How to know when you can get pregnant
How to Chart Your Cycle to Know When You Can Get Pregnant
Written by Jennifer Rainey Marquez
In this Article
- Check Your Basal Body Temperature (BBT)
- Check Your Cervical Mucus
Getting pregnant is all about timing. You want to make sure the conditions are right for egg and sperm to meet. Your menstrual cycle can give you clues about when your body is ready to start the process.
The first step is to learn the days when you're most fertile. Most women have a 28-day menstrual cycle. That means you have about 6 days each month when you can get pregnant. That includes the day that one of your ovaries releases an egg, called ovulation, and the 5 days before. Having sex within that window is key. You can’t get pregnant without ovulation, and tracking your monthly periods is one way to get familiar with your body’s fertility.
To figure it out, you'll need to chart your menstrual cycle and record how long it lasts. Day 1 is the first day of your period. Since the length of your cycle can vary slightly from month to month, it's best to keep track for a few months.
Once you have an average, subtract 18 days from the length of your shortest cycle. This is the first day you're likely to be fertile. Next, subtract 11 days from the length of your longest cycle. This is the last day you're likely to be fertile. Having sex between those two dates will give you the best shot at getting pregnant.
Check Your Basal Body Temperature (BBT)
It's also a good idea to pay attention to the signs that your body is ready to ovulate. Checking your basal body temperature (BBT) is one way to do this.
The BBT is your temperature first thing in the morning. Just after you ovulate, it rises slightly -- sometimes by less than a degree -- and stays higher until your period starts. If you record your temperature every day, you can spot the subtle changes that mean one of your ovaries has released an egg.
To take your BBT, you need to:
Use a basal body thermometer. It's more sensitive than a standard one and will show temperature changes down to a fraction of a degree. You can get them at many pharmacies for less than $20.
It's more sensitive than a standard one and will show temperature changes down to a fraction of a degree. You can get them at many pharmacies for less than $20.
Take your temperature at the same time each morning. Always do it before you get out of bed. (To make it easier, keep the thermometer on your nightstand.) Even getting up to go to the bathroom can affect your body temperature. So can smoking, drinking, or getting a bad night's sleep.
Remember, your BBT won't tell you exactly when you've ovulated, and it may take a couple of months before you start to see a pattern. You're most likely to get pregnant 2 or 3 days before your ovary releases an egg, and then another 12 to 24 hours after that. When your temperature has spiked for 3 days, your chances of conceiving drop.
Check Your Cervical Mucus
The same hormones that control your menstrual cycle also affect the mucus that your cervix makes. Just before and during ovulation, the amount, color, and texture of it change to make it easier for you to get pregnant.
As your ovaries prepare to release an egg, your cervix makes more mucus. A few days before ovulation, it may be sticky and cloudy or whitish. Then, right before you ovulate, the mucus gets slippery, like egg whites. It may stretch across your fingers if you spread them apart. This stage usually lasts 3 or 4 days, which is when you're most likely to get pregnant.
To check your cervical mucus:
- Use your fingers or a tissue to check the opening of your vagina for mucus a few times a day. Make sure your hands are clean before you start. Write down whether it's cloudy and sticky or clear and slippery.
- Chart your cervical mucus changes and your basal body temperature to get a clear picture of where you are in your cycle.
Keep in mind that other things, like breastfeeding, can change your mucus. Using douches or other hygiene products can also affect it. Gynecologists usually don't recommend these products.
Right Time For Sex , When Do You Ovulate ?
When are you more likely to conceive?
We’re talking about the 'fertile window’ – the days in a woman’s menstrual cycle when pregnancy is possible. The ‘fertile window’ depends on the length of the menstrual cycle, which varies among women.
The ‘fertile window’ depends on the length of the menstrual cycle, which varies among women.
The ‘fertile window’ is the day an egg is released from the ovary (ovulation) and the five days beforehand. Having sex (intercourse) during this time gives you the best chance of getting pregnant.
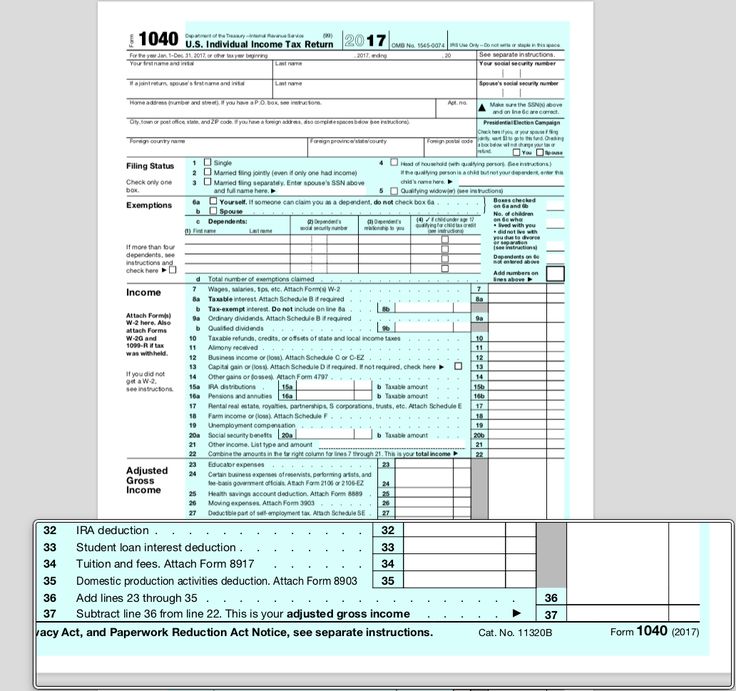
Ovulation Calculator
What day did you your most recent period start?
Number of days in your cycle Please select20 Days21 Days22 Days23 Days24 Days25 Days26 Days27 Days28 Days29 Days30 Days31 Days32 Days33 Days34 Days35 Days36 Days37 Days38 Days39 Days40 Days41 Days42 Days43 Days44 Days45 Days
Your ovulation day
Most fertile time
-
What is an ovulation calculator and how does it help you get pregnant?
This ovulation calculator or ovulation calendar can help you work out your most fertile time.
 These are the days you are most likely to get pregnant.
These are the days you are most likely to get pregnant.It can also estimate your due date if you do become pregnant during your next fertile days.
Others ways to help you work out when you're ovulating:
- Notice changes in vaginal mucus
A few days before ovulation, you may notice your vaginal mucus becomes clear, slick and slippery, and feels a bit like egg white.
This is a sign that ovulation is about to happen. It’s the best time to have sex, as sperm travel more easily in this kind of mucus.
- Use an ovulation predictor kit
You can use a predictor kit from a supermarket or pharmacy, to test your urine for signs of ovulation. If you start testing your urine a few days before the day you next expect to ovulate, a positive result means you are going to ovulate within the next 24 to 36 hours (one to two days).

-
Facts about timing
Ovulation is when a mature egg is released from the ovary. The egg then moves down the fallopian tube where it can be fertilised. If sperm are in the fallopian tube when the egg is released, there is a good chance that the egg will be fertilised, creating an embryo, which can grow into a baby.
Pregnancy is technically only possible if you have sex during the five days before ovulation or on the day of ovulation. But the most fertile days are the three days leading up to and including ovulation. Having sex during this time gives you the best chance of getting pregnant.
By 12-24 hours after ovulation, a woman is no longer able to get pregnant during that menstrual cycle because the egg is no longer in the fallopian tube.
There’s almost no chance of getting pregnant if you have sex before or after the fertile window (but if you’re not trying to get pregnant, don’t rely on this – contraception is your best option!).

-
How to know when you’re ovulating
Knowing when you ovulate can help you plan for sex at the right time and improve your chance of getting pregnant. You can keep track of your menstrual cycles on a chart, in a diary, or on a free period-tracker app on your smartphone.
To work out the length of your menstrual cycle, record the first day you start bleeding (first day of your period). This is day 1. The last day of your cycle is the day before your next period begins.
- What is a ‘menstrual cycle’ and a ‘period’?
Some people think the ‘menstrual cycle’ and a ‘period’ are the same thing.
A period is when you bleed (or menstruate).
A menstrual cycle starts on the day when a period starts (day 1) and ends the day before the next period. A cycle’s length is considered normal if it’s between 21 and 35 days. They can vary between women and from one cycle to the next.
- Working out your ‘average’ menstrual cycle length
If your menstrual cycles are different lengths (most women’s cycles are) you can work out your average cycle length.
The number of days in a woman’s menstrual cycle can vary month to month. Periods are not always regular. It can be useful to work out an ‘average’ cycle length, based on the length of three menstrual cycles, to estimate when you’re most likely to be ovulating.
If you add the number of days in three cycles and divide the total number by three, it gives you your average cycle length.
Example
Sarah tracked her last three menstrual cycles by counting the time from the first day of one period, to the day before the next period.

Cycle 1 was 28 days; Cycle 2 was 32 days; Cycle 3 was 27 days
28 + 32 + 27 = 87
87 divided by 3 = 29
So the average length of Sarah’s menstrual cycles is 29 days.
- Working out your most fertile days
When you know your average menstrual cycle length, you can work out when you ovulate.
Ovulation happens about 14 days before your period starts.
- If your average menstrual cycle is 28 days, you ovulate around day 14, and your most fertile days are days 12, 13 and 14.
- If your average menstrual cycle is 35 days ovulation happens around day 21 and your most fertile days are days 19,20 and 21.
- If you have shorter cycles, say 21 days, ovulation happens around day 7 and your most fertile days are days 5, 6 and 7.
Your most fertile days are the three days leading up to and including the day of ovulation.

Some women have very irregular cycles or find it difficult to work out an average cycle length. This can make it hard to work out when ovulation happens. If it’s all too hard, having sex every 2-3 days covers all bases and improves your chance of getting pregnant.
Myth busting
- MYTH
A woman can get pregnant any time of the month.
- FACT
A woman can only get pregnant on a few days during her menstrual cycle.
Why?
Because eggs and sperm only live for a short time:
- Sperm live for around five days.
- Eggs can only be fertilised for around 24 hours (one day) after being released from the ovary.
Eggs and sperm need to come together at the right time for fertilisation to happen to create an embryo.
Getting the timing right
If you're trying to get pregnant, timing is everything. Dr Karin Hammarberg explains how to work out when you are ovulating and the right time to have sex to improve your chance of pregnancy.
-
What are the chances?
Having sex as close as possible to the time of ovulation increases the chance of pregnancy.
If a woman has sex six or more days before she ovulates, the chance she will get pregnant is virtually zero.
If she has sex five days before she ovulates, her probability of pregnancy is about 10 percent.
If she has sex on the day of ovulation, or the two days before, the chance of getting pregnant is around 30 percent.
These are average figures and depend on a woman’s age.
When does preconception health begin?
Professor Sarah Robertson, Director of Robinson Research Institute, University of Adelaide, highlights the key time before pregnancy that your health is most important to ensure your child has the best start to life.
How to know you are ovulating
Kerry Hampton, a registered nurse and fertility specialist, discusses the importance of fertility awareness, and how to determine your fertile window to improve your chances of conceiving.
- References
- American Society for Reproductive Medicine, Optimizing natural fertility, https://www.reproductivefacts.org/news-and-publications/patient-fact-sheets-and-booklets/documents/fact-sheets-and-info-booklets/optimizing-natural-fertility/
- Berglund Scherwitzl, et al. (2015). Identification and prediction of the fertile window using Natural Cycles. The European Journal of Contraception and Reproductive Health Care, 20(5), 403-408. doi:10.3109/13625187.2014.988210
- Ecochard, R., et al. (2015). Self-identification of the clinical fertile window and the ovulation period.
 Fertility and Sterility, 103(5), 1319-1325.e1313. doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.fertnstert.2015.01.031
Fertility and Sterility, 103(5), 1319-1325.e1313. doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.fertnstert.2015.01.031 - Pfeifer, S., et al. (2017). Optimizing natural fertility: a committee opinion. Fertility and Sterility, 107(1), 52-58. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2016.09.029
- Stanford, J. B. (2015). Revisiting the fertile window. Fertility and Sterility, 103(5), 1152-1153. doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.fertnstert.2015.02.015
- Stanford, et al. (2002). Timing intercourse to achieve pregnancy: current evidence. Obstetrics and Gynecology, 100(6), 1333-1341.
- Stephenson, J., et al. (2018). Before the beginning: nutrition and lifestyle in the preconception period and its importance for future health. The Lancet, 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)30311-8 doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)30311-8
- Vélez, M. Pet al. (2015). Female exposure to phenols and phthalates and time to pregnancy: the Maternal-Infant Research on Environmental Chemicals (MIREC) Study. Fertility and Sterility.
 doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2015.01.005
doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2015.01.005 - Verón, G. L., et al. (2018). Impact of age, clinical conditions, and lifestyle on routine semen parameters and sperm kinematics. Fertility and Sterility, 110(1), 68-75.e64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fertnstert.2018.03.016
- Waylen, A. Let al. (2009). Effects of cigarette smoking upon clinical outcomes of assisted reproduction: a meta-analysis. Hum Reprod Update, 15(1), 31-44.
- Zenzes, M. T. (2000). Smoking and reproduction: gene damage to human gametes and embryos. Hum Reprod Update, 6(2), 122-131.
Page created on: 28/08/2018 | Last updated: 11/01/2023
How do I know exactly what day I got pregnant?
Many women are very concerned about this issue, because the more accurately you can determine the date of conception, the easier it will be to predict the date of birth of the baby. But is it realistic to determine the exact date of conception and how to do it? Let's find out.
But is it realistic to determine the exact date of conception and how to do it? Let's find out.
First of all, you should know that the date of conception always coincides with the date of ovulation, since the egg remains viable only for the first day after leaving the follicle. Another issue is that few women can accurately determine the day of ovulation - only ultrasound control will show this with absolute accuracy. nine0005
The second point worth knowing is that the date of sexual intercourse will not always be the date of conception. Why? Because spermatozoa remain viable in the uterus for 4-7 days, which means that pregnancy can occur even a week after sexual contact.
How then to determine the day of pregnancy? Here are some methods.
-
Early ultrasound.
If ultrasound is done for up to 7 weeks, then the date of conception can be determined most accurately, with an error of 2-3 days. During this period, the embryo develops proportionally and its size is approximately the same in all women.
 At later dates, the size of the fetus can vary greatly, so it will be almost impossible to calculate the exact day of conception. nine0005
At later dates, the size of the fetus can vary greatly, so it will be almost impossible to calculate the exact day of conception. nine0005 -
Last period.
This method is quite accurate, but only if you have a stable, regular cycle. To determine the date of birth, you need to add 280 days to the day of the last menstruation. To simplify the calculation, you can use the following formula: subtract three months from the month of the last menstruation, and add 7 days to the day of the last menstruation.
-
First fetal movement.
Not the most accurate method, but still helps to determine the approximate gestational age. Usually, women begin to feel the movement of the baby at 18-20 weeks. Thin and multiparous women can feel the movement of the fetus as early as 16 weeks. nine0005
So, as you can see, the most reliable ways to determine the exact date of pregnancy is the day of ovulation and ultrasound in the early stages. That is why it is important not to delay with an ultrasound and visit a doctor as soon as possible after a positive result of a rapid pregnancy test. The best way to do this in a comfortable atmosphere is to choose our medical center. Here are friendly and highly qualified specialists who will answer all your questions.
That is why it is important not to delay with an ultrasound and visit a doctor as soon as possible after a positive result of a rapid pregnancy test. The best way to do this in a comfortable atmosphere is to choose our medical center. Here are friendly and highly qualified specialists who will answer all your questions.
Share
To get the consultation
Current
November 24, 2022
What is a woman entitled to in a maternity hospital?
It just so happens that the rights of ordinary citizens are not taught in medical institutions, therefore, in order to achieve respect for these rights, you need to know about them in advance.
November 22, 2022
Postpartum recovery
Already in the first hours after childbirth, a restructuring begins in a woman's body, which helps to prepare for a new stage - lactation.
November 15, 2022
Cervical dysplasia
Dysplasia is a pathological change in the epithelial cells of the cervix. This process, developing from stage to stage, leads to malignant degeneration of cells.
This process, developing from stage to stage, leads to malignant degeneration of cells.
Get advice
Enter your name and contact phone number. We will call you back and schedule you at a convenient time.
Fomin's clinic — a network of multidisciplinary clinics
Today's world is full of information: literally with one click, each of us can open the Universe and learn everything - from string theory to concert posters for the next week. It is all the more interesting that, having unlimited access to knowledge, we still live in myths - and sometimes they arise, including thanks to the Internet, replicating untruth and absurdity. nine0005
We have prepared for you a short “blitz” of six questions or myths about pregnancy and conception, so that you are fully equipped and do not believe the tales on the Internet.
Well... not exactly. Firstly, the idea of a “full examination” is a clear exaggeration, because there is no single list of tests that an expectant mother needs to pass. Ideally, visit a doctor three months before the end of contraception, get tested for STIs and antibodies to rubella. If additional examinations are required, you will be individually prescribed everything you need - including, probably, vaccinations that should be “updated”. As for alcohol and smoking, they are really contraindicated at the stage of pregnancy planning, so if you have these addictions, you will have to give them up. However, it should be remembered that smoking cessation applies to both electronic cigarettes and “passive smoking”, which can lead to dangerous consequences for the fetus. nine0005
Ideally, visit a doctor three months before the end of contraception, get tested for STIs and antibodies to rubella. If additional examinations are required, you will be individually prescribed everything you need - including, probably, vaccinations that should be “updated”. As for alcohol and smoking, they are really contraindicated at the stage of pregnancy planning, so if you have these addictions, you will have to give them up. However, it should be remembered that smoking cessation applies to both electronic cigarettes and “passive smoking”, which can lead to dangerous consequences for the fetus. nine0005
Spoiler: no big deal. Do not panic and blame yourself for all mortal sins because of a glass of wine. With the recognized insecurity of alcohol, scientists have proven that a woman drinking 1-2 servings a couple of times a week should not harm the unborn child. For men, the allowable figures are slightly higher - 3-4 doses of alcohol per week. The main thing is to know the measure and not to overdo it.
The main thing is to know the measure and not to overdo it.
There is, of course, a simplified formula for calculating the estimated due date: plus 7 days and minus 3 months from the date of the last period, but to be honest, it doesn’t work like that: the fact is that it is very difficult to “program” pregnancy and make sure that the child is born when you want. If you have a plan and are going to stick to it, be prepared for the fact that things can go wrong, if only because:
- the duration of pregnancy is not 40 weeks, but 37-42 weeks, which means that you can easily fall into a five-week “loop”, which will reduce the chances of fulfilling the plan to zero;
- with regular sex, the probability of conception is not 1 time per month (exactly when you guessed it), but 1 time per year.
Nothing is impossible... However, it is worth clarifying the question a little: you can get pregnant only during ovulation (more precisely, shortly after it), but you can have sex, which will lead to a long-awaited pregnancy, on different days. Of course, on the days of menstruation, the probability is lower than on the days that precede ovulation, but on none of the days of the menstrual cycle this probability is not zero. nine0005
Of course, on the days of menstruation, the probability is lower than on the days that precede ovulation, but on none of the days of the menstrual cycle this probability is not zero. nine0005
Let's just say that trying multiple times a day is a bad idea. Why? At least because ejaculation more than once a day worsens the quality of sperm, as a maximum - such perseverance and zeal can create tension in the relationship of partners. Doctors advise to have sex every 2-3 days throughout the cycle, and not try to guess the moment and throw all your strength into this short period.
Planning the sex of a child is an extremely prolific topic for myth-makers. Some believe that with the help of a special table that takes into account such indicators as the age of the father and mother, the month of conception, it is possible to accurately calculate the sex of the child. This "method" is anti-scientific and has nothing to do with reality. nine0005
nine0005
Another myth is that to have a boy you have to get pregnant on the day you ovulate. Previously, scientists really believed that X and Y spermatozoa differ from each other (Y are faster), and the sex of the child is formed due to the first one that broke through the defenses of the female egg. If you want to conceive a boy, you need to have sex on the day of ovulation so that the Y-sperms responsible for the "male sex" have more time to get to the egg located farthest from the entrance to the uterus. nine0005
However, this myth does not hold water either: the fact is that there is no difference between the X and Y chromosomes, which means that the sex of the child does not depend on which of the sperm reaches the egg first. Moreover, not the fastest fertilizes the egg: thousands of spermatozoa simultaneously break its shell.
From this follows the conclusion: modern science does not know how to determine the sex of the child during natural conception, and therefore there is no universal recipe.