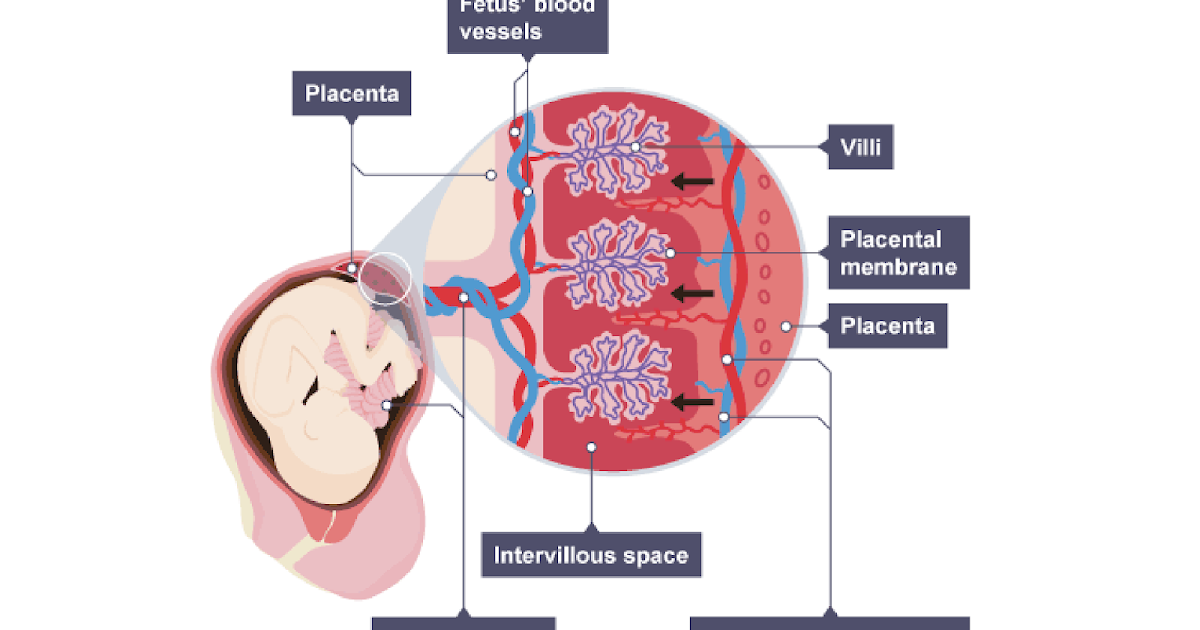
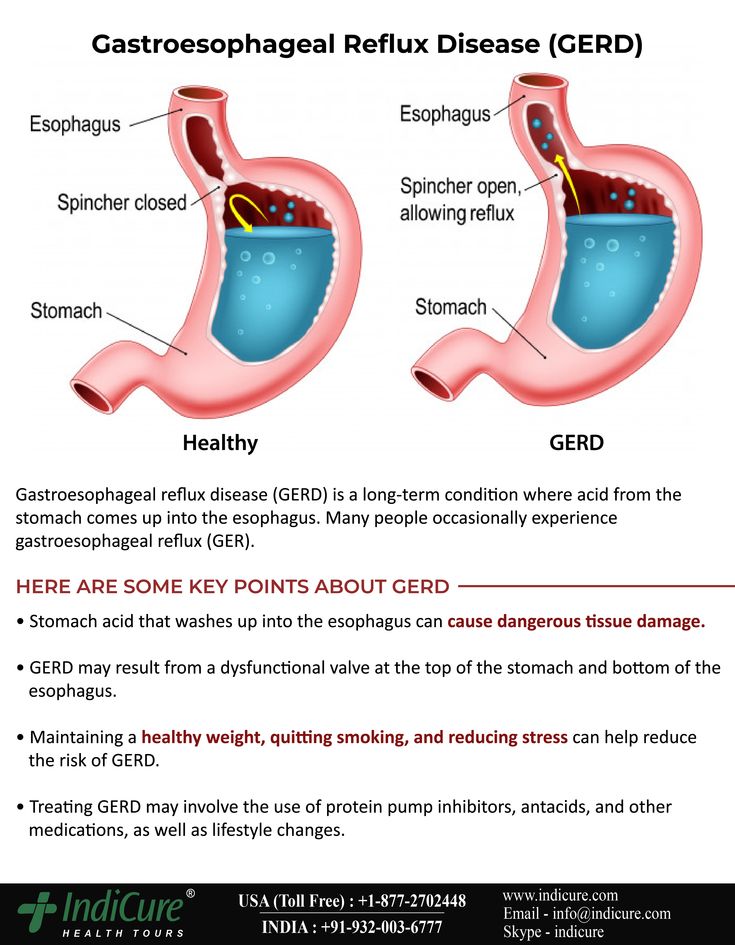
How to get assistance with child care
Child Care Financial Assistance Options
Paying for quality child care can be a struggle for many families in the United States. The cost of child care is often the biggest part of a family’s budget and can be higher than the cost of housing, food, or even college tuition.
If you need help paying for child care, there are programs that can help. Below is a summary of different programs that may be available to help with the cost of child care.
Note: Your state or territory’s online child care search may indicate if a provider participates in a government financial assistance program or offers its own assistance or discounts. To find your state or territory’s online child care search, visit the “Find Child Care” page.
Government Programs
- Child care financial assistance (also called vouchers, certificates, or subsidies): States and territories receive funding from the federal government to provide child care financial assistance for low-income families in their state.
These programs help low-income families pay for child care so they can work or attend school. Eligibility requirements are different in each state. Select your state or territory on the “See Your State’s Resources page and review the “Financial Assistance for Families” tab to find your local child care financial assistance program.
- Head Start and Early Head Start: Head Start and Early Head Start programs help prepare children from birth to age 5 for school and provide services to support children’s early learning and development, mental well-being, and physical health. Head Start and Early Head Start are available at no cost to eligible low-income families. Select your state or territory on the “See Your State’s Resources page and review the “Child Development and Early Learning” tab to find Head Start and Early Head Start programs in your state or territory.
- State-funded prekindergarten: State-funded prekindergarten programs serve children between 3 and 5 years of age and focus on helping children get ready for kindergarten.
 Some states offer these programs to eligible families at low or no cost. Programs may be part-day or full-day. Select your state or territory on the “See Your State’s Resources”page and review the “Child Development and Early Learning” tab to see if public prekindergarten is available in your state or territory.
Some states offer these programs to eligible families at low or no cost. Programs may be part-day or full-day. Select your state or territory on the “See Your State’s Resources”page and review the “Child Development and Early Learning” tab to see if public prekindergarten is available in your state or territory. - Military child care financial assistance programs: There are several programs that help military families pay for child care, wherever they are stationed. To learn more, visit the Child Care Financial Assistance for Military Families page.
Local and Provider-Specific Assistance and Discounts
- Local assistance and scholarships: Local nonprofit organizations and individual child care providers may offer fee assistance or scholarships. Ask the providers that you are considering if they offer any child care assistance or scholarships.
- Sibling discount: Some child care programs offer a discount to families that enroll siblings.
 They may take a percentage or a specific dollar amount off of a child’s weekly or monthly fee. They may also waive the registration fee or other fees. If you need care for more than one child, ask providers whether they offer sibling discounts.
They may take a percentage or a specific dollar amount off of a child’s weekly or monthly fee. They may also waive the registration fee or other fees. If you need care for more than one child, ask providers whether they offer sibling discounts. - Military discount: Some civilian child care providers (not associated with military child care) offer discounts for military service members. Ask potential providers if they offer a military discount.
Work- and School-Related Programs
- Employer-sponsored Dependent Care Flexible Spending Account: Some employers may allow employees to put a portion of each paycheck into a special fund called a Dependent Care Flexible Spending Account, or “FSA,” to pay for child care services while the employees work. The money you contribute to a Dependent Care FSA is not subject to payroll taxes, so you end up paying less in taxes and taking home more of your paycheck. It can only be used to pay for dependent care, such as child care.
 Check with your human resources department to see if your employer offers this program.
Check with your human resources department to see if your employer offers this program. - Other employer resources: Some companies offer child care onsite for employees’ children. In addition, some child care programs may offer discounts for employees of certain companies. Find out if your employer has relationships with any nearby child care programs that offer employee discounts.
- College or university child care: Some colleges and universities offer child care on campus. These programs may offer special discounts to students, faculty, and staff.
Native Hawaiian, Native Alaskan, and American Indian Programs
- Tribal Child Care Financial Assistance: Many Tribes and Tribal organizations receive child care grants from the federal government to provide child care financial assistance to Tribal families. There are also more than 150 Head Start and Early Head Start programs that serve American Indian and Alaska Native children.
 Find these programs with the Head Start Center Locator.
Find these programs with the Head Start Center Locator. - Child Care Assistance for Indigenous People of Hawai’i and other Pacific Islands child care and preschool programs: There are programs in Hawaii that assist with cost of child care and preschool for children of Indigenous People of Hawai’i and other Pacific Islands. Families should contact PATCH (the local child care resource and referral agency) for more information.
Tax Credits and Support
Tax credits reduce the amount of tax you owe and may result in a tax refund. To claim tax credits, you need to meet certain requirements and file a tax return, even if you have no other filing requirement or owe no income tax.
- Child and dependent care tax credit: This credit is available to people who had to pay for child care for their children (younger than age 13) so they could work or look for work.
- Earned income tax credit: This tax credit helps low- to moderate-income workers and families get a tax break.
 If you qualify, you can use the credit to reduce the taxes you owe and possibly increase your refund.
If you qualify, you can use the credit to reduce the taxes you owe and possibly increase your refund. - IRS Volunteer Income Tax Assistance: This program provides free tax help to eligible low-income taxpayers.
Speak with a tax specialist or visit https://www.irs.gov/ to learn more about these tax credits and more.
Child Care Options | Childcare.gov
You want the best for your child.
Children need care that keeps them safe, healthy, and learning.
And you need a child care provider that supports you as your child’s most important teacher and works with you to ensure your child’s healthy development and learning.
When you have peace of mind that your child is safe, happy, and learning, you can focus on your work and providing for your family.
There are many types of child care to choose from, and it is important to find a provider that fits the needs of your child and your family.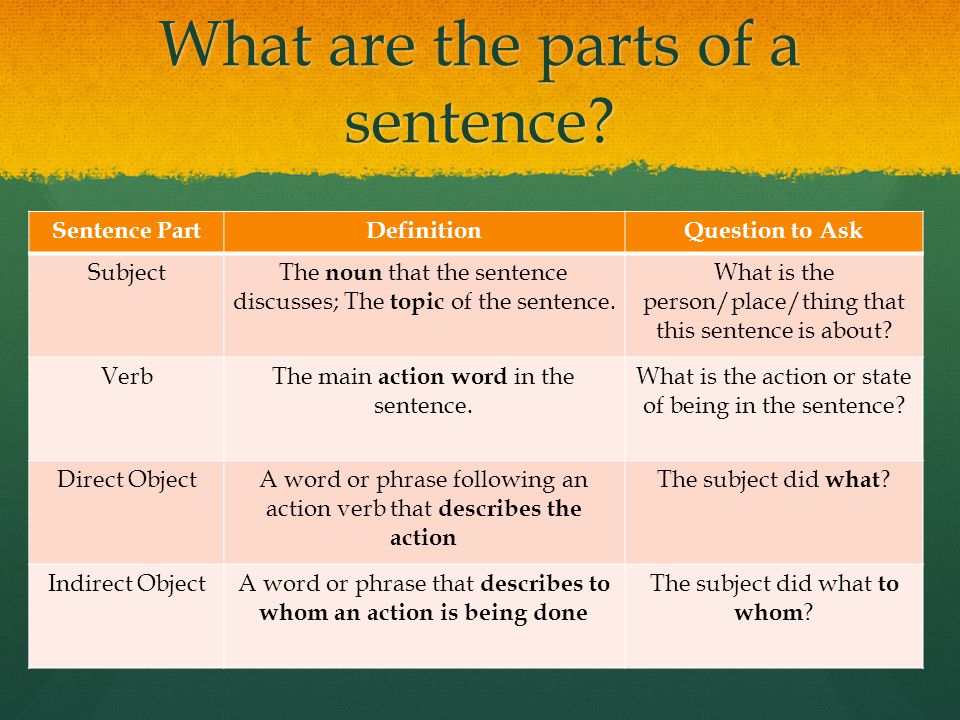 When choosing a child care provider, there are many factors to consider.
When choosing a child care provider, there are many factors to consider.
This section provides important information about different kinds of child care programs, including how different types of programs are regulated.
You will also find some tips and tools to help make your child care choice easier.
If you have questions or want to talk with someone about the types of child care available in your community, there are state and local agencies that can help you. They can provide additional information to help you make the best choice for your child.
You can select any of the agency types below to find more information about these services in your state. Once you select one of the agencies below, select your state under the “Get Child Care Resources”. You will then see a variety of child care related resources including information about finding quality child care and financial assistance for families.
Child care resource and referral (CCR&R) agencies: CCR&R agencies can help you by phone, in person, online, or via email. Most of these agencies also have websites with child care information and resources.
Most of these agencies also have websites with child care information and resources.
Child care licensing agencies: Licensing agencies set basic rules that must be followed to legally run a child care program. The purpose of these basic licensing regulations is to help protect the health and safety of children in child care. When states set these rules, they include different rules for different kinds of child care programs, such as child care centers and family child care homes. Here are some examples of topics covered by basic licensing regulations:
-
Safety in the building and physical environment
-
The number of children and child care providers on site
-
Preventing the spread of infectious diseases
-
Staff qualifications and training
Not all child care providers are required to be licensed, so it is important to check to see if the child care program you are considering is licensed.
The requirements for licensing vary across states and there are many different kinds of programs that may not be required to be licensed. You may not be able to tell if a provider is licensed just by visiting or talking to with the provider. Ask to see a license and check with the agency that is responsible for child care licensing in your state.
Child care assistance agencies: If you need help paying for child care, assistance may be available. Each state has an agency that is responsible for a child care assistance program that helps low-income families pay for child care. Each state has its own guidelines for who is eligible for assistance. These agencies may also help you learn about child care options in your state and local area.
Requirements and quality standards for child care programs: Child care requirements can be very confusing, and there are many different types of requirements to consider.
-
First, States have several types of requirements that child care providers must meet in order to operate legally.
 These may be called licensing, certification, or registration requirements. These requirements outline what providers must do to operate legally and what types of basic requirements must be met.
These may be called licensing, certification, or registration requirements. These requirements outline what providers must do to operate legally and what types of basic requirements must be met. - In addition, there are often requirements that providers must meet in order to receive public funding. There are many sources of public funding, but two of the biggest are Head Start and the Child Care and Development Fund. If you need assistance with child care, these programs may be able to help you with free or low-cost care and early education. Even if you don’t need assistance, you may end up choosing a child care program that receives public funding, so your program may be required to follow these requirements. Click here to learn more about child care financial assistance.
- Finally, many states have additional child care quality standards. These types of quality standards are often part of a state or community quality rating and improvement system (QRIS).
 These quality rating and improvement systems award child care programs with stars or other symbols for rating levels to indicate higher quality. Looking for a higher rating is a great way to find high quality care. Check to see if your state operates a quality rating and improvement system and if the providers you are considering are part of it. Click here to learn more about what is available in your state.
These quality rating and improvement systems award child care programs with stars or other symbols for rating levels to indicate higher quality. Looking for a higher rating is a great way to find high quality care. Check to see if your state operates a quality rating and improvement system and if the providers you are considering are part of it. Click here to learn more about what is available in your state.
Quality standards such as those included in licensing and QRIS reflect what child care programs should be doing to provide safe, legal, and effective care and early learning services for your family. To learn more about what you should look for and questions you should ask when you are looking for a high-quality program use this tool.
Monthly allowance for child care for persons not subject to compulsory social insurance
The applicant has the right to file a complaint against the decisions and (or) actions (inaction) of the authorized body, its officials in the provision of public services (complaint), including in the pre-trial (out of court) procedure in the following cases:
- violation of the application registration deadline;
- violation of the term for the provision of public services; nine0006
- requirement from the applicant of documents, information or actions not provided for by the regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation for the provision of public services;
- refusal to provide a public service, if the grounds for refusal are not provided for by federal laws and other regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation adopted in accordance with them;
- refusal to accept documents, the submission of which is provided for by regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation for the provision of public services; nine0006
- requesting from the applicant, when providing a public service, a fee not provided for by the regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation;
- refusal of the authorized body, its officials to correct the misprints and errors made by them in the documents issued as a result of the provision of public services or violation of the deadline for such corrections;
- violation of the term or procedure for issuing documents based on the results of the provision of public services; nine0006
- suspension of the provision of public services, if the grounds for suspension are not provided for by federal laws and other regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation adopted in accordance with them, laws and other regulatory legal acts of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation, municipal legal acts.

Subject of complaint
The subject of the complaint is a violation of the rights and legitimate interests of the applicant, unlawful decisions and (or) actions (inaction) of the authorized body, its officials in the provision of public services, violation of the provisions of the administrative regulations and other regulatory legal acts that establish requirements for the provision of public services. nine0003
A citizen has the right to file a complaint in writing on paper by mail or in person to any PFR Client Service, as well as in electronic form:
- on the official website pfr.gov.ru;
- portal vashkontrol.ru;
- portal do.gosuslugi.ru.
The reason for the appeal may be dissatisfaction with the quality of the provision of public services by the PFR, violation of the terms for the provision of services, violation of the terms for registering a request for a service, refusal to correct errors or typos, refusal to provide a public service, refusal to accept documents, demand for an additional fee. nine0003
nine0003
Procedure for filing and handling a complaint
The complaint must contain:
- name of the authorized body, last name, first name, patronymic (if any) of its officials providing the public service and (or) their leaders, decisions and actions (inaction) of which are being appealed;
- last name, first name, patronymic (if any) of the applicant, information about the place of residence, as well as contact phone number (numbers), e-mail address (s) (if any) and postal address to which the answer should be sent to the applicant; nine0006
- information about the appealed decisions and (or) actions (inaction) of the authorized body, an official of the authorized body, its head;
- arguments on the basis of which the applicant does not agree with the decisions and (or) actions (inaction) of the authorized body, an official of the authorized body, its head.
The applicant shall submit documents (if any) confirming his arguments or copies thereof.
When filing a complaint in electronic form, the documents specified in paragraph 106 of the administrative regulations may be submitted in the form of an electronic document signed with an electronic signature, the form of which is provided for by the legislation of the Russian Federation. In this case, an identity document of the applicant is not required.
In the authorized body, officials authorized to consider complaints are determined, who ensure:
- receiving and handling complaints; nine0006
- sending complaints to the body authorized to consider them.
Complaints against decisions and (or) actions (inaction) of an official of the authorized body are considered by the head of the authorized body or an official of the authorized body authorized to consider complaints. Complaints against decisions and (or) actions (inaction) of the head of the authorized body are considered by an official of the executive authority of the constituent entity of the Russian Federation authorized to consider complaints. nine0003
If the complaint is filed by the applicant with a body whose competence does not include making a decision on the complaint, within 3 working days from the date of its registration, the said body sends the complaint to the body authorized to consider it and informs the complainant in writing about the redirection of the complaint.
The authorized body ensures:
- equipment for receiving complaints;
- informing applicants about the procedure for appealing against decisions and (or) actions (inaction) of the authorized body, officials of the authorized body by posting information on information boards in places where public services are provided, on the website of the authorized body, on the Single portal, service portal; nine0006
- advising applicants on the procedure for appealing against decisions and (or) actions (inaction) of the authorized body, officials of the authorized body at a personal appointment, by phone, using the website of the authorized body;
- conclusion of agreements on interaction between the multifunctional center and the authorized body in terms of the implementation by the multifunctional center of receiving complaints and issuing the results of consideration of complaints to the applicant;
- formation and quarterly submission to the Federal Service for Labor and Employment of reports on received and considered complaints (including the number of satisfied and unsatisfied complaints).
nine0006
Deadlines for considering a complaint
A complaint received by the authorized body shall be subject to registration no later than the working day following the day of its receipt.
The complaint is subject to consideration within 15 working days from the date of its registration, and in the event of an appeal against the refusal of the authorized body to accept documents from the applicant or to correct misprints and errors, or in the event of an appeal against a violation of the established deadline for such corrections - within 5 working days from the date of its registration. nine0003
Result of consideration of the complaint
The result of the consideration of the complaint is the adoption of one of the following decisions:
- satisfy the complaint, including in the form of cancellation of the decision made by the authorized body, correction of typos and errors in documents issued as a result of the provision of public services, return to the applicant of funds, the collection of which is not provided for by the regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation, regulatory legal acts of the subjects Russian Federation, municipal legal acts; nine0006
- refuse to satisfy the complaint.

When satisfying the complaint, the authorized body takes comprehensive measures to eliminate the identified violations, including the issuance of the result of the public service to the applicant no later than 5 working days from the date of the relevant decision, unless otherwise provided by the legislation of the Russian Federation.
A complaint may be denied in the following cases:
- availability of a court decision that has entered into legal force on a complaint about the same subject and on the same grounds;
- filing a complaint by a person whose powers have not been confirmed in the manner prescribed by the legislation of the Russian Federation;
- the presence of a decision on a complaint made earlier in accordance with the requirements of the Rules for filing and considering complaints against decisions and actions (inaction) of federal executive bodies and their officials, federal civil servants, officials of state non-budgetary funds of the Russian Federation, state corporations endowed with in accordance with federal laws, the powers to provide public services in the established field of activity, and their officials, organizations provided for by Part 1.
 1 of Article 16 of the Federal Law "On the organization of the provision of state and municipal services", and their employees, as well as multifunctional centers for the provision of state and municipal services and their employees, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 840 dated August 16, 2012, in respect of the same applicant and on the same subject of the complaint. nine0006
1 of Article 16 of the Federal Law "On the organization of the provision of state and municipal services", and their employees, as well as multifunctional centers for the provision of state and municipal services and their employees, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 840 dated August 16, 2012, in respect of the same applicant and on the same subject of the complaint. nine0006
A complaint may be left unanswered in the following cases:
- presence in the complaint of obscene or offensive expressions, threats to life, health and property of an official of the authorized body, as well as members of his family;
- the inability to read any part of the text of the complaint, the last name, first name, patronymic (if any) and (or) the postal address of the applicant indicated in the complaint.
In response to the results of the consideration of the complaint, the following shall be indicated: nine0003
- name of the public service provider that considered the complaint, position, last name, first name, patronymic (if any) of the official who made the decision on the complaint;
- number, date, place of the decision, including information about the official of the authorized body, the decision and (or) action (omission) of which is being appealed;
- last name, first name, patronymic (if any) of the applicant;
- grounds for making a decision on the complaint; nine0006
- decision made on the complaint;
- if the complaint is found to be justified, the terms for eliminating the identified violations, including the term for providing the result of the public service;
- information on the procedure for appealing against the decision taken on the complaint.

In the event that, during or as a result of consideration of a complaint, signs of an administrative offense or crime are established, an official of the authorized body authorized to consider complaints shall send the available materials to the prosecutor's office. nine0003
The procedure for informing the applicant about the results of the consideration of the complaint
A reasoned response based on the results of the consideration of the complaint is signed by the official authorized to consider the complaint and sent to the applicant in writing or, at the request of the applicant, in the form of an electronic document signed by the electronic signature of the official authorized to consider the complaint, the type of which is established by the legislation of the Russian Federation, no later than the day following the day the decision is made on the results of the consideration of the complaint. nine0003
Procedure for appealing a decision on a complaint
The applicant has the right to appeal the decision taken on the complaint by sending it to the Federal Service for Labor and Employment.
If the applicant is not satisfied with the decision made during the consideration of the complaint or the absence of a decision on it, then he has the right to appeal the decision in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation.
The applicant's right to receive information and documents necessary to substantiate and consider the complaint
The applicant has the right to receive comprehensive information and documents necessary to substantiate and consider the complaint.
Ways to inform complainants about the procedure for filing and considering a complaint
Information on the procedure for filing and considering a complaint is posted on information boards in places where public services are provided, on the website of the authorized body, on the Single Portal, Services Portal, and can also be communicated to the applicant orally and (or) in writing. nine0003
List of regulatory legal acts regulating the procedure for pre-trial (out-of-court) appeal against decisions and actions (inaction) of the authorized body, as well as its officials
The procedure for pre-trial (out-of-court) appeals against decisions and actions (inaction) of the body providing the public service, as well as its officials, is regulated by Federal Law No. 210-FZ of July 27, 2010 “On the organization of the provision of state and municipal services” and the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of August 16 .2012 No. 840 “On the procedure for filing and considering complaints against decisions and actions (inaction) of federal executive bodies and their officials, federal civil servants, officials of state non-budgetary funds of the Russian Federation, state corporations vested in accordance with federal laws with powers to provision of public services in the established field of activity, and their officials, organizations provided for by Part 1.1 of Article 16 of the Federal Law "On the organization of the provision of state and municipal services", and their employees, as well as multifunctional centers for the provision of I am state and municipal services and their employees”. nine0003
210-FZ of July 27, 2010 “On the organization of the provision of state and municipal services” and the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of August 16 .2012 No. 840 “On the procedure for filing and considering complaints against decisions and actions (inaction) of federal executive bodies and their officials, federal civil servants, officials of state non-budgetary funds of the Russian Federation, state corporations vested in accordance with federal laws with powers to provision of public services in the established field of activity, and their officials, organizations provided for by Part 1.1 of Article 16 of the Federal Law "On the organization of the provision of state and municipal services", and their employees, as well as multifunctional centers for the provision of I am state and municipal services and their employees”. nine0003
list of documents, detailed instructions for obtaining
According to the law, you can be on parental leave for three years.
Diana Shigapova
lawyer
Mothers, fathers or other relatives, while on such leave, receive benefits until the child reaches one and a half years.
We have already written how to calculate maternity payments. In this article I will tell you how benefits are calculated and assigned for a child up to three years old.
What laws govern the granting of allowance for a child up to three years of age
The right to a monthly allowance for child care is guaranteed by the federal law "On State Benefits for Citizens with Children".
The right to a monthly allowance for child care
The same law states that the allowance is paid from the day the leave is granted until the child reaches one and a half years. The law does not say anything about benefits from one and a half to three years.
Duration of payment of the monthly child care allowance
Instead of a benefit from one and a half to three years, mothers or other relatives who have taken parental leave are entitled to compensation - 50 R. But only for children born before 2020. nine0003
But only for children born before 2020. nine0003
What has changed in 2020. Families with children born in 2020 and later are no longer paid monthly compensation in the amount of 50 R for children from one and a half to three years old: the presidential decree on the payment of such compensation has become invalid.
So what? 11/26/19
Payments for children under three years of age have been cancelled. What does it mean?
If you already receive 50 R for children under three years old, then you will continue to receive money until the children's third birthday.
Who is entitled to benefits up to three years
In this article, I will talk about mothers, because they are the ones who most often take parental leave.
Allowance up to one and a half years is due to all mothers who care for children. It doesn’t matter if a woman worked under an employment contract or not, she will receive a child care allowance. But the amount of the benefit is different. Here is what affects him:
But the amount of the benefit is different. Here is what affects him:
- The salary that the mother received before pregnancy.
- Family status - for example, a family may be considered indigent. nine0006
- The status of the child - for example, a child with a disability.
/papa-mozhet/
How a man can go on maternity leave
A mother without work experience will receive the least, and a mother with a good salary and a special child will receive the most.
I will tell you more about the possible amounts of benefits for a child up to one and a half years below.
Compensation in the amount of 50 R is due only to those who are employed, and provided that the child was born before 2020. This amount is fixed. nine0003
Which family is considered poor
In Russia, a poor family is one whose average per capita income per family member is less than the subsistence minimum established in the region of residence.
Determine if the family is poor, as follows:
- Calculate the family income for the last three months from the date of application to social protection. Income includes all salaries, pensions, allowances, scholarships.
- The amount of income divided by 3 is the average monthly family income. nine0006
- The average monthly income is divided by the number of family members to get the average per capita family income. It is he who is compared with the subsistence minimum per capita in the region where the family lives.
st. 7 of the Federal Law No. 178 "On State Social Assistance"
For the poor, the state has developed a special program, according to which, in addition to the child care allowance, the mother receives additional money.
Types of allowances for a child up to three years old
A pregnant woman, and then a woman who has given birth, is entitled to a pregnancy and childbirth allowance, child care allowance and sometimes other payments - this depends on the situation in the family. nine0003
nine0003
Maternity payments , or maternity allowance, are due to women who work under an employment contract, and also to those who were fired due to the liquidation of the organization or the termination of the individual entrepreneur.
What to do? 07/15/19
How can an individual entrepreneur receive maternity payments?
In addition to them, individual entrepreneurs who pay contributions to the Social Insurance Fund, the Social Insurance Fund, as well as civil servants, full-time students of universities and colleges can receive maternity payments. nine0003
This money is paid once - before maternity leave.
Child allowance is a child care allowance that is paid by the FSS every month until the child reaches one and a half years.
Child allowance up to one and a half years for the unemployed is issued in the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation. A certificate is needed from the second parent that he does not receive such benefits.
If a parent applies for benefits through an employer or the Social Insurance Fund, then certificates from a spouse or other relatives are not needed. Since 2022, the Social Insurance Fund itself determines whether someone already receives an allowance for caring for this child. nine0003
Payments to parents of a disabled child . In addition to child care allowance, a mother can apply for a social pension, as well as monthly assistance.
Disability pension and caregiver's benefit are paid up to the age of 18.
Payments to low-income families are provided for by federal and regional legislation. At the federal level, this is a monthly allowance for the first or second child, the so-called Putin's payments. The allowance is not intended specifically for low-income families, but with a high degree of probability, it is the low-income family that will have the right to Putin's payments. This allowance is paid for up to three years.![]() nine0003
nine0003
In some regions, support measures are provided directly to low-income families with small children. For example, in Moscow, children under three years old from low-income families are paid from 8,896 R to 17,791 R per month.
Other types . There are also additional payments to families in which fathers serve on conscription. They are paid until the child is three years old, but payments stop if the father has served and returned home.
/benefits/
Payments and child benefits in 2022
Who pays the benefits
The allowance for caring for a child up to one and a half years old is paid by the FSS or the PFR. Some employees who have become parents are also entitled to financial assistance from their employers.
FSS. Today, in all regions of the Russian Federation, there is a project for direct payments from the FSS - child care benefits are paid directly by the fund. But, if you are employed, you still need to apply for benefits to the employer: he will transfer the information to the FSS, and he will transfer the money. nine0003
But, if you are employed, you still need to apply for benefits to the employer: he will transfer the information to the FSS, and he will transfer the money. nine0003
PFR. The unemployed and women apply to the pension fund, who were fired during parental leave due to the liquidation of the organization.
/posobiya-roditelyam-bez-raboty/
What child benefits are due to parents without work
Employer. Some corporations and other large employers are developing a company's social policy: they think over when and how they will financially support their employees. Such programs operate, for example, in Gazprom and Tatneft. nine0003
Parental leave is often the case when an employer provides financial assistance to employees. That is, a woman receives both child care allowance and financial assistance from the employer.
Payments for a child with a disability come from the pension fund. To support low-income families, money is allocated from the federal and regional budgets, but these payments are processed in social security.
The procedure for assigning benefits
Most of the benefits are assigned on a declarative basis - that is, in order for a woman to receive them, she must write an application and provide documents. nine0003
Documents for receiving benefits
If a woman works under an employment contract, she needs to bring a child's birth certificate to the accounting department at work. A certificate from the father stating that he did not apply for child care allowance for up to one and a half years, from 2022, it is no longer necessary to submit for work.
You also need to bring a certificate from the previous employer about the amount of wages in order to calculate the allowance if the woman changed jobs during the previous two years.
/guide/moneyforborn/
How to receive payments at the birth of a child
If a woman is unemployed, then she needs to prepare a copy of her passport, a copy of the birth certificate of the child, a copy of the employment record, a certificate of non-receipt of unemployment benefits, as well as a certificate from her father that he did not take leave for child care. The FIU has no information about this, so it needs such a certificate.
The FIU has no information about this, so it needs such a certificate.
If a woman wants to make payments for a low-income family, then in addition to the basic documents, she needs to prepare certificates of her and her husband's income. nine0003
Application for benefit is filled in in any form.
Application deadline for benefits up to one and a half years - up to two years of the child. Children up to three years of age can apply for Putin's payments.
Art. 12 of the Federal Law "On compulsory social insurance in case of temporary disability and in connection with motherhood"
Where to submit documents: to the accounting department at the place of work, to the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation, the Social Insurance Fund, social security or the MFC. In some regions, working parents can apply for benefits up to a year and a half through public services. nine0003
Amount of benefits
Maternity allowance. The amount of maternity leave is calculated according to one of two formulas: based on salary or based on the minimum wage. The formula is chosen depending on the length of service and the amount of the woman's earnings two years before pregnancy.
The amount of maternity leave is calculated according to one of two formulas: based on salary or based on the minimum wage. The formula is chosen depending on the length of service and the amount of the woman's earnings two years before pregnancy.
Formulas for calculating maternity payments
Formula for calculating maternity payments based on salary in 2022:
Salary and other labor income for 2020-2021, but not more than 1,878,000 R ÷ 730 the woman was on sick leave, on maternity or childcare leave) × number of days of decree
The formula for calculating maternity payments based on the minimum wage from June 2022:
15,279 R × 24 months ÷ 730 days × number of days of the decree
Term of the decree and the amount of payments
| Term | Amount | |
|---|---|---|
| Ordinary Decree | 140 days | 70,324.8 R |
| Complicated labor | 156 days | R 78,361. 92 92 |
| Multiple pregnancy | 194 days | 97450.08 R |
Ordinary decree
term
140 days
Sum
70 324.8 R
Complicated birth
days 156 days
Multiple pregnancy
Term
194 days
Amount
97,450.08 R
Child care allowance . How much they will be paid in 2022 is calculated according to the following formula:
Salary and other labor income for 2020-2021, but not more than 1,878,000 R ÷ 730 days (minus the number of days that a woman was on sick leave or on vacation for pregnancy or on parental leave) × 30.4 × by 40%
In 2022, you should get at least 7677.81 R and no more than 31 282.82 R per month. The maximum for the whole of Russia is the same.
The unemployed and those whose average salary for two years is less than the minimum wage are paid a fixed allowance - 7677. 81 R. This amount is increased by the regional coefficient, if it is applied in the locality. nine0003
81 R. This amount is increased by the regional coefficient, if it is applied in the locality. nine0003
Putin's payments depend on the subsistence minimum - PM. Families in which the average monthly income per family member is not higher than twice the regional subsistence level are entitled to the subsistence level per child. On average, this is 14,000-15,000 rubles.
Since June 1, 2022, the minimum wage and living wages have grown. As a result, social payments tied to the PM also increased.
Duration of payments
Child care allowance is paid strictly until the child reaches the age of 1 year and 6 months. If this date falls, for example, in the middle of the month, then the amount of the benefit is calculated in proportion to the days. nine0003
For example, the child of an unemployed mother turned one and a half years old on 15 June. The allowance will be calculated as follows: 7677.81 R ÷ 30 days × 15 days. The woman will receive 3838.91 rubles.
Putin's payments are paid for a year, after which they must be extended, but no longer than until the child is three years old.
Payments to low-income families continue as long as established in the regional law. For example, in Tatarstan they pay for six months, and then the applicant needs to confirm his need: re-write the application, bring income certificates. nine0003
When payments stop
Child care benefits stop in two cases:
- The child is one and a half years old.
- The parent refused the allowance.
All other benefits are terminated in the following cases:
- If the payment period has expired, and the family could no longer prove their need or comply with the conditions prescribed by law.
- If the social security authority found that the family's real income is higher than declared. nine0006
- If the child is 3 years old.
What parents say about the fairness of payments
Many people think that the principle by which they determine who and how much to pay is unfair. This is especially true of Putin's payments.
Date of birth . The resentment is connected with the fact that the date of birth of children is prescribed in the law, starting from which the family has the right to the allowance.
/money-for-baby/
How I got Putin's payments for a child
Putin payments can only be issued by families in which a child was born after January 1, 2018. That is, if the child was born on December 31, 2017 or earlier, the parents will not be able to apply for benefits.
There is also a second condition: the child must be the first or second. Parents of babies born after January 1, 2018, but no longer the first or second in a row, cannot issue Putin's payments either.
The criterion of need in the law is quite clear: no more than two living wages established in the region where the family lives. If the income in the family is at least 1 R more, you will not be able to apply for benefits. nine0003
Source of payments for the second child . If money is allocated for the first child from the federal budget, then money for payments for the second child is taken from maternity capital. Families have to choose: reduce the amount of maternity capital and receive benefits, or refuse benefits and spend maternity capital for other purposes.
If money is allocated for the first child from the federal budget, then money for payments for the second child is taken from maternity capital. Families have to choose: reduce the amount of maternity capital and receive benefits, or refuse benefits and spend maternity capital for other purposes.
What payments are due to a family with children of a different age
There are many child allowances and payments, there are even more conditions for receiving them - it is easy to get confused in all this. Our test will help you figure it out:
What a woman will receive for a child under three years old
- Pregnancy and childbirth allowance if she works under an employment contract or quit due to the liquidation of the organization or the termination of the individual entrepreneur. And also if he independently pays contributions to the FSS as an individual entrepreneur.
- Monthly allowance for caring for a child up to one and a half years.