How to emancipate a child in pa
Your Online Guide to Legal Information and Legal Services in Pennsylvania
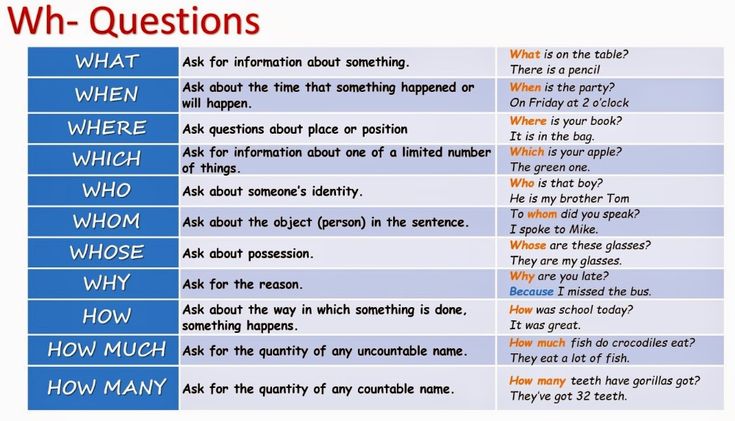
I. GENERAL INFORMATION
Most people think someone less than 18 can just go to court and get emancipated. But in Pennsylvania, emancipation is not a right, and there are no clear procedures to get a declaration of emancipation from a court. However, rarely is such a declaration necessary for a minor to achieve his or her goal.
Certain actions automatically result in a minor becoming emancipated--these include marriage or entry into the military. However, a minor usually wants to be declared emancipated to get a specific benefit or service. Government agencies usually have the authority to decide if a minor is emancipated, to authorize the benefit or service they administer. Therefore, it is usually not necessary for a minor to go to court to be declared emancipated.
Please note: specific laws forbid minors from participating in certain activities, such as alcohol purchase and consumption, whether or not a minor is emancipated.
II. SCHOOL ATTENDANCE AND RESIDENCE
A minor must normally attend school in the public school district where his or her parents reside. This is not required if the student is homeless or lives with a relative or other adult who resides in another school district. Pennsylvania law says if that adult provides all housing, financial support and parental guidance for the minor, the minor may attend school in the school district where the adult supporting him or her lives. However, before the minor can enroll, the adult resident must sign a notarized affidavit which says he or she is providing all financial support to the minor, and will be responsible for the minor's school attendance and behavior.
Northwestern Legal Services has affidavit forms that conform to the requirements of Pennsylvania law. (Provided here in PDF is a copy of the School Affidavit Form for use in Pennsylvania).
Homeless students, defined as: "individuals who lack a fixed, regular, and adequate nighttime residence. ..due to loss of housing, economic hardship, or a similar reason" do not need to get an adult to sign a residency affidavit. They can attend school in the district where they are staying, even if their "residence" is a homeless shelter, park or car. The law that provides this right is called the McKinney-Vento Act. If you are homeless and are having trouble getting accepted into school, call the McKinney-Vento state coordinator for Pennsylvania at (717) 772-2066 for help.
..due to loss of housing, economic hardship, or a similar reason" do not need to get an adult to sign a residency affidavit. They can attend school in the district where they are staying, even if their "residence" is a homeless shelter, park or car. The law that provides this right is called the McKinney-Vento Act. If you are homeless and are having trouble getting accepted into school, call the McKinney-Vento state coordinator for Pennsylvania at (717) 772-2066 for help.
State law says a minor must stay in school from age eight until age 17. This is known as the compulsory age for school attendance. At age 17, a minor may leave school without permission from the school, or from the minor's parents or guardians. A 16-year-old minor who has a job during school hours, and holds an employment certificate, may also drop out of school. However, dropping out of school is strongly discouraged, as most jobs that provide decent wages require a high school and/or additional education. In addition, the military services often refuse to enlist persons who have not graduated from high school.
In addition, the military services often refuse to enlist persons who have not graduated from high school.
According to Pennsylvania truancy law, "Every parent, guardian, or person in parental relation, having control or charge of any child . . . of compulsory school age . . . " may be fined or put in jail if the child in their care does not go to school. Therefore, unless a minor's parents, guardians or other adult who has previously assumed responsibility for the minor, can prove they no longer have actual "control or charge" over the minor, they may be subject to a penalty if the minor in their care does not go to school.
The law does not require the minor, or the minor's parents/guardians or other adult who previously assumed care for the minor, to get a declaration of emancipation of the minor from the court, to be relieved from responsibility under truancy law. Instead, the school district can decide if a minor is still under "control or charge" of an adult, by evaluating the circumstances. The school district should focus on whether the minor still lives with his or her parents/guardians or other adult, and whether the minor is getting financial support from parents/guardians or another adult. If a school district is unwilling to collect the information it needs to determine if the minor is emancipated, legal assistance may be required.
The school district should focus on whether the minor still lives with his or her parents/guardians or other adult, and whether the minor is getting financial support from parents/guardians or another adult. If a school district is unwilling to collect the information it needs to determine if the minor is emancipated, legal assistance may be required.
III. FAMILY LAW
Custody and Adoptions
Minors have the same legal rights as adults, to custody of their own child(ren). The actual custody or visitation granted in any case, depends on the best interest of the child involved, determined by the facts of the case. If the Court decides a minor needs help preparing and presenting his or her custody case to the court, a guardian may be appointed to assist the minor.
The Pennsylvania Adoption Act defines a minor parent as someone under the age of 18. A minor parent who wants to place his or her own child up for adoption does not need the consent of his or her parents or guardians. A minor 12 years of age or older cannot be adopted, unless he or she consents to the adoption.
A minor 12 years of age or older cannot be adopted, unless he or she consents to the adoption.
Marriage
Minors under the age of 16 can marry, but only if a judge at the county courthouse decides the proposed marriage would be in the best interests of the minor.
Minors between the ages of 16 and 18 can marry with the written, notarized consent of a parent or legal guardian, witnessed by two other adults. Alternately, a parent or legal guardian may give oral consent for the marriage at the marriage license office. When the minor has no parent or guardian available to give consent, a judge can approve the marriage. If no judge is available, the marriage license office can appoint a guardian to consent to the marriage.
IV. MEDICAL CONSENT
A minor less than 18 years of age may give consent for his or her own medical treatment, if he or she:
- was graduated from high school or
- was married or
- was pregnant.

In addition, a minor may consent to medical treatment for his or her minor child(ren).
V. PARENTAL LIABILITY
Under the law, parents are liable for property damage and personal injury caused by their child. However, they can only be required to pay a maximum of $300 of any damage claim where one person is injured, and $1,000 where two or more persons are injured.
A parent does not have to pay damages for injury caused by their child if:
- the parent does not have custody of the child and is not entitled to custody of the child or
- the child is institutionalized or
- the child is emancipated.
Again, emancipation is not defined under this statute. In this situation, a parent who is being sued for property damage and personal injury caused by their child should raise emancipation as a defense. A court would then determine the parent's liability, using the emancipation factors discussed in the section of this pamphlet on Judicial Determination of Emancipation.
VI. PUBLIC ASSISTANCE BENEFITS
For a minor to get benefits from the county assistance office (cash/Food Stamps/medical assistance) in his or her name, the minor's age, and certain other factors, depending on the type of benefit requested, must be determined by the assistance office.
Medical Assistance: A health insurance program for very low income individuals. For medical assistance purposes, a minor is any person less than 21 years of age (19 if the person is applying for medical assistance under the Healthy Beginnings program). A minor can get medical assistance in his or her own name if he or she is under age 21. However, the assistance office must determine if the minor's parents resources and income must be included in the eligibility determination, unless they find the minor is emancipated. For purposes of medical assistance eligibility, a minor is emancipated if:
- married; or
- not under the care and control of his or her parents or legal guardians, whether living with them or not; or
- not getting most of his or her financial support from his or her parents or legal guardians, whether living with them or not; or
- the minor's parents or guardians are not viewed as the responsible party for the minor by the school district where the minor attends school.

Food Stamps: Vouchers that can be used to purchase food.
If the minor is less than 22 years of age, and living with his or her natural, adoptive or stepparent(s), the Food Stamp grant must be in the parent(s) name, and the parent(s) income must be included in determining whether the minor is eligible. There are exceptions to this rule, but they all require the minor to purchase and prepare meals separately from his or her parents. The exceptions include:
- A parent is elderly or disabled and the minor is at least 18 years old, or, if less than 18, not under parental control.
- The minor has children of his or her own who live in the household.
- The minor is married, and the minor's spouse lives in the household.
If the minor is living with another adult, the Food Stamp grant must be in the other adult's name, and the income of the other adult must be included in determining eligibility for benefits, unless the adult is not exercising care and control over the minor.
Once the minor is 22 years of age, he or she can establish separate eligibility for Food Stamps. However, the income of the parent(s) must still be included in determining eligibility, if the parent(s) and child are purchasing and preparing meals together.
General Assistance: A cash grant funded with state money. The age of the minor and certain other factors determine if the minor can get General Assistance in his or her name.
- A single minor, between the ages of 16 and 18, who is not the primary caretaker for his or her child, may get his or her own General Assistance grant, if otherwise eligible. (As a practical matter, it is unlikely that a minor actually living with and/or receiving financial support from his or her parents, would be otherwise eligible for General Assistance.)
- A single person, between the ages of 18 and 21, who is attending high school or vocational school, and is expected to graduate before age 21, may also get a General Assistance grant, if otherwise eligible.
- A minor who is married, even if he or she lives with his or her parents, may get a General Assistance grant, if otherwise eligible.
Temporary Assistance to Needy Families: A cash grant funded with federal and state money for parents who are caring for their own minor children.
- As a general rule, parents under age 18 must live in their parent(s) home to get cash assistance. In addition, the cash grant must be in the name of the minor parent's parent(s). There are exceptions to this rule, but those exceptions are limited. Contact Northwestern Legal Services for help, if you are a minor parent and need to get a cash grant in your name.
VII. SUPPORT
Parents must support their children who are unemancipated and 18 years of age or younger. Parents are not required to support their emancipated children. The support law fails to give specific rules to decide if a minor child is emancipated. Instead, a parent desiring to stop paying support because he or she believes his or her child is emancipated, must file a petition with the court to get a declaration of emancipation. The next section, Judicial Determination of Emancipation, contains the rules the court would use to decide if the parent(s) of a minor must continue to support him or her.
The next section, Judicial Determination of Emancipation, contains the rules the court would use to decide if the parent(s) of a minor must continue to support him or her.
Finally, a minor child may move "in and out of emancipation" for support purposes. In other words, circumstances may change the child's emancipated status so that he or she becomes again dependent on parental support. In support matters, therefore, the main issue in determining if a minor child is emancipated is whether the child relies on the parents for support.
VIII. JUDICIAL DETERMINATION OF EMANCIPATION
As stated earlier, a minor may ask a court to declare him or her emancipated but, as shown above, court action is often unnecessary for the minor to get what he or she wants.
A minor may petition a court to confirm his or her emancipated status by either submitting a "Petition for Emancipation" or by filing a "Complaint For Declaratory Judgment On Plaintiff's Emancipation Status. " A minor should get legal assistance when asking a court for a judicial decree of emancipation.
" A minor should get legal assistance when asking a court for a judicial decree of emancipation.
A hearing will be held on any request for emancipation, so the court can get the information necessary to decide if the minor should be declared emancipated. Information given to the court at the hearing should include facts showing: whether the minor is living with his or her parents or guardians; whether the minor is dependent on his or her parents for financial support; whether the parents and the minor intend for the minor to be independent; whether the parents are actually exercising control and authority over the minor; and whether the minor can financially support him or herself.
For example, a 13-year-old who wants to leave home is not likely to be declared emancipated because he or she cannot support him/herself. In effect, the minor child must already be living independently for a court to determine that the child is emancipated.
Parents or guardians of a minor emancipated by court order, are no longer required to give the minor any financial support. This means they do not have to provide food, housing, clothing or any other assistance to the minor.
This means they do not have to provide food, housing, clothing or any other assistance to the minor.
If you have further questions on this topic, contact your local legal services program for more information.
We have attempted to insure the accuracy of the information in this pamphlet at the time it was created or revised. However, the law does change, sometimes quickly and unexpectedly. Therefore, you should consult an attorney before taking or refraining from any action based on the information in this pamphlet.
Last Reviewed: January 2006
321.3 Emancipation
321.3 EmancipationIf an individual is emancipated and under age 21, he or she may apply for MA on his or her own.
55 Pa. Code § 148.2
NOTE: For MAGI-related MA, an individual is emancipated if he or she is:
(a) age 19 or older.
(b)
under age 19 and either married or no longer
under the care and control of a parent.
An individual under age 21 (or under 19 for MAGI-related MA) is considered emancipated if one or more of the following conditions apply:
55 Pa Code
§ 145.62
The parent, caretaker relative, legal guardian, or other individual who had care and control of him or her is no longer paying for most of his or her support.
The individual is not living with the parent, caretaker relative, legal guardian, or other individual who had care and control of him or her.
The parents, caretaker relative, legal guardian, or other individual who had care and control of the individual is not considered the responsible party by school officials.
An individual can be considered emancipated whether or
not he or she is living with a parent or legal guardian.
An unmarried individual under age 21 (or under 19 for MAGI-related MA) who is not living with a parent or legal guardian is usually emancipated. However, the must find out who has care and control of the minor if he or she left the parent's household shortly before applying or if there are other factors that make the CAO unsure about the individual’s status.
When an unmarried minor is living with a parent or legal guardian, the CAO must verify with the adult whether or not the minor is under the adult’s care and control. The CAO must always try to get proof of emancipation in writing. The CAO must base the emancipation decision on all available facts.
An individual of any age may submit a completed, signed
Application for Benefits (PA 600)
or
Application for Health Care Coverage (PA
600HC) to the CAO.
If the CAO finds that the individual is an unemancipated minor, the minor's
parent or other adult with care and control of him or her must complete
the application process.
Note: If the application is submitted by a , the CAO must determine on MA eligibility using the date the application was signed by the minor.
Note: An unemancipated minor may submit an application and be reviewed for the Family Planning Services Program. If the unemancipated minor does not have the signature of a parent or guardian and/or does not or cannot provide all household information, they cannot be reviewed for full MA coverage, but may still be reviewed for the Family Planning Services Program only.
The CAO must not count the resources of a child under age
21 and of the child’s parents when deciding on the child’s MA eligibility,
whether or not he or she is emancipated. Also, the CAO must not consider
the child’s emancipation status when deciding the amount of a parent's
income
that is deemed available to the child when the child is living in the
parental household.
Note: If an unemancipated minor is claimed as a tax dependent by his other parent(s) and the minor resides with the parent(s), and the minor resides with the parent(s), the minor will be included for purposes of determining the MAGI-related MA tax filing household composition.
Updated September 26, 2019, Replacing November 4, 2016
full legal capacity at 16
Tamara Skokova
guardianship and guardianship specialist
Author profile
A child under 18 cannot open a bank account or buy a car without parental approval. But sometimes coming of age can be accelerated.
For adolescents who seek independence, the law provides for an emancipation procedure - early declaration of legal independence from parents. This can be done as early as 16 years old. nine0003
I will tell you how to declare a teenager emancipated, what are the conditions, pros and cons of obtaining early legal capacity.
What do you learn
- who and in what cases can recognize the teenager as fully capable of
- How to get full legal capacity through the guardianship authority
- How to get full legal capacity through the court
- What does emancipation for a teenager
- Plus and minuses of emancipation
How to raise children and not go broke
The best materials on how to cope with parenthood and get the most out of the state - every Tuesday in your mail. Free of charge
Who and in what cases can recognize a teenager as fully capable
As a general rule, a person is recognized as fully capable from the day following the day on which he turned 18 years old. For example, if the birthday is on Wednesday, then the age of majority will come on Thursday. From this day on, a person has the right to independently exercise his rights and obligations. nine0003
Up to this point, the adolescent's legal capacity is limited: without parental approval, he can only manage the money he receives, such as salary, scholarships, royalties, gifts.
paragraph 2 of Art. 26 Civil Code of the Russian Federation
From the age of 16, a teenager has the opportunity to pass exams and drive a moped, motorcycle and ATV. For everything else, written parental consent is required.
Art. 26 Federal Law "On Road Safety"
But sometimes you can get legal capacity ahead of schedule. There are two options:
- Marriage - from the date of receipt of the marriage registration certificate.
- Emancipation of a teenager who has reached the age of 16 and has gained financial independence. A child can be declared emancipated either by a territorial guardianship body with the consent of both parents, or in a disputable situation - by a court of general jurisdiction.
Let's take a closer look at both options.
Marriage. According to the civil code, a teenager under the age of 18 acquires legal capacity in full from the date of receipt of a marriage certificate. And does not lose it even in the event of a divorce. nine0003
And does not lose it even in the event of a divorce. nine0003
item 2 art. 21 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation
But there is a nuance: marriage before the age of majority is possible only if there are good reasons and with the consent of local governments. Valid reasons may be, for example, pregnancy, the birth of a child in adolescents, and others.
paragraph 2 of Art. 13 SK RF
If the administration refuses to lower the marriageable age, you can appeal its decision in court. You also need to take into account that the procedure and conditions for early marriage may depend on the region. For example, in the Murmansk region, you can get married from the age of 15, and in the Moscow region - from 14.
Emancipation. The procedure is available only to adolescents who have gained financial independence from their parents: they work under an employment contract or are engaged in entrepreneurial activities.
paragraph 1 of Art. 27 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation
27 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation
Therefore, two conditions must be met:
- Reach the age of 16 years.
- Conclude an agreement with an employer or obtain the status of an individual entrepreneur.
Other financial sources of a teenager are not taken into account, for example, income from securities, bank deposits. It turns out that we are not talking about the actual income of a teenager, but about recognizing him the possibility of labor or entrepreneurial activity with a constant income. Therefore, if an emancipated teenager quits or stops registering an individual entrepreneur, his emancipation will not be canceled.
In contrast to the marriage of a teenager, where the acquisition of full legal capacity by him occurs automatically, emancipation requires an "announcement". This is done by the decision of the guardianship authority or by the court - in case of disagreement of the parents or refusal of the guardianship authority. nine0003
nine0003
/list/early-marriage/
5 reasons why teenagers can get married
How to get full legal capacity through the guardianship authority
A teenager who has reached the age of 16 can apply to the guardianship authority at the place of registration and attach to application:
- Birth certificate.
- Passport.
- Passports of their legal representatives - that is, parents or guardians.
- Written consent of legal representatives in free form. nine0018
- Documents confirming labor activity: an agreement with an employer or an entry sheet in the USRIP on registration of an individual entrepreneur.
What to do? 06/26/19
I am 16 years old and I want to move out from my parents
The application will be considered within a maximum of 15 business days. If all is well, the teenager will be declared fully capable.
Sample application of a teenager to the guardianship authority for recognition of full legal capacity. Be sure to indicate your source of income and provide parental consent
Be sure to indicate your source of income and provide parental consent Each region has its own administrative regulations, and documents for emancipation should be submitted taking it into account: for example, in some regions you can apply for emancipation at the MFC, and in others - only at the guardianship authority.
You can find the addresses and phone numbers of guardianship authorities on the official website of the region. So, for Moscow it is "Mos-ru", and for St. Petersburg - "Portal of public services of St. Petersburg".
How to get full legal capacity through the court
If one of the legal representatives of a teenager does not agree or the guardianship authority does not recognize emancipation, the teenager has the right to obtain status in the district court at the place of residence. nine0003
To do this, he must apply to the court to recognize him as fully capable. It is not difficult to determine the right court: most likely, it bears the name of the registration area indicated in the passport. You can check whether your address is within the jurisdiction of the court on its website in the "Territorial Jurisdiction" section.
You can check whether your address is within the jurisdiction of the court on its website in the "Territorial Jurisdiction" section.
/kak-podat-v-sud/
How to file a lawsuit in court
The following must be indicated in the application to the court: income and the like. nine0018
The application is considered at a court session with the obligatory participation of the applicant himself, at least one legal representative, a representative of the guardianship and guardianship authority, and a prosecutor. If the legal representative fails to appear, he is obliged to notify the court of the reasons for the non-appearance and present evidence of the validity of these reasons. If the failure to appear is due to the fact that the representative was not properly notified, the trial is postponed. nine0003
If the failure to appear is due to the fact that the representative was not properly notified, the trial is postponed. nine0003
Art. 288 Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation
As a result, the court either satisfies the application of the minor or refuses. The latter is possible, for example, if the court doubts the financial independence of a teenager.
Here is an example of a court decision that found a teenager to have full legal capacity despite his father's opposition. The latter believed that his son was still too young in his development and did not give an account of his actions. And he wants to emancipate himself in order to sell the share in the apartment registered to him without the consent of his father. nine0003
In addition to the employment contract, the court of first instance drew attention to the characteristic from the school that the teenager brought: teachers noted that in his actions he is always guided by the interests of the good of the cause, and not by his own benefit, speaks the truth, actively fights against what he considers unfair, enjoys prestige among classmates. This allowed the court to conclude that the father’s doubts about the immaturity of his son are unfounded and the boy has no obstacles to gain legal capacity. nine0003
This allowed the court to conclude that the father’s doubts about the immaturity of his son are unfounded and the boy has no obstacles to gain legal capacity. nine0003
What emancipation means for a teenager
An emancipated teenager and a person who is married before the age of 18 receive the same rights and obligations. Here are the main ones:
- the right to engage in entrepreneurial activities without parental consent;
- the right to independently defend one's rights and legitimate interests in court;
- the right to independently dispose of real estate;
- liability for his obligations with property belonging to him; nine0018
- parents or guardians are no longer liable for his obligations, in particular those arising from harm caused to them.
Emancipated adolescents become full-fledged participants only in civil legal relations. Other age restrictions and qualifications - electoral and administrative - are not cancelled. That is, such a teenager will not be able, for example, to vote in elections or buy alcohol and cigarettes. Also, he can be drafted into the army only from the age of 18. nine0003
That is, such a teenager will not be able, for example, to vote in elections or buy alcohol and cigarettes. Also, he can be drafted into the army only from the age of 18. nine0003
sign. 11 p. 2 art. 16 of the Federal Law on the regulation of the production and circulation of alcohol
paragraph 1 of Art. 22 of the Federal Law on military duty and military service
Here is another thing that a teenager under 18 has no right to do:
- drive a car;
- acquire self-defense weapons, as well as sporting, hunting, signal weapons and edged weapons;
- be a guardian or custodian, adopt a child.
Rights and guarantees in the field of labor protection do not change after emancipation. According to labor legislation, a sparing regime is applied to a teenager: he cannot work in hazardous and dangerous industries, business trips and overtime are unacceptable, and his working week must be reduced - a maximum of 35 hours. nine0003
nine0003
Art. 92, 265, 268 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation
Even minors are given extended paid leave - 31 calendar days. From the age of 18, it is reduced to 28 days.
Pluses and minuses of emancipation
The plus of emancipation, in addition to the expansion of civil rights, is in the formation of legal consciousness: a teenager learns to be accountable for his actions and to bear responsibility.
Of the minuses, it can be noted:
- a minor is still a child who will not always be objective and firm in his decisions. Until he gets enough life experience, he can act impulsively. And his indiscretion in the field of entrepreneurship can lead to financial losses; nine0018
- Parents or guardians are involved in the process. Some parents push their children to emancipation for selfish reasons in order to stop supporting them. Others, on the contrary, do not give consent, because, for example, they are afraid that the teenager will sell the property registered to him;
- becoming emancipated, an adolescent loses his former rights and acquires new ones.
 For example, a minor under 18 is entitled to receive alimony from his parents, an emancipated teenager is not. Moreover, he is now obliged to pay alimony to disabled parents. nine0018
For example, a minor under 18 is entitled to receive alimony from his parents, an emancipated teenager is not. Moreover, he is now obliged to pay alimony to disabled parents. nine0018
/prava/prava-deti/
Rights of children under 18
What is the result
- Emancipation is the recognition of a teenager from 16 to 18 years of age as fully capable. To do this, he must be financially independent - work under an employment contract or engage in entrepreneurial activities with the consent of his parents.
- There is another way to get the rights of an adult under 18 years old - to marry. Moreover, depending on the region of the country and circumstances, the status can be obtained after 14 years. nine0018
- Some emancipation age limits remain: such a teenager under 18 still cannot, for example, drive a car, vote or buy alcohol.
- An emancipated adolescent is fully and independently responsible for his obligations, including for harm caused to him.
 Legal representatives are no longer responsible for this, even if the teenager does not have money to compensate for the damage.
Legal representatives are no longer responsible for this, even if the teenager does not have money to compensate for the damage. - An emancipated teenager no longer receives alimony and must also support disabled parents. nine0018
- Emancipation is an irrevocable act and cannot be undone.
Materials that will help parents save their budget and sanity are in our telegram channel @t_dety.
How to write an article about your parenting experience, we tell in our manual: read it and become our author.
How to get legal independence from parents - an expert tells
Loudspeakers
Speakers
Ekaterina Grigorieva
Specialist in civil law, labor, corporate and PIL issues
Anna Melikyan
You become an entrepreneur in order to be independent and do your own thing. But what kind of independence can there be when you are not yet 18 and your parents are responsible for you? It can be difficult for an entrepreneur without freedom of action, because you cannot do business with you directly, without the involvement of your parents or guardians (Article 26 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation), you will not be able to register your company yourself either. One way out is to go through the process of emancipation. How to do this, tells a legal expert. nine0003
But what kind of independence can there be when you are not yet 18 and your parents are responsible for you? It can be difficult for an entrepreneur without freedom of action, because you cannot do business with you directly, without the involvement of your parents or guardians (Article 26 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation), you will not be able to register your company yourself either. One way out is to go through the process of emancipation. How to do this, tells a legal expert. nine0003
Anna Melikyan
Why emancipate
The meaning of emancipation is the early acquisition of full legal capacity, so that the minor does not need to receive consent from his parents / adoptive parents / guardian each time to engage in entrepreneurial activity. A capable citizen is a person who can understand the meaning of his actions or manage them, that is, he is aware of the legal consequences. nine0003
nine0003
According to art. 27 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, a minor who has reached the age of 16 may be declared fully capable:
- If he works under an employment contract, including under a contract;
- With the consent of the parents, adoptive parents or guardian is engaged in entrepreneurial activities.
The guardianship and guardianship authority can recognize a minor as fully capable by its decision - with the consent of both parents / adoptive parents / guardian. In the absence of such consent, the issue is resolved through the court. nine0003
It is important to understand that such a decision, if it was made legally, is irrevocable! Parents, adoptive parents and guardian are not liable for the obligations of an emancipated minor (clause 2, article 27 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
How to emancipate
The administrative regulations for the provision of public services for declaring a minor fully capable (emancipation), which is applied by the guardianship and guardianship authorities, are adopted in each region, therefore, when preparing documents, you must be guided by the act of your region. nine0003
nine0003
For example, in Moscow, all information is presented in detail on the website of the Mayor of Moscow.
In order to become emancipated, you first need to prepare the following documents:
| Document | Form, return |
| Birth certificate of a minor | Original Provided only for viewing (copying) at the beginning of the service |
| Passport of a minor nine0276 | Original Provided only for viewing (copying) at the beginning of the service |
| Passports of the legal representatives of the minor | Originals Provided only for viewing (copying) at the beginning of the service |
| Request (application) for the provision of public services | Original Provided without refund |
| Written consent of the legal representatives of the minor nine0276 | Original Provided without refund |
| Documents confirming labor activity | Originals Provided without refund |
Documents are submitted to the district department of social protection of the population at the place of residence. The term for the provision of the service is 15 working days.
The term for the provision of the service is 15 working days.
As a result you will get:
- Announcement on the recognition of a minor as fully capable
OR
- Refusal to recognize a minor as fully capable.
What to do if you were denied emancipation
There are two reasons for refusal:
- You provided incorrectly executed or invalid documents, if these circumstances were established in the process of reviewing the documents.
- The provision of a public service is not in the interests of a minor.
If your parent/adoptive parent/custodian does not give their consent to emancipation or you were refused, then there is an opportunity to apply to the court of general jurisdiction at the place of residence:
You write an application ⇛ attach a document confirming your work activity, and a written refusal of the parent / adoptive parent / guardian, or guardianship and guardianship authority ⇛ participate in the court session ⇛ the court makes a decision.
State bodies approach the emancipation procedure not only formally. Since the main goal is to protect the interests of a minor, many factors are taken into account: stability of activity, level of earnings, availability of property, state of health. nine0003
Once you receive confirmation that you are fully capable, you become a fully independent figure from a legal point of view and receive all the rights and obligations of a fully capable citizen of the Russian Federation, without restrictions, for example, you can be a defendant in court, get a driver's license or adopt a child.
Materials on the topic:
Rusbase Young is looking for authors for the youth editorial office
"Conclude an agreement - and only then start working." Advice from a corporate lawyer
How to sign a lease as an entrepreneur
Cover photo: Unsplashed
- Career
- Children
- Parents
- Teenagers
- YAuthor
- RB Young nine0018
Found a typo? Select the text and press Ctrl + Enter
Related materials
- one How can I get on the budget? I'm not a prodigy!" — and other fears of graduates
- 2 “Unified State Examination can be taken for three years”: how college students prepare for exams nine0018
- 3 I lived and studied in the USA for a year - how it changed me
- 4 Flexible schedule and nothing more: why transfer to distance learning in grade 11 nine0018
- five “On the way back, I accidentally hit a pole and didn’t even feel pain.
 ” How to survive the Olympiad for schoolchildren
” How to survive the Olympiad for schoolchildren
POSSIBILITIES
December 18, 2022 nine0003
VK Cup 2022
December 18, 2022
Academy of Innovators
December 26, 2022
"Safe Internet"
December 26, 2022 nine0003
Goznak Startup Lab
December 30, 2022
Softlanding Program
All possibilities
Stories
OpenAI: creator of Chat GPT and a potential "threat to humanity" nine0015
News
VK introduced NFT avatars and announced the launch of a token marketplace
News
The founders of the Russian brand of tattoo gloves Glove.