How much is nys child support
NYS DCSS | Custodial Parent Information
To access your account information, please enable JavaScript in your browser. Follow these instructions to enable JavaScript.
You can receive your payment information by phone at 1-888-208-4485 (TTY: 1-866-875-9975), Monday–Friday, 8:00 AM–7:00 PM.
Custodial parents are often the first to need information about child support services.
The following links provide the information most often requested by custodial parents.
- What is child support?
- What is the Child Support Program?
- Who can apply for child support services?
- What services does the Child Support Program provide?
- Is there any charge for child support services?
- How is the amount of support decided?
- What information is needed to open a case?
- What if the custodial parent moves?
- How do I contact my local child support office?
The following videos are available on YouTube:
-
What You Need to Know about Child Support Hearings and Services, 20 minutes
Explains what you should bring with you to a child support hearing, what to expect during the hearing, and what to do after you receive a child support order -
Acknowledgment
of Parentage in New York, 11 minutes
Explains when parentage needs to be acknowledged, what signing a voluntary Acknowledgment of Parentage form means, and who should (or should not) sign this form -
Reconocimiento de paternidad en Nueva York, 11 minutos
Este video informa a los padres de los beneficios de establecer la paternidad y proporciona información sobre los derechos y las consecuencias vinculadas a la firma de un AOP -
Completing the Acknowledgment of Parentage Form, 9 minutes
Explains how to complete and file a voluntary Acknowledgment of Parentage form -
Completar el formulario de reconocimiento de paternidad (AOP), 9.
5 minutos
- What is child support?
-
Child support is financial support provided by the noncustodial parent. Child support includes
- Cash payments (based on the parent's income and the needs of the child)
- Health insurance for the child (medical support)
- Payments for child care, and
- Payments for reasonable health care costs that are not covered by health insurance.
Family Court officials (Support Magistrates)determine the amount of child support the noncustodial parent will pay (see how much, below). Under New York State law, parents are responsible for supporting their child until the child is 21 years old.
top of page
- What is the Child Support Program?
-
Every state in the United States has a child support program, and many foreign countries have one also.
 The Child Support Program began in 1975, when Congress passed Title IV-D of the Social
Security Act. Title IV-D required every state to
The Child Support Program began in 1975, when Congress passed Title IV-D of the Social
Security Act. Title IV-D required every state to
- Establish and maintain statewide child support enforcement laws
- Provide procedures to establish legal parentage and to obtain court orders for child support
- Collect and distribute child support payments, and
- Enforce child support orders when payments are not made.
In New York State, child support services are provided by Child Support Enforcement Units (CSEU) and Support Collection Units (SCU) in every county and in New York City.
top of page
- Who can apply for child support services?
-
Any parent, guardian, caretaker of a child, or child who needs support can apply for child support services.

Please note that anyone who applies for temporary or safety net assistance automatically receives child support services.
top of page
- What services does the Child Support Program provide?
-
The Child Support Program offers the following services:
- Locating Non-Custodial Parents
The Child Support Program can use federal, state, and local resources and information to help locate the noncustodial parent. - Establishment of Parentage
Establishing parentage is the process of determining the legal parents of a child. Being the legal parent means that the parent has parental rights and responsibilities to the child, such as the right to seek custody or visitation and the responsibility for the child's care and support, including financial and medical support. See the
Establishment of Parentage page for
detailed information about becoming a legal parent.
See the
Establishment of Parentage page for
detailed information about becoming a legal parent.
- Support Establishment
The Child Support Program can help a custodial parent file a petition in Family Court for an order of support. - Support Collection
A child support order directs the noncustodial parent to pay child support to the Support Collection Unit (SCU). The SCU collects, tracks, and disburses payments to the custodial parent. However, if the custodial parent is receiving temporary or safety net assistance, all but the first $200 of current child support payments is sent to the Department of Social Services as reimbursement for the assistance. - Support
Enforcement—Administrative
Federal and New York State laws require the local CSE unit to enforce a child support order when the noncustodial parent does not pay. Administrative procedures are actions
the CSE unit can take without going to
court.
Administrative procedures are actions
the CSE unit can take without going to
court.
The SCU will enforce a child support order automatically through payroll deductions. The SCU can also collect unpaid support by taking State and federal income tax refunds and lottery winnings; seizing assets—including bank accounts; suspending driver's licenses; suspending or denying passports; and notifying credit reporting agencies of overdue child support payments (arrears). The SCU can also refer the case for collection to the New York State Department of Taxation and Finance.
- Support Enforcement—Court
When administrative enforcement is not successful, the SCU will assist in filing an enforcement petition with the family court. The court can order money judgments for the arrears; order the
noncustodial parent into a work program; order that a hearing
take place to suspend state-issued business, professional, or occupational
licenses; or issue probation or jail sentences.
The court can order money judgments for the arrears; order the
noncustodial parent into a work program; order that a hearing
take place to suspend state-issued business, professional, or occupational
licenses; or issue probation or jail sentences.
- Medical Support Establishment and
Enforcement
Child support services also include obtaining and enforcing court-ordered health insurance for children. If an existing order does not include health insurance coverage, the Child Support Program will help file a petition with family court to get health insurance included in the support order. - Review and Adjustment of Child Support
Amounts
The amount that is owed for child support may be changed over time based on a cost of living adjustment.Every two years the Child Support Program automatically reviews each child support order to determine whether the amount to be paid should be increased due to cost of living increases.
 Cost of living adjustments can be made without going to court.
Cost of living adjustments can be made without going to court.
For non-temporary assistance or non-safety net assistance cases, a notice is sent to both parents when a case is eligible for a cost of living adjustment, and either parent may request the adjustment. When the custodial parent or child is receiving temporary or safety net assistance, the cost of living adjustment is automatically made when the case becomes eligible—without either parent requesting the adjustment.
- Modification of Child Support Orders
If either the custodial or noncustodial parent's circumstances change significantly (such as loss of job, change in custody of a child, etc.), the Child Support Program can help the parent file a petition in family court to request a modification (change) to the existing child support order.
top of page
- Locating Non-Custodial Parents
- Is there any charge for child support services?
-
The annual service fee is now $35 and will be applied after more than $550 of support is collected and paid to the family.
Custodial parents may be charged a service fee once a year. The fee applies only when all these conditions are met.
- The custodial parent has never received assistance through the Temporary Assistance for Needy Families program (TANF).
- Child support is being paid to the family.
- More than $550 of support is collected and paid to the family during the federal fiscal year (October 1–September 30).
For more information, visit the service fee questions and answers page.
Legal services are available on request. Costs for legal services will be collected from clients who are not receiving public assistance benefits.

top of page
- How is the amount of support decided?
-
The court uses a standard guideline to calculate what the noncustodial parent will pay, based on the noncustodial parent's adjusted gross income and on the number of children involved. The court first determines the noncustodial parent's gross income, and then makes certain deductions (including Medicare, Social Security, and New York City or Yonkers tax) to establish the noncustodial parent's adjusted gross income. The court then multiplies the adjusted gross income by the standard guideline percentage for the number of children. These percentages are as follows:
- 17% for one child
- 25% for two children
- 29% for three children
- 31% for four children
- at least 35% for five or more children.
Then the noncustodial parent's share of child care, medical, and educational expenses is added to the income percentage amount. The combined amount, percentage of income plus share of expenses, is the basic child support amount.
For the combined parental income amount over $163,000, the court may consider either the standard guideline percentages and/or other factors in setting the full child support obligation.
top of page
- What information is needed to open a case?
-
When custodial parents call or visit their county child support agency, they should provide as much information about themselves, their child(ren), and the noncustodial parent as they can. The more information custodial parents can provide, the more quickly their child support agency can assist them.

Information about the noncustodial parent:
- full name and date of birth
- current or last known address and phone number
- current or last known work address and phone number
- Social Security number (look on old pay stubs, tax, military, or medical records)
- income information (tax records, pay stubs, bank and business records)
- health insurance information
Other helpful information:
- acknowledgment of paternity/parentage or order of filiation or judgment of parentage for each child
- marriage license
- divorce decree or separation agreement
- copies of child support orders
- custodial parent's income information (tax records, pay stubs, bank records)
- information about child-related expenses and the child's needs
Information about the child(ren):
- birth certificate
- Social Security number
- health insurance coverage information
- current or last known address (if different than custodial parent's)
top of page
- What if the custodial parent moves?
-
If a custodial parent moves while receiving child support services, the parent must notify their county child support office of any change in home and/or mailing address, telephone number, or personal information, such as name or Social Security number.
 Otherwise, support payments and other important
notices may be delayed or lost.
Otherwise, support payments and other important
notices may be delayed or lost.
top of page
- How do I contact my county child support office?
-
Get the address and telephone number of your county child support office. Most offices are open Monday through Friday, 9:00 AM to 4:00 PM.
Child Support Calculator NY | Calculating Child Support in NY
By Sari M. Friedman, Legal Counsel
Fathers' Rights Association – NYS & Long Island
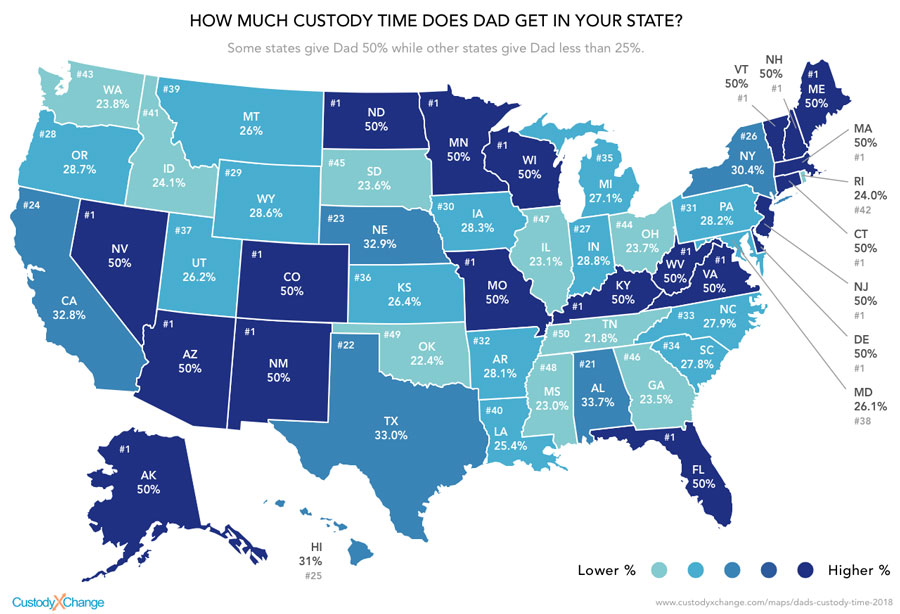
In New York State, who pays child support in a 50/50 joint custody arrangement since there there is no one "custodial parent"? Generally, the lower-earning parent will be treated as the “custodial parent” and the higher-earning parent will end up paying child support. Continue reading for more details about child support in NYC, Long Island, and all of New York.
Continue reading for more details about child support in NYC, Long Island, and all of New York.
In an earlier article we wrote about the Court of Appeals decision in Bast v. Rossoff 91 N.Y.2d.723. In this case, the Court held that shared custody arrangements do not alter the scope and methodology of the Child Support Standards Act (CSSA).
The act, passed in 1989, states that the three-step statutory formula for calculating NY child support must be applied in all shared custody cases.
Related Reading:
- Child Support & Extra Curricular Activities
- Child Support & College Expenses
- Interstate Child Support Laws
- New Child Support Law
- When Is My Child Emancipated?
Contact a Child Support Lawyer Today! Serving Long Island, NYC & All of NYS.
How Much Is Child Support in NY?
New York State child support is calculated using the NY child support calculator formula. NYC.gov also has an online NY child support calculator. You can use their child support calculator to help you get an idea of how much child support may be required for your case in NY.
The three-step formula for calculating NY child support is:
- Calculate the combined income and each parent's pro-rata share of the same
- Use the correct percentage of total income CSSA says should be devoted to child support:
- 17% for one child
- 25% for two children
- 29% for three children
- 31% for four children
- 35% for five or more children
- Calculate each parent's share thereof.
The non-custodial parent is directed to pay a pro-rater share of the child support obligation unless the court finds the amount to be unjust or inappropriate based on consideration of specified factors in Section F of CSSA.
The problem is that Bast (in Bast v. Rossoff) does not specifically address how to apply the CSSA in cases of equal shared custody. Indeed, the Bast case did not recognize cases of equal shared custody.
In Equal Shared Custody, Who Is the Custodial Parent?
The Appellate Division, 3rd Department did address the shared custody issue in Baraby v. Baraby 250 A.D 2d 2201, and the Appellate Division, 4th Department addressed it again in Carlino v. Carlino 277 A.D. 22d 897.
In Baraby, the third department stated the parent with the larger income would be deemed the non-custodial parent for purposes of calculating support under CSSA. The parent with the non-custodial designation must be directed to pay his or her pro rata share of the child support obligation to the other parent unless the statutory formula yields a result that is unjust or improper. In that situation, the trial court can resort to the "Paragraph F" factor in CSSA and order an amount that is just and appropriate under the circumstances.
The parent with the non-custodial designation must be directed to pay his or her pro rata share of the child support obligation to the other parent unless the statutory formula yields a result that is unjust or improper. In that situation, the trial court can resort to the "Paragraph F" factor in CSSA and order an amount that is just and appropriate under the circumstances.
The 4th department in Carlino, citing the Baraby case, which said in a 50/50 shared custody arrangement, if the parent with the larger income demonstrates that expenses incurred in having equal time substantially reduces the cost the parent with the lesser income has to bear as non-custodial parent, then the court should find that it would be unjust or inappropriate to award the statutory amount. Instead, the court should determine a proper support amount based on the specific expenses and the degree such expenses have been substantially reduced as a result of the time spent with the non-custodial parent. That court, as in Baraby, also remanded the case to the Trial Court for a hearing to calculate support in accordance with its decision. It found the Trial Court record lacked sufficient requisite information necessary to make the calculation.
That court, as in Baraby, also remanded the case to the Trial Court for a hearing to calculate support in accordance with its decision. It found the Trial Court record lacked sufficient requisite information necessary to make the calculation.
What Does This Mean To You?
If you live in New York State in the first or second Judicial Department, chances are the principles laid out in Baraby as well as in Carlino will be adhered to. This further means that if you are the larger wage earner and thus the non-custodial parent for purposes of CSSA in a case of equal time, then you should be prepared to demonstrate how your time with the child reduces the custodial parent's expenses for things such as, but not limited to, food, electricity, telephone, transportation, entertainment, etc.
Prior to these decisions, Bast made clear the statutory formula should be applied and courts were quite reluctant to deviate from the Act on the principle of "unjust or inappropriate". These two cases may well have provided a platform for arguing that people with close to 50/50 time should obtain the same treatment of analyzing to what extent the custodial parent's expenses are reduced by the substantial time the non-custodial parent spends with the child.
These two cases may well have provided a platform for arguing that people with close to 50/50 time should obtain the same treatment of analyzing to what extent the custodial parent's expenses are reduced by the substantial time the non-custodial parent spends with the child.
What If You Do Not Have 50/50 Time, but More Than Standard Visitation Time?
The unknown question at this point is how far the New York courts, as a parochial matter, will extend their willingness to deviate from CSSA based upon the time each parent spends with the child. An environment has been created where individual treatment of each case, based on its unique set of acts, has been discouraged in favor of applying a uniform standard.
| Request a Case Evaluation |
Up to this point, courts have been reluctant to find that the statutory formula produced a result that is unjust or improper, and therefore, to permit deviation. The Baraby and Carlino cases would re-encourage a case by case analysis by the trial courts based upon the sensitivity of its own individual facts. This possibly results in a wide variance of case decisions because of un-uniform discretion applied by different judges. Elimination of this discretion was what was originally sought when CSSA was enacted. It was felt that there should not be similar cases decided differently because two different judges chose to exercise discretion differently
The Baraby and Carlino cases would re-encourage a case by case analysis by the trial courts based upon the sensitivity of its own individual facts. This possibly results in a wide variance of case decisions because of un-uniform discretion applied by different judges. Elimination of this discretion was what was originally sought when CSSA was enacted. It was felt that there should not be similar cases decided differently because two different judges chose to exercise discretion differently
Conclusion
Hopefully, we are coming full circle with Baraby and Carlino in recognizing that justice cannot be dispensed without consideration of the individual facts of each case. The CSSA Act was passed when most men were the sole or primary wage earners. It does not recognize the two wage earner household where wives may indeed earn as much as - or more - than their husbands. New arguments and decisions on this issue will help to change the current standard rules to conform to current societal practices. Until then, you and your attorney will have to work to establish these changes. The good news is that you can.
Until then, you and your attorney will have to work to establish these changes. The good news is that you can.
Call Friedman & Friedman at (516) 688-0088 for further information about New York State child support or divorce.
Amount of maintenance per child \ Acts, samples, forms, contracts \ Consultant Plus
- Main
- Legal resources
- Collections
- Amount of maintenance for one child
A selection of the most important documents upon request The amount of maintenance per child (legal acts, forms, articles, expert advice and much more).
- Alimony:
- Maintenance obligations of children to support their parents
- Alimony obligations of spouses
- Alimony in 6-NDFL
- Alimony in a solid amount of
- Alimony of individual entrepreneur
- more .
 ..
..
Judicial practice : the amount of alimony per child
register and get test access to the survivor system ConsultantPlus free for 2 days
Open the document in your system ConsultantPlus:
Selection of court decisions for 2020: Article 120 "Termination of maintenance obligations" of the RF IC
(R.B. Kasenov) The court satisfied the plaintiff's claims to invalidate the decision of the bailiff on the calculation of alimony arrears. As the court pointed out, by virtue of paragraph 2 of Art. 120 of the Family Code of the Russian Federation, the payment of alimony, collected in court, stops when the child reaches the age of majority or in the event that minor children acquire full legal capacity before they reach the age of majority. In the case under consideration, one of the two children of the plaintiff, for the maintenance of which alimony was payable, had reached the age of majority. Thus, alimony for the maintenance of one child was subject to withholding, however, the bailiff-executor calculated the amount of alimony based on 1/3 of the plaintiff's earnings, which is not based on the law. nine0015
nine0015
Register and get the trial access to the ConsultantPlus system free for 2 days
Open the document in your ConsultantPlus system:
Selection of court decisions for 2019: Article 120 "Continuation of alimony obligations" of the IC of the Russian Federation
(R. B. Kasenov) By virtue of paragraph 2 of Art. 120 of the Family Code of the Russian Federation, the payment of alimony, collected in court, stops when the child reaches the age of majority. At the same time, the court order of the justice of the peace did not contain information that the collection of alimony in the amount of 1/3 of the share stops when one of the children reaches the age of majority and then the alimony is subject to collection in the amount of 1/4 of the share. To reduce the amount of alimony established by the court, the bailiff-executor is not entitled to reduce. The reference to the fact that the bailiff had to apply to the court for clarification of the court order, but did not do this, does not indicate the illegality of his actions, since this appeal is a right, and not an obligation, of the bailiff. On the contrary, the debtor, being an interested party of enforcement proceedings, being active, was not deprived of the opportunity to resolve this issue. In addition, the court order contained no ambiguities and did not require clarification. Thus, the court dismissed the claim of the administrative plaintiff to declare illegal the decision on the calculation of the alimony arrears, the obligation to determine the alimony arrears. nine0015
On the contrary, the debtor, being an interested party of enforcement proceedings, being active, was not deprived of the opportunity to resolve this issue. In addition, the court order contained no ambiguities and did not require clarification. Thus, the court dismissed the claim of the administrative plaintiff to declare illegal the decision on the calculation of the alimony arrears, the obligation to determine the alimony arrears. nine0015
Articles, comments, answers to questions : the amount of alimony per child
Register and receive trial access to the consultantPlus system free 2 days
Open the Consultant Pluss:
Situation: Whoever Do I have to pay child support and how much?
("Electronic journal "Azbuka Prava", 2022) If an agreement on the payment of alimony for minor children has not been concluded, they can be collected in court. The amount of alimony that must be paid monthly will be determined by the court. As a general rule, the amount of alimony is: for one for a child - one quarter, for two children - one third, for three or more children - half of the earnings and (or) other income of the parents. the court may increase or decrease the amount of these shares.
the court may increase or decrease the amount of these shares.
Regulations : Amount of maintenance per child
How is the amount of maintenance determined? | Juristaitab
From now on, the subsistence minimum is separated from the so-called minimum wage, which has been increasing the subsistence minimum every year until now. HUGO lawyer Vahur Kõlvart explains the nature of the new system below.
In the future, minimum child support will have five different components.
A base amount of at least 200 euros per child, indexed annually to the previous year's consumer price index (which will be officially published by Statistics Estonia on 1 April). After indexation, the base amount resulting from indexation in the previous year is considered the base amount for the next year. nine0015
3% of the average monthly gross salary in the country for the previous year is added (which is also officially published by Statistics Estonia on 1 April).
Number of children supported in one family - in this case, the amount of maintenance for subsequent children is reduced by 15 percent compared to the amount of maintenance for the first child. The amount of maintenance is not reduced in the case of twins/twins and in the case of children with a difference in age of more than three years. nine0015
Family allowances - as compared to the past, the law clearly states that the parent is not obliged to support the child to the extent that the needs of the child can be met by the child allowance and the allowance for a large family. If the benefit claimant receives these benefits, half of the benefit is deducted from the allowance for each child. However, if the recipient of the benefit is a payer, this amount is added to the alimony.
Child living together - if the child lives with the parent who pays support for an average of at least 7 days per month per year, the amount of support is reduced in proportion to the time spent with the obliging parent. Therefore, if the child lives equally with both parents, maintenance can only be collected if this is due to the greater needs of the child, a significant difference in the income of the parents, or an uneven distribution of expenses related to the child between the parents. nine0015
Therefore, if the child lives equally with both parents, maintenance can only be collected if this is due to the greater needs of the child, a significant difference in the income of the parents, or an uneven distribution of expenses related to the child between the parents. nine0015
Example:
The child lives with the mother, stays with the father for an average of 10 days per month, and a child allowance of 60 euros is paid into the child's mother's bank account. The minimum allowance per child is 70.43 euros.
Base amount: 200 euros 3% of the average salary for the previous year: the average gross salary in 2020 was 1448 euros per month, of which 3% is 43.44 euros.
Family allowances: half of the child allowance is deducted from the parent's maintenance obligations (60/2=30), so the maintenance amount is 213.44 euros (243.44-30). nine0045 Co-habitation: If the child lives with the supporting parent between 7 and 15 days per month, the amount of support may be further reduced according to the number of those days.