Jaundice at 4 weeks
Jaundice in Newborns: Parent FAQs
Jaundice is the yellow color seen in the skin of many newborns. It happens when a chemical called
bilirubin builds up in the baby's blood. Read on for answers to some common questions parents have about this condition and how its treated.
Why is jaundice common in newborns?
Everyone's blood contains bilirubin, which comes from red blood cells and is removed by the liver. Before birth, the mother's liver does this for the baby. Most babies develop jaundice in the first few days after birth because it takes a few days for the baby's liver to get better at removing bilirubin.
How can I tell if my baby has jaundice?
The skin of a baby with jaundice usually appears yellow. The best way to see jaundice is in white light, such as daylight or under fluorescent lights. Jaundice usually appears first in the face and then moves to the chest, abdomen, arms and legs as the bilirubin level increases. The whites of the eyes may also be yellow. Jaundice may be harder to see in babies with darker skin color.
Can jaundice hurt my newborn?
Most babies have mild jaundice that is harmless. But in rare cases, the bilirubin level can get very high and might cause brain damage. This is why testing bilirubin levels as recommended is important.
Does breastfeeding affect jaundice?
Breast milk (human milk) is the ideal food for your baby. Jaundice is more common in babies who are breastfed than babies who are formula-fed. This happens more often in newborns who are not getting enough breast milk because their mothers are not producing enough milk (especially if the milk comes in late) or if breastfeeding is not going well, such as babies not latching on properly.
For the first 24 hours after birth, normal breastfed newborns receive only about 1 teaspoon of milk with each feeding. The
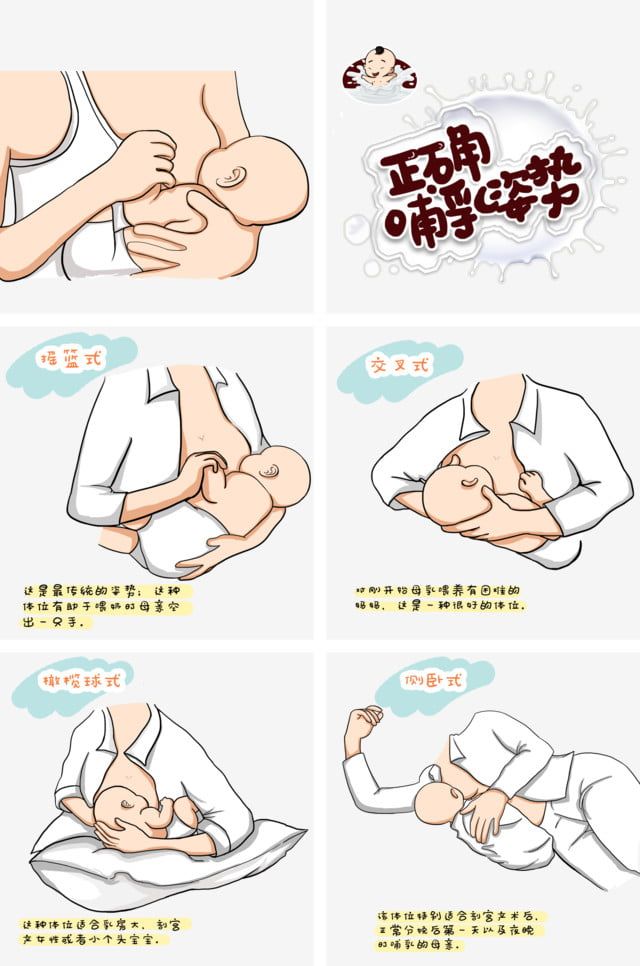
amount of breast milk provided increases with each day.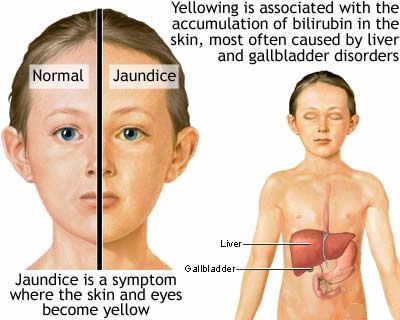 If you are breastfeeding, you should breastfeed your baby at least 8 to 12 times a day for the first few days. This will help you produce enough milk and will help keep the baby's bilirubin level down. If you are having trouble breastfeeding, ask your baby's doctor or nurse or a lactation specialist for help.
If you are breastfeeding, you should breastfeed your baby at least 8 to 12 times a day for the first few days. This will help you produce enough milk and will help keep the baby's bilirubin level down. If you are having trouble breastfeeding, ask your baby's doctor or nurse or a lactation specialist for help.
When should my baby's bilirubin level be measured?
Any baby that has jaundice in the first 24 hours after birth should have the bilirubin level measured right away. All babies should have at least one bilirubin measurement with skin or blood test before discharge from the hospital. Whether a baby needs additional bilirubin levels measured depends on the baby's age, the level of bilirubin, and whether the baby has other things that make jaundice more likely.
It is important for your baby to get checked soon after leaving the hospital. In most cases, babies discharged before 48 hours should be seen within 2 days by a healthcare provider. Ask your baby's healthcare provider about their bilirubin level and schedule a follow-up appointment.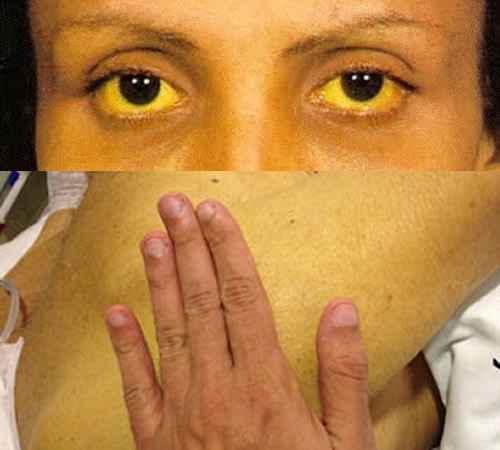
Why do some babies need an earlier follow-up visit after leaving the hospital?
Some babies have a greater risk for high levels of bilirubin and may need to be seen sooner after discharge from the hospital. Ask your doctor about an early follow-up visit if your baby has any of the following symptoms:
A high bilirubin level before leaving the hospital
Early birth (more than 2 weeks before the due date)
Jaundice in the first 24 hours after birth
Breastfeeding that is not yet going well
Bleeding under the scalp or a lot of bruising related to labor and delivery
A parent, brother or sister who had a high bilirubin level and received light therapy
Also, let your baby's doctor know if you eat fava beans (broad beans) or use any of the following products: mothballs, antibiotics, henna, or herbal remedies. Eating fava beans and using these products should be avoided because in rare cases this can cause severe jaundice.
When should I call my baby's doctor?
Call your baby's doctor if you notice these symptoms:
Your baby's skin turns more yellow.
Your baby's abdomen, arms, or legs are yellow.
The whites of your baby's eyes are yellow.
Your baby is hard to wake, fussy, or not nursing or taking formula well.
How is jaundice in babies treated?
Treatment can prevent the potentially harmful effects of jaundice. Most jaundice requires no treatment. When treatment is needed, babies are placed undressed under special lights (phototherapy). Phototherapy helps lower the bilirubin level. This is typically done in the hospital, but depending on your baby's bilirubin level, age, and other things, it can sometimes be done at home. In some babies, supplementing breast milk with formula can help lower the bilirubin level.
Very high bilirubin levels are a medical emergency that might require admission to the intensive care unit and other treatment, including a special type of blood transfusion that can rapidly decrease the bilirubin level.
Note: Putting your baby into sunlight is not a safe way to treat jaundice.
When does infant jaundice go away?
In breastfed babies, it is common for jaundice to last 1 month or occasionally longer. In formula-fed babies, most jaundice goes away by 2 weeks. Let your baby's doctor know if your baby has jaundice for more than 2 weeks if your baby is formula fed or longer than 4 weeks if your baby is primarily breastfed.
More information
- 11 Common Conditions in Newborns
- Health Issues in Premature Babies
- Symptom Checker: Jaundiced Newborn
- AAP Revises Clinical Guidelines for Hyperbilirubinemia in Newborns
The information contained on this Web site should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your pediatrician. There may be variations in treatment that your pediatrician may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.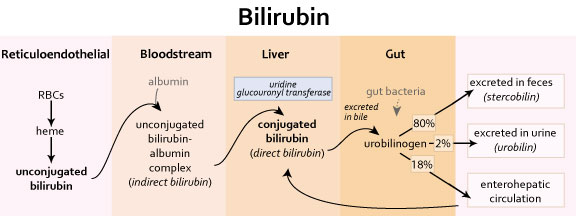
Jaundice in newborns | Raising Children Network
About jaundice in newborns
Jaundice in newborns happens when there’s an overload of bilirubin in a baby’s blood. This can make the baby’s skin and eye whites go yellow.
Bilirubin is a waste product that’s produced when old red blood cells break down. Usually, the liver processes bilirubin and mixes it into bile. Bile then goes from the liver to the digestive tract and finally comes out of the body in poo. In newborns, several things can stop this happening properly, which leads to a bilirubin overload.
Types of jaundice in newborns
Physiological jaundice
In physiological jaundice, babies’ livers aren’t yet developed enough to get rid of bilirubin.
This type of jaundice is very common. It occurs in about 3 in 5 newborns. It usually gets better when your baby’s liver is mature enough to process bilirubin properly.
Breastmilk jaundice
Breastfed babies often get breastmilk jaundice. This is when a chemical in the mother’s breastmilk interferes with the baby’s ability to get rid of bilirubin. This type of jaundice often happens a few days after birth.
This is when a chemical in the mother’s breastmilk interferes with the baby’s ability to get rid of bilirubin. This type of jaundice often happens a few days after birth.
Breastmilk jaundice isn’t harmful and usually sorts itself out after several weeks.
Breastfeeding jaundice
Breastfeeding jaundice happens when babies get dehydrated because of problems with breastfeeding. They need fluids to reduce bilirubin levels.
Breastfeeding jaundice usually gets better when babies get more fluids.
Jaundice from delayed cord clamping
Babies can get jaundice if there’s been a delay in getting their umbilical cord clamped and cut. Delayed clamping can cause there to be too many red blood cells in a baby’s blood. It means that there are more red blood cells than normal for the liver to process, so the bilirubin builds up.
This type of jaundice usually just needs monitoring and gets better by itself after 1-2 weeks.
Jaundice from birth interventions
Babies can get jaundice when they’re bruised because of interventions at birth, like forceps birth.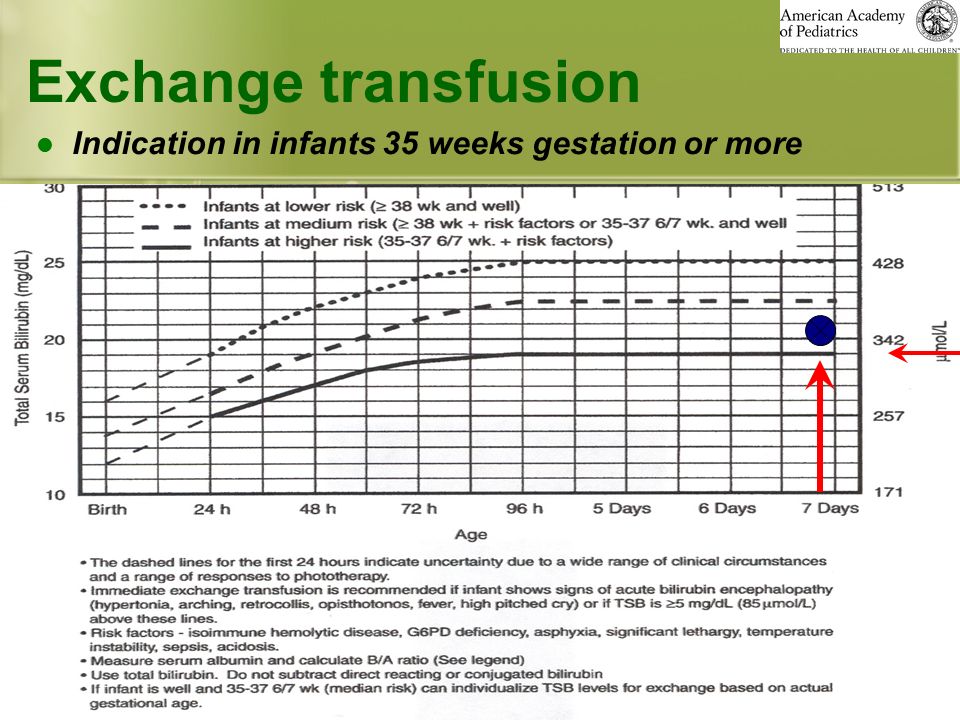 The red blood cells from this bruising break down and bilirubin builds up.
The red blood cells from this bruising break down and bilirubin builds up.
This type of jaundice usually just needs monitoring and gets better by itself after 1-2 weeks.
Blood type incompatibility jaundice
This is a rare type of jaundice, which happens when the mother’s and baby’s blood groups are incompatible.
This isn’t usually a problem during a first pregnancy because the mother’s and the baby’s bloodstreams don’t mix. But during the delivery, some of the baby’s blood might mix with the mother’s blood. The mother then develops antibodies that become active during her next pregnancy and cross the placenta to attack a second baby’s red blood cells.
The destruction of these red blood cells in the second baby releases bilirubin into that baby’s bloodstream, which results in jaundice. If this happens, you usually see it in the first 24 hours after birth.
Babies with this kind of jaundice need treatment.
Biliary atresia
Biliary atresia is a rare cause of jaundice in babies.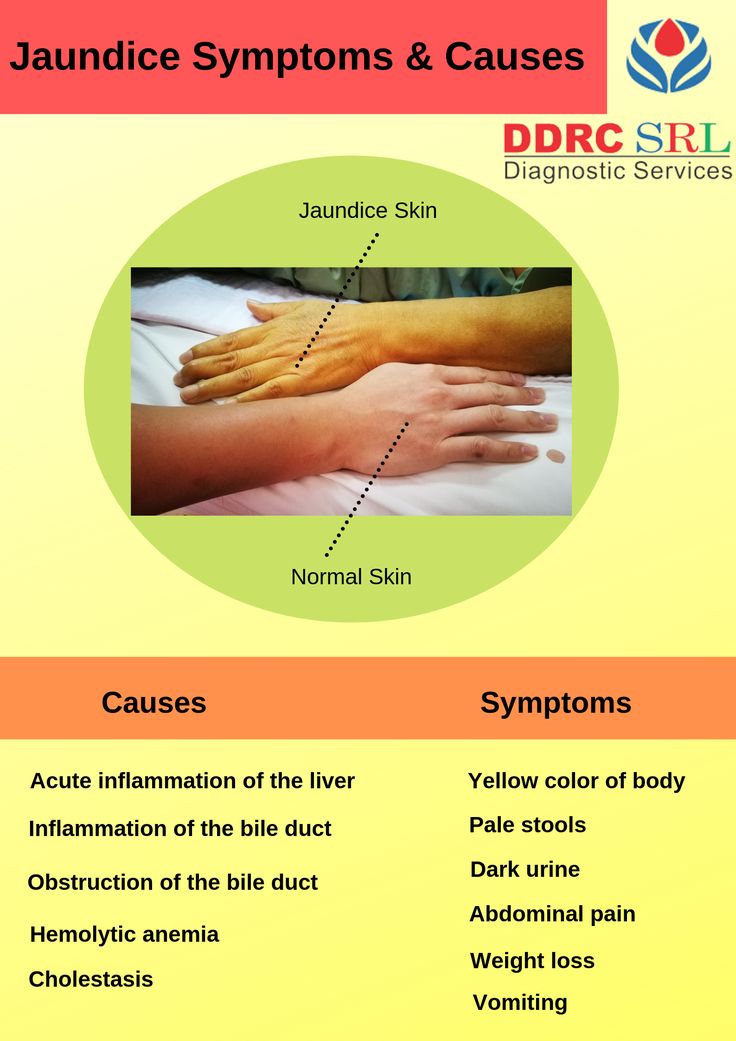
It happens when the tiny tubes that carry bile from the liver to the intestine don’t work. Babies with this condition usually grow as expected and look well at first, but they get very ill with serious liver disease if they aren’t diagnosed and treated early.
Babies with this kind of jaundice usually start to show signs at 2-8 weeks of age.
Babies with this kind of jaundice need surgical treatment.
Symptoms of jaundice in newborns
Newborn jaundice causes your baby’s skin and the whites of their eyes to go a yellow colour.
The jaundice typically starts on the face and head. If the level of bilirubin increases, the colour spreads to the body.
Babies might also be drowsy and have feeding difficulties.
Babies with biliary atresia also have pale-looking poo and darker urine.
Medical help: when to get it for newborns who have jaundice
Your child and family health nurse, midwife, GP or paediatrician should check and monitor your newborn for jaundice.
You should take your baby to the GP if your baby:
- is unwell, feeding poorly and not gaining enough weight
- has pale poo or dark wee
- looks jaundiced.
Tests for jaundice in newborns
Medical staff might measure the level of your baby’s jaundice using a bilirubinometer, which is a special machine that’s briefly placed on your baby’s skin. But they might also need to do a heel prick test to get a more accurate measurement of the level of bilirubin in your baby’s blood.
Sometimes if the levels of jaundice are high or medical staff are worried that your baby has a more serious condition, your baby will need other tests to find the cause.
Treatment of jaundice in newborns
Treatment for newborn jaundice depends on how serious it is and what has caused it.
Physiological jaundice and jaundice from delayed cord clamping or birth interventions
Babies who develop jaundice several days after birth usually just need careful monitoring by their parents. These babies don’t usually have to stay in hospital.
These babies don’t usually have to stay in hospital.
If your baby’s bilirubin levels are high, they might have phototherapy treatment for a few days. This treatment uses a special type of blue light that helps break down the bilirubin overload.
Babies most commonly get phototherapy by being placed naked in a cot under a phototherapy lamp for 2-3 days in hospital. Some hospitals offer a biliblanket. This is a special blanket for wrapping your baby. You can use a biliblanket to give your baby phototherapy treatment at home. It’s important to supervise your baby when they’re wrapped in a biliblanket.
Most babies cope well with phototherapy treatment. Phototherapy has minimal side effects, although your baby might have a mild rash and runny poo for a few days. Some babies have small fluid losses during phototherapy, so they might need extra feeds.
Breastmilk jaundice
If your baby has breastmilk jaundice, you can keep breastfeeding.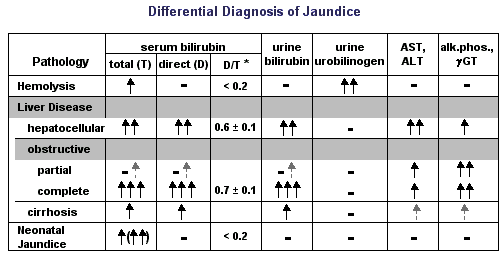 This type of jaundice is usually mild and should get better by itself with time. Talk with your child and family health nurse or doctor if you’re worried about what to do.
This type of jaundice is usually mild and should get better by itself with time. Talk with your child and family health nurse or doctor if you’re worried about what to do.
Breastfeeding jaundice
Babies with breastfeeding jaundice get better when they have more feeds. Your child and family health nurse or a lactation consultant can help with breastfeeding.
Severe or blood type incompatibility jaundice
Severe jaundice, in which bilirubin levels are very high, might need treatment with an exchange transfusion. This is when a baby’s own blood is replaced with compatible fresh blood. This is usually a treatment for blood type incompatibility jaundice, but it isn’t common.
Biliary atresia jaundice
If your baby has jaundice caused by biliary atresia, they’ll need an urgent operation to help with bile drainage.
If severe jaundice isn’t treated, it can cause brain damage.
Prevention of jaundice in newborns
Only jaundice caused by a certain type of blood incompatibility is preventable.
If your doctor or health professional thinks this type of jaundice might be a problem, you’ll get an anti-D injection immediately after delivery. This can prevent complications in subsequent pregnancies.
Newborn jaundice: causes, treatment, consequences, prevention
Newborn jaundice is faced by many parents. This is especially true for premature babies, but in babies who were born at term, this is also a common occurrence.
Jaundice develops in the first few days after the birth of the baby, and the change in skin color usually becomes noticeable on the 3rd-4th day, just when the mother and baby return home from the hospital.
Why does this happen and what is the difference between physiological neonatal jaundice, which does not require treatment, and dangerous pathological neonatal jaundice? We deal with doctors.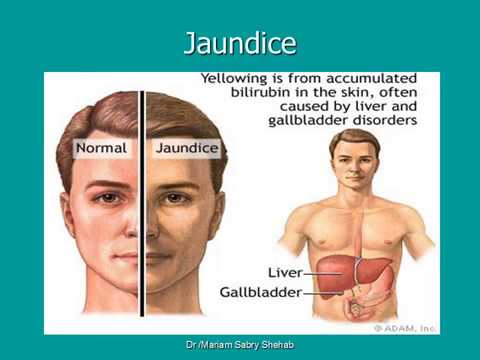 nine0003
nine0003
What you need to know about jaundice in newborns
Bilirubin is formed from the breakdown of red blood cells (blood cells that are responsible for transporting oxygen) throughout life and is excreted from the body without problems with the help of the liver. All body systems in a newborn do not work well enough, for example, the liver may not have enough enzymes to break it down and excrete it. Because of this, bilirubin accumulates in the blood, and the skin color becomes yellow. It happens that the whites of the eyes acquire the same shade. nine0003
Physiological jaundice differs from pathological jaundice in that the former does not require treatment and resolves on its own. This usually happens after the first month of a baby's life. But the pathological condition is important and needs to be tracked in time. It affects the general well-being, has negative consequences, but with a competent approach, it is treated by a pediatrician or neonatologist.
| Physiological jaundice - a variant of the norm | In the first days of life, many parents experience yellowing of the baby's skin. At the same time, nothing threatens the condition of children, and the shade of the skin is normalized after 7-10 days. The only thing that can overshadow the first days of a baby’s life is vomiting. Occurs against the background of a bunch of bilirubin with albumin to prevent the toxic effects of the first (1). But such a phenomenon is rare. nine0020 At the same time, nothing threatens the condition of children, and the shade of the skin is normalized after 7-10 days. The only thing that can overshadow the first days of a baby’s life is vomiting. Occurs against the background of a bunch of bilirubin with albumin to prevent the toxic effects of the first (1). But such a phenomenon is rare. nine0020 |
| There are several types of pathological jaundice | Conjugative jaundice develops due to liver enzyme deficiency. Hemolytic jaundice is associated with a change in the structure of red blood cells. And the problem of obstructive jaundice is a violation of the outflow of bile. |
| Things to pay attention to when treating jaundice (in addition to the general condition) | The doctor first of all specifies whether the child has prematurity and other factors that can complicate the course of the disease, whether there is a hereditary predisposition to this disease. It is worth paying attention to the appetite of the baby, and his mother, the level of lactation is also important. nine0020 nine0020 |
| There is a "bilirubin encephalopathy" | In this condition, bilirubin enters the child's nervous system due to the fact that there is not enough albumin to neutralize it. The baby shows symptoms such as drowsiness, convulsions, and a weakened grasping reflex. |
| Jaundice is not contagious | It cannot be transmitted by airborne droplets. The cause of the disease is the increased breakdown of red blood cells and the insufficient functionality of the liver, which does not have time to process bilirubin secreted in large quantities. nine0020 |
| When phototherapy is used for jaundice | At risk of hyperbilirubinemia, with physiological jaundice, with incompatibility of the baby's blood type with the mother's blood type, with an increase in bilirubin level above 5 µmol / l per hour. |
How long does jaundice last in newborns
The duration of jaundice in a newborn depends on the characteristics of the organism. Physiological jaundice usually reaches its maximum on the 3-4th day of the baby's life. Gradual fading begins on days 4-5, and on days 7-14, the child's body completely copes with this condition. nine0003
Physiological jaundice usually reaches its maximum on the 3-4th day of the baby's life. Gradual fading begins on days 4-5, and on days 7-14, the child's body completely copes with this condition. nine0003
- Parents are not always able to reliably determine whether the baby's jaundice is normal or not. Therefore, this condition is given maximum attention by the medical staff (first in the maternity hospital, then on patronage), - explains Albina Yusupova, pediatric neonatologist Lahta Clinic . - Before discharge in the maternity hospital, doctors examine the child, determine the presence of jaundice, evaluate the skin color in dynamics, whether the yellowness of the skin / sclera increases or not. Often they resort to using a percutaneous method for measuring the level of bilirubin (it is he who gives such staining of the skin) or take blood for analysis. With high numbers, phototherapy is prescribed (a special lamp or mattress). There are no exact numbers for this, it depends on many factors: gestational age (term baby or not), the presence of cephalohematoma or bruising at birth, the color of feces / urine, whether there are concomitant pathologies or not, the blood type of the mother and child, how the mother eats and gains weight baby. nine0003
nine0003
In most cases, pathological jaundice develops on the first day of a newborn's life. The duration may vary depending on the reason why the child suffers from this disease: sometimes the treatment takes 2 months, and in complex cases where enhanced therapy is required, jaundice can last up to a month.
Higher bilirubin levels have been reported in breastfed neonates with large postpartum weight loss (≥8%), diabetic mothers, low gestational age, and drug induction of labor with oxytocin (2). nine0003
Causes of jaundice in newborns
Jaundice can appear in a baby for various reasons. Most often it is the accumulation of bilirubin in the blood. But there are other conditions that newborns face in the first weeks of life.
Bilirubin
Signs of pathology:
- deviations from the normal course of physiological jaundice (earlier or later onset, prolonged persistence, undulating course),
- appearance of pallor or a greenish hue of the skin,
- increase in the concentration of total bilirubin in the blood serum,
- relative increase in the level of the direct fraction of bilirubin (3).

Unlike physiological, pathological jaundice, as a rule, develops in the first hours after the baby is born. There may be dark urine and discoloration of feces, anemia, and pale skin. At the same time, the level of bilirubin is very high:
- above 256 µmol/l in children born at term,
- above 171 µmol/l in premature babies. nine0078
This condition is called hyperbilirubinemia. The most common cause of its development is hemolysis due to the incompatibility of the blood of the mother and child for erythrocyte antigens.
Other causes
“Pathological jaundice can be caused by several reasons,” says pediatrician Anna Levadnaya, PhD, author of the blog about pediatrics . - The most common is an increased breakdown of hemoglobin due to an Rhesus conflict or a blood type conflict between mother and child. Also, the cause of jaundice can be a pathology of the liver or a pathology of excretion of bile into the intestines.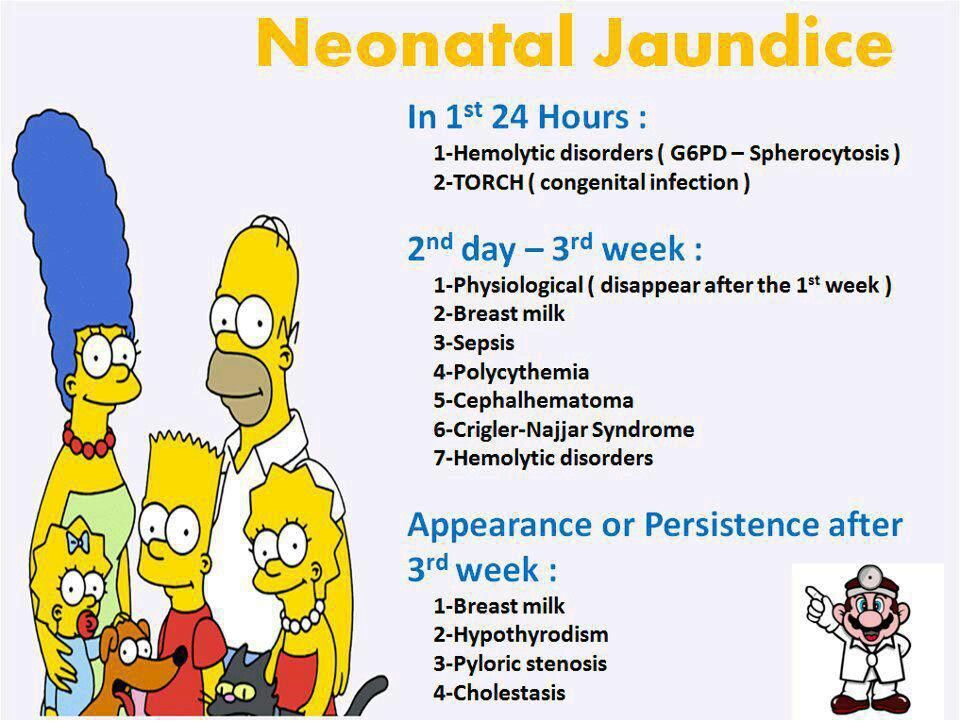 In addition, jaundice can be a sign of an infection, hypothyroidism (due to a decrease in thyroid function), polycythemia (an increased level of red blood cells in the blood), intestinal obstruction, or pyloric stenosis (this is a congenital narrowing of the stomach before entering the intestines, which makes it difficult for food to pass through). into it). It can occur with certain medications and for other reasons. nine0003
In addition, jaundice can be a sign of an infection, hypothyroidism (due to a decrease in thyroid function), polycythemia (an increased level of red blood cells in the blood), intestinal obstruction, or pyloric stenosis (this is a congenital narrowing of the stomach before entering the intestines, which makes it difficult for food to pass through). into it). It can occur with certain medications and for other reasons. nine0003
Hepatic jaundice occurs when a child's liver is exposed to viruses or bacteria. It can also develop with hepatitis B and hepatitis C, blood sepsis. At this time, the liver and spleen increase in size, the baby's urine acquires a more pronounced color. Hepatic jaundice is treated comprehensively, primarily by acting on the cause.
Violation of the outflow of bile can cause obstructive jaundice. This happens when the patency of the bile ducts worsens due to malformations, underdevelopment, or the appearance of neoplasms. Here, all attention should be paid to the place where bile accumulates and the reason why it accumulates. After all, it is because of her that the baby may show symptoms of jaundice. nine0003
After all, it is because of her that the baby may show symptoms of jaundice. nine0003
Another cause is neonatal cholestasis. To confirm the diagnosis, it is necessary to make sure that the content of the direct fraction of bilirubin in the blood is more than 15-20% of the total level, an increase in the concentration of cholesterol, beta-lipoproteins, bile acids, as well as alkaline phosphatase and gamma-glutamyltransferase enzymes (3). This pathology occurs due to an increased level of bile acid synthesis, for which the newborn's liver is not ready. It happens that neonatal cholestasis occurs for reasons not related to the work of the liver. For example, against the background of hypoxia or the development of cardiovascular insufficiency. nine0003
There is also the so-called breastfeeding jaundice. There are studies that show that in healthy full-term infants who are bottle-fed, the level of bilirubin reaches a peak on the 5th day of life and becomes completely normal, on average, on the 13th day, while with natural feeding, two peaks of bilirubin rise are possible ( 3–5 and 10–15 days of life) with a gradual slow decrease (4). Jaundice from breast milk (from which certain hormones that increase bilirubin levels enter the baby's body) can last up to 6 weeks. nine0003
Jaundice from breast milk (from which certain hormones that increase bilirubin levels enter the baby's body) can last up to 6 weeks. nine0003
If the doctor makes this diagnosis, he must exclude the presence of hyperbilirubinemia. Because breastfeeding jaundice cannot cause it. If, when HB is canceled for 1-2 days, bilirubin begins to decrease, and yellowness disappears, the diagnosis is confirmed. But with positive dynamics, the abolition of breastfeeding is not required: it is resumed after 1-2 days. During the pause, the mother must definitely express herself in order to maintain lactation at the required level.
Treatment of neonatal jaundice
Physiological neonatal jaundice, as we have said, does not require treatment. Sometimes pediatricians recommend supplementing such children with water, but only if lactation is established and using a spoon, not a bottle.
As for the pathological jaundice of a newborn, it requires mandatory treatment, which is prescribed by a doctor.
The most effective treatment for this condition is phototherapy. For this, a special lamp with blue light is used: under the influence of ultraviolet radiation, bilirubin breaks down and is excreted from the body of the newborn with urine and feces. The intensity and duration of phototherapy depends on the baby's body weight at birth and the level of bilirubin, which is constantly monitored. As a rule, three-hour sessions under the lamp are prescribed with a break of 2-3 hours. The newborn must be undressed, but the eyes must be protected, the boys also have the genitals. nine0003
In severe cases of neonatal jaundice, when the life of the baby is at risk, a blood transfusion may be indicated.
Doctors have almost abandoned the use of drugs to treat neonatal jaundice. Some of them, for example, ascorbic acid and albumin, negatively affect the functioning of the nervous system, the effectiveness of allochol and B vitamins has not been proven, and Karsil and Essentiale have not been sufficiently tested specifically for newborns (3).
- It is important to note that most experts now agree that the appointment of sorbents, drugs such as phenobarbital, Essentiale, LIV-52, the abolition of breastfeeding, UV (ultraviolet blood enrichment), electrophoresis or excessive infusion therapy for jaundice is ineffective ( and it’s not safe for phenobarbital), says Anna Levadnaya. nine0003
Consequences of jaundice in newborns
Physiological jaundice in newborns, as we have already noted, passes by itself and does not bear negative consequences for the health of the baby. But the consequences of pathological jaundice in a newborn can be extremely serious, especially if treatment is not started on time.
— Too high blood levels of bilirubin can lead to brain damage, says Anna Levadnaya. - As a rule, this occurs in children with hemolytic disease according to the Rh factor, with an increase in the level of bilirubin above 298-342 µmol/l. And the higher the level of bilirubin, the higher the risk of encephalopathy.
Prevention of jaundice in newborns
The best prevention of jaundice in newborns is a healthy lifestyle for a mother during pregnancy, giving up bad habits, good nutrition.
In addition, the expectant mother must be tested to detect Rh-negative blood factor. Children born to mothers with Rh-negative blood are at risk for jaundice. After the birth of such babies, they carefully examine and monitor the content of bilirubin in the blood, and also determine the blood group. nine0003
- Women who may have a child with hemolytic jaundice are treated already during pregnancy. They are injected with anti-rhesus gamma globulin, and at birth, the child is immediately clamped on the umbilical cord and tested for bilirubin. If there are indications according to the tests, then the child is immediately put on phototherapy, - adds neonatologist Nadezhda Shurtakova . - The mother of the baby can also influence the fact that the child does not have jaundice. She needs to feed the baby more on the first day, try to get milk so that the baby does not lose weight. Jaundice often occurs with a large loss of initial weight. Bilirubin is a fat-soluble substance, and if the body of a newborn does not have enough fats, proteins and carbohydrates, then jaundice occurs at certain values of body weight loss. nine0003
Mother's milk is the best food for a newborn, it is easily digested, the intestines are stimulated faster, it is populated with beneficial microflora, the necessary enzymes are produced. All this helps the body of the newborn to cope with jaundice faster and more efficiently.
Frequently asked questions and answers
Nadezhda Shurtakova, neonatologist, head of the neonatal department at Maternity Hospital No. 4 (Moscow) answered frequently asked questions.
When is jaundice in newborns considered normal? nine0073
There are physiological and pathological jaundice. Physiological jaundice, which appears at the end of the second or third day of life, does not require treatment. Such jaundice is not pronounced and disappears on its own in 7-10 days. Physiological jaundice is present in 80% of children. Such children are discharged home without any additional examinations and treatment.
In what case is the child placed under the lamp and how long does the child need to stay there?
The child is placed under a lamp, for phototherapy, with pathological jaundice. The duration of therapy depends on what causes it. nine0003
Hemolytic jaundice of the newborn due to the Rh factor may appear already in the prenatal period, the child may be born with it and need an exchange transfusion. Such children are laid out under the lamp immediately at birth.
Jaundice caused by AB0 incompatibility (blood group incompatibility) appears at the age of 1.5 days. It is necessary to look at a biochemical blood test, and if there are indications, also put the child on phototherapy.
There is also conjugative jaundice, it, like physiological, also appears on the third day, but with it the amount of bilirubin (yellow substance) in the blood is significantly increased. Such children are also subject to phototherapy. nine0003
In different situations, phototherapy lasts from 1 to 4 days, usually 2-3 days, it is carried out under the control of biochemical and clinical blood tests. When the indicators are normal, the child is removed from phototherapy.
How long does it take to stay in the hospital if a newborn has jaundice?
Hemolytic jaundice lasts 5-7 days. We stabilize such children, wait for the end of the increase in bilirubin and then transfer them to another hospital. However, if treatment is started on time, the indicators return to normal faster, and the mother and child are already discharged from the hospital. nine0003
In case of conjugative jaundice, which may appear on the 4th day, already after discharge from the maternity hospital, children are admitted to hospitals from the districts.
Sources
- E.I. Yulish. Jaundice syndrome in newborns: approaches to therapy // Health of the child.
2014. URL: https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/sindrom-zheltuhi-u-novorozhdennyh-podhody-k-terapii
- A.N. Goryainova. Jaundice in a healthy newborn: causes, course, prognosis // Medical Council. 2017. URL: https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/zheltuhi-zdorovogo-novorozhdennogo-prichiny-techenie-prognoz
- S. Ergieva. Jaundice of newborns // Vestnik VolGMU. 2007. URL: https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/zheltuhi-novorozhdennyh/viewer
- Gartner LM. Breastfeeding and Jaundice. J. Perinatol. 2001
Jaundice in newborns
It happens that on the second or third day after birth, the child turns yellow. This is not a pathology, it is a natural process that occurs due to the infant's adaptation to environmental conditions. And it is called physiological jaundice. Let's look at what jaundice is and how it develops. nine0003
Jaundice is a symptom, not a disease. And it is not necessary to treat him, but the cause that caused the condition.
In human blood, there are red blood cells - erythrocytes, designed to carry oxygen and carbon dioxide in the body. The period of their existence is 120 days, after which they die. Thus, every day 1% of the total pool of erythrocytes is destroyed. In the process of destruction, metabolic products are released into the blood. One of them is the pigment bilirubin, which gives the skin its yellow color. Bilirubin is toxic to the body, so it neutralizes it and removes it with the help of the liver. In it, liver enzymes produce neutralization, and the pigment is excreted by the intestines. If this process is disturbed, the level of bilirubin rises, which is manifested by jaundice. nine0003
And now about a specific condition - jaundice in newborns. She is not dangerous. Immediately after birth, a large amount of fetal hemoglobin breaks down in the baby's body, as a result of which a lot of bilirubin is released into the blood. And in the liver, the liver enzymes necessary to neutralize bilirubin have not yet matured. Therefore, 50-60% of newborns develop physiological jaundice 2-3 days after birth. It takes time for the liver to learn how to neutralize and remove bilirubin. The probability of development is higher in premature babies and is 80-90%. And that's okay.
- How do I know if my child has physiological jaundice? And not dangerous jaundice?
Only a pediatrician can accurately determine the cause of jaundice and the degree of danger. However, it is worth knowing that with physiological jaundice, the yellowness of the sclera, skin and mucous membranes is not accompanied by other symptoms. With jaundice caused by other causes, the baby does not feel well, cries, eats poorly and does not gain weight. nine0003
- Is it possible to vaccinate against hepatitis B with physiological jaundice?
Neonatal jaundice does not appear to be a contraindication for hepatitis B and other vaccinations.
- Does physiological jaundice affect the child's condition in the future?
No, neonatal jaundice does not affect the health of the child.
Features of the treatment of neonatal jaundice
In most cases, jaundice resolves in 2-3 weeks. Complications in such jaundice are extremely rare, however, an excessive increase in bilirubin (especially indirect) is dangerously toxic, and the lack of appropriate treatment can lead to adverse consequences.
The doctor takes into account all the accompanying factors in order to plan the frequency of examinations and find out the risk of an increase in bilirubin:
- current bilirubin content; nine0078
- the presence of prematurity;
- activity and appetite of the child;
- the level of lactation in the mother;
- hereditary predisposition to severe jaundice.
Treatment that lowers the level of bilirubin in the blood may be as follows.
- Phototherapy. The child is placed under special lamps with high intensity blue-green light. Such light has the ability to transform the structure and shape of indirect hemoglobin so that it becomes water soluble enough to be disposed of in urine and feces.
This procedure is harmless, as the ultraviolet spectrum is blocked by a special filter and does not fall on the baby's skin. nine0078
- Intravenous injections of immunoglobulin. If the cause of jaundice is the incompatibility of the blood of the mother and child, you can use the introduction of immunoglobulin intravenously. This method will help reduce the level of antibodies. This may be enough.
- Blood transfusion. It is used to quickly reduce bilirubin and is carried out in the intensive care unit. A certain volume of blood is taken from a child with a high level of bilirubin, and at the same time, donor blood with normal values is injected. Thus, bilirubinemia decreases and hemoglobin normalizes. nine0078
- Plasmapheresis. This method is applicable in complex medical cases. Small volumes of blood are repeatedly taken from a child, they are purified from plasma with a high level of bilirubin and antibodies, diluted with saline or donor plasma and injected back intravenously.