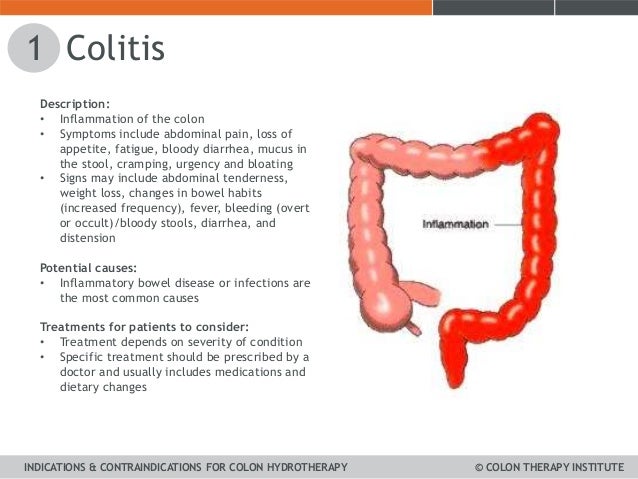
Mucus diarrhea during pregnancy
Mucus In Stool During Pregnancy? Should you be worried? Is it Normal? Reasons
Pregnancy brings about various physiological changes in the body. There are some common problems faced by pregnant women like nausea, vomiting, fatigue, changes in dietary preference, etc. which are caused due to the widespread changes going on in the body. However, sometimes pregnant women may face some uncommon symptoms which may put them to worry. Presence of mucus is one such condition that most pregnant women do not know of and hence, it is necessary to be more aware of it.
Book an appointment online to consult with Dr. Ritambhra Bhalla for gynecological issues.
What causes mucus in stool?
Mostly, mucus in stool is caused due to some digestive problems. Common causes of mucus in stool in pregnant women are:
- Hormonal changes can result in the presence of mucus in stool.
Since during pregnancy, there are high hormonal fluctuations taking place in the body, there is an increased chance of finding mucus in stool.
- The increase in the size of the uterus during pregnancy disrupts the intestine which may also lead to excretion of mucus.
- Dehydration can also lead to mucus in stool.
- Infection in the stomach or other parts of the digestive tract may also result in mucus.
- Food allergies can also result in mucus excretion.
Must Read: How To Tackle Backaches During Pregnancy
- Many doctors recommend various vitamin supplements to women before or during pregnancy. This can also cause mucus in stool, especially if the vitamins have an excess of iron or calcium.
Is it normal?
Though rather uncommon, it is completely okay to find some mucus in your stool during pregnancy.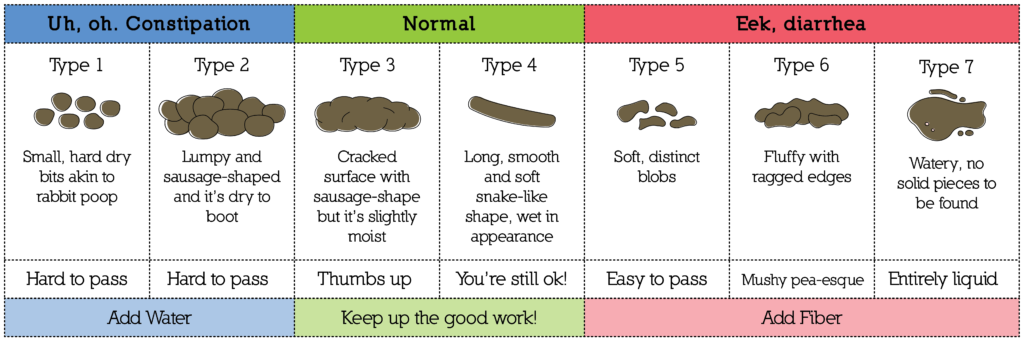 Especially during the first trimester, when the body is undergoing a lot of changes, there is an increased risk of mucus excretion which is completely normal. Also, if your doctor prescribes supplements, there is an increased chance of finding mucus in stool and is nothing to worry about.
Especially during the first trimester, when the body is undergoing a lot of changes, there is an increased risk of mucus excretion which is completely normal. Also, if your doctor prescribes supplements, there is an increased chance of finding mucus in stool and is nothing to worry about.
Want to consult a doctor? Book Online Consultation with Doctor, consult the best Gynecologist in India
Join our Cloudnine Community to discuss further regarding - Pregnancy Daily Care, Pregnancy Nutrition, Pregnancy Fitness, Nutrition.
Prevention:
There are certain guidelines which can help in reducing the risk of mucus excretion during pregnancy like:
- Staying hydrated helps in prevention of mucus and various other health problems during pregnancy.
 Drink plenty of water during pregnancy, and if needed, use hydration salts too.
Drink plenty of water during pregnancy, and if needed, use hydration salts too. - Performing light exercises which are suitable for pregnant women (with the prior recommendation of your doctor) can also help.
- Maintaining a healthy diet is also important, not just for mucus prevention but for a healthier pregnancy in general.
To know more About Uterine rupture during pregnancy
When to see a doctor?
Mostly the presence of mucus in stool is not a cause of worry. However, if you notice additional symptoms like the presence of blood along with the presence of mucus, it is highly advisable to contact your health provider.
Moreover, if you have extreme abdominal pain or haemorrhoids, it is also advisable to contact a maternity doctor. Additionally, excretion of very high quantities of mucus or persistent presence of mucus in the stool should also be not taken lightly.
Good news, now you can shop right away from wide range of products on Cloudnine Momeaze.
Watch Video on Do's and Don'ts of Pregnancy
Cloudnine is one of the leading maternity and childcare hospitals in the country. When it comes to pregnancy and maternity, we are renowned for providing world-class facilities and care. Our specialists are extremely qualified and experienced and are dedicated to providing you with the best possible treatment and care.
Do you have questions in your mind like How Many Weeks Pregnant Am I? Check out Cloudnine's Pregnancy Due Date Calculator now!
Our customers had a few questions regarding this blog, check them out now!
Stomach upset during pregnancy?
Constipation during pregnancy?
Have Similar Questions?
Get answers from our Experts, browse through hundreds of Q&A, attend live sessions, and much more
Ask your question!
Want to consult the best gynecologists in India? Please find the links below.
- Best Gynecologists in Bangalore
- Best Gynecologists in Chennai
- Best Gynecologists in Mumbai
- Best Gynecologists in Pune
- Best Gynecologists in Chandigarh
- Best Gynecologists in Gurgaon
- Best Gynecologists in Noida
Want to consult the best Maternity Packages in India? Please find the links below.
- Best Maternity Packages in Bangalore
- Best Maternity Packages in Chennai
- Best Maternity Packages in Mumbai
- Best Maternity Packages in Pune
- Best Maternity Packages in Chandigarh
- Best Maternity packages in Gurgaon
- Best Maternity Packages in Noida
Mucus In Stool During Pregnancy: Causes And Treatment
It should not cause worry unless there is pain, blood, or discomfort in passing stool.
Research-backed
MomJunction believes in providing reliable, research-backed information to you. As per our strong editorial policy requirements, we base our health articles on references (citations) taken from authority sites, international journals, and research studies. However, if you find any incongruencies, feel free to write to us.
Image: iStock
Excess mucus in stool during pregnancy may occur due to gastrointestinal issues or pregnancy-related factors, such as hormonal changes. Gastric mucus is produced in the stomach and helps in the motility of the digested food in the gastrointestinal tract. We excrete some mucus in stools usually. However, pregnancy may increase the amount of mucus excreted, making it more noticeable (1).
Excess mucus due to underlying issues is treatable. Read this post to learn the various causes and treatment options for excess mucus in stool during pregnancy.
Is It Normal To Have Mucus In Stool During Pregnancy?
You may sometimes pass mucus in the stool due to multiple gastrointestinal issues (2) (3). We pass a small amount of mucus in the stool, which is generally unnoticeable. Pregnant women may pass excess mucus in their stool during the first trimester.
We pass a small amount of mucus in the stool, which is generally unnoticeable. Pregnant women may pass excess mucus in their stool during the first trimester.
The appearance of mucus in stool is due to the rapid changes in your body during the gestational period. Safety measures and precautions may be taken if there is an excess of mucus secretion or followed by pain and bleeding. You may consult a doctor to help determine the cause of the condition.
Related: Bleeding During Pregnancy: Causes, Diagnosis And Treatment
What Causes Mucus in Stool During Pregnancy?
Some possible causes of secretion of excess mucus in stool during pregnancy are (3) (4) (5) (6):
- Dehydration: Hydration is for a healthy gut and mind. During pregnancy, water intake is crucial for the mother and her fetus. Dehydration might be one of the prime factors for the excretion of mucus in the stool.
Related: 12 Signs Of Dehydration During Pregnancy And Ways To Avoid It
- Irritable bowel syndrome: Change in routine, stress, and infection may cause irritable bowel syndrome.
 The symptoms may include mucus in stool, abdominal pain, and alternating diarrhea and constipation.
The symptoms may include mucus in stool, abdominal pain, and alternating diarrhea and constipation. - Hormonal change: Various hormonal changes occur in your body during the gestational period. Some pregnancy-specific hormones may directly or indirectly regulate the mucus secretion in the stool during pregnancy.
- Infection in the stomach: Bacterial or viral infection in the gastrointestinal tract may result in excess mucus secretion in the stool. Intestinal parasites such as tapeworms, hookworms, amoeba, and pinworms could be the reasons.
Some symptoms of stomach infection that may accompany the secretion of mucus in the stool are diarrhea, cramping, vomiting, nausea, and fever
- Irritable bowel syndrome: Change in routine, stress, and infection may cause irritable bowel syndrome.
Image: iStock
Quick fact
Giardiasis is an intestinal parasite infection that may cause greasy stools with stomach cramps and nausea. Pregnant women may face more dehydration than others (12).
- Food allergies: Lactose intolerance and specific food allergies may also result in mucus secretion in the stool.
- Intestine blockage: The fetus might be pushing against the intestine wall, resulting in blocked intestine and constipation. The body might be oversecreting mucus in the stool to ease constipation.
- Medications or vitamins: Prenatal intake of vitamins fortified with iron or calcium during pregnancy may be associated with excess mucus excretion in stool.
Image: Shutterstock
- Hemorrhoids: Piles or hemorrhoids are swollen veins around the anus usually accompanied by constipation during pregnancy. During pregnancy, hemorrhoids may occur due to constipation and pressure from the growing baby.
Health tip
Gently applying a cloth wrung out in iced water to the affected area may help ease the pain and reduce inflammation (13).
- Other gastrointestinal conditions: These include Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis, colon polyps, and diverticulitis.
Related: Crohn's Disease And Pregnancy: Symptoms, Diagnosis & Treatment
What Are The Treatment Options And Ways To Prevent Mucus In Stool?
Identifying the cause behind mucus secretion is essential for the treatment.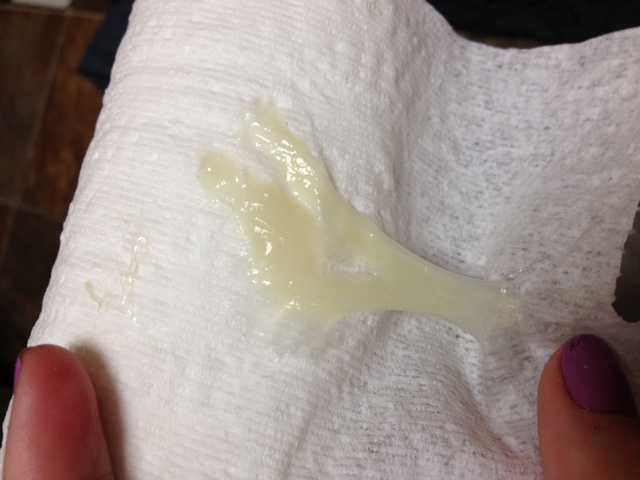 Some treatments options available for reducing mucus in the stool during pregnancy are (7) (8) (9 ):
Some treatments options available for reducing mucus in the stool during pregnancy are (7) (8) (9 ):
- Stay hydrated: Taking plenty of water during pregnancy may help reduce dehydration-induced constipation. It can also avoid the accumulation of various toxins in the body. The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) recommends drinking around 8 to 12 cups (64 to 96 ounces) of water every day. Excess fluids, including more fresh juices in your diet, are beneficial. Water also helps absorb water-soluble vitamins (vitamins B and C) from the diet into the body.
Image: iStock
- Take a healthy diet: A healthy and balanced diet rich in green leafy vegetables and fiber supplements can help reduce constipation during pregnancy.
- Change medication: If you have mucus secretion in the stool followed by vitamin intake, you may consult your physician. It might be possible to change the particular medication to help you relieve mucus in the stool.

- Use laxatives: In constipation, your health care provider may suggest a laxative or a stool softener. The laxatives are over-the-counter medication and may help reduce constipation and mucus secretion in the stool.
Health fact
Mild laxatives such as milk of magnesia, bulking agents (metamucil) and stool softeners (docusates) may be prescribed during pregnancy (14).
- Get the infection cured: If the origin of mucus in the stool is an infection, your doctor may suggest an antibiotic regime to control the infection. It is best practice to complete the course of antibiotics for complete recovery and reduce recurrence.
- Avoid allergic food: In case of food allergies, try to identify and avoid the allergen in your food. Abstaining from the source of allergy may help regain a healthy gut and reduce mucus secretion in the stool. It is always good to limit junk and spicy foods for better health during pregnancy.
Did you know?
Celiac disease, which is caused due to gluten sensitivity, has been linked to an increased risk of adverse pregnancy outcomes (15).
- Include mild exercises: Exercising during pregnancy can help you stay healthy and fresh. A little warmup followed by movement exercise will keep your gut healthy. It may help ease constipation-induced mucus secretion. Mild exercises and physical activities are safe during the pregnancy. Walking and jogging may keep you active and aid digestion.
Image: iStock
Related: 17 Safe Pregnancy Exercises And Workouts For Women
When Should You Call The Doctor?
Image: Shutterstock
Mucus in stool is not a sign to worry about. You may improve your lifestyle and undertake preliminary measures to reduce the excess secretion of mucus in stool.
When stool has an excess amount of visible mucus during pregnancy, it may be due to health conditions, such as (10) (11) :
- Irritable bowel syndrome
- Ulcerative colitis
- Crohn’s disease
One may take note of the symptoms and consult a doctor in the following cases:
- There is an excess amount of mucus in the stool
- Blood or pus in the stool
- Pain while passing stool
- Having stomach pain, cramping, or bloating
- Sudden changes in stool frequency, consistency, or color
1. Can probiotics cause mucus in stool?
Can probiotics cause mucus in stool?
Research indicates that probiotics may alter the composition and volume of stool, causing gassiness and increased mucus secretion in stools. If you notice these symptoms after consuming probiotics during pregnancy, you should talk to your gynecologist or nutritionist (12).
2. Can anxiety cause mucus in stool?
Anxiety may increase mucus secretion in stool in some individuals (13). However, the underlying reason is not known, and it may not happen to everyone.
Mucus in stool during pregnancy is usually normal. It may happen due to dehydration, hormonal changes, or food allergies. Understanding your body and making lifestyle changes such as drinking more water, avoiding allergic food, or eating healthy helps keep the problems at bay. However, do not ignore symptoms such as blood or pus in the stool or pain in passing stool, as these may indicate more severe conditions such as irritable bowel syndrome or Crohn’s disease. In such cases, it is necessary to consult a doctor.
Key Pointers
- Pregnant women may pass mucus in their stool during the first trimester due to dehydration, hormonal changes, stomach infections, and other issues.
- Some treatment options that may relieve the condition are proper hydration, a healthy diet, mild exercises, and avoiding allergic foods.
- Consult a doctor if you notice excess mucus, pus, or blood in the stool or experience pain, cramps, or bloating.
References:
MomJunction's articles are written after analyzing the research works of expert authors and institutions. Our references consist of resources established by authorities in their respective fields. You can learn more about the authenticity of the information we present in our editorial policy.
- The gastrointestinal mucus system in health and disease.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3758667/ - Gastrointestinal Infections in Pregnancy.
https://patient.info/doctor/gastrointestinal-infections-in-pregnancy - Bladder and bowel problems during pregnancy.
https://www.pregnancybirthbaby.org.au/bladder-and-bowel-problems-during-pregnancy - Hormones in pregnancy.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3640235/ - Piles in pregnancy.
https://www.nhs.uk/pregnancy/related-conditions/common-symptoms/piles/ - Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS).
https://www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au/health/conditionsandtreatments/irritable-bowel-syndrome-ibs - Nutrition Column An Update on Water Needs during Pregnancy and Beyond.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1595116/ - How much water should I drink during pregnancy?
https://www.acog.org/womens-health/experts-and-stories/ask-acog/how-much-water-should-i-drink-during-pregnancy - Constipation in Pregnancy.
https://americanpregnancy.org/healthy-pregnancy/pregnancy-health-wellness/constipation-during-pregnancy/ - The Diagnosis and Treatment of Crohn’s Disease and Ulcerative Colitis.

https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2695363/ - The Effect of Phloroglucinol in Patients With Diarrhea-predominant Irritable Bowel Syndrome: A Randomized, Double-blind, Placebo-controlled Trial.
https://www.jnmjournal.org/journal/view.html?uid=1563&vmd=Full& - What is giardiasis?
https://www.cdc.gov/parasites/giardia/general-info.html - Piles in pregnancy.
https://www.nhs.uk/pregnancy/related-conditions/common-symptoms/piles/ - Laxatives During Pregnancy.
https://americanpregnancy.org/healthy-pregnancy/is-it-safe/laxatives-during-pregnancy/#:~:text=One%20mild%20laxative%2C%20considered%20to - Stephanie M. Moleski et al.; Increased rates of pregnancy complications in women with celiac disease.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4367213/
The following two tabs change content below.
- Reviewer
- Author
Dravet Syndrome In Babies: Causes, Symptoms And Treatment
Dravet Syndrome In Babies: Causes, Symptoms And Treatment
Group B Strep In Pregnancy: Symptoms, Diagnosis And Treatment
Group B Strep In Pregnancy: Symptoms, Diagnosis And Treatment
How Much Water Should A Pregnant Woman Drink?
How Much Water Should A Pregnant Woman Drink?
Vitamin K Shot At Birth: Importance, Safety And Side Effects
Vitamin K Shot At Birth: Importance, Safety And Side Effects
FPIES in Babies: Symptoms, Causes And Treatment
FPIES in Babies: Symptoms, Causes And Treatment
HypnoBirthing: How It works, Techniques And Benefits
HypnoBirthing: How It works, Techniques And Benefits
UTI During Pregnancy: Causes, Symptoms, Risks And Treatment
UTI During Pregnancy: Causes, Symptoms, Risks And Treatment
Vitamin D During Pregnancy: Importance, Dosage And Foods
Vitamin D During Pregnancy: Importance, Dosage And Foods
Pea Allergy In Babies: Symptoms, Treatment And Prevention
Pea Allergy In Babies: Symptoms, Treatment And Prevention
Diarrhea during pregnancy: symptoms, causes and consequences, diagnosis and treatment
Diarrhea during pregnancy: causes, diagnosis and treatment Average reading time: 9 minutes
Contents:
Causes and symptoms of diarrhea during pregnancy
Diagnostic features
The consequences of diarrhea in pregnant women
Directions of treatment
When treatment is required in the hospital
Diets
Can I use the Imodium ® Express during pregnancy
of pregnancy in the early periods can be earned during pregnancy, not only a deterioration in well-being, but also unwanted unrest for a woman who is expecting a baby. Frequent defecation causes significant discomfort and is often accompanied by additional unpleasant symptoms. In addition, this condition can pose a serious danger to the woman and the fetus due to the threat of dehydration and other risks. One of the difficulties is that with diarrhea in pregnant women in the first trimester, not all antidiarrheal drugs can be drunk. The active components of some drugs can have a negative effect on the fetus. That is why with frequent bowel movements it is necessary to consult a specialist. The doctor will diagnose and tell you what to do with diarrhea. nine0003
Frequent defecation causes significant discomfort and is often accompanied by additional unpleasant symptoms. In addition, this condition can pose a serious danger to the woman and the fetus due to the threat of dehydration and other risks. One of the difficulties is that with diarrhea in pregnant women in the first trimester, not all antidiarrheal drugs can be drunk. The active components of some drugs can have a negative effect on the fetus. That is why with frequent bowel movements it is necessary to consult a specialist. The doctor will diagnose and tell you what to do with diarrhea. nine0003
Back to top
Causes and symptoms of diarrhea during pregnancy
Infectious. Bacterial and viral infections (eg, noro- or rotavirus) can cause bowel dysfunction. They are usually transmitted by airborne droplets or the fecal-oral route. Pathogenic microorganisms also often enter the gastrointestinal tract through the use of low-quality foods or contaminated water. Infectious diarrhea during pregnancy in the second and third trimester may be accompanied by fever, chills, nausea and vomiting, painful abdominal cramps, and general weakness. An admixture of mucus often appears in the feces. nine0003
An admixture of mucus often appears in the feces. nine0003
Non-infectious. This form of diarrhea can be caused by a variety of factors: changes in diet, frequent stress, disorders of digestion and absorption, some chronic diseases, taking certain medications. In this case, the pregnant woman may be disturbed by frequent defecation (sometimes with imperative, i.e., strongly pronounced, irresistible urges), abdominal pain in the upper or lower section. With organic lesions of the colon, an admixture of blood sometimes appears in the feces. In the later stages, violations of the frequency of bowel movements may be associated with fetal pressure on the digestive tract. nine0003
Up to content
Diagnostic features
When diagnosing a disease that caused diarrhea, it is important to exclude surgical, urological and obstetric pathologies. For this, an examination is mandatory, if necessary, the doctor prescribes an additional examination. Early diarrhea may be a manifestation of ectopic pregnancy, appendicitis, urinary tract infections, pyelonephritis, inflammatory bowel disease, and acute pancreatitis. That is why it is important to quickly establish the cause of the disruption of the intestines and select adequate therapy. It is also mandatory to monitor (monitor observation) the condition of the fetus at 37, 38 and 39weeks of pregnancy.
That is why it is important to quickly establish the cause of the disruption of the intestines and select adequate therapy. It is also mandatory to monitor (monitor observation) the condition of the fetus at 37, 38 and 39weeks of pregnancy.
Back to Contents
Effects of Diarrhea in Early Pregnancy
Prolonged diarrhea can lead to dehydration, a condition that is dangerous for both the expectant mother and the fetus. It is manifested by severe weakness, dry mucous membranes, thirst. With a strong degree of dehydration, cardiac and respiratory activity can be disturbed. Diarrhea can also in some cases increase the risk of miscarriage due to an increase in the contractile activity of the uterus, and can lead to impaired uteroplacental blood flow. nine0003
Up to content
Directions for treatment
How to treat diarrhea should be decided by the doctor, taking into account the woman's condition, the cause of indigestion, gestational age and other factors. Typically, therapy includes the following areas.
Typically, therapy includes the following areas.
| Restoration of water and electrolyte balance | Replenishment of fluid deficiency in pathologies accompanied by diarrhea is an important measure to prevent severe and life-threatening conditions. To restore the water and electrolyte balance, pregnant women, on the recommendation of a doctor, can drink non-carbonated mineral water or rehydration solutions. The latter contain the salts necessary for the body, which are excreted from it along with the liquid. It should be borne in mind that with severe dehydration, drinking a solution of salts may no longer be enough. In this case, rehydration drugs are infused intravenously (in a hospital setting, if recommended by a doctor). nine0003 |
| Elimination of toxins | To reduce the load on the body, it is necessary to help it get rid of toxic substances. In some cases, gastric lavage is performed for this purpose. |
| Restoration of normal intestinal microflora | To normalize the processes of digestion and absorption, it is necessary that beneficial bacteria be present in the intestine. They can be obtained from food (for example, fermented milk products with live cultures). In addition, according to indications, the doctor may prescribe probiotic preparations that help restore intestinal microflora. |
| Relieve the cause of diarrhea | If frequent bowel movements are a symptom of a bacterial infection, antibiotics may be used to treat them. |
Back to Table of Contents
When Hospital Treatment is Necessary
Diarrhea is not always treated at home. With severe dehydration, the risk of miscarriage, severe concomitant diseases, the doctor may suggest that the pregnant woman go to the hospital. Such a measure allows for constant medical supervision, which in such cases is often simply necessary. Urgently seek medical attention and urgent hospitalization may be required if:
- severe abdominal pain of any location;
- blood in feces;
- general lethargy.
Standard clinical indications for inpatient treatment are moderate to severe diarrhea accompanied by dehydration. It is also necessary to go to the hospital if home therapy does not work for 3-4 days (the pregnant woman does not get better, the symptoms persist).
Important! Even on an outpatient basis, the treatment of conditions accompanied by diarrhea should be carried out under the supervision of a physician. nine0003
Back to Contents
Diet
During the treatment of diarrhea, it is very important to adjust your diet in order to reduce the load on the digestive tract and help the body cope with the problem faster. In case of violations of the intestines, accompanied by frequent defecation, spicy, sour, fatty foods are excluded from the diet. With an intestinal disorder, you can not use whole milk, fresh fruits and vegetables, legumes, sweets, spices, smoked snacks. Liquid, semi-liquid, pureed, steamed products are allowed. They should be served warm, but not hot or cold. In the early days of infectious diarrhea, experts may recommend a starvation diet. Then, rice water, liquid cereals from oatmeal or buckwheat are introduced into the diet. nine0003
Up to content
Can I use IMODIUM
® Express in early pregnancy? The active substance of the drug is loperamide, data on the teratogenic or embryotoxic effect of which are absent. However, the drug can not be used at any stage of pregnancy. According to the instructions, in the first trimester and while breastfeeding, the use is not allowed 1 . In the II and III trimesters IMODIUM ® Express can be taken only on the recommendation of a doctor 1 . A remedy for diarrhea is prescribed only if the expected benefit to the woman outweighs the risk to the fetus. Before use, you should consult with a specialist and read the instructions.
However, the drug can not be used at any stage of pregnancy. According to the instructions, in the first trimester and while breastfeeding, the use is not allowed 1 . In the II and III trimesters IMODIUM ® Express can be taken only on the recommendation of a doctor 1 . A remedy for diarrhea is prescribed only if the expected benefit to the woman outweighs the risk to the fetus. Before use, you should consult with a specialist and read the instructions. The information in this article is for reference only and does not replace professional medical advice. For diagnosis and treatment, contact a qualified specialist. nine0178
1 According to the instructions for medical use of the drug IMODIUM ® Express.
* Among products based on Loperamide. According to sales in money for February 2018 - January 2019, according to IQVIA.
Diarrhea during pregnancy. What is Diarrhea During Pregnancy?
IMPORTANT
The information in this section should not be used for self-diagnosis or self-treatment. In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, only the attending physician should prescribe diagnostic tests. For diagnosis and proper treatment, you should contact your doctor. nine0003
Diarrhea during pregnancy is a pathological condition during gestation, characterized by the rapid release of unformed feces. Disorder of the stool can proceed painlessly or be accompanied by belching, nausea, vomiting, discomfort in the mouth, abdominal pain, imperative urge to defecate, fever, weight loss, weakness, fatigue. To determine the cause of diarrhea, clinical, bacteriological, biochemical studies of feces, blood, probing, sigmoidoscopy are carried out. Treatment is most often conservative - medications, dietary adjustments. nine0003
ICD-10
K59. 1 A09.0
1 A09.0
- Causes
- Pathogenesis
- Classification
- Symptoms
- Complications
- Diagnostics
- Treatment
- Prognosis and prevention
- Prices for treatment
General
Diarrhea (diarrhea) - an increase in the frequency of bowel movements up to four or more times a day with the separation of liquid or mushy stools, the volume of which exceeds 200-300 ml. Diarrhea is not a separate disease, but one of the manifestations of a violation of the functions or anatomical structure of any organ or body system. Sometimes diarrhea is the first symptom of a pathology that can complicate gestation. The frequency of diarrhea in obstetrics is 34%. Diarrhea is recorded less frequently than constipation, it is more susceptible to age-related (after 35 years), as well as young (under 19years) mother. Usually there are forms with a mild course, ending in a quick recovery. Severe forms pose a serious threat to the life of the mother and fetus. Inpatient treatment with intensive care is necessary for 1.5% of pregnant women suffering from diarrhea.
Inpatient treatment with intensive care is necessary for 1.5% of pregnant women suffering from diarrhea.
diarrhea during pregnancy
Causes
Most often, diarrhea during pregnancy is caused by physiological (that occurred during gestation, associated with this condition, which is a variant of the norm during this period) changes in the digestive, endocrine, and nervous systems. Another common reason is dietary errors. Diarrhea is manifested by diseases that developed during gestation in women whose body could not adapt to increased stress, and that arose before conception. There are the following sources of intestinal upset in pregnant women: nine0003
- Non-communicable diseases of the digestive system. Diarrhea may be accompanied by a physiological decrease in gastric secretion during gestation, as well as pathologies: dysbiosis, cholestatic hepatosis of pregnant women, hypoacid gastritis, less often - ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease, chronic pancreatitis, tumors.

- Features of the diet. Diarrhea can lead to addiction to coffee, excessive consumption of fatty (including nuts), spicy, spicy foods, sweets, pastries, as well as foods containing a large amount of fiber (fruits, vegetables, cereals). In addition, diarrhea may be accompanied by hypovitaminosis of pregnant women, which occurs due to an imbalance or scarcity of the diet. nine0142
- Food intolerance. The cause of diarrhea can be a food idiosyncrasy associated with a lack of enzyme production (for example, lactulose with intolerance to whole milk) or an allergic reaction (more often to citrus fruits, berries, cereals, eggs, chocolate, legumes). At the same time, hypersensitization often develops for the first time during the gestational period.
- Neurogenic factors. By the last trimester of pregnancy, the processes of excitation of the cerebral cortex begin to prevail over the mechanisms of inhibition, which increases the likelihood of developing irritable bowel syndrome.
 Other causes of neurogenic diarrhea are prolonged psycho-emotional stress, neuropathy. nine0142
Other causes of neurogenic diarrhea are prolonged psycho-emotional stress, neuropathy. nine0142 - Infections and infestations. Diarrhea is caused by acute intestinal infections - bacterial, viral, protozoal, affecting the digestive tract. Nonspecific infections may be the result of the growth of opportunistic flora against the background of a natural decrease in immune activity during pregnancy. The flu is often accompanied by diarrhea. Of the helminths, roundworms are most often involved in diarrhea.
- Taking medications. Iron preparations, magnesium salts, antibiotics, antacids, sugar substitutes, antidiabetic, laxatives, dietary supplements cause diarrhea, using various mechanisms of gastrointestinal dysfunction. nine0142
Other, more rare causes of diarrhea in pregnant women include metabolic endocrine diseases (diabetes mellitus, hyperthyroidism, amyloidosis), surgical pathologies (acute appendicitis, intestinal obstruction, mesenteric vascular embolism). False diarrhea is sometimes accompanied by persistent constipation, which is often observed in pregnant women: a prolonged stay of feces leads to irritation of the colon wall, increased secretion of mucus, and the release of liquid stools.
False diarrhea is sometimes accompanied by persistent constipation, which is often observed in pregnant women: a prolonged stay of feces leads to irritation of the colon wall, increased secretion of mucus, and the release of liquid stools.
Pathogenesis
About nine liters of fluid enter the intestinal lumen daily, 22% of which is water obtained from food, the rest is formed as a result of the secretion of the digestive organs. About 89% of this liquid is absorbed by the small intestine, about 10% - by the large intestine, only 1.1% (about 100 ml) is excreted in the feces. Diarrhea occurs with increased fluid intake (mostly due to excess intestinal secretion) or as a result of a decrease in absorption capacity. Hypersecretion of the small intestine is associated with infection by pathogenic microorganisms, the use of irritant laxatives. The secretion of the lower intestine is most often increased due to a decrease in the absorption of bile acids. nine0003
Enzymatic deficiency and acceleration of the passage of contents leads to a disorder in the absorption capacity of the small intestine. At the same time, unabsorbed substances accumulate in its lumen, retaining water due to their osmotic action. Reduced absorption in the lower sections is a consequence of increased fluid intake from the ileum, damage to the epithelium, impaired motility of the colon, and a lack of bacteria that ferment carbohydrates. As a result of severe diarrhea, hypovolemia, acidosis, deficiency of nutrients, vitamins, microelements develop. Irritation of the colon leads to a reflex increase in the tone of the pregnant uterus, and the release of active substances associated with inflammation into the blood enhances the effect. nine0003
At the same time, unabsorbed substances accumulate in its lumen, retaining water due to their osmotic action. Reduced absorption in the lower sections is a consequence of increased fluid intake from the ileum, damage to the epithelium, impaired motility of the colon, and a lack of bacteria that ferment carbohydrates. As a result of severe diarrhea, hypovolemia, acidosis, deficiency of nutrients, vitamins, microelements develop. Irritation of the colon leads to a reflex increase in the tone of the pregnant uterus, and the release of active substances associated with inflammation into the blood enhances the effect. nine0003
Classification
According to the form of the flow, acute and chronic diarrhea are distinguished. The acute form is characterized by vivid symptoms observed for no more than 3 weeks. The chronic course is characterized by a longer duration of manifestations and less pronounced symptoms. According to the pathogenetic mechanism that contributed to the development of the disorder, four types of diarrhea are distinguished:
- Secretory.
 This type of diarrhea develops with an increase in the secretion of fluid and electrolytes in the intestine due to damage by pathogenic microorganisms, their toxins, as well as an excess of bile acids. nine0142
This type of diarrhea develops with an increase in the secretion of fluid and electrolytes in the intestine due to damage by pathogenic microorganisms, their toxins, as well as an excess of bile acids. nine0142 - Hyperosmolar. Occurs due to the influx of water during the accumulation in the intestine of osmotically active substances (potassium and sodium ions, glucose) as a result of impaired digestion and absorption (with chronic pancreatitis, dysbiosis, enteritis, food intolerance, amyloidosis, obstruction of the biliary tract), intake of excessively salty or sweet food .
- Hyperexudative. Diarrheal syndrome is caused by sweating of exudate through the damaged mucosa in autoimmune, neoplastic diseases of the intestine, some infections (dysentery, salmonellosis, intestinal tuberculosis, campylobacteriosis). nine0142
- Motor (dyskinetic). The cause of diarrhea is an increase or decrease in the rate of chyme transit due to impaired intestinal motility. Hyperkinetic diarrhea is accompanied by nervous shocks, neuroses, neuropathies, hyperthyroidism, taking laxatives.
 The hypokinetic type is associated with small bowel obstruction.
The hypokinetic type is associated with small bowel obstruction.
Symptoms
Symptoms of diarrhea during pregnancy depend on the causes of diarrhea, its type, localization of the lesion, intensity of manifestation. Enteritis is manifested by abundant voluminous loose stools without impurities, bowel emptying is often "explosive" in nature. Colitis is characterized by sharp tenesmus (frequency up to 30 times a day), increased defecation with scanty mucous discharge, often mixed with pus and blood. A significant increase in stool in acute diarrhea leads to a rapid decline in strength, severe weakness. Chronic diarrhea is characterized by fatigue, weight loss. nine0003
Secretory diarrhea is characterized by abundant light watery or frothy stools without severe abdominal pain, the disorder does not depend on diet, and is not stopped by fasting. Osmolar diarrhea is manifested by an abundant separation of feces containing particles of undigested food: light, pasty in case of pathologies of the hepatobiliary system and gray, with a rancid odor in case of pancreatic insufficiency; diarrhea usually resolves after fasting. The exudative type is characterized by an admixture of blood and pus in the feces. A distinctive feature of hyperkinetic diarrhea is a slight increase in the daily volume of liquefied yellow or greenish stools. With diarrhea caused by decreased motor function, mucus is usually present in the stool. nine0003
The exudative type is characterized by an admixture of blood and pus in the feces. A distinctive feature of hyperkinetic diarrhea is a slight increase in the daily volume of liquefied yellow or greenish stools. With diarrhea caused by decreased motor function, mucus is usually present in the stool. nine0003
Diarrhea may be accompanied by other pathological manifestations. Fever accompanies infectious and autoimmune enterocolitis. Tachycardia, sweating is accompanied by a significant loss of water and electrolytes, hyperthyroidism, irritable bowel syndrome. The latter also proceeds with alternating diarrhea with constipation, epigastric discomfort; there may be intense pain, simulating a picture of an acute abdomen, characteristic of surgical pathologies. Epigastric discomfort is also observed with diarrhea associated with the pathology of the liver, pancreas, dysbiosis. Cholestatic diarrhea is accompanied by jaundice, and caused by autoimmune colitis, amyloidosis - inflammation of the joints. With diarrhea associated with Addison's disease, diabetes mellitus, skin pigmentation disorders are observed. nine0003
With diarrhea associated with Addison's disease, diabetes mellitus, skin pigmentation disorders are observed. nine0003
Complications
The most common and dangerous complication of diarrhea is miscarriage. In 30-44% of cases, the cause of spontaneous abortion is gastrointestinal diseases that occur with diarrhea. Severe diarrhea with a large loss of fluid poses a threat to the life of the patient due to the development of collapse and shock, often leading to death. For the mother and the unborn child, it is also not the intestinal disorder itself that can be dangerous, but its causes. So, the result of an intestinal infection can be purulent-inflammatory gynecological complications (the most formidable is obstetric sepsis) in a woman and intrauterine infection with the development of fetal pathology in the fetus. nine0003
Diagnostics
Diagnostic search is aimed at finding out the causes of diarrhea (alimentary factors, internal diseases, endocrine, neurological or obstetric pathology). Most often, to establish the root cause, it is enough to consult a therapist and an obstetrician-gynecologist: differential diagnosis is carried out on the basis of anamnesis data (information on the frequency and volume of defecation, the nature of the stool, dietary characteristics, the presence of general somatic diseases) and the results of an objective examination (identification and evaluation of concomitant symptoms). To clarify the diagnosis, narrow specialists (gastroenterologist, infectologist, endocrinologist) are involved and instrumental and laboratory research methods are used: nine0003
Most often, to establish the root cause, it is enough to consult a therapist and an obstetrician-gynecologist: differential diagnosis is carried out on the basis of anamnesis data (information on the frequency and volume of defecation, the nature of the stool, dietary characteristics, the presence of general somatic diseases) and the results of an objective examination (identification and evaluation of concomitant symptoms). To clarify the diagnosis, narrow specialists (gastroenterologist, infectologist, endocrinologist) are involved and instrumental and laboratory research methods are used: nine0003
- Fecal tests. Bacterial culture allows you to identify the pathogen in case of infection and choose an antibiotic for its treatment. According to the results of the coprogram, it is possible to confirm or exclude functional pathologies of the stomach, digestive glands, intestines, and also to suspect a violation of the integrity of the mucous membranes (by occult blood). A positive test result for helminth eggs indicates a helminthic invasion.

- Blood tests. Based on the results of the general clinical analysis, it is possible to establish the inflammatory, allergic nature of diarrhea, suggest malabsorption or malignancy. Biochemical research allows to reveal pathologies of the hepatobiliary system, pancreas, diabetes mellitus. nine0142
- Endoscopy. Sigmoidoscopy is performed to detect colitis, tumor changes. With the help of gastric and duodenal sounding, it is possible to detect a decrease in the pH of gastric juice, an increase in the concentration of bile acids, and violations of the exogenous function of the pancreas.
Treatment
Treatment of diarrhea during pregnancy is carried out under the supervision of an obstetrician-gynecologist. In mild cases, symptomatic and etiotropic therapy is prescribed, aimed at eliminating intoxication and correcting the water-salt balance: enterosorbents, oral rehydration solutions. Particular attention is paid to the diet: food should not irritate the mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract, increase peristalsis, or cause fermentation. Fresh pastries, cabbage, legumes, onions, garlic, spices, seasonings, strong broths, fried and stewed foods, carbonated drinks are excluded from the diet. With severe dehydration, intensive therapy is used. Specific treatment is prescribed for chronic, severe acute diarrhea and is selected depending on the underlying disease. nine0003
Fresh pastries, cabbage, legumes, onions, garlic, spices, seasonings, strong broths, fried and stewed foods, carbonated drinks are excluded from the diet. With severe dehydration, intensive therapy is used. Specific treatment is prescribed for chronic, severe acute diarrhea and is selected depending on the underlying disease. nine0003
Prognosis and prevention
The prognosis depends on the cause of the intestinal disorder. With alimentary diarrhea, neurogenic diarrhea, easily occurring infections, recovery occurs quickly, complications do not develop. With advanced, progressive pathologies manifested by chronic diarrhea, severe infections, the prognosis worsens, especially for the fetus. Preventive measures include the identification and treatment of chronic internal diseases before pregnancy, regular visits to the antenatal clinic during the gestational period, hygiene, eating fresh, optimally balanced in vitamins, macro- and micronutrients food, avoiding uncontrolled intake of drugs, herbs, dietary supplements, fight against constipation.
 Also, strictly according to the doctor's prescription, you can take enterosorbents. These drugs, passing through the gastrointestinal tract, can bind toxic substances and promote their removal from the body in a natural way. By themselves, such drugs do not interact with the intestinal mucosa or other parts of the digestive tract. nine0003
Also, strictly according to the doctor's prescription, you can take enterosorbents. These drugs, passing through the gastrointestinal tract, can bind toxic substances and promote their removal from the body in a natural way. By themselves, such drugs do not interact with the intestinal mucosa or other parts of the digestive tract. nine0003 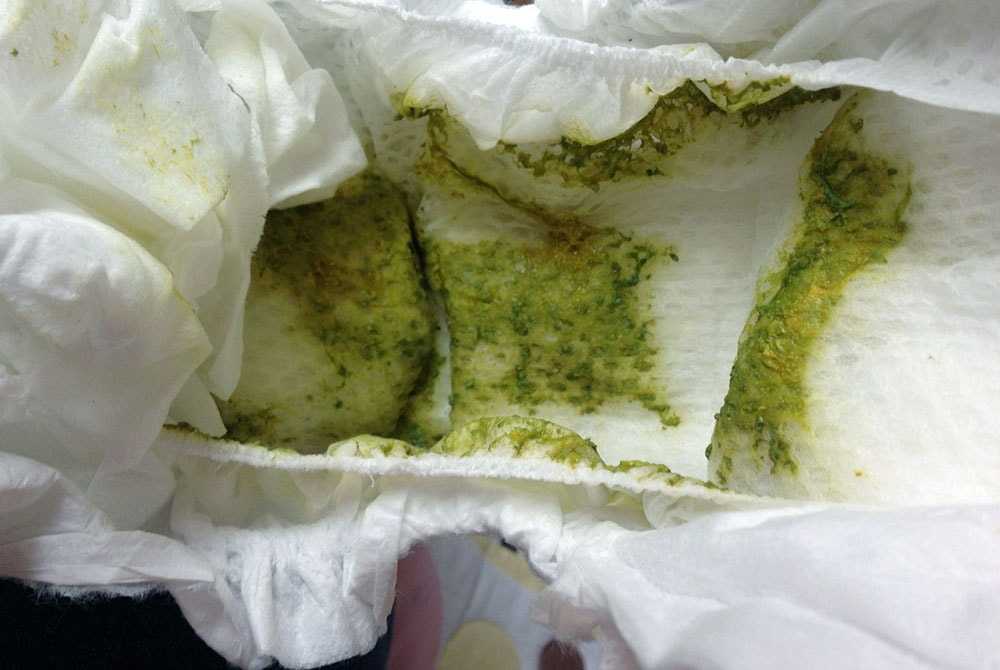 Such remedies can help eliminate the cause of diarrhea by destroying pathogenic microorganisms. The drugs are used strictly according to the doctor's prescription.
Such remedies can help eliminate the cause of diarrhea by destroying pathogenic microorganisms. The drugs are used strictly according to the doctor's prescription.