Light bleeding at 31 weeks pregnant
Vaginal bleeding in late pregnancy: MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia
One out of 10 women will have vaginal bleeding during their 3rd trimester. At times, it may be a sign of a more serious problem. In the last few months of pregnancy, you should always report bleeding to your health care provider right away.
You should understand the difference between spotting and bleeding:
- Spotting is when you notice a few drops of blood every now and then on your underwear. It is not enough to cover a panty liner.
- Bleeding is a heavier flow of blood. With bleeding, you will need a liner or pad to keep the blood from soaking your clothes.
When labor begins, the cervix starts to open up more, or dilate. You may notice a small amount of blood mixed in with normal vaginal discharge, or mucus.
Mid- or late-term bleeding may also be caused by:
- Having sex (most often just spotting)
- An internal exam by your provider (most often just spotting)
- Diseases or infections of the vagina or cervix
- Uterine fibroids or cervical growths or polyps
More serious causes of late-term bleeding may include:
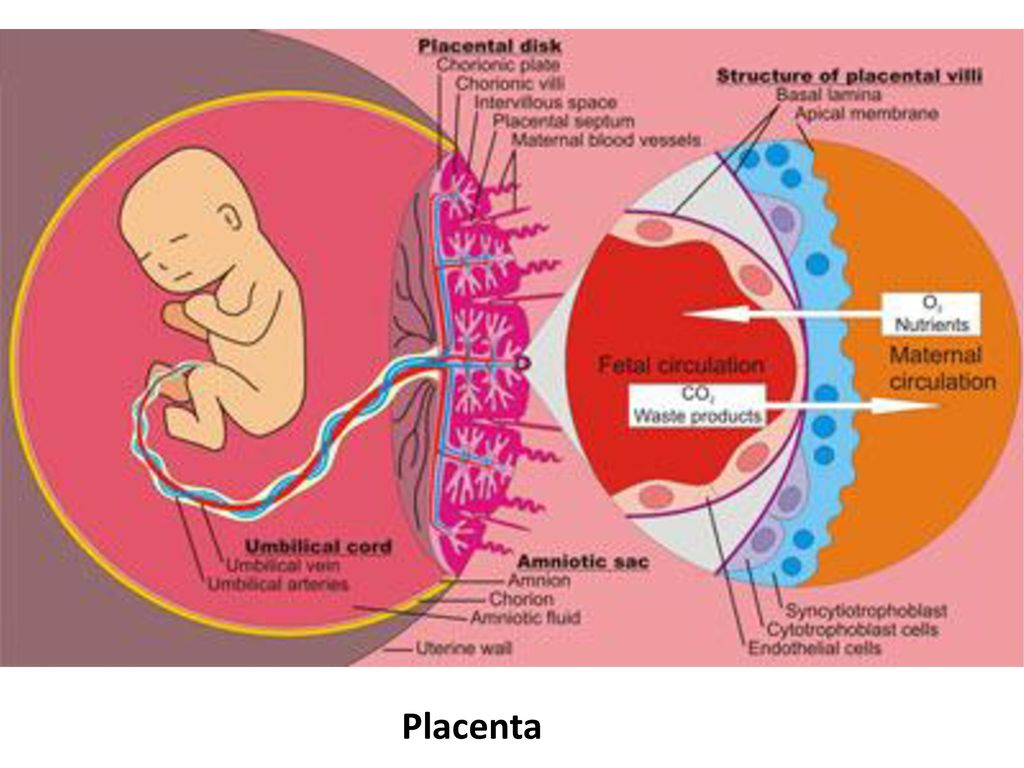
- Placenta previa is a problem of pregnancy in which the placenta grows in the lowest part of the womb (uterus) and covers all or part of the opening to the cervix.
- Placenta abruptio (abruption) occurs when the placenta separates from the inner wall of the uterus before the baby is born.
To find the cause of your vaginal bleeding, your provider may need to know:
- If you have cramping, pain, or contractions
- If you have had any other bleeding during this pregnancy
- When the bleeding began and whether it comes and goes or is constant
- How much bleeding is present, and whether it is spotting or a heavier flow
- The color of the blood (dark or bright red)
- If there is an odor to the blood
- If you have fainted, felt dizzy or nauseated, vomited, or had diarrhea or a fever
- If you have had recent injuries or falls
- When you last had sex and if you bled afterward
A small amount of spotting without any other symptoms that occurs after having sex or an exam by your provider can be watched at home. To do this:
- Put on a clean pad and recheck it every 30 to 60 minutes for a few hours.
- If spotting or bleeding continues, call your provider.
- If the bleeding is heavy, your belly feels stiff and painful, or you are having strong and frequent contractions, you may need to call 911 or your local emergency number.
For any other bleeding, call your provider right away.
- You will be told whether to go to the emergency room or to the labor and delivery area in your hospital.
- Your provider will also tell you whether you can drive yourself or you should call an ambulance.
Baeseman ZJ. Vaginal bleeding in pregnancy. In: Kellerman RD, Rakel DP, eds. Conn's Current Therapy 2021. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier 2021:1227-1229.
Francois KE, Foley MR. Antepartum and postpartum hemorrhage. In: Landon MB, Galan HL, Jauniaux ERM, et al, eds. Gabbe's Obstetrics: Normal and Problem Pregnancies. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 18.
Hull AD, Resnik R, Silver RM. Placenta previa and accreta, vasa previa, subchorionic hemorrhage, and abruptio placentae. In: Resnik R, Lockwood CJ, Moore TR, Greene MF, Copel JA, Silver RM, eds. Creasy and Resnik's Maternal-Fetal Medicine: Principles and Practice. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2019:chap 46.
In: Resnik R, Lockwood CJ, Moore TR, Greene MF, Copel JA, Silver RM, eds. Creasy and Resnik's Maternal-Fetal Medicine: Principles and Practice. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2019:chap 46.
Salhi BA, Nagrani S. Acute complications of pregnancy. In: Walls RM, Hockberger RS, Gausche-Hill M, eds. Rosen's Emergency Medicine: Concepts and Clinical Practice. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2018:chap 178.
Updated by: John D. Jacobson, MD, Professor of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Loma Linda University School of Medicine, Loma Linda Center for Fertility, Loma Linda, CA. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
Browse the Encyclopedia
Vaginal bleeding in late pregnancy Information | Mount Sinai
What Causes Bleeding Later in Pregnancy?
When labor begins, the cervix starts to open up more, or dilate.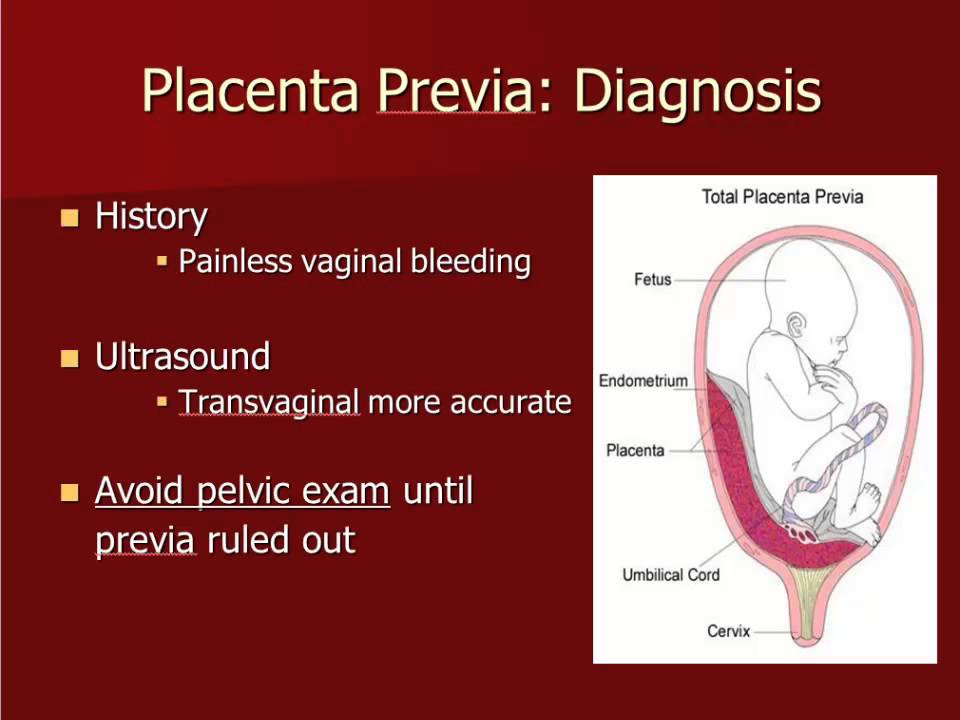 You may notice a small amount of blood mixed in with normal vaginal discharge, or mucus.
You may notice a small amount of blood mixed in with normal vaginal discharge, or mucus.
Mid- or late-term bleeding may also be caused by:
- Having sex (most often just spotting)
- An internal exam by your provider (most often just spotting)
- Diseases or infections of the vagina or cervix
- Uterine fibroids or cervical growths or polyps
More serious causes of late-term bleeding may include:
- Placenta previa is a problem of pregnancy in which the placenta grows in the lowest part of the womb (uterus) and covers all or part of the opening to the cervix.
- Placenta abruptio (abruption) occurs when the placenta separates from the inner wall of the uterus before the baby is born.
What to Tell Your Health Care Provider
To find the cause of your vaginal bleeding, your provider may need to know:
- If you have cramping, pain, or contractions
- If you have had any other bleeding during this pregnancy
- When the bleeding began and whether it comes and goes or is constant
- How much bleeding is present, and whether it is spotting or a heavier flow
- The color of the blood (dark or bright red)
- If there is an odor to the blood
- If you have fainted, felt dizzy or nauseated, vomited, or had diarrhea or a fever
- If you have had recent injuries or falls
- When you last had sex and if you bled afterward
- If you're feeling the baby move
- If you've had other complications during the pregnancy
What Should Happen Next?
A small amount of spotting without any other symptoms that occurs after having sex or an exam by your provider can be watched at home. To do this:
To do this:
- Put on a clean pad and recheck it every 30 to 60 minutes for a few hours.
- If spotting or bleeding continues, call your provider.
- If the bleeding is heavy, your belly feels stiff and painful, or you are having strong and frequent contractions, you may need to call 911 or your local emergency number.
For any other bleeding, call your provider right away.
- You will be told whether to go to the emergency room or to the labor and delivery area in your hospital.
- Your provider will also tell you whether you can drive yourself or you should call an ambulance.
Baeseman ZJ. Vaginal bleeding in pregnancy. In: Kellerman RD, Rakel DP, Heidelbaugh JJ, Lee EM, eds. Conn's Current Therapy 2023. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier 2023:1273-1276.
Francois KE, Foley MR. Antepartum and postpartum hemorrhage. In: Landon MB, Galan HL, Jauniaux ERM, et al, eds. Gabbe's Obstetrics: Normal and Problem Pregnancies. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 18.
In: Landon MB, Galan HL, Jauniaux ERM, et al, eds. Gabbe's Obstetrics: Normal and Problem Pregnancies. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 18.
Henn MC, Lall MD. Complications of pregnancy. In: Walls RM, ed. Rosen's Emergency Medicine: Concepts and Clinical Practice. 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 173.
Hull AD, Resnik R, Silver RM. Placenta previa and accreta, vasa previa, subchorionic hemorrhage, and abruptio placentae. In: Lockwood CJ, Copel JA, Dugoff L, et al, eds. Creasy and Resnik's Maternal-Fetal Medicine: Principles and Practice. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 43.
Last reviewed on: 11/21/2022
Reviewed by: LaQuita Martinez, MD, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Emory Johns Creek Hospital, Alpharetta, GA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
Bloody discharge during pregnancy ᐈ Blood during early pregnancy
Seeing bloody discharge, a pregnant woman is always frightened. They are considered a symptom of miscarriage and other equally serious pathologies. At the same time, in some cases, the appearance of a small amount of blood is considered the norm and does not pose a threat to the life and health of the fetus or the expectant mother.
They are considered a symptom of miscarriage and other equally serious pathologies. At the same time, in some cases, the appearance of a small amount of blood is considered the norm and does not pose a threat to the life and health of the fetus or the expectant mother.
In early pregnancy, bloody discharge occurs in 25% of women. In most cases, they are associated with the implantation of the fetal egg to the wall of the uterus. Also, scanty spotting may appear on the dates of the expected menstruation. If they end quickly, are not accompanied by pain, and the woman has not had miscarriages or pregnancy complications before, most likely she has nothing to worry about. However, it is necessary to consult an obstetrician-gynecologist and undergo an examination.
Why bloody discharge can appear and when it is dangerous, said Elena Petrovna Domnich, obstetrician-gynecologist of the highest category, gynecologist-endocrinologist, ultrasound specialist of the ADONIS medical center.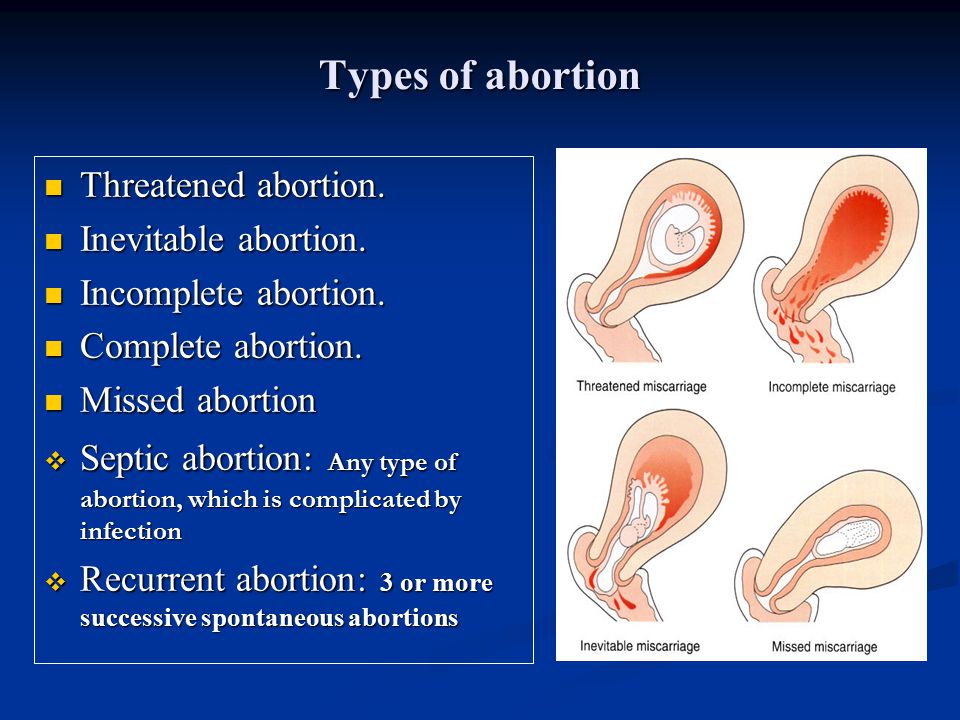
Elena Nikolaevna, tell me, can a woman have periods during pregnancy?
- Sometimes during pregnancy, a woman may experience spotting, but this should not be interpreted as menstruation. Menstruation occurs at the end of the menstrual cycle, during which the endometrium changes, first proliferative, then secretory. During the cycle, the endometrium prepares for pregnancy, and if it does not occur, then menstruation begins.
In the event of pregnancy, menstruation is not possible, although bleeding may occur at the expected time. Because of this, some women do not immediately know that they are pregnant. However, when the obstetrician-gynecologist at the reception asks them about the nature of the discharge, it always turns out that they are different from menstrual. As a rule, they are more scarce, pass faster and are not accompanied by other symptoms. Sometimes a woman says that her period was very recent, but at the time of examination and examination, we find that she is already 8 or 12 weeks pregnant.
How often does this happen? Is spotting during pregnancy an exception or a fairly common occurrence?
- Bloody discharge is not common in pregnant women, but still it cannot be said that these are exceptional cases.
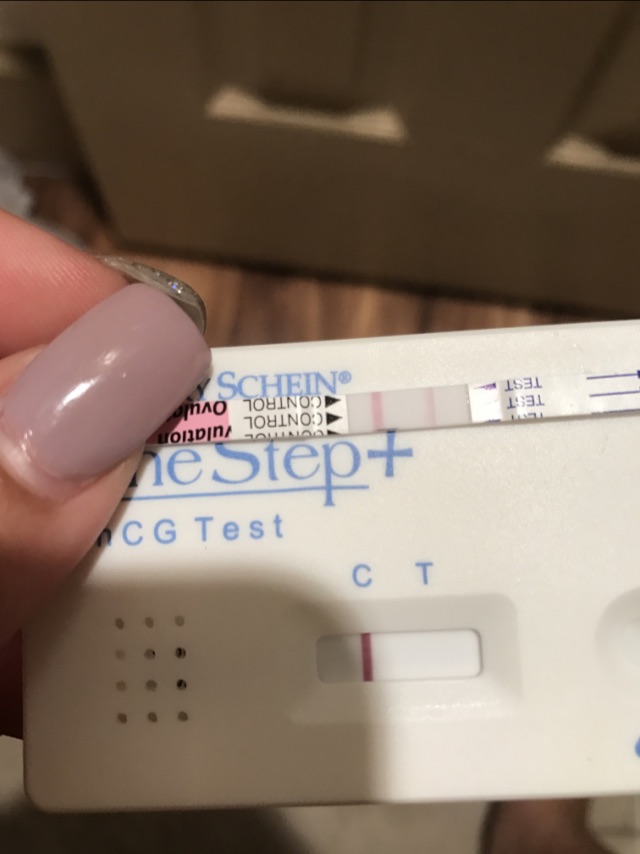
Tell me, if a woman is planning to conceive a child, and during the expected period she has atypical discharge, should she take a pregnancy test?
– Yes, but it is better to visit an obstetrician-gynecologist. There are cases when a woman is pregnant, but the test strip shows a negative result. To accurately determine whether there is a pregnancy, allows a blood test for the level of hCG.
So bleeding during pregnancy is not menstruation, but bleeding? Why can it appear and why is it dangerous?
- Yes, that's right. This is bleeding, not menstruation. It can be a symptom of a miscarriage, ectopic pregnancy, or other pathology. For diagnosis, you must consult a doctor.
For diagnosis, you must consult a doctor.
Tell me more, if a woman has a discharge and thinks she is menstruating, but a previous pregnancy test came back positive, could it be wrong?
- A pregnancy test is sometimes positive even if it is not. This happens if a woman has formed luteal cysts or developed a thyroid disease.
Bloody discharge during pregnancy requires contacting the antenatal clinic or the medical center where the woman was registered for pregnancy management. Sometimes they may not be dangerous, but without diagnosis, it cannot be ruled out that this is a symptom of a serious disorder.
Bleeding may occur with:
- threatened miscarriage;
- ectopic pregnancy;
- infectious diseases of the reproductive system;
- cysts;
- myomas;
- cervical erosion;
- placental abruption;
- threatened preterm birth.
You can watch the video version of Elena Petrovna Domnich's interview here. More helpful videos on our YouTube channel.
More helpful videos on our YouTube channel.
What you need to know about bleeding in the 1st trimester of pregnancy
Bleeding or spotting occurs in 20-30% of women in the first trimester of pregnancy. Although any bleeding before 20 weeks of gestation is by definition a "threat of miscarriage", the type of bleeding present is of great importance. Some causes of first trimester bleeding are serious and others are not. Since it is difficult to tell the difference between "normal" and serious bleeding during pregnancy, consultation with a doctor is essential in every case.
Possible causes of bleeding in the first trimester.
Implantation bleeding is a non-hazardous bleeding that occurs when an embryo is implanted into the lining of the uterus (endometrium). This happens during the expected day of menstruation, i.e. even before a woman realizes that she is pregnant. In fact, this type of bleeding is often mistaken for a scanty period. It is quite difficult to distinguish between implantation bleeding and menstruation, since they have similar symptoms: mild pulling pains in the lower abdomen and lower back, headache, mild nausea, breast engorgement. But the discharge from implantation bleeding is scant in quantity, usually lighter than during menstruation - from light pink to dull brown, and, as a rule, short - from several hours to several days.
It is quite difficult to distinguish between implantation bleeding and menstruation, since they have similar symptoms: mild pulling pains in the lower abdomen and lower back, headache, mild nausea, breast engorgement. But the discharge from implantation bleeding is scant in quantity, usually lighter than during menstruation - from light pink to dull brown, and, as a rule, short - from several hours to several days.
Bleeding due to changes in the cervix. In early pregnancy, the cervix becomes loose and its blood supply is greater than before pregnancy. Anything that can irritate the cervix, any physical impact (vaginal examination, swabs, exercise or sexual intercourse) can lead to bleeding from the cervix, which can be considered an injury. This type of bleeding does not pose a threat to pregnancy and, as a rule, they stop by the end of the first trimester, when the woman's body begins to get used to all the changes that occur during pregnancy. In very rare cases, bleeding from the cervix after physical impact may be due to cervical cancer.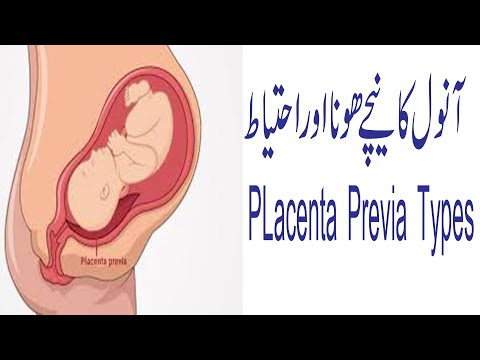
Bleeding due to cervical polyp. A cervical canal polyp is a benign growth of tissue that occurs in approximately 2 to 5% of women. Bleeding can be triggered by sexual intercourse or vaginal examination. In addition, polyps can become inflamed and lead to bright spotting. They are often not dangerous for pregnancy, and are easily diagnosed during a routine examination of the cervix in the mirrors.
Bleeding due to infection. Any infection in the vagina, such as bacterial vaginosis or a sexually transmitted infection such as chlamydia, gonorrhea, or herpes, can cause first trimester bleeding. In addition to pink to red blood spots, there may be other symptoms such as: itching; burning sensation when urinating; slight pulling pains in the lower abdomen; soreness in or around the vagina. While this bleeding has nothing to do with pregnancy, the infection must be treated as soon as possible to stop the bleeding.
Bleeding from the urinary tract or rectum.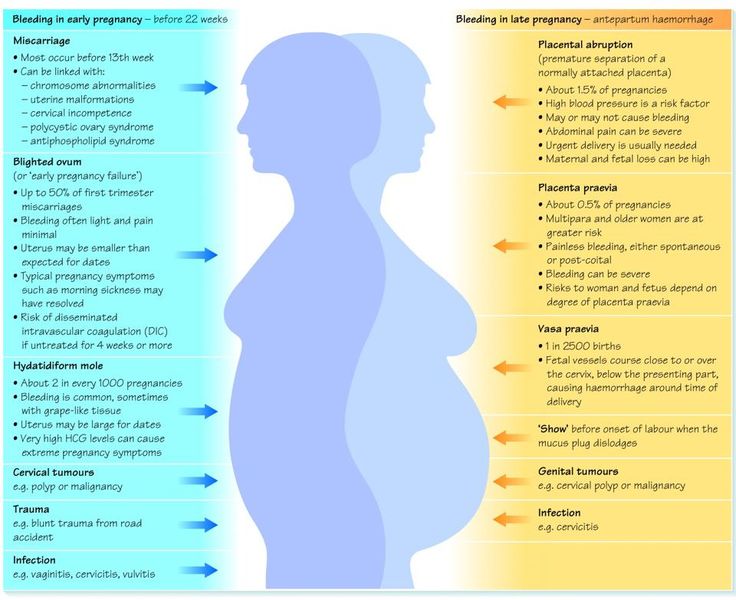 These bleedings are often mistaken for vaginal bleeding, although they are not related to pregnancy. They are found on toilet paper after visiting the toilet. Bright red blood from the rectum or urethra may be caused by a urinary infection, a bladder or rectal polyp, hemorrhoids, or a fissure in the rectum. Although such bleeding is not a cause for concern regarding the safety of pregnancy, it is necessary to consult a doctor for examination and choice of treatment.
These bleedings are often mistaken for vaginal bleeding, although they are not related to pregnancy. They are found on toilet paper after visiting the toilet. Bright red blood from the rectum or urethra may be caused by a urinary infection, a bladder or rectal polyp, hemorrhoids, or a fissure in the rectum. Although such bleeding is not a cause for concern regarding the safety of pregnancy, it is necessary to consult a doctor for examination and choice of treatment.
Bleeding associated with chemical pregnancy. A chemical pregnancy is a type of miscarriage where bleeding and lower abdominal pain occur immediately after a very early positive pregnancy test. A miscarriage occurs because the fertilized egg has not been fully implanted in the uterus. If the fetal egg is completely out of the uterus, then only dynamic control is carried out to reduce the level of beta-hCG. In case of incomplete miscarriage, medical or surgical removal of the remnants of the fetal egg is carried out.
Subchorial hemorrhage or subchorial hematoma occurs when the chorion (placenta) peels off slightly from the wall of the uterus, and a cavity filled with blood forms in the gap between them.
These hematomas vary in size. The most common are small hematomas, which dissolve on their own and have little effect on the course of pregnancy. Large - can cause severe bleeding, lead to a significant detachment of the chorion, and in the future - to a miscarriage. These hematomas are often asymptomatic and are detected only by ultrasound.
Bleeding associated with spontaneous miscarriage is one of the most serious bleeding problems in the first trimester and occurs in 15-20% of women. In addition to severe bleeding, the symptoms of a miscarriage are severe cramps in the lower abdomen and lower back, radiating to the vagina. While miscarriage is most common during the first 12 weeks of pregnancy, however, bleeding doesn't always mean it will happen. If the ultrasound determines the fetal heartbeat and the cervix is \u200b\u200bclosed, then at 90% of cases manage to keep the pregnancy.
If the ultrasound determines the fetal heartbeat and the cervix is \u200b\u200bclosed, then at 90% of cases manage to keep the pregnancy.
Ectopic pregnancy - when the embryo is implanted outside the uterus (in the fallopian tube, ovaries, abdominal cavity). This type of pregnancy cannot develop normally and can lead to life-threatening bleeding for the mother. Suspicion of an ectopic pregnancy causes a beta-hCG level above 1500-2000 mIU per ml, but according to ultrasound, a fetal egg in the uterus is not detected. Symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy include bleeding, cramping, and sharp pains in the abdomen. In these cases, careful monitoring is necessary, and if the diagnosis is confirmed, surgical treatment is necessary.
Bleeding due to gestational trophoblastic disease (also called hydatidiform mole). This is a very rare condition when an anomaly occurs during fertilization in which a fertilized egg forms in the uterus without an embryo, and abnormal tissue grows inside the uterus.