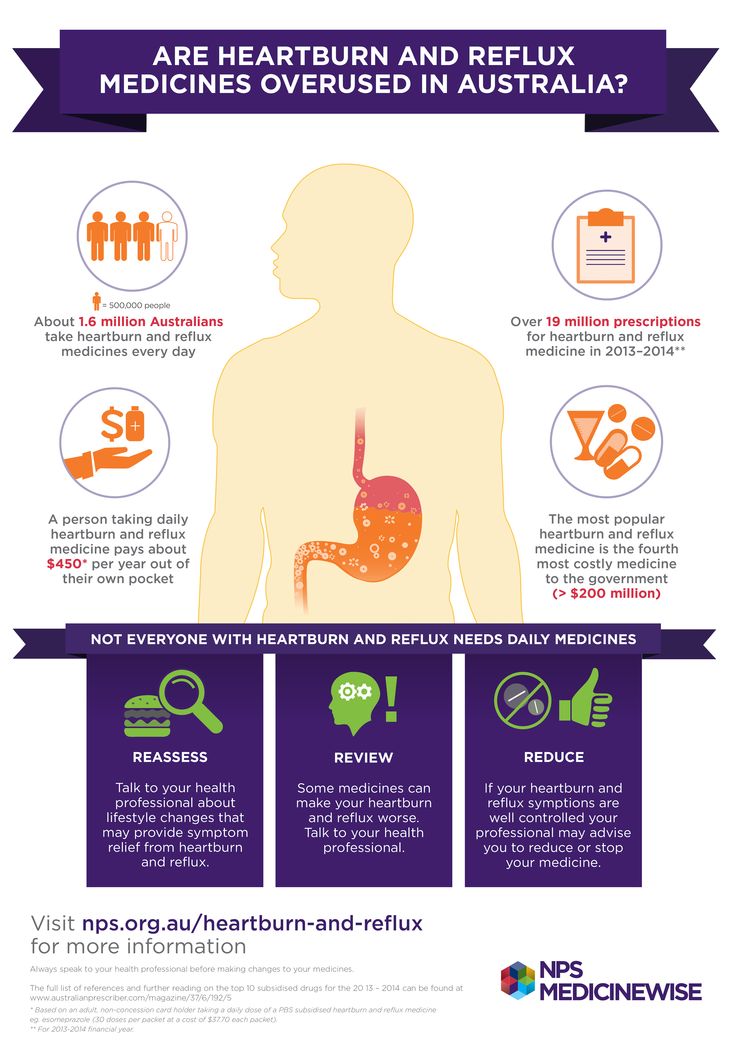
Most tired weeks of pregnancy
Daily Naps and Other Ways to Cope With Pregnancy Fatigue
Written by Stephanie Watson
In this Article
- Why Am I So Tired?
- How to Beat Pregnancy Fatigue
- When to Call Your Doctor
Baby isn't even here yet, and already you're exhausted. It's hard to drag your big weary body out of bed each morning. By dinnertime, all you want to do is plop back down and climb underneath the covers.
Fatigue was one of the first signs of your pregnancy. And it can keep nagging you throughout most of the 9 months until you deliver.
Why Am I So Tired?
During your first trimester, fatigue is at least partly due to changing levels of pregnancy hormones. You'll perk back up in your second trimester, but that renewed energy likely won't last long.
By the last 3 months of your pregnancy, you may be wiped out again. The extra stress on your body can wear you out. Plus, with your belly weighing you down in bed and your baby pressing on your bladder all night, you may struggle to get a full night's sleep.
Sometimes fatigue during pregnancy can be a sign of a medical problem, such as:
- Anemia
- Infection
- Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome)
- Fibromyalgia
- Gestational diabetes
- Underactive thyroid gland (hypothyroidism)
- Depression
If fatigue is just one of several new symptoms you're experiencing, see your doctor. You may feel more energetic once you get treated for any condition that's sapping your energy.
How to Beat Pregnancy Fatigue
During your pregnancy you need to be well rested. In just a few months, you'll be on call 24/7, and a full night's sleep will seem like a luxury.
To get as much sleep as possible right now, follow these restful suggestions:
- Take naps. Most pregnant women can't make it through the night without full bladders or other pregnancy discomforts waking them up. Make up for the sleep you're losing at night by catching a short nap or two during the day.

- Get help. Ask for help at home so you don't get so rundown and you'll have time for a daily nap or two. Get a family member to clean your house, or hire a housekeeper. Let your partner run errands for you.
- Change your sleep posture. Shift from sleeping on your front or back to your left side. You'll feel more comfortable, and you'll take pressure off the blood vessels that nourish your baby. Tuck a pillow in between your legs or underneath you to support your sore back.
- Exercise. Even though you might not feel up to it, exercising can actually help beat fatigue. Getting in a daily walk or swim can also help you sleep more soundly.
- Relax. Practice deep breathing, take a warm bath, or ask your partner to give you a massage to help you wind down before bed.
- Stay hydrated. Drink plenty of fluids during the day. Dehydration can sap energy.
- Eat regular meals and snacks to keep your blood sugar stable. Avoid food or drinks that are high in sugar.

Don't stop your pregnancy sleep routine once your baby is born. Use these same tips to help you through the first few months of motherhood. Continue to get the help -- and the rest -- you need, so you can keep up with your growing baby.
When to Call Your Doctor
Get medical help if:
- Fatigue occurs suddenly.
- Fatigue doesn't ease with rest.
- Fatigue doesn't ease during the second trimester.
The Most Tired You've Ever Felt
Growing a human is exhausting. It’s as if a magical spell was cast the day your pregnancy test came back positive — except Sleeping Beauty’s fairy didn’t gift you with 100 years of rest and true love’s kiss is what got you into this.
If only you could sleep more…
It’s completely normal for a pregnant woman to feel fatigued, especially during the first and third trimesters.
Somewhere between morning sickness and elastic waistbands, Little Bo-Peep has lost your sheep (she probably sold them to Sleeping Beauty) and there are none left for you to count to sleep.
One of the first signs of pregnancy is fatigue. It smacks you by surprise, like the sliding glass door you assumed to be open.
Beginning as early as conception and implantation, pregnancy hormones instantly affect your body, mood, metabolism, brain, physical appearance, and sleep pattern.
In the second trimester, which begins at week 13, many women get a fresh surge of energy. This is a great time to tackle those important before-baby-arrives chores, because as you enter the third trimester, which begins at week 28, that extreme exhaustion returns.
Simply put, you feel tired because you’re growing a baby.
In addition to hormonal changes, physical and emotional changes also lower your energy levels and make you feel fatigued.
Some of these changes include:
- increased levels of estrogen and progesterone (which, by the way, acts as a natural sedative)
- lower blood pressure and blood sugar
- increased blood flow
- disrupted sleep
- digestion issues
- morning sickness
- stress and anxiety
- frequent urination
- heartburn
- back, hip, and pelvic pain
When to contact your doctor or midwife
If insomnia, restless legs syndrome (the uncontrollable urge to move your legs while resting), sleep apnea (a potentially serious disorder in which breathing repeatedly stops and starts), preeclampsia, or any other condition is hindering your sleep, talk to your doctor or midwife during your next appointment.
Other reasons to contact your doctor or midwife include, if you:
- feel concerned that the pregnancy fatigue is a sign of something more, like anemia, gestational diabetes, or depression
- develop any changes in your vision
- experience dizziness
- urinate less frequently
- have shortness of breath, pain in your upper abdomen, or heart palpitations
- experience severe headaches
- notice a swelling of your hands, ankles, and feet
Your healthcare practitioner can help you uncover any problems and offer additional solutions.
Growing a baby obviously takes a toll on your body. Don’t ignore the signals your body is sending you. Reach out to others if you’re struggling to sleep throughout your pregnancy. Ask for help from your partner.
No matter how tired you get, you should avoid taking any over-the-counter medicines as a sleeping aid.
Most pregnant women should spend at least 8 hours in bed, aiming for at least 7 hours of sleep every night. If possible, try going to sleep a little earlier than usual.
If possible, try going to sleep a little earlier than usual.
As your body changes, make sleep a priority and follow these tips to combat pregnancy fatigue:
Keep your bedroom dark, clean, and cold
Create the right atmosphere for optimal rest.
In order for your body to reach deep sleep, cover any windows with blackout curtains. Turn off any digital clocks and unplug nightlights illuminating a glow (cover the display with electrical tape if you don’t want to completely turn the device off).
Set the bedroom temperature a little cooler than the rest of your home, for optimal quality of sleep. Eliminate any needless clutter and wash your bedsheets often. Save your bed for sleep, cuddling, and sex.
Take a nap
Napping can make up for any sleep lost at night, due to frequent trips to the bathroom, body aches, and every other pregnancy irritation. Avoid napping in the late afternoon and early evenings.
If your employer frowns upon nap time, find a good spot in the breakroom and put your feet up while you eat lunch.
Eat healthy meals and stay hydrated
In the beginning, pregnancy can also lower your blood pressure and blood sugar, which can make you feel tired. But a lack of sleep can cause your blood sugar levels to rise, increasing the risk for gestational diabetes.
Keep your blood sugar and energy levels balanced by eating often, such as six small meals a day. Frequent meals that are high in nutrients and protein help to combat fatigue.
To avoid nighttime leg cramps, stay hydrated by drinking enough water and fluids throughout the day.
Keep a pregnancy journal or dream diary
Keep a journal throughout your pregnancy. If you’re feeling anxious or stressed, try writing in it.
Pregnant women experience more vivid dreams and better dream recall, due to hormonal shifts affecting sleep patterns, increased fatigue, and repeatedly waking in the middle of a sleep cycle.
Sleep diaries can also be enlightening, providing concrete data about your bedtime, how long it takes for you to fall asleep, nighttime awakenings, awake time, and sleep quality.
Avoid caffeine after lunchtime
As far as stimulants go, caffeine may keep you awake long into the night or cause you to wake more frequently. It can also keep your baby active, kicking and rolling around inside your belly as you try to sleep.
Experts recommend pregnant women limit their caffeine intake to two home-brewed cups of coffee, or less than 200 milligrams, per day.
Pamper yourself
Ask for help from family and friends. Take a warm bath. Ask your partner for a massage. Take a break.
Wear soft, non-restrictive clothing and sit in a cozy chair with a good book and read for a little bit. Light a lavender candle. Play soothing instrumental music. Have a cup of warm chamomile tea.
You get it.
Exercise
The demands of pregnancy together with the weight gained puts an enormous amount of pressure on your body.
In addition to more restful sleep, The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists states the following benefits of exercise during pregnancy:
- reduced back pain
- eased constipation
- decreased risk of gestational diabetes, preeclampsia, and cesarean delivery
- healthier weight gain during pregnancy
- improved overall general fitness
- strengthened heart and blood vessels
- improved ability to lose the baby weight after your baby is born
It can take a few hours for your body to fully wind down after energetic workouts, so plan for any physical activity to take place earlier in the day. If the exercise is light, like yoga, it’s unlikely to interfere with your sleep.
If the exercise is light, like yoga, it’s unlikely to interfere with your sleep.
Always check with your medical practitioner or midwife before beginning a new exercise program during pregnancy.
Pregnancy can be a tiring experience — both emotionally and physically. It’s important to remember: You are not alone.
Nearly all women experience more fatigue than usual at some point during their pregnancy. Take it as a message from your body. It’s telling you to rest, and you should definitely listen.
Critical stages of pregnancy - why are they dangerous?
Services
Virtual tour. Clinic "ARNIKA"
The wonderful period of waiting for a baby for almost every woman is far from serene: how many anxieties, worries and doubts arise in expectant mothers at this time - they simply cannot be counted. In most cases, all fears are in vain - the baby develops and grows safely. However, it must be remembered that there are also so-called critical periods of pregnancy, when inattention to oneself and one's body can lead to a disastrous result - its spontaneous termination. nine0007
nine0007
First trimester
The beginning of a new life in a woman's body, or 2-3 weeks of pregnancy, is considered the first critical period. This is due to the fact that the egg can be fertilized, but due to changes as a result of inflammation, hormonal imbalances, the presence of nodes, scars, fibroids or synechia on the inner mucous membrane of the uterus, implantation does not occur, the embryo dies and is removed from the mother's body during menses. However, even if implantation has occurred, the embryo may stop developing and early miscarriage , and the main reason for this course of events is chromosomal abnormalities.
The second critical period of the first trimester begins at 8 and ends at 12 weeks of gestation. At this time, the main cause of interruption is considered to be hormonal deficiency, which disrupts the process of placental formation. This condition may be associated with reduced work of the corpus luteum of the ovaries, excessive production of androgens by the adrenal glands - male sex hormones, as well as malfunctions of the pituitary gland or thyroid gland. nine0015 The threat of abortion can be eliminated with the help of properly selected and timely prescribed hormonal treatment, which will allow the baby to safely reach the due date.
nine0015 The threat of abortion can be eliminated with the help of properly selected and timely prescribed hormonal treatment, which will allow the baby to safely reach the due date.
In addition, throughout the first trimester of pregnancy, the fetus may stop developing due to the following adverse environmental factors:
- harmful working conditions
- bad habits
- physical effects - radiation, vibration, intense sports training, etc.
- acute infectious diseases (influenza, cytomegalovirus, herpes, rubella and others)
- severe stressful situations
And even if the fetus develops further, the negative impact of most of these factors may appear after a few months of pregnancy or even after the baby is born: these may be anatomical disorders or severe malformations. Therefore, the entire first trimester of the development of a new life can be considered "critical". nine0007
Second trimester
The third critical period of pregnancy occurs at 18-24 weeks of gestation and is largely associated with the active growth of the uterus. At this time, spontaneous interruption most often occurs due to isthmic-cervical insufficiency (ICI), as a result of which the fetal egg descends under the influence of gravity, loses its integrity and triggers the mechanism of labor activity. However, shortening and expansion of the cervical canal, detected in time, allows suturing the cervix or installing an obstetric pessary and safely prolonging the pregnancy. Here we should also remember about infectious diseases, including intrauterine infection, which can disrupt the functions of the placenta, lead to the outflow of water from the fetal bladder and late miscarriage. nine0007
At this time, spontaneous interruption most often occurs due to isthmic-cervical insufficiency (ICI), as a result of which the fetal egg descends under the influence of gravity, loses its integrity and triggers the mechanism of labor activity. However, shortening and expansion of the cervical canal, detected in time, allows suturing the cervix or installing an obstetric pessary and safely prolonging the pregnancy. Here we should also remember about infectious diseases, including intrauterine infection, which can disrupt the functions of the placenta, lead to the outflow of water from the fetal bladder and late miscarriage. nine0007
Another common reason for interrupting the process of bearing a fetus at this time is placenta previa or its low location: for various reasons, it can exfoliate, cause severe bleeding and death of the fetus. In addition, at this time, pregnancy may stop developing due to violations in the development of the brain and the most important functional systems of the baby, caused by the harmful effects of various negative factors on them in the first trimester.
Third trimester
In this trimester - at 28-32 weeks - the fourth critical period takes place. nine0015 The threat of premature birth may occur due to insufficiency of the placenta, its premature detachment, severe forms of late toxicosis of pregnant women, ICI and various hormonal disorders. In addition, due to the overdistension of the uterus, most multiple pregnancies end at this time. Children born during this period are already viable, but they need long-term qualified medical care.
In addition to all the periods listed above, the critical periods for women who have had reproductive losses in the past are the days of planned menstruation, miscarriages or "fading" pregnancies. Doctors believe that during these periods the body can “remember” the need for hormonal changes, so they carefully monitor the condition of the expectant mother and baby and prescribe treatment in a timely manner if any threat arises. nine0007
In order to safely overcome the dangerous periods of pregnancy , it is necessary to avoid any physical exertion, stress, and, if necessary, visit a doctor when these dates are approaching. In addition, if you experience pain, bleeding or other warning signs, you should also seek medical attention as soon as possible. Only an attentive attitude to oneself will help to safely endure a healthy baby and give birth to him at the time set by nature.
In addition, if you experience pain, bleeding or other warning signs, you should also seek medical attention as soon as possible. Only an attentive attitude to oneself will help to safely endure a healthy baby and give birth to him at the time set by nature.
Take care of yourself and your baby!
40th week of pregnancy - what happens at the fortieth week of pregnancy: nausea, discharge, signs of labor
WHAT HAPPENS
There is very little space in the uterus now, so do not be surprised if the number of movements is reduced. Be sure to listen to every movement of the baby: both excessive activity and complete cessation are not very good signs. Normally, at 40 weeks of pregnancy, in 12 hours you should feel about 10 movements. nine0007
Like the mother, the baby is preparing for the birth. In order for the process of childbirth to go smoothly, the hormones adrenaline and norepinephrine are produced in the tiny body, which should reduce pain during the passage of the fetus through the birth canal.
By the 39th - 40th week of pregnancy, the baby's blood circulation is established, the digestive system is actively functioning, processing the amniotic fluid and dead skin cells. The meconium formed from them will leave the intestines of the child only after birth. The bones of the skull are still flexible, so that the fetus can pass through the birth canal unhindered. nine0007
The 40th week of pregnancy should be the final one, but in practice, only a few women give birth at the expected time. So be patient and wait, continuing to lead a normal life. In any case, very soon you will hug your baby.
YOUR FEELING
If you have not yet had signs of childbirth, they may appear at the 40th week of pregnancy.
- Lowering of the abdomen. The baby in the uterus moves down and presses the head against the pelvic floor. Due to this, heartburn disappears in the expectant mother and it becomes much easier for her to breathe. But due to the strong pressure on the bladder, pregnant women at this time are forced to go to the toilet more often; nine0028
- Disorders of the food system.
 Approximately 24 to 48 hours before the onset of labor, stool liquefaction may occur;
Approximately 24 to 48 hours before the onset of labor, stool liquefaction may occur; - Loss of appetite;
- Weight loss. Before childbirth, body weight may decrease by 1 - 2 kg;
- Mucus plug outlet. During 40 weeks of pregnancy, the cork closed the entrance to the cervix, protecting the baby from infections. Her separation (you will learn about this from lumps of mucus on panties) frees the birth canal for the child; nine0028
- Descent of amniotic fluid. Amniotic fluid is poured out immediately before childbirth. Most often it is transparent, but if meconium particles have got into it, the color may be yellowish or greenish;
- Painful and false contractions at 40 weeks. Primiparous women can confuse training contractions with real ones, especially since by the time of 39-40 weeks of pregnancy, false uterine contractions are also accompanied by pain and are repeated more often than in previous periods. To understand exactly what kind of contractions you have, change the position of the body during muscle contractions.
 Lie down or, conversely, stand up, walk around the room, then sit on a chair. If the contractions have stopped, then this is not childbirth. nine0028
Lie down or, conversely, stand up, walk around the room, then sit on a chair. If the contractions have stopped, then this is not childbirth. nine0028
RISK FACTORS
The main danger of 40 weeks of pregnancy is rapid delivery. A baby can be born very quickly, especially in multiparous women. Therefore, it is better to go to the hospital in advance, about a week before the expected date of birth. And if you live near a hospital, avoid long trips and tiring shopping trips.
At the 40th week of pregnancy, it is necessary to monitor the nature of the discharge. If they have changed their smell, color and texture (for example, they have become purulent or curdled), this indicates an infectious disease that requires immediate treatment. The presence of pathogenic microbes in the vagina creates a risk of infection of the child. nine0007
As at any time, anemia is dangerous at 39-40 weeks of gestation, due to which the level of oxygen in the tissues decreases. Low hemoglobin provokes fetal hypoxia, and the expectant mother faces an increased risk of developing late toxicosis and complications in childbirth.
Low hemoglobin provokes fetal hypoxia, and the expectant mother faces an increased risk of developing late toxicosis and complications in childbirth.
Possible signs of anemia during pregnancy:
- Dry skin;
- Brittle nails and hair;
- Feeling weak and easily fatigued; nine0028
- Paleness of skin and mucous membranes;
- Insomnia;
- Headaches;
- Feeling of impending fainting;
- Arrhythmia and bradycardia;
- Constipation;
- The presence of taste perversions.
Anemia is treated with iron supplements and a special diet.
MEDICAL SUPERVISION
At the 40th week of pregnancy, you will have another trip to the doctor, where the usual procedures will be carried out: measuring blood pressure, weighing, determining the height of the fundus of the uterus and, of course, listening to the baby's heartbeat. nine0007
And in order to monitor the work of the kidneys, you will need to pass urine for analysis. If the date of delivery, which was set by the doctor, has passed, you may be prescribed a Doppler ultrasound. This study makes it possible to assess the blood flow of the fetus, blood circulation in the placenta and uterine vessels, and also to determine whether the baby receives enough oxygen and necessary substances. Another study, sometimes prescribed at 40 weeks of gestation, is cardiotocography, thanks to which the specialist will be able to exclude intrauterine hypoxia. nine0007
If the date of delivery, which was set by the doctor, has passed, you may be prescribed a Doppler ultrasound. This study makes it possible to assess the blood flow of the fetus, blood circulation in the placenta and uterine vessels, and also to determine whether the baby receives enough oxygen and necessary substances. Another study, sometimes prescribed at 40 weeks of gestation, is cardiotocography, thanks to which the specialist will be able to exclude intrauterine hypoxia. nine0007
RECOMMENDATIONS
In the time remaining before the birth, try to relax properly, because after the birth of the child this is unlikely to work. It is very important to remain calm now, because your emotional state greatly affects the baby. Tune in to the upcoming birth and think only about the good.
At the 39th - 40th week of pregnancy, you should not experiment with nutrition. Eat foods high in protein and carbohydrates. They will help to accumulate strength and stock up on energy that you will need during childbirth. Don't forget about vitamins. Now the body needs vitamin K (it is found in spinach, in all types of cabbage, in asparagus, herbs, plums and prunes). This element improves blood clotting, which is very important for childbirth. You also need vitamin A, which is found in yellow, red and orange vegetables and fruits, beef liver, egg yolks and full-fat dairy products. Its lack can lead to a lack of baby weight. And at 39– At 40 weeks pregnant, you need B vitamins: they ensure not only the proper development of the fetus, but also the well-being of the mother. Their most valuable source is dry brewer's yeast, but they can be used only after consulting a doctor. Also, B vitamins are present in oatmeal, millet, meat, fish, eggs, legumes and dairy products.
Don't forget about vitamins. Now the body needs vitamin K (it is found in spinach, in all types of cabbage, in asparagus, herbs, plums and prunes). This element improves blood clotting, which is very important for childbirth. You also need vitamin A, which is found in yellow, red and orange vegetables and fruits, beef liver, egg yolks and full-fat dairy products. Its lack can lead to a lack of baby weight. And at 39– At 40 weeks pregnant, you need B vitamins: they ensure not only the proper development of the fetus, but also the well-being of the mother. Their most valuable source is dry brewer's yeast, but they can be used only after consulting a doctor. Also, B vitamins are present in oatmeal, millet, meat, fish, eggs, legumes and dairy products.
If at 40 weeks of pregnancy you feel the onset of contractions, do not rush to go to the hospital. Before childbirth, you should replenish energy reserves, and for this you can drink sweet tea, jelly or compote, eat a little low-fat cottage cheese or yogurt. As soon as the duration of the contractions reaches 1 minute, and the interval between them is 5-7 minutes, go to the hospital. nine0007
As soon as the duration of the contractions reaches 1 minute, and the interval between them is 5-7 minutes, go to the hospital. nine0007
Many future parents are interested in the question of whether it is harmful to have sex at the 39th - 40th week of pregnancy. In the absence of contraindications, this is not prohibited. And in some cases, sexual intercourse is even recommended as a means of preparing for childbirth. The semen contains the hormone prostaglandin, which softens the cervix, and the orgasm experienced by a woman stimulates the onset of contractions.
Pregnancy and childbirth nine0002 Ninth month of pregnancy: changes in the female body and fetal development by week Newborn careDowry for a newborn
What do you need to have at home for discharge, what stroller and crib to choose, and what equipment to buy?
Pregnancy and childbirth nine0002 What to take with you to the maternity hospital Pregnancy and childbirthPsychology of pregnancy and motherhood
Positive attitude and overcoming fears during pregnancy, psychological hygiene and well-being of a woman.