Nt ultrasound results
NT Scan During Pregnancy: What Your Results Mean
Written by Cheryl Whitten
In this Article
- What Is an NT Scan for Down Syndrome?
- What Does an NT Scan Check For?
- What Happens at a Nuchal Translucency Scan?
- What Are the Risks of an NT Scan?
- Is an NT Scan Necessary?
- What Do Your NT Scan Results Mean?
- What Happens if an NT Scan Is Abnormal?
- The Takeaway
If you’re pregnant, your doctor might have mentioned an NT scan or first-trimester screening. An NT scan is a simple test that shows your baby’s risk for some genetic conditions.
What Is an NT Scan for Down Syndrome?
An NT scan, or nuchal translucency scan, is a non-invasive ultrasound screening for Down syndrome and other genetic conditions during pregnancy. It’s usually done between weeks 11 and 14 of pregnancy.
Some people also have blood tests done at the same time that look for certain hormones and proteins, including:
- Free beta-human chorionic gonadotropin, or b-hCG
- Pregnancy-associated plasma protein-A, or PAPP-A
- Alpha-fetoprotein, or AFP
All pregnant people have these hormones and proteins, but the levels can be higher or lower than average when the baby has Down syndrome or other disorders. These screenings together are called the combined or integrated first-trimester screening.
What Does an NT Scan Check For?
All unborn babies have a skin fold, called a nuchal fold, at the back of the neck that holds fluid. Babies with certain genetic conditions have more fluid than normal, and the nuchal fold is thicker.
An NT scan measures this fold to check for the risk of genetic conditions like:
Down syndrome. Down syndrome, or trisomy 21, is a genetic disorder where babies have an extra 21st chromosome. Chromosomes are packages of genes that tell the body how to grow. An extra chromosome changes how the brain and body develop and can cause intellectual and physical disability, birth defects, and health problems.
Trisomy 13 and 18.Trisomy 13 and trisomy 18 happen when babies have an extra copy of either chromosome 13 or chromosome 18, respectively. These genetic disorders cause serious birth defects and intellectual disability, often leading to early death.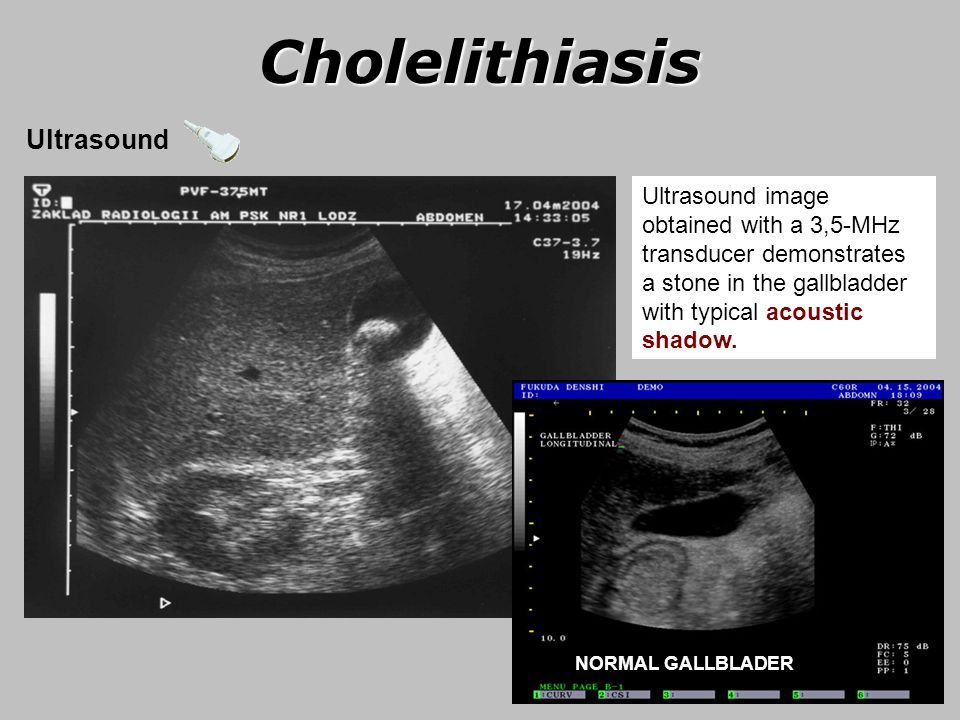
Turner syndrome. A baby with Turner syndrome is missing all of or part of the X chromosome. This only affects babies with X chromosomes and can cause growth problems and heart and ovary defects at birth.
Congenital heart disease. Babies with congenital heart disease are born with heart defects that change how blood flows through the heart. Some defects are life-threatening, and some don’t cause any problems.
An NT scan doesn’t diagnose or confirm any of these disorders, though. Instead, it tells you whether your baby has a higher risk of having one of these conditions.
Since an NT scan is an ultrasound, your doctor might also check for other things, including:
- How your baby is growing
- How many babies you’re carrying
- Whether multiple babies share a placenta
- Exactly how far along you are in your pregnancy
What Happens at a Nuchal Translucency Scan?
An NT scan is a routine ultrasound. You need to have a full bladder, so the ultrasound technician will ask you to drink 2 to 3 glasses of water an hour before the scan. You can’t urinate before the test, so you might feel full and uncomfortable.
You need to have a full bladder, so the ultrasound technician will ask you to drink 2 to 3 glasses of water an hour before the scan. You can’t urinate before the test, so you might feel full and uncomfortable.
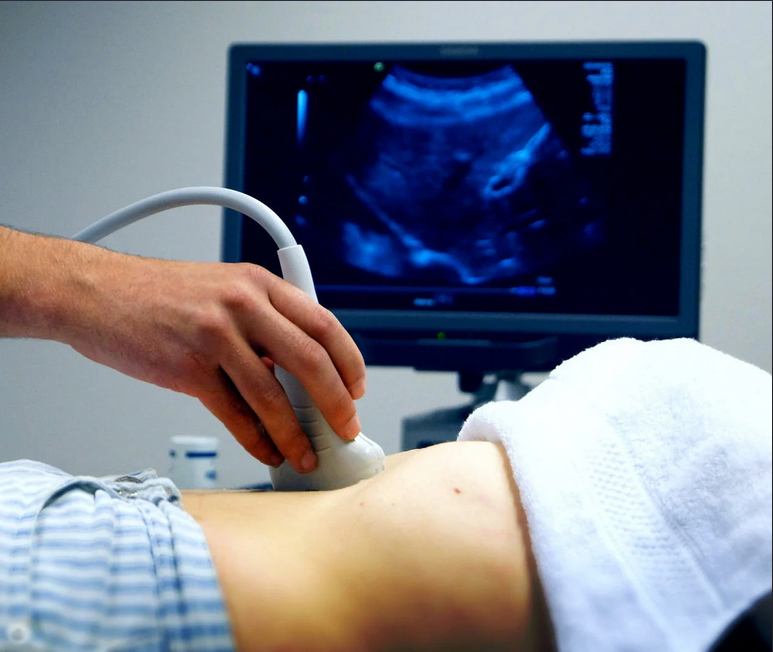
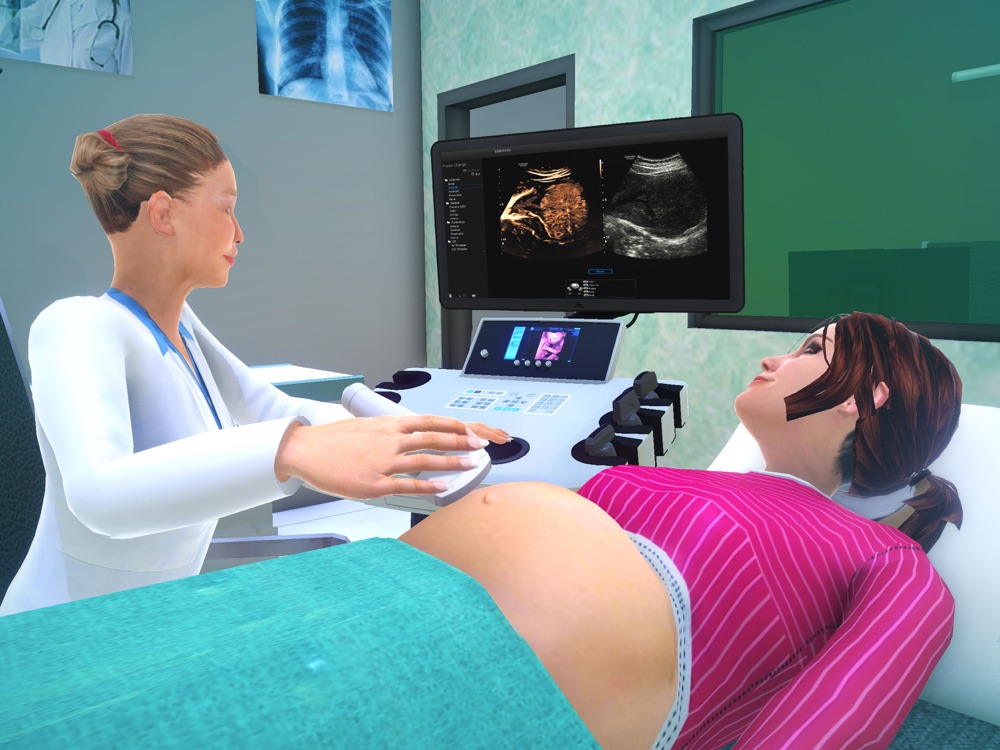
During the test, you'll lay down on a table and the technician will put gel on your lower belly. They'll move a wand across your abdomen and take some pictures. Once they have the pictures, your scan will be done, and you can go back to your regular activities. A radiologist will read the scans and send the results to your doctor.
What Are the Risks of an NT Scan?
There are no known risks for an NT scan. Ultrasounds are safe and non-invasive, and you can’t feel the ultrasound waves. You might feel some pressure as the technician moves the wand around your belly. This is normal and helps get the best view of your baby.
Is an NT Scan Necessary?
NT scans are optional. You have the option of getting this test early in your pregnancy, which will give you results early on. Early results can help you plan for the possibility of caring for a child with disabilities.
Early results can help you plan for the possibility of caring for a child with disabilities.
You can also decline this test. If you think it would cause too much stress, or if it won’t change how you manage your pregnancy or plan for your child, you might decide against it.
What Do Your NT Scan Results Mean?
The skin fold grows as unborn babies grow, so the test measures the thickness of the skin fold and compares it to babies of the same age in the womb. If the measurement is higher than the average measurement, then the risk for some genetic conditions is higher.
What is the NT scan normal range? At 11 weeks, the skin fold measures up to 2 mm. At 13 weeks and 6 days, it can be up to 2.8 mm. If your baby’s measurements are within this range, they have a low chance of having Down syndrome or other genetic disorders.
What is an abnormal NT scan measurement? An abnormal measurement is when the skin fold measure is larger than the normal range of up to 2 mm at 11 weeks or 2. 8 mm at 13 weeks 6 days.
8 mm at 13 weeks 6 days.
Your doctor will consider the measurements along with your age and your blood tests. While testing only shows the chances of having a condition, an NT scan with bloodwork can correctly predict genetic conditions in 85% of cases. About 5% of test results are false positives, which means they incorrectly suggest a higher chance.
What Happens if an NT Scan Is Abnormal?
If your NT scan has abnormal measurements, your doctor might suggest more testing. These tests can include:
- Chorionic villus sampling, where they test a tiny piece of the placenta
- Amniocentesis, where they test a small amount of amniotic fluid from your uterus
- Prenatal cell-free DNA (cfDNA) screening, where they take some of your blood and look at your baby’s DNA
These tests do have a risk of causing pregnancy loss, so your doctor will go over the risks and benefits for your situation. If you decide to have the test, your doctor will discuss your results with you and help you understand what they mean.
The Takeaway
An NT scan is a safe and routine — but optional — ultrasound scan that can help predict the chances of your baby having Down syndrome. It’s sometimes done along with bloodwork in your first trimester.
NT Scan During Pregnancy: What Your Results Mean
Written by Cheryl Whitten
In this Article
- What Is an NT Scan for Down Syndrome?
- What Does an NT Scan Check For?
- What Happens at a Nuchal Translucency Scan?
- What Are the Risks of an NT Scan?
- Is an NT Scan Necessary?
- What Do Your NT Scan Results Mean?
- What Happens if an NT Scan Is Abnormal?
- The Takeaway
If you’re pregnant, your doctor might have mentioned an NT scan or first-trimester screening. An NT scan is a simple test that shows your baby’s risk for some genetic conditions.
What Is an NT Scan for Down Syndrome?
An NT scan, or nuchal translucency scan, is a non-invasive ultrasound screening for Down syndrome and other genetic conditions during pregnancy. It’s usually done between weeks 11 and 14 of pregnancy.
It’s usually done between weeks 11 and 14 of pregnancy.
Some people also have blood tests done at the same time that look for certain hormones and proteins, including:
- Free beta-human chorionic gonadotropin, or b-hCG
- Pregnancy-associated plasma protein-A, or PAPP-A
- Alpha-fetoprotein, or AFP
All pregnant people have these hormones and proteins, but the levels can be higher or lower than average when the baby has Down syndrome or other disorders. These screenings together are called the combined or integrated first-trimester screening.
What Does an NT Scan Check For?
All unborn babies have a skin fold, called a nuchal fold, at the back of the neck that holds fluid. Babies with certain genetic conditions have more fluid than normal, and the nuchal fold is thicker.
An NT scan measures this fold to check for the risk of genetic conditions like:
Down syndrome. Down syndrome, or trisomy 21, is a genetic disorder where babies have an extra 21st chromosome. Chromosomes are packages of genes that tell the body how to grow. An extra chromosome changes how the brain and body develop and can cause intellectual and physical disability, birth defects, and health problems.
Chromosomes are packages of genes that tell the body how to grow. An extra chromosome changes how the brain and body develop and can cause intellectual and physical disability, birth defects, and health problems.
Trisomy 13 and 18.Trisomy 13 and trisomy 18 happen when babies have an extra copy of either chromosome 13 or chromosome 18, respectively. These genetic disorders cause serious birth defects and intellectual disability, often leading to early death.
Turner syndrome. A baby with Turner syndrome is missing all of or part of the X chromosome. This only affects babies with X chromosomes and can cause growth problems and heart and ovary defects at birth.
Congenital heart disease. Babies with congenital heart disease are born with heart defects that change how blood flows through the heart. Some defects are life-threatening, and some don’t cause any problems.
An NT scan doesn’t diagnose or confirm any of these disorders, though. Instead, it tells you whether your baby has a higher risk of having one of these conditions.
Instead, it tells you whether your baby has a higher risk of having one of these conditions.
Since an NT scan is an ultrasound, your doctor might also check for other things, including:
- How your baby is growing
- How many babies you’re carrying
- Whether multiple babies share a placenta
- Exactly how far along you are in your pregnancy
What Happens at a Nuchal Translucency Scan?
An NT scan is a routine ultrasound. You need to have a full bladder, so the ultrasound technician will ask you to drink 2 to 3 glasses of water an hour before the scan. You can’t urinate before the test, so you might feel full and uncomfortable.
During the test, you'll lay down on a table and the technician will put gel on your lower belly. They'll move a wand across your abdomen and take some pictures. Once they have the pictures, your scan will be done, and you can go back to your regular activities. A radiologist will read the scans and send the results to your doctor.
What Are the Risks of an NT Scan?
There are no known risks for an NT scan. Ultrasounds are safe and non-invasive, and you can’t feel the ultrasound waves. You might feel some pressure as the technician moves the wand around your belly. This is normal and helps get the best view of your baby.
Is an NT Scan Necessary?
NT scans are optional. You have the option of getting this test early in your pregnancy, which will give you results early on. Early results can help you plan for the possibility of caring for a child with disabilities.
You can also decline this test. If you think it would cause too much stress, or if it won’t change how you manage your pregnancy or plan for your child, you might decide against it.
What Do Your NT Scan Results Mean?
The skin fold grows as unborn babies grow, so the test measures the thickness of the skin fold and compares it to babies of the same age in the womb. If the measurement is higher than the average measurement, then the risk for some genetic conditions is higher.
What is the NT scan normal range? At 11 weeks, the skin fold measures up to 2 mm. At 13 weeks and 6 days, it can be up to 2.8 mm. If your baby’s measurements are within this range, they have a low chance of having Down syndrome or other genetic disorders.
What is an abnormal NT scan measurement? An abnormal measurement is when the skin fold measure is larger than the normal range of up to 2 mm at 11 weeks or 2.8 mm at 13 weeks 6 days.
Your doctor will consider the measurements along with your age and your blood tests. While testing only shows the chances of having a condition, an NT scan with bloodwork can correctly predict genetic conditions in 85% of cases. About 5% of test results are false positives, which means they incorrectly suggest a higher chance.
What Happens if an NT Scan Is Abnormal?
If your NT scan has abnormal measurements, your doctor might suggest more testing. These tests can include:
- Chorionic villus sampling, where they test a tiny piece of the placenta
- Amniocentesis, where they test a small amount of amniotic fluid from your uterus
- Prenatal cell-free DNA (cfDNA) screening, where they take some of your blood and look at your baby’s DNA
These tests do have a risk of causing pregnancy loss, so your doctor will go over the risks and benefits for your situation. If you decide to have the test, your doctor will discuss your results with you and help you understand what they mean.
If you decide to have the test, your doctor will discuss your results with you and help you understand what they mean.
The Takeaway
An NT scan is a safe and routine — but optional — ultrasound scan that can help predict the chances of your baby having Down syndrome. It’s sometimes done along with bloodwork in your first trimester.
Ultrasound: the result of the study is not yet a diagnosis
September 19, 2021
Reading time: 3 minutes
No time to read?
11045 views
Many patients, having received a diagnostic report based on the results of a medical examination, believe that this is the diagnosis. And once there is a diagnosis, then treatment can be prescribed. It's a delusion. Such diagnostic conclusions are only part of the diagnostically significant data necessary for the attending physician to establish a diagnosis and prescribe effective therapy. nine0003
One of the most popular, non-invasive diagnostic methods is ultrasound.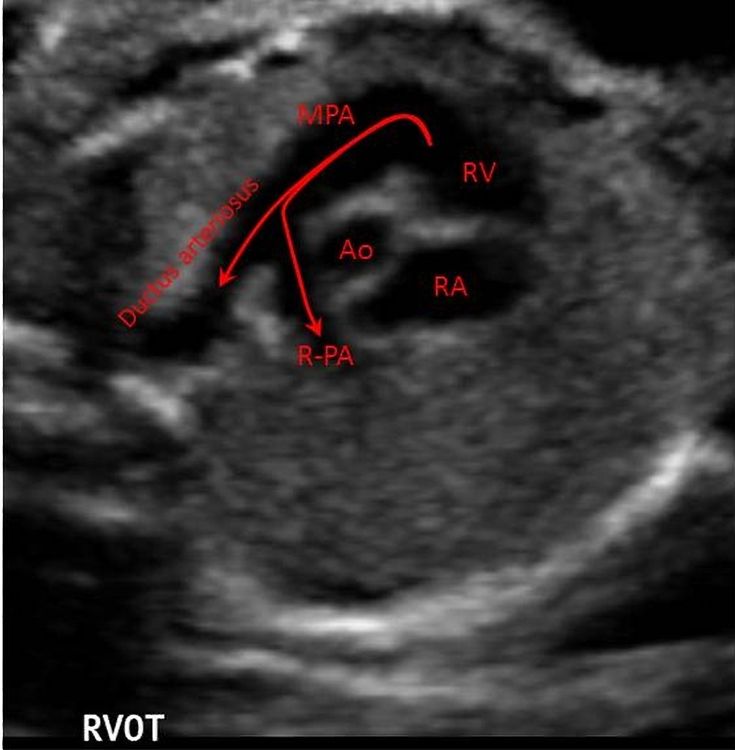 It allows you to visualize various changes in organs and tissues at an early stage, when even symptoms do not appear. It is widely used in gynecology, when detecting pathologies in the reproductive system or assessing the development of the fetus.
It allows you to visualize various changes in organs and tissues at an early stage, when even symptoms do not appear. It is widely used in gynecology, when detecting pathologies in the reproductive system or assessing the development of the fetus.
Thanks to ultrasound at an early stage, changes in the organs of the abdominal cavity and small pelvis can be detected. With the help of ultrasound, cirrhosis of the liver, fatty hepatosis, the presence of stones in the gallbladder or kidneys, mechanical damage to internal organs and other pathologies are determined with great accuracy. nine0003
In cardiology, research is done on people who have suffered such dangerous acute diseases as stroke and heart attack, patients with high blood pressure, suffering from fainting, and children with poor digestibility of study material. Ultrasound allows you to identify the state of the lumen of the vessels, the state of the tissues surrounding them, the presence of cholesterol plaques and blood clots, to assess the blood flow of the entire vascular system.
The results of the study provide invaluable assistance in the diagnosis of vascular diseases such as aneurysm or atherosclerosis, even in the early stages, when there are no clinical manifestations yet. Based on the data obtained, the cardiologist can assess future risks, including the development of a stroke. nine0003
Ultrasound is performed as a preventive measure. For women and men over 40 years of age, for the purpose of early diagnosis of oncology, it is recommended to do an ultrasound scan annually.
But it should be remembered that the results of one single examination are not enough to make a diagnosis. According to the diagnostic conclusion, it is impossible to determine the causes of the disease, the sources of pathological processes. In some cases, ultrasound can reveal only indirect signs of the presence of pathological changes or determine the condition of the organs or tissues under study. This is not enough to determine the danger of changes detected by ultrasound. Accordingly, it is impossible to prescribe adequate therapy. nine0003
Accordingly, it is impossible to prescribe adequate therapy. nine0003
In this case, as a rule, for control and clarification, additional diagnostics, including MRI, CT, biopsy, and others, depending on the clinical picture, may be necessary. Their need is determined by the attending physician. These are the features of a diagnostic search, which can be lengthy and multi-stage and begins with a hypothesis, its confirmation, clarification or refutation.
Therefore, the diagnostic conclusion, no matter how perfect the instrumental diagnostic method, is not a diagnosis! The final diagnosis is determined only after a complete examination of the patient. And this can only be done by the attending physician, who has a complete picture of the patient's condition, obtained as a result of analyzing the totality of data obtained both during a consultation appointment - examination and questioning of the patient, and during highly informative diagnostic studies and tests. nine0003
Do not neglect the advice of a specialist and do not limit yourself to diagnostic studies. Be healthy. Take care of yourself and those you love.
Be healthy. Take care of yourself and those you love.
| To the list of articles | Share article: |
Recent publications
January 23, 2023
Obstetric pathologies and stroke: when you need help from a neurologist
Antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) is an autoimmune disease in which blood clots form in the blood vessels. That is why APS is one of the topical multidisciplinary problems of modern medicine. The clinical manifestations of APS are very diverse and affect the areas of interest of doctors of many specialties: rheumatologists, cardiologists, obstetricians-gynecologists, and therapists.
Read
August 16, 2022 nine0003
Answering questions about infertility treatment
Every fifth couple in Russia faces the problem of infertility. At the same time, it is important not to waste time. Statistical studies have shown that the main medical causes of infertility in 36% of cases were problems with ovulation, in 30% of cases - obstruction of the fallopian tubes and in 18% - endometriosis.In this article, we will answer questions about the causes and treatment of infertility.
Read
April 24, 2022 nine0003
Habits to help lower blood pressure
With high blood pressure, vulnerabilities appear in the arteries, where atherosclerotic plaques quickly form. In this case, there is a risk of damage to them. This is a life-threatening phenomenon. When this happens, a blood clot, a thrombus, immediately forms around the atherosclerotic plaque. It blocks the flow of blood to parts of the body.
It blocks the flow of blood to parts of the body.
Read
nine0006 August 14, 2022Inflammatory diseases of the reproductive system
Female inflammatory diseases are one of the most urgent problems of modern gynecology. To stay healthy and avoid unwanted problems, every woman should have an examination by a gynecologist once a year.
Read
April 12, 2022
Many changes in the structure and functioning of the female organs are asymptomatic at first
Most people do not pay attention to health, because this is our normal state. We don't notice it. After all, health is a state of the body when there is no disease and nothing hurts. And this inattention sometimes costs us dearly. Often, in some hospitals, a person can hear from a doctor that if there is no illness, then he is healthy, and there is nothing for us to do with you. But the gynecologists of the Medservice clinic (Izhevsk) are sure that women's health needs their attention, it needs to be maintained and strengthened. A stable, calm life filled with bright colors and emotions directly depends on physical and reproductive health. nine0003
But the gynecologists of the Medservice clinic (Izhevsk) are sure that women's health needs their attention, it needs to be maintained and strengthened. A stable, calm life filled with bright colors and emotions directly depends on physical and reproductive health. nine0003
Read
March 20, 2022
We treat pain without drugs
The Medservice clinic (Izhevsk) successfully uses the modern method of interstitial electrical stimulation (VTES). It helps to treat pain and eliminate muscle spasms in diseases and injuries of the musculoskeletal system and peripheral nervous system. The technique is especially effective in the treatment of chronic pain syndrome. nine0003
Read
March 12, 2022
Postcovid syndrome in children. A pediatric neurologist tells
We are used to the fact that children easily tolerate a new coronavirus infection. But, as the experience of doctors who monitor young patients shows, the disease does not pass without a trace. What is the peculiarity of post-covid syndrome in children? The pediatric neurologist of the clinic "Medservice"
But, as the experience of doctors who monitor young patients shows, the disease does not pass without a trace. What is the peculiarity of post-covid syndrome in children? The pediatric neurologist of the clinic "Medservice"
Read
February 27, 2022
What does a pediatric neurologist treat and when to see him
We all want to see our children successful and happy people. And in many ways, their life path depends on health and it must be taken with all responsibility. From the first days of the birth of a new life, it is desirable to form correct and healthy habits. Both for myself and for the child. And a pediatric neurologist will help you with this. nine0003
Read
Popular clinic articles
March 22, 2019
Will the child be clubfoot if the mother sat cross-legged during pregnancy
All peoples have long shown great interest in the birth of a new life, the bearing of a child and childbirth. And no matter how far medicine has stepped today, we still perceive pregnancy as a sacred sacrament, the magic of nature. Until our time, many signs and superstitions associated with intrauterine development and growth of the baby have been preserved. nine0003
And no matter how far medicine has stepped today, we still perceive pregnancy as a sacred sacrament, the magic of nature. Until our time, many signs and superstitions associated with intrauterine development and growth of the baby have been preserved. nine0003
Read
March 23, 2022
Inhale-exhale: how to quickly check the quality of your breathing
We cannot stop breathing, no breath means no life. To be healthy and energetic, you need to have even and easy breathing. What is your breath like? Maybe you don't know something about yourself? This test should help determine if you have respiratory problems. nine0003
Read
March 23, 2022
Pain in the arm turned out to be a symptom of a life-threatening illness
A 53-year-old woman addressed a neurologist at the Medservice clinic (Izhevsk) with complaints of severe pain in her left shoulder, neck, and supraclavicular region radiating to her left arm.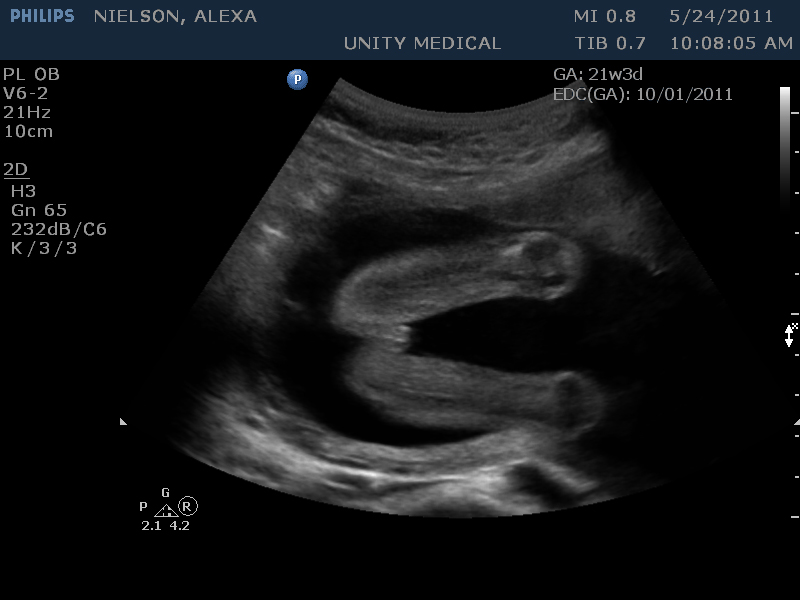 It turned out that it was a symptom of a life-threatening disease.
It turned out that it was a symptom of a life-threatening disease.
Read
nine0006 September 19, 2021How to recover from COVID-19
For most of those who have encountered COVID-19 or suffered from viral pneumonia, the question arises - how to return to their usual way of life, work, physical activity? Weakness, distracted attention, apathy or even panic - this is not a complete list of what you have to deal with. Sometimes the complications that the virus leaves behind can lead to more serious consequences. nine0003
Read
September 19, 2021
Easy to check lungs
This test should help determine if you have respiratory problems. Find out about the quality of your breathing by answering the following questions.
Read
November 2, 2021
Hypertensive crisis - what is it and first aid
High blood pressure (arterial hypertension or hypertension) is one of the most common and dangerous diseases of the cardiovascular system of our body. According to statistics, one third of the entire adult population of Russia suffers from increased pressure. This disease requires special treatment and constant monitoring. Otherwise, there is a risk of complications, one of which is a hypertensive crisis (HC).
According to statistics, one third of the entire adult population of Russia suffers from increased pressure. This disease requires special treatment and constant monitoring. Otherwise, there is a risk of complications, one of which is a hypertensive crisis (HC).
Read
March 23, 2022
SARS masks
Inflammation of the lungs "learned" to disguise itself. The insidiousness of this disease lies in the fact that recently it very often proceeds without characteristic symptoms and signs that allow it to be suspected. Moreover, on popular radiography, or, as they say in everyday life, “X-ray”, pneumonia is not always detected.
Read
November 2, 2021
Three reasons to have a second lung CT scan
Patients often ask our doctors the question - why is it necessary to do a repeated CT scan of the lungs? Let's try to understand this issue and consider two main situations.
Read
All clinic articles
Explanation of ultrasound of the thyroid gland: the norm - MEDSI
01/20/2018
What is an ultrasound?
Ultrasound (ultrasound examination, sonography) is a procedure for examining the body using ultrasonic waves. Their frequency is about 20,000 Hz, it is higher than that which the human ear can perceive. This analysis is safe for the body and, if necessary, can be performed frequently.
The thyroid gland produces iodine-containing hormones and stores iodine. It consists of two lobes and an isthmus and is located in front of the neck. Its correct operation is extremely important for the normal functioning of the whole organism, and violations lead to a number of diseases: cancer, Graves' disease, cretinism, adenoma, myxedema, etc.
Ultrasound of this gland allows you to find out what condition it is in, whether there are any pathologies or neoplasms. It shows a change in its structure, due to which various health problems may arise.
It shows a change in its structure, due to which various health problems may arise.
How is an ultrasound performed?
There is no long preparation required before the examination, but there are several rules:
- It is recommended not to eat a few hours before the examination
- If dopplerography is to be done, an iodine preparation should be taken 3-4 hours in advance
- Before lying down on the couch, remove all jewelry from the neck and get rid of the collar, scarf and any other item of clothing or decor
Doppler ultrasound is a type of analysis that allows you to combine a black and white image of the thyroid gland with color display of blood flow. It allows you to determine:
- Patency of blood vessels
- Violations of their walls (thinning/thickening) nine0210 Direction and speed
- Resistance index
The procedure itself goes like this:
- The patient lies down on the couch
- A special cream is applied to his neck
- The sonologist drives the device over the area of the thyroid gland, and at this time the data is transmitted to the screen and recorded on the hard drive of the computer
The total examination time is about 15 minutes.
Adult Indications for Testing
An ultrasound of the thyroid gland is prescribed in the following cases:
- The patient is pale and feels unwell
- He has a sore throat/neck and does not have a cold
- Hormone tests show abnormalities
- Arrhythmia
- Drowsiness, apathy and lethargy
- Sudden obesity or wasting
- Too frequent mood swings
When planning a pregnancy, this study should also be carried out.
When is a thyroid ultrasound necessary for a child?
Children may also have problems with the functioning of this organ. Therefore, the doctor may prescribe such an examination if the following symptoms occur:
- During the examination, a lump on the neck was found in the child
- He has difficulty breathing, there is shortness of breath
- Sudden weight gain/loss
- Arrhythmia
- If the patient has had a serious illness that could lead to complications
There are several reasons why a child should have a routine thyroid exam:
- Living in an area with a low iodine content in foods
- In large industrial cities
- If the child has a genetic predisposition to problems with this organ
Thyroid norms
As a result of the study of this organ, the condition of its lobes is important.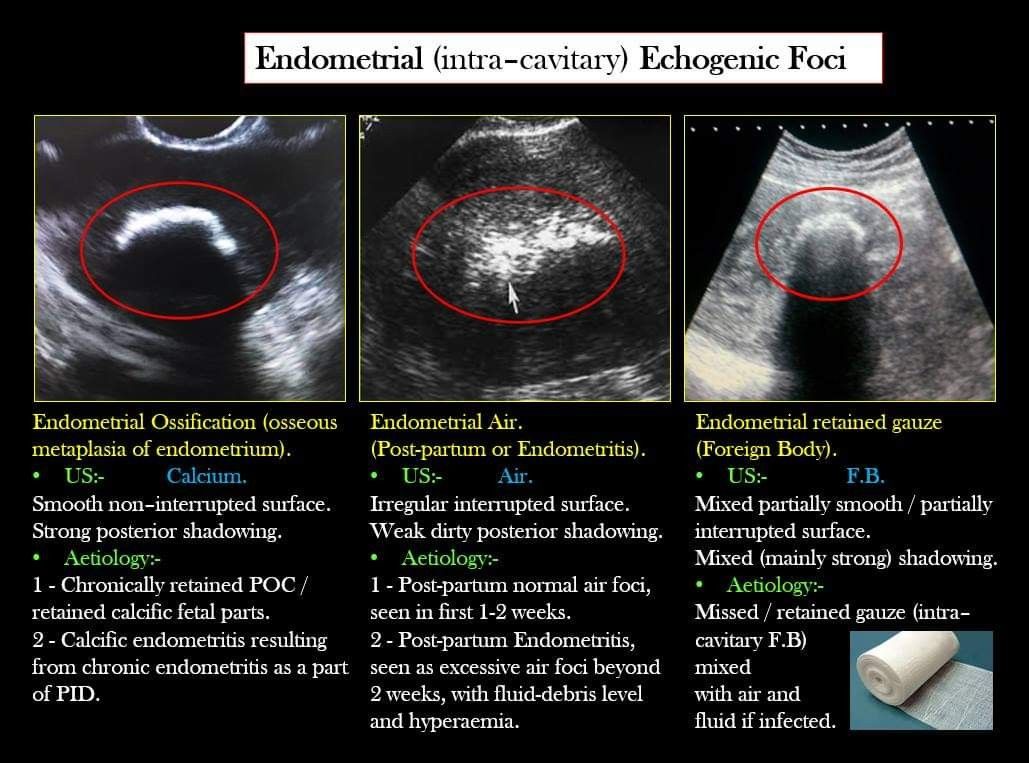 The isthmus between them in a healthy person may or may not be present. The main indicators are:
The isthmus between them in a healthy person may or may not be present. The main indicators are:
- Dimensions
- Fabric structure
- Echogenicity
- Presence or absence of neoplasms
Dimensions normal
On the results of ultrasound of the thyroid gland, dimensions and volumes are important. The maximum volume should be calculated according to the weight of the patient and can range from 12.3 cm3 at a weight of up to 40 kg to 35 cm3 at 110 kg. Often in women it is less than in men, due to differences in some processes in the endocrine system. If the gland is working correctly, but at the same time its volume is 1 or more cm3 more, then this is also considered the norm. nine0003
Share parameters are considered separately. On ultrasound of the thyroid gland, their normal dimensions should correspond to the following categories:
- Width 1.5-2 cm
- Length 2.5-6 cm
- Thickness 1-1.
 5 cm
5 cm
Isthmus can be from 4 to 8 mm. The size of the parathyroid glands is 2-8 mm. Normally, the right lobe may be slightly larger than the left (occasionally, the left is larger than the right).
During pregnancy, the size of this organ may increase while maintaining normal functioning. 3-4 months after birth, he returns to his usual state. nine0003
In children under 16-18, the thyroid gland grows gradually from birth. May be increased during puberty.
Parameters of gland tissues
The structure should be granular, homogeneous, glandular and consist of small follicles in which hormones are produced. There are about 30 million of them in total.
Its heterogeneity may be a sign of inflammatory diseases (diffuse toxic goiter and others), although it also occurs in healthy elderly people. This is due to the high production of antibodies to certain enzymes. nine0003
Echogenicity
This is a parameter that indicates how much tissue reflects or does not reflect ultrasound. It is characterized by the density of matter.
It is characterized by the density of matter.
There are 4 types of echogenicity:
- Anaechoic - black tissue on the monitor, absorbs ultrasound (blood vessels, benign tumors)
- Isoechogenic - partially reflective, light gray on screen (healthy tissue)
- Hypoechoic - low reflection, dark area (cysts)
- Hyperechoic - completely reflective, very light parts (connective tissue)
If the echogenicity of the thyroid gland is increased, this may be a sign of immune diseases.
Neoplasms
The analysis helps to identify different types of neoplasms. These can be:
- Benign colloid nodules, adenomas
- Cysts (containing fluid)
- Cancer
When echogenicity is low on thyroid ultrasound, the likelihood of a cyst or malignancy is increased. Blurred borders of the spot on the sonogram testify to it.
If such lumps are found, other tests are performed to clarify the diagnosis.
What diseases can be detected by ultrasound?
During the ultrasound examination, the doctor can detect a number of abnormalities. They are determined depending on the size, volume, tissue structure and echogenicity. Changes in these parameters may be a sign of diseases such as:
- Hypothyroidism - organ reduction
- Nodular goiter - the appearance of one or more foci of dense tissue
- Diffuse-toxic goiter - excessive enlargement of the gland
- Inflammation - the appearance of swelling and, in some cases, pus
- Adenoma - benign tumor formation
- Cyst - a cavity filled with fluid nine0210 Cancer tumor
Adenoma can be distinguished from cancer by the clarity of the tumor boundaries:
- in a benign tumor they are clearly defined and clearly visible on the sonogram
- in malignant - vague, germinated in a healthy area
To establish an accurate diagnosis in such cases, additional methods are used: blood test, CT, MRI, and others.