How old when child loses first tooth
When do kids start losing teeth?
It might feel like it was just yesterday that your child’s baby teeth were starting to come in. But just a few years later, it’s already time for those baby teeth to start making way for permanent adult teeth.
Whether your little one already has a loose tooth or you’re getting ready for when they do, here’s everything to know about this next step in their dental development.
Below, we cover when kids start losing teeth, the process of losing a tooth and what to expect from adult teeth. We also give some oral care tips that can help your child’s permanent teeth last a lifetime.
When do kids lose their first tooth?
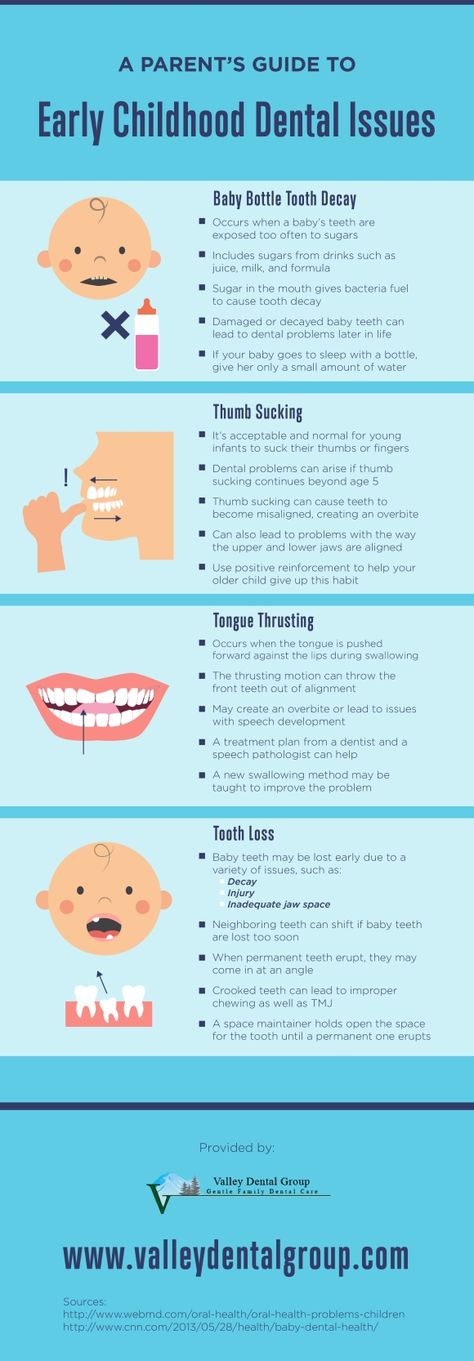
Children usually lose their first tooth around 5 or 6 years old. But every child is unique. Some will lose their first tooth as early as 4 years old or as late as 7 years old.
How many baby teeth do kids lose?
Kids have 20 baby teeth, which dentists call primary teeth. Usually, kids will lose all of their baby teeth to make room for their permanent teeth.
Occasionally, one or more baby teeth may stick around long after they’re supposed to have fallen out. If this is the case for your child, talk to their dentist. These “retained” teeth aren’t always a problem – sometimes it’s best to remove them, other times they can stay right where they are. It’ll take a physical exam and X-rays to know for sure.
Which baby teeth fall out first?
Much like the song “All I Want for Christmas (Is My Two Front Teeth),” kids’ front teeth are often the first to fall out. But again, every child is different. Children will usually continue to lose their baby teeth through age 12.
The timeline for losing baby teeth
You can typically expect your child’s baby teeth to fall out in the order they came in. The resulting timeline tends to look like this:
- Central incisors: 6-7 years old
- Lateral incisors: 7-8 years old
- Canines: 9-12 years old
- First molars: 9-11 years old
- Second molars: 10-12 years old
How can I prepare for my child’s first loose tooth?
Most of the time, there isn’t much you need to do about a loose tooth. Usually, the process of losing a tooth happens naturally.
Usually, the process of losing a tooth happens naturally.
Many kids don’t have much discomfort from a loose tooth, but it may feel weird to them. You can help by simply reminding them that it’s normal and nothing to be afraid of.
If your child feels soreness or discomfort, an ice pack or an age-appropriate dose of anti-inflammatory pain medication can help. And of course, if you want to get your child excited about losing teeth, you can get the Tooth Fairy involved.
The gum may bleed a bit once the tooth falls out. Usually, swishing their mouth out with water can take care of bleeding. But if the bleeding continues, have your child bite down on a piece of gauze. If bleeding lasts longer than an hour, contact your child’s dentist.
When do kids get adult teeth?
The permanent teeth that kids will have for the rest of their lives usually start coming in around age 6 – about the same time that they start losing their baby teeth. The first molars are usually the first permanent teeth to come in.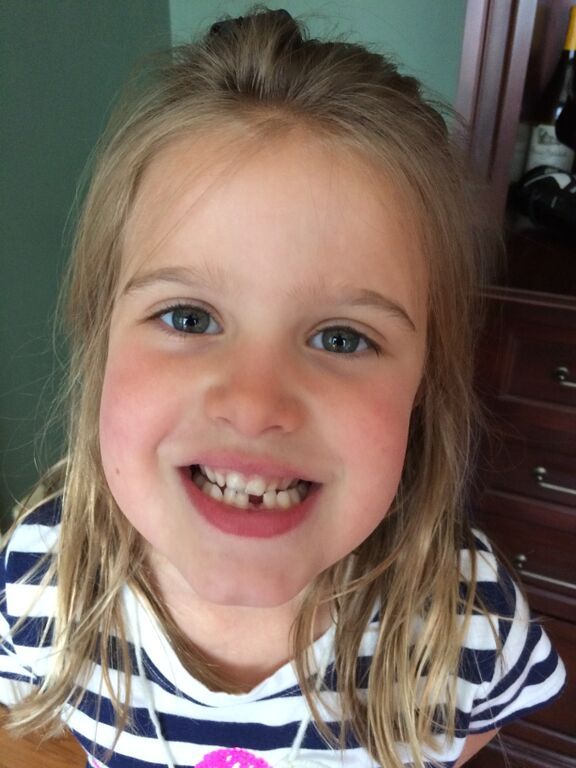 Other permanent teeth will come in as their baby counterparts fall out.
Other permanent teeth will come in as their baby counterparts fall out.
Most people end up with 32 permanent teeth, including the third molars or wisdom teeth.
Oral care tips for kids: Answers to commonly asked questions
Permanent teeth are just that – permanent. And that means it’s important to practice good oral hygiene, even before they come in, so that teeth and gums stay as healthy as possible.
How often should my child brush their teeth?
Your child should brush their teeth twice a day, for at least two minutes. Make sure they’re using a soft toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste.
Does my child need to floss their teeth?
Yes. Your child’s teeth should be flossed daily, even if you have to do it for them at first – baby teeth need flossing too.
How often does my child need to see the dentist?
It’s recommended that you take your child to the dentist every 6 months or so. Regular dental visits help catch any issues as early as possible, and the dentist can partner with you to create a personalized oral care plan for your child. Of course, you can also contact your child’s dentist outside of their regular appointment schedule if you have questions or concerns about something in your child’s mouth.
Of course, you can also contact your child’s dentist outside of their regular appointment schedule if you have questions or concerns about something in your child’s mouth.
What else can I do for my child’s dental health?
In addition to brushing, flossing and regular dental appointments, a balanced diet is an important factor in keeping teeth healthy. The bacteria that cause tooth decay and cavities feed on sugar and starches, so minimizing how much sugar your child’s teeth are exposed to goes a long way. In particular, focus on limiting sugary fluids and chewy sweets that can stick to teeth.
Look after your child’s smile
Again, regular dental appointments are a key part of keeping your child’s teeth healthy. And if your child has permanent teeth coming in, it’s more important than ever to make sure they get all the care they need. A dentist can do exactly that.
Pediatric Dentists | Savannah, Statesboro & Pooler, GA
Krista C. Hinchey, DMD
Hinchey, DMD
Phillip Strickland, DMD
Morgan Boaen Smith, DMD
Phillip B. Gordon, DMD
Board Certified Pediatric Dentists
Covid-19
Patient Forms
Savannah Location
912-298-KIDS (5437)
map
Statesboro Location
912-402-KIDS (5437)
map
Meet our Doctors
Drs. Krista, Phillip, Morgan and Gordon are dedicated to you and your child. They are committed to ensuring each patient has a positive experience.
Schedule a Visit at one of our 2 Convenient Locations...
912-298-KIDS (5437)
Savannah Location
4849 Paulsen Street, Suite 101
Savannah, Georgia 31405
912-402-KIDS (5437)
Statesboro Location
123 Hill Pond Lane
Statesboro, Georgia 30458
Fill out a Request a Visit Form and one of our team members will get back to you promptly.
Our Offices
Seeing our patients smile is the best part of our day. Schedule your visit with us.
Savannah Office Tour
Statesboro Office Tour
Click to watch our videos of each location!
Loved by Kids. Approved by Parents....
Approved by Parents....
powered by BirdEye
We’d love a review from you!
You’ll be surprised how much they look forward to their next visit!
Schedule a Visit Today!
Email!
Refer
Privacy
Member:
American Academy
of Pediatric Dentistry
Member:
American Dental
Association
Sitemap Dogwood Pediatric Dentistry complies with applicable Federal civil rights laws and does not discriminate on the basis of race, color, national origin, age, disability, or sex. About discrimination and translations.
Member:
American Academy
of Pediatric Dentistry
Member:
American Dental
Association
Sitemap Dogwood Pediatric Dentistry complies with applicable Federal civil rights laws and does not discriminate on the basis of race, color, national origin, age, disability, or sex. About discrimination and translations.
Krista C. Hinchey, DMD
Phillip Strickland, DMD
Morgan Boaen Smith, DMD
Phillip B.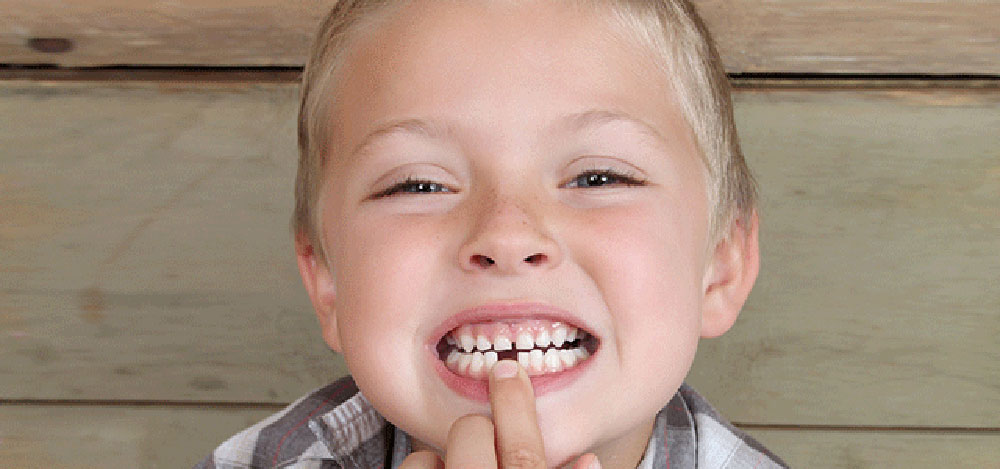 Gordon, DMD
Gordon, DMD
Board Certified Pediatric Dentists
Savannah Location
912-298-KIDS (5437)
map
Statesboro Location
912-402-KIDS (5437)
map
Loved by Kids. Approved by Parents....
You’ll be surprised how much they look forward to their next visit!
Schedule a Visit Today!
Member:
American Academy
of Pediatric Dentistry
Member:
American Dental
Association
Sitemap Dogwood Pediatric Dentistry complies with applicable Federal civil rights laws and does not discriminate on the basis of race, color, national origin, age, disability, or sex. About discrimination and translations.
Krista C. Hinchey, DMD
Phillip Strickland, DMD
Morgan Boaen Smith, DMD
Phillip B. Gordon, DMD
Board Certified Pediatric Dentists
WelcomeOur DoctorsDr. Krista HincheyDr. Phillip StricklandDr. Morgan Boaen SmithDr. Phillip GordonOur OfficeOffice InformationOffice TourMeet Our TeamFinancial & InsuranceFirst VisitWhat to ExpectFirst Visit FAQ’sPediatric DentistryWhy Choose a Pediatric Dentist?Pediatric Dentistry FAQ’sServicesSedationSedation Dentistry FAQ’sOrthodonticsSpecial NeedsEmergenciesEmergency FAQ’sReviewsRequest a VisitBlog
Meet our Doctors
Drs. Krista, Phillip, Morgan and Gordon are dedicated to you and your child. They are committed to ensuring each patient has a positive experience.
Krista, Phillip, Morgan and Gordon are dedicated to you and your child. They are committed to ensuring each patient has a positive experience.
Schedule a Visit at one of our 2 Convenient Locations...
Fill out a Request a Visit Form and one of our team members will get back to you promptly.
get social with us!!
see how much fun we have at dogwood...
Loved by Kids.
Approved by Parents....
Member:
American Academy
of Pediatric Dentistry
Member:
American Dental
Association
Sitemap Dogwood Pediatric Dentistry complies with applicable Federal civil rights laws and does not discriminate on the basis of race, color, national origin, age, disability, or sex. About discrimination and translations.
Savannah
912-298-KIDS (5437)
map
Statesboro
912-402-KIDS (5437)
map
Covid-19
Patient Forms
Krista C. Hinchey, DMD
Phillip Strickland, DMD
Morgan Boaen Smith, DMD
Phillip B. Gordon, DMD
Gordon, DMD
Board Certified Pediatric Dentists
Drs. Krista, Phillip, Morgan and Gordon are dedicated to you and your child. They are committed to ensuring each patient has a positive experience.
get social with us!!
see how much fun we have at dogwood...
Statesboro
912-402-KIDS (5437)
Savannah
912-298-KIDS (5437)
Meet our Doctors
Seeing our patients smile is the best part of our day." Schedule your visit with us.
Schedule a Visit at one of our 2 Convenient Locations...
Fill out a Request a Visit Form and one of our team members will get back to you promptly.
Email!
Privacy
Member:
American Academy
of Pediatric Dentistry
Member:
American Dental
Association
Sitemap Dogwood Pediatric Dentistry complies with applicable Federal civil rights laws and does not discriminate on the basis of race, color, national origin, age, disability, or sex. About discrimination and translations.
Change of milk teeth to permanent ones: what is important to know?
Many parents still think that pediatric dentistry is needed only in exceptional cases: if the child has a severe toothache and the pain does not go away by itself. There is also an opinion that there is no need to do anything with milk teeth, because they will fall out anyway and give way to molars. These are erroneous opinions that the doctors of our clinic would even call dangerous.
Why does a child need a pediatric dentist? First of all, for preventive examinations and monitoring of the growth of teeth, their change. Many factors influence the health of milk teeth. In turn, the health of the first teeth affects the condition of the molars even before they erupt. Next, we will understand how the change process takes place. Every parent should know this to help their little one get straight, beautiful teeth and not experience problems as an adult.
If you are still not accustomed to taking your child to the pediatric dentist once every six months, it's time to write down the date of the next visit in the calendar and make an appointment in advance at our clinic. This simple action will help prevent unpleasant problems, positively affect the formation of bite and oral health.
This simple action will help prevent unpleasant problems, positively affect the formation of bite and oral health.
In addition, getting to know the doctor early will help children form a good impression of the clinic. Caring for teeth in Mira children's dentistry in Krasnoyarsk will be associated with something festive and exciting! This is completely opposite to the situation when you bring a baby to the clinic with a severe toothache that requires treatment. A visit to the dentist will inevitably be remembered as something unpleasant.
The first teeth during eruption will cause discomfort in the child, and this is a natural process. During this period, salivation increases, a runny nose may occur due to the eruption of the upper teeth. The normal pace involves the appearance of new teeth every few weeks.
Be prepared for the fact that the child will be capricious and refuse to eat, he may have a fever. In order to facilitate this period, you can use special teething toys.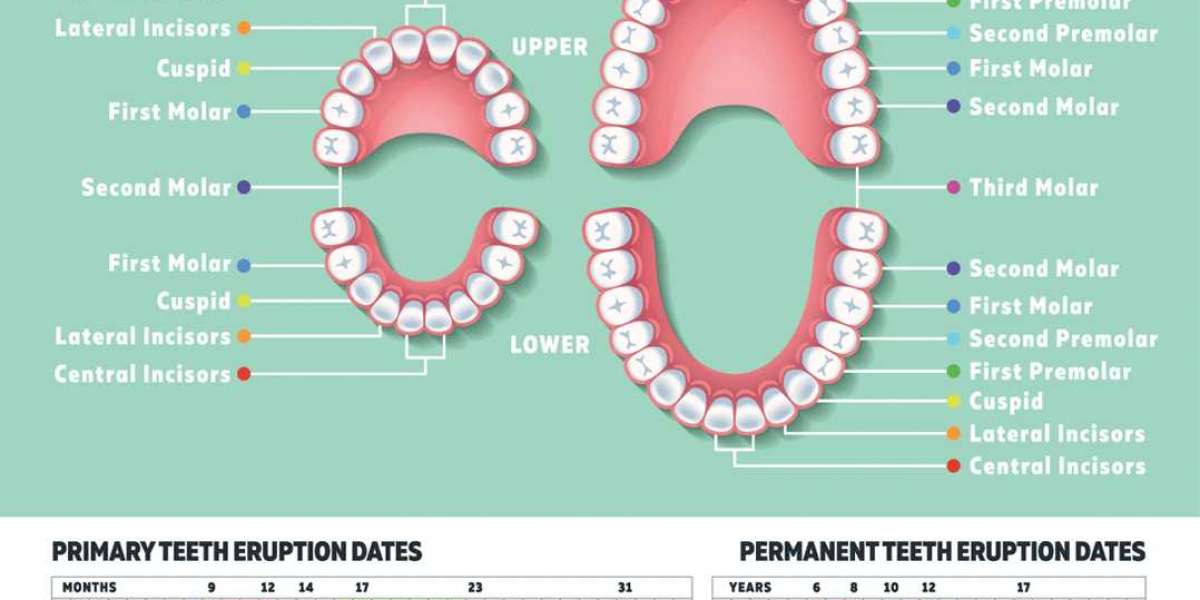 During this period, the gums become inflamed and cause discomfort - they can itch and hurt. Talk to your dentist: There are safe cooling gels for children that can help reduce the intensity of teething and teething symptoms in children.
During this period, the gums become inflamed and cause discomfort - they can itch and hurt. Talk to your dentist: There are safe cooling gels for children that can help reduce the intensity of teething and teething symptoms in children.
It is also recommended to replace drinks with plain water. Juices and other drinks that contain sugar create an acidic environment in the mouth. Because of this, an inflammatory process can begin. Care should be taken to disinfect pacifiers and toys that children may place in their mouths.
The first teeth appear at the age of six months. The first chewing teeth appear at the age of 1 to 1.5 years. Fangs are cut in a period of up to 2 years. After that, by the age of 3, the following chewing teeth appear. Each new group requires attention. So, it is important to clean chewing teeth well after eating, since the enamel of milk teeth is quite weak. Food retention on the surface can easily cause inflammation.
It is also important to make sure that the child weaned from the pacifier and stopped putting his fingers in his mouth.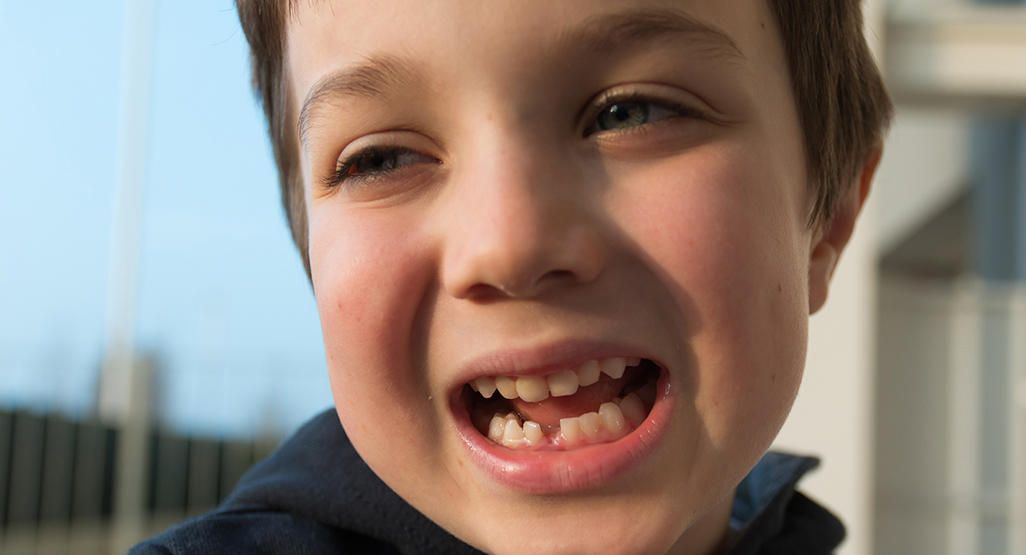 If this does not happen, an incorrect bite will be formed.
If this does not happen, an incorrect bite will be formed.
At the age of about 5 years, milk teeth begin to fall out, giving way to molars. It is important not to stimulate this process. It is not necessary to remove teeth, as this will negatively affect the growth of molars. In exceptional cases, the doctor may prescribe surgery if there is severe caries, too early or late eruption.
If a tooth is loose and about to fall out, no help is needed. It is better to take the baby to the doctor to get an individual recommendation and confidence that the processes are going naturally.
Do not forget to take your child to the doctor about once every 3 months in order to carry out mineralization, fluoridation and treatment of caries in time. If the pain during teething is very strong, it is allowed to give painkillers to children.
After the age of 3, parents can take a break from the changes. And then, at about 5 years of age, milk teeth are replaced by permanent ones. The process begins with the lower incisors. Then, after about a year, chewing "sixes" are cut, which parents may mistakenly take for dairy. A year later, the upper incisors change.
The process begins with the lower incisors. Then, after about a year, chewing "sixes" are cut, which parents may mistakenly take for dairy. A year later, the upper incisors change.
To make this journey with your child without problems and pain, visit the dentist regularly. Children may experience pain simply from jaw expansion. The doctor can easily tell you the cause of the discomfort. The age of 6-7 years shows the prospect of bite formation. Here you can quickly fix the problems that arise so that by adolescence the child has an even beautiful smile.
Further, the procedure for replacing milk teeth continues with the upper lateral incisors by 8 years. aged 9-10 years old, the primary first premolars appear, and a year later they are followed by the second premolars. 12-13 years old is the age of the appearance of fangs, and at 14 years old the last second molars are cut.
The procedure for replacing milk teeth ends with the full formation of a bite in the amount of 24 teeth.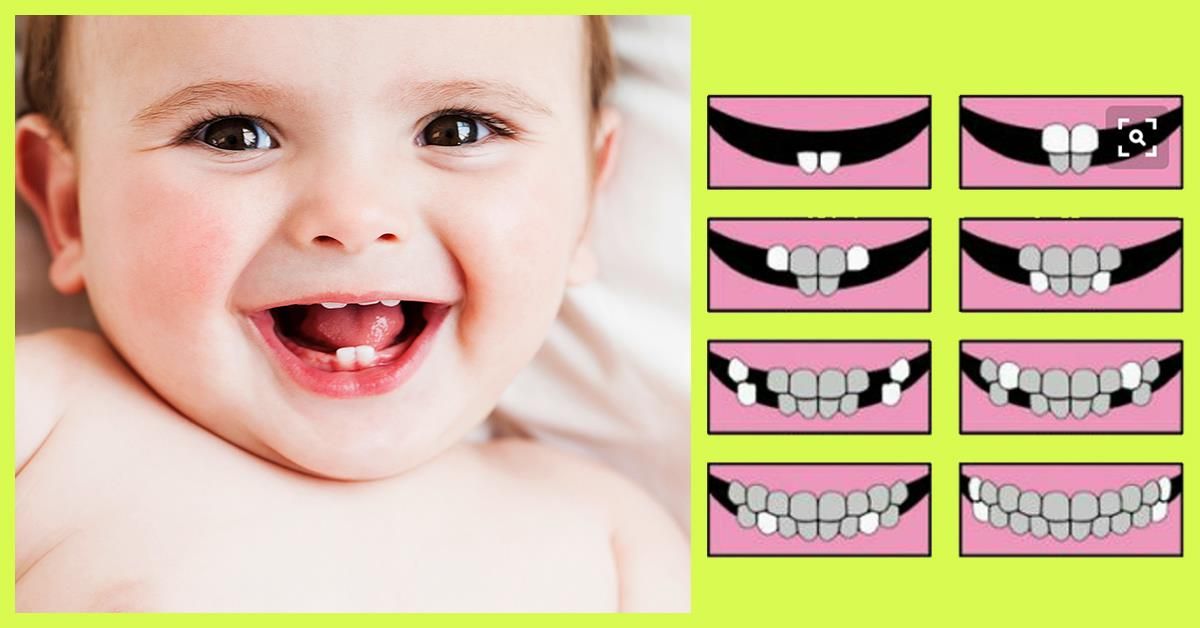
It is recommended to bring your baby to the dentist as soon as the first tooth begins to cut. In some cases, if there are problems, this should be done earlier. You already know that adults are advised to visit the dentist once every six months to prevent and treat problems in the early stages.
Speaking about children, they need preventive meetings with the doctor more often. The growth, condition and change of teeth in children must be carefully monitored. Milk teeth are less resistant to caries, therefore, to detect inflammatory processes in the early stages, you need to go to the dentist more often.
Of course, any unpleasant symptom in the oral cavity requires a visit to a doctor. But, even if everything is fine, visiting the clinic is highly recommended. A child cannot always tell his parents about any symptoms, and the stage of the white spot, from which caries begins, is very difficult to notice with an inexperienced eye.
What do we do as part of prevention? Milk teeth can be strengthened, saturate with minerals. Periodic mineralization will strengthen the enamel and protect against caries.
Periodic mineralization will strengthen the enamel and protect against caries.
Parents who regularly take their kids to pediatric dentistry do not have to worry about the formation of bite and the health of molars: the dentist will always warn about possible risks, correct the situation and recommend the necessary procedures. In addition, it is the pediatrician who is able to explain to parents the importance and rules of home hygiene of children's teeth. He can easily instill in a child an interest and a desire to properly brush his teeth on his own.
Regular check-ups also benefit from your child's positive attitude towards dentists. He will not be afraid of treatment, he will get used to visiting the clinic, he will learn to take care of his teeth himself.
When you give your child to the Mira pediatric dentistry team, you don't have to worry. The kid will leave the children's office in a good mood and without unpleasant symptoms!
Photo source: © ru.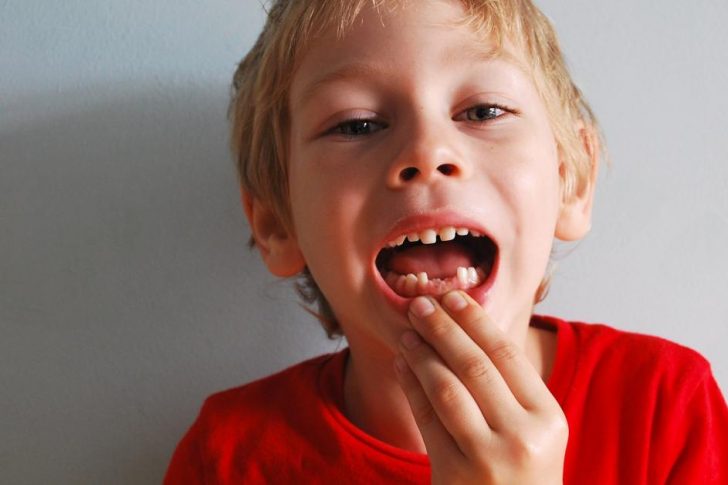 depositphotos.com/ oksun70
depositphotos.com/ oksun70
At what age do milk teeth fall out: teeth change in children
Many parents are interested in the question “ At what age do milk teeth fall out? ". Initially, parents are interested in the question at what age do milk teeth appear in children. And with the age of the child, parents begin to worry about the age at which teeth change. This issue is relevant, since the period of changing milk teeth to permanent teeth may be accompanied by discomfort. Every parent cares about the health and comfort of their child. Therefore, it is important to know at what age milk teeth fall out, and what is the sequence of this process.
How does the process when milk teeth change into molars
To understand how milk teeth change in a child, one should know the fact that the process of formation of milk teeth occurs in the womb. After birth, the child begins to form molars.
This process is quite long and is influenced by various factors.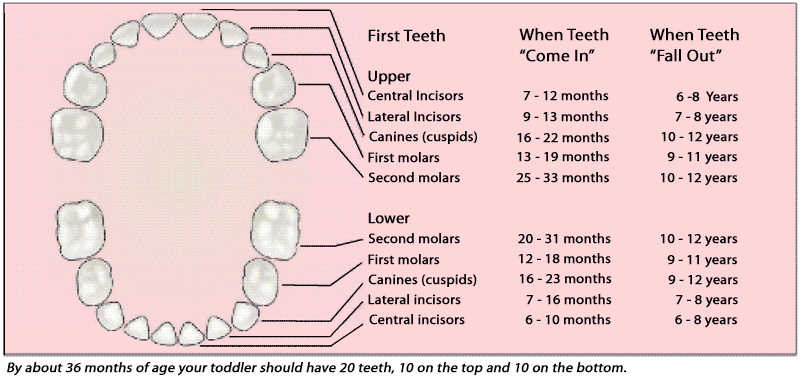 At what age milk teeth begin to fall out depends on the individual and genetic characteristics of the child. Another factor that affects the age at which teeth fall out is quality nutrition. It is also worth noting that the quality of drinking water affects the process of tooth loss.
At what age milk teeth begin to fall out depends on the individual and genetic characteristics of the child. Another factor that affects the age at which teeth fall out is quality nutrition. It is also worth noting that the quality of drinking water affects the process of tooth loss.
For example, when drinking water is of poor quality, there is a risk of caries in children. Drinking water can affect the quality of milk and molars in a child. In order to avoid the occurrence of caries on the molars, the milk tooth should be removed. Treatment of milk teeth is of course possible, but it should be assessed to what extent this is advisable. The choice of method lies within the competence of the specialist.
Another factor that influences the age at which milk teeth are replaced is the region where the child lives. It should also be noted that the level of quality of life of the family and what diseases were suffered by the child affect the age at which milk teeth are replaced by permanent ones.
At what age do teeth change
Many parents are concerned about the order in which baby teeth fall out. The sequence of loss of milk teeth coincides with the sequence of their growth. So, those teeth that first appeared in a child will be the first to fall out.
The process of loss of milk teeth begins at the age of 6-8 years. The duration of this period is 5-8 years.
In order to understand when children's milk teeth change to permanent teeth, you should indicate the order of tooth loss and the approximate age:
1. The lower incisors, which are located in the center, fall out first in children. This occurs at the age of 6-8 years. The lower molars appear first, followed by the upper.
2. At the age of 8-9 years, the child's upper incisors fall out, which are located in the center, and then the lateral incisors, located on the lower jaw.
3. Also at the age of 8-9 years, the lateral incisors located on the upper jaw change.
4. At the age of 9-11 years, the fangs on the lower jaw change in children.
5. By the age of 10-12, small molars appear in the upper and lower jaws.
6. At the age of 11-13, the fangs on the upper jaw fall out, and the second small molars also appear.
7. At the age of 11-14, children have second molars in the lower and upper jaws.
Also, many parents are interested in the question at what age do “wisdom teeth” fall out? We are talking about the third molars on the upper and lower jaws. Often this process occurs from 18 to 26 years.
What can be done to ease the loss of teeth in a child
The process of losing the first tooth in a child can cause various emotions. This can be a joyful event, but at the same time, a tooth falling out can frighten a child. Parents should be prepared for different reactions. Whatever the reaction in children, they will still have questions related to tooth loss. For parents, the main thing in this situation is to focus on the behavior and reaction of the child. It is necessary to act, given his behavior. Indeed, for someone, tooth loss can be an insignificant event, while someone will attach more importance to this process.
It is necessary to act, given his behavior. Indeed, for someone, tooth loss can be an insignificant event, while someone will attach more importance to this process.
The main thing that specialists pay attention to is that it is not necessary to speed up the process of tooth loss. Even if your child has a very loose tooth, you should not get it by various methods. After all, many have come across stories when a loose tooth was tied with a string, and then pulled on it. In no case should you do this, as this can harm your child.
If you have such a situation that a tooth that is loose causes noticeable discomfort, then you should consult a dentist. After all, a loose tooth can bleed. A situation may also arise when the milk tooth has not yet fallen out, and the root has already begun to erupt. In such cases, you can not hesitate, as this is dangerous for the health of your child's teeth.
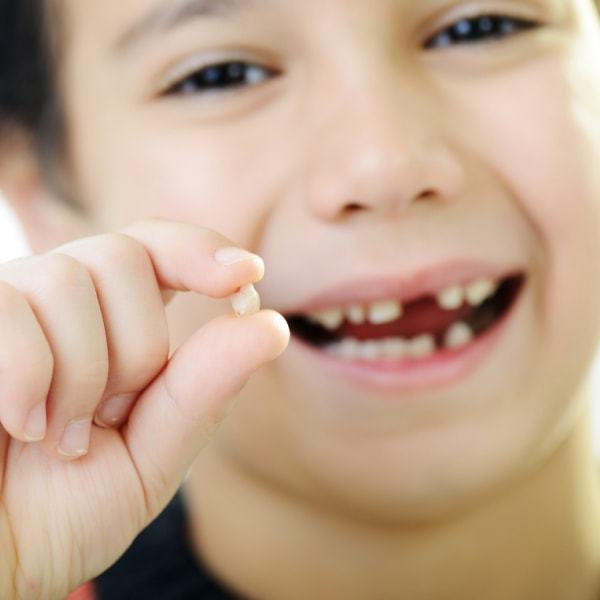
What to do when a baby tooth has fallen out
Being interested in the age at which children's teeth change, many parents wonder what to do when a tooth has already fallen out. In the case when the process of changing teeth occurs favorably, there is no bleeding in the place where the tooth fell out. Under such circumstances, no complex measures are required.
In the case when the process of changing teeth occurs favorably, there is no bleeding in the place where the tooth fell out. Under such circumstances, no complex measures are required.
It is enough to observe safety measures - do not eat or drink liquids for 2 hours after the tooth has fallen out. This will protect the child from the possibility of infecting the place where the tooth fell out. To comply with additional preventive measures, it is possible to use a saline solution with the addition of iodine for rinsing. To do this, you need to dissolve 2 tablespoons of salt in a glass of water and add a couple of drops of iodine.
In case of gum bleeding, the bleeding must be stopped. To do this, you need to bite on a cotton swab and hold it for 5-10 minutes. If after this procedure the bleeding does not stop, then it is necessary to consult a doctor in pediatric dentistry.
In what cases it is necessary to remove a milk tooth
Indications for the removal of milk teeth are:
1. The presence of an inflammatory process.
The presence of an inflammatory process.
2. The situation when the milk tooth is loose, but has not fallen out, and the root has already begun to erupt. This situation can contribute to the curvature of the teeth in a child.
Is everything okay with the baby if the milk teeth fall out of schedule?
It is important to understand that all existing tables and graphs, at what age children's teeth change, are very average. After all, the process of changing teeth is influenced by many factors mentioned above. Therefore, there may be discrepancies at what age milk teeth begin to fall out. This process may start earlier than the specified period or later. This shouldn't be cause for concern.
At the same time, it is possible to determine at what stage the process of changing teeth is in your child. To do this, you can take a panoramic x-ray of the upper and lower jaw. The picture shows how many rudiments of molars are there, and at what stage the process of changing milk teeth.
It should be noted that there is no strict time frame when a molar tooth should begin to grow after a milk tooth falls out. This process can be delayed due to lack of space in the jaw. Also, tooth growth retardation may be due to the fact that the rudiment of the molar tooth has not yet been formed.
Is there a risk of early loss of molars when changing dairy quickly?
Very often in children there is a rapid change of teeth. This situation does not affect the early loss of molars. It is also important to note that the existence of problems and diseases of milk teeth is in no way connected with diseases of molars. So, if a child had caries of milk teeth, then this does not indicate poor quality of molars. The main thing is proper care, compliance with the rules of oral hygiene.
Is it necessary to correct the bite when the child has milk teeth
There is one correct answer to this question - it is necessary to correct the milk bite .