Mucus in stool while pregnant
Mucus In Stool During Pregnancy? Should you be worried? Is it Normal? Reasons
Pregnancy brings about various physiological changes in the body. There are some common problems faced by pregnant women like nausea, vomiting, fatigue, changes in dietary preference, etc. which are caused due to the widespread changes going on in the body. However, sometimes pregnant women may face some uncommon symptoms which may put them to worry. Presence of mucus is one such condition that most pregnant women do not know of and hence, it is necessary to be more aware of it.
Book an appointment online to consult with Dr. Ritambhra Bhalla for gynecological issues.
What causes mucus in stool?
Mostly, mucus in stool is caused due to some digestive problems. Common causes of mucus in stool in pregnant women are:
- Hormonal changes can result in the presence of mucus in stool.
Since during pregnancy, there are high hormonal fluctuations taking place in the body, there is an increased chance of finding mucus in stool.
- The increase in the size of the uterus during pregnancy disrupts the intestine which may also lead to excretion of mucus.
- Dehydration can also lead to mucus in stool.
- Infection in the stomach or other parts of the digestive tract may also result in mucus.
- Food allergies can also result in mucus excretion.
Must Read: How To Tackle Backaches During Pregnancy
- Many doctors recommend various vitamin supplements to women before or during pregnancy. This can also cause mucus in stool, especially if the vitamins have an excess of iron or calcium.
Is it normal?
Though rather uncommon, it is completely okay to find some mucus in your stool during pregnancy. Especially during the first trimester, when the body is undergoing a lot of changes, there is an increased risk of mucus excretion which is completely normal. Also, if your doctor prescribes supplements, there is an increased chance of finding mucus in stool and is nothing to worry about.
Especially during the first trimester, when the body is undergoing a lot of changes, there is an increased risk of mucus excretion which is completely normal. Also, if your doctor prescribes supplements, there is an increased chance of finding mucus in stool and is nothing to worry about.
Want to consult a doctor? Book Online Consultation with Doctor, consult the best Gynecologist in India
Join our Cloudnine Community to discuss further regarding - Pregnancy Daily Care, Pregnancy Nutrition, Pregnancy Fitness, Nutrition.
Prevention:
There are certain guidelines which can help in reducing the risk of mucus excretion during pregnancy like:
- Staying hydrated helps in prevention of mucus and various other health problems during pregnancy.
 Drink plenty of water during pregnancy, and if needed, use hydration salts too.
Drink plenty of water during pregnancy, and if needed, use hydration salts too. - Performing light exercises which are suitable for pregnant women (with the prior recommendation of your doctor) can also help.
- Maintaining a healthy diet is also important, not just for mucus prevention but for a healthier pregnancy in general.
To know more About Uterine rupture during pregnancy
When to see a doctor?
Mostly the presence of mucus in stool is not a cause of worry. However, if you notice additional symptoms like the presence of blood along with the presence of mucus, it is highly advisable to contact your health provider.
Moreover, if you have extreme abdominal pain or haemorrhoids, it is also advisable to contact a maternity doctor. Additionally, excretion of very high quantities of mucus or persistent presence of mucus in the stool should also be not taken lightly.
Good news, now you can shop right away from wide range of products on Cloudnine Momeaze.
Watch Video on Do's and Don'ts of Pregnancy
Cloudnine is one of the leading maternity and childcare hospitals in the country. When it comes to pregnancy and maternity, we are renowned for providing world-class facilities and care. Our specialists are extremely qualified and experienced and are dedicated to providing you with the best possible treatment and care.
Do you have questions in your mind like How Many Weeks Pregnant Am I? Check out Cloudnine's Pregnancy Due Date Calculator now!
Our customers had a few questions regarding this blog, check them out now!
Stomach upset during pregnancy?
Constipation during pregnancy?
Have Similar Questions?
Get answers from our Experts, browse through hundreds of Q&A, attend live sessions, and much more
Ask your question!
Want to consult the best gynecologists in India? Please find the links below.
- Best Gynecologists in Bangalore
- Best Gynecologists in Chennai
- Best Gynecologists in Mumbai
- Best Gynecologists in Pune
- Best Gynecologists in Chandigarh
- Best Gynecologists in Gurgaon
- Best Gynecologists in Noida
Want to consult the best Maternity Packages in India? Please find the links below.
- Best Maternity Packages in Bangalore
- Best Maternity Packages in Chennai
- Best Maternity Packages in Mumbai
- Best Maternity Packages in Pune
- Best Maternity Packages in Chandigarh
- Best Maternity packages in Gurgaon
- Best Maternity Packages in Noida
Mucus In Stool During Pregnancy: Causes And Treatment
It should not cause worry unless there is pain, blood, or discomfort in passing stool.
Research-backed
MomJunction believes in providing reliable, research-backed information to you. As per our strong editorial policy requirements, we base our health articles on references (citations) taken from authority sites, international journals, and research studies. However, if you find any incongruencies, feel free to write to us.
Image: iStock
Excess mucus in stool during pregnancy may occur due to gastrointestinal issues or pregnancy-related factors, such as hormonal changes. Gastric mucus is produced in the stomach and helps in the motility of the digested food in the gastrointestinal tract. We excrete some mucus in stools usually. However, pregnancy may increase the amount of mucus excreted, making it more noticeable (1).
Excess mucus due to underlying issues is treatable. Read this post to learn the various causes and treatment options for excess mucus in stool during pregnancy.
Is It Normal To Have Mucus In Stool During Pregnancy?
You may sometimes pass mucus in the stool due to multiple gastrointestinal issues (2) (3).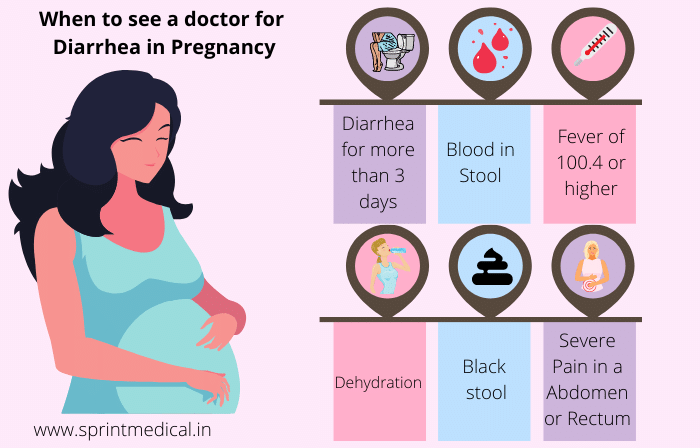 We pass a small amount of mucus in the stool, which is generally unnoticeable. Pregnant women may pass excess mucus in their stool during the first trimester.
We pass a small amount of mucus in the stool, which is generally unnoticeable. Pregnant women may pass excess mucus in their stool during the first trimester.
The appearance of mucus in stool is due to the rapid changes in your body during the gestational period. Safety measures and precautions may be taken if there is an excess of mucus secretion or followed by pain and bleeding. You may consult a doctor to help determine the cause of the condition.
Related: Bleeding During Pregnancy: Causes, Diagnosis And Treatment
What Causes Mucus in Stool During Pregnancy?
Some possible causes of secretion of excess mucus in stool during pregnancy are (3) (4) (5) (6):
- Dehydration: Hydration is for a healthy gut and mind. During pregnancy, water intake is crucial for the mother and her fetus. Dehydration might be one of the prime factors for the excretion of mucus in the stool.
Related: 12 Signs Of Dehydration During Pregnancy And Ways To Avoid It
- Irritable bowel syndrome: Change in routine, stress, and infection may cause irritable bowel syndrome.
 The symptoms may include mucus in stool, abdominal pain, and alternating diarrhea and constipation.
The symptoms may include mucus in stool, abdominal pain, and alternating diarrhea and constipation. - Hormonal change: Various hormonal changes occur in your body during the gestational period. Some pregnancy-specific hormones may directly or indirectly regulate the mucus secretion in the stool during pregnancy.
- Infection in the stomach: Bacterial or viral infection in the gastrointestinal tract may result in excess mucus secretion in the stool. Intestinal parasites such as tapeworms, hookworms, amoeba, and pinworms could be the reasons.
Some symptoms of stomach infection that may accompany the secretion of mucus in the stool are diarrhea, cramping, vomiting, nausea, and fever
- Irritable bowel syndrome: Change in routine, stress, and infection may cause irritable bowel syndrome.
Image: iStock
Quick fact
Giardiasis is an intestinal parasite infection that may cause greasy stools with stomach cramps and nausea. Pregnant women may face more dehydration than others (12).
- Food allergies: Lactose intolerance and specific food allergies may also result in mucus secretion in the stool.

- Intestine blockage: The fetus might be pushing against the intestine wall, resulting in blocked intestine and constipation. The body might be oversecreting mucus in the stool to ease constipation.
- Medications or vitamins: Prenatal intake of vitamins fortified with iron or calcium during pregnancy may be associated with excess mucus excretion in stool.
Image: Shutterstock
- Hemorrhoids: Piles or hemorrhoids are swollen veins around the anus usually accompanied by constipation during pregnancy. During pregnancy, hemorrhoids may occur due to constipation and pressure from the growing baby.
Health tip
Gently applying a cloth wrung out in iced water to the affected area may help ease the pain and reduce inflammation (13).
- Other gastrointestinal conditions: These include Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis, colon polyps, and diverticulitis.
Related: Crohn's Disease And Pregnancy: Symptoms, Diagnosis & Treatment
What Are The Treatment Options And Ways To Prevent Mucus In Stool?
Identifying the cause behind mucus secretion is essential for the treatment. Some treatments options available for reducing mucus in the stool during pregnancy are (7) (8) (9 ):
Some treatments options available for reducing mucus in the stool during pregnancy are (7) (8) (9 ):
- Stay hydrated: Taking plenty of water during pregnancy may help reduce dehydration-induced constipation. It can also avoid the accumulation of various toxins in the body. The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) recommends drinking around 8 to 12 cups (64 to 96 ounces) of water every day. Excess fluids, including more fresh juices in your diet, are beneficial. Water also helps absorb water-soluble vitamins (vitamins B and C) from the diet into the body.
Image: iStock
- Take a healthy diet: A healthy and balanced diet rich in green leafy vegetables and fiber supplements can help reduce constipation during pregnancy.
- Change medication: If you have mucus secretion in the stool followed by vitamin intake, you may consult your physician. It might be possible to change the particular medication to help you relieve mucus in the stool.

- Use laxatives: In constipation, your health care provider may suggest a laxative or a stool softener. The laxatives are over-the-counter medication and may help reduce constipation and mucus secretion in the stool.
Health fact
Mild laxatives such as milk of magnesia, bulking agents (metamucil) and stool softeners (docusates) may be prescribed during pregnancy (14).
- Get the infection cured: If the origin of mucus in the stool is an infection, your doctor may suggest an antibiotic regime to control the infection. It is best practice to complete the course of antibiotics for complete recovery and reduce recurrence.
- Avoid allergic food: In case of food allergies, try to identify and avoid the allergen in your food. Abstaining from the source of allergy may help regain a healthy gut and reduce mucus secretion in the stool. It is always good to limit junk and spicy foods for better health during pregnancy.
Did you know?
Celiac disease, which is caused due to gluten sensitivity, has been linked to an increased risk of adverse pregnancy outcomes (15).
- Include mild exercises: Exercising during pregnancy can help you stay healthy and fresh. A little warmup followed by movement exercise will keep your gut healthy. It may help ease constipation-induced mucus secretion. Mild exercises and physical activities are safe during the pregnancy. Walking and jogging may keep you active and aid digestion.
Image: iStock
Related: 17 Safe Pregnancy Exercises And Workouts For Women
When Should You Call The Doctor?
Image: Shutterstock
Mucus in stool is not a sign to worry about. You may improve your lifestyle and undertake preliminary measures to reduce the excess secretion of mucus in stool.
When stool has an excess amount of visible mucus during pregnancy, it may be due to health conditions, such as (10) (11) :
- Irritable bowel syndrome
- Ulcerative colitis
- Crohn’s disease
One may take note of the symptoms and consult a doctor in the following cases:
- There is an excess amount of mucus in the stool
- Blood or pus in the stool
- Pain while passing stool
- Having stomach pain, cramping, or bloating
- Sudden changes in stool frequency, consistency, or color
1. Can probiotics cause mucus in stool?
Can probiotics cause mucus in stool?
Research indicates that probiotics may alter the composition and volume of stool, causing gassiness and increased mucus secretion in stools. If you notice these symptoms after consuming probiotics during pregnancy, you should talk to your gynecologist or nutritionist (12).
2. Can anxiety cause mucus in stool?
Anxiety may increase mucus secretion in stool in some individuals (13). However, the underlying reason is not known, and it may not happen to everyone.
Mucus in stool during pregnancy is usually normal. It may happen due to dehydration, hormonal changes, or food allergies. Understanding your body and making lifestyle changes such as drinking more water, avoiding allergic food, or eating healthy helps keep the problems at bay. However, do not ignore symptoms such as blood or pus in the stool or pain in passing stool, as these may indicate more severe conditions such as irritable bowel syndrome or Crohn’s disease. In such cases, it is necessary to consult a doctor.
Key Pointers
- Pregnant women may pass mucus in their stool during the first trimester due to dehydration, hormonal changes, stomach infections, and other issues.
- Some treatment options that may relieve the condition are proper hydration, a healthy diet, mild exercises, and avoiding allergic foods.
- Consult a doctor if you notice excess mucus, pus, or blood in the stool or experience pain, cramps, or bloating.
References:
- The gastrointestinal mucus system in health and disease.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3758667/ - Gastrointestinal Infections in Pregnancy.
https://patient.info/doctor/gastrointestinal-infections-in-pregnancy - Bladder and bowel problems during pregnancy.
https://www.pregnancybirthbaby.org.au/bladder-and-bowel-problems-during-pregnancy - Hormones in pregnancy.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3640235/ - Piles in pregnancy.

https://www.nhs.uk/pregnancy/related-conditions/common-symptoms/piles/ - Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS).
https://www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au/health/conditionsandtreatments/irritable-bowel-syndrome-ibs - Nutrition Column An Update on Water Needs during Pregnancy and Beyond.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1595116/ - How much water should I drink during pregnancy?
https://www.acog.org/womens-health/experts-and-stories/ask-acog/how-much-water-should-i-drink-during-pregnancy - Constipation in Pregnancy.
https://americanpregnancy.org/healthy-pregnancy/pregnancy-health-wellness/constipation-during-pregnancy/ - The Diagnosis and Treatment of Crohn’s Disease and Ulcerative Colitis.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2695363/ - The Effect of Phloroglucinol in Patients With Diarrhea-predominant Irritable Bowel Syndrome: A Randomized, Double-blind, Placebo-controlled Trial.

https://www.jnmjournal.org/journal/view.html?uid=1563&vmd=Full& - What is giardiasis?
https://www.cdc.gov/parasites/giardia/general-info.html - Piles in pregnancy.
https://www.nhs.uk/pregnancy/related-conditions/common-symptoms/piles/ - Laxatives During Pregnancy.
https://americanpregnancy.org/healthy-pregnancy/is-it-safe/laxatives-during-pregnancy/#:~:text=One%20mild%20laxative%2C%20considered%20to - Stephanie M. Moleski et al.; Increased rates of pregnancy complications in women with celiac disease.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4367213/
The following two tabs change content below.
- Reviewer
- Author
Is It Safe To Bend Over When Pregnant?
Is It Safe To Bend Over When Pregnant?
Ice Cream When Pregnant: Safety Profile, Nutrition And Side Effects
Ice Cream When Pregnant: Safety Profile, Nutrition And Side Effects
Bad Breath During Pregnancy: Causes, Symptoms, And Treatment
Bad Breath During Pregnancy: Causes, Symptoms, And Treatment
Tea Tree Oil For Babies: Safety, Uses And Side Effects
Tea Tree Oil For Babies: Safety, Uses And Side Effects
Custard Apple (Sharifa) During Pregnancy: Health Benefits And Recipes
Custard Apple (Sharifa) During Pregnancy: Health Benefits And Recipes
6 Key Benefits Of Using Olive Oil For Babies
6 Key Benefits Of Using Olive Oil For Babies
Is It Safe To Use Eucalyptus Oil For Babies
Is It Safe To Use Eucalyptus Oil For Babies
Stomach Ulcer During Pregnancy - Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis & Treatments
Stomach Ulcer During Pregnancy - Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis & Treatments
Dog Allergy In Babies: Symptoms, Causes, Treatment And Prevention
Dog Allergy In Babies: Symptoms, Causes, Treatment And Prevention
Toxemia, Intestinal Problems, and Heartburn
Find out how pregnancy affects your digestive tract, which trimesters are more likely to cause indigestion and nausea, and what to do to manage them.
During pregnancy, the burden on the mother's body increases. The body needs more nutrients, the body produces additional hormones. And the growing fetus puts pressure on neighboring organs, including the stomach and intestines. We tell you what symptoms are observed in each trimester, how to cope with toxicosis and get rid of heartburn. nine0005
Contents:
- 2. Toxicosis and pregnancy
- 3. Causes, risks and treatment of diarrhea during pregnancy
- 4. Heartburn and stomach pain during pregnancy
- 5. Bloating, constipation and microbiota during pregnancy
- 6. Note
Changes in the work of the gastrointestinal tract by trimesters of pregnancy
The average duration of pregnancy is 40 weeks, which are usually divided into trimesters in accordance with the stages of intrauterine development of the child. nine0005
Each trimester is accompanied by a number of changes in the body, including in the gastrointestinal tract:
| The first trimester 1–13 weeks | 900 26 weeks | Third trimester of pregnancy 27–40 weeks |
| Morning sickness Morning sickness Zapor Intestinal disorder increased appetite TREAM to certain products Acid reflux | Constipation Acid Office 9000 9000 9000 9000 Flatulence Constipation Heartburn Violation of the outflow of bile Hemorrhoids |
The Atlas Genetic Test will help you find out how your genes affect the level of female sex hormones necessary for fertility and pregnancy.

Causes of gastrointestinal problems during pregnancy
Every pregnancy is accompanied by inevitable changes in the functioning of the digestive system. They are most often caused by hormonal changes and increased stress on organs, but they can also be associated with lifestyle and health conditions, for example:
- Sedentary lifestyle and unbalanced diet;
- Certain drugs, including calcium or aluminum antacids;
- Viral and bacterial infections;
- Intolerance to certain nutrients and allergic reactions;
- Stress;
- Diseases of the thyroid gland.
If you have chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and you are planning a pregnancy, try to consult your doctor in advance. Symptoms of conditions such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) or acid reflux are more likely to get worse during pregnancy. Your doctor will help prepare your body and create a prevention plan to help relieve symptoms during this time. nine0005
nine0005
Irritable bowel syndrome, or IBS, is a functional bowel disease that causes frequent abdominal pain, impaired peristalsis, bloating, constipation, or diarrhea.
Morning sickness, vomiting and general malaise during pregnancy
Morning sickness and morning sickness during early pregnancy are common, because the body undergoes important changes necessary for the development of the child.
up to 90%
women experience nausea during pregnancy
Doctors find it difficult to say with certainty why pregnant women feel sick in the morning. The main theory is hormonal changes. But there are some patterns associated with an increased risk of morning sickness:
- Multiple pregnancy;
- Toxicosis during previous pregnancy;
- History of morning sickness during pregnancy in close relatives;
- Tendency to motion sickness in transport;
- Use of oral contraceptives containing estrogen before pregnancy; nine0010
- Frequent migraines;
- BMI 30 and above;
- Elevated levels of stress hormones
Risks of severe morning sickness and how to reduce nausea
Nausea and vomiting are usually not associated with a risk for mother and child and disappear by 16-20 weeks of pregnancy, but it is not necessary to wait so long - there are ways that can help reduce nausea and enjoy the process of waiting for a new person:
- Get plenty of rest - fatigue increases toxicosis; nine0010
- Avoid smells and foods that cause nausea;
- Eat something right after waking up.
 A toast or a slice of bread will help reduce nausea;
A toast or a slice of bread will help reduce nausea; - Avoid hunger - empty stomach increases nausea. Eat small meals often, prefer low-fat, high-carbohydrate foods;
- Try ginger - studies show it helps with nausea;
- Sip as often as possible and prefer still water. nine0010
In rare cases, pregnant women may develop hyperemesis gestationis or excessive vomiting. This is a serious condition that can lead to dehydration, kidney damage, seizures, abnormal heart rhythms, and even death.
Signs of dehydration include dry mouth, dizziness, dark urine, infrequent urination and/or dizziness.
Symptoms of excessive pregnancy vomiting:
- frequent nausea for a long time and regular vomiting after meals;
- dry skin and lips;
- sudden weight loss;
- low blood pressure (below 90/60).
If symptoms of excessive pregnancy vomiting occur, do not wait until the condition resolves on its own. It is necessary to seek medical help as soon as possible - the doctor will prescribe treatment, help adjust the diet and lifestyle of the expectant mother.
It is necessary to seek medical help as soon as possible - the doctor will prescribe treatment, help adjust the diet and lifestyle of the expectant mother.
0.5–2%
pregnant women experience excessive vomiting
Diarrhea in pregnancy
The word "diarrhea" comes from the Greek language and literally means "to flow through". This is a condition during which bowel movements or bowel movements occur three times a day or more often. This phenomenon is especially typical for the third trimester of pregnancy, but it can also occur earlier.
Symptoms of diarrhea:
- Three or more bowel movements per day
- Urgent urge to have a bowel movement
- Abdominal pain and cramps
- Bloating
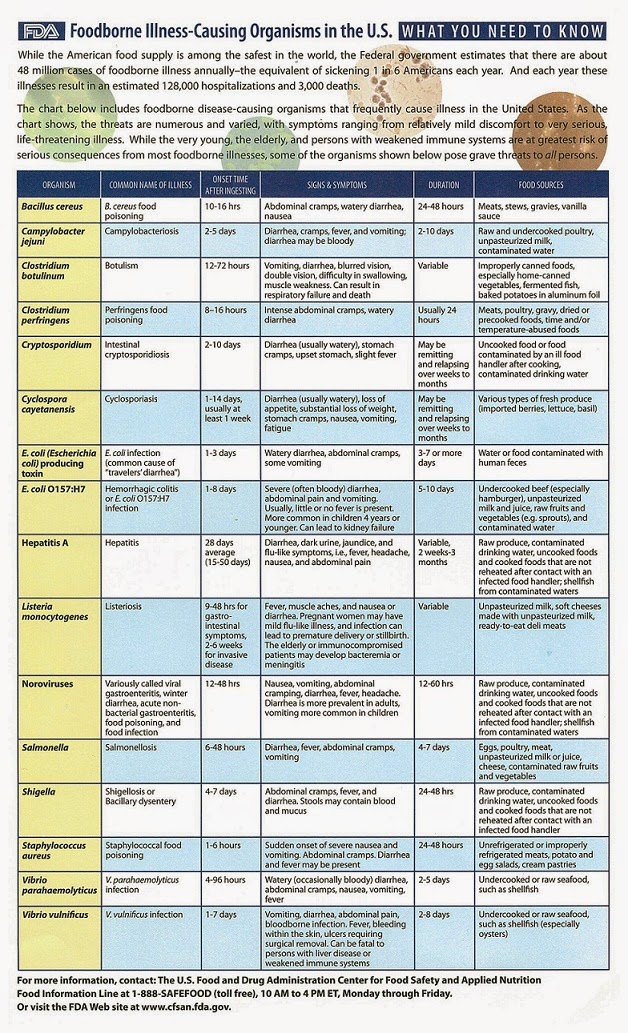
Causes of diarrhea during pregnancy poisoning, dysbacteriosis, bacterial and viral infections:
| Gastroenteritis | Use of lactose and gluten in case of intolerance to these nutrients |
| Bacterial infections: listeriosis or salmonella | Chronic gastrointestinal diseases: Crohn's disease, IBS, ulcerative colitis |
| Certain antibiotics and antacids to reduce acidity | Laxatives |
| Sugar substitutes such as sorbitol | Overconsumption of certain foods |
Tip: If you have recently returned from a vacation in an exotic country with nausea and diarrhea and find out you are pregnant, see your doctor as soon as possible. nine0126
nine0126
Gastroenteritis
One common cause of diarrhea during pregnancy is gastroenteritis or stomach flu. It is caused by bacterial or viral infections: norovirus, rotavirus, E. coli, salmonella, which enter the body through contact with contaminated surfaces, dishes, food and water.
Gastroenteritis usually lasts about three days. However, severe illness is a health hazard, especially during pregnancy, as it can cause dehydration, electrolyte imbalance, and lead to preterm labor. nine0005
The main symptoms of gastroenteritis are diarrhea without blood, nausea and vomiting, stomach cramps and pain, slight fever, headache and muscle pain.
Take extra precautions to reduce your risk of getting sick: frequent handwashing and surface disinfection. If the expectant mother has small children, they are not recommended to use the same cutlery.
Risks of diarrhea during pregnancy
Usually diarrhea during pregnancy is not a cause for concern. However, you should consult a doctor if the following symptoms occur during this period:
However, you should consult a doctor if the following symptoms occur during this period:
- Diarrhea for more than two days;
- Blood or mucus stools;
- Sudden weight loss;
- Pain in the abdomen;
- Dehydration.
How to treat diarrhea during pregnancy
If you have diarrhea during pregnancy, drink plenty of fluids, avoid foods high in fat and sugar, avoid dairy products, and caffeinated drinks.
Dehydration is a serious risk, especially during pregnancy, so electrolyte balance should be restored first with fluids and simple foods:
| Moderate fruit juices | Drinks without alcohol and caffeine |
| Bananas | Potato |
| Rice | Toast |
| Rusks | Light soups and broths |
| Pasta | Applesauce |
Find out about your body's ability to break down lactose and gluten with the Atlas Microbiota Test. nine0126
nine0126
Stomach pain and heartburn during pregnancy
Many women experience stomach pain during pregnancy, especially in the upper part of the stomach, as well as heartburn - a burning sensation in the chest and esophagus.
This is more common in the third trimester, after about 27 weeks. This is an unpleasant but natural phenomenon during pregnancy: the baby grows inside the uterus and presses on other organs, including the stomach. And hormones cause the muscles to relax, which causes acid from the stomach to enter the esophagus and irritate it. In addition, pain can be caused by problems with certain organs such as the gallbladder, or inflammation of the pancreas. nine0005
Symptoms of heartburn during pregnancy:
- Burning in chest and esophagus;
- Feeling of overeating, heaviness or bloating;
- Belching, including with acid and/or food particles;
- Nausea.
It is unlikely that you will be able to avoid cramps and heartburn during pregnancy. However, some tips can help reduce their frequency:
However, some tips can help reduce their frequency:
Nutrition : try to avoid overeating - eat easily digestible food in small portions; do not eat three hours before bedtime; watch your posture while eating - so the pressure on your stomach will be less. nine0005
Smoking and alcohol: In addition to known harms to mothers and babies, tobacco smoke also relaxes the muscles in the lower esophagus, allowing acid to enter the esophagus. And alcohol provokes heartburn and acid reflux.
Although stomach pain and heartburn often accompany pregnancy, abdominal pain, especially in the third trimester, should be taken seriously. It can be a sign of preterm labor or placental abruption, and puts mother and baby at risk. nine0005
If you experience severe abdominal pain during pregnancy that is accompanied by the following symptoms, seek medical attention as soon as possible:
| Abdominal pain and fever | Bleeding |
| Regular convulsions | Unusual vaginal discharge / spotting |
| Vomiting | Low back pain |
| Pain or burning when urinating | Severe pain that lasts 30-60 minutes |
Bloating, constipation and microbiota during pregnancy
Excessive gas and constipation during pregnancy can be caused by hormonal changes, such as increased production of progesterone. This hormone, essential for nourishing the uterus and fetus, relaxes the muscles of the body, including the muscles in the intestines, which slows down digestion and increases flatulence. A similar reaction of the body can be observed before each menstruation, when the production of progesterone increases. nine0005
This hormone, essential for nourishing the uterus and fetus, relaxes the muscles of the body, including the muscles in the intestines, which slows down digestion and increases flatulence. A similar reaction of the body can be observed before each menstruation, when the production of progesterone increases. nine0005
Flatulence - bloating of the abdomen due to the accumulation of gases.
Here are a few simple rules that will help improve bowel movements and avoid constipation and bloating:
- If you don't usually eat a lot of fiber and indigestible foods like legumes, try to gradually introduce them into your diet;
- Avoid carbonated drinks and fatty foods;
- Move more;
- Drink plenty of fluids.
If bloating and constipation are accompanied by severe pain that lasts more than 30 minutes, or if you have been constipated for two or more weeks, see your doctor. nine0005
Gut microbiota and bacteria during pregnancy
A woman's body goes through many changes during pregnancy, and this can affect the microbiota, the bacterial ecosystem that lives in the gut. Trillions of microorganisms do important work for the whole body: they synthesize vitamins and essential acids, keep your intestines working and protect it from disease and inflammation.
Trillions of microorganisms do important work for the whole body: they synthesize vitamins and essential acids, keep your intestines working and protect it from disease and inflammation.
The additional influx of female hormones that accompanies pregnancy alters gut function and affects the microbiota. This is good, because the bacterial community is constantly adjusting to external and internal conditions in order to keep up with the needs of the body. nine0005
To keep your gut bacteria running smoothly, they need your help. Provide them with healthy foods and plant fibers. Fruits, vegetables, whole grains, nuts, and seeds contain prebiotics, special substances that beneficial bacteria feed on. When properly balanced, the bacteria even increase your body's defenses against harmful microorganisms that can cause gastroenteritis during pregnancy.
The Atlas Microbiota Test will help you understand how to prepare your intestines for future pregnancy and reduce the risk of digestive problems. nine0126
nine0126
☝️ Take note
Now you have all the necessary knowledge and tools to help you deal with digestive problems during pregnancy. They are quite varied and quite natural, but in some cases it is necessary to immediately seek medical help:
- Vomiting blood;
- Blood in stool;
- Diarrhea for more than two days;
- Constipation for more than two weeks;
- Sudden weight loss;
- Severe pain interfering with daily activities; nine0010
- Difficulty breathing;
- Pain when swallowing or difficulty swallowing;
- Excessive fatigue.
More articles on the causes of digestive problems in the blog:
- 7 foods that cause gas and bloating
- Lindsey J Wegrzyniak, Treatment of Hyperemesis Gravidarum, 2012 nine0009 Edwards A. et al., The Maternal Gut Microbiome During Pregnancy, 2018
- National Health and Safety (NHS), Vomiting and morning sickness in pregnancy
- Kudzai Kanhutu, Travel and pregnancy: an infectious diseases perspective, 2011
- CDC, Pregnant travelers
- U.
 S. Department of Health and Human Services, Agency for healthcare research and quality, Abdominal Pain in Early Pregnancy
S. Department of Health and Human Services, Agency for healthcare research and quality, Abdominal Pain in Early Pregnancy - Robyn Horsager-Boehrer, M.D., UT Southwestern Medical Center, Should pregnant moms be concerned about gastroenteritis?, 2018
- International Foundation for Gastrointestinal Disorders, Pregnancy and Irritable Bowel Syndrome, 2016
- NHS Vomiting and morning sickness in pregnancy
- NHS, Severe vomiting in pregnancy
- Lindsey J Wegrzyniak et al., Treatment of Hyperemesis Gravidarum, 2012
- Karen Miles, Diarrhea during pregnancy, 2020
- Cleveland Clinic, Diarrhea
- You and your hormones, Progesterone
- Traci C. Johnson, MD, Pregnancy, Bloating, 2020
Diarrhea during pregnancy: symptoms, causes and consequences, diagnosis and treatment
Diarrhea during pregnancy: causes, diagnosis and treatment
Average reading time: 9 minutes
Content:
Causes and symptoms of diarrhea during pregnancy
Diagnostic features
The consequences of diarrhea in pregnant women
treatment areas
When treatment is required in the hospital
Diet
Can I use the Imodium ® Express during pregnancy 9000 9000 9000) not only a deterioration in well-being, but also unwanted unrest for a woman who is expecting a baby. Frequent defecation causes significant discomfort and is often accompanied by additional unpleasant symptoms. In addition, this condition can pose a serious danger to the woman and the fetus due to the threat of dehydration and other risks. One of the difficulties is that with diarrhea in pregnant women in the first trimester, not all antidiarrheal drugs can be drunk. The active components of some drugs can have a negative effect on the fetus. That is why with frequent bowel movements it is necessary to consult a specialist. The doctor will diagnose and tell you what to do with diarrhea. nine0005
Frequent defecation causes significant discomfort and is often accompanied by additional unpleasant symptoms. In addition, this condition can pose a serious danger to the woman and the fetus due to the threat of dehydration and other risks. One of the difficulties is that with diarrhea in pregnant women in the first trimester, not all antidiarrheal drugs can be drunk. The active components of some drugs can have a negative effect on the fetus. That is why with frequent bowel movements it is necessary to consult a specialist. The doctor will diagnose and tell you what to do with diarrhea. nine0005
Back to content
Causes and symptoms of diarrhea during pregnancy
Infectious. Bacterial and viral infections (eg, noro- or rotavirus) can cause bowel dysfunction. They are usually transmitted by airborne droplets or the fecal-oral route. Pathogenic microorganisms also often enter the gastrointestinal tract through the use of low-quality foods or contaminated water. Infectious diarrhea during pregnancy in the second and third trimester may be accompanied by fever, chills, nausea and vomiting, painful abdominal cramps, and general weakness. An admixture of mucus often appears in the feces. nine0005
Infectious diarrhea during pregnancy in the second and third trimester may be accompanied by fever, chills, nausea and vomiting, painful abdominal cramps, and general weakness. An admixture of mucus often appears in the feces. nine0005
Non-infectious. This form of diarrhea can be caused by a variety of factors: changes in diet, frequent stress, disorders of digestion and absorption, some chronic diseases, taking certain medications. In this case, the pregnant woman may be disturbed by frequent defecation (sometimes with imperative, i.e., strongly pronounced, irresistible urges), abdominal pain in the upper or lower section. With organic lesions of the colon, an admixture of blood sometimes appears in the feces. In the later stages, violations of the frequency of bowel movements may be associated with fetal pressure on the digestive tract. nine0005
Up to content
Diagnostic features
When diagnosing a disease that caused diarrhea, it is important to exclude surgical, urological and obstetric pathologies.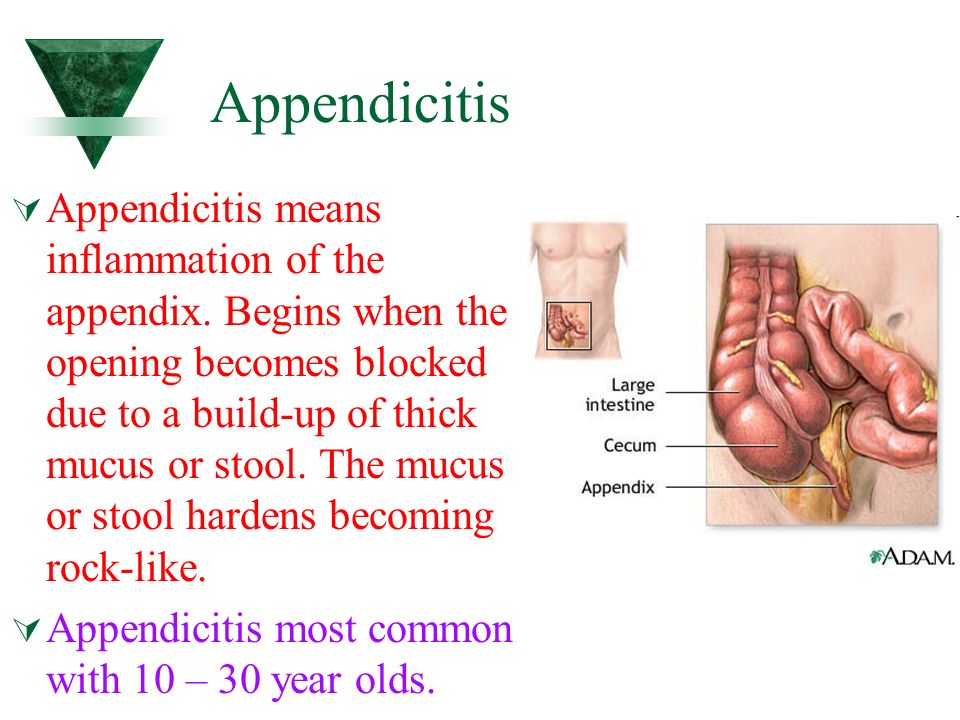 For this, an examination is mandatory, if necessary, the doctor prescribes an additional examination. Early diarrhea may be a manifestation of ectopic pregnancy, appendicitis, urinary tract infections, pyelonephritis, inflammatory bowel disease, and acute pancreatitis. That is why it is important to quickly establish the cause of the disruption of the intestines and select adequate therapy. It is also mandatory to monitor (monitor observation) the condition of the fetus at 37, 38 and 39weeks of pregnancy.
For this, an examination is mandatory, if necessary, the doctor prescribes an additional examination. Early diarrhea may be a manifestation of ectopic pregnancy, appendicitis, urinary tract infections, pyelonephritis, inflammatory bowel disease, and acute pancreatitis. That is why it is important to quickly establish the cause of the disruption of the intestines and select adequate therapy. It is also mandatory to monitor (monitor observation) the condition of the fetus at 37, 38 and 39weeks of pregnancy.
Back to Contents
Effects of Diarrhea in Early Pregnancy
Prolonged diarrhea can lead to dehydration, a condition that is dangerous for both the expectant mother and the fetus. It is manifested by severe weakness, dry mucous membranes, thirst. With a strong degree of dehydration, cardiac and respiratory activity can be disturbed. Diarrhea can also in some cases increase the risk of miscarriage due to an increase in the contractile activity of the uterus, and can lead to impaired uteroplacental blood flow. nine0005
nine0005
Up to content
Directions for treatment
How to treat diarrhea should be decided by the doctor, taking into account the woman's condition, the cause of indigestion, gestational age and other factors. Typically, therapy includes the following areas.
| Restoration of water and electrolyte balance | Replenishment of fluid deficiency in pathologies accompanied by diarrhea is an important measure to prevent severe and life-threatening conditions. To restore the water and electrolyte balance, pregnant women, on the recommendation of a doctor, can drink non-carbonated mineral water or rehydration solutions. The latter contain the salts necessary for the body, which are excreted from it along with the liquid. It should be borne in mind that with severe dehydration, drinking a solution of salts may no longer be enough. In this case, rehydration drugs are infused intravenously (in a hospital setting, if recommended by a doctor). |
| Elimination of toxins | To reduce the load on the body, it is necessary to help it get rid of toxic substances. In some cases, gastric lavage is performed for this purpose. Also, strictly according to the doctor's prescription, you can take enterosorbents. These drugs, passing through the gastrointestinal tract, can bind toxic substances and promote their removal from the body in a natural way. By themselves, such drugs do not interact with the intestinal mucosa or other parts of the digestive tract. nine0005 |
| Restoration of normal intestinal microflora | To normalize the processes of digestion and absorption, it is necessary that beneficial bacteria be present in the intestines. They can be obtained from food (for example, fermented milk products with live cultures). In addition, according to indications, the doctor may prescribe probiotic preparations that help restore intestinal microflora. |
| Treating the cause of diarrhea | If frequent bowel movements are a symptom of a bacterial infection, antibiotics may be used to treat. Such remedies can help eliminate the cause of diarrhea by destroying pathogenic microorganisms. The drugs are used strictly according to the doctor's prescription. |
Back to Table of Contents
When Hospital Treatment is Necessary
Diarrhea is not always treated at home. With severe dehydration, the risk of miscarriage, severe concomitant diseases, the doctor may suggest that the pregnant woman go to the hospital. Such a measure allows for constant medical supervision, which in such cases is often simply necessary. Urgently seek medical attention and urgent hospitalization may be required if:
- severe abdominal pain of any location;
- blood in feces;
- general lethargy.
The standard clinical indications for inpatient treatment are moderate to severe diarrhea accompanied by dehydration. It is also necessary to go to the hospital if home therapy does not work for 3-4 days (the pregnant woman does not get better, the symptoms persist).
It is also necessary to go to the hospital if home therapy does not work for 3-4 days (the pregnant woman does not get better, the symptoms persist).
Important! Even on an outpatient basis, the treatment of conditions accompanied by diarrhea should be carried out under the supervision of a physician. nine0005
Back to Contents
Diet
During the treatment of diarrhea, it is very important to adjust your diet in order to reduce the load on the digestive tract and help the body cope with the problem faster. In case of violations of the intestines, accompanied by frequent defecation, spicy, sour, fatty foods are excluded from the diet. With an intestinal disorder, you can not use whole milk, fresh fruits and vegetables, legumes, sweets, spices, smoked snacks. Liquid, semi-liquid, pureed, steamed products are allowed. They should be served warm, but not hot or cold. In the early days of infectious diarrhea, experts may recommend a starvation diet. Then, rice water, liquid cereals from oatmeal or buckwheat are introduced into the diet.
 nine0005
nine0005