection of overt and latent genital infections, glucose and hormone tests, examination of partners for biological compatibility. Planning is an important step towards having a healthy baby. After the studies, the woman is prescribed strengthening therapy. It is important to completely reconsider eating habits, to exclude factors that are harmful to well-being. Vitamins, folic acid are used. Fast food, food containing carcinogens and preservatives are excluded from the diet. Subject to the rules recommended by the doctor, a successful pregnancy with a favorable outcome is likely.
It is not uncommon for a pregnancy test to show two lines after a miscarriage. This is due to the restructuring of the body, the organs of the reproductive system. It is important to report the incident to your doctor. The presence of remnants of embryonic tissue in the uterus can provoke a positive test result. In this case, immediate curettage is necessary, which neutralizes the risk of inflammation and infection. To accurately determine her condition, a woman needs to undergo an ultrasound diagnosis, take tests to determine hCG in the blood.
The question of whether it is possible to get pregnant after a miscarriage worries many parents. The answer is unequivocal - yes, if you follow the recommendations of experts, carefully plan a new conception, monitor your well-being and state of your health.
Components of success after a miscarriage
Spontaneous abortion can provoke not only the health of the patient, but non-compliance with simple rules can be a threat. To reduce the risk of losing a child during pregnancy, you need to:
1. Keep calm – it is important for a mother to eliminate all factors that make her nervous from her life. Irritation is not the best way to normalize the condition. In order to stabilize the emotional background, rest is recommended, the use of soothing teas with the permission of the doctor. Good results are given by decoctions of chamomile, lemon balm, mint.
2. Avoid taking unnecessary medicines and preparations. But it is unacceptable to stop the therapy prescribed by the doctor on your own. Each step must be discussed with the gynecologist.
3. Eliminate harmful occupational factors. Work in the chemical industry and other hazardous facilities can create an undesirable background in the body, which prevents normal gestation. It is important to understand what is of great value to the mother - the birth of a healthy baby or a career factor. Many refuse to work to increase the chance of having a baby.
4. Eliminate bad habits. It is unacceptable for a woman who has experienced miscarriage to drink alcohol and smoke. It is forbidden to do this and the future father. This negatively affects the quality of spermatozoa, provokes difficulties with conception and risks of deviations in the development of the embryo.
5. Take vitamin complexes, specially designed to prepare the body for pregnancy, the formation of basic conditions for its favorable course.
6. Eat right. A complete, balanced diet works wonders. With a lack of weight, a nutritionist will develop an adequate diet for a woman with the inclusion of a large amount of protein foods rich in vitamins and trace elements of vegetables, fruits, and cereals. Recommended fats contained in fish, seeds, nuts, avocados, olives.
7. Get rid of extra pounds. Obesity adversely affects the development of pregnancy. Science has proven that enhanced nutrition during this period is not required. The main thing is its balance.
Infections during pregnancy
Infectious processes transferred before pregnancy develop immunity in the mother to similar agents of influence. Primary infection poses a great threat, so vaccination will be useful before planning conception. Perinatal diagnosis allows you to detect the infectious process at the initial stage and prevent its harmful effects. This is possible if the pregnant woman is registered from an early date.
Infection may develop due to an infection transmitted by airborne droplets. It is the most dangerous, since it is almost impossible to prevent it. This applies to mumps, measles, rubella. HIV and hepatitis infect the body through sexual contact, similar to chlamydia. Listeriosis is transmitted with poor-quality products. A pregnant woman can pass infections to a developing baby. Pathology is determined by profile tests of latent infection.
Routine pregnancy monitoring involves regular testing. Sexual infections are determined using a smear, ultrasound shows deviations in the development of the baby, and KGT is aimed at listening to the work of the fetal heart muscle. If there is a suspicion of a serious infection of the embryo, blood sampling from the umbilical cord and amniotic fluid analysis are practiced.
Infection of a child also depends on concomitant factors. The speed of diagnosis, the literacy of the treatment, the type of pathogen, the duration of the pregnancy are taken into account. The following infectious processes deserve special attention:
1. Viral etiology - a huge number of viruses poses a danger to a pregnant woman. The threat is genital herpes, rubella, infectious type erythema, cytomegalovirus, hepatitis B, measles, mumps, chickenpox.
2. Bacterial infections, detected during the analysis of biological materials (feces, urine, blood), examination of certain organs of the body. Active reproduction provokes a rapid growth in the number of bacteria in the vagina. Not all microorganisms pose a threat to the child. Dangerous candidiasis, streptococcus, chlamydia, bacterial vaginosis, cystitis.
The successful course of pregnancy is threatened by intestinal infections, often activated in the summer. Their carriers can be animals and poorly processed food before consumption. Of particular danger are listeriosis, salmonellosis, toxoplasmosis.
Prevention of infections during pregnancy
Infection of the mother poses a threat to the life of the fetus. From the 3rd to the 12th week, the infected organism responds with a miscarriage or the formation of malformations of the child. From the 11th to the 25th - developmental delay. At a later date, organs are deformed and prerequisites for premature birth are created. In order to prevent intrauterine infection, it is recommended to apply a number of rules:
- be examined for the detection of STIs;
- examine blood, determine the presence of antibodies to infection carriers, pathogens;
- avoid contact with sick people, visits to crowded places where there is a possibility of infection by airborne droplets;
- screen pets for dangerous infections, treat them if necessary, or remove them from the home until the threat is eliminated;
- exclude fast food, store-bought semi-finished products from the diet, thoroughly heat treat meat, fish;
- remove from the diet sushi and other culinary delights purchased in restaurants, cafes;
- thoroughly wash hands, fruits, vegetables with special disinfectants that are not capable of harming the pregnant woman and the child;
- it is planned to visit a gynecologist, undergo examinations recommended by a doctor, take tests, take vitamins;
- register at the first sign of pregnancy;
- prepare for conception, cure infections, vaccinate.
It is also important for the child's father to follow most of the recommended rules. If only the mother undergoes treatment, a relapse is likely during sexual intercourse, neutralizing the beneficial effect of therapy.
A woman who has had a miscarriage in the past should be alerted to any deviations from the norm in her state of health. It is important to pay attention to ailments, pain, weakness, dizziness. Accounting for an early consultation will create conditions for the bearing of the fetus and the birth of a child. There is no need to be afraid that a miscarriage will forever deprive the joy of motherhood.
Having completed a course of examinations, passing tests and following the measures prescribed by the doctor to treat imbalances in the body, you will create all the conditions for a favorable pregnancy outcome. Tune in to the positive, protect yourself from worries, worries, stress. Feel the support of loved ones, hope for the best! Get advice from good specialists to rule out any unfavorable prognosis before conception or take steps to neutralize them. Health and prosperity to you, your families and loved ones!
Blood clots in uterus after medical abortion!!!
Blood clots in the uterus ...
ago
1
...
...
6
forward
9000
- 9000
Operation of the thyroid gland
25,375 responses
-
Life after cervical cancer0515 Breast cancer (breast cancer). What research is needed?
8 905 answers
-
Launched face neuritis
3 220 answers
-
Chronic urethritis ... There is no more forces
19 317 answers
-
Vladimir Titarenko
Fitness nutritionist
227 answers
-
Vladimir Weiss
Neopsychologist
135 answers
-
Maria Burlakova
Psychologist
357 answers
-
Irina Kostoglodova
Family psychologist
7 answers
-
Basenkova Olga
Psychologist
37 answers
-
Sadovnikov Ernest
Psychologist.
...
100 answers
-
Ivanova Svetlana
Coach
91 answers
-
Yuri Anatolyevich Ionov
Psychologist, Supervisor,...
13 answers
-
Anna Antonchik
Female psychologist
231 answers
-
Nikita Nosov
Practicing psychologist
43 answers
-
I am infuriated with my children and grandchildren .
..
1,527 answers
-
The man immediately warned that all property was recorded for children
1 177 answers
-
This salary - I don't want to work
777 answers
-
A 22-year-long lie. How to destroy?
1025 answers
-
Husband left, 2 months of depression... How will you cope if you are left all alone?
208 replies
-
Pulling the ovary and throwing up
3 answers
-
Life with one kidney
No answers
-
My joints started to hurt after the virus.
Who faced?
2 answers
-
The lower abdomen sticks out, there is no pregnancy!
2 Answer
-
Periodic pain after urination
No answers
260 22 Go to
#1
#4
Polina
I also had blood in the uterus after cleaning the polyps in the uterus, so the doctor told me that it was a spasm spaced spasmodics, everything turned out to be
#5
#6
# 7
#8
Guest
Author, stay safe. Everything will fall out with the next menstruation, even without Duphaston.
#9,0003
#11
9000
Don't go cleaning. This is a very harmful traumatic operation! It cannot be allowed.
#13
#14
Kralya
And what do you propose to do if it doesn't work out by itself?
#15
#16
9000 2014, 22:15
#18
Guest
It happened to me, I drank weed and duphaston, and they did uterine massage and oxytocin pricked me, but the clot did not come out. But I didn’t go for a cleaning .., I drank a course of antibiotics, I suffered a little back pain and that’s all, perhaps. I forgot about it for two years. And now, according to the ultrasound, I have an uneven endometritis, it seems to me that I have chronic endometritis.
#19
#21
9000 9000 #22
GOOD
GOST
GOSTIC I also had clots after a honey abortion, oxytocin pricked, everything was removed with menstruation.
#24
Guest
it may turn out that this is not a clot, but a fertilized egg. I advise you to closely monitor your condition. if bleeding opens from time to time, especially after intercourse, then just run for cleaning.
#25,0003
#26
Guest
I had a spasm and blood did not go out (generally did not go out (generally blood (generally there was not a drop of blood after the abortion). At first I was happy, but on the fifth day my stomach began to hurt badly. I pumped the press and did special exercises (rhythmic contractions of the muscles of the perineum), the spasm passed, the blood came out and everything returned to normal. I really didn’t want to clean and the exercises helped me, but sex didn’t help. The gynecologist advised me to do the exercises. Although rest is usually recommended after an abortion, in such cases it is sometimes impossible to cope with a spasm in a different way. I also tried No-shpu and oxytocin. Didn't help.
#27
Guest
It happened to me, after the abortion there was a spasm and the blood did not come out (in general, there was not a drop of blood after the abortion). At first I was happy, but on the fifth day my stomach began to hurt badly. I pumped the press and did special exercises (rhythmic contractions of the muscles of the perineum), the spasm passed, the blood came out and everything returned to normal. I really didn’t want to clean and the exercises helped me, but sex didn’t help. The gynecologist advised me to do the exercises. Although rest is usually recommended after an abortion, in such cases it is sometimes impossible to cope with a spasm in a different way. I also tried No-shpu and oxytocin. Didn't help.
Woman.ru experts
#28
#29
9000 #30,000 #30,000 #30,000 #30,000 #30,000 #30,000 #30,000 #30,000 #30000 # December 2014, 23:30
#31
Unreliable stories
#33
Guest
It happened to me, after the abortion there was a spasm and the blood did not come out (in general, there was not a drop of blood after the abortion). At first I was happy, but on the fifth day my stomach began to hurt badly. I pumped the press and did special exercises (rhythmic contractions of the muscles of the perineum), the spasm passed, the blood came out and everything returned to normal. I really didn’t want to clean and the exercises helped me, but sex didn’t help. The gynecologist advised me to do the exercises. Although rest is usually recommended after an abortion, in such cases it is sometimes impossible to cope with a spasm in a different way. I also tried No-shpu and oxytocin. Didn't help.
#34
Natalia
I have a similar situation now, I don’t know what to do either, after an abortion for a period of 5-6 weeks (there were two fetal eggs), I had a little cover and it stopped, after 10 days I did a control test, showed 2 strips, went for an ultrasound, they said that there was nothing, everything is fine, like, the body has not yet rebuilt ... I foolishly went to the gym (before that I went), it looked like a week, not strong I gave a load, a week later the blood went - in the literal sense - it beat like a fountain, from half a liter it poured into the bathroom - it’s good that I was at home, there was blood for two days, then a daub for a couple more days, after 2 days I did the test again - again two strips, but the second one is very weak, went for an ultrasound, they said that it is not clear - the uterus is filled with liquid, it is enlarged for 7-8 weeks, the echo is 5 times more than on the first ultrasound, when they put 5-6, they gave some aconite and Sekale to drink, they said a week later again on the ultrasound . .. I'm in shock, in general ... the daub is a little bit completely, the color of melted milk chocolate ... there is no smell, my lower back hurts, I'm depressed ... I don't know what to do.
#35
#36
#37
27 2015, 16:00
#38
#39
#41
#42
Diana
Hello dear women!!! Today I was on a control ultrasound after a honey abortion, the ultrasound showed a clot of 9 mm, the doctor said that the clot would come out with subsequent menstruation; I am very worried!!! Maybe someone has come across such a situation, maybe they can drink something so that the clot comes out! Please tell me!
New Topics
9000 #43
Eva Ket
Do not worry! The doctor should prescribe drugs that increase uterine contractions for the next menstruation, and everything will come out. My situation has not been resolved! The whole reception of duphaston smeared continuously. Now the delay is already 9days! I'm going for an ultrasound on Monday. I don’t want to drink hormones without analysis anymore (why did the doctors take it that I don’t have enough progesterone???), but I’m very afraid to do a purge. It seems to me that a lot of my condition is due to improper therapy! Well, what prevented you from prescribing an ultrasound IMMEDIATELY after an abortion and not after 10 days? And help the uterus with oxytocin during an abortion.