How to adopt a child from russia
Children of All Nations Russia Adoption
| We are currently not accepting Russia applications. This website will provide you with updates and announcements regarding when we will accept new applications in our Russia adoption program. About Russia is home to over 143 million people and is the world’s largest country by land mass. Though Russian is the national language, and the vast majority of the population claims it as their native tongue, there are over 100 different ethnic groups, many of which speak different languages throughout Russia. The fall of the Soviet Union brought Russia into an economic tailspin, causing many skilled workers and their families to fall into poverty. Governance of Russian Adoptions Russia’s Adoption Authority is the Ministry of Education and Science, which requires any agency wishing to facilitate adoptions in Russia to be fully accredited by the Russian government. Children of All Nations partners with a fully accredited Russian agency with over 13 years of experience, and an excellent relationship with the Russian adoption authority, to help families welcome home their children adopted from Russia. If you would like more information about our Russia program, our adoption consultants are standing by to help! Call us today at 1.877.827.5226 or send us an email! Children Available Russian children are placed in orphanages due to voluntary relinquishment by their parents, involuntary removal from their homes, or the death of their parents. Poverty is a major reason for parents abandoning or relinquishing their children because they simply cannot feed or clothe them. When selecting a child, consider that you may adopt the following:
When adopting from Russia, through CAN, families are not allowed to pursue an adoption at the same time through a different agency. If you would like more information, please give us a call today at 1.877.827.5226 or send us an email! Russia Adoption Requirements In addition to the USCIS eligibility requirements for prospective adoptive parent(s), Russia has the following requirements, which may vary by region.
Russia adoption eligibility requirements are subject to change per Russia’s adoption laws. CAN updates these guidelines as necessary. If you would like more information about our program, our specialized adoption consultants are standing by to help! To have your questions answered, call us today at 1.877.827.5226 or email us. Adoption Timeline The time frame to complete international adoption from Russia is currently about 12 to 16 months, depending on the time families take to complete their dossier paperwork, their preferences for age and gender, and country processes. Cost Overview Our Russian adoption fees are among the lowest available. We strive to keep costs low so that we may help as many children as possible find their loving, forever family. For a full list of program fees for your adoption from Russia, please request our Children of All Nations Outreach Guide. The Process 1. Application and Approval To adopt a child, please complete our agency application. For your convenience, you may access the application online. We will promptly review your eligibility to adopt from Russia once we receive your application. If approved, we will provide you with our agency contract that outlines our fees, services and important information regarding the Russia adoption process. Upon receipt of your signed contract, CAN will start to provide you with placement services for children from Russia. 2. The Paper Chase Once your agency contract is in place, it is time to start assembling your dossier. This will include a home study, which will assess your readiness for international adoption from Russia and help prepare you for adoptive parenthood, filing with USCIS for international adoption approval, and gathering your dossier documents. Please consult CAN before beginning your home study, as certain home study agencies will not be accepted by MED. All dossier documents must go through the appropriate notarization, certification and authentication processes before being sent to Russia. We offer a complete Dossier Preparation Service to ease your international adoption process and give you peace of mind. To ensure that prospective adoptive parents are prepared for their international adoption journey, our agency requires that parents complete 80 hours of adoption training as mandated by the Hague Convention. To satisfy these hours, we have developed an online parent training program that we are proud to include in CAN’s service plan. 3. Identifying a Child After the Ministry of Education reviews your dossier, they will issue preliminary information on a child based on the family’s specifications. This is normally referred to as a “referral”, but the Russian government does not consider it as such until you meet the child and agree to adopt them. The matching process may take anywhere from one month to nine months, depending on the region and the age and number of children you wish to adopt, or if they have special needs. 4. Picking Up Your Child After you are matched with a child, you will plan your first trip to Russia to meet your child and decide whether you would like to proceed with the adoption. You will then return home until it is time to return to Russia for your court hearing. Both parents are required to travel to Russia to attend the court hearing, but in special circumstances one parent’s appearance on the first or second trip may be waived. 5. Post Adoption Requirements Russia requires that you submit four post adoption reports at 6, 12, 24, and 36 months following your return home from Russia. The first report will be completed by your family and will not require a social worker. These reports demonstrate to the Russian government the benefits of international adoption for their children. In addition, simpler reports at 2, 4, 8, and 10 months are required, which can be less in-depth than the major reports. CAN’s post-adoption staff will guide you through the post-adoption process. You can now begin your new life with your children! Orphanage Information Orphanages in Russia are scattered throughout the country, with multiple regions, and a subcentral authority in control over the region’s orphanages. Resources Hague Adoption GlossaryClick here to review important terms related to adoption and The Hague Convention. Books for Parents
Children’s Books
Articles
WebsitesHealth and Wellness
Support and Education
|
Russia Adoption Program- Suspended Indefinitely
The Russia Adoption Program is currently suspended indefinitely due to Russian Ban on Adoptions. While the program is suspended please consider our Kazakhstan, Ukraine, Bulgaria and Romania Adoption Programs.
Nightlight has programs in several regions of Russia, including St. Petersburg and Tomsk. Until we are able to obtain a permit for in-country activities, we are partnering with other agencies which hold permits and have temporarily assumed responsibility for our in-country staff. We continue to maintain an office and staff in Moscow as a registered Non-Governmental Organization.
Petersburg and Tomsk. Until we are able to obtain a permit for in-country activities, we are partnering with other agencies which hold permits and have temporarily assumed responsibility for our in-country staff. We continue to maintain an office and staff in Moscow as a registered Non-Governmental Organization.
CHILDREN AVAILABLE
The orphanages in Russia are called Baby Houses and Detsky Dom’s (Children’s Homes). Babies from a few months of age to about 3-4 years stay in Baby Houses, while older children stay in Children’s Homes. Children’s Homes are further divided between preschool orphanages (ages 4-7), school age orphanages (7-16) and combined orphanages. Some orphanages specialize in children with special needs, such as learning disabilities, vision impairments, orthopedic problems, etc. Many times children who have not been put in school by their parents will be assigned to orphanages where they will receive more remedial assistance, even though their intellectual capabilities may be good.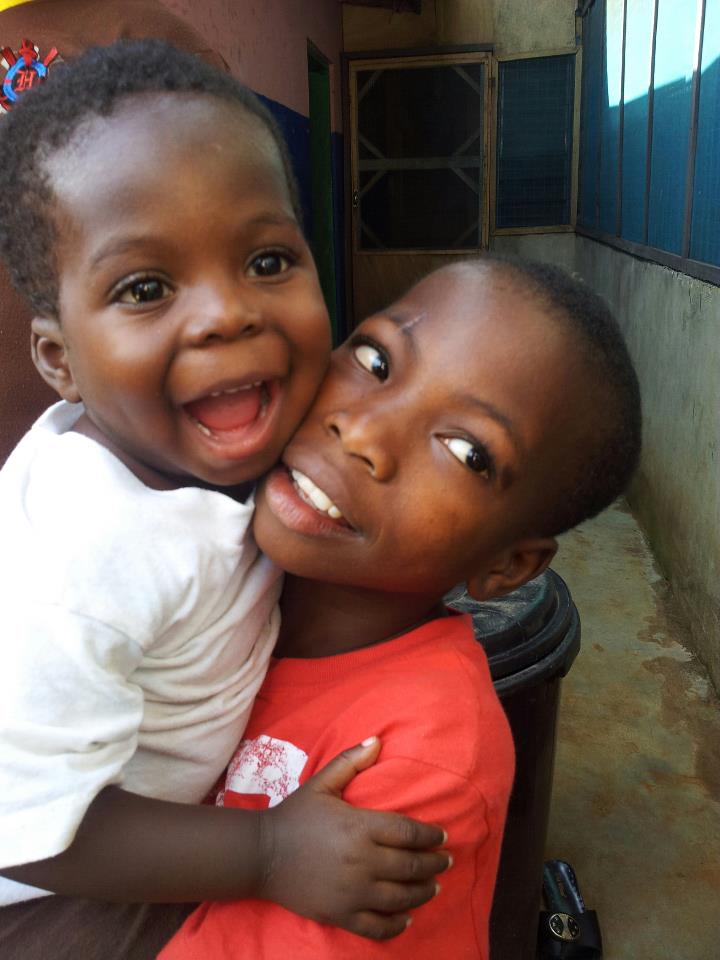
ELIGIBILITY TO ADOPT
Married couples or single women may apply to adopt from Russia. We require that the adopting parents be no more than 45 years older than the child, although this requirement may be relaxed somewhat in the cases of older children. The parents must be in good health. Questions as to the number of other children in the family and other considerations are evaluated on a case by case basis depending on the characteristics of the child who is sought for adoption. The orphanage director, the adoption officials or the court may impose other restrictions as they consider necessary or advisable.
PROCESS
It generally takes around 8-14 months to complete the adoption process (and sometimes longer for little girls). First you will need to complete your home study, get CIS (formerly INS) approval and prepare your dossier for Russia (about 3-5 months). Once your dossier has been filed with the local adoption officials in Russia, you will be considered for a referral of a child.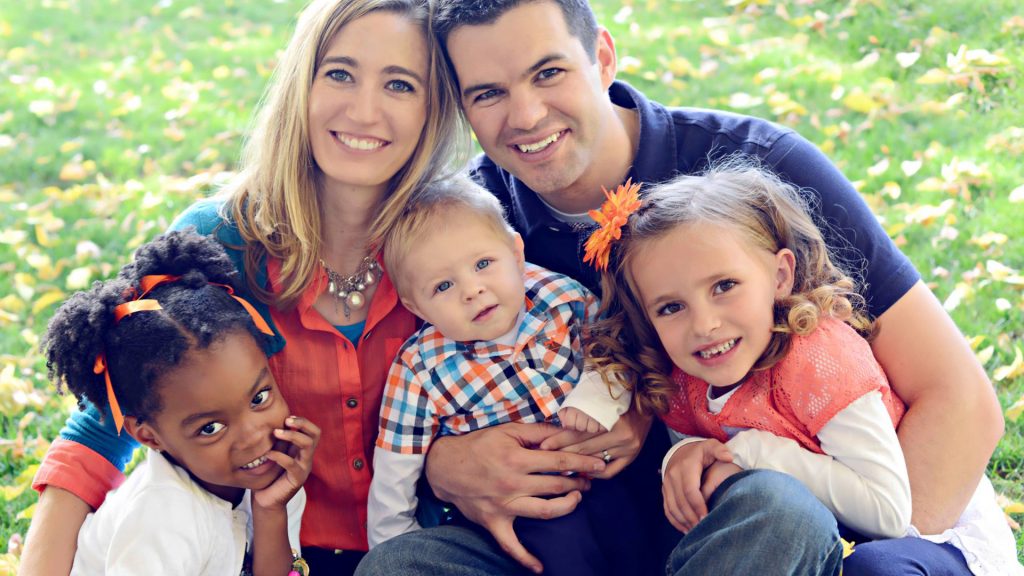 The more flexible you are and the older the child you hope to adopt is, the shorter the time frame to wait for a child. No advance information on available children can be provided by persons other than the Russian adoption officials. Providing videos and medical information on children are specifically not allowed. (When older children have been identified through activities unrelated to adoption ( i.e., hosting programs or missionary trips, the referral of the identified child can usually be obtained if they are legally eligible for adoption.)
The more flexible you are and the older the child you hope to adopt is, the shorter the time frame to wait for a child. No advance information on available children can be provided by persons other than the Russian adoption officials. Providing videos and medical information on children are specifically not allowed. (When older children have been identified through activities unrelated to adoption ( i.e., hosting programs or missionary trips, the referral of the identified child can usually be obtained if they are legally eligible for adoption.)
Both parents must make the first trip, lasting about one week, to Russia to receive the official referral of a child. On this trip, you will receive a referral and get to know the child. You will be able to ask a variety of questions concerning the child’s medical and social history. In addition, you will be able to access independent physicians to assist you in evaluating a child. If you do not accept the first referral, you may be able to receive a second referral on the same trip, depending on the age of the child requested. Once you have accepted the referral, you return home to await a court date. The court date is usually set around 8 weeks after your first trip (allowing time for verification to be received from Moscow that your child has been on the Federal Data Bank for more than six months and the court to review your dossier).
Once you have accepted the referral, you return home to await a court date. The court date is usually set around 8 weeks after your first trip (allowing time for verification to be received from Moscow that your child has been on the Federal Data Bank for more than six months and the court to review your dossier).
Both adopting parents are required to be present in court. Russian law provides for a 10-day waiting period before an adoption decree becomes effective. This 10-day period can be waived by the judge if s/he believes it is in the best interest of the child, but such a waiver is not common. Once the adoption is completed, a new birth certificate is issued for the child, a Russian passport is issued in the child’s new name and you travel to Moscow to obtain the child’s immigrant visa. You would normally travel directly home from Moscow.
TRAVEL
Once your dossier is completed, we will provide you with a “Travel Package” which outlines all of the details of your travel (2-3 trips). We will make all of your in-country lodging reservations and you may make whatever air travel arrangements you prefer (although we will also help you with this step if requested). Your first trip will be about 5 days and your court trip will typically be 5 days. Assuming the 10 days are not waived, your third trip will be about 7 days (only one parent needs to travel on the third trip).
We will make all of your in-country lodging reservations and you may make whatever air travel arrangements you prefer (although we will also help you with this step if requested). Your first trip will be about 5 days and your court trip will typically be 5 days. Assuming the 10 days are not waived, your third trip will be about 7 days (only one parent needs to travel on the third trip).
POST ADOPTION
Once you return home, you will need to immediately register your child’s passport with the Russian Embassy (we will provide you with instructions). At this time, Russia requires that you complete a minimum of 4 post-adoption visits with your homestudy provider to evaluate your child’s adjustment into your family. Along with several pictures, these reports will be sent to the orphanage staff and officials for receipt in Russia at 6 months, 1 year, 2 years and 3 years after your child’s adoption is finalized. (Please be prepared to be flexible as government requirements for post-adoption reports occasionally change and you will be expected to fulfill the most recent requirements. )
)
COSTS
The costs for an adoption from Russia are explained on the current Fee Schedule and range from $33,400 to $42,300. The Fees and Costs include Program Fees, Orphanage Donations, and Estimated Client Coordinated Expenses including travel, lodging, CIS fees and misc. costs. The fees for children 7 and older are reduced to so that families can be encouraged to adopt older children. We make every effort to give you a realistic budget to avoid surprises. However, variations may result from differences in homestudy costs, travel and actual length of stay in Russia. If you receive the full tax credit of $13,170, then your fees and expenses can be as low as $23,230. Also, if you adopt a sibling group of two, you may receive up to $26,340 in the tax credit/ for each additional sibling, the tax credit/refund can be increased by $13,170. This may mean that the cost of your adoption could be nearly paid for by the tax credit. This usually takes a few years to recoup all these tax credits if you adopt more than one child.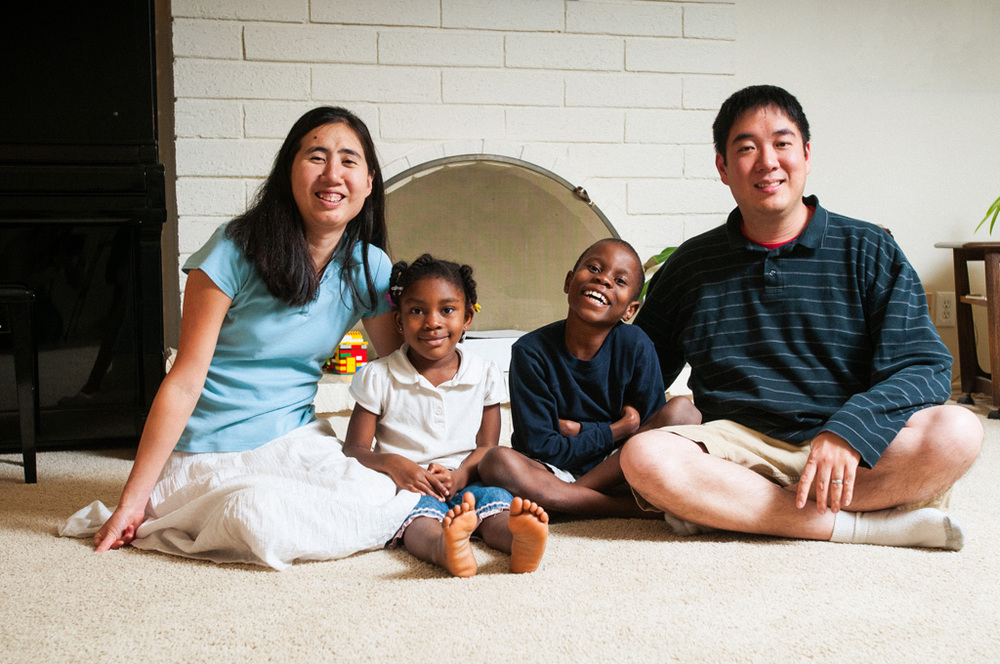
In addition, your out-of-pocket expenses may further be reduced if you receive scholarships or other employer-provided adoption benefits.
procedure and legal consequences of adoption, what is needed, conditions, documents, consent of the child, rights and obligations of foster parents
Tamara Skokova
creates a benefit for the family
Author profile 37 thousand children.
In the understanding of many people, "to adopt a child" means to take an orphan from an orphanage. However, from a legal point of view, everything is not so simple. Today in Russia there are several forms of family placement for children, and they are regulated differently by law.
I worked in the guardianship and guardianship authorities for 17 years, 14 of them as a supervisor. In the article I will tell you who and under what conditions has the right to take a child into a family, what documents are required for adoption and how the procedure takes place.
What is adoption of a child
In Russia, there are several forms of placement of orphans and children left without parental care. Federal legislation establishes three main ones: adoption, guardianship and guardianship, foster family. At the regional level, others may be provided, but so far this is only patronage. Briefly describe how they differ from each other.
Custody and guardianship. The most common form of placement for children: often used as an intermediate step on the path to adoption.
Guardianship and Custody Act
Guardianship is established over children under 14 years of age, and guardianship over minors from 14 to 18 years of age. Guardians and trustees have all the rights and obligations of a legal representative in matters of upbringing, education, maintenance of the child and responsibility for him.
Unlike the guardian, the guardian is liable for harm caused by the ward. He is also obliged to make all transactions on behalf of the ward, except for those that the child can conclude personally: for example, these are donation transactions when a minor receives some thing or money as a gift.
Art. 1073, paragraph 2 of Art. 26 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation
The trustee usually must give consent to the transactions of the ward, with a few exceptions: for example, minors aged 14 to 18 years have the right to independently manage their income or make small household transactions.
Art. 12.1 of the Federal Law on state benefits to citizens with children
p. 3 art. 38.1 of the Social Code of the Belgorod Region
Monthly, the guardian and trustee are paid an allowance for the maintenance of an orphan child. Its size depends on the region: for example, in the Belgorod region, where I live, in 2022 the allowance is 10,310 R.
In addition, guardians are entitled to a one-time payment from the federal budget - 22,472.77 RUR. This amount is set for all guardians from the Russian Federation, regardless of place of residence.
Lump-sum allowance when a child is brought up to a family
If a child is brought up by a guardian or custodian, the biological parents are not released from the obligation to support him and must monthly transfer alimony to his personal account: the amount of alimony is determined by the court.
Art. 148, paragraph 2 of Art. 71 SK RF
At the same time, the guardian decides whether the biological parents will be able to communicate with the child, but if the child is 10 years old, then his opinion will also be taken into account.
Art. 148.1 SK RF
Foster family. This form of arrangement is similar to guardianship, but in addition to child support and a lump sum payment, foster parents also receive remuneration for their work.
Art. 152 SK RF
The amount depends on the region of residence. For example, in 2022 in Moscow it is 18,150 R, and if a family accepts a child with a disability, then the amount of the payment will be higher - 30,885 R.
Clause 2.5.1 of Appendix 1 to the Decree of the Government of Moscow on establishing the amount of social payments for 2022
In the Belgorod Region, foster parents are paid 8288 R per month for the first child taken into the family, and for each subsequent adopted child the amount is increased by 20%. If a family accepts up to four children, the remuneration is paid to one of the parents, five or more children to both. In rural areas, there is still a monthly supplement of 25% of the remuneration due to foster parents. Foster parents have more privileges than guardians: they are provided with a 50% discount on utility bills, fuel, gas, telephone.
If a family accepts up to four children, the remuneration is paid to one of the parents, five or more children to both. In rural areas, there is still a monthly supplement of 25% of the remuneration due to foster parents. Foster parents have more privileges than guardians: they are provided with a 50% discount on utility bills, fuel, gas, telephone.
paragraph 5 art. 148.1 of the RF IC
Law of the Belgorod Region on Foster Family
Law of the Belgorod Region on Amendments to Article 2 of the Law of the Belgorod Region “On Foster Family”
The seniority can be accrued to both one parent and both - it all depends on who has concluded a civil law contract with guardianship.
Art. 7 Federal Law on compulsory pension insurance
The foster child and biological parents can communicate. Foster parents have the right to prevent this only if communication does not meet the interests of the child.
Section 5, Art. 148.1 SK RF
Patronage .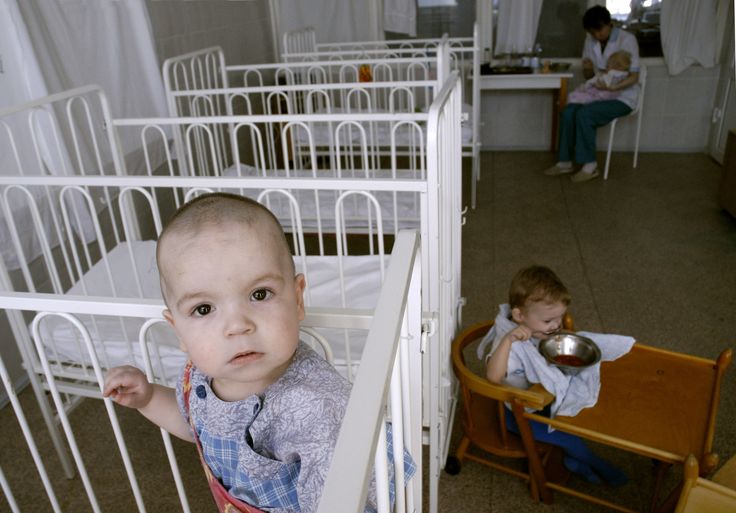 Foster care is a relatively new form of family structure, in which the rights and obligations to protect the rights of children are delimited between the foster caregiver and the guardianship and guardianship authority. Laws supporting patronage have been adopted in 42 constituent entities of the Russian Federation, for example, in Moscow, Vladimir, Kaluga, Ivanovo and Kaliningrad regions.
Foster care is a relatively new form of family structure, in which the rights and obligations to protect the rights of children are delimited between the foster caregiver and the guardianship and guardianship authority. Laws supporting patronage have been adopted in 42 constituent entities of the Russian Federation, for example, in Moscow, Vladimir, Kaluga, Ivanovo and Kaliningrad regions.
Laws and regulations on patronage of the Moscow, Vladimir, Kaluga, Ivanovo, Kaliningrad regions shelter.
The child is transferred to foster care under a fixed-term contract. The period of stay in the family is set individually: it can be a short period - up to six months or a long one - over six months. The maximum term is until the minor reaches the age of eighteen.
For a long time, a child is placed in a foster family only if, for some reason, it is not possible to transfer the child to a guardian, custodian or foster family. In this case, the foster family receives a monthly allowance from the state for the maintenance of the child. The amount is similar to that allocated for guardianship and guardianship. But the right to receive a one-time allowance when a child is adopted into a family does not apply to foster parents.
The amount is similar to that allocated for guardianship and guardianship. But the right to receive a one-time allowance when a child is adopted into a family does not apply to foster parents.
Foster care gives the child the opportunity to prepare for an independent adult life - this is difficult to do in an orphanage. But this form of arrangement has one big drawback - children often become attached to new families and parting with it causes them stress. With all this, the child does not lose touch with the blood family: he can maintain relations with his parents, if they are not deprived of parental rights and do not pose a danger to him, brothers, sisters and other people significant to him.
/list/sos-dd/
9 uncomfortable questions about orphans
Adoption. The Family Code of the Russian Federation considers this form of placement of children a priority: only it allows you to most effectively ensure both the interests of the child and the interests of foster parents.
Adoptive parents completely replace the child's parents. Here there is no such temporary nature of upbringing as in guardianship, guardianship or when transferring a child to a foster family. The state does not provide adoptive parents with any special assistance, with the exception of social support measures established in each subject separately, as well as measures that are provided to all families with children on a general basis.
Adoptive parents can change the child's first and last name. For children under one year old, even the date of birth can be changed, but not more than three months from the actual one. This happens in order to ensure the secrecy of the adoption, as well as for other reasons, if the court considers them valid. In my practice, there was such a case: the spouses raised an adopted boy born on September 8, 2007, and then adopted a girl born on July 25, 2007. The adoptive parents asked the court to change the boy's date of birth to July 25, 2007, so that the children could be considered twins. The court granted the request.
The court granted the request.
Art. 139 SK RF
art. 155 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation
In many regions, adoptive parents receive benefits for an adopted child. To apply for it, you must apply to the guardianship authorities at the place of residence. For example, in the Belgorod region, the amount of the allowance depends on how much money was allocated for the monthly maintenance of a child in an orphanage in the current year, the adoptive parent is entitled to 50% of this amount. And in the Stavropol Territory, a monthly allowance for adoptive parents is not provided, but a lump sum payment is made - 150,000 R.
cl. 1 art. 60 of the social code of the Belgorod region
art. 2 of the Law of the Stavropol Territory on the amount and procedure for assigning a lump-sum allowance to adoptive parents
In Moscow, the monthly compensation payment to persons who have adopted or adopted an orphan child or a child left without parental care in the city of Moscow is:
- 18 937 R for each child from 0 to 12 years old who is not a disabled child;
- 25,249Р for each child from 12 to 18 years old who is not a child with a disability;
- R 31,561 for each disabled child.

Clause 2.9 of Appendix 1 to the Decree of the Government of Moscow on establishing the amount of social payments for 2022
Also, adoptive parents are entitled to a lump-sum allowance, which is issued for all forms of family placement. From February 1, 2022, this is 20,472.77 R. But in the case of the adoption of a disabled child, a child over seven years old, as well as children who are brothers or sisters, the allowance will be higher - 156,428.66 R. To receive a payment, you need to apply to the Pension Fund at the place of residence.
Lump-sum allowance when a child is placed in a family for upbringing
What is the difference between the forms of placement of a child in a family
| Form | Who is considered the child's parents | What rights do carers have | What are the duties of caregivers | How the state supports child caregivers |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adoption | Adoptive parents | The rights of adoptive parents are identical to those of natural parents | Obligations of adoptive parents are identical to those of natural parents | Adoptive parents receive payments provided by the regional authorities. Also, adoptive parents receive the right to use maternity capital, if it was not used by the birth mother, and all child benefits in accordance with age. A child who at the time of adoption has the right to a pension and benefits due to the death of his parents retains this right after adoption Also, adoptive parents receive the right to use maternity capital, if it was not used by the birth mother, and all child benefits in accordance with age. A child who at the time of adoption has the right to a pension and benefits due to the death of his parents retains this right after adoption |
| Custody and guardianship | Blood family | The guardian or custodian has the right to raise the child and act as his legal representative | Guardians and trustees are obliged to take care of the maintenance of the wards, to provide them with care and treatment, to protect their rights and interests. At the same time, biological parents are not released from the obligation to pay alimony | Guardians and custodians receive a one-time allowance upon adoption of a child into a family, allowance for the maintenance of a ward, alimony payments, survivor's pension, if it is due to the child |
| Foster family | Blood family | Similar rights as under guardianship | Similar duties as under guardianship | The foster family receives a one-time allowance when the child is adopted into the family, a monthly remuneration to the foster parent for the performance of duties and an allowance for the maintenance of the child in the family of the guardian, depending on the legislation of the region, benefits for utilities. The period while the child is in the family is counted towards the foster parents in the insurance period The period while the child is in the family is counted towards the foster parents in the insurance period |
| Patronage | Blood family | Determine the daily routine of the pupil, resolve current issues of the pupil's life in accordance with the plan for the protection of the rights of the child and the concluded agreement | Raise a child, protect his rights and legitimate interests, take care of his health and development | The amount of payment for a foster caregiver is determined by a fixed-term employment contract of the region. The monthly payment to foster care providers for the maintenance of an orphan child or a child left without parental care is established by each region separately |
Adoption
Who is considered the parents of the child
adoptive parents
What rights arise in persons to care for the child
Rights of the adoptive parents are identical to blood parents
What are the obligations to ensure care of child
The obligations of adoptive parents are identical to those of natural parents
How the state supports persons providing care for a child
Adoptive parents receive benefits provided by the regional authorities. Also, adoptive parents receive the right to use maternity capital, if it was not used by the birth mother, and all child benefits in accordance with age. A child who at the time of adoption is entitled to a pension and benefits due to the death of his parents retains this right after adoption
Also, adoptive parents receive the right to use maternity capital, if it was not used by the birth mother, and all child benefits in accordance with age. A child who at the time of adoption is entitled to a pension and benefits due to the death of his parents retains this right after adoption
Guardianship and guardianship
Who is considered the child's parents
Blood family
What rights do caregivers have
A guardian or custodian has the right to raise a child and act as his legal representative.
What obligations do persons who provide care for a child have? At the same time, biological parents are not released from the obligation to pay alimony
How the state supports child caregivers
Guardians and guardians receive a one-time allowance for the adoption of a child into a family, support for the maintenance of a ward, alimony payments, survivor's pension, if the child is entitled to it
Foster family
3
3 Who is considered the child's parents
Blood family
What rights do caregivers have
Similar rights as in guardianship and guardianship
What are the obligations of persons providing care for a child
Similar obligations as in guardianship and custody
How the state supports persons providing care for a child for the performance of duties and allowance for the maintenance of a child in the family of the guardian, depending on the legislation of the region, benefits for utilities. The period while the child is in the family is counted towards the foster parents in the insurance period
The period while the child is in the family is counted towards the foster parents in the insurance period
Employment
Who are considered the parents of the child
Blood family
What rights do caregivers have
Determine the child’s daily routine, resolve current issues of the child’s life in accordance with the contract and child protection plan
What are the responsibilities of those who care for a child
Raise a child, protect his rights and legitimate interests, take care of his health and development
How the state supports child caregivers
The amount of payment for a foster caregiver is determined by the region's fixed-term employment contract. Monthly payment to foster care for the maintenance of an orphan or a child left without parental care is established by each region separately
Who can adopt a child
Married couples or single adults can adopt a child: if citizens are not married to each other, they cannot jointly adopt the same child.
Art. 128 SK RF
Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation on approval of the rules for the transfer of children for adoption
Another important condition is that a man or woman must reach the age of majority, and the age difference between the adopter and the child must be at least 16 years. But if the adoptive parents are a married couple, and the age difference is less than the established norm with only one of them, then the guardianship department may, as an exception, give consent.
Other requirements for an adopter:
- Legal capacity: own and spouse, if any.
- Absence of a conviction for a grave and especially grave crime.
- A health condition that allows you to fulfill parental responsibilities: for example, a child will not be allowed to be adopted by patients with tuberculosis or people with disabilities of the first group.
- Home ownership or rental.
- Substitute parents have a school leaving certificate.

- No information about deprivation or restriction of parental rights, cancellation of adoption, removal from the duties of a guardian.
If there are several people who want to adopt a child, his relatives will have the priority right, but taking into account the interests of the adoptee: they are expressed in trusting relationships, attachment to relatives, long-term cohabitation.
Community 24.05.22
How is the secrecy of adoption protected in Russia?
Next, I will tell you what documents future parents will need to collect and how the adoption procedure goes.
Step 1
Get to know the guardianship authorities at your place of residence As a rule, there is an adoption specialist in each district municipality. He can work both at the education department and at the department of social protection of the population: this needs to be clarified in the social protection or education authorities at the place of residence.
In some cities, for example, in St. Petersburg, Vladimir, Krasnoyarsk, special adoption and guardianship centers have been created, where future adoptive parents are assisted in paperwork, passing medical examinations, and selecting children. Such an integrated approach greatly simplifies and speeds up the entire procedure.
Center for Family and Children Assistance, St. Petersburg
Center for the Development of Family Forms of Education, Krasnoyarsk
Center for Psychological, Pedagogical, Medical and Social Assistance, Vladimir
At the first visit, candidates for adoptive parents should simply talk with an employee of the guardianship authority is, in fact, an acquaintance. The task of a specialist is to listen to you, to find out the motive for adoption, to understand how fully you understand the responsibility of such a step, whether your housing, family and material conditions meet the requirements of the law.
The guardian must explain your future rights and obligations in relation to the adopted child, the procedure for the adoption procedure, answer your questions, and issue the necessary forms, referrals and a list of documents. Here it is:
Here it is:
- A copy of the adoptive parent's marriage certificate, if he is not married, then a copy of the birth certificate: sometimes the court asks him to see if the adoptive parent's surname has changed.
- Passport copies.
- Original and copy of the medical certificate for each of the adoptive parents.
- Certificate of criminal record or non-conviction.
- When a child is adopted by one of the spouses, the consent of the other spouse or a document confirming that the spouses have terminated family relations and have not lived together for more than a year.
- Certificate from the place of work on the position held and salary, or a copy of the income statement or other document confirming the income of the adoptive parent or family of adoptive parents.
- Documents confirming the right to use the residential premises or the ownership of the residential premises.
- Certificate of completion of training for persons wishing to adopt a child without parental care into their family.

- CV (needed only for the guardianship authority).
The main part of the documents is required to obtain an opinion from the guardianship authorities on the possibility of being an adoptive parent. Later, they will also be needed to apply for adoption to the court. Documents for the child will be prepared by guardianship officials.
Step 2
Obtain a certificate of no criminal recordI recommend that you start collecting documents from this certificate. Since the request is sent to the Main Information Center of the Ministry of Internal Affairs, a response will have to wait from a week to a month.
An application for issuing a certificate can be filled out at the MFC or independently on the public services portal.
/guide/ne-sudim/
Why do you need a certificate of non-conviction
To order a certificate through the public services portal, you need to go to your personal account and select the public service: "Obtaining a certificate of the presence (absence) of a criminal record. " Source: gosuslugi.ru This is what a certificate of no criminal record looks like
" Source: gosuslugi.ru This is what a certificate of no criminal record looks like Step 3
Pass a medical examinationPeople without serious health problems can take a child from an orphanage.
The list of diseases preventing adoption includes:
- Tuberculosis - patients of the 2nd and 3rd dispensary groups.
- Infectious diseases.
- Mental illness.
- Drug and alcohol addiction, substance abuse.
- Grade 3 and 4 malignancies.
- The first group of disability.
List of diseases that make it impossible to adopt a child
The form for referral for a medical examination is issued by the guardianship and guardianship authorities along with a list of documents for adoption.
It will not be possible to pass an examination in private clinics: according to the law, only state medical institutions are engaged in this, and free of charge. The medical report will be valid for six months from the date of its approval by the chief physician or the head of the polyclinic.
Medical examination procedure and conclusion form
What is included in the medical examination - public services website
To avoid misunderstandings, immediately after issuing the completed form, you must carefully check whether everything is in order with the execution. In particular, the conclusion of each doctor must be certified by the round official seal of the institution.
A list of examinations and examinations that you will definitely need to pass. Source: gosuslugi.ru Conclusion form, which is issued to future adoptive parentsStep 4
Obtain a certificate of income and positionAdoptive parents must prove to the specialists of guardianship authorities the ability to financially support the child.
To do this, you will need to provide a certificate from the place of work on salary and position or copies of the income declaration certified by the tax office. The certificate is prepared in free form indicating the salary and other payments for 12 months.
/prava/opecunam/
What rights do guardians have
Step 5
Write a CVCV is only for guardianship. It should reflect the main points of the life path: education, marriages and divorces, labor activity. Based on this information, the specialist judges the stability of the financial and family situation of the candidate for adoptive parents, as well as his experience of communicating with children. An autobiography should not be too voluminous: one or two A4 pages is enough. The document can be either written by hand or printed on a computer.
CV must include:
- Personal information. Surname, name, patronymic; date and place of birth; information about parents or persons replacing them; information about sisters, brothers, if any; place of permanent registration and address of actual residence, if it differs from the address of registration.
- Education. Basic education - years of study, school number and city where one is located.
 Higher education (if any) - years of study, name of the university, specialty.
Higher education (if any) - years of study, name of the university, specialty. - Professional activity. Beginning of work experience - place of work and profession; listing periods of work and the name of employers, positions. The last place of employment is included with an indication of the position and salary; awards or events that positively characterize the candidate.
- Marital status. Family composition: spouse, children (last name, first name, patronymic, date of birth, occupation). Data on previous marriages and divorces (if any): information about spouses and children born in these marriages; the facts of changing the surname (if any) indicating the reason and the previous surname.
- Interests and additional information. Creative, sports, achievements in them; participation in public organizations, volunteer movement, awards and promotions; experience working with children or helping elderly relatives.
It is also necessary to briefly explain the reason for contacting the guardianship department.
Step 6
Complete a course or school for adoptive parentsThe list of required documents for adoption includes a certificate of completion of a program of psychological, pedagogical and legal training, or a school for future parents.
Art. 127 SK RF
Only close relatives of the child, namely grandparents, older full and half brothers and sisters, stepfathers and stepmothers, as well as those who are already a guardian, trustee or adoptive parent, can not be trained.
At school, prospective adoptive parents are helped to understand if they are ready for this serious step, and to figure out what form of guardianship will suit them; introduce the legislation, talk about the psychological difficulties that children and adults face both during the period of adaptation and after.
The length of study varies from school to school: a course can last from 56 to 80 academic hours. At the end, a final certification is carried out: after it, future adoptive parents will be issued a certificate of completion of training.
/child-custody/
I took three children from the orphanage
You can study for free at any school, regardless of the place of registration.
Foster Parent School Certificate FormStep 7
Get an act of checking housing conditionsWhen all the documents on the list are collected and transferred to the guardianship authorities, the adoptive parents will be assigned an inspection check of living conditions.
The guardian must inspect the housing and assess whether the child can live there. If other people live in an apartment or house in addition to the adoptive parents, guardianship workers will take an interest in their state of health and the relationship that connects them with the candidates for adoptive parents.
For verification, potential adoptive parents provide:
- An extract from the USRN confirming the ownership of housing or a contract of social or commercial employment.

- Information on the number of residents registered in the housing area.
/guide/get-egrn/
How to get an extract from the USRN
Adoptive parents are not required to provide any other documents other than the above. The conclusion on the possibility of being a candidate for adoptive parents and registration takes place within ten days after checking the housing conditions.
What should be the place of residence of the adoptive parent. The place of residence of a person wishing to adopt a child does not have to coincide with the place of his registration. But it is necessary to have a permanent registration. If the candidate rents an apartment, he must provide a lease for more than one year. If living with relatives - a written agreement between them for the right to use.
A room in a hostel or apartment cannot be considered a permanent place of residence, no matter how comfortable it may be.
What should be the living conditions. In order for the child to live safely for his health and development, the living space of the adoptive parent must comply with sanitary standards. The main criterion is the availability of communal amenities: water supply, sewerage, central heating, gas supply, and so on.
Guardianship authorities can evaluate this without involving SES, BTI and other third-party organizations.
There are no federal restrictions on the size of housing for adoptive parents - the issue is at the mercy of the regions. For example, in Moscow, there should be at least 18 m² per person. But even when this rule is not observed, the final decision remains with the court: if the adoption is in the interests of the child, permission can be given to families with a smaller apartment area.
Art. 50 ZhK RF
Law on amendments to the RF IC
Step 8
Find a child for adoption To select a child, candidates can apply, at their choice, to any municipality in whose territory the orphanage is located, to a regional operator that is in each subject of the Russian Federation or in the Federal Data Bank on orphans and children left without parental care. But the law does not prohibit the independent search for a child in orphanages. You can also search for a child before the candidate receives a conclusion on the possibility of being an adoptive parent, but they will not give a referral to view the child until that moment.
But the law does not prohibit the independent search for a child in orphanages. You can also search for a child before the candidate receives a conclusion on the possibility of being an adoptive parent, but they will not give a referral to view the child until that moment.
Federal Child Data Bank
When and which child can be adopted. A child who has the status of an orphan, or a child left without parental care, can be adopted at least a day before his or her majority.
Requirements for adoptive parents do not depend on the age of the child they want to take into the family. But if the case concerns a baby, whom the mother abandoned in the maternity hospital, then from her, as a legal representative, an additional statement of consent to adoption will be required.
Community 26.04.22
Is it possible to adopt an adult?
This is how the statement of consent to adoption looks like, which the biological mother writes in the maternity hospital What are the health groups of children during adoption. Health groups is a scale that determines the state of the body and the development of the child. This information is provided to adoptive parents by the regional operator of the database of orphans.
Health groups is a scale that determines the state of the body and the development of the child. This information is provided to adoptive parents by the regional operator of the database of orphans.
There are five health groups:
- The child is absolutely healthy.
- Practically healthy children without chronic diseases, but with some functional disorders. For example, children who have had severe and moderate infectious diseases, children with a general delay in physical development without endocrine pathology - short stature, low or overweight. The same group includes frequently ill children and children with noticeable consequences of injuries or operations.
- Children with mild curable pathologies and chronic diseases with rare exacerbations who are in remission at the time of the examination.
- Children with chronic diseases, injuries or operations that limit the child's life or require supportive care.
- Children with disabilities.

Pathologies in children are not an obstacle to adoption. However, before you take a child with a complex diagnosis, you need to soberly assess the strengths and capabilities. It is better to consult with specialists in advance on how to organize the process of education. You can also discuss this topic with foster parents whose families have children with similar diagnoses.
In reality, completely healthy orphans are rare. Children of the 1st-2nd health group, as a rule, are babies, who are abandoned in the maternity hospital by very young mothers. Basically, children of the 3rd group are taken to families, and orphans of groups 4-5 more often remain in children's homes.
/plastic-lids-help-kids/
How I became a foster mother to three girls
How is the meeting with the child. After the child is found, prospective adoptive parents go to the guardianship to which the specific institution belongs, or to the operator of the regional data bank through which the information was received, clarify the details and request a referral for a face-to-face visit.
The referral is valid for 10 days, during this time, future parents can see the child one or more times, talk with his caregivers, pediatrician, psychologist. A conversation with the institution's specialists takes place before meeting the child. If, after this conversation, the failed parents turn around and leave, the child will not be traumatized by failure.
The number of referrals issued is not limited by law, that is, the search continues until the future adopter finds "his" child. A child who is ten years old will also have to express his opinion: agree in writing to a family placement or refuse it.
Art. 132 SK RF
At the end of the ten-day period, the candidate for adoptive parents will have to write on the referral one of the words that can radically change their future life: “I refuse” or “I agree”. If it was possible to find contact with the child and the consent in the guardianship authorities was recorded, the next step is to file an application with the court.
Step 9
Apply for adoption to the courtThis is a rather formal process: you need to come to the court during office hours, submit the documents according to the list, get their list in your hands and wait for the notice of acceptance of the case for proceedings, appointment of the court date. You don't need to pay state duty.
sign. 14 p.1 art. 333.36 TC RF
By law, the period for consideration of an application should not exceed two months from the date of its acceptance in the office. But the judges, as a rule, schedule a hearing for the next possible day.
How is the court session. Adoption cases are handled in a special manner. The adoptive parent, the representative of guardianship, the prosecutor and the child, if he is over 14 years old, must necessarily participate in the process.
/prava/prava-deti/
Rights of children under 18 years of age
Usually, a court decision enters into force 10 days after it is issued: only from this time do mutual rights and obligations arise between the adoptive parent and the child. If there are special circumstances and there are no objections on the merits of the case from all the participants, the judge may decide on the immediate execution of the decision: for example, if something threatens the life and health of the child and he needs urgent hospitalization.
If there are special circumstances and there are no objections on the merits of the case from all the participants, the judge may decide on the immediate execution of the decision: for example, if something threatens the life and health of the child and he needs urgent hospitalization.
An adopted baby can be taken home immediately after a positive adoption decision has been made by the court. At the same time, the maternity hospital must issue a postpartum sick leave from the date the decision enters into force when the baby reaches the age of 70 days, and when adopting two or more children - 110 days. A sick leave is needed to apply for maternity leave at the work of one of the adoptive parents.
Art. 157 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation
Step 10
Obtain an adoption registration certificateTo do this, you need to contact the registry office: they will issue an adoption certificate and a new birth certificate of the child.
ch. V Federal Law on acts of civil status
V Federal Law on acts of civil status
The child is registered at the place of residence of the adoptive parents.
When can an adoption be canceled and parental rights deprive
Most often, cancellation occurs due to the guilty behavior of the adoptive parents. For example, if they shirk parental responsibilities, abuse their rights, abuse a child, abuse alcohol or take drugs.
A claim for the annulment of an adoption may be filed by the adoptive parents themselves, the guardianship and guardianship authorities, the prosecutor and the child if he has reached the age of 14.
Art. 142 SK RF
However, the court has the right to cancel the adoption even if there are no violations on the part of the parents.
Such cases include the identification of hereditary developmental abnormalities in a child that make it difficult or impossible to bring up. As a rule, when receiving an expert medical opinion on an adoptee, the future adopter confirms in writing his consent to familiarize himself with the diagnosis of the child and the history of the mother. If the violation was not listed in the document and appeared later, or the adopter for some reason was not notified under the signature about the presence of a pathology in the child, the adoption may be canceled.
If the violation was not listed in the document and appeared later, or the adopter for some reason was not notified under the signature about the presence of a pathology in the child, the adoption may be canceled.
/guide/lishenie-parent/
Why they can deprive of parental rights
But in practice, I came across the fact that foster parents became attached to children and even when a serious illness was detected, they left them in the family.
Adoption in brief
- Before adopting a child, you need to analyze your motives, weigh the pros and cons.
- When visiting guardianship authorities and other authorities, be sure to ask and write down the last name, first name, patronymic of the specialist, as well as his position. You are required to provide this information. This way you will show that you are competent in matters of communication with officials and are able to appeal against illegal actions.
 In the future, this may be useful for contacting higher and regulatory authorities.
In the future, this may be useful for contacting higher and regulatory authorities. - Submission of applications, medical examinations of adoptive parents and children, obtaining all certificates - all this is free of charge for future adoptive parents. The court fee is also not charged.
- You can study at any school for foster parents, regardless of the place of registration.
- A child can be adopted not only by a married couple, but also by unmarried persons. The main thing is that they comply with the requirements established by law.
- The conclusion on the possibility of being a candidate for adoptive parents is valid for two years.
Adoption of a child - German Federal Foreign Office
Foreign adoption
Attention! The Russian Federation is not a party to the Hague Convention on the Protection of Children and Cooperation with regard to Foreign Adoption (HAÜ). With the entry into force of the German Adoption Assistance Act on April 1, 2021, it became mandatory to conduct a procedure for recognizing and determining the entry into force of the Russian decision on adoption before the German Family Court.
Only so-called assisted adoptions, ie those carried out with the participation and mediation of a German accredited adoption agency, can be recognized. It is possible to confirm the support of the adoption by the authorities of the state of residence of the child and the state of residence of the adoptive parents by presenting a certificate from an intermediary organization dealing with adoption, in accordance with § 2d of the Adoption Law (AdVermiG).
With regard to national adoption, nothing changes with the entry into force of the Adoption Assistance Act.
How can I adopt a child, a citizen of the Russian Federation?
If you, as a German citizen, wish to adopt a child from the Russian Federation, you must contact an accredited intermediary organization dealing with adoption issues. There you will receive advice on the adoption procedure, as well as assistance in the implementation of your intentions.
Please note that, in accordance with the laws of the Russian Federation, adoption of children by same-sex couples is not possible.
Your German mission abroad at the place of residence of the child in the Russian Federation will support you by issuing a certificate in Russian, briefly explaining the impact of the adoption of a child on his citizenship from the point of view of German law. Experience shows that Russian courts require the presentation of such a certificate. As a rule, the specified intermediary organization dealing with adoption issues takes care of the submission of documents necessary for the issuance of this certificate, and the issuance itself.
How can my adopted child obtain German citizenship/passport?
According to German law, a child under the age of 18 , who is adopted in accordance with German law, acquires German citizenship automatically upon adoption.
In the case of adoption proceedings initiated after 04/01/2021, the acquisition of citizenship takes place only after the German family court has declared its recognition.
 S. Department of State to ensure that agencies are properly overseen in the U.S.
S. Department of State to ensure that agencies are properly overseen in the U.S. Children available for adoption from Russia range from infants to teens. Russian children are of ethnically diverse, and may be Caucasian, Asian, or Roma. Most, however, will have fair skin and lighter hair or eyes. Most of the children are healthy while a few others have minor, correctable special needs.
Children available for adoption from Russia range from infants to teens. Russian children are of ethnically diverse, and may be Caucasian, Asian, or Roma. Most, however, will have fair skin and lighter hair or eyes. Most of the children are healthy while a few others have minor, correctable special needs. If you feel you are not eligible to adopt from Russia, or you are unsure, we may be able to work with you. Please contact us for a free case-by-case consultation.
If you feel you are not eligible to adopt from Russia, or you are unsure, we may be able to work with you. Please contact us for a free case-by-case consultation.
 This time frame is subject to change; please consult CAN for the most current processing times for your adoption from Russia.
This time frame is subject to change; please consult CAN for the most current processing times for your adoption from Russia.
 For an overview of the program, please click here. Please contact us for more information regarding adoption from Russia.
For an overview of the program, please click here. Please contact us for more information regarding adoption from Russia. After the ruling and the release letter are received, parents will file immigration paperwork with the U.S. Embassy in Moscow as well as Consulate Registration. Once these requirements have been met and you receive your child’s visa, you may bring your child home!
After the ruling and the release letter are received, parents will file immigration paperwork with the U.S. Embassy in Moscow as well as Consulate Registration. Once these requirements have been met and you receive your child’s visa, you may bring your child home! The care the children receive in the orphanages varies greatly, depending on the region in which the children are. There are approximately 250 children in each orphanage. Children less than three years of age live in baby homes. Children ages 3 to 15 years old live in children’s homes. There are physicians on staff in each orphanage. Children with serious health conditions are generally housed in hospitals to allow them to receive adequate care.
The care the children receive in the orphanages varies greatly, depending on the region in which the children are. There are approximately 250 children in each orphanage. Children less than three years of age live in baby homes. Children ages 3 to 15 years old live in children’s homes. There are physicians on staff in each orphanage. Children with serious health conditions are generally housed in hospitals to allow them to receive adequate care. Keck, Regina M. Kupecky, Lynda Gianforte Mansfield (Pinion Press 2002)
Keck, Regina M. Kupecky, Lynda Gianforte Mansfield (Pinion Press 2002)