How to file for abandonment of a child in nebraska
State of Nebraska Legal Rights for Spousal Abandonment
Stockbyte/Stockbyte/Getty Images
Being abandoned by a spouse is a horrible emotional blow, and often a financial blow as well, especially if you have children. If you are a spouse who has been abandoned in the state of Nebraska, you have the right to end your marriage without having to prove abandonment in court. You also have the right to legally separate. You have the right to seek alimony and child support as well. Nebraska is a no-fault divorce state. Generally speaking, a no-fault divorce in Nebraska only requires the parties to state the marriage is "irretrievably broken" and reconciliation efforts have failed before a divorce is granted.
Abandonment Statute
Nebraska makes abandonment of a child a Class I misdemeanor punishable by a fine of $1,000, a jail sentence up to one year or both. Abandonment of a spouse is defined as a "person who abandons and neglects or refuses to maintain or provide for his or her spouse or his or her child or dependent stepchild, whether such child is born in or out of wedlock. " A child is defined as an individual under the age of 16. The neglect or abandonment must be for a period of at least three consecutive months.
Divorce
If you are abandoned, one of your legal rights is to file for divorce. Since Nebraska is a no-fault divorce state, you simply have to file a petition stating your marriage is "irretrievably broken." There is a 60-day waiting period to encourage reconciliation before the divorce is granted. If your spouse doesn't object to the divorce, it will be granted and, if he can't be located, you just have to serve legal notice at his last known place of residence.
Legal Separation
Sometimes an abandoned spouse wants the legal benefits offered by a divorce without a formal dissolution of the marriage. Often, it is out of religious conviction or to retain medical coverage under a family insurance policy. Nebraska law allows legal separations and these are designed to resolve the same issues as a divorce, including support for the abandoned spouse and children and a separation of marital assets.
Financial Issues
Financial support for you and your children will be resolved by the court in a legal separation or divorce proceeding. You can come to an agreement with the spouse who has abandoned you, or the court will resolve these issues. Financial support depends on a number of factors, such as the duration of the marriage, history of contributions to the marriage by you and your spouse, and ability of the abandoned spouse to work without harming the interests of any minor children.
Criminal Complaint
Since abandonment of a spouse or child is a crime in Nebraska, an abandoned spouse is free to file a criminal complaint with the local or state police department. In situations where the other spouse can't be easily located, involvement by the police improves the chances of tracking him or her down, which can be particularly important if you are seeking alimony or child support.
Five Key Requirements – SNC
When a parent decides that they no longer want to be responsible for their child, they may choose to sign over their parental rights. This means that the child will no longer be their legal responsibility and the other parent will gain full custody of the child. In Nebraska, there are a few specific requirements that must be met in order to sign over parental rights.
This means that the child will no longer be their legal responsibility and the other parent will gain full custody of the child. In Nebraska, there are a few specific requirements that must be met in order to sign over parental rights.
The first requirement is that the parent must be at least eighteen years old. If the parent is under eighteen, they must have the consent of their legal guardian in order to sign over their parental rights. The second requirement is that the parent must be willing to give up all legal rights to their child. This includes the right to make decisions about the child’s education, medical care, and religious upbringing.
The third requirement is that the parent must be willing to have no further contact with their child. This means that the parent will not be able to visit the child, call the child, or send the child any communication. The fourth requirement is that the parent must be willing to provide financial support for the child. This support can be in the form of child support payments or medical insurance.
The fifth and final requirement is that the parent must sign a document called a “ waiver of parental rights”. This document must be signed in the presence of a notary public and it must be filed with the court. Once the waiver of parental rights is filed, the parent will no longer have any legal rights or responsibilities to their child.
The Nebraska Supreme Court stated that no state can refuse to terminate parental rights simply because it wants to collect child support. It is illegal for parents to grant custody to an outside party without court permission. A parent may delegate legal authority to a family member or friend. As part of an adoption case, a man must sign over his parental rights.
If you want to change the terms of your current parenting plan or change the amount of time you have with your children, you must file a Complaint for Modification with your local court in Nebraska. It is critical that the other parent be notified of the complaint.
A parent has a right to raise his or her child, as well as to support him or her. If the father’s name appears on the birth certificate, his right to the child is guaranteed. A father has the right to visit with his children on a regular basis, as well as joint custody and supervised visits.
If the father’s name appears on the birth certificate, his right to the child is guaranteed. A father has the right to visit with his children on a regular basis, as well as joint custody and supervised visits.
How Do I Sign Over My Rights To My Child In Nebraska?
Credit: blogspot.com
There is no specific process in Nebraska for signing over your parental rights, but there are some general requirements that must be met. First, you must be willing and able to completely relinquish all custody and control of your child. This means that you will have no say in future decisions regarding their education, medical care, or any other aspects of their life. You also must be able to demonstrate that you have not been involved in your child’s life for an extended period of time and that it would not be in their best interests to continue a relationship with you. Finally, you must be willing to undergo a background check and have your fingerprints taken. Once these requirements are met, you can sign a document relinquishing your parental rights, which will be filed with the court.
Once these requirements are met, you can sign a document relinquishing your parental rights, which will be filed with the court.
How Do I Stop Child Support In Nebraska?
You should bring with you the following documents: Application and Affidavit to Obtain Termination of Child Support (DC 6:22) and the child support order (DC 6:22) filed in the district court clerk’s office. The waiver of the notice of termination of child support (if signed by the person receiving child support) in paragraph 6 of Delaware Code (DC) 62.1
What Are Parental Rights In Nebraska?
Credit: nebraskafamilyalliance.org
The law in Nebraska governs the division of parental property, regardless of a parent’s marital status. Children of both parents have the right to seek custody, parenting time, and child support in this situation.
You can find out what you should know about child custody in the first of a three-part series. The legal concept of best interests was explained in the first part. Five pointers were provided in Part II for developing a parenting plan. In this article, we’ll go over parental unfitness as a factor in child custody cases. It is more likely that unfitness will be discovered if the behaviors are egregious. It is unlikely that the judge will consider marital infidelity against a parent if the child is present when or has been exposed to sexual activity. There is no gender bias in Nebraska child custody decisions, according to state law.
Five pointers were provided in Part II for developing a parenting plan. In this article, we’ll go over parental unfitness as a factor in child custody cases. It is more likely that unfitness will be discovered if the behaviors are egregious. It is unlikely that the judge will consider marital infidelity against a parent if the child is present when or has been exposed to sexual activity. There is no gender bias in Nebraska child custody decisions, according to state law.
It can be difficult for people to understand Nebraska’s laws regarding parental unfitness and parental rights. To navigate this area of law successfully, you must have a certain amount of experience. If you require assistance, speak with a Reff representative. The fourth and final part of our Must-Have Information on Child Custody series will explore sole and joint custody.
When a parent is barred from being present for the child’s care, the child is likely to suffer. The child may not have a stable environment in which to grow up and may suffer from emotional and physical abuse. When children are not properly cared for, they may be more vulnerable to developmental issues.
When children are not properly cared for, they may be more vulnerable to developmental issues.
Nebraska Abolishes Preference For Mothers In Child Custody Cases
In Nebraska, there are no longer any laws that favor mothers, such as the tender years doctrine and other similar laws. In contrast to some states that have adopted a legal preference for joint custody, Nebraska law requires the court to consider the child’s best interests when determining custody.
In a child custody case in Nebraska, parental unfitness is defined as a personal deficiency or incapacity that has prevented or will almost certainly prevent, the performance of a reasonable parental obligation in the rearing of a child and, most likely, has harmed or If a father is absent from his child’s care for an extended period of time, he may lose custody.
Can You Terminate Parental Rights?
Credit: wikiHow
There are five types of parental rights that can be terminated by terminating them: abandonment, permanent neglect, mental illness, mental retardation, and severe and repetitive abuse. When a judge believes a parent cannot afford a lawyer, the parent may be entitled to a free, court-appointed attorney for the termination case.
When a judge believes a parent cannot afford a lawyer, the parent may be entitled to a free, court-appointed attorney for the termination case.
A parent’s parental rights will be terminated. The petition seeks to revoke the legal rights of the child’s parents. You must submit the petition to a social service or foster care agency that has an authorized foster parent or an authorized foster care agency. If a child has been in foster care for 15 of the previous 22 months, he or she must file an application with the ASFA.
Signing Over Parental Rights Forms Nebraska
In Nebraska, a parent may sign over their parental rights to another person or entity through a legal process called voluntary relinquishment. This may be done for a variety of reasons, such as if the parent is unable to care for the child, if the child has been placed in foster care, or if the parent is incarcerated. The relinquishment must be done through a court order, and the parent must consent to the relinquishment.
Can A Parent Voluntarily Relinquish Parental Rights In Nebraska?
When a child has been adjudicated and is seeking permanent residency, a juvenile court may order the Department of Health and Human Services to accept a voluntary relinquishment of parental rights.
How To Sign Over Your Parental Rights
Signing over your parental rights is a legal process that can be done through a family law attorney. The attorney will help you fill out the necessary paperwork and file it with the court. Once the paperwork is filed, you will need to appear in court to finalize the process.
In cases where a city agency files a petition in Family Court to terminate parental rights, parental rights are terminated as well. In most cases, you must obtain court approval before you can terminate your parental rights. If someone else wants to adopt your child, you may agree to give up parental rights. A court order can be used to terminate parental rights. A parent can sign an affidavit relinquishing parental rights as part of the voluntary relinquishment process. If a parent’s rights are terminated, he or she loses their right as a parent. The rights of parents to raise their children have been abolished.
If a parent’s rights are terminated, he or she loses their right as a parent. The rights of parents to raise their children have been abolished.
Parental rights are to be terminated only with judicial consent. Parental rights cannot be terminated without the consent of the parents, especially if the parents do not want to support their children. All actions must be taken with the consent of the parties concerned and the forms must be completed and signed. Only after parental rights have been relinquished can an adoption be completed.
When Can You Sign Over Your Parental Rights In Kentucky?
In most cases, you must first obtain court approval before you can terminate parental rights. However, courts will not grant you parental rights unless someone else, such as your ex-wife’s new husband, is willing to adopt the child for you.
What age can a child decide who to live with? Children in Kentucky are given the option of choosing their parents as young as the age of 13. Judges will continue to inquire about a younger child’s preferences, despite the fact that they don’t hear them.
Judges will continue to inquire about a younger child’s preferences, despite the fact that they don’t hear them.
Can A Parent Voluntarily Relinquish Parental Rights In Nebraska
A parent can voluntarily relinquish their parental rights in Nebraska as long as they go through the proper legal channels. This can be done by working with an attorney to file the necessary paperwork with the court. The parent must also show that they understand what they are doing and that it is in the best interests of the child.
If a father voluntarily terminates his parental right, is he still liable for child support? What could be the logical reason why someone might do such thing? There are currently 116 lawyers who are online. This information is not intended to be used for legal purposes and should not be viewed as such. This conversation has not resulted in any attorney-client relationships or privilege. If you are in need of a lawyer, AkaonCall.com connects you with one who has experience with your situation. The more you save, the less time and money you will waste.
The more you save, the less time and money you will waste.
You won’t be forced to miss time from work, incur costly consult fees, or pay for inconvenient scheduling. If you pay for JustAnswer monthly, you will save a significant amount of time and money. 593 lawyers from around the world, who have at least ten years of experience
Parental Responsibility Can Only Be Terminated By The Court
Parental responsibility can be terminated only by a court. This is usually only done when the child is adopted or when the father’s behavior warrants it. Children in Nebraska cannot refuse visitors unless they are 19 years old and legally able to do so. A judge must consider a child’s wishes in making a custody determination, but only if the child is of sufficient age and maturity and wishes to do so based on a good reason.
Can A Parent Sign Away Parental Rights
A parent may sign away their parental rights, but only under certain circumstances. A parent may not sign away their parental rights if it would be in the child’s best interest, if the child is not being adequately cared for, or if the parent is unable to care for the child.
If you want to stop child support, you can by a simple act of signing away parental rights. Breeden Law Office. Despite the fact that people are unable to become stable parents in North Carolina, the state recognizes their right. If this is the case, the court may have the authority to terminate your parental rights for an indefinite period of time. If a court finds you to be physically dangerous or harmful to the child’s well-being, your rights may be terminated. Furthermore, you lose your legal rights to care for your child once you are terminated. It’s like you and your child are strangers again when the child’s child support obligation is removed.
New York State Courts Can Terminate Parental Rights Based On Abandonment
In New York, parental rights can be terminated based on an abandonment claim if the parent fails to maintain contact with the child for at least 12 months and fails to make reasonable plans for the child’s future. It must have occurred within the last six months.
Petition To Terminate Parental Rights
The use of a petroleum product is prohibited. To terminate a child’s parental rights, a petition is filed, in which the legal rights of the child’s natural parents are permanently revoked. A B petition can be submitted by a foster parent or an authorized foster care or social services agency for the child.
On this page, you will find answers to the most frequently asked questions about terminating parental rights. When a parent’s rights are terminated, their rights as a parent are terminated as well. This page is only applicable to the child if he or she resides in Nevada. You should contact your local court if you want to terminate your rights. There are several different reasons why a judge may revoke a parent’s parental rights. If the child’s best interests are to be considered, it must be proven unequivocally and clearly. You have the right to file a termination request in the District Court of the county in which the child lives.
If the judge finds that the other parent is a good match, he or she will expect you to do everything you can to find them. If you do not know where the parent is, you may find it more difficult to terminate their rights. It is extremely serious to violate someone’s parental rights. There are numerous rules and procedures that must be followed in order to follow the law.
New York Penal Law: Abandoning A Child Can Lead To Jail Time
Under Section 2600.00 of the Penal Code of the State of New York, it is illegal to abandon a child. When someone is charged with caring for or holding custody of a child under the age of fourteen and is intent on abandoning that child, he or she is guilty of abandonment of a child.
An abandonment is defined by New York state law as leaving a child without the intent of returning. This offense could result in a four-year prison sentence.
In order to convict a defendant of this crime, the prosecutor must be able to prove that the defendant abandoned the child with the intent to abandon it. As a result, the defendant must have been aware that he was leaving the child and had no intention of returning.
As a result, the defendant must have been aware that he was leaving the child and had no intention of returning.
When you abandon your child, you are breaking the law. When a parent commits such a crime, he or she may be sentenced to jail and lose custody of their child. If a child is abandoned in New York state, parents should be aware of the state’s laws. If they suspect their child is at risk of being abandoned, they should contact the police or Child Welfare Services.
How Long Does A Father Have To Be Absent To Lose His Rights In Nebraska
Though there is no definitive answer to this question, in general, a father in Nebraska will lose his rights if he is absent for an extended period of time and does not maintain contact with his child. If the father is not listed on the child’s birth certificate, he may also lose his rights if he does not take steps to establish paternity.
In recent years, the role of a father in a child’s life has been a hot button topic during custody discussions. Establishing paternity is one of the first steps taken by fathers to ensure their parental rights in court. Children whose fathers are involved in their lives perform better academically and socially than children whose fathers are not. One of two methods for establishing paternity is through the Voluntary Acknowledgement of Paternity form. If parents are unable to resolve their child’s custody dispute through traditional channels, they can file a Paternity Petition through the family court system. Parental paternity can be established for a variety of reasons, the most important of which is to protect the child’s best interests. In the state of Nebraska, child custody cases are based on the child’s best interests.
Establishing paternity is one of the first steps taken by fathers to ensure their parental rights in court. Children whose fathers are involved in their lives perform better academically and socially than children whose fathers are not. One of two methods for establishing paternity is through the Voluntary Acknowledgement of Paternity form. If parents are unable to resolve their child’s custody dispute through traditional channels, they can file a Paternity Petition through the family court system. Parental paternity can be established for a variety of reasons, the most important of which is to protect the child’s best interests. In the state of Nebraska, child custody cases are based on the child’s best interests.
In Nebraska, there are several options for custody that courts must consider. If joint custody is not an option, one parent is appointed as the primary custodial parent. In such cases, the non-custodial parent is frequently ordered to pay child support in order to provide for the child’s needs.
How To File For Abandonment Of A Child In Nebraska
Abandonment is defined as a parent’s failure to maintain a normal parental relationship with their child for a period of at least six months. In order to file for abandonment, a parent must file a petition with the court and provide evidence to support their claim. The court will then determine whether or not the child has been abandoned and if so, grant the parent’s request.
In Nebraska, there is no fault divorce. If your spouse is unwilling or unable to care for you, you have the right to file for divorce. Children can be imprisoned for up to one year if they are abandoned by an adult. Abandoning a child is a Class I misdemeanor punishable by a $1,000 fine. A petition for divorce must be filed stating that the marriage is irretrievably broken, in order to proceed. It is customary for a divorce to be granted within 60 days of reconciliation. If your spouse does not object to the divorce, you will be granted one; however, if your spouse is unable to locate you, you will need to serve legal notice at his most recent address. A Nebraska husband or wife is guilty of the crime of abandoning his or her spouse.
A Nebraska husband or wife is guilty of the crime of abandoning his or her spouse.
Abandonment Of Children In Nebraska
An abandonment of a child is defined by Nebraska law as the failure by a parent to provide for or maintain a child or stepchild, as well as their own neglect. Any child who has been or is currently living in or out of wedlock can be considered. There is no law that defines child abandonment, but the State’s policy is to provide alternative protection and assistance to every child who is abandoned.
Parent Voluntarily Relinquish Parental Rights
A parent who voluntarily relinquishes parental rights is giving up all legal rights and responsibilities to their child. This includes the right to make decisions about their child’s education, healthcare, and welfare. The parent is also giving up their financial responsibility for their child.
When a parent relinquishes parental rights voluntarily, the child’s biological parents are the ones who give them up. Before an adoption can take place, the child must be legally allowed to be adopted. As a result, the legal relationship between the child’s parents and the biological parents has ended. In either case, the surrender is conditioned or irreversible. A child’s parental rights are terminated if the city files a petition in Family Court on behalf of the city claiming that a parent has failed to meet the requirements of parental responsibility. In a petition for termination, the petition must provide a legal reason for the termination. There are five legal reasons to terminate parental rights: abandonment, permanent neglect, mental illness, mental retardation, and severe and repeated abuse.
Before an adoption can take place, the child must be legally allowed to be adopted. As a result, the legal relationship between the child’s parents and the biological parents has ended. In either case, the surrender is conditioned or irreversible. A child’s parental rights are terminated if the city files a petition in Family Court on behalf of the city claiming that a parent has failed to meet the requirements of parental responsibility. In a petition for termination, the petition must provide a legal reason for the termination. There are five legal reasons to terminate parental rights: abandonment, permanent neglect, mental illness, mental retardation, and severe and repeated abuse.
How Long Does It Take To Terminate Parental Rights Ny?
It was negligent in failing to plan for the child’s future and maintain contact with him or her for at least a year. If you have abandoned the child for more than six months, he or she is legally required to do so.
Parental Rights: What To Know Before You Surrender Them
In general, if the parent agrees to relinquish their parental rights, but the child is in danger or the parent is unable to provide a safe and stable environment, their rights may be reinstated. If the surrender is unconditional, the parent will no longer have contact with the child and will be completely stripped of their rights.
If the surrender is unconditional, the parent will no longer have contact with the child and will be completely stripped of their rights.
There are a few reasons why parents might want their rights to be surrendered. They may not be capable of caring for their child anymore, or they no longer wish to be responsible for their child’s well-being. A parent who has been convicted of a crime may not want to contact their child because they fear that the criminal justice system will contact them in some way.
To relinquish parental rights, you must follow a few simple steps. To schedule an appointment to meet with an adoption agency, contact them and make an appointment. During the consultation, the agency will ask the parent questions about their child and their relationship with the child. In addition, the agency may require a parent to take a parenting course before allowing them to relinquish their parental rights.
The agency will petition the court after parental rights have been surrendered. Following that, a hearing will be held to determine if there is a case for terminating parental rights. Parents have the right to attend the hearing, but they may be unable to communicate with their child. There is no appeal after the court’s decision is final.
Following that, a hearing will be held to determine if there is a case for terminating parental rights. Parents have the right to attend the hearing, but they may be unable to communicate with their child. There is no appeal after the court’s decision is final.
When parents relinquish parental rights, they make a decision that cannot be reversed. The parents may still occasionally interact with the child, but this is up to the agency. It is critical to understand the steps that must be taken in order to surrender parental rights, which are necessary to protect the child involved and ensure a smooth transition into the adoptive family.
Can A Father Terminate His Parental Rights In Ny?
In New York, there are four legally permissible grounds for terminating parental rights. If the parent did not change his or her behavior within six months, the child has been abandoned. Because of a severe mental health condition, the parent is unable to provide for the child.
The Unmarried Mother’s Right To Refuse Visitation
Unmarried mothers in New York are given sole legal and physical custody of their children when both parents are not married. An unmarried mother has the right to visitation with her child if he is born outside of marriage. Visiting is required by law, but a child may refuse to see the judge if they do not want to.
An unmarried mother has the right to visitation with her child if he is born outside of marriage. Visiting is required by law, but a child may refuse to see the judge if they do not want to.
What Is Considered Child Abandonment In New York?
There are penalties in New York State that are determined by Section 2600.00 of the Penal Code. An abandoned child is defined as one who is not cared for. When, as a parent, guardian, or other person legally responsible for the care or custody of a child less than fourteen years old, he desertes such child in any place with the intent to abandon him, he is guilty of abandonment of a child.
The High Cost Of Divorce In New York
When your spouse abandons you for at least a year, you are considered to be abandoned in New York. If your spouse has served a prison sentence for more than three years, the divorce cannot be granted. If your spouse was released from prison more than five years ago, you cannot divorce him or her.
What Constitutes An Unfit Parent In New York?
If a parent fails to provide proper guidance, care, or support, the court can terminate the parent’s parental rights. Furthermore, if the parents have substance abuse, abuse, or neglect, the court may unfit them. In most cases, Child Welfare Services is forced to intervene once a court determines that a parent is unfit.
Furthermore, if the parents have substance abuse, abuse, or neglect, the court may unfit them. In most cases, Child Welfare Services is forced to intervene once a court determines that a parent is unfit.
When One Parent Doesn’t Want To Play Nice: How To Deal With Partial Custody
If the custodial parent and the other parent do not reach an agreement on a custody order that gives you full custody, the court may award partial custody to the other parent. A number of factors, including the child’s best interests, will be considered by the court.
Juvenile Necessary Parental Care
While all children need parental care, some children require more care than others due to their age or circumstances. Juvenile necessary parental care refers to the care that these children need in order to thrive. This care can include everything from providing a safe and nurturing home environment to ensuring that their basic needs are met. It is important for parents to be able to provide this care so that their children can grow up to be healthy and happy adults.
The Importance Of Parenting In The Development Of A Child’s Personality
According to the Nebraska Juvenile Code, a juvenile under the age of 14 is not eligible for admission to an adult jail or lookup facility. Most children who engage in criminal behavior are influenced by parents who fail to discipline them or demonstrate to them that certain actions may be detrimental. According to a study of juvenile criminals, the majority of their crimes are committed by children who have been privileged in their homes. The three essential components of parenting are care, control, and boundaries. Parents must be committed to loving, accepting, encouraging, and guiding their children so that they can grow into healthy adults. Children must be raised in a nurturing environment in order to develop their personality and identity, and parents must establish boundaries to keep their children safe.
How to abandon a child in order not to pay child support?
Russian legislation does not provide for a procedure by which it is possible to renounce paternal rights and maintenance obligations only at the father's request. And in the event that it is still possible to renounce paternity , alimony will still have to pay until the moment the child is adopted.
And in the event that it is still possible to renounce paternity , alimony will still have to pay until the moment the child is adopted.
Cancellation of child support can be by a court decision or by agreement of the parents . At the same time, it is necessary that the property interests of the child are not violated. Therefore, the cancellation procedure is controlled by the court or notary.
How is it legal not to pay child support?
5 ways not to pay child support
- Method 1. Entry into full legal capacity of a minor
- Method 2. Lump sum payment or provision of property
- Method 3. Relocation of the child to the payer of maintenance
- Method 4: Exclusion of paternity of a child
- Method 5.
Can child support be waived?
It is impossible to refuse alimony completely, but it is possible to temporarily stop paying them until the child reaches the age of majority. There are several mechanisms that allow one of the parents to be released from the obligation to pay money for the maintenance of the child.
There are several mechanisms that allow one of the parents to be released from the obligation to pay money for the maintenance of the child.
What happens if a mother writes a refusal of a child?
Abandonment of a child is equivalent to deprivation of parental rights. However, despite such a decision, the parent is not exempt from maintenance obligations.
How to formalize the abandonment of the mother's child?
Procedure refusal
One of the parents writes an application for abandonment of the child , which is certified by a notary. A sample can be found there. After this refusal is transferred to the second parent, who provides it to the guardianship authority. It is also desirable to find two witnesses who are ready to confirm the fact failure .
When can a father not pay child support?
First of all, you can stop paying alimony when the circumstances specified in the voluntary agreement occur. For example, if the child got a job or the ex-wife remarried. Not paying child support is also legally possible if the child was adopted by another man.
For example, if the child got a job or the ex-wife remarried. Not paying child support is also legally possible if the child was adopted by another man.
When does child support debt expire?
According to article 107 of the Family Code, the limitation period for maintenance debts is 3 years.
How can a mother refuse child support?
You can refuse alimony : Through the court Through a bailiff Through a notary
How can alimony debt be annulled?
Many people are worried about how to get rid of child support, but the answer is simple and unequivocal - no way. It is impossible to write off the debt - neither through the court, nor through the MFC, nor through the bailiffs. Even after the bankruptcy of , the child support debt will remain with you.
How to refuse alimony in Ukraine?
Refusal of a child is not provided for by the current legislation Ukraine . 190 UK of Ukraine spouses, with the permission of the guardianship and guardianship authority, can agree by concluding an agreement on the termination of the right to alimony for a child on the basis of transferring ownership of real estate to him.
190 UK of Ukraine spouses, with the permission of the guardianship and guardianship authority, can agree by concluding an agreement on the termination of the right to alimony for a child on the basis of transferring ownership of real estate to him.
What happens if the father writes the refusal of the child?
There is no provision in the Family Law of the Russian Federation that would provide for refusal of parents from children. If the parents refuse to do this, then the deprivation of parental rights occurs in court, and alimony is also collected for the abandoned child .
What to do when the child's father has abandoned him?
Russian legislation does not contain a procedure by which it is possible to waive father's rights and maintenance obligations only at the request of the father . And in the event that when it is still possible to renounce paternity, alimony will still have to be paid until children will not be adopted.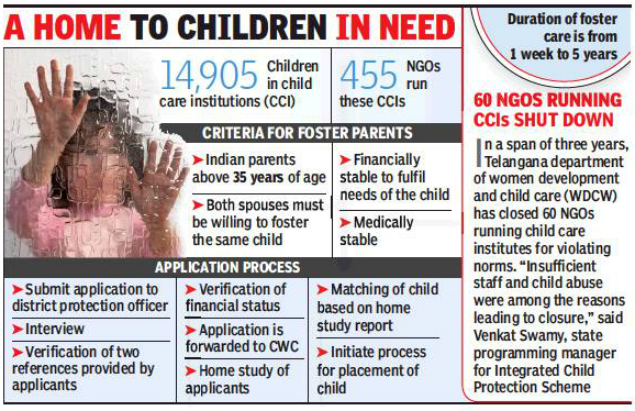
Is it possible to give up your father?
The legislation of the Russian Federation does not provide for the possibility of a child abandoning his mother or father . Even if the parents do not cope with their duties or do not fulfill them at all, he does not have such opportunities. Refusal by parents of their rights on a voluntary basis is also not carried out.
What should be done to deprive a mother of parental rights?
To deprive the mother of the rights to the child, it is necessary to file a claim with the court. The plaintiff may be a guardian or custodian, a person with whom the child lives, a prosecutor, guardianship authorities, or the child himself when he reaches 14 years of age. Other documents must be submitted along with the application.
How can a mother give up her rights to a child in favor of a father?
According to the norms of the RF IC, adoptive parents have the right to abandon the child by filing the relevant documents by filing a claim with the court at the place of residence children . In this case, the protection of the rights and interests of a minor in court will be handled by the body of guardianship and guardianship (part 1 of article 56 of the RF IC).
In this case, the protection of the rights and interests of a minor in court will be handled by the body of guardianship and guardianship (part 1 of article 56 of the RF IC).
Is it possible to write a refusal of a child at a notary?
sample document - STATEMENT OF CLAIM for deprivation of parental rights. In society, such a concept has arisen, as “ abandonment of the child ” in connection with. Notarial waiver of parental rights is not possible.
40 reasons for refusal of a student visa
For those applying for an F-1 student visa, the stakes are incredibly high. The results of the interview will determine where university applicants will spend the next four (or more) years of their lives. Their own dreams and the hopes and aspirations of their families depend on this interview. For those who plan to enroll in language courses, promotion or competitiveness may be at stake. For graduate students, earning an MBA from a U.S. university can mean the difference between an exhilarating career and a life of stagnation. And yet, with so much at stake and hundreds of thousands of applicants denied student visas every year, these people often neglect the basic rules that can maximize their chances of getting a visa.
And yet, with so much at stake and hundreds of thousands of applicants denied student visas every year, these people often neglect the basic rules that can maximize their chances of getting a visa.
Categories of Student Visa Applicants
In general, each student visa applicant must show that they: 1) are a legitimate student; 2) has the ability to cover the cost of education and living in the United States; and 3) has strong ties to the home country and will leave the country upon completion of the educational program. But the consul will interpret the definition of “strong connection” differently, depending on the type of student visa applicant: 1) if this is a 17–20-year-old candidate entering the university for the first time, the consul will take into account the fact that the applicant does not have the traditionally required connections (spouse / spouses, children, property) or clear long-term plans, and therefore the main attention will be paid directly to the current intentions, academic and family background of the student; 2) if it is a graduate student over 20 years of age applying for an MBA or other academic degree, the consul will focus on his academic performance, career plans and how graduate studies will contribute to their implementation; 3) if the student visa applicant expressed a desire to study in the middle of his career (he is about 30-45 years old), the consul will focus on his current job, connections, career stability, ambition, academic program and ability to complete it; 4) in the case of those who are going to study English, the consul's decision will depend on their age/origin and how the English language program will affect their lives in the future; 5) if the applicant decides to learn the language for themselves, as a hobby - for example, a housewife or someone whose knowledge of English is not an integral part of their career, the consul will focus on their ties with their homeland; 6) for elementary or high school students, consular control will focus on ties with the home country and parental finances; 7) and in the case when a student returns to a previously started academic program, the consul is supposed to respect his aspirations and allow him to finish the course if there have been no significant changes in the student's life over the past time.
Reasons for rejection
In over 25 years of practice, we have seen the full spectrum of student visa rejections. We were able to select for you some of the most commonly mentioned or implied reasons. And while some of them are listed under section 214(b) on this site, below we have focused on the most common reasons for rejection of student visas:
- Country of origin. The first decisive factor affecting the issuance of a student visa is the country of citizenship. A student from economically developed and politically stable Germany should not have any problems getting a visa at all, while applicants from Afghanistan, Congo and Uzbekistan have much lower chances. (The Department of State does not publish country-by-country rejection statistics for student visa applicants, but B-visa rejection rates are published and provide at least a rough guess as to how students from these countries fared.) In some cases, if an applicant from a less developed country does not have a prestigious job waiting in their home country, it can be very difficult to overcome such prejudices and obtain a student visa.

- Communications. As mentioned above, the strength of one's ties with one's homeland is viewed through the prism of age. For young applicants, the profession of their parents is the so-called "Who's your daddy?" test. - can play a key role in making a decision (whether it is fair or not). If the applicant's father is a "laborer", he will be considered from a poor family, and therefore a potential immigrant candidate. Within the framework of such an analysis of the standard of living, the consul may be distrustful of residents of rural areas or small towns, therefore, their chances of being denied a visa will be higher than that of residents of megacities. The absence of trips to the EU countries can be considered as a negative factor, indicating, in the opinion of the consul, the precarious financial situation of the family and the lack of earning opportunities, or exposing the applicant in the light of a recluse who has not yet seen the world. The consul seems to be saying - "Drive around other countries, then you will "grow up" to an American student visa.
 " Applicants over 20 years of age appear to him as a sort of “middle half”: they are a little old for beginners, but too young to start a career or have strong ties to their homeland. If the applicant has worked for a company for less than 1 year after graduation in their home country, this may be considered as instability or a desire to take a walk, which is not conducive to the issuance of a student visa.
" Applicants over 20 years of age appear to him as a sort of “middle half”: they are a little old for beginners, but too young to start a career or have strong ties to their homeland. If the applicant has worked for a company for less than 1 year after graduation in their home country, this may be considered as instability or a desire to take a walk, which is not conducive to the issuance of a student visa. - Problems at the interview. Because a student visa interview typically only lasts 2-3 minutes, the applicant only has one chance to make a first impression. It turns out to be decisive. Although the Consul's authority does not include an assessment of your English, poor command of it will still be taken into account. Failure to clearly articulate the reasons for choosing a particular university can be fatal. As well as the inability to explain how the curriculum will contribute to career plans. Failure to answer simple standard questions (for example, what are your plans after graduation? What is your father doing?) will be just as detrimental to your chances as long, incoherent answers.
 The behavior of the applicant at the interview is also crucial: inertia, passivity or inability to show ambition can tip the scales against him. Nervousness, poor self-presentation, unwillingness to look the interlocutor in the eye, sloppy or, conversely, frilly clothes - all these are negative factors.
The behavior of the applicant at the interview is also crucial: inertia, passivity or inability to show ambition can tip the scales against him. Nervousness, poor self-presentation, unwillingness to look the interlocutor in the eye, sloppy or, conversely, frilly clothes - all these are negative factors. - Insufficient or incorrectly documented facilities. The student visa applicant must be able to demonstrate the ability to pay for the first year of the study program. Consuls who have received posts in developing countries are well aware of cases of fraud and are always on the lookout. A bank statement showing a transfer of $50,000 to your sponsor's account 2 days before the interview will raise questions about the source of these funds and the reality of their purpose for paying for tuition. Sponsoring parents in low-paying public positions may be viewed with skepticism. And friends and relatives paying for your education will also raise a number of questions: how serious are their intentions? How close are you to your sponsor uncle? When did you last see each other?
- Previous visa refusal.
 While the recent US visa denial is not a verdict for a student visa applicant, it can still be considered a black mark. Considering the reason for the refusal, the consul will definitely check whether it also applies to the issuance of a student visa. So, for example, if you applied for a U.S. tourist visa to attend a friend's wedding and were denied due to "lack of strong ties to your home country", this could result in your student visa being denied. If that refusal was very recent, the current officer may even consult with the consul who conducted the last interview and ask him how it was. He may get the impression that you want to get a visa "by hook or by crook": "Two months ago you tried to go to the USA "to a friend's wedding", and now you" expressed a desire to become a student "". Extremely suspicious. The problem with the B visa is not solved by applying for the F visa.
While the recent US visa denial is not a verdict for a student visa applicant, it can still be considered a black mark. Considering the reason for the refusal, the consul will definitely check whether it also applies to the issuance of a student visa. So, for example, if you applied for a U.S. tourist visa to attend a friend's wedding and were denied due to "lack of strong ties to your home country", this could result in your student visa being denied. If that refusal was very recent, the current officer may even consult with the consul who conducted the last interview and ask him how it was. He may get the impression that you want to get a visa "by hook or by crook": "Two months ago you tried to go to the USA "to a friend's wedding", and now you" expressed a desire to become a student "". Extremely suspicious. The problem with the B visa is not solved by applying for the F visa. - Change of status in the USA. After arriving in the United States, many tourists, visitors, and Summer Work Travel program participants decide to stay and enroll in a school, for which they change their status.
 What they forget to think about is the "warm welcome" that awaits them when they return to their home country, when they decide to apply for a student visa. After all, they will not be considered as “returning” students with a valid right of entry, but as persons applying for a student visa for the first time. In the worst case, the consul may feel deceived that the applicant did not return home after the expiration of his original status and issue a 212(a)(6)(C)(i) waiver. Another consul may refuse under section 214(b). And this is regardless of how long a person has studied in the USA, how much time is left before graduation, and how much money has already been spent on incomplete education.
What they forget to think about is the "warm welcome" that awaits them when they return to their home country, when they decide to apply for a student visa. After all, they will not be considered as “returning” students with a valid right of entry, but as persons applying for a student visa for the first time. In the worst case, the consul may feel deceived that the applicant did not return home after the expiration of his original status and issue a 212(a)(6)(C)(i) waiver. Another consul may refuse under section 214(b). And this is regardless of how long a person has studied in the USA, how much time is left before graduation, and how much money has already been spent on incomplete education. - 221(g) waiver. Although a 221(g) denial is temporary, its effects may become permanent. If a student misses a semester due to delays or is unable to return to a temporary job, they will start looking for other options. STEM participants from China and Russia who are suspected of spying in foreign territory fall under Article 221(g) most frequently.
 Central to the Consul's radar are technologies in accordance with the Technology Alert List. For a STEM student in need of a new visa, going home to a friend's wedding in the middle of the semester is a recipe for disaster. The "twilight zone" of Article 221(g) can fall into people with a common combination of first and last name, stuck in the unknown between the issuance of a visa or a hard refusal. If the decision under section 221(g) is delayed, it is advisable to file a lawsuit (writ of mandamus).
Central to the Consul's radar are technologies in accordance with the Technology Alert List. For a STEM student in need of a new visa, going home to a friend's wedding in the middle of the semester is a recipe for disaster. The "twilight zone" of Article 221(g) can fall into people with a common combination of first and last name, stuck in the unknown between the issuance of a visa or a hard refusal. If the decision under section 221(g) is delayed, it is advisable to file a lawsuit (writ of mandamus). - Visa consultants/travel agents/notaries. Often, these individuals are rewarded upon issuance of a visa, and therefore their desire to maximize the chances of obtaining it sometimes knows no bounds. They can obtain fake educational documents for their client, as well as fake or forged bank statements. The problem for the student here is that all of this can lead not only to a 214(b) denial, but to a lifetime 212(a)(6)(C)(i) ban. And even if you did not know about this forged document, the consul will succumb to the reflex to impute this knowledge to you, referring to your responsibility for the actions of your agent.

- Other document problems. Forgetful applicants who fail to bring a required document, such as TOEFL or GRE scores, a certificate of admission with a scholarship, or sponsor's account statements, may fail. While in these situations it is more appropriate to issue a 221(g) provisional waiver depending on the applicant's presentation of the missing document, sometimes a busy consul is not particularly lenient and issues section 214(b).
- Relatives in the United States. One of the most frequently asked interview questions is about having relatives in the United States. In the DS-160 questionnaire, you are asked to indicate not only the next of kin, but also other people who are related to you and live in the United States. Withholding such information may be considered a material misrepresentation and result in a Section 212(a)(6)(C)(i) waiver. The main topic at the interview may be the question of how your relative moved to the United States.
 If he applied for asylum there, this could seriously reduce the applicant's chances of obtaining a student visa. If the applicant's brother or sister stayed in the US after the Summer Work Travel program, this can also be considered a negative factor (due to the loss of "trust in the family"). If one of them is currently studying there, the consul may consider that one family member in the United States is "already enough."
If he applied for asylum there, this could seriously reduce the applicant's chances of obtaining a student visa. If the applicant's brother or sister stayed in the US after the Summer Work Travel program, this can also be considered a negative factor (due to the loss of "trust in the family"). If one of them is currently studying there, the consul may consider that one family member in the United States is "already enough." - Filing an I-130 immigrant petition for an F-1 visa. If a student visa applicant has previously filed an immigration petition, they may have problems. Questionnaire DS-160 asks this directly. Failing to file such a petition may result in a permanent entry ban. And an honest answer will lead to a whole series of questions. How long ago was it filed? At what stage is the process of applying for an immigrant visa? If the applicant has a chance of obtaining one in the near future, the consul may decide that there is no need for a student visa.

- Questionable source of funds. Test titled "Who's your daddy?" can backfire if your father (or mother) — or even one of their close business associates — made money in a “dubious way,” especially if that money goes to pay for an education in the US. Likewise, if your father belongs to an "elite" close to an unfriendly US regime, this may negatively affect the consul's decision.
- Suspicious courses or institutions. Certain courses or educational institutions may sound a dangerous signal to the consul. Suppose a consular audit showed that students of this institution often do not return back to their homeland. Or the consul suspected that the two-week English course was just an excuse for a long trip to the United States. “How can you improve your English in just a couple of weeks?” he will think.
- Small, unknown secondary colleges. While the "quality" of an institution should not be considered in a consul's decision, it sometimes matters a lot.
 The consul will favorably treat a person entering a major league school, considering him a "serious, intelligent student", than one who wants to enter a community college somewhere in the outback of Nebraska.
The consul will favorably treat a person entering a major league school, considering him a "serious, intelligent student", than one who wants to enter a community college somewhere in the outback of Nebraska. - Errors in the DS-160 questionnaire. Common sense dictates that there should be no errors in the DS-160 questionnaire, but experience shows that they happen all the time. Cultural differences, language barriers, simple negligence, and ignorance of US laws can sometimes play a role. For example, a person may indicate that he is "unemployed" just because he does not work for someone else. Although he indicated his real position: for example, a private entrepreneur who created his own non-profit organization with a staff of 8 employees, he would most likely receive a visa. An incomplete list of previously visited countries may also lead to rejection. Another common mistake is to remain silent about a conviction that has been expunged - this can lead to a standard 214(b) denial as well as a misrepresentation denial (and a possible lifetime ban).

- "Flimsy" DS-160. Alas, the DS-160 does not provide many opportunities for detailed disclosure of the information provided, but in those places where such an opportunity exists, the applicant should use the space allotted as efficiently as possible. Failure to do so may result in rejection. For example, if a specialist at the height of her career applies for a student visa in order to obtain an MBA degree and indicates that her duties in the bank are simply “administration and budgeting”, while being completely passive during the interview, it is unlikely that the consul will remain impressed.
- Losers. The Consul may question the need for a visa for a returning student whose performance in the States was below average (poor grades or poor attendance on the original F-1 visa).
- Too long stay in the USA. If the student visa applicant has previously spent significant time in the United States, the consul may decide that it is "time to stay at home" to re-establish ties with the home country.
 For example, an applicant who has become strongly "Americanized" after 4 years of study in a US high school and wishes to continue his studies in the States may face such an approach.
For example, an applicant who has become strongly "Americanized" after 4 years of study in a US high school and wishes to continue his studies in the States may face such an approach. - Illegal employment in the USA. The consul has a short conversation with a student visa applicant who previously worked illegally in the United States. After all, he not only broke the law, but also clearly demonstrated his cramped financial situation and the lack of economic ties with his homeland. His student visa will be denied.
- Arrest in the USA. Arrest in the United States will result in visa revocation and, at the very least, severe 214(b) denial issues. Take, for example, a Summer Work Travel member who is arrested for shoplifting in an American store and decides to apply for a US student visa a year later. Usually, in such a case, the consul may consider that not enough time has passed since the incident. There are many reasons for such a delay.
 This may be the desire of the consul to punish the delinquent student, and a doubt about his maturity, or maybe simple caution: is there a risk that this person will break the law again?
This may be the desire of the consul to punish the delinquent student, and a doubt about his maturity, or maybe simple caution: is there a risk that this person will break the law again? - Participation in the SWT program. If the applicant has previously visited the United States under the Summer Work Travel program, the consul may expect a certain level of English proficiency from him and refuse a student visa, noting that after a previous stay in the United States, there is no particular progress in mastering the language.
- Politics. Some denials of visas, including student visas, are due to fluctuations in the political environment. As can be seen from Trump's entry ban on people from predominantly Muslim countries, as well as visa denials for Chinese scientists (Visas as the latest weapon in the confrontation between the US and China) and Russian students, when geopolitical tensions increase, the number of denials and delays also increases.
 .
. - Mistakes and forgery when submitting admission documents. A consul who decides to dig into the applicant's qualifications can be a potential source of problems. For example, if admission to a university is dependent on passing a certain exam and the applicant applies for a visa with an I-20 already issued, the consul may doubt that the university is fully aware of the applicant's "insufficient" qualifications. Was it a university oversight or did the applicant submit fake academic documents?
- Rejection due to unacceptability. Student visa applicants are subject to common ineligibility criteria, including health, criminal, security, and immigration violations. For example, if an applicant was convicted of a serious crime against morality - even if it took place 10 years ago and was subsequently expelled - he is not eligible for a student visa until he receives a nonimmigrant waiver. If an applicant-owned company provided someone with a fake employment letter to apply for a U.
 S. visa, the applicant may be charged with smuggling aliens, which is another ground for ineligibility and will require a non-immigrant waiver.
S. visa, the applicant may be charged with smuggling aliens, which is another ground for ineligibility and will require a non-immigrant waiver. - The applicant is sponsored by his significant other living in the USA. Earlier in this article, we have already touched on the topic of obligations of a financial sponsor. If the visa applicant and the American sponsor are in a romantic relationship, this may raise questions about their motives: perhaps a student visa is just a way to move to the United States? The consul will carefully consider the applicant's ties to the home country and his/her intentions and may consider that a fiancé/fiance visa would be a more appropriate option.
- Dependents stay at home, while the breadwinner goes to study in the States. Although at first glance this situation looks more than beneficial - after all, the applicant is much more likely to return home if there is a family waiting for him - the consul may wonder: “If the applicant leaves his job and goes to study in the United States, who will support his family? After all, he goes there as a student, and not for work, so where will his relatives receive income?
- Separate applications for family members.
 Although in a situation where an applicant has already received an F-1 visa, it is assumed that the consul is “unlikely” to deny it to other close family members, nevertheless, if it is suspected that they were trying to trick the system by filing applications separately from each other friend, he can give them a refusal.
Although in a situation where an applicant has already received an F-1 visa, it is assumed that the consul is “unlikely” to deny it to other close family members, nevertheless, if it is suspected that they were trying to trick the system by filing applications separately from each other friend, he can give them a refusal. - Social networks. If in social networks the applicant appears as a drug addict, a party-goer, or belongs to the spoiled "golden youth", the consul may doubt the seriousness of his intentions to study.
- Questionable contacts in DS-160. Applicant's DS-160 asks for a couple of contacts. If the specified contact is on the "black list" of the embassy or has previously been denied a visa to the United States, this may adversely affect the applicant's chances.
- Inconsistencies, oddities, lack of logic and meaning. Consular officers are people of habit, and therefore, as soon as something strange pops up in the applicant's application form, they will not hesitate to put a refusal stamp.
 If the applicant indicates that he previously studied in Germany, but there are no marks on entry into this country in his passport, the consul may doubt the accuracy of the information. Likewise, a consul may be suspicious of a story that after just a few months with the company, the employer wants to send the applicant to the US for a three-month English course.
If the applicant indicates that he previously studied in Germany, but there are no marks on entry into this country in his passport, the consul may doubt the accuracy of the information. Likewise, a consul may be suspicious of a story that after just a few months with the company, the employer wants to send the applicant to the US for a three-month English course. - Applying to a foreign country. Although not prohibited by law, a consul may be particularly suspicious of a person who has recently immigrated or resettled elsewhere. For example, if he legally moved to the UK from Nigeria last year and now wants to study in the US, the consul may advise "to apply for a visa later, when he settles in a new place."
- The problem of the "eternal student". A student visa applicant who seems to be more interested in collecting diplomas or leading a student lifestyle than work and career may not find understanding with the consul. This is especially true in cases where a visa candidate has no clear goal - for example, he is already working on his third candidate, or after 6-7 years he still cannot complete a 4-year program.

- Consul's misunderstanding of facts or laws. Consideration of documents, questioning and making a decision in just 2–3 minutes of an interview inevitably lead to errors. Factual errors, interview misunderstandings, language problems, and legal errors are far from uncommon (for example, the consul may not remember that a shoplifting charge falls under the petty offense exception or decide that the grace period after training is only 30 days, and not 60).
- Selected courses are "not useful" in the applicant's home country or for career development. Although consuls must remain impartial about the choice of study program, a rational consul may question its necessity: "Why is this applicant going to study agriculture in the United States when his home country does not produce its own food?" Or “She works as a financial consultant, why does she need a journalism course?”
- Status violations. There are many rules and regulations that a student must comply with while in the United States, such as a minimum level of study, work restrictions, and the requirement to report a change of address or major.
 Failure to comply with these rules may result in visa refusal.
Failure to comply with these rules may result in visa refusal. - Admission to wrongful conduct. While smoking marijuana may be legal in a state, it is still considered a violation of federal law. Therefore, even if a student has not been detained, arrested or convicted for possession or smoking of marijuana, his confession to the above consul (or airport inspector) may become the basis for declaring him ineligible. A student visa applicant in this situation will require a non-immigrant waiver, which may take several months to obtain. In addition, the consul may require the student to visit a doctor to make sure he is not suffering from an addiction.
- Problems with OPT. The rules regarding Optional Practical Training (student temporary work) are quite complex. For example, if a person has an OPT permit but leaves the US before receiving a job offer, the permit may become invalid. And while consuls should understand the importance of OPT to the program, the very fact that an applicant is returning to the US to “work” and not to study may make them question the strength of their ties to their home country.

- Technical problems. As trivial as typographical errors, errors in the SEVIS system, failure to report information, oversight on the part of a school worker may seem, such technical errors can lead to delays and refusals.
- Late application. Needless to say, it is important to apply by the deadline given in I-20. Being late may result in your student visa being denied.
- Older applicants with no specific goals. This category includes people with unstable work experience and lack of clear plans. An intention to travel to the US out of sheer whim with no real academic purpose may indicate an applicant's lack of ties to their home country and, as a result, a potential illegal immigrant.
How to prevent or overcome rejection
Whatever your situation, we hope it does not turn into a quest that one of our clients fell into when she asked for help after 7 student visa rejections. While you can't change your country of origin or change your parents, you can still do a lot. The reasons listed above clearly demonstrate what actions need to be taken to avoid rejection: competent planning, preparation, good English, well-chosen clothes and self-serve are just the beginning. Professional legal assistance—even if it comes down to checking your DS-160, supporting documentation, and rehearsing for an upcoming interview—can make all the difference in avoiding rejection. If you have already been denied, you need to analyze the problem. And here, a professional can also help you determine exactly what it is, prepare the DS-160 and supporting documents for resubmission, and then provide invaluable tips for a successful interview. If the problem is related to an entry ban under an article of misrepresentation or a crime, the lawyer may request a more precise wording of the refusal, followed by a review of the case or the issuance of a waiver. And finally, some of the above reasons have no legal basis, and therefore can and should be challenged.
While you can't change your country of origin or change your parents, you can still do a lot. The reasons listed above clearly demonstrate what actions need to be taken to avoid rejection: competent planning, preparation, good English, well-chosen clothes and self-serve are just the beginning. Professional legal assistance—even if it comes down to checking your DS-160, supporting documentation, and rehearsing for an upcoming interview—can make all the difference in avoiding rejection. If you have already been denied, you need to analyze the problem. And here, a professional can also help you determine exactly what it is, prepare the DS-160 and supporting documents for resubmission, and then provide invaluable tips for a successful interview. If the problem is related to an entry ban under an article of misrepresentation or a crime, the lawyer may request a more precise wording of the refusal, followed by a review of the case or the issuance of a waiver. And finally, some of the above reasons have no legal basis, and therefore can and should be challenged.