How much money does a foster parent receive per child
How much do foster parents get paid in California – Knotts Family Agency
Although parenting is a full-time job, you cannot think of foster parenting as a way to cash out. If you’re in it for the money, then you’re fostering for the wrong reasons. Foster families don’t actually get “paid” for taking care of a child. They receive reimbursements for the money they spend taking care of the child’s needs. This money is not meant to be used to buy a new car or pay for your rent or some other expenses that don’t have anything to do with the immediate essential needs of the foster child. Bear in mind that irrespective of the subsidy or financial assistance you receive, you will still be responsible for providing the essential items needed to adequately care for the child and the financial cost of that will be borne by you. If you’re planning on being approved and serving as a foster parent in California, you’ll probably still want to know how much reimbursement you can expect to receive to help offset some of the costs of raising your foster child. In this article, we answer some of the most common questions prospective foster parents have about much they can expect to get paid, how the amount is determined, and other incentives they might be given to help take some of the weight of raising a foster child off their shoulders.
- How much do foster parents get paid monthly per child: Depending on the county where you’re licensed as a foster parent, the reimbursement package ranges from $25 to $30 per day for each child. This amount increases if you’re fostering a child with additional needs.
- When do the payments start coming in: It usually takes a few weeks for the first payment to arrive, but that depends on the day the child was placed in your home. If you are with a Foster Family Agency (FFA), the counties generally send checks to the FFA around the initial 15 days of the month, so it could be that you have to wait a few weeks. Once the first payment arrives, you can expect to get a paycheck once every month to cover the essential needs of the child(ren) in your home.

- Take advantage of the cost-saving opportunities available to you: We know that bringing up a child today is an expensive affair. The state tries to soften the impact on your finances even further by giving valuable tax breaks to foster parents. There are also programs offering free stuff like clothing for foster children.
To qualify as a foster parent, you must have a stable and verifiable source of income which you can use to meet your family’s basic needs—food, shelter, and clothing. The reimbursements you get cannot be used as a primary source of income to cater to your family’s financial needs.
1. How much do foster parents get paid monthly per child?
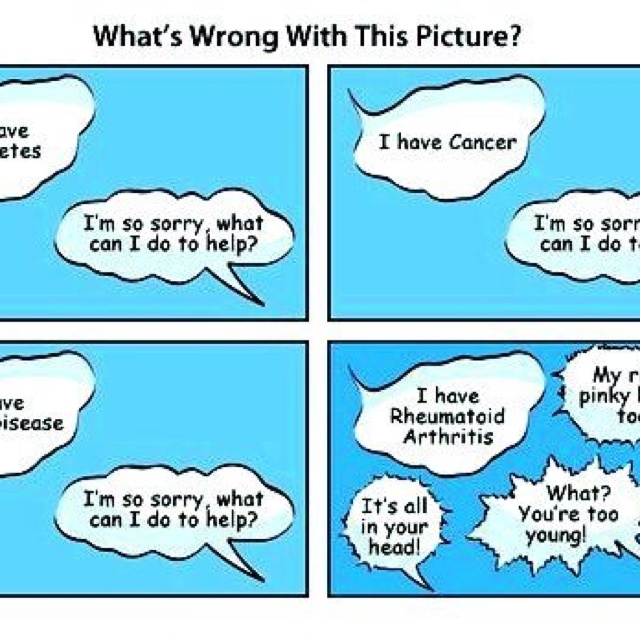
The state of California pays foster parents an average of $1000 to $2,609 per month to help with the expenses from taking care of the child. It is one of the highest-paying states in the nation in this regard. This figure is for each child you take into your home. The highest rates correspond to children with additional needs, because they will require more attention, time, and tending to than other children. Know that you can’t just pocket the payments and take the child to the hospital or to visit other professionals that help with taking care of them. You need to be patient with children, shower them with more attention, listen and learn their needs, and basically find ways to care for them that wouldn’t complicate their situation even further. Children may have been severely neglected, suffered physical/sexual/emotional abuse, and may be carrying around complex emotional issues as a result of what they’ve been through. They may also have some condition—depression, anxiety, autism, or physical disablement—that prevents them from acting appropriately for their age or being able to respond normally to certain situations. Whatever their challenge is, you need to be understanding. Remember that you’re dealing with a person’s life. The child entrusted to your care will come to depend on you for so much, and you cannot afford to do wrong by them.
The highest rates correspond to children with additional needs, because they will require more attention, time, and tending to than other children. Know that you can’t just pocket the payments and take the child to the hospital or to visit other professionals that help with taking care of them. You need to be patient with children, shower them with more attention, listen and learn their needs, and basically find ways to care for them that wouldn’t complicate their situation even further. Children may have been severely neglected, suffered physical/sexual/emotional abuse, and may be carrying around complex emotional issues as a result of what they’ve been through. They may also have some condition—depression, anxiety, autism, or physical disablement—that prevents them from acting appropriately for their age or being able to respond normally to certain situations. Whatever their challenge is, you need to be understanding. Remember that you’re dealing with a person’s life. The child entrusted to your care will come to depend on you for so much, and you cannot afford to do wrong by them. It is also important to identify a foster family agency that is committed to providing you with the ongoing support needed. This will go a long way in ensuring that you are successful as a foster parent. You need to constantly examine yourself, be open to learning new skills and training that will allow you to communicate better with your foster child, and be an incredible parent to them. Raising a child is a lot to undertake, but it’s one of the most fulfilling things you can do. Even if you decide to adopt your foster child, you’ll still be entitled to receive a small monthly payment to assist with the child’s upkeep. The amount of money you’ll receive will depend on the child’s age and personal needs. The amount you receive in reimbursement depends on the county you reside in or the foster family. In California, the state prescribes a minimum monthly payment, but agencies may provide higher than the minimum. Talk to a foster family agency to learn more about what your foster care reimbursement payments may be.
It is also important to identify a foster family agency that is committed to providing you with the ongoing support needed. This will go a long way in ensuring that you are successful as a foster parent. You need to constantly examine yourself, be open to learning new skills and training that will allow you to communicate better with your foster child, and be an incredible parent to them. Raising a child is a lot to undertake, but it’s one of the most fulfilling things you can do. Even if you decide to adopt your foster child, you’ll still be entitled to receive a small monthly payment to assist with the child’s upkeep. The amount of money you’ll receive will depend on the child’s age and personal needs. The amount you receive in reimbursement depends on the county you reside in or the foster family. In California, the state prescribes a minimum monthly payment, but agencies may provide higher than the minimum. Talk to a foster family agency to learn more about what your foster care reimbursement payments may be. Hopefully, this payment will help make foster care a little less stressful for you and your family.
Hopefully, this payment will help make foster care a little less stressful for you and your family.
2. When do the payments start coming in?
Every county or Foster Family Agency has its own timeline for payments, which you’ll be informed of after your application is approved and you’re given the clearance to start fostering. You will need to have some funds available while you wait at least one month before the payments are sent to you. Some counties are better at expediting payment than others, so the time for the first check to arrive may vary. Make sure you have money saved up to cover the childcare costs until the subsidy payments start coming in. In some cases, the county social worker may approve a one-time extra allowance for purchasing clothes for your foster child, but that also takes a while to arrive. So, be prepared to go shopping for clothes for your new ward out of your own pocket. But no need to go overboard with shopping. Like we mentioned earlier, this payment is not meant to cover all of the child’s expenses, only the basic needs. This includes:
Like we mentioned earlier, this payment is not meant to cover all of the child’s expenses, only the basic needs. This includes:
- Transportation
- Food
- Clothing
- Personal expenses
You won’t have to worry about medical bills because every foster child is covered under the state’s health insurance. Behavioral or mental health needs are also included under their insurance coverage.
3. Take advantage of the cost-saving opportunities available to you
The reimbursement payment you get is not the only financial aid that you can receive as a foster parent. There are a number of other options you can explore as well to help you cut costs such as a tax credit. Although foster children do not qualify for many of the same deductions and credits as biological or adopted children, they’re still eligible for a couple of tax breaks. For starters, the reimbursements you receive from the state are non-taxable so you don’t have to worry about it being cut down any further.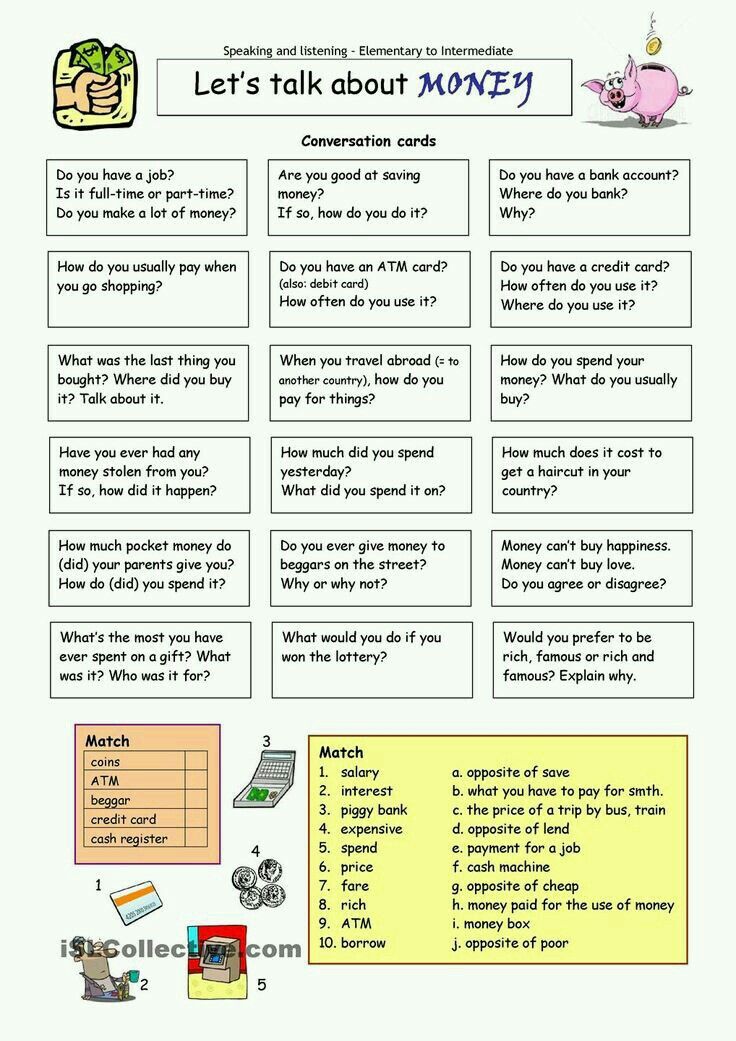 Check to see whether your county also provides childcare coverage so you can work while being a foster parent without having to carry the entire cost of childcare alone. This can help you save money that would have been spent on babysitting and other related expenses. There are programs that provide free clothing and gifts for foster children. Signing up for them is another great way to cut down on the costs of foster parenting. Additionally, if your foster child is an infant, toddler, or under the age of 5, they are probably eligible for the Women, Infants, and Children (WIC) special supplemental nutrition program, which is aimed at providing nutritious foods to supplement diets for women and children at nutritional risk. Don’t be ashamed about needing a little extra help to care for the foster child in your care. You’re doing the best that you can to see that they have a good life and that’s all that matters.
Check to see whether your county also provides childcare coverage so you can work while being a foster parent without having to carry the entire cost of childcare alone. This can help you save money that would have been spent on babysitting and other related expenses. There are programs that provide free clothing and gifts for foster children. Signing up for them is another great way to cut down on the costs of foster parenting. Additionally, if your foster child is an infant, toddler, or under the age of 5, they are probably eligible for the Women, Infants, and Children (WIC) special supplemental nutrition program, which is aimed at providing nutritious foods to supplement diets for women and children at nutritional risk. Don’t be ashamed about needing a little extra help to care for the foster child in your care. You’re doing the best that you can to see that they have a good life and that’s all that matters.
Conclusion
When you take into account the responsibilities that come with being a foster parent, the stipend, it becomes evident that the money received should not be the primary reason for deciding to be a foster parent. Just remember that financial gain is not an incentive to foster. You shouldn’t consider the reimbursement you receive as payment for doing your job because you’re not being paid for providing a service. The payment is to help cover the costs of caring for the child in your home. Your true reward is in being able to help a vulnerable child feel safe, supported, and loved. If after looking at the numbers above and understanding what exactly you’ll be signing up for and you’re still interested in becoming a foster parent in California, all you need to do is contact a reputable foster family agency and get started on your application.
Just remember that financial gain is not an incentive to foster. You shouldn’t consider the reimbursement you receive as payment for doing your job because you’re not being paid for providing a service. The payment is to help cover the costs of caring for the child in your home. Your true reward is in being able to help a vulnerable child feel safe, supported, and loved. If after looking at the numbers above and understanding what exactly you’ll be signing up for and you’re still interested in becoming a foster parent in California, all you need to do is contact a reputable foster family agency and get started on your application.
How Much Money Do You Get For Being a Foster Parent – Knotts Family Agency
If you are considering becoming a foster parent (also known as Resource Parent) or host-guardian, at some point you’re going to wonder how much foster parents get paid in California. That’s a perfectly fair question.
In theory, a resource or foster family can earn as much more than $9,000 per month, prorated per night.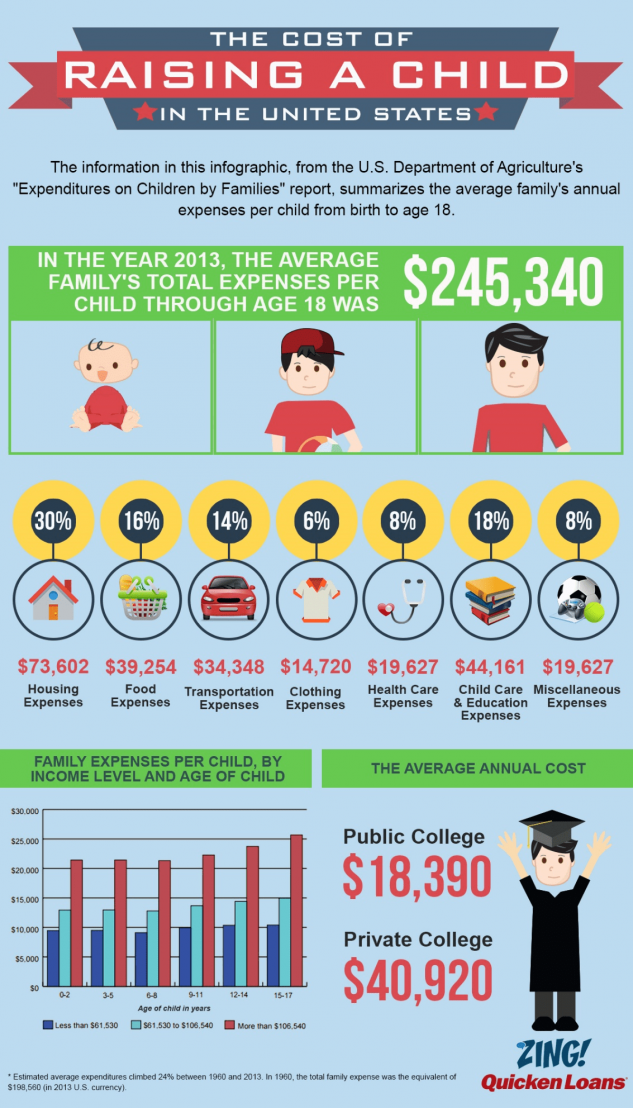 But it’s all based on variables like the number of kids you’re fostering, their ages and any special needs they may have. So what’s the actual payment range?
But it’s all based on variables like the number of kids you’re fostering, their ages and any special needs they may have. So what’s the actual payment range?
In the state of California, foster parents currently (2020) may receive between $1000 to $2609 each month per child, depending on the Level of Care. You may have up to 6 children in one home, depending on their needs; but it is more reasonable to have less than 6. A foster family agency may opt to give foster parents more than the minimum, so you should check with your agency.
How Foster Parent Payments Work:
Technically, foster parents get reimbursed, not paid. But for the sake of simplicity, lets call it a payment that comes completely tax free.
As a foster parent or host-guardian you take on the responsibility of ensuring the kids are safe, well fed and clothed. You’ll need to provide everything a child needs to grow healthy in a safe environment. So, regardless of whether you are fostering on a temporary or a long-term basis, there are legitimate costs involved in supporting the child or children you’re helping.
That’s what makes the money reimbursement programs such an important part of foster care programs.
Here are some of the factors that impact the payment scale:
- The medical and emotional needs of the child
- The state you live in (but we’re only focusing on California in this article)
- Any bonuses offered by your chosen foster care agency
In general, the pay scale increases depending on the specific health or emotional needs of the children. For example, foster parents in Intensive Service Foster Care (ISFC), and care for a child with significant mental or health needs, may receive up to $2,609 per month.
Figuring Out How Much YOU Will Get Paid
It should go without saying, but I’m going to say it anyways: don’t become a foster parent just for the money. Fostering children should be about providing a safe, nurturing for the kids while emotionally enhancing your own life as well.
That being said, we know the money matters. That’s the way the world works and you need money to create the best possible environment for the kids.
That’s the way the world works and you need money to create the best possible environment for the kids.
So the question is, how much will YOU get paid?
It’s nice to know the general numbers. But your situation is different from everyone else’s. Here are some things to consider:
- You have a certain amount of space in your home.
- You may be interested in foster kids within a certain age group.
- You may or may not be able to help children who have special medical or emotional needs. You may be interested in children with serious health needs (e.g. medically-fragile children).
- If you’re working with Knotts Family Agency, we pay a monthly compensation bonus that is over and beyond the minimum rate established by the state. But you may be working with an agency that doesn’t. Contact us to learn more about our benefits.
- You may want to be a host-guardian (part-time foster parenting) instead of being a full-time foster parent
Because your situation is unique, you’re going to need help navigating the process and figuring out the best possible outcome for yourself and your family.
That’s where we come in. Knotts Family Agency has offered friendly, no-rush, no-obligation coaching to foster parents for nearly two decades. Although money is not the only factor, when selecting an agency, consider one that is willing to provide higher than the minimum.
For example, although the state of California currently has a rate of approximately $2,600 per month for children in LOC 5 (also known as Intensive Service Foster Care), Knotts Family Agency adds up to $400, bringing the total to $3000, for children in certain IFSC sub-categories.
Give us a call today at 909-301-0504 or click here to Contact Us.
We’d be happy to answer any questions you have – and walk you step by step through the process of becoming a foster parent.
One-time allowance for the transfer of a child to a family (at the expense of the budget of St. Petersburg)
Applicants have the right to a pre-trial (out-of-court) appeal against decisions and actions (inaction) taken (carried out) by the Administration, officials of the Administration, civil servants of the Administration in the course of providing public services. The pre-trial (out-of-court) appeal procedure does not exclude the possibility of appealing against decisions and actions (inaction) taken (carried out) in the course of providing public services in court. The pre-trial (out-of-court) appeal procedure is not mandatory for the applicant. nine0003
The pre-trial (out-of-court) appeal procedure does not exclude the possibility of appealing against decisions and actions (inaction) taken (carried out) in the course of providing public services in court. The pre-trial (out-of-court) appeal procedure is not mandatory for the applicant. nine0003
The procedure for pre-trial (out-of-court) appeal against decisions and actions (inaction) of the executive body providing the public service, officials of the executive body providing the public service is determined by Federal Law No. 210-FZ.
Information on the procedure for filing and considering a complaint is provided to applicants by posting information on the page of the Administration and the Committee for Social Policy of St. Petersburg on the official website of the Administration of St. Petersburg, on the portal, as well as using telephone means, in writing, by e-mail, upon personal appointment. nine0003
The applicant may file a complaint in the following cases:
- violation of the deadline for registering a request for the provision of a public service;
- violation of the term for the provision of public services;
- requiring the applicant to provide documents or information or perform actions, the submission or implementation of which is not provided for by the regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation, regulatory legal acts of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation for the provision of public services; nine0012
- refusal to accept documents, the provision of which is provided for by the regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation, the regulatory legal acts of St.
 Petersburg for the provision of public services, from the applicant;
Petersburg for the provision of public services, from the applicant; - refusal to provide a public service, if the grounds for refusal are not provided for by federal laws and other regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation adopted in accordance with them, regulatory legal acts of St. Petersburg; nine0012
- requirement from the applicant when providing a public service of a fee not provided for by the regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation, the regulatory legal acts of St. Petersburg;
- refusal of the Administration, an official of the Administration, a civil servant of the Administration to correct typographical errors and errors in documents issued as a result of the provision of a public service, or violation of the deadline for such corrections; nine0012
- violation of the term or procedure for issuing documents based on the results of the provision of public services;
- suspension of the provision of a public service, if the grounds for suspension are not provided for by federal laws and other regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation adopted in accordance with them, laws and other regulatory legal acts of St.
 Petersburg;
Petersburg; - requirement from the applicant when providing the public service of documents or information, the absence and (or) unreliability of which was not indicated upon the initial refusal to accept the documents necessary for the provision of the public service, or in the provision of the public service, except for the cases provided for in clause 4 of part 1 of the article 7 of Federal Law No. 210-FZ. nine0012
If the complaint is filed through a representative, a document confirming the authority to act on behalf of the complainant is also submitted. As a document confirming the authority to act on behalf of the applicant, the following can be submitted:
- power of attorney issued in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation (for individuals).
Subject of complaint nine0003
The complaint must contain:
- name of the Administration, position and surname, first name, patronymic (last name, if any) of an official or civil servant of the Administration whose decisions and actions (inaction) are being appealed;
- last name, first name, patronymic (the last one - if available), information about the place of residence of the applicant-individual, as well as the contact phone number (numbers), email address (s) (if any) and the postal address to which the application should be sent response to the applicant; nine0012
- information about the appealed decisions and actions (inaction) of the Administration, an official of the Administration or a civil servant of the Administration, including in the case of filing a complaint with the MFC or through the portal-type of violation specified in paragraph 5.
 1.1 of the administrative regulation;
1.1 of the administrative regulation; - arguments on the basis of which the applicant does not agree with the decision and action (inaction) of the Administration, an official of the Administration or a civil servant of the Administration. The applicant may submit documents (if any) confirming the applicant's arguments, or copies thereof. nine0012
Executive bodies and officials authorized to consider a complaint, to whom a complaint can be sent in a pre-trial (out-of-court) procedure
The complaint is submitted to the Administration providing the public service.
A complaint against decisions and actions (inaction) of the head of the Administration may also be filed with the Vice-Governor of St. Petersburg, who directly coordinates and controls the activities of the Administration, or, in his absence, with the head of the Administration. nine0003
Methods for filing and handling a complaint
A complaint may be filed:
- in electronic form;
- in writing on paper.
Submission of a complaint on paper is carried out:
- by mail;
- through the MFC;
- at the personal reception of the applicant at the Administration (at the place of provision of the public service, i.e. at the place where the applicant applied for a public service, the violation of the procedure for the provision of which is being appealed, or at the place where the applicant received the result of the specified public service). nine0012
At a personal reception, the applicant presents a document proving his identity in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation.
The documents specified in paragraph 5.1.2 of the Administrative Regulations may be submitted in electronic form, while the identity document of the applicant is not required.
An electronic complaint is filed through the official website of the Administration of St. Petersburg (domain name of the site on the Internet - gov. spb.ru) in the section of the Administration, portal (domain name of the site on the Internet - gu.spb.ru) . nine0003
spb.ru) in the section of the Administration, portal (domain name of the site on the Internet - gu.spb.ru) . nine0003
Filling out an application for consideration of a complaint through the portal is carried out by the applicant personally, subject to the authorization of the applicant on the portal through the ESIA.
Complaint Procedure
A complaint against decisions and actions (inaction) of the Administration, its officials and civil servants is considered by the Administration.
A complaint against decisions and actions (inaction) of the head of the Administration is considered by a higher authority. nine0003
The MFC, in case of filing a complaint through the MFC, ensures the transfer of the complaint to the Administration in the manner and terms established by the agreement on interaction between the MFC and the Administration, but no later than the next working day from the date of receipt of the complaint.
If the complaint is filed by the applicant with a body whose competence does not include making a decision on the complaint, within three working days from the date of its registration, the said body sends the complaint to the body authorized to consider it and informs the complainant in writing about the redirection of the complaint. In this case, the period for considering a complaint is calculated from the date of registration of the complaint with the body authorized to consider it. nine0003
In this case, the period for considering a complaint is calculated from the date of registration of the complaint with the body authorized to consider it. nine0003
If a different procedure (procedure) for filing and considering complaints is established by federal law in respect of a complaint received, the provisions of this section shall not apply, and the applicant shall be notified that his complaint will be considered in the manner and within the time limits stipulated by federal law.
The administration has the right to leave the complaint unanswered in the following cases:
- presence in the complaint of obscene or offensive language, threats to life, health and property of an official, as well as members of his family; nine0012
- the inability to read any part of the text of the complaint, the last name, first name, patronymic (if any) and (or) the postal address of the applicant indicated in the complaint.
If the complaint is left unanswered, the Administration, within three working days from the date of registration of the complaint, informs the citizen who filed the complaint about this, if his name and postal address are legible.
Deadlines for considering a complaint
The term for considering a complaint is calculated from the date of registration of the complaint with the Administration. nine0003
A complaint received by the Administration is subject to registration no later than the next working day from the date of its receipt. The complaint is subject to consideration by an official, an employee empowered to consider complaints, within fifteen working days from the date of its registration, unless shorter periods for considering a complaint are established by the Administration.
In the event of an appeal against the refusal of the Administration to accept documents from the applicant or to correct typographical errors and (or) errors, or in case of an appeal against a violation of the deadline for such corrections, the complaint is considered within five working days from the date of its registration. nine0003
Result of consideration of the complaint
Based on the results of consideration of the complaint, the Administration takes one of the following decisions:
- the complaint is satisfied, including in the form of cancellation of the decision, correction of misprints and errors in documents issued as a result of the provision of public services, return to the applicant of funds, the collection of which is not provided for by the regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation, regulatory legal acts of St.
 Petersburg ; nine0012
Petersburg ; nine0012 - refuses to satisfy the complaint.
This decision is taken in the form of an act of the Administration.
Based on the results of the audit, if there are no arguments in the complaint confirming the existence of the type of violation of the procedure for the provision of services indicated by the applicant, the official responsible for considering the complaint makes a decision to refuse to consider the complaint on the merits due to the inconsistency of the information contained in the complaint with the indicated type of violation. nine0003
The administration refuses to satisfy the complaint in the following cases:
- the presence of a court decision that has entered into legal force, an arbitration court on a complaint about the same subject and on the same grounds;
- filing a complaint by a person whose powers have not been confirmed in the manner prescribed by the legislation of the Russian Federation;
- the presence of a decision on the complaint, taken earlier in accordance with the requirements of the administrative regulations in relation to the same applicant and on the same subject of the complaint.
 nine0012
nine0012
If, during or as a result of the consideration of a complaint, signs of an administrative offense or crime are established, the official, employee empowered to consider complaints in accordance with paragraph 5.3 of the administrative regulation, immediately send the available materials to the prosecutor's office.
Procedure for informing the applicant about the results of the consideration of the complaint
Upon satisfaction of the complaint, the Administration takes comprehensive measures to eliminate the identified violations, including the issuance of the result of the public service to the applicant, no later than five working days from the date of the decision, unless otherwise provided by the legislation of the Russian Federation. nine0003
Not later than the day following the day of the decision, the applicant in writing and at the request of the applicant in electronic form shall be sent a reasoned response on the results of the consideration of the complaint.
In response to the results of the consideration of the complaint, the following shall be indicated:
- name of the Administration, position, surname, name, patronymic (if any) of its official who made the decision on the complaint;
- number, date, place of the decision, including information about the official, employee whose decision or action (inaction) is being appealed; nine0012
- surname, name, patronymic (if any) or name of the applicant;
- grounds for making a decision on the complaint;
- decision made on the complaint;
- if the complaint is found to be justified - the terms for eliminating the identified violations, including the term for providing the result of the public service;
- if the complaint is found unfounded - reasoned explanations about the reasons for the decision, as well as information on the procedure for appealing the decision. nine0012
Also, in the response on the results of the consideration of the complaint, they apologize for the inconvenience caused and indicate information on further actions that the applicant needs to take in order to receive the public service.
The response based on the results of the consideration of the complaint is signed by an official of the Administration authorized to consider the complaint, endowed with the authority to consider complaints.
At the request of the applicant, a response based on the results of consideration of the complaint may be submitted no later than the day following the day the decision was made, in the form of an electronic document signed by an electronic signature of an official of the Administration authorized to consider the complaint, the form of which is established by the legislation of the Russian Federation. nine0003
Procedure for appealing a decision on a complaint
The decision made as a result of consideration of the complaint may be appealed to the Vice-Governor of St. Petersburg, who directly coordinates and controls the activities of the Administrations (Smolny proezd, 1, letter B, St. Petersburg, 191060, tel. (812) 576-62- 62, adm@gov. spb.ru), to the Government of St. Petersburg, as well as to the court in the manner and within the time limits stipulated by the current legislation. nine0003
spb.ru), to the Government of St. Petersburg, as well as to the court in the manner and within the time limits stipulated by the current legislation. nine0003
The applicant has the right to receive information and documents necessary to substantiate and consider the complaint.
Informing applicants about the procedure for filing and considering a complaint is carried out by posting information on the portal.
Informing applicants about the procedure for appealing decisions and actions (inaction) is also carried out when the applicant contacts by phone, e-mail addresses, as well as in person at the addresses indicated on the official website of the Administration and on the portal. nine0003
The provisions of this section, which establish the procedure for filing and considering complaints of applicants about violations of their rights in the provision of public services, do not apply to relations regulated by the Federal Law "On the Procedure for Considering Appeals from Citizens of the Russian Federation" (Law No. 59-FZ).
59-FZ).
Complaints of applicants about the organization of the provision of public services in the Administration are submitted and considered in the manner prescribed by Law No. 59-FZ. nine0003 90,000 for adoptive parents - municipality
Former Forms
Adoption:
· adoption is approved by the court decision at the place of residence
· In its legal position, the adopted child is equated to the owned. The legislation of the Russian Federation prohibits the restoration of parental rights or the withdrawal of consent to adoption in relation to an adopted child
An adoptive parent can give the child his last name, change his patronymic, date of birth (up to a year), place of birth, information about parents
Secrecy of adoption protected by law
In addition to the one-time federal payment when placing a child in foster care, adoptive parents are entitled to public forms of social support for families (postnatal leave, maternity capital, etc. )
)
Guardianship and guardianship authority at the place of residence of the adoptive parents exercises control over the living conditions of the child for 3 years after the adoption, but always with the observance of the secrecy of the adoption. nine0003
CUSTODY:
Guardianship is established by decision of the Custody and Guardianship Authority at the location of the child and terminates upon reaching the age of 18
The guardian has practically all the rights of parents in matters of upbringing, education, maintenance of the ward and is fully responsible for him, however, the guardian is not entitled to give the child his last name, change the first name, patronymic, date and place of birth
The guardian receives monthly payments for the maintenance of the child, guardianship duties. The guardian performs his duties free of charge. However, the body of guardianship and guardianship may conclude an agreement with the guardian on paid guardianship (foster family)
· If necessary, a child under 18 years of age is provided with housing
· The guardianship and guardianship authority controls the maintenance, upbringing and education of the ward throughout the entire period of guardianship (guardianship). Every year, the guardian is obliged to submit a report on the funds spent to the guardianship and guardianship authority
Every year, the guardian is obliged to submit a report on the funds spent to the guardianship and guardianship authority
Biological parents have the right to visit the child. Upon restoration of parental rights, the child may be returned to the parents. nine0003
FOSTER FAMILY:
· } This agreement is concluded between the body of guardianship and foster parents for a certain period, but in any case, it is valid until the child reaches the age of majority reach 8 people
· In a foster family, one or both parents are empowered as guardians and receive payments for his maintenance and remuneration for performing parental functions ward. Every year, the adoptive parent is required to submit a report on the funds spent to the guardianship and guardianship authority
The biological parents have the right to visit the child. Upon restoration of parental rights, the child may be returned to the parents.
Requirements for adoptive parents
According to the Family Code, adoptive parents may be adults of both sexes, with the exception of:
- recognized by the court as incompetent or disclosure by invalid invoices;
- persons deprived of parental rights by court or limited by court in parental rights; nine0012 90,011 persons suspended from the duties of a guardian (custodian) for improper performance of the duties assigned to him by law;
- former adoptive parents, if the adoption is canceled by the court due to their fault;
- persons who, for health reasons, cannot exercise parental rights; 90,011 persons who, at the time of the establishment of adoption, do not have an income that provides the adopted child with the subsistence minimum established in the constituent entity of the Russian Federation in whose territory the adoptive parents live; nine0012
- persons without a permanent place of residence;
- persons who have or had a criminal record, who are or have been prosecuted for crimes against life and health, freedom, honor and dignity, sexual inviolability and sexual freedom of the individual, against the family and minors, public health and public morality, as well as against public security, as well as persons who have an unexpunged or outstanding conviction for grave or especially grave crimes.
 nine0012
nine0012 - Unmarried persons may not jointly adopt the same child.
- persons who, for health reasons, cannot exercise parental responsibilities. 90,011 persons who have not completed training under a program that meets the requirements of the Ministry of Education of the Russian Federation.
REQUIREMENTS FOR GUARDIAN CANDIDATES, FOSTER PARENTS
Guardians (custodians), adoptive parents can be:
- adults (spouses, as well as individual citizens)
EXCEPT:
- persons recognized as legally incompetent or partially incapacitated by the court,
- spouses, one of whom is recognized by the court as incapacitated or partially incompetent,
- persons deprived of parental rights or limited in 903
- former adoptive parents, if the adoption is canceled by the court due to their fault,
- persons removed from the duties of a guardian for improper performance of duties,
- persons who, for health reasons, cannot perform parental duties,
- persons without a permanent place of residence,
- persons who have or had a criminal record, subjected to criminal prosecution for crimes against life and health, freedom, honor and dignity, sexual integrity and sexual freedom of the individual, against the family and minors, public health and public morality, as well as against public safety, as well as persons who have an unexpunged or outstanding conviction for serious or especially serious crimes. nine0003
nine0003
- persons who have not completed training under a program that meets the requirements of the Ministry of Education of the Russian Federation
To obtain an opinion, candidates for adoptive parents, guardians (trustees), adoptive parents submit documents to the guardianship and guardianship authority at the place of residence:
§ brief autobiography
§ copy of marriage certificate
§ copy of personal financial account and extract from the house (apartment) register from the place of residence or certificate of ownership of the dwelling (valid for 1 year)
§ a certificate from the place of work indicating the position and salary for 12 months or another document on income, including a certificate of income, including a certificate of income of the spouse (valid for 1 year)
§ certificate from the Department of Internal Affairs of the absence of a criminal record for an intentional crime against the life and health of citizens (valid for 1 year)
§ medical certificate (valid for 1 year)
§ certificate of completion of the school of the adoptive parent
§ written consent of adults family members, taking into account the opinion of children who have reached the age of 10, who lived with the candidate (for guardians (custodians), foster parents)
For candidates for adoptive parents:
The body of guardianship and guardianship within 7 calendar days after the submission of all documents is obliged to examine the living conditions of the candidate and no later than 5 working days after the examination issue CONCLUSION.
For candidates for guardians and adoptive parents:
Guardianship and guardianship authority within within 7 calendar days after submitting all housing and living conditions is required0205 within 3 days to draw up an examination report, after 15 days from the date of submission of documents to prepare a conclusion and within 3 days after signing to issue it to the candidate.
CONCLUSION IS VALID FOR TWO YEARS.
The status of a child on a family device
adoption (trushy) is subject0211
- died,
- unknown (found or abandoned), left in the maternity hospital,
- recognized by the court as missing or dead,
- deprived of parental rights (adoption is possible no earlier than 6 months after the entry into force of the court decision on deprivation of parental rights)
- gave consent to adoption
0002 - death of parents
- deprivation of parental rights or restriction of parental rights
- recognition of parents as incapacitated
- recognition of parents as missing, dead
- illness of parents (under guardianship)
- prolonged absence of parents - avoidance of parents from education
- when parents create conditions that endanger the life and health of the child
- whose parents are serving a sentence or are under investigation
A FOSTER FAMILY can accept a child left without parental care:
- death of parents
- deprivation of parental rights or restriction of parental rights
- recognition of parents as incapacitated
- recognition of parents as missing from 9003 parental illness.
OBTAINING INFORMATION ABOUT ORPHANS.
To obtain information about orphans and children left without parental care, a candidate for adoptive parents, guardians (trustees), foster parents must contact the guardianship and guardianship authority at the location of the child institution or the regional operator of the regional data bank of orphans and children left without parental care. A candidate for adoptive parents, guardians (custodians), adoptive parents personally comes to the guardianship and guardianship authority or to the regional operator and presents
1 .
3. Application form (issued by the guardianship and guardianship authority).
Specialist of the guardianship and guardianship authority, operator of the data bank is obliged to provide questionnaires for all children that meet the wishes of the candidates.
A candidate for adoptive parents, guardians, adoptive parents is issued a referral to visit the child.