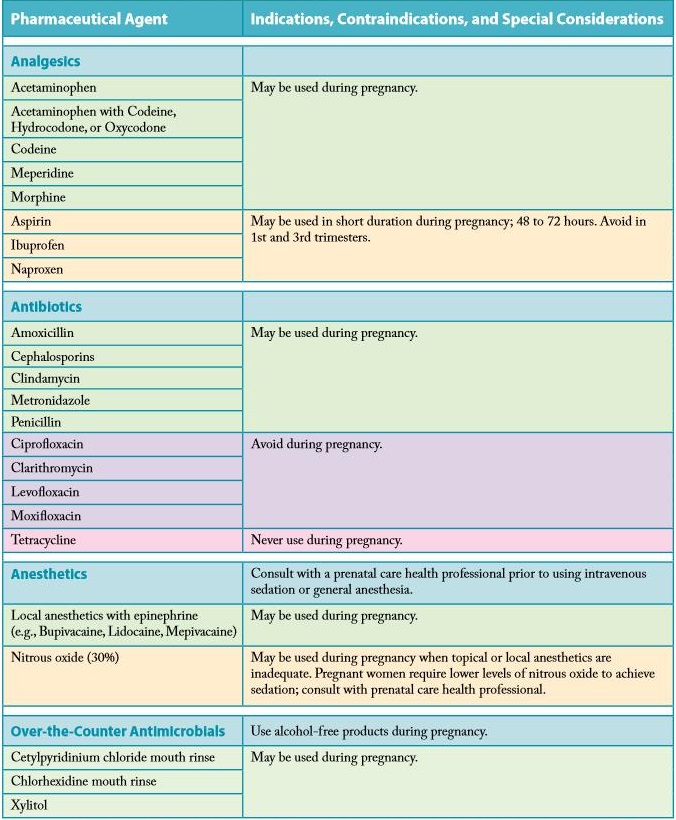
Is it safe to take vitamin b12 while pregnant
Vitamin B12 during pregnancy | BabyCenter
Vitamin B12 during pregnancy is essential for your baby's developing brain and spinal cord. It also helps make healthy red blood cells and DNA. Vitamin B12 is only found naturally in animal foods (fish, meat, poultry, eggs, and dairy) and fortified plant foods. If your prenatal vitamin doesn't include vitamin B12, and you're vegetarian or vegan, check with your doctor or midwife about taking a supplement.
Photo credit: iStock /mphillips007
Why you need vitamin B12 during pregnancy
Vitamin B12 is essential for the development and function of your baby's brain and spinal cord, and for forming healthy red blood cells. Vitamin B12 also helps make DNA, the genetic material in all your baby's cells.
Some studies suggest that babies born to women with low levels of vitamin B12 during pregnancy may have an increased risk of neural tube defects.
How much vitamin B12 do pregnant women need?
When you're pregnant or breastfeeding, you need slightly more vitamin B12 than usual.
Pregnant women: 2.6 micrograms (mcg) per day
Breastfeeding women: 2.8 mcg per day
Nonpregnant women: 2.4 mcg per day
Best foods with vitamin B12 during pregnancy
Vitamin B12 is only naturally found in animal foods (fish, meat, poultry, eggs, and dairy products). Plant foods don't have vitamin B12 unless they're fortified. If you're looking for foods fortified with B12, breakfast cereals as well as some soy and other plant milks are good bets. Check labels to be sure.
Here are some good food sources of vitamin B12:
- 3 ounces Atlantic salmon, cooked: 2.6 mcg
- 3 ounces ground beef, 85-percent lean, pan browned: 2.4 mcg
- 8 ounces 2-percent milk: 1.3 mcg
- 6 ounces plain, fat-free yogurt: 1.0 mcg
- 1 serving breakfast cereal fortified with 25 percent of the daily value for vitamin B12: 0.6 mcg
- 1 1/2 ounces cheddar cheese: 0.5 mcg
- 1 large egg, cooked: 0.
 5 mcg
5 mcg - 3 ounces turkey breast meat, roasted: 0.3 mcg
Advertisement | page continues below
(Note that a 3-ounce serving of meat or fish is about the size of a deck of cards.)
Do you need a vitamin B12 supplement during pregnancy?
You may need a vitamin B12 supplement if you're a vegan or vegetarian during pregnancy, you don't eat B12-fortified foods every day, and your prenatal vitamin doesn't include B12. Check with your doctor or midwife to make sure you're getting enough vitamin B12 from your pregnancy diet or prenatal vitamin.
Was this article helpful?
Yes
No
Eva Dasher
Eva Dasher writes, researches, and edits content on a wide variety of subjects, including parenting, medicine, travel, natural history, science, business, and the arts. Her favorite pastimes include experimenting with new foods, libations, and restaurants, as well as traveling the world with her two college-age children, husband, extended family, and friends.
Vitamin B12 Benefits During Pregnancy – feedmomandme
Written by: Caroline Misiano; LIU Post Dietetic Interns
Medically Reviewed by Dr. Nicole Palmer, DO
In this article:
As a pregnant mother or someone trying to conceive, you have probably read about the importance of certain vital nutrients during pregnancy, like folate or folic acid. But did you know that Vitamin B12 is just as essential for a healthy and safe pregnancy? In fact, adequate daily consumption of vitamin B12 can prevent certain birth defects and significantly impact the overall health and development of your baby.
It is also important to mention that Folate and Vitamin B12 work together in the body. Together, they help with the formation of DNA for your baby as well as maintaining a healthy heart for your baby!
We will discuss the importance of Vitamin B12, the food sources of Vitamin B12, if you can take b12 while pregnant, how much you should have, and signs and symptoms of inadequate Vitamin B12 in the body.
Vitamin B12, also known as cobalamin, is an essential, water-soluble vitamin needed for the body to function. “Water-soluble” means that any extra Vitamin B12 in the body will not cause any harm to the body and will be excreted in the urine. This nutrient helps keep the body's blood and nerve cells healthy, and helps produce DNA, the genetic material in all of your cells. It is also known to help prevent megaloblastic anemia, a blood condition that makes people tired and weak.
After eating foods with Vitamin B12, a special protein called an intrinsic factor, picks up Vitamin B12 in the stomach and carries it to the small intestine, where it can then be absorbed in the bloodstream. This special protein is essential for Vitamin B12 to be absorbed into the body. In some cases, people have impaired secretion of the intrinsic factor, which makes absorbing Vitamin B12 in the bloodstream a little more difficult and can also increase the risk of deficiency.
Vitamin B12 plays an important role in developing the baby’s neural tube formation, brain and spine development, nerve tissue, and the formation of their red blood cells. It is also essential in the formation of their DNA! Some studies suggest that mothers who have low Vitamin B12 levels are at an increased risk of birthing a baby with neural tube defects. Vitamin B12 is an essential nutrient for the body, as well as during pregnancy and while breastfeeding.
★ IS IT SAFE TO TAKE VITAMIN B12 WHILE PREGNANT?Yes, taking Vitamin B12 while pregnant is safe, and is very important for the development and overall health of your baby. Most mothers experience several pregnancy symptoms, like nausea and vomiting, that may interfere with their dietary intakes and affect the amount of Vitamin B12 being consumed daily. Instances like these can increase your risk of developing certain deficiencies, like vitamin B12 deficiency, which can be harmful to both mother and baby and may increase the risk of certain birth defects.
Those trying to conceive or who are currently pregnant should eat a diet rich in vitamin B12 to ensure a healthy pregnancy and a healthy, developed baby. Along with a diet high in Vitamin B12, a prenatal vitamin is recommended to ensure that there is enough of this vitamin for both mother and for your baby.
★ HOW MUCH VITAMIN B12 DURING PREGNANCY?
The amount of Vitamin B12 that a pregnant woman’s body needs is 2.6 micrograms daily. For non-pregnant adults, the Vitamin B12 recommendation is lower, at 2.4 micrograms per day.
Yes, Vitamin B12 is a standard component of human breast milk. The recommendation for breastfeeding mothers is 2.8 micrograms of Vitamin B12 daily and for infants aged 6 months or less is 0.4 mcg. Some studies recommend 5.5 mcg per day during lactation. (1)
★ WHAT ARE THE SIGNS/SYMPTOMS OF VITAMIN B12 DEFICIENCY?Symptoms of Vitamin B12 deficiency can include weakness, fatigue, light-headedness, pale skin, rapid heartbeat, and being easily bruised. Most people don’t know the lasting effects that Vitamin B12 deficiency can have on both mother and baby. You are at a higher risk for developing a Vitamin B12 deficiency if you avoid meat, poultry, or eggs in your diet. A lack of Vitamin B12 in your diet can lead to deficiency, also known as pernicious anemia.
Most people don’t know the lasting effects that Vitamin B12 deficiency can have on both mother and baby. You are at a higher risk for developing a Vitamin B12 deficiency if you avoid meat, poultry, or eggs in your diet. A lack of Vitamin B12 in your diet can lead to deficiency, also known as pernicious anemia.
Some studies suggest that the risk of Vitamin B12 deficiency in vegetarians can be reduced by eating a diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids. Foods high in omega-3 fatty acids include salmon, tuna, green leafy vegetables, plant oils, nuts, and seeds. Eating a diet high in both omega-3 fatty acids and vitamin B12 can increase brain development and help to avoid the risk of a deficiency.
Talk to your doctor if you believe you are experiencing symptoms of a vitamin B12 deficiency.
★ BEST VITAMIN B12-RICH FOODS DURING PREGNANCYVitamin B12 is only found in animal products. Plant foods do not contain Vitamin B12 unless fortified. Other good sources of Vitamin B12 include fortified breakfast cereals as well as plant milks, like soy.
Foods high in Vitamin B12 include:
- Beef, liver, and chicken
- Fish and Shellfish
- Eggs
- Low-fat dairy products
So, you may be wondering, how do I get enough Vitamin B12 in my diet if I don’t eat animal products? If you are vegan or vegetarian or do not consume enough of the foods listed above, it is essential to take a prenatal vitamin during your pregnancy.
★ BEST PRENATAL VITAMINS WITH VITAMIN B12The Feed Mom and Me Prenatal Vitamin is one of the best over-the-counter prenatal Vitamins. It contains 2.6 micrograms of Vitamin B12 to be sure that both mother and baby are receiving adequate supplementation while your baby is developing!
This prenatal is formulated by an OBGYN & Registered Dietitian, containing all the nutrients needed to conceive and during pregnancy. Each small and easy-to-swallow pill is packed with 22 key natural nutrients to provide nutritional support for you and your growing baby. It contains Folate (methyl folate form), DHA, Iron, Calcium, Choline, Biotin, Zinc, Magnesium, and Selenium.
It contains Folate (methyl folate form), DHA, Iron, Calcium, Choline, Biotin, Zinc, Magnesium, and Selenium.
The vegetarian formula is free of artificial colors or flavors, chemicals, preservatives, non-GMO, dairy, soy, or gluten-free. Each of their capsules contains B6, Organic Ginger, and Peppermint Powder, which can help alleviate morning sickness and nausea.
Adding to that, it is a women-owned company. Who better than a female would understand pregnancy!
Click here for more info on Feed Mom & Me Complete Prenatal with Vitamin B12!
+SOURCES
- https://www.parents.com/pregnancy/my-body/nutrition/is-b12-as-crucial-as-folic-acid-during-pregnancy/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/7832046/
- https://www.indushealthplus.com/benefits-of-vitamin-b12-during-pregnancy.html
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26249019/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK534419/#
- (1) Ströhle A, Richter M, González-Gross M, et al. The revised D-A-CH-reference values for the intake of vitamin B12: Prevention of deficiency and beyond.
 Mol Nutr Food Res. 2019;63:e1801178.
Mol Nutr Food Res. 2019;63:e1801178. - https://feedmomandme.com/products/complete-prenatal-vitamin-with-dha
- https://feedmomandme.com/blogs/mama-blog/benefits-of-folate-during-pregnancy
- https://feedmomandme.com/blogs/mama-blog/ginger-during-pregnancy
- https://feedmomandme.com/blogs/mama-blog/iron-during-pregnancy
- https://feedmomandme.com/blogs/mama-blog/importance-of-choline-during-pregnancy
- https://feedmomandme.com/blogs/mama-blog/morning-sickness-during-pregnancy
- https://feedmomandme.com/blogs/mama-blog/calcium-during-pregnancy
What vitamins are needed during pregnancy: a list and norms
Healthy intrauterine development of a baby directly depends on the nutrition, lifestyle and habits of the expectant mother. In the first trimester, women ask doctors and pharmacists a question: what are the vitamins for pregnant women? If proper nutrition is not enough to cover the norm for vitamins and minerals, the doctor may prescribe the necessary elements in the form of tablets or drops. There is no universal prescription for multivitamins for pregnant women. But there is a list of drugs that are safe and useful for pregnant women. nine0003
There is no universal prescription for multivitamins for pregnant women. But there is a list of drugs that are safe and useful for pregnant women. nine0003
Before buying pharmaceutical products, you should familiarize yourself with what vitamins for pregnant women exist and how they affect the body of the child and mother. In addition, there is a trimester approach to the selection of the necessary trace elements. They are all prescribed based on deficiencies, tests, the age of the woman, general health, and other factors.
Numerous studies over the past 60 years have shown the need to increase intake of beneficial micronutrients and vitamins during pregnancy. If in the last century doctors agreed on a common value for all vitamins, then for the last ten years, the necessary increase in dose has been selected for each microelement. In addition, the consumption of individual elements does not require an increase, and some should be reduced. nine0003
The daily requirement of vitamins for pregnant women is:
- vitamin A - 770 mcg (norm 700 mcg),
- vitamin B6 - 1.
 9 mg (norm 1.3 mg),
9 mg (norm 1.3 mg), - vitamin B12 - 2.6 mcg (norm 2.4 mcg),
- vitamin C - 85 mg (norm 75 mg),
- folic acid - 600 mcg (normal 400 mcg),
- nicotinic acid - 18 mg (norm 14 mg).
Such a system for calculating the norm of vitamins was relevant until the 2000s and is quite applicable now, although outdated. Modern experts approach the selection of the diet and additional components more differentiated. Since pregnancy is a dynamic process, a trimester approach to prescribing vitamins is considered more appropriate. The generalized norm will fluctuate slightly depending on the stage of fetal development and the general condition of the mother. nine0003
It may be erroneously assumed that the longer the gestation period, the more food and vitamins should be taken. But in reality, the expectant mother should not consume twice as much food and useful trace elements. A trimester approach to nutrition and fortification meets the needs of mother and child in a certain period. Each stage of fetal development is a separate physiological process that requires different elements.
Each stage of fetal development is a separate physiological process that requires different elements.
1st trimester: the beginning of the formation of the embryo
During the first three months of pregnancy, the placenta is still absent or incompletely formed, which is an important factor for prescribing micronutrients. During this period, it is dangerous to exceed the norm of vitamin A, C, copper and iron. Consumption of excess doses of vitamin A in the early stages of pregnancy can lead to fetal malformations. Vitamin C, as a rule, is not prescribed separately in the first months, and already in the 2nd and 3rd trimester the dose is gradually increased. nine0003
Vitamins for pregnant women in the 1st trimester should help the expectant mother feel good. For example, the need for vitamin B6 (pyridoxal phosphate) is due to toxicosis. Taking B6 at a rate of 10 mg per day can reduce vomiting and help a woman to endure the first three months more easily. In addition, a deficiency of pyridoxine leads to further dental caries in a child.
The weight of the embryo in the first 3 months reaches 23 grams, but during this period the main elements of the fetus develop. This formation process requires a slight increase in vitamins Bc, B12 and zinc. Intensive cell growth is provided by folic acid (BC), additional micronutrient intake is the prevention of birth defects. Vitamin B12, like folic acid, is involved in cell division and is especially important from weeks 1 to 13. The need for B12 increases as the fetus grows. Zinc is needed in the period of preparation for pregnancy and in the first three months, as it is a key element for the work of more than 500 enzymes. nine0003
During the first three months, the fetus develops a brainstem and general architecture of the brain, which requires a sufficient amount of iodine. It is important at all stages of pregnancy, including preparation for conception. Iodine deficiency reduces fertility and increases the risk of perinatal mortality. The daily norm in the 1st trimester is 200-250 micrograms of iodine - this dose should be adjusted in case of a serious trace element deficiency.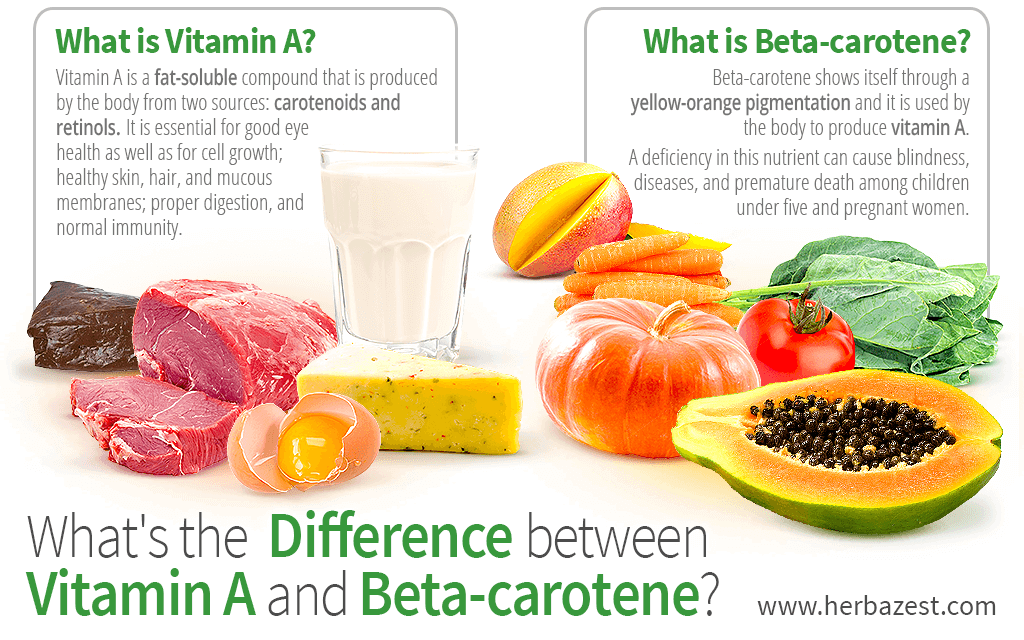
The beginning of the formation of cartilage and bone tissue requires a slight increase in the dose of magnesium. Magnesium intake increases to 360-400 mg per day and ensures normal uterine tone and promotes good sleep for the mother. In addition, magnesium helps reduce cramps and improves mood. nine0003
Summing up, the complex of vitamins for pregnant women in the first three months should include: magnesium, iodine, zinc and vitamins Bs, B6, B12. This set of micronutrients ensures the initial development of the fetus and supports the mother's body in the early stages of pregnancy.
2nd trimester: intensive fetal growth
The next three months of pregnancy are very dynamic, both for the fetus and the mother. Vitamins for pregnant women in the 2nd trimester should ensure the active growth of the child, a sufficient amount of hormones and cover the mother's need for nutrients. nine0002 After the 13th week of pregnancy, it is already safe to prescribe minimal doses of vitamins A, C and D. Vitamin A at this stage is needed for weight gain of the fetus and detailing of external structures, development of cartilage and bone tissues, appearance and development of the lymphatic system. As a rule, with a lack of vitamin A in the second trimester, it is prescribed no more than 770 mcg per day. During this period, a deficiency is still not as dangerous as an excess of vitamin A. Vitamins C, E and D are necessary for the mother to support the body during the period of active development of the fetus, but their dose, as a rule, remains normal or slightly increased to prevent their excess. nine0003
Vitamin A at this stage is needed for weight gain of the fetus and detailing of external structures, development of cartilage and bone tissues, appearance and development of the lymphatic system. As a rule, with a lack of vitamin A in the second trimester, it is prescribed no more than 770 mcg per day. During this period, a deficiency is still not as dangerous as an excess of vitamin A. Vitamins C, E and D are necessary for the mother to support the body during the period of active development of the fetus, but their dose, as a rule, remains normal or slightly increased to prevent their excess. nine0003 B vitamins are actively involved in the development of the fetus and changes in the mother's body. They are involved in weight gain, the formation of the external structures of the baby's body, the development of white matter. Another important function of B vitamins is to help increase maternal estrogen levels. Vitamin B1 (thiamine) is necessary for a woman starting from the 2nd trimester and its need increases towards the end of pregnancy. The normal dose of thiamine begins to increase during this period by 16%-20%. At 9-15 weeks of gestation, the need for vitamin B2 and PP (B3) slightly increases for the formation of the placenta. After the 1st trimester, vitamin B12 deficiency may begin to appear, and in the second trimester they are provided by the mother's body, as a rule, hepatoprotectors. But taking cyanocobalamin will be useless if a pregnant woman does not consume animal protein, the best absorption of B12 shows when eating liver and red meat. Vitamins B5 and B6 in the second trimester are important, but, as a rule, their daily dose should not be much higher than the norm, and closer to childbirth, the dose can be increased if there is a deficiency. nine0003
The normal dose of thiamine begins to increase during this period by 16%-20%. At 9-15 weeks of gestation, the need for vitamin B2 and PP (B3) slightly increases for the formation of the placenta. After the 1st trimester, vitamin B12 deficiency may begin to appear, and in the second trimester they are provided by the mother's body, as a rule, hepatoprotectors. But taking cyanocobalamin will be useless if a pregnant woman does not consume animal protein, the best absorption of B12 shows when eating liver and red meat. Vitamins B5 and B6 in the second trimester are important, but, as a rule, their daily dose should not be much higher than the norm, and closer to childbirth, the dose can be increased if there is a deficiency. nine0003
The complex of vitamins for pregnant women 2nd trimester should contain vitamins A, B, C, D, E without a significant increase in the norm. These elements are important, but should not be in excess. It is important to understand that taking pharmaceuticals is not a substitute for proper nutrition.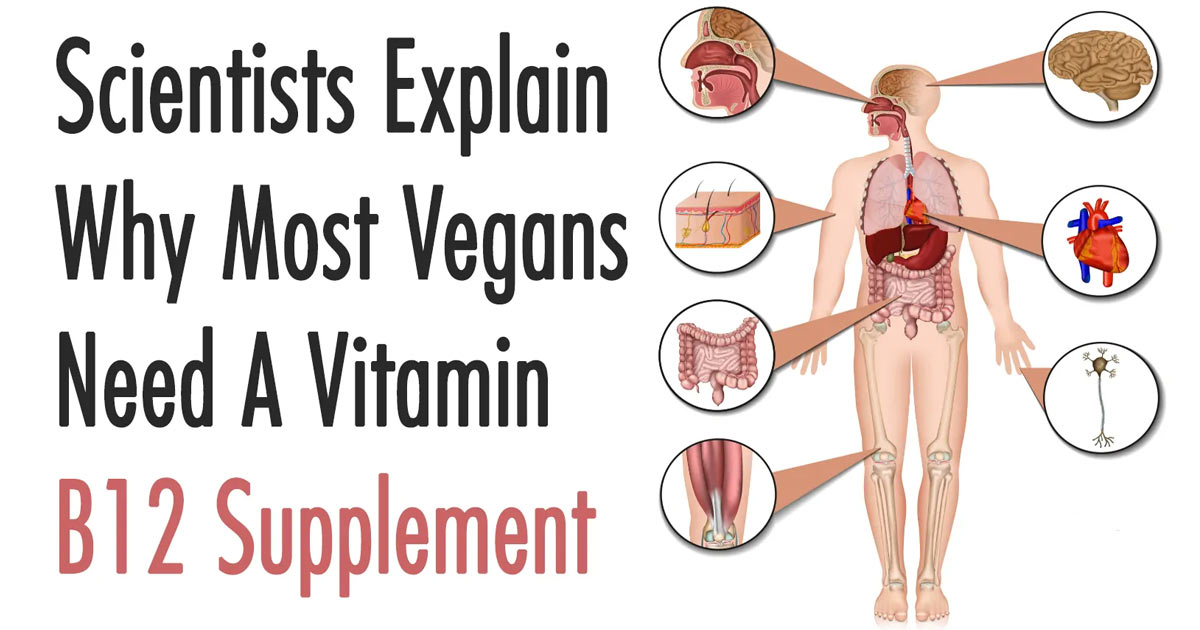 The diet or diet should be adjusted by the doctor, based on the results of the tests. The intake of additional vitamins should be confirmed by a deficiency, and not by the desire of the pregnant woman. An excess of most elements can adversely affect the development of the fetus and the health of the woman. An example of an overabundance would be the displacement of vitamin K by excessive intake of vitamin E, which provokes the risk of bleeding. nine0003
The diet or diet should be adjusted by the doctor, based on the results of the tests. The intake of additional vitamins should be confirmed by a deficiency, and not by the desire of the pregnant woman. An excess of most elements can adversely affect the development of the fetus and the health of the woman. An example of an overabundance would be the displacement of vitamin K by excessive intake of vitamin E, which provokes the risk of bleeding. nine0003
Important elements during the 2nd trimester are iron, manganese, magnesium, selenium, copper, zinc. They are involved in the formation of external and internal structures of the body. Doses may be slightly increased, but a serious excess of the norm can be prescribed on the basis of tests.
3rd trimester: preparation for childbirth
Vitamins for pregnant women for the 3rd trimester are significantly different from the first two periods. Before childbirth, the need for choline and cysteine increases. The consumption rate can increase by almost 2 times. But the results of the tests still remain the reasons for increasing the dose. nine0003
But the results of the tests still remain the reasons for increasing the dose. nine0003
Intensive development of the nervous system and brain requires a slight increase in the intake of B vitamins, except for B6 and folic acid.
During the third trimester, the active intrauterine growth of the child increases the load on the internal organs of the mother, especially on the urinary system and hormone-producing organs. Support will be provided by iron, vitamin E, selenium, lutein, B vitamins.
Preparation for childbirth is necessarily accompanied by a control blood donation for deficiencies. Usually, third trimester prenatal vitamins do not contain folic acid, vitamin B6, rutoside, iodine, and magnesium. The lack of these elements may appear in the first trimester, and later they should be enough with a normal diet and lifestyle. Other vitamins and minerals can be prescribed individually or in combination. nine0003
Vitamins of different groups are essential for the healthy development of the fetus. The proportions and doses are very different, this is due not only to individual characteristics, but also to the methods of absorption, solubility and availability of vitamins. Some vitamins are easy to get through food, others are absorbed in combination with certain foods, and the concentration of others is difficult to obtain without additional pharmacological products.
The proportions and doses are very different, this is due not only to individual characteristics, but also to the methods of absorption, solubility and availability of vitamins. Some vitamins are easy to get through food, others are absorbed in combination with certain foods, and the concentration of others is difficult to obtain without additional pharmacological products.
Vitamin A for pregnant women: the norm of the vitamin and what contains
Vitamin A is found in foods of animal origin (retinoids) and vegetable origin (carotenoids). The group of this vitamin is involved in many body processes, the most famous of which is associated with the visual pigment, which contains retinal (vitamin A aldehyde).
Vitamin A for pregnant women is important because of its participation in the process of growth and development of cells. In the early stages, as a rule, they are not prescribed additionally because of the danger of excess vitamin A, which has negative consequences for the fetus. The deficiency may appear in the third trimester - the active growth of the child requires the use of chemicals of the vitamin A group.
The deficiency may appear in the third trimester - the active growth of the child requires the use of chemicals of the vitamin A group.
The daily dose of vitamin A for pregnant women is 700 mcg in the first trimester and 770 mcg in the second and third trimester. The high content of retinoids in the liver - more than 6000 mcg in 80 grams of fried beef liver, even more in lamb and pork. The record content of vitamin A in cod liver is 30,000 micrograms per 100 grams of the product. Carotenoids are contained in large quantities in red sweet pepper - 2,100 mcg per 100 gr. No less useful is sweet potato - 1,000 mcg and carrots - 830 mcg per 100 g of the product. nine0003
Vitamin A is fat soluble and foods rich in this element should be consumed with vegetable or butter. When using the pharmacological form of vitamin A, it is worth noting that it is usually available in soft capsules or as a liquid oil. The usual dosage is 10,000 micrograms taken once a day. Earlier we already wrote about the dangers of vitamin A for pregnant women, so you need to take an additional drug only as directed by the doctor and after the tests. nine0003
nine0003
Vitamin B for pregnant women: the norm of the vitamin and what it contains
B vitamins for pregnant women play an important role in the development of the fetus. They take part, both in the formation of the internal organs of the embryo, and already during the growth of the fetus, the development of the nervous system. For the expectant mother, the optimal level of folic acid and vitamin B6 is important, which in the second and third trimesters are responsible for the stable growth of estrogens.
Since thiamine (vitamin B1) does not accumulate in the body, foods containing this element should be present in the diet of a pregnant woman. Vitamin B1 is found in sufficient quantities in the usual foods: fruits, eggs, cereals, liver. nine0003
Riboflavin - vitamin B2 is rapidly destroyed by high temperatures, during defrosting and from sunlight. So fresh salads, cheeses and nuts are what you need to get B2 into the body.
Record holders for the content of nicotinic acid (vitamin B3) - pumpkin seeds. The vitamin is important for the skin and protecting it from UV rays. Almonds, trout and beef liver are also rich in B3.
The vitamin is important for the skin and protecting it from UV rays. Almonds, trout and beef liver are also rich in B3.
Vitamin B12 for pregnant women is one of the most important elements. It is present in the processes of formation of the nervous system of the baby and helps the mother overcome the stresses associated with bearing a child. Cobalamin is present in animal products and is degraded by ultraviolet light and oxygen. You can get enough B12 thanks to beef liver and cheeses. nine0003
As a rule, vitamins of group B are produced in opaque jars to preserve the properties of trace elements. The storage rules usually prescribe the optimum temperature and protection from sunlight. This group of vitamins is present both in vitamin complexes and is produced in separate monodoses to prevent deficiency.
Vitamin C for pregnant women: the norm of the vitamin and what it contains
One of the controversial vitamins to take during pregnancy is vitamin C. Along with vitamin A, it is forbidden to use it in the first trimester of pregnancy. The daily dose of vitamin C for pregnant women is 85 mg. But an additional intake of ascorbic acid can only be prescribed closer to the third trimester of pregnancy. Vitamin is important for the formation of cartilage, skin and bones. Its important function is also considered to be participation in the fight against infections. nine0003
Along with vitamin A, it is forbidden to use it in the first trimester of pregnancy. The daily dose of vitamin C for pregnant women is 85 mg. But an additional intake of ascorbic acid can only be prescribed closer to the third trimester of pregnancy. Vitamin is important for the formation of cartilage, skin and bones. Its important function is also considered to be participation in the fight against infections. nine0003
Vitamin C is very important for the proper development of the fetus and the normal well-being of the pregnant woman, but high doses of ascorbic acid can cause premature birth and bleeding. This is the main reason why doctors rarely and very carefully prescribe high doses of vitamin C for pregnant women. Most often, with small deficiencies, doctors prescribe a diet with a sufficient content of the necessary products. The most elementary products cover the norm of ascorbic acid: sweet bell pepper, rose hips, parsley, kiwi, lemon, strawberries, black currants and other fruits and vegetables. nine0003
nine0003
Vitamin D for pregnant women: the norm of the vitamin and what it contains
The norm of vitamin D for pregnant women is 800-1200 IU per day, but in case of deficiency, a daily dosage of 2000 IU may be prescribed. Vitamin D deficiency in the mother's blood can negatively affect not only the development of the fetus, but also the course of pregnancy. In the third trimester, it is important to maintain optimal levels of provitamin to reduce the likelihood of preterm labor. Recent studies have shown a relationship between maternal vitamin D levels and good fetal-placenta-uterus interactions. Vitamin D is also involved in the formation of the circulatory system, bone tissue and internal organs. nine0003
Vitamin D for pregnancy can be obtained from plant and animal products. But the main formation of vitamin D occurs due to the interaction of the skin with ultraviolet rays. From April to September, exposure to the sun for 5 to 30 minutes provides minimal vitamin D synthesis.
In the autumn-winter period, doctors advise to consume fatty varieties of fish. So, 150 grams of salmon per day cover the norm of vitamin D. Dairy products contain much less vitamin in the composition, but are more affordable than expensive varieties of fish. Unfortunately, the consumption of foods with the maximum content of vitamin D does not provide the required dose for pregnant women, so doctors advise taking additional vitamin complexes or monovitamins. nine0003
Vitamin D for pregnant women is available in drops and capsules. Both options are well absorbed and have a positive effect on pregnancy. But uncontrolled intake of a vitamin is strictly prohibited - in order to start taking additional drugs, you need to find out the level of deficiency, its effect on the body and really assess the condition of the mother and child - if you can get by with a diet high in vitamin D and walks in the fresh air, then the pharmacological form is not required.
Vitamins E for pregnant women: the norm of the vitamin and what contains
Folic acid and vitamin E for pregnant women plays an important role in the development of the fetus and maintaining the well-being of the expectant mother. Vitamin E is involved in the process of moving oxygen from mother to child. He is also one of the "defenders" of the body from viruses and bacteria, being present in the immune system. For the mother's body, the vitamin E group is important because of their participation in the production of hormones and the formation of the placenta.
Vitamin E is involved in the process of moving oxygen from mother to child. He is also one of the "defenders" of the body from viruses and bacteria, being present in the immune system. For the mother's body, the vitamin E group is important because of their participation in the production of hormones and the formation of the placenta.
Tocopherol is fat-soluble, found in oils, herbs, fruits and vegetables. Vitamin E in capsules for pregnant women is prescribed individually, depending on the condition of the mother and the results of the tests. Often, an additional dose of a vitamin is prescribed in a small amount and for a short period of time. This is more of a preventive measure than a cure for the deficiency. nine0003
Foods that can meet our vitamin E intake are common in our diet: vegetable oil, almonds, broccoli, sunflower seeds, bell peppers. From more exotic products: avocado, pine nuts, Atlantic salmon. So, a spoonful of wheat germ oil covers the daily requirement of vitamin E for pregnant women. And sunflower seeds require only 50 grams per day.
And sunflower seeds require only 50 grams per day.
Vitamin E is available in capsules for pregnant women, the dosage of the drug is usually 400 IU. The liquid in the capsule can be used as a regular tablet, as well as for skin and hair care. For cosmetic purposes, the oily liquid is added to creams, lotions, shampoos and hair masks. nine0003
The best prenatal vitamins have three main indicators:
- state certification;
- tight, high-quality and suitable packaging;
- high dosage element.
Vitamins for pregnant women: TOP 10
- VITAMIN D2000 caps No. 60
Polish-made mono-preparation with a high content of vitamin D is the leader of our sales - and for good reason! One capsule per day covers deficiencies during pregnancy and during illness. The drug is prescribed in the second or third trimester of pregnancy, one capsule per day. nine0012 - VITAMIN C 500 SR WELLCAPS No. 60
Monovitamin C 500 SR WELLCAPS is usually prescribed in the third trimester of pregnancy for severe indications of vitamin C deficiency or during the struggle with respiratory diseases. The dietary supplement contains extracts of rose hips with sustained release micropellets.
The dietary supplement contains extracts of rose hips with sustained release micropellets. - FOLIC ACID tab. N100 fl.
Folic acid Country Life is available in a dosage of 400 micrograms (the norm for pregnant women is 600 micrograms) and is an additional drug during planning and early pregnancy. Reception is carried out after meals and the vitamin is not a substitute for the diet, but is prescribed to help the mother's body. nine0012 - NOW B-50 COMPLEX CNS Support Capsule #30 (NAU)
Nervous System B vitamins to help build your baby's nervous system. Quality Nau Foods vitamins are popular among women in the second and third trimesters of pregnancy. - NOW VITAMIN A 10,000 IU Softgels #30 (NAU)
Inexpensive but high-quality remedy for vitamin A deficiency during pregnancy. It is worth noting that the drug is prescribed exclusively in late pregnancy and always under the strict supervision of a doctor. nine0012
nine0012 - Metagenics VITAMIN D 3000 IU tablets #168
Metagenics Vitamin D is a high quality product to cover deficiencies during fetal development. A safe remedy for a serious vitamin deficiency with a dosage of 3000 units. - FERTILOVIT OMEGA-3/ Fertilovit Omega-3 caps. №30
Fertilovit Omega-3 complex tops the rating of vitamins for pregnant women. The drug is prescribed, both when planning pregnancy, and at any time when comprehensive support is needed for the mother's body. Fertilovit is specially designed to help the reproductive system of women. nine0012 - VITRUM PRENATAL PLUS Т.П/О No. 100
Vitrum for pregnant and lactating women includes all the necessary vitamins during the prenatal development of the child and to maintain the mother's body after childbirth. Prenatal plus is a complex for optimal maintenance of vitamin balance. - Folic acid + iodine 400 mg / 200 mg, 240 pcs.
 (The Nutri Store)
(The Nutri Store)
A beneficial combination of folic acid and iodine is suitable for pregnant women. Vitamin complex Nutri Store covers the daily intake of iodine and folic acid, but does not replace a good diet. May be prescribed during the first trimester of pregnancy. nine0012 - MEGAN / MEGAN caps. #30
Megan's specially formulated Pregnancy Complex contains the most important vitamins and minerals for healthy fetal development. High-quality Italian-made vitamins fully cover the need for vitamin D and provide the body with a norm of iodine, B vitamins, zinc and other important components.
Vitamin B12 deficiency during pregnancy as a consequence of type 2 diabetes in infants
August 27, 2018
According to a study presented at the annual meeting of the Society of Endocrinologists in Brighton, vitamin B12 deficiency during pregnancy can cause a child to develop type 2 diabetes.
As you know, vitamin B12 (cyanocobalamin) is found in animal products, including fish, meat, poultry, eggs and milk. Accordingly, the risk groups are starving people and vegetarians. Also, mothers with low levels of cyanocobalamin had a low body mass index (BMI) and a chance of having an underweight baby with high cholesterol. In addition to the above, high insulin resistance was observed in newborns, which is one of the risk factors for developing type 2 diabetes. nine0003
Accordingly, the risk groups are starving people and vegetarians. Also, mothers with low levels of cyanocobalamin had a low body mass index (BMI) and a chance of having an underweight baby with high cholesterol. In addition to the above, high insulin resistance was observed in newborns, which is one of the risk factors for developing type 2 diabetes. nine0003
A study conducted at the University of Warwick School of Medicine (Coventry, UK) showed that changes associated with vitamin B12 deficiency may be the result of abnormal levels of the hormone leptin. Leptin is synthesized by fat cells of the body and is actively involved in energy metabolism and the regulation of hunger. Obesity is directly related to a violation of the metabolism of this hormone. It is believed that in this case, the standard mechanism of dependence of hunger on the level of leptin fails. The brain simply does not notice this hormone and the mechanism of "sharp starvation" is activated. So high levels of leptin in obesity and increased insulin resistance in combination lead to the development of type 2 diabetes. nine0003
nine0003
Researcher Ponnusami Saravanan says that the processes occurring in the mother's body affect the health of the child. Children whose mothers suffered from vitamin B12 deficiency had elevated levels of leptin, which contributed to an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
But how exactly is an increase in leptin concentration associated with the development of type 2 diabetes? There are two scenarios. The essence of the first mechanism is an increase in the level of leptin, due to a low concentration of cyanocobalamin and the subsequent accumulation of fat cells in the fetus. The second mechanism is the rearrangement of placental genes responsible for leptin production caused by low levels of B12. Since cyanocobalamin is involved in methylation reactions, the second option associated with the inclusion and exclusion of genes is most likely. nine0003
Expert opinion: is the first study to report a possible association between maternal vitamin B12 deficiency during pregnancy and increased leptin levels in infants.