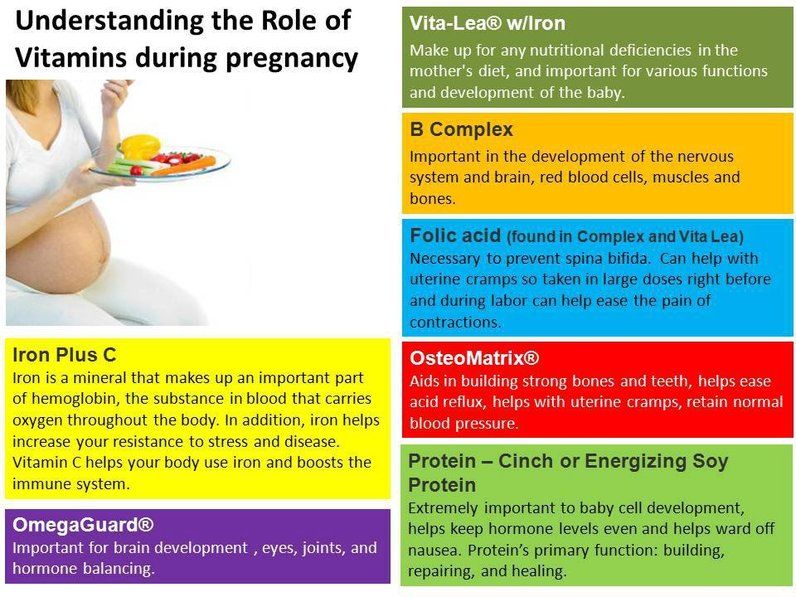
Importance of folic acid for pregnancy
Folic Acid | CDC
CDC urges all women of reproductive age to take 400 micrograms (mcg) of folic acid each day, in addition to consuming food with folate from a varied diet, to help prevent some major birth defects of the baby’s brain (anencephaly) and spine (spina bifida).
About folic acid
Folic acid is a B vitamin. Our bodies use it to make new cells. Think about the skin, hair, and nails. These–and other parts of the body – make new cells each day. Folic acid is the synthetic (that is, not generally occurring naturally) form of folate used in supplements and in fortified foods such as rice, pasta, bread, and some breakfast cereals
Why folic acid is important before and during pregnancy
When the baby is developing early during pregnancy, folic acid helps form the neural tube. Folic acid is very important because it can help prevent some major birth defects of the baby’s brain (anencephaly) and spine (spina bifida). The neural tube forms the early brain and spine.
Women of reproductive age need 400 mcg of folic acid every day
- All women of reproductive age should get 400 mcg of folic acid every day to get enough folic acid to help prevent some birth defects because
- About half of U.S. pregnancies are unplanned, and
- Major birth defects of the baby’s brain or spine occur very early in pregnancy (3-4 weeks after conception), before most women know they are pregnant.
- When taking folic acid, a higher dose than 400 mcg of folic acid each day is not necessarily better to prevent neural tube defects, unless a doctor recommends taking more due to other health conditions.
- When planning to become pregnant, women who have already had a pregnancy affected by a neural tube defect should consult with their healthcare provider. CDC recommends that these women consume 4,000 mcg of folic acid each day one month before becoming pregnant and through the first 3 months of pregnancy.

- When planning to become pregnant, women who have already had a pregnancy affected by a neural tube defect should consult with their healthcare provider. CDC recommends that these women consume 4,000 mcg of folic acid each day one month before becoming pregnant and through the first 3 months of pregnancy.
Learn more about CDC’s folic acid recommendations here.
Learn more about the recommended intake level of folic acid here.
When to start taking folic acid
Every woman of reproductive age needs to get folic acid every day, whether she is planning to get pregnant or not, to help make new cells.
Are folate and folic acid the same thing?
The terms “folate” and “folic acid” are often used interchangeably, even though they are different. Folate is a general term to describe many different types of vitamin B9.
Types of folate can include
- Dihydrofolate (DHF)
- Tetrahydrofolate (THF)
- 5, 10-methylenetetrahydrofolate (5, 10-Methylene-THF)
- 5-methyltetrahydrofolate (5-Methyl-THF or 5-MTHF)
Food fortification is a way to add vitamins or minerals, or both, to foods. Some rice, pasta, bread, and breakfast cereals are fortified with folic acid. These foods are labeled “enriched.” Folic acid is a specific type of folate that does not generally occur naturally.
Folic acid is the ideal form of folate to use for food fortification. It is more stable than types of natural food folate, which can easily be broken down by heat and light. Folic acid is better suited for food fortification because many fortified products, such as bread and pasta, are cooked.6
CDC recommends that women of reproductive age who could become pregnant consume at least 400 micrograms (mcg) of folic acid every day. However, it’s difficult to get 400 mcg of folic acid through diet alone. You can get 400 mcg of folic acid each day by taking a vitamin with folic acid in it, eating fortified foods, or a combination of the two, in addition to consuming a balanced diet rich in natural food folate.
How to get enough folic acid to prevent neural tube defects
In addition to eating foods with folate from a varied diet, women can get folic acid from
- Taking a vitamin that has folic acid in it:
- Most vitamins sold in the United States have the recommended daily amount of folic acid (400 mcg) that women need for the prevention of neural tube defects.
 Vitamins can be found at most local pharmacy, grocery, or discount stores.
Vitamins can be found at most local pharmacy, grocery, or discount stores.
- Most vitamins sold in the United States have the recommended daily amount of folic acid (400 mcg) that women need for the prevention of neural tube defects.
- Eating fortified foods:
- You can find folic acid in some breads, breakfast cereals, and corn masa flour.
- Getting a combination of the two: taking a vitamin that has folic acid in it and eating fortified foods.
If taking folic acid for reasons other than neural tube defect prevention, talk to your healthcare provider.
Learn more about where to find folic acid in the United States here.
More Information
For more information, visit the Frequently Asked Questions page.
You can also contact CDC-INFO in English or Spanish:
- 1-800-CDC-INFO (800-232-4636)
- TTY: 1-888-232-6348
- In English
- en español
Folic Acid Benefits in Pregnancy
Written by Stephanie Watson
In this Article
- What Is Folic Acid?
- When Should I Start Taking Folic Acid?
- How Much Folic Acid Should I Take?
- What Are the Benefits of Folic Acid?
- Good Food Sources of Folic Acid
Folic acid is a pregnancy superhero! Taking a prenatal vitamin with the recommended 400 micrograms (mcg) of folic acid before and during pregnancy can help prevent birth defects of your baby's brain and spinal cord. Take it every day and go ahead and have a bowl of fortified cereal, too.
Take it every day and go ahead and have a bowl of fortified cereal, too.
What Is Folic Acid?
Folic acid is a man-made form of a B vitamin called folate. Folate plays an important role in the production of red blood cells and helps your baby's neural tube develop into their brain and spinal cord. The best food sources of folic acid are fortified cereals. Folate is found naturally in dark green vegetables and citrus fruits.
When Should I Start Taking Folic Acid?
Birth defects occur within the first 3-4 weeks of pregnancy. So it's important to have folate in your system during those early stages when your baby's brain and spinal cord are developing.
If you talked to your doctor when you were trying to conceive, they probably told you to start taking a prenatal vitamin with folic acid. One study showed that women who took folic acid for at least a year before getting pregnant cut their chances of delivering early by 50% or more.
The CDC recommends that you start taking folic acid every day for at least a month before you become pregnant, and every day while you are pregnant. However, the CDC also recommends that all women of childbearing age take folic acid every day. So you'd be fine to start taking it even earlier.
However, the CDC also recommends that all women of childbearing age take folic acid every day. So you'd be fine to start taking it even earlier.
If you picked out your own prenatal vitamin, take it to your OB once you're pregnant to make sure it has the recommended amounts of everything you need, including folic acid. All prenatal vitamins are not the same and some may have less or more of the vitamins and minerals you need.
How Much Folic Acid Should I Take?
The recommended dose for all women of childbearing age is 400 mcg of folate each day. If you take a multivitamin every day, check to see if it has the recommended amount. If for some reason you don't want to take a multivitamin, you can take folic acid supplements.
Here's how much folic acid is recommended each day in terms of pregnancy:
- While you're trying to conceive: 400 mcg
- For the first three months of pregnancy: 400 mcg
- For months four to nine of pregnancy: 600 mcg
- While breastfeeding: 500 mcg
What Are the Benefits of Folic Acid?
Without enough folic acid in your body, your baby's neural tube may not close correctly and they could develop health problems called neural tube defects.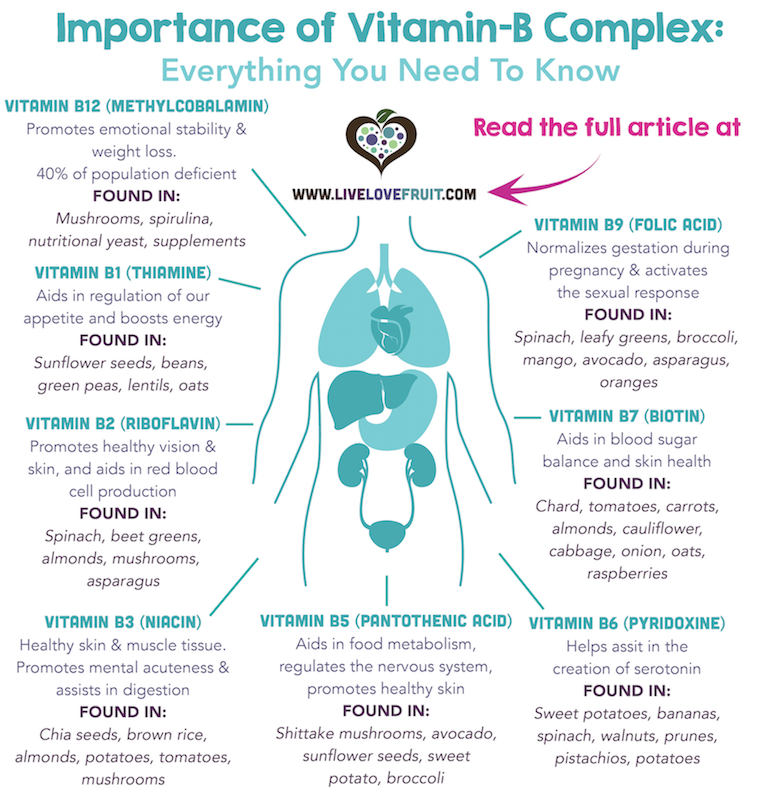 These include:
These include:
- Spina bifida: incomplete development of the spinal cord or the vertebrae
- Anencephaly: incomplete development of major parts of the brain
Babies with anencephaly usually do not live long, and those with spina bifida may be permanently disabled. These are scary problems, to say the least. But the good news is that getting enough folic acid may protect your baby from neural tube defects by at least 50%. According to the CDC, if you've already had a baby with a neural tube defect, getting enough folic acid may reduce your risk of having another child with a neural tube defect by as much as 70%. If you have had a previous child with a neural tube defect, tit is recommended that you increase your daily amount of folic acid to 4000 mcg (same as 4 mg) each day. Check with your doctor about how much you should take.
When taken before and during pregnancy, folic acid may also protect your baby against:
- Cleft lip and palate
- Premature birth
- Low birth weight
- Miscarriage
- Poor growth in the womb
Folic acid has also been suggested to reduce your risk of:
- Pregnancy complications (One report found that women who took folic acid supplements during the second trimester had a reduced risk of preeclampsia.
 )
) - Heart disease
- Stroke
- Some types of cancers
- Alzheimer’s disease
Good Food Sources of Folic Acid
Foods that can help you get more folic acid in your diet include:
- 400 mcg: Breakfast cereals fortified with 100% of the DV, 3/4 cup
- 215 mcg: Beef liver, cooked, braised, 3 oz
- 179 mcg: Lentils, mature seeds, cooked, boiled, 1/2 cup
- 115 mcg: Spinach, frozen, cooked, boiled, 1/2 cup
- 110 mcg: Egg noodles, enriched, cooked, 1/2 cup
- 100 mcg: Breakfast cereals, fortified with 25% of the DV, 3/4 cup
- 90 mcg: Great Northern beans, boiled, 1/2 cup
what you need to know, why you need it during pregnancy
In 1931, the English physician and scientist Lucy Wills decided to prescribe brewer's yeast extract to pregnant women with anemia. After a short time, the condition of the patients improved markedly. Scientists have long tried to understand what kind of healing component helped them.
Thanks to the improvement of technologies for extraction and isolation of substances in the form of crystals, it was possible to identify the secret component. In 1941, a team of scientists led by Professor Mitchell managed to get what they were looking for from spinach leaves. It turned out that this is an organic acid, which was called folic acid (from the Latin folium - "leaf"). nine0003
What you need to know about folic acid
Folic acid (or vitamin B9) is a water-soluble vitamin that is essential for many vital processes. Bacteria synthesize it in small amounts in the body, but most of it comes from food. These are leafy vegetables, seaweed, nuts, sunflower seeds, etc.
Among the main functions of folic acid are:
- participation in the processes of cell division during the period of active growth and development in childhood and adolescence; nine0014
- participation in DNA synthesis;
- stimulation of hematopoiesis;
- participation in metabolic processes.

Help: what are water-soluble and fat-soluble vitamins
Water-soluble vitamins are eliminated from the body naturally within a few hours. Therefore, you need to use them regularly. As for fat-soluble ones, they can be deposited, for example, in the liver. Among these are vitamins A, E, K, D.
Benefits of folic acid for women
For a woman, folic acid is one of the essential components to maintain youth. Sufficient consumption of this vitamin promotes tissue regeneration, maintaining skin firmness and elasticity.
B9 is also essential for successful conception. He takes part in the maturation of female germ cells (oocytes), implantation and the formation of the placenta.
Important! Folic acid isn't just for women. Vitamin B9takes an active part in spermatogenesis - the formation of male germ cells (spermatozoa). Therefore, for successful conception, both partners need a sufficient level of its consumption. It's over 200 micrograms. per day.
per day.
Why folic acid is so important during pregnancy
Pregnant women need more vitamin B9. The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends taking at least 400 micrograms of folic acid per day during pregnancy. This is most important in the first trimester, when the organs of the future baby are laid. For their development, it is necessary to ensure intensive cell division, which requires a large amount of folate. This is especially true of the neural tube of the fetus, from which the brain and spinal cord are then formed. nine0003
Lack of vitamin B9 in the diet can lead to serious adverse effects on the fetus, including:
- malformations of the nervous system;
- heart defects;
- increased risk of developing Down syndrome;
- vascular disorders.
Taking folic acid (and other vitamins and minerals) in the first half of pregnancy is also justified by the woman's relatively poor appetite. This happens against the background of toxicosis. Due to malnutrition, there is a shortage of biologically active substances necessary for mother and fetus. nine0003
Due to malnutrition, there is a shortage of biologically active substances necessary for mother and fetus. nine0003
Note that a pregnant woman needs not only folic acid, but also other B vitamins (B1, B2, B6, B12), vitamins A, D, E, C, biotin and minerals. Therefore, expectant mothers are often prescribed special complexes, for example, Elevit *, Complivit, Multi-tabs and others. Such preparations contain several vitamins and minerals at once, which are necessary for maintaining a healthy pregnancy. Folic acid is also available separately, mainly in the form of tablets - Foliber, Folacin and others. nine0003
Folic acid intake during pregnancy and lactation is important to coordinate with your doctor, who will determine the need for prescribing the drug and dosage. The drug is contraindicated in the absence of an established deficiency of vitamin B9, individual intolerance, malignant tumors, as well as pernicious anemia without additional intake of vitamin B12.
*dietary supplement. Not a drug
Not a drug
Folic acid for pregnancy planning
Our services
Surrogate mothers are urgently needed.
Requirements: physical and mental health, presence of own children is obligatory, age up to 35 years. For all questions, please contact:
8(495)2235324, 8(926)0423057
home » About clinic » Folic acid when planning a pregnancy
Any woman who plans to soon become pregnant and become a mother should consciously and carefully prepare for this new status. And if everyone knows about a healthy lifestyle, parting with bad habits and walking in the fresh air, then expectant mothers often ignore the intake of certain vitamins and medicines before pregnancy. One such remedy is folic acid. nine0003
What is folic acid?
Folic acid is vitamin B9. Often you can hear the generalized name - folates, they are derivatives of this vitamin. We must understand that we get them from food, and folic acid tablets are a synthetic agent that is already converted into folates inside the body.
All derivatives of vitamin B9 play an important role in hematopoiesis, that is, the formation of new blood cells. Therefore, the lack of these substances leads to anemia - a condition in which there are not enough red blood cells, or they are irregular in shape and do not perform their functions. Folates have another very important feature: they stimulate the formation of nucleic acids (DNA and RNA), which are the basis of all body cells. Therefore, it is folic acid that is necessary for all rapidly dividing human tissues, including embryonic tissues. nine0003
The role of folic acid:
- is involved in the formation of DNA in all cells, that is, the source of hereditary information;
- stimulates hematopoiesis;
- indirectly blocks the formation of cancer cells;
- restores muscle tissue;
- during pregnancy: plays a role in the formation and development of the nervous tissue of the fetus, participates in the formation of placental vessels.

Why do you need folate during pregnancy? nine0007
During pregnancy, especially in the early stages, the consumption of folate increases dramatically. All cells of the embryo are intensively dividing in order to eventually form full-fledged tissues. The nervous tissue of the future man is transformed especially quickly and difficultly. And it is she who requires a large amount of folic acid.
Folic acid deficiency during pregnancy can occur due to the following reasons:
- Inadequate dietary folate intake. nine0013 Folate malabsorption (in chronic inflammatory diseases of the stomach and intestines).
- Genetic disorders of the folate cycle. In rare cases, a woman's body lacks the necessary enzymes (MTHFR). As a result, folic acid is not converted to folates, and they do not perform the necessary functions. Intermediate metabolic products accumulate in the body, which can lead to cardiovascular diseases, tumor processes, infertility and miscarriage.
 In the presence of such a mutation, it is recommended to take folic acid derivatives, for example, Metafolin. It is absorbed faster and in greater volume. nine0014
In the presence of such a mutation, it is recommended to take folic acid derivatives, for example, Metafolin. It is absorbed faster and in greater volume. nine0014 - Taking certain anti-epilepsy drugs and hormonal drugs dramatically reduces blood folate levels:
- oral contraceptives;
- barbiturates, diphenylhydantoin;
- sulfa drugs (for example, biseptol), which inhibit the synthesis of vitamin B9 by the intestinal microflora;
- drinking alcohol also lowers their levels.
At what stage of pregnancy should I take folic acid supplements? nine0007
Folic acid intake to prevent fetal malformations should be started already at the stage of preparation for pregnancy, at least three months before the intended conception. That is why pregnancy should be planned. If conception occurred unexpectedly, then you need to start taking the drug as soon as it became known.
Reasons for taking folates at the stage of pregnancy planning:
- With an unbalanced diet, a woman can have a low level of folic acid, so it takes time to replenish her reserves.
 It usually takes three to four months. nine0014
It usually takes three to four months. nine0014 - The neural tube of the fetus is laid at such an early stage that a woman may not yet be aware of the pregnancy, especially with a long menstrual cycle.
- Folate deficiency can make pregnancy difficult.
Doctors at the Intime Family Planning Clinic give the following recommendations for taking folic acid: in most cases, three months before conception and throughout pregnancy, you need to take 400 micrograms of folic acid per day. In some cases, the dosage is advised to increase: up to 1 mg per day for epilepsy and diabetes; up to 4 mg per day if there have been children with neural tube defects in the past Increased doses of folates can only be prescribed by a doctor after a thorough examination. The dose of folic acid during pregnancy remains the same. nine0003
We wish you an easy pregnancy and healthy babies!
×
Send a request for a free consultation
We provide the first free consultation for new patients.