Not eating in pregnancy
Appetite changes and food aversions during pregnancy
Appetite changes and food aversions during pregnancy | Pregnancy Birth and Baby beginning of content6-minute read
Listen
Key facts
- Appetite changes are very common during pregnancy and may affect weight changes.
- A food aversion is an intense dislike of a specific food, together with unpleasant physical symptoms when you see or smell a particular food.
- Eating for 2 during pregnancy is a myth. It is the quality not quantity of food that matters.
- When you are pregnant, your body needs certain vitamins, minerals and nutrients, including iron, folate and iodine.
- If your nausea prevents you from getting enough nutrition, or if you are vomiting, not able to keep food or fluids down or losing weight, see your doctor or maternal health nurse.
What are food aversions, and why does appetite change during pregnancy?
A food aversion is an intense dislike of a specific food, together with unpleasant physical symptoms when you see or smell a particular food. These reactions are usually triggered by emotions associated with food rather than the food itself. You might also experience food cravings (an intense urge to eat a specific food). While these appetite changes are quite common, they can make healthy eating during pregnancy a challenge.
Is it normal for my appetite to change during pregnancy?
It is normal to experience either a loss of appetite or a change in food preferences during pregnancy. This may play a part in how much your weight changes during pregnancy.
Food aversions are common, and around 6 in 10 people experience a food aversion while pregnant.
When are food aversions likely to start and end?
You can experience food aversions resulting from generalised nausea (also known as 'morning sickness') at any time of day, and it tends to peak between week 6 and week 14 of pregnancy.
For this reason, if you've gone off certain foods that are important for your diet, you can try again later in your pregnancy to see if the aversion has passed. If your nausea prevents you from getting enough nutrition, or you are vomiting, not able to keep food or fluids down or losing weight, it's time to see your doctor.
What food aversions are common?
Common food aversions include:
- alcohol
- coffee / tea
- meat
- fatty food
- spicy food
- eggs
What causes food aversions?
While the cause of food aversions during pregnancy isn't clear, hormonal changes could affect the food you enjoy, particularly early in your pregnancy. For example, human gonadotropin (also known as hCG) is a hormone produced during pregnancy. It can cause feelings of nausea, appetite changes and food aversion. Pregnancy can also cause a greater sensitivity to smell and taste, which can influence the foods you prefer to eat.
More research is needed to better understand why food cravings and aversions occur. Some reasons may include hormonal balance or protecting the unborn baby from harmful substances and/or nutritional deficiencies. This is to encourage good nutrition and growth in the pregnancy.
Some reasons may include hormonal balance or protecting the unborn baby from harmful substances and/or nutritional deficiencies. This is to encourage good nutrition and growth in the pregnancy.
How can I eat well and have a healthy diet?
A healthy diet is important for both you and your baby. Eating for 2 during pregnancy is a myth. It is the quality not quantity of food that matters, and there is no need to eat twice as much. It is the quality not the quantity of food that matters most. Your diet should include a variety of the five food groups:
- vegetables and legumes
- breads and cereals
- milk, yoghurt and cheese
- meat, poultry, fish and alternatives
- fruit
During pregnancy, your body also needs plenty of water (8 to 10 glasses each day). You will also need extra vitamins, minerals, and nutrients to help your baby develop, including these:
- Folate (Folic acid) helps build your baby’s brain cells and prevents risk of the baby being born with a birth defect of the brain and/or spinal cord.
 This is especially important in the early stages of pregnancy. Folate-rich foods include green leafy vegetables, broccoli, legumes, oranges, avocado, or fortified breads and cereals.
This is especially important in the early stages of pregnancy. Folate-rich foods include green leafy vegetables, broccoli, legumes, oranges, avocado, or fortified breads and cereals. - Iodine is also important for your baby’s growth and development. Choose foods that are sources of iodine, such as low-fat milk products, eggs, cooked fish and seafood. Foods that contain seaweed, such as sushi, are also a good source of iodine, but if you’re pregnant only eat sushi without raw fish, cold meat or egg, and that is freshly prepared. If you add salt to your food or in cooking, choose iodised salt. If you have a thyroid condition, seek advice from your doctor before taking an iodine supplement.
- Iron-rich foods are recommended during pregnancy. These include red meat, poultry, tofu, and iron-fortified cereals. Eating foods high in vitamin C such as oranges, kiwi fruit, capsicum and broccoli can help iron absorption. Do not take an iron supplement during pregnancy without first checking with your doctor.
 Too much iron can pose health risks to you and your baby. A blood test will help your doctor know if you need to take iron tablets.
Too much iron can pose health risks to you and your baby. A blood test will help your doctor know if you need to take iron tablets.
If you develop an aversion to meat or another essential food, consider how you might substitute these for alternatives. For example, substitute meat for nuts.
It is also important to limit foods containing:
- saturated fats (biscuits, cakes, pies, butter and cream)
- added salt (processed meats, pickled fish, fast foods)
- added sugars (confectionary, sugar sweetened soft drinks, fruit juice and cordial)
Alcohol is not safe for developing babies, and not drinking alcohol is the safest option while you’re pregnant.
There are also certain foods you should avoid during pregnancy, so ask your doctor or maternal health nurse for more information.
Appetite changes during pregnancy are unlikely to harm you or your baby or significantly compromise your nutrition. If you are not sure which foods are most important for your diet, or you have no appetite for foods containing important nutrients, seek advice.
More information on changes in appetite
For more advice on food aversions or appetite loss in pregnancy speak to your:
- doctor
- midwife
- obstetrician
- accredited practising dietitian
Sources:
Epworth Hospital (Ask an Epworth midwife Your guide to early pregnancy), Royal Women Hospital Melbourne (Common concerns in early pregnancy), Queensland Health (During pregnancy), ACT Government (Good Nutrition in pregnancy), Australasian Society of Clinical Immunology and Allergy (Food Intolerance), University of Queensland (What the health: Why do women crave certain foods when they are pregnant), Australian Government (Healthy eating during your pregnancy), Science and Education Publishing (Psychological Factors in Food Aversions, Nausea, and Vomiting During Pregnancy), National Health and Medical Research Council (Australian guidelines to reduce health risks from drinking alcohol)Learn more here about the development and quality assurance of healthdirect content.
Last reviewed: July 2022
Back To Top
Related pages
- Guide to a healthy pregnancy
- Food cravings during pregnancy
- Foods to avoid when pregnant
Need more information?
Healthy diet during pregnancy
A healthy diet is an important part of a healthy lifestyle at any time, but especially vital if you're pregnant or planning a pregnancy.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Pregnancy health & wellbeing | Raising Children Network
Pregnant? Here’s all you need to stay healthy during pregnancy, including tips for healthy diet and lifestyle and a guide to pregnancy health care.
Read more on raisingchildren. net.au website
net.au website
Pregnancy and Healthy Eating
It’s especially important to eat healthy food during pregnancy and while breast feeding.
Read more on Healthy Eating Active Living NSW website
Healthy eating when you’re pregnant or breastfeeding | Eat For Health
Eating well during pregnancy and while breastfeeding has health benefits for you and your baby.
Read more on NHMRC – National Health and Medical Research Council website
Having a healthy pregnancy
Having a healthy pregnancy means following a healthy diet, getting regular exercise, knowing what to avoid and making sure your vaccinations are up to date. Find out more here.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Things to avoid during pregnancy
From hair dye to house paints, there are a few products or lifestyle habits pregnant women and their partners should be cautious of during pregnancy.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Pregnancy and diet - Better Health Channel
Good nutrition during pregnancy can help to keep you and your developing baby healthy.
Read more on Better Health Channel website
Gi and Pregnancy | GI Foundation
Home / Gi Health Benefits / Gi and Pregnancy Gi and Pregnancy Following a healthy low Gi diet during pregnancy helps protect your child’s future health and improves health and wellbeing for lifelong benefits
Read more on Glycemic Index Foundation website
Healthy Weight During Pregnancy
Weight gain is a normal part of pregnancy. The amount of weight you put on partly depends on your weight before pregnancy.
Read more on SA Health website
Losing weight after birth safely
Tips for losing weight after birth, including how to enjoy a healthy lifestyle, setting realistic goals, breastfeeding and weight loss and when to seek help.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Disclaimer
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is not responsible for the content and advertising on the external website you are now entering.
OKNeed further advice or guidance from our maternal child health nurses?
1800 882 436
Video call
- Contact us
- About us
- A-Z topics
- Symptom Checker
- Service Finder
- Subscribe to newsletters
- Sign in
- Linking to us
- Information partners
- Terms of use
- Privacy
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is funded by the Australian Government and operated by Healthdirect Australia.
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby’s information and advice are developed and managed within a rigorous clinical governance framework.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
Healthdirect Australia acknowledges the Traditional Owners of Country throughout Australia and their continuing connection to land, sea and community. We pay our respects to the Traditional Owners and to Elders both past and present.
This information is for your general information and use only and is not intended to be used as medical advice and should not be used to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any medical condition, nor should it be used for therapeutic purposes.
The information is not a substitute for independent professional advice and should not be used as an alternative to professional health care. If you have a particular medical problem, please consult a healthcare professional.
If you have a particular medical problem, please consult a healthcare professional.
Except as permitted under the Copyright Act 1968, this publication or any part of it may not be reproduced, altered, adapted, stored and/or distributed in any form or by any means without the prior written permission of Healthdirect Australia.
Support this browser is being discontinued for Pregnancy, Birth and Baby
Support for this browser is being discontinued for this site
- Internet Explorer 11 and lower
We currently support Microsoft Edge, Chrome, Firefox and Safari. For more information, please visit the links below:
- Chrome by Google
- Firefox by Mozilla
- Microsoft Edge
- Safari by Apple
You are welcome to continue browsing this site with this browser. Some features, tools or interaction may not work correctly.
Pregnant Not Eating Food? 7 Appetite Loss Tips for Expecting Moms
Share with:
Pregnancy triggers ravenous hunger but not for everyone.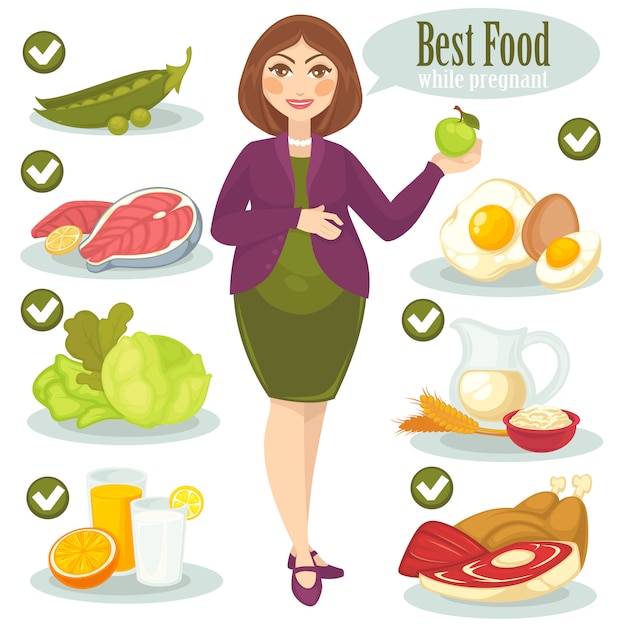
Having a bun in the oven usually leads to cravings and an increased appetite. Yet, some women feel turned off of food completely. Why? And what can you do about it?
In this article, we’re discussing why you might be pregnant, not eating, and experiencing a decreased appetite.
Is Appetite Loss Normal? Pregnant Not Eating FoodMost people know that pregnancy can make you furiously hungry, have weird cravings, and develop taste aversions. However, it can also impact your appetite in the opposite way. While many women experience a bigger appetite, some don’t change their eating patterns at all. Others feel their appetite has come to a sudden halt.
If you’re pregnant and not eating food, it may be concerning. When you should be eating more for the baby, why are you eating less?
Fortunately, losing your appetite can be normal during pregnancy. Although you need more nutrients for the baby, your body may go through changes while it adapts.
Your appetite will likely return. If it doesn’t or if you’re unable to eat, contact your doctor. Since your baby needs specific nutrients to develop, eating right during pregnancy is important.
Pregnant Not Eating Food: 7 CausesIf you’re pregnant, not eating food and have a reduced appetite, you’re probably wondering why. There’s a variety of reasons you may want to eat less—instead of more—during pregnancy. Scroll the list of possible causes below and see if you can relate to any.
#1 AversionsWhether triggered by taste or smell, an aversion is a food that completely turns you off. They’re one of the biggest reasons for decreased appetite. Between 50% and 90% of pregnant women experience cravings and aversions.
The most common aversions include:
- Caffeinated drinks
- Meats
- Fish
- Eggs
Research shows that changes to food cravings and aversions usually happen in the first and third trimesters.
You might wonder why you’ve developed an aversion to a specific food. However, the answer isn’t clear. Some women believe their aversions or cravings are nature’s way of altering their diet, making it healthier for pregnancy. There is no evidence that’s true. You shouldn’t assume your diet is healthy just because you’ve listened to your aversions or cravings.
In fact, it’s possible your aversions could weaken your diet and affect your baby. For example, meats and eggs are a common aversion that can lower your protein intake. Low maternal protein can cause embryo loss, restriction of intrauterine growth, and reduced postnatal growth.
Experts say that a combination of factors likely causes your appetite and preferences to change. That could include biological, psychological, and environmental factors.
#2 Morning SicknessA second major reason why you might be pregnant not eating food is because of morning sickness. Up to 80% of women experience nausea and vomiting in the first trimester.
There’s a variety of reasons morning sickness may happen. Some experts believe hormones play a large role. For other women, food aversions can trigger vomiting.
In any case, if you feel sick when you eat, eating can become less appealing. If you’re afraid of vomiting, you might only eat when necessary.
#3 Decreased Food = Adjusted Feelings of FullnessFood aversions and morning sickness are normal. However, if eating less becomes a pattern, it can change your appetite in the long term.
When you eat less food, your body will begin to adjust. Over time, it will take less food to make you feel full. Instead of feeling full after a meal, eating only half may leave you stuffed.
Many people attribute this change in appetite to their “stomach shrinking.” However, your stomach doesn’t actually shrink—it just gets more sensitive to small amounts of food. If this happens, you’ll probably notice a reduced appetite as your body learns to feel full from less food.
It’s important to recognize that even though you feel full, you might not be getting enough nutrients for the baby.
#4 ConstipationConstipation is another common pregnancy symptom that can affect your appetite. If you’re unable to pass stools normally, you might avoid eating in fear that the problem will worsen. You might also be afraid of the gas pains constipation can cause.
Another reason could be that constipation reduces your appetite. If food stays in your system longer, you might feel fuller longer. When there’s not much room for new food, your body won’t send hunger cues.
#5 Extra Stomach AcidWhile you’re expecting, the extra acid in your stomach can create numerous problems. Most commonly, women experience heartburn, AKA acid reflux or gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). It can also worsen nausea and vomiting. One lesser-known impact is that it can also decrease your appetite. The excess stomach acid could be making you feel full too quickly.
We’ve covered the physical reasons why you might lose your appetite while expecting. Next, we need to consider that mental health changes could be why you’re pregnant and not eating.
Research has shown that anxiety and depression can lead to appetite changes. Pregnancy can bring about a slew of new emotions. You might experience anxiety about your health, the baby, or upcoming life changes. Pregnancy depression can also reduce your appetite.
#7 Body Image ConcernsAnother psychological reason why you might be pregnant and not eating is because of body image concerns.
Most women gain weight during pregnancy; however, it might be difficult to accept. If you’ve experienced body image issues or disordered eating before, pregnancy can trigger these concerns or make them worse.
Knowingly or unknowingly, you may be reducing your food intake to try to limit weight gain.
7 Tips for Those Pregnant Not Eating FoodIf you’re pregnant and not eating food, try to pinpoint the cause. When you understand why your appetite has decreased, you can brainstorm possible solutions. Consider the suggestions below.
When you understand why your appetite has decreased, you can brainstorm possible solutions. Consider the suggestions below.
If aversions are the reason you’re pregnant and not eating, get specific about the foods you don’t like. For example, maybe you loved spicy foods before but now anything with a kick kills your hunger. Pay attention to other types of aversions too. Perhaps a specific scent or the temperature of food is throwing you off.
#2 Try Morning Sickness SnacksIf the reason you’re pregnant and not eating food is because of morning sickness, explore your options.
After you’ve pinpointed your aversions using the tip above, brainstorm new snack ideas. When you discover foods that don’t turn you off, add them to your daily staples. Make sure to stock up and keep snacks in your purse to ensure you’re frequently eating.
Need ideas? Read 33 Satisfying Pregnancy Snacks Perfect for Morning Sickness
#3 Eat Frequent, Smaller MealsInstead of eating big meals, break it up into more frequent, smaller meals. This trick is helpful for those experiencing morning sickness or acid reflux.
This trick is helpful for those experiencing morning sickness or acid reflux.
You probably can’t fully rid yourself of nausea—but you can take steps to reduce the intensity of it. Try a few anti-morning sickness tricks and see what works for you:
- Carry a pleasant scent to sniff when you smell something nauseating
- Stay hydrated
- Take B6 vitamin
- Reduce cybersickness before eating (scrolling through your phone or on the computer)
- Use deep breathing
- Take your prenatal vitamin at a different time of day
Read: 16 Best Morning Sickness Relievers to Ban Nausea
Try Our Acupressure Anti-Nausea Wristband to Alleviate Morning Sickness!
#5 Improve Your DigestionIf you think constipation is affecting your appetite, take steps to get things moving again. You can free up space in your stomach and alleviate constipation by:
- Slowly increasing your fiber intake
- Drinking more water
- Exercising
- Using a poop stool (AKA squatty potty)
- Choosing the right iron supplement (or prenatal with iron)
For more tips on improving constipation, read Constipation in Pregnancy: 7 Fixes
#6 Address Your Mental Health
Pregnancy can be overwhelming and you don’t have to go through it alone. If you suspect you’re pregnant and not eating because of anxiety or depression, reach out for help. Your doctor can recommend a therapist, free community resources, or coping mechanisms.
If you suspect you’re pregnant and not eating because of anxiety or depression, reach out for help. Your doctor can recommend a therapist, free community resources, or coping mechanisms.
Also look at science-backed ways to improve your mental health, including:
- Exercise
- Journaling
- Meditation
- Self-guided workbooks
Read:
- 7 Actionable Tips to Manage Panic Attacks in Pregnancy
- What’s The Difference Between Postpartum Depression and Baby Blues?
- Pregnancy Worry: 10 Practical Remedies for Anxiety During Pregnancy
- How to Prevent Postpartum Depression Before Delivery: 8 Ways
- Pregnancy Mood Swings: 9 Powerful Remedies
Thoughts about your weight and body image may be affecting your appetite. Whether these are new or old patterns of thinking, pregnancy is a good time to tackle them.
If you’re pregnant and think you may be struggling with disordered eating, talk to your doctor. They can put you in touch with a counselor, nutritionist, and/or community resources.
They can put you in touch with a counselor, nutritionist, and/or community resources.
Talking about body image is difficult and being pregnant can double the shame. Try to remember that other women struggle with disordered eating when pregnant. Along with advice from your healthcare provider, consider joining a support group for moms-to-be with eating disorders.
Summary: Pregnant Not Eating FoodIf you’re pregnant, not eating food, and wondering why, there’s a few possible causes. Nausea, constipation, extra stomach acid, and mental health problems can all contribute to changes. To increase your appetite, use the tips above. If your appetite doesn’t go back to normal, contact your doctor. Remember that your baby needs nutrients to develop properly, so eating right is extra important during pregnancy.
P.S. If nausea is causing a lack of appetite, try an acupressure wristband. They’re designed to press your P6 acupressure point, alleviating feelings of sickness.
Is Morning Sickness Wrecking Your Appetite? Try Our Anti-Nausea Wristband!
Share with:
What Not to Eat During Pregnancy
Your body works like a finely tuned machine to support a growing fetus, but a healthy and balanced diet (and avoiding certain foods) can help Mother Nature do her job even better. So, how is the nutrition of pregnant women different from the usual proper nutrition? What exactly should you be eating? Many pregnant women also wonder what foods to avoid and what not to eat during pregnancy. Here you will find answers to your questions, as well as practical advice on nutrition during pregnancy. nine0003
We are always ready to help you with advice, but remember that each woman's pregnancy is different, so our advice cannot replace the advice of a doctor. Contact your doctor to discuss any individual changes to your diet.
What not to eat during pregnancy
The good news is that healthy eating during pregnancy is very similar to healthy eating for non-pregnant women. You should eat regularly and try to eat mostly natural foods such as vegetables, fruits and whole grains. Also, try to limit high-sugar and processed foods in your diet. nine0005
You should eat regularly and try to eat mostly natural foods such as vegetables, fruits and whole grains. Also, try to limit high-sugar and processed foods in your diet. nine0005
For safety reasons, avoid raw or undercooked meat, liver, raw fish sushi, raw eggs, soft cheeses, and unpasteurized milk and juices. Below you will find more information on some of the foods that should not be consumed during pregnancy: 1 2 3
mercury content, which include marlin, swordfish, king mackerel, mackerel, shark, tuna and tilefish. Only canned light tuna is allowed in moderation. nine0002 To the dismay of all sushi lovers, raw fish, shellfish and crustaceans are also among the foods that are highly discouraged during pregnancy, as they may contain bacteria or even parasites. Smoked seafood should also be excluded from the diet.
- Soft cheeses made from unpasteurized milk
Soft cheeses such as feta, brie, dorblu and camembert are also on the list of foods that pregnant women should avoid. Because these cheeses are made from raw milk, they can be contaminated with Listeria. nine0016 4
Because these cheeses are made from raw milk, they can be contaminated with Listeria. nine0016 4
Rule of thumb: look for the label that says the product is pasteurized!
- Unpasteurized milk and juices
Similar rules apply to milk and juices. Freshly squeezed juice or any unpasteurized juice may contain disease-causing bacteria (E. coli, Listeria, Salmonella) 5 , so these products should not be consumed during pregnancy. nine0030
- Raw eggs
Also on your pregnancy avoid list are raw eggs or foods that contain raw or half-baked eggs: muffin mix, cookie dough, soft-boiled eggs, and fried eggs. Also be aware of foods that may contain half-baked eggs, such as salads, condiments, scrambled eggs, and ice cream. During pregnancy, it is necessary to consume only those eggs that have been heat-treated until fully cooked. nine0030
- Semi-cooked or raw meat and poultry
Semi-cooked or raw meat may contain listeria. During pregnancy, be careful to avoid such deli meats, or steam the meat until it is fully cooked. Cold meat pâtés are also prohibited. As for sliced meat, make sure that it has been heat-treated until it is fully cooked before eating it.
During pregnancy, be careful to avoid such deli meats, or steam the meat until it is fully cooked. Cold meat pâtés are also prohibited. As for sliced meat, make sure that it has been heat-treated until it is fully cooked before eating it.
- Raw or semi-cooked foods of plant origin
Eating raw vegetables, fruits, berries, lettuce, legumes, root vegetables, etc. carries the risk of food poisoning and should be thoroughly washed or cooked before consumption to reduce the risk of bacterial growth . Foods to Avoid During Pregnancy0005- Pre-cooked fresh minced meat
Be careful when eating pre-cooked fresh minced meat. If you decide to buy a whole stuffed bird, you need to buy it frozen and do not defrost before cooking. Bacteria can grow in fresh meat in combination with stuffing. 7
- Sweets, carbohydrate-rich foods, fast food
Although there is no conclusive scientific evidence, sweets, fast food, and foods high in fat and carbohydrates are usually on the list of foods that expectant mothers crave to eat.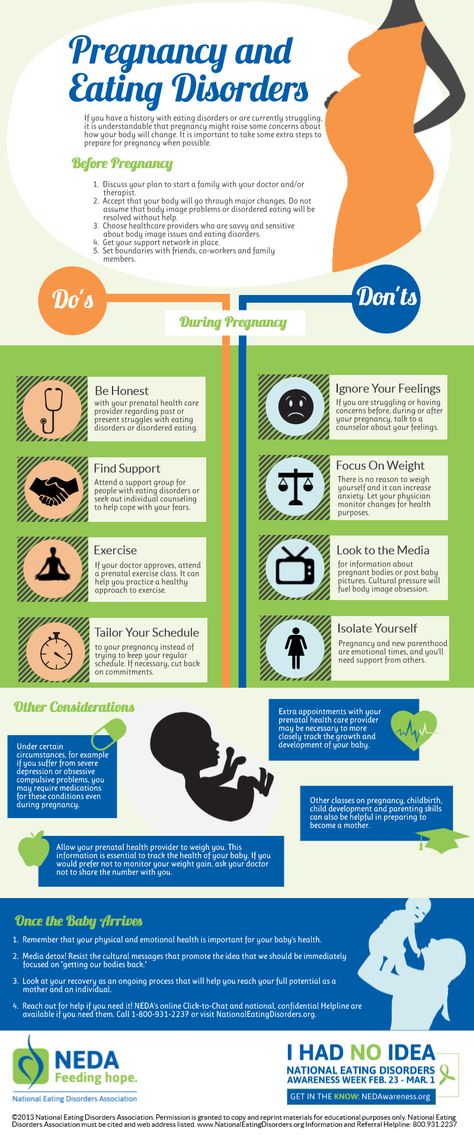 If you have an overwhelming craving for certain foods during pregnancy, try choosing healthier options. Can't imagine a meal without french fries? Fry foods in little or no oil with the Airfryer Airfryer, a healthy alternative that lets you enjoy delicious fried food at 9% less0%*fat content. You must remember that a balanced, healthy diet is important for maintaining your health and the health of your unborn baby.
If you have an overwhelming craving for certain foods during pregnancy, try choosing healthier options. Can't imagine a meal without french fries? Fry foods in little or no oil with the Airfryer Airfryer, a healthy alternative that lets you enjoy delicious fried food at 9% less0%*fat content. You must remember that a balanced, healthy diet is important for maintaining your health and the health of your unborn baby.
- Excess caffeine
During pregnancy, restrictions are placed not only on food, but also on drinks, among which drinks containing caffeine should be avoided. Remember that caffeine is found not only in coffee, but also in drinks such as tea, cocoa, cola.The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends that “women with daily high caffeine intake (more than 300 mg per day) reduce their daily intake during pregnancy to reduce the risk of miscarriage or low birth weight.” nine0016 8
After the birth of a child, the diet of a nursing mother is no less important than during pregnancy.
 Watch a webinar from a Philips Avent expert on nutrition during this period:
Watch a webinar from a Philips Avent expert on nutrition during this period:
Healthy nutrition for expectant mothers
Pregnancy is a period of intensive growth and development of your unborn child, as well as a time of many physiological changes in the mother's body, so the nutrition of a pregnant woman should contribute in every possible way to the success of passing this path. It's a good idea to discuss this with your doctor so you can make sure you're getting enough of the right nutrients. Here are some key tips for a healthy, balanced diet during pregnancy:- Eat whole grains such as whole grain bread and pasta; Choose lean meat or poultry and aim for 225-350 grams of boiled fish per week (remember to choose low-mercury fish).
- Your diet should include five food groups: grains, fruits, vegetables, protein, and dairy. 9 Have half your plate of vegetables and fruits and the other half whole grains.
 nine0030
nine0030 - And the easiest way to eat more fruits and vegetables is to make smoothies. Now there is a huge variety of recipes, and Philips blenders will help you cook them quickly and achieve the most delicate texture. Make new recipes from your favorite foods and add greens and nuts to them.
- Talk to your doctor about your diet, vitamin supplements, and other prenatal medications, such as folic acid and iron supplements. During pregnancy, there is an increased need for vitamins and minerals, the full amount of which food products alone cannot provide. nine0030
- Choose monounsaturated or polyunsaturated fats, such as olive oil and avocados, and limit saturated fats and empty-calorie foods, such as candy or sugary drinks.
Stay on top of your pregnancy health with the Pregnancy+ mobile app. This application is specially designed for the entire pregnancy and childbirth period and provides comprehensive guidance through all stages of pregnancy.
 Always check with your doctor before embarking on any particular diet. nine0005
Always check with your doctor before embarking on any particular diet. nine0005 Philips Avent Articles & Tips
8 Foods You Shouldn't Eat While Pregnant
June 15, 2019 Likbez Health
Even scrambled eggs and healthy fish oil can do harm.
If you are pregnant, you should reduce the amount of coffee and avoid alcohol altogether. Everyone knows this.
But there are far more insidious foods. At first glance, they seem innocent and even useful. But in fact, they can harm mom or an unborn baby more than a couple of cups of double espresso three times a day. nine0005
Here is a list of popular foods to avoid during pregnancy. Or at least think twice before you eat.
1. Raw eggs
As well as products containing them: eggnog, homemade mayonnaise, raw dough, poached eggs, fried eggs with raw yolk, tiramisu.
What is the danger
One word is enough: salmonellosis. This acute intestinal infection is fortunately not fatal, but is accompanied by severe diarrhea and vomiting that can cause dehydration.
 But this is already bad: the normal blood supply to the fetus and the level of amniotic fluid in the uterus depend on the amount of moisture. Water deficiency can result in violations in the development of the unborn baby, as well as an increased risk of miscarriage. nine0005
But this is already bad: the normal blood supply to the fetus and the level of amniotic fluid in the uterus depend on the amount of moisture. Water deficiency can result in violations in the development of the unborn baby, as well as an increased risk of miscarriage. nine0005 What to do
If you have no strength to refuse eggs, make sure that they are thoroughly washed and heat-treated. Hard boiled eggs, scrambled eggs, baked goods are safe.
2. Raw meat
As well as rare fried steaks (“with blood”), raw smoked and cured sausages, poorly fried minced meat, for example, in fast food.
What is the danger
Raw meat can be infected with parasites. For example, Toxoplasma. They are able to penetrate the placental barrier and cause serious disturbances in the development of the unborn baby. nine0005
What to do
It's easy to get rid of parasites - cook it properly. If we are talking about dried or smoked products, freezing them for four days will help reduce the risk.

3. Raw fish
Be especially careful with river and wild ocean fish, shellfish (oysters, mussels), dried, smoked fish of all kinds and sushi.
What is the danger
The range of troubles that you can get by eating a roll or dried perch is wide:0005
- like meat, fish can be infested with parasites;
- in the pulp there are also pathogenic bacteria - for example, listeria or botulinum bacteria, which cause deadly botulism (for mothers as well);
- river fish can be caught in chemically polluted reservoirs - and all toxic substances will go to both mother and baby;
- oceanic fish accumulate mercury. Shark, swordfish, king mackerel and tilefish are especially dangerous in this regard. Mercury poisoning affects the health of both the mother and the unborn baby - this element can cause brain damage and developmental delays. nine0030
What to do
Eat only properly cooked fish. You can take a chance with canned food: just keep an eye on the expiration date and in no case use the product from swollen cans.

4. Liver
Also liver pate and sausage, cod liver oil.
What is the danger
Too much vitamin A. Its excess can lead to the development of birth defects in the fetus.
What to do
Do not abuse liver products. Especially if for some reason you are taking vitamin A supplements. Yes, and in no case should you prescribe vitamins and supplements for yourself - only your doctor can do this. nine0005
5. Soft cheeses
Special attention:
- soft cheeses with white mold - brie and camembert;
- blue cheeses - gorgonzola, roquefort, danish blue.
What is the danger
Due to the high humidity and mold, such cheeses are an ideal environment for the development of all kinds of bacteria, including those dangerous to the fetus. The same listeria, once in the body of a future baby, can provoke severe developmental disorders, miscarriage or stillbirth. nine0005
What to do
The ideal option is to switch to hard cheese (cheddar, parmesan, stilton and others): it is safe.
 Soft cheeses can also be consumed, but only if they are made from pasteurized milk. These are mozzarella, feta, ricotta, cream cheeses, halloumi, processed cheeses.
Soft cheeses can also be consumed, but only if they are made from pasteurized milk. These are mozzarella, feta, ricotta, cream cheeses, halloumi, processed cheeses. 6. Unpasteurized milk
As well as yogurt and ice cream prepared from it.
What is the danger
All in the same high risk of bacteria content. Unpasteurized milk is a product that has not undergone heat treatment. Therefore, the same listeria, which is deadly for the unborn child, can be found in it. nine0005
What to do
Try to drink only pasteurized milk. If for some reason only raw is available, be sure to boil it before drinking.
7. Caffeinated products
Not only coffee, but also green tea, chocolate, cola, energy drinks, and some cold and flu medications.
What is the danger
An excess of this substance can cause the baby to have a low birth weight - and this increases the risk of health problems in the future. Sometimes the abuse of caffeine products provokes a miscarriage.
 nine0005
nine0005 What to do
You don't have to cut out caffeine completely - just don't go over 200 mg a day. In order not to cross the line, be guided by approximate values:
- 1 cup of instant coffee - 100 mg of caffeine;
- 1 cup espresso - 140 mg;
- 1 cup tea - 75 mg;
- 1 can cola (330 ml) - 40 mg;
- 1 can Energy Drink (250 ml) - 80 mg;
- 50 g dark chocolate - up to 25 mg;
- 50 g milk chocolate - up to 10 mg.
Once again, we emphasize: these are approximate figures. But they can be used for calculation. For example, if you drank a cup of espresso in the morning and a can of cola in the middle of the day, you received almost 200 mg of caffeine.
8. Poorly washed vegetables and fruits
As well as berries that grow close to the soil - the same strawberries or currants on the lower branches of the bush. Freshly squeezed juices are also questionable if you do not know how thoroughly you washed the ingredients before cooking.

- Pre-cooked fresh minced meat