Pimple like rashes in children
Molluscum Contagiosum (for Parents) - Levine Children's Hospital
What Is Molluscum Contagiosum?
Molluscum contagiosum is a skin rash caused by a virus. The rash has small clear or flesh-colored bumps. The bumps can spread from one part of the body to another or from person to person. For most kids, the rash goes away on its own in 6–12 months, but can take longer.
Molluscum contagiosum (mol-US-kum kon-tay-jee-OH-sum), or molluscum for short, usually goes away on its own without medical treatment.
What Are the Signs & Symptoms of Molluscum?
The rash is the telltale sign of molluscum. Its bumps:
- Start as very small spots about the size of a pinhead.
- Grow over a few weeks. They can be as large as a pea or pencil eraser.
- Are soft and smooth and may have a small dent in the center.
- Often are painless, but can get itchy, sore, red, and/or swollen.
- Can get infected with bacteria if kids scratch or pick at them.
- Can appear alone or in groups, or rows. Most people get between 1 and 20 bumps.
- Can show up almost anywhere on the skin except for the palms and soles. In kids, they're most often on the trunk, arms, and face.
What Causes Molluscum?
The molluscum virus causes the rash after it enters a small break in the skin. Bumps usually appear 2–6 weeks after that.
The molluscum virus spreads easily from skin touching skin that has bumps. Kids also can get it by touching things that have the virus on them, such as toys, clothing, towels, and bedding. Sexually active teens and adults with bumps in the groin or inner thighs can spread them to partners.
Who Gets Molluscum?
Molluscum most often happens in healthy kids between 1 and 12 years old. But it also happens in:
- athletes who have close contact, such as wrestlers, or athletes who share equipment, such as gymnasts
- people with health problems treated with long-term steroid medicine use
How Is Molluscum Diagnosed?
Doctors can usually tell a rash is molluscum by looking at it.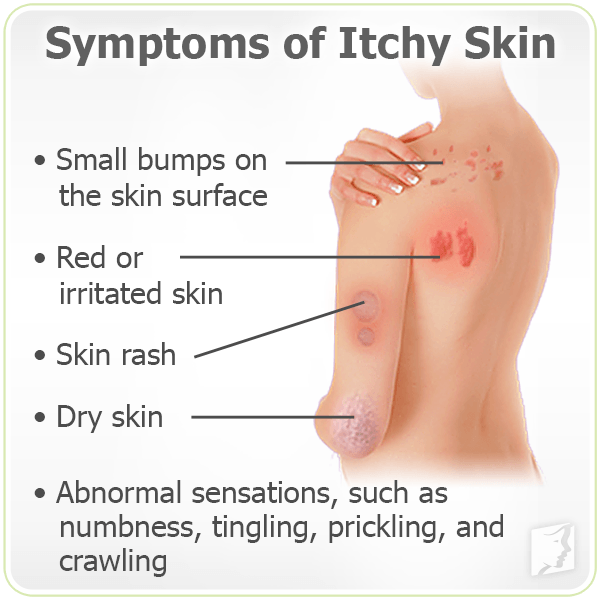 Sometimes they might suggest that kids see a dermatologist (skin doctor), but most kids won't need this.
Sometimes they might suggest that kids see a dermatologist (skin doctor), but most kids won't need this.
Can Molluscum Be Prevented?
Kids with molluscum can still go to daycare, school, and sports. To prevent the spread of molluscum to other places on their body and to other people, they should:
- Wash their hands well and often with soap and water.
- Cover the bumps with clothing or a bandage.
- Cover the bumps with a watertight bandage before swimming or doing activities with close contact (like wrestling) or shared equipment (like gymnastics).
- Not share towels or pool toys.
- Not shave over areas that have bumps.
- Not touch, scratch, or rub the bumps.
How Is Molluscum Treated?
Most of the time, molluscum clears up on its own without treatment. Each bump goes away in about 2–3 months. New bumps can appear as old ones go away, so it can take 6-12 months (and sometimes longer) for molluscum to fully go away.
Sometimes, doctors remove the bumps or help them go away more quickly. To do this, they can:
To do this, they can:
- Freeze the bumps off.
- Scrape or cut the bumps off.
- Put a chemical on the bumps to make the body fight them away faster.
- Put medicine on the bumps or give medicine to swallow.
Many doctors don't recommend these treatments for kids, though. That's because they can be painful and burn, blister, stain, or scar the skin. When deciding to treat a rash, they consider where the bumps are and if they're causing itching, pain, or other problems.
How Can Parents Help?
To avoid molluscum and other skin infections, have your kids follow these tips:
- Wash hands well and often with soap and water.
- Do not share towels or clothing.
- Do not share kickboards and other water toys.
- Do not touch or scratch bumps or blisters on their skin or other people's skin.
Talk with your child's doctor about the pros and cons of treating molluscum. The rash usually doesn't cause long-term problems or leave scars. Often, the best way to handle it is to be patient, as hard as that might be.
Often, the best way to handle it is to be patient, as hard as that might be.
Reviewed by: Melanie L. Pitone, MD
Date reviewed: February 2020
What are those bumps on my child's skin?
Diseases & conditions
- Coronavirus Resource Center
- Acne
- Eczema
- Hair loss
- Psoriasis
- Rosacea
- Skin cancer
- A to Z diseases
- A to Z videos
- DIY acne treatment
- How dermatologists treat
- Skin care: Acne-prone skin
- Causes
- Is it really acne?
- Types & treatments
- Childhood eczema
- Adult eczema
- Insider secrets
- Types of hair loss
- Treatment for hair loss
- Causes of hair loss
- Hair care matters
- Insider secrets
- What is psoriasis
- Diagnosis & treatment
- Skin, hair & nail care
- Triggers
- Insider secrets
- What is rosacea
- Treatment
- Skin care & triggers
- Insider secrets
- Types and treatment
- Find skin cancer
- Prevent skin cancer
- Raise awareness
- Español
Featured
How Natalie cleared her adult acneNatalie tried many acne products without success. Find out how a board-certified dermatologist helped Natalie see clear skin before her wedding.
Find out how a board-certified dermatologist helped Natalie see clear skin before her wedding.
This contagious skin disease will usually clear on its own, but sometimes dermatologists recommend treating it. Find out when.
Everyday care
- Skin care basics
- Skin care secrets
- Injured skin
- Itchy skin
- Sun protection
- Hair & scalp care
- Nail care secrets
- Basic skin care
- Dry, oily skin
- Hair removal
- Tattoos and piercings
- Anti-aging skin care
- For your face
- For your skin routine
- Preventing skin problems
- Bites & stings
- Burns, cuts, & other wounds
- Itch relief
- Poison ivy, oak & sumac
- Rashes
- Shade, clothing, and sunscreen
- Sun damage and your skin
- Aprenda a proteger su piel del sol
- Your hair
- Your scalp
- Nail care basics
- Manicures & pedicures
Featured
Practice Safe SunEveryone's at risk for skin cancer. These dermatologists' tips tell you how to protect your skin.
These dermatologists' tips tell you how to protect your skin.
Find out what may be causing the itch and what can bring relief.
Darker Skin Tones
- Skin care secrets
- Hair care
- Hair loss
- Diseases & Conditions
- Acne
- Dark spots
- Dry skin
- Light spots
- Razor bumps
- Caring for Black hair
- Scalp psoriasis
- Weaves & extensions
- Central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia
- Frontal fibrosing alopecia
- Hairstyles that pull can cause hair loss
- Acanthosis nigricans
- Acne keloidalis nuchae
- Hidradenitis suppurativa
- Keloid scars
- Lupus and your skin
- Sarcoidosis and your skin
- Skin cancer
- Vitiligo
- More diseases & conditions
Featured
Fade dark spotsFind out why dark spots appear and what can fade them.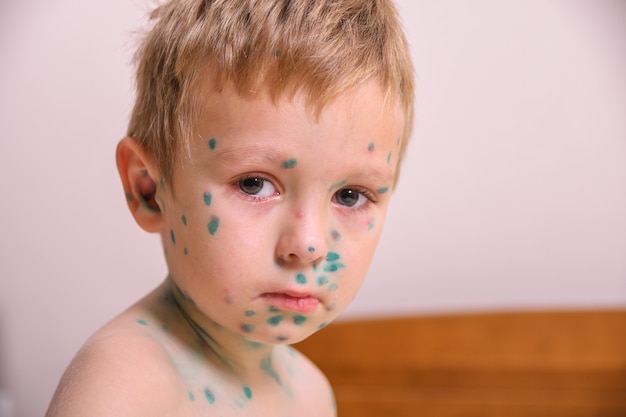
If you have what feels like razor bumps or acne on the back of your neck or scalp, you may have acne keloidalis nuchae. Find out what can help.
Cosmetic treatments
- Your safety
- Age spots & dark marks
- Cellulite & fat removal
- Hair removal
- Scars & stretch marks
- Wrinkles
- Younger-looking skin
Featured
Laser hair removalYou can expect permanent results in all but one area. Do you know which one?
Do you know which one?
If you want to diminish a noticeable scar, know these 10 things before having laser treatment.
BotoxIt can smooth out deep wrinkles and lines, but the results aren’t permanent. Here’s how long botox tends to last.
Public health programs
- Skin cancer awareness
- Free skin cancer screenings
- Kids' camp
- Good Skin Knowledge
- Shade Structure grants
- Skin Cancer, Take a Hike!™
- Awareness campaigns
- Flyers & posters
- Get involved
- Lesson plans and activities
- Community grants
Featured
Free materials to help raise skin cancer awarenessUse these professionally produced online infographics, posters, and videos to help others find and prevent skin cancer.
Free to everyone, these materials teach young people about common skin conditions, which can prevent misunderstanding and bullying.
Find a dermatologist
- Find a dermatologist
- What is a dermatologist?
- FAAD: What it means
- How to select a dermatologist
- Telemedicine appointments
- Prior authorization
- Dermatologists team up to improve patient care
Featured
Find a DermatologistYou can search by location, condition, and procedure to find the dermatologist that’s right for you.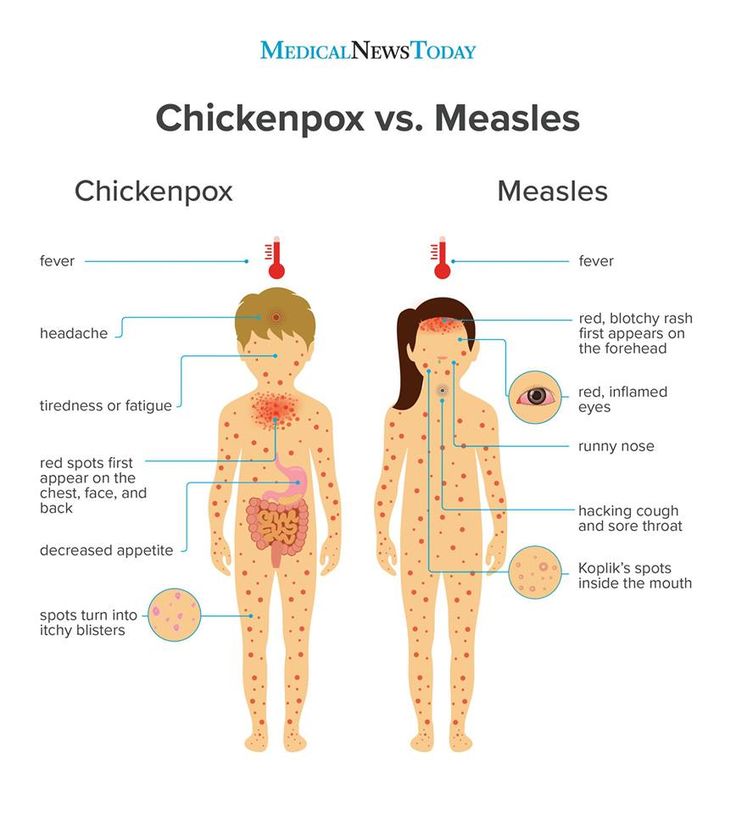
A dermatologist is a medical doctor who specializes in treating the skin, hair, and nails. Dermatologists care for people of all ages.
Rash in a child on the body, legs, back
We treat children according to the principles of evidence-based medicine: we choose only those diagnostic and treatment methods that have proven their effectiveness. We will never prescribe unnecessary examinations and medicines!
Make an appointment via WhatsApp
Prices Doctors
The first children's clinic of evidence-based medicine in Moscow
No unnecessary examinations and medicines! We will prescribe only what has proven effective and will help your child.
Treatment according to world standards
We treat children with the same quality as in the best medical centers in the world.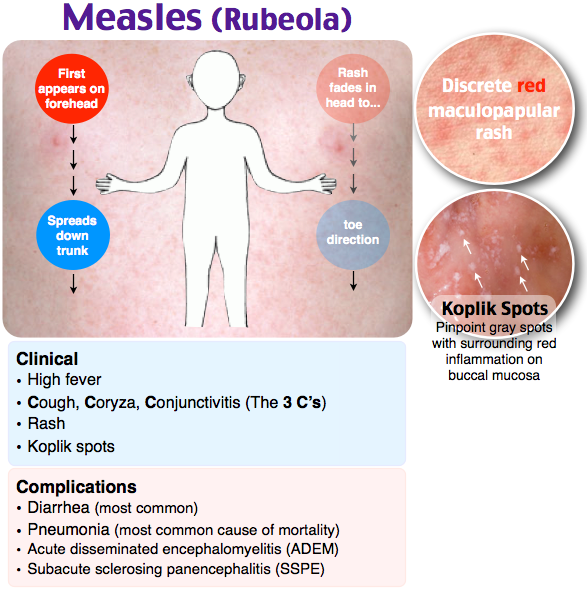
The best team of doctors in Fantasy!
Pediatricians and subspecialists Fantasy - highly experienced doctors, members of professional societies. Doctors constantly improve their qualifications, undergo internships abroad.
Ultimate treatment safety
We made pediatric medicine safe! All our staff work according to the most stringent international standards JCI
We have fun, like visiting best friends
Game room, cheerful animator, gifts after the reception. We try to make friends with the child and do everything to make the little patient feel comfortable with us.
You can make an appointment by calling or by filling out the form on the site
Other Pediatric services
- Pediatrician's consultation
- Child Health Management Program
Frequent calls
- Acute bronchiolitis in children: diagnosis and treatment
- SARS
- Angina streptococcal tonsillitis
- Frequently ill child nine0034
- Intestinal infections
- Pneumonia (pneumonia) in children
- Colic
- Feeding problems
- Prolonged cough in a child: diagnosis and treatment
- Acute bronchitis in children: diagnosis and treatment
- Pneumonia (pneumonia) in children: diagnosis and treatment nine0034
- False croup in a child
- Coxsackie virus in a child
- The child was bitten by a tick! What to do?
Online payment
Documents online
Online services
- nine0079
 Types, diagnosis and treatment
Types, diagnosis and treatment Have you noticed a rash on your child's skin? Contact your pediatrician to find out the reason. Redness itself is not a disease, but can signal internal disorders in the body.
In the article we will talk about the causes, types and methods of treating rash in children. nine0003
What causes a rash?
Rashes on the skin of a child do not appear just like that. In any case, this is the body's immune response to the influence of external or internal factors.
Different types of rashes are similar in appearance, especially for parents who are faced with a problem for the first time. But if some spots are completely harmless, then others can threaten health. That is why it is important to understand their origin.
The main causes of the rash: nine0003
- Reaction to stimuli. If the child is dressed too warmly, the rash may be due to overheating and excessive sweating.
 Most often, prickly heat occurs on the back, neck, chest and abdomen. The same goes for the diaper. If you do not arrange air baths and do not change it to a new one in time, the skin in the inguinal region and on the buttocks will disappear.
Most often, prickly heat occurs on the back, neck, chest and abdomen. The same goes for the diaper. If you do not arrange air baths and do not change it to a new one in time, the skin in the inguinal region and on the buttocks will disappear.
Prickly heat does not require special treatment, it is only important to eliminate the irritating factor. - Physiological. In the first months of life, breastfed babies are often diagnosed with infantile acne. With milk, maternal hormones enter the body, which activate the sebaceous glands. As a result, small comedones and pimples appear on the face. Over time, they disappear. nine0034
- Viral and bacterial infections. Measles, chicken pox, rubella, herpes simplex virus, roseola, scarlet fever, meningococcal infection, fungus and streptoderma. These diseases are characterized by specific rashes on the arms, legs and other parts of the body. Many are accompanied by itching and a steady increase in body temperature for 3-5 days.
- Allergy. Urticaria and various types of atopic dermatitis: eczema, diathesis, neurodermatitis. Spots without suppuration may cover the head, face, shoulders, armpits, back and groin. nine0034
- Comorbidities. Rash may indicate gastrointestinal, vascular, or kidney problems.
Eruptions in children
Depending on the appearance, localization and size, the following types are distinguished:
- Tubercles.
- Vesicles.
- Blisters.
- Purples.
- Pustules.
- Stains.
- Erythema.
Why are rashes dangerous?
With any kind of redness, it is important to consult a doctor to determine the cause. The most dangerous rash of viral and bacterial origin, especially if there are other symptoms: nine0003
- cough;
- sore throat;
- enlarged tonsils and lymph nodes;
- tearing;
- temperature increase.
Without timely treatment, complications are possible. For example, measles can lead to pneumonia, meningitis, and hearing loss.
With skin allergic reactions, it is important to determine the source of the problem. A neglected allergy can cause swelling and suffocation.
What should parents do?
nine0002 If you find bumps, vesicles or redness on the child's body, proceed in sequence:- examine the entire skin;
- estimate the area and number of lesions;
- check throat, tonsils and take temperature;
- remember what the child ate, did or touched before the redness appeared.
Is the baby already talking? Then try to figure out what's bothering him. Ask about the sensations (spots hurt, itch) and general well-being. nine0003
If you have a high temperature, call your doctor at home. It could be a contagious infectious disease that definitely shouldn't be spread. But even if the child looks healthy and vigorous, do not postpone a visit to a specialist - make an appointment at a medical facility.
It is strictly forbidden to self-medicate, comb or squeeze out neoplasms.
Diagnostics
Diagnostic measures help to choose the right therapy. First, the pediatrician prescribes to small patients: nine0003
- blood, urine and feces analysis;
- skin scrapings;
- collection of exudate samples, in the presence of watery formations.
Based on the results, the doctor makes a preliminary conclusion and sends the parents with the child for examination to narrow specialists: an allergist, dermatologist, endocrinologist or gastroenterologist.
Treatment
Treatment of rashes is carried out in a complex way to eliminate both the symptoms and the cause. A young patient is prescribed anti-allergic, anti-inflammatory or hormonal drugs in the form of tablets, ointments or suspensions. nine0003
Along with this, parents are advised to reconsider nutrition and living conditions:
- exclude potentially allergenic products;
- use gentle detergents for the body, dishes and laundry;
- wear loose clothing made from natural fabrics;
- dress the child according to the weather, do not wrap too tightly to avoid overheating;
- change the diaper in a timely manner, arrange air baths and lubricate the groin area with a special cream.