How much weight should my newborn be gaining
Your Newborn's Growth (for Parents)
From your baby's first day, doctors will keep track of weight, length, and head size. Growth is a good indicator of general health. Babies who are growing well are generally healthy, while poor growth can be a sign of a problem.
How Big Are Newborns?
Newborns come in a range of healthy sizes. Most babies born between 37 and 40 weeks weigh somewhere between 5 pounds, 8 ounces (2,500 grams) and 8 pounds, 13 ounces (4,000 grams).
Newborns who are lighter or heavier than the average baby are usually fine. But they might get extra attention from the doctors and nurses after delivery to make sure there are no problems.
Different things can affect a baby's size at birth. The length of the pregnancy is important. Babies born around their due date or later tend to be larger than those born earlier.
Other factors include:
- Size of parents. Big and tall parents may have larger-than-average newborns; short and petite parents may have smaller-than-average newborns.
- Multiple births. If you have twins, triplets, or more, you can count on your babies being a bit small. Multiples have to share their growing space in the uterus, and they're often born early, which leads to small size at birth.
- Birth order. First babies are sometimes smaller than brothers or sisters born later.
- Gender. Girls tend to be smaller, boys larger, but the differences are slight at birth.
- Mom's health during pregnancy. Things that can lead to a lower birth weight include a mother with high blood pressure or heart problems; or one who used cigarettes, alcohol, or illegal drugs during the pregnancy. If the mother has diabetes or is obese, the baby may have a higher birth weight.
- Nutrition during pregnancy. Good nutrition is vital for a baby's growth — before and after birth. A poor diet during pregnancy can affect how much a newborn weighs and how the infant grows.
 Gaining a lot of weight can make a baby more likely to be born bigger than average.
Gaining a lot of weight can make a baby more likely to be born bigger than average. - Baby's health. Medical problems, including some birth defects and some infections during the pregnancy, can affect a child's birth weight and later growth.
p
What About Preemies?
Premature babies generally are smaller and weigh less than other newborns. A preemie's weight will largely depend on how early he or she was born. The time an infant missed being in the womb was growing time, so the baby has to do that growing after birth.
Many pre-term babies are classified as having "low birth weight" or "very low birth weight." In medical terms:
- Low birth weight means a baby weighs less than 5 pounds, 8 ounces (2,500 grams) at birth. That's the case for about 1 in every 12 babies in the United States, so it's quite common.
- Very low birth weight means a baby weighs less than 3 pounds, 5 ounces (1,500 grams).
Most babies with low birth weight or very low birth weight were born prematurely.
Premature babies get special medical attention right away after they're born. A specialist called a neonatologist may help care for them. Many preemies spend time in the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) while they get medical care.
Is Bigger Better?
A baby with chubby cheeks and dimpled thighs once was many people's picture of a healthy newborn. But a baby born much larger than average may have special medical problems that need attention.
Some very large babies — especially those born to mothers with diabetes, including gestational diabetes — may have problems for a few days keeping blood sugar levels up. They might need extra feedings or even IV (given into a vein)
glucoseto keep those levels from falling too low.
Will My Baby Lose Weight?
Yes, at first. Babies are born with some extra fluid, so it's normal for them to drop a few ounces when they lose that fluid in the first few days of life. A healthy newborn is expected to lose 7% to 10% of the birth weight, but should regain that weight within the first 2 weeks or so after birth.
A healthy newborn is expected to lose 7% to 10% of the birth weight, but should regain that weight within the first 2 weeks or so after birth.
During their first month, most newborns gain weight at a rate of about 1 ounce (30 grams) per day. They generally grow in height about 1 to 1½ inches (2.54 to 3.81 centimeters) during the first month. Many newborns go through a period of rapid growth when they are 7 to 10 days old and again at 3 and 6 weeks.
p
Should I Be Concerned?
Newborns are so small, and it can be hard to know if your baby is gaining weight the way he or she should. You may worry that your baby has lost too much weight in the first few days or isn't taking enough breast milk or formula. If so, talk to your doctor, who may ask you about:
- How many feedings a day your baby gets. A breastfed baby may feed about 8 or more times in a 24-hour period; formula-fed babies usually eat less often, perhaps every 3 to 4 hours. A lactation (breastfeeding) counselor can make suggestions to increase comfort and improve technique, if a mom needs extra help.
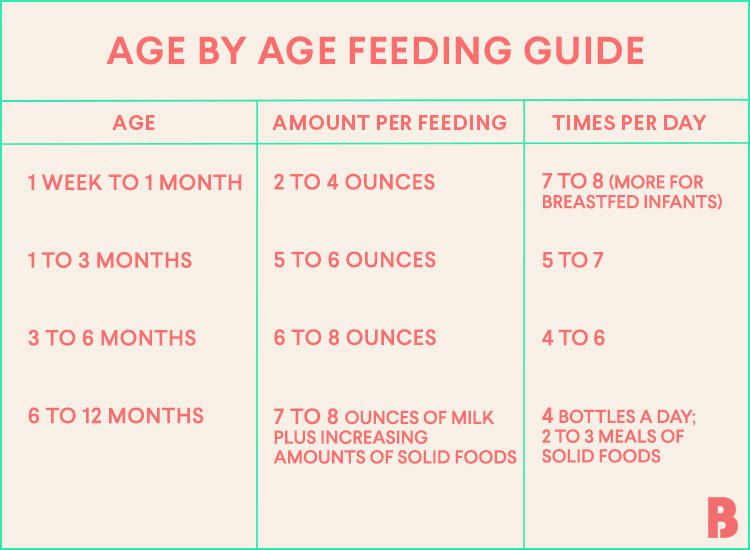
- How much your baby eats at each feeding. A baby generally nurses for at least 10 minutes, should be heard to swallow after 3 or 4 sucks, and should seem satisfied when done. At this age, formula-fed babies may drink up to 3 to 4 ounces (90 to 120 milliliters) at a time.
- How often your baby pees. A breastfed baby may have only 1 or 2 wet diapers a day until the mother's milk comes in. Expect about 6 wet diapers by 3 to 5 days of age for all babies. After that, babies should have at least 6 to 8 wet diapers a day.
- How many bowel movements your baby has each day, and what they're like. Newborns may have only one poopy diaper a day at first. Poop is dark and tarry the first few days, then becomes soft or loose and greenish-yellow by about 3 to 4 days. Newborns usually have several poopy diapers a day if breastfed and fewer if formula-fed.
What Else Should I Know?
Being small or large at birth doesn't mean a baby will be small or large later in childhood or as an adult.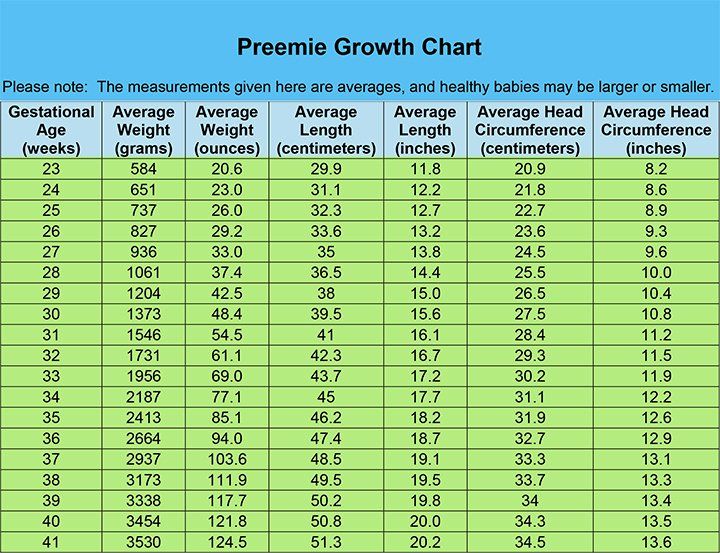 Plenty of tall teens began life as small babies, and the biggest baby in the family can grow up to be a petite adult.
Plenty of tall teens began life as small babies, and the biggest baby in the family can grow up to be a petite adult.
By the time they're adults, kids tend to resemble their parents in size. Genetics, as well as good nutrition and your attention, will play a large part in how your baby grows in the years to come.
Whether your baby starts out large, small, or average, in the next few months you can expect your little one to keep growing fast.
Reviewed by: Madhu Desiraju, MD
Date reviewed: October 2018
Averages for Breastfed & Formula-Fed Kids
Congratulations, you have a new little bean in your household! If your tiny one seems ravenous all the time, it’s because they are. Babies have a lot of growing and developing to do!
In the first 5 months of life, your baby will about double their birth weight. By the time they’re 1 year old, most babies triple their birth weight. But just like adults, babies come in all sizes and body types.
Some babies gain a lot of weight quickly. According to the World Health Organization’s (WHO) child growth standards, overall, boys gain weight faster than girls.
Squishiness and “rolls” can be normal and healthy for babies. Other babies might have leaner body types and appear thinner. This may also be completely normal.
Your pediatrician will weigh your baby regularly during well visits to make sure they’re within the range of normal weight gain for their length and age. It’s OK if your baby is off the charts sometimes — every baby is a little bit different and each gain weight at their own speed.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), breastfed babies have a tiny head start in weight gain shortly after birth, but their overall weight gain in the first year is typically slower than formula-fed babies.
Still, up until age 2, physicians use the WHO growth charts as the standard growth curve for both breastfed and formula-fed babies.
In general, here’s what you can expect for your baby’s weight gain by week:
| Baby’s age | Average weight gain in ounces | Average weight gain in grams |
| 5 days to 4 months | 5–7 ounces per week | 170 grams per week |
| 4 months to 6 months | 4–6 ounces per week | 113–150 grams per week |
| 6 months to 12 months | 2–4 ounces per week | 57–113 grams per week |
Breastfed babies
Generally, breastfed newborns gain weight faster than formula-fed babies for the first 3 months of life.
One likely reason for this is that breast milk is a dynamic and ever-changing food, composed of the exact nutrition a baby needs at that stage. On the other hand, formula is a static composition of ingredients.
For the same reason, the amount of pumped breast milk a baby receives in a bottle will sometimes differ than the amount of formula a baby of the same age receives.
When formula-fed babies need more calories, they must drink more at each feeding. Breast milk, however, will change in its composition and caloric content depending on the baby’s needs.
On average, breastfed babies drink around 800 milliliters (27 ounces) of milk per day in the first 6 months of life. As a rule of thumb, feed your breastfed baby on demand so they receive all the calories and nutrients they need.
How much breast milk should I put in a bottle?
A lot of breastfeeding parents returning to work want to know how much milk they should leave for their babies while they’re gone. If you’re planning to bottle-feed expressed milk, expect to give your baby about an ounce of milk per hour.
So, if you’re working an 8-hour day, for example, your baby might consume two 4-ounce bottles or three 3-ounce bottles during the time you’re gone.
Of course, this may depend on your baby’s age and how much they typically drink in a feeding. But in general, this will give you a baseline from which you can adjust to suit your baby’s needs.
If you’re breastfeeding exclusively, you may need to track your baby’s weight a bit more carefully in the early weeks.
Weight gain is one way to determine how well breastfeeding is going — it’s not only a sign of how much milk you’re producing, but how well your baby is extracting the milk from the breast.
Formula-fed babies
Babies who are formula fed generally gain weight faster than breastfed babies after the first 3 months of life.
With formula feeding, it’s easier to know how much milk your baby is getting. You can tell how many ounces of formula your baby has finished by looking at their bottle.
But it’s also easier to accidentally overfeed your baby at times. This is because you’re more likely to keep feeding until the bottle is empty, even if your baby is already full. Sometimes momma’s eyes are bigger than baby’s stomach!
In fact, a 2016 study found that using a bigger bottle to feed formula to your baby can lead to faster weight gain in babies under 6 months old.
The researchers checked the weight of 386 two-month old babies. They found that babies who were fed with bottles 6 ounces or bigger were about 0.21 kilograms heavier than babies fed with smaller bottles.
This is kind of like adults eating from a smaller plate to feel fuller faster and avoid overeating!
Almost all babies lose some weight in the first week after birth. Don’t worry, though. As long as they’re feeding appropriately, they will quickly make up for it in coming weeks.
Most babies lose an average of 7 to 10 percent of their birth weight in the first few days. Ideally, they should be back to their birth weight by 10–14 days after birth. If not, be sure to speak with your pediatrician and possibly a lactation consultant to see if there are underlying problems with feeding.
If you experience breastfeeding challenges in the first few days after birth, you’re completely normal! Breastfeeding is often more complex than new parents expect.
Seek the help of a lactation consultant if you’re experiencing any of the following:
- your baby doesn’t latch on deep enough, or it’s painful for mama
- suckling seems weak during breastfeeding
- baby’s urine is dark yellow
- there’s red-brown “dust” in your baby’s diaper
- you hear clicking or gagging when baby is drinking
- your baby doesn’t have at least 2 to 4 poopy diapers a day
- your baby is extra sleepy at the breast or has low energy
- baby has a weak cry
- your baby looks a bit yellow or has other signs of jaundice
- there are other signs of dehydration in your baby
Weighing your baby regularly — at home or at your doctor’s office — is important because any amount of healthy weight gain is a sign that your baby is feeding well.
If your newborn hasn’t gained back their birth weight by day 10 to 14, has lost too much weight, or growth is too slow, your pediatrician, often along with a lactation consultant, can help.
And, if you find you need to supplement with formula, don’t stress! You’re not alone.
Breastfeeding offers numerous benefits, and your baby will still take advantage of them no matter how much breast milk they receive.
Babies gain weight and grow quickly in their first year. But weight gain can happen at different speeds and ranges for each little one.
Your baby’s weight gain depends on a lot of things, including genetics, how active they are, and whether you’re breastfeeding, formula feeding, or both.
Use the right growth chart and weighing methods to track your baby’s growth.
Don’t worry if your baby’s growth curve looks a little different than average. Talk to your doctor if you’re concerned, but as long as your baby is consistently gaining weight at their own pace, they’re doing just fine.
Baby height and weight norms
Newborns come into this world completely unadapted to the environment. Therefore, your care and care will help the kids become strong and strong. During the year, the child acquires many new skills, becomes mobile and inquisitive, and also increases the mass and length of the body more than twice.
Each person on Earth is individual, but despite this, there are general patterns and principles for increasing the weight and length of the body of children. And every mom can rely on them. But you don’t need to check to the gram and centimeter! nine0003
The average birth weight for girls is 2800 - 3300 grams, and for boys 2900 - 3500 grams. The average body length for both sexes is 48-51 centimeters. But if your child does not meet these parameters, this is not a reason to panic.
In the first few days of life, a newborn can lose up to 10% percent of the mass, but by 10-14 days he should restore the parameters that he had at birth.
During the first month, the child adds 25-30 grams every day, and in a month the total increase is about 600 grams. Then the monthly weight gain is 800 grams for up to six months and 400 grams monthly for up to 1 year. In a year, the average weight of your baby should be approximately 10 kg. nine0003
How do you know if your baby is gaining enough weight?
The first thing you need to pay attention to is the well-being of the child. It is also necessary to note the rate of absorption of food. If he eagerly sucks milk or formula, requires feeding every 20-30 minutes, then it is worth counting the amount of food eaten by the baby.
If your baby is bottle-fed, you can easily determine how much he eats at a time. But how to understand how much a child receives at one meal if you are breastfeeding? The answer is very simple - weigh it before and after eating. The difference in weight is the amount of food eaten. You can find the approximate volume of feeding a child in the first year of life in table No.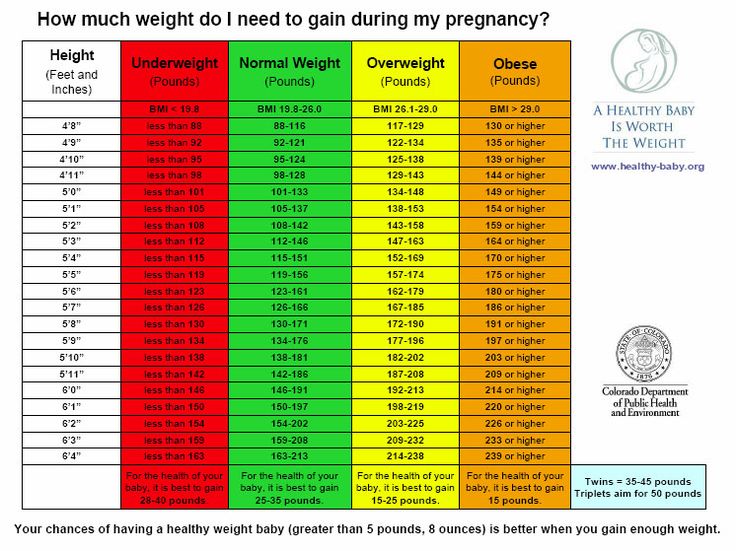 1. If your child is not eating enough, do not try to adjust the diet yourself, it is better to contact a pediatrician. nine0003
1. If your child is not eating enough, do not try to adjust the diet yourself, it is better to contact a pediatrician. nine0003
To measure the baby's body weight, conventional scales will not work, since accuracy is very important for your child in the first months of life.
It is better to use special children's scales, which are specially adapted for the smallest. It is convenient to put the baby on them, and they are accurate to the gram, which is very important for newborns.
| Child's age | Amount of milk eaten per feeding, ml | Number of milk eaten per day. |
| 3-4 days | 20-60 | 200-300 ml |
| 1 Week | 50-80 | 400 ml |
| 2 weeks | 60-90 | nine0028 20% of the child's weight|
| 1 month | 100-110 | 600 ml |
| 2 months | 120-150 | 800 ml |
| 3 months | 150-180 | 1/6 of the child's weight | nine0040
| 4 months | 180-210 | 1/6 of the child's weight |
| 5-6 months | 210-240 | 1/7 of the child's weight (800 ml -1 liter) |
| 7-12 months | 210-240 | 1/8 - 1/9 of the child's weight | nine0040
As for the length of the body of the baby.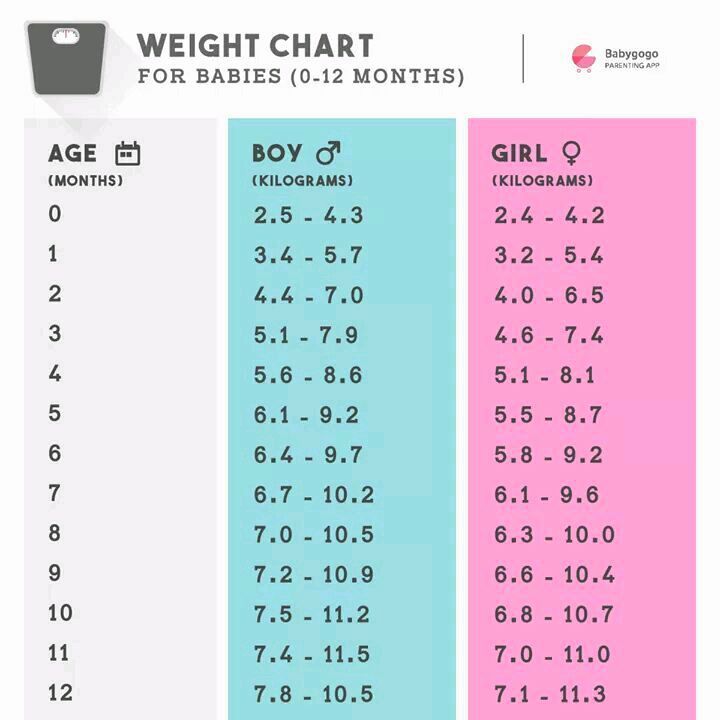 For the first three months, children grow on average by 3 cm per month, from the third to the sixth month by 2.5 cm. After six months, the growth rate slows down a little, and the child begins to add 1-1.5 cm per month. The average body length per year is approximately 75-80 cm. The correct measurement of height in children of the first year of life is carried out in a supine position using a horizontal stadiometer in the form of a board eighty centimeters long with a fixed bar in the upper part. The child is laid so that the top of the head is pressed tightly into the fixed bar. The legs of the crumbs are straightened by light pressure on the knees. nine0003
For the first three months, children grow on average by 3 cm per month, from the third to the sixth month by 2.5 cm. After six months, the growth rate slows down a little, and the child begins to add 1-1.5 cm per month. The average body length per year is approximately 75-80 cm. The correct measurement of height in children of the first year of life is carried out in a supine position using a horizontal stadiometer in the form of a board eighty centimeters long with a fixed bar in the upper part. The child is laid so that the top of the head is pressed tightly into the fixed bar. The legs of the crumbs are straightened by light pressure on the knees. nine0003
If your baby differs from the average norms for weight and body length, do not panic, but be sure to contact your pediatrician! After all, the lag or, conversely, the acceleration of development can have many reasons. And also remember that every person on Earth and every child is individual and has its own pace of physical development.
Height and weight gain for children of the first year of life. Tables
Dear parents, your baby is growing and you are worried about whether he is gaining enough weight and height. For control, there are centile tables for assessing the physical development of children, weight and height indicators. At the same time, you must remember that each baby is individual, he cannot grow according to the textbook. These weight and height recommendations are based on an average number of children and 10% deviation is normal. In addition, the centile corridor from 25% to 75% is an average physical indicator. That is why they say: Physical development is mesosomatic, macrosomatic, microsomatic. nine0003
It is important that the weight and height indicators are in the same centile corridor, but no more than two adjacent ones. Then we can talk about harmonious development. If the gap is more than two centile corridors, the development is disharmonious. Then we can think either about an unbalanced diet or about a pathology associated with obesity (paratrophy), or protein-energy deficiency (hypotrophy). In addition, one should not forget about the constitutional characteristics of the child, about genetic predisposition. Therefore, in no case should you compare your child with a neighbor's. To talk about the health of a child, we evaluate his condition according to many criteria. This is neuropsychic development, laboratory examination data, anamnesis, heredity. How many times in my practice have I met children who gained 400-450 g in weight every month, by the year they barely gained 7.8-8 kg. But at the same time, children already at 10 months began to walk, pronounce syllables, and follow complex instructions. nine0003
In addition, one should not forget about the constitutional characteristics of the child, about genetic predisposition. Therefore, in no case should you compare your child with a neighbor's. To talk about the health of a child, we evaluate his condition according to many criteria. This is neuropsychic development, laboratory examination data, anamnesis, heredity. How many times in my practice have I met children who gained 400-450 g in weight every month, by the year they barely gained 7.8-8 kg. But at the same time, children already at 10 months began to walk, pronounce syllables, and follow complex instructions. nine0003
We'll talk about weight and height gain for term babies. In preterm infants, rates of weight gain and height differ according to the degree of prematurity. In addition, children can be born with intrauterine malnutrition.
The tables for girls and boys are different in terms of numerical indicators, but at 1 year of age, these differences are quite minimal.
Centile tables for assessing the physical development of girls from 0 to 12 months. nine0003
| Body length (height), cm. Centiles in % | Age in months | Body weight, kg. Centiles in % | ||||||||||||
| 3 | nine0002 10 | 25 | fifty | 75 | 90 | 97 | 3 nine0003 | 10 | 25 | fifty | 75 | 90 | 97 | |
| nine0002 45.8 | 47.5 | 49.8 | 50.7 | 52.0 | 53.1 | 53.9 nine0031 | 0 | 2. | 2.8 | 3.0 | 3.3 | 3.7 | 3.9 | 4.1 |
| 48.5 | 50.3 | 52.1 | 53.5 | 55.0 | nine0028 57.3 | one | 3.3 | 3.6 | 3.8 | 4.2 nine0003 | 4.5 | 4.7 | 5.1 | |
| 51.2 | 53.3 | 55.2 | nine0028 58.0 | 59.3 | 60.6 | 2 | 3.8 | 4.2 nine0003 | 4.5 | 4. | 5.2 | 5.5 | 5.9 | |
| 54.0 | nine0002 56.2 | 57.6 | 59.3 | 67.7 | 61.8 | 63.6 | 3 nine0031 | 4.4 | 4.8 | 5.2 | 5.5 | 5.9 | 6.3 | 6.7 nine0003 |
| 56.7 | 58.4 | 60.0 | 61.2 | 62.8 | 64.0 | nine0028 4 | 5.0 | 5.4 | 5.8 | 6.2 | 6.6 nine0003 | 7.0 | 7. | |
| 59.1 | 60.8 | 62.0 | 63.8 | nine0028 66.0 | 68.0 | five | 5.5 | 5.9 | 6.3 nine0003 | 6.7 | 7.2 | 7.7 | 8.1 | |
| 60.8 | 62.5 | nine0028 65.5 | 67.1 | 68.8 | 70.0 | 6 | 5.9 nine0003 | 6.3 | 6.8 | 7.3 | 7.8 | 8.3 | 8.7 | |
| nine0002 62.7 | 64.1 | 65. | 67.5 | 69.2 | 70.4 | 71.9 nine0031 | 7 | 6.4 | 6.8 | 7.3 | 7.7 | 8.4 | 8.9 | 9.3 |
| 64.5 | 66.0 | 67.5 | 69.0 | 70.5 | nine0028 73.7 | eight | 6.7 | 7.2 | 7.6 | 8.2 nine0003 | 8.8 | 9.3 | 9.7 | |
| 66.0 | 67.5 | 69.1 | nine0028 72.0 | 74. | 75.5 | nine | 7.1 | 7.5 nine0003 | 8.0 | 8.6 | 9.2 | 9.7 | 10.1 | |
| 67.5 | nine0028 70.3 | 71.9 | 73.2 | 75.3 | 76.8 | 10 nine0003 | 7.4 | 7.9 | 8.4 | 9.0 | 9.6 | 10.1 | nine0002 10.5 | |
| 68.9 | 70.1 | 71.5 | 73.0 | 74.7 | 76.5 nine0003 | 78.1 | eleven | 7. | 8.3 | 8.7 | 9.3 | nine0002 9.9 | 10.5 | 10.9 |
| 70.1 | 71.4 | 72.8 | 74.1 nine0003 | 75.8 | 78.0 | 79.6 | 12 | 8.0 | 8.5 | nine0002 9.0 | 9.6 | 10.2 | 10.8 | 11.3 |
At the same time, until the age of three months, the child adds 20-30 grams per day daily, respectively, from 140 to 200 per week. If we talk about the average weight gain by months, then it is only 600 g per month, since the child after birth has physiological weight loss (with urine, feces, transition from intrauterine feeding to breastfeeding during the adaptation period), approximately 10% of the weight, which is 200-300 grams. nine0003
nine0003
More often, by 3-4 days, the child restores its original weight, and then there is an increase. But I had a case in practice when the child began to gain weight from the 20th day of life, while the girl was active, reflexes were alive, her appetite was good, she could withstand the night interval, stool 4-5 times a day, urination was sufficient, developed according to age. Therefore, do not worry. Our indicator is the well-being of the child. If the baby is active, eats with appetite, sleep is calm, the skin is clean, physiological functions are not disturbed, be calm, your baby is healthy and not hungry. You see from the table the range of weight per year is from 8 to 13 kg. This is the norm. There is no reason to run to the endocrinologist, genetics, to examine the child. nine0003
Or the opposite situation: in the first months of life, a child gains 1-1.5 kg while breastfeeding. If the baby does not have colic, he does not spit up, there are no gastrointestinal manifestations, he is active, the skin is clean, physiological functions are not disturbed - this is also the norm. Remember, as often happens, premature babies quickly gain weight and catch up with their peers by the year. And large babies gain weight more slowly. In my entire thirty-year practice, only two children weighed 14-15 kg by the year, although their parents were large and tall. By the age of three, they weighed almost the same, added only in height, the rest of their peers caught up with them. nine0003
Remember, as often happens, premature babies quickly gain weight and catch up with their peers by the year. And large babies gain weight more slowly. In my entire thirty-year practice, only two children weighed 14-15 kg by the year, although their parents were large and tall. By the age of three, they weighed almost the same, added only in height, the rest of their peers caught up with them. nine0003
| Month | Weight gain in grams |
| one | 600.0 |
| 2 | 800.0 nine0003 |
| 3 | 800.0 |
| 4 | 750.0 |
| five | 700.0 nine0031 |
| 6 | 650.0 |
| 7 | 600.0 |
| eight | 550. | nine0040
| nine | 500.0 |
| 10 | 450.0 |
| eleven | 400.0 |
| 12 | 350.0 |
It is believed that by 4-4.5 months the child should double the weight, and triple by the end of the year.
It happens that the increase in height and weight goes in leaps, seasonality, unevenness, and sometimes asymmetry of growth are noted. Pediatricians are concerned about the circumference of the head and chest, by 2-3 months they should be equal. Further, the breast grows faster. This is important so as not to miss the pathology. nine0003
The younger the child, the faster his growth. In the first 3 months of life, body length increases by 3 cm monthly, in the second quarter by 2.5-2 cm monthly. In the third - 1.5-2 cm, in the fourth - 1 cm monthly. The total increase in height in the first year of life is about 25 cm.
The total increase in height in the first year of life is about 25 cm.
Centile tables for assessing the physical development of boys from 0 to 12 months.
| Body length (height), cm. nine0003 Centiles in % | Age in months | Body weight, kg Centiles in % | ||||||||||||
| 3 | 10 | 25 nine0003 | fifty | 75 | 90 | 97 | 3 | 10 nine0031 | 25 | fifty | 75 | 90 | 97 | |
| 46.5 | 48.0 nine0003 | 49.8 | 51.3 | 52.3 | 53. | 55.0 | 0 | nine0002 2.7 | 2.9 | 3.1 | 3.4 | 3.7 | 3.9 | 4.4 nine0031 |
| 49.5 | 51.2 | 52.7 | 54.5 | 55.6 | 56.5 | nine0002 57.3 | one | 3.3 | 3.6 | 4.0 | 4.3 | 4.7 | nine0028 5.4 | |
| 53.6 | 53.8 | 55.3 | 57.3 | 58.2 nine0003 | 59.4 | 60.9 | 2 | 3. | 4.2 | 4.6 | nine0002 5.1 | 5.6 | 6.0 | 6.4 |
| 55.3 | 56.5 | 58.1 nine0003 | 60.0 | 60.9 | 62.0 | 63.8 | 3 | 4.5 | nine0002 4.9 | 5.3 | 5.8 | 6.4 | 7.0 | 7.3 |
| 57.5 nine0031 | 58.7 | 60.6 | 62.0 | 63.1 | 64.5 | 66.3 | 4 nine0003 | 5.1 | 5.5 | 6.0 | 6. | 7.2 | 7.6 | nine0002 8.1 |
| 59.9 | 61.1 | 62.3 | 64.3 | 65.6 | 67.0 nine0003 | 68.9 | five | 5.6 | 6.1 | 6.5 | 7.1 | nine0002 7.8 | 8.3 | 8.8 |
| 61.7 | 63.0 | 64.8 | 66.1 nine0003 | 67.7 | 69.0 | 71.2 | 6 | 6.1 | 6.6 | nine0002 7.1 | 7.6 | 8.4 | 9.0 | 9. |
| 63.8 | 65.1 nine0003 | 66.3 | 68.0 | 69.8 | 71.1 | 73.5 | 7 | nine0002 6.6 | 7.1 | 7.6 | 8.2 | 8.9 | 9.5 | 9.9 nine0031 |
| 65.5 | 66.8 | 68.1 | 70.0 | 71.3 | 73.1 | nine0002 75.3 | eight | 7.1 | 7.5 | 8.0 | 8.6 | 9.4 | nine0028 10.5 | |
| 67.3 | 68.2 | 69. | 71.3 | 73.2 nine0003 | 75.1 | 75.5 | nine | 7.5 | 7.9 | 8.4 | nine0002 9.1 | 9.8 | 10.5 | 11.0 |
| 68.8 | 69.1 | 71.2 nine0003 | 73.0 | 75.1 | 76.9 | 78.8 | 10 | 7.9 | nine0002 8.3 | 8.8 | 9.5 | 10.3 | 10.9 | 11.4 |
| 70.1 nine0003 | 71.3 | 72.6 | 74.3 | 76.2 | 78. | |||||||||
 6
6  8
8  5
5  9
9  1
1  7
7  0
0  5
5  9
9  5
5  4
4  8
8