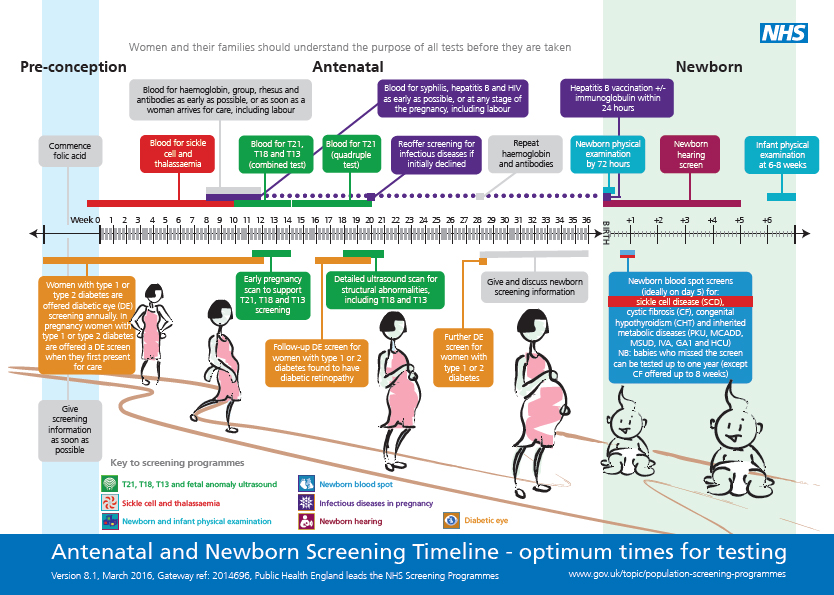
How much child support before jail
Child Support Enforcement in California
Learn how to enforce child support orders and collect overdue payments in California.
Most parents want to support their children, both financially and emotionally, whether they are married to one another or not. Some parents, however, refuse to pay child support for their children even when ordered to do so by a court. Each state has specific resources and remedies available to help custodial parents enforce child support orders and collect past due payments.
This article will explain how to enforce a child support order in California. If you have additional questions after reading this article, you should consult a local family law attorney for help.
Establishing Child Support in California
Before you can enforce child support, you must make sure to have court-ordered child support in place. If you and your child's other parent have nothing more than an oral agreement regarding child support, you won't be able to enforce that agreement in court. If you're able to agree on an amount for support, you must memorialize your agreement in writing and have it approved by a judge; if the court determines the amount is in your child's best interests, a judge will issue a child support order based on your agreement.
If you and the other parent can't agree, and you need to have child support established in your case, you will have to file an action for child support in your county superior court. You can do this in one of the following ways:
- on your own, using the child support forms found on the California Courts' website
- hiring a private attorney to file a petition for child support on your behalf, or
- asking your local child support agency to open a case and file for child support on your behalf. In California, the local child support agency is called the California Department of Child Support Services (DCSS). Check the DCSS website to find an office near you.
Enforcement of Child Support in California
Once child support has been established, there are several ways a court can enforce the child support order and help a custodial parent collect overdue payments.
Motion for Contempt
California courts can enforce a child support order by holding the delinquent parent in "contempt" of court. Being held in contempt means the judge believes you have willfully disobeyed a court order.
Contempt can be criminal or civil. If the delinquent parent is held in criminal contempt, the court can order him or her to pay fines or serve jail time.
A parent held in civil contempt may also be sent to jail, but can be released as soon as he or she pays a certain amount of the past due child support. A court can also order a combination of penalties for civil and criminal contempt.
The party seeking to enforce child support in court (called the "plaintiff") must file a motion (written legal request) for contempt. The custodial parent that is supposed to receive child support, the county where the child lives (if the county has paid support for the child), or the local DCSS office can file the motion, unless the custodial parent has died, in which case the child, or someone acting on the child's behalf, may file it.
In California, there is a statute of limitations (meaning a time limit) on bringing a motion for contempt related to non-payment of support. You have three years from the date a payment was due (but not paid) to file a contempt action against a delinquent parent. For example, if the other parent doesn't pay child support for six years, you can only file contempt regarding the last three years' worth of payments. If the noncustodial parent isn't paying, be sure to file for contempt at least every three years to ensure you are eligible to receive all past due child support.
Additional Court Orders Aimed at Collecting Support
If you've filed for contempt against a delinquent parent for failure to pay child support, the court will hold a hearing. If the court believes that the delinquent parent willingly refused to pay, a judge has a number of penalties that he or she can order. After finding a delinquent parent in contempt, the judge can:
- fine a delinquent parent up to $1,000 and sentence him or her to up to five days in jail, but generally, judges don't fine parents, since that money could go towards past due child support
- sentence a delinquent parent to community service up to 120 hours for a first or second contempt and up to 240 hours for a third contempt
- order a delinquent parent to pay the custodial parent's attorney's fees and other costs associated with enforcing the child support order
- order that a delinquent parent's property be sold to pay child support
- order that a lien be placed on a delinquent parent's real property, like a house or land
- order that a delinquent parent's wages be withheld to pay child support
- order that money for past due child support be garnished from a delinquent parent's bank accounts, or
- order that past due child support be paid from a delinquent parent's pension plan, veteran's disability benefits, community property owned by a delinquent parent's spouse, Social Security disability benefits, unemployment compensation disability benefits, workers compensation, lottery winnings, and most other sources of income for a delinquent parent.

Some federal benefits may be exempt from garnishment, but for the most part, a court can order that any income a delinquent parent receives be taken away and given to a custodial parent for child support. If you have specific questions about whether a court can garnish certain benefits to pay for child support, contact a local family law attorney for advice.
You should know that if the delinquent parent doesn't have the financial ability to make the child support payments, the court won't hold him or her in contempt. However, parents that claim an inability to pay must prove this in court with evidence of their income and assets (or lack thereof).
Just because a child has reached 18 doesn't mean the noncustodial paying parent is suddenly off the hook; if a parent is behind on child support, that money is still owed until it's paid in full. You still need to file within three years of the time support is due.
If you are a custodial parent seeking to enforce support and collect overdue payments, you can bring your own motion for contempt or you can hire a private attorney to file for contempt on your behalf. You can also apply for child support services, including enforcement services, with your local DCSS. Find contact information for your local child support agency here.
You can also apply for child support services, including enforcement services, with your local DCSS. Find contact information for your local child support agency here.
Other Penalties for Nonpayment of Child Support in California
In California, there are other penalties for failing to pay child support. If a parent is more than 30 days behind on child support, the Department of Motor Vehicles may refuse to issue or renew his or her driver's license. Delinquent parents may get a temporary license (valid for 150 days), but if they don't get caught up on child support, the state won't extend the temporary license or issue a permanent one. If a parent is behind by 120 days or more, the state will revoke the license altogether.
Finally, DCSS keeps a list of delinquent parents and reports them to credit reporting agencies, which may result in a negative credit rating.
If you have additional questions about enforcement of child support in California, you can click here to speak with a local family law attorney.
How Far Behind on Child Support Constitutes Jail Time in Texas?
By Her Lawyer on January 31st, 2022
How Much Child Support can You Owe Before Going to Jail in Texas?
Failure to pay child support payments can be punishable up to a federal offense in the United States. Here’s what to know about how far behind on child support leads to jail time in Texas.
Only 43.5% of parents reported receiving child support from the noncustodial parent. Texas enforces the payment of child support with several penalties. A parent’s continued neglect of child support payments can lead to up to two years in jail.
Possible Consequences of Not Paying Child Support in Texas
The party not receiving child support may contact the Texas Attorney General Child Support Division to enforce payments. Neglecting to pay child support in Texas can lead to the following penalties:
- Wage garnishment
- Interception of the income tax return
- A lien on the property
- Suspension of license
- Revoked license
- Denial of passport
- Negative credit rating
- Civil or criminal contempt
- Continuation of debt building while incarcerated
- Denial of visitation rights
Related: My Child’s Father Wants Custody to Avoid Child Support
Civil Contempt Cases
Neglecting a court order is contempt of court.:quality(80)/granite-web-prod/c4/8d/c48d18bdbee44382acae582295ace8f5.jpg) The parent who does not receive overdue child support payments may file a civil or criminal contempt case against the noncustodial parent.
The parent who does not receive overdue child support payments may file a civil or criminal contempt case against the noncustodial parent.
In a civil contempt case, the court will assess a specific number of days the defendant will need to complete in jail and/or a fine the defendant will have to pay if due child support is not paid. Fines for each nonpayment can be up to $500, or the court can sentence a defendant up to 6 months in jail. If the defendant does pay after serving jail time, they must serve their full sentence.
Criminal Contempt and Nonsupport Cases
The court views contempt as a crime. The defendant must serve allotted jail time until the custodial parent receives overdue child support payments in full. A Texas judge can place the defendant in jail for up to six months due to the violating court-ordered child support payment.
The court may charge the noncustodial parent for criminal nonsupport in Texas. Criminal nonsupport is an enforceable state jail felony due to the intentional payment failure of court ordered child support. A state jail felony in Texas is a punishable offense allotting jail time and a fine of up to $10,000.
A state jail felony in Texas is a punishable offense allotting jail time and a fine of up to $10,000.
After child support payments are enforced at a state or local level, the enforcement may proceed to federal court. If the non-custodial parent still does not pay child support payments in full after two years or the amount has amounted to $10,000, the charge can increase to a criminal felony. A criminal felony for a failure of court ordered child support payments can lead to up to 2 years of jail time.
Related: What Happens to Child Support If a Parent Goes to Jail?
FAQs About How Far Behind on Child Support Constitutes Jail Time in Texas
Why does the court assign child support?Child support benefits help ensure that the child has the same financial benefits as a household with both parents. Texas intends for child support to help offset the cost of caring for a child or it may be used to assist in the payment of housing and utility costs. The noncustodial parent is expected to pay child support to the custodial parent to provide for their portion of child care.
The noncustodial parent is expected to pay child support to the custodial parent to provide for their portion of child care.
A failure to pay child support can constitute up to 6 months in jail. If the non-custodial parent continues to not pay child support for 2 years or the amount totals beyond $10,000, jail time can increase for up to 2 years.
How much missed child support constitutes jail time?The party neglecting to pay child support must first be held in contempt of court. Contempt of court can lead to fines, jail time, and criminal charges.
How much are fines for missed child support?Fines for each child support nonpayment can be up to $500. A non-custodial parent’s continual neglect of child support payments can lead to a felony and a fine of up to $10,000.
Contact Us
If you or a loved one would like to learn more about failure to pay child support and if this constitutes jail time in Texas, get your free consultation with one of our child support attorneys today!
How to get alimony from a convict?
By the way: We can collect maximum child support More The current Family Law does not establish restrictions or any benefits on the payment of alimony by a person who is in places of detention by a court verdict.
All the time during which a person is serving a sentence in prison, he retains the obligation to ensure the material maintenance of the child. Payments may be deducted from his wages paid to him in places of detention for work in the factories of the colonies, but only from the remaining amount after deducting the cost of his food and maintenance, as well as all deductions laid down by law (taxes, contributions to the pension fund and etc.). nine0003
Note: According to paragraph 3. Art. 107 of the Penal Code of the Russian Federation, less than 25% of all earnings received by them in the colony, including salaries or pensions, should be credited to the personal accounts of convicts. For men over 60, women over 55, disabled people and juvenile prisoners, this amount is increased to 50%. These amounts are inclusive of all possible deductions, including alimony.
How to get alimony from a convict and how realistic is it today?
The actions required to receive alimony from a convicted person differ for two key situations: nine0003
- Incarcerated parent does not have a court order or agreement to pay child support.

- There is a court decision on recovery, but the payer is serving real imprisonment according to the court verdict.
How to get alimony if the father is in prison?
Each of the circumstances listed has its own specifics for the recovery of alimony from the convict, as a result of which we will analyze them in detail further. nine0003
If there is no court order and the paying parent is in prison
Do not believe the rumors that alimony cannot be recovered from the convict. Legally, there are absolutely no obstacles to this! A person serving a sentence in prison can also be sued for alimony, as well as any citizen who is at large. Filing a claim is carried out in a general manner for the recovery of alimony with jurisdiction at the request of the plaintiff: a claim can be filed both at the place where the defendant is serving his term, and at the place of his registration. nine0003
The defendant is notified of the consideration of the case, and, if necessary, and if the claim is filed at the place of residence of the plaintiff, the court that accepted the application for proceedings instructs another court at the location of the colony to question the defendant and record in writing all the answers given by him to the questions specified in the ruling.
Taking into account the position of the defendant, the court makes a decision on the recovery of alimony from the convicted person.
Theoretically, if the marriage has not yet been dissolved, you can demand a divorce with the simultaneous collection of alimony, but the law allows you to divorce the convict in absentia, without litigation, and even regardless of the presence of children. But only on condition that the person is sentenced to a term of 3 years or more. nine0003
How to get alimony from a convict already having a writ of execution?
If the court decision was in your favor and you received a writ of execution, the procedure for the forced recovery of maintenance from a parent imprisoned will not differ in any way from the recovery of alimony through bailiffs.
The writ of execution is transferred to the territorial department of the FSSP at the location of the colony, and then, by analogy with the recovery of alimony from a working citizen, it is transferred to the correctional institution where the payer is located. nine0003
nine0003
From this moment on, all duties for calculating the amounts of alimony and their transfer fall on the accounting department of the institution for the execution of sentences, and the bailiffs continue to exercise a supervisory function.
If the convict is transferred to another institution for the execution of sentences, the administration of the colony is obliged to send along with him a writ of execution to the new place of serving the sentence. Upon release from prison, the sheet is returned by the bailiffs, after which they again begin work on the collection of alimony - but already from wages. nine0003
In a similar way, collection is carried out under a notary agreement on the voluntary payment of maintenance payments.
Read on our blog: All about child support
If the prisoner does not work in the prison
Alas, the harsh realities of life are such that only a few colonies are able to constantly provide work for prisoners. Most of the time, citizens in prison do not work and do not have the opportunity to pay alimony, not only in full, but in any amount at all! The insignificant amounts charged to them for episodic going to work do not even cover maintenance costs. nine0003
Most of the time, citizens in prison do not work and do not have the opportunity to pay alimony, not only in full, but in any amount at all! The insignificant amounts charged to them for episodic going to work do not even cover maintenance costs. nine0003
This does not deprive the bailiff of the right to calculate the amount of the alimony debt according to the rules for collecting alimony from the unemployed, and the payer, having been released from prison, will immediately have an impressive debt, which will subsequently need to be paid. But the law, again, allows a person released from prison to petition for a reduction in the amount of the debt or even to demand its complete cancellation if there are good reasons.
Note: If during imprisonment the colony was not able to provide the prisoner with paid work, then the court, most often, will take the side of the debtor and write off the calculated alimony debt to him - after all, he would not have been able to pay them, even if he really wanted to! nine0007If you follow the law, then the formal recovery of alimony from a convicted person is quite feasible and even a simple procedure, but actually getting money for alimony from a convicted person is a truly difficult task!
Experienced lawyers of the MCPI Planet of the Law will advise you on any issue related to alimony and provide a full range of legal assistance within the framework of the special program “Alimony? - Elementary! Call + 7 (495) 722-99-33 or write to WhatsApp.nine0007
If alimony debts have accumulated...
Veronika Salnikova
Lawyer, partner of Yakovlev & Partners
June 16, 2021
Tips
Pay attention to the date of publication of the material: the information may be out of date due to changes in legislation or law enforcement practice.
How to collect them, what threatens the parent-debtor and in what case will he be released from liability?
Through which court to collect alimony from a father with many children? nine0009
“In 2018, the world court decided to collect alimony from her husband for the maintenance of two minor children. In 2020, we had twins. Currently, the marriage is not dissolved. Tell me where to apply (to the world or district court) and how to file an application to collect alimony for twins?
Alimony (funds for the maintenance of minor children) can be collected through the court in the order of writ or action proceedings.
Writ proceedings are a simplified procedure for collecting alimony in the Magistrate's Court. When filing an application, the court issues a court order without summoning the plaintiff and the defendant. Claim proceedings are carried out in the district court with the summons of the parties. nine0003
As a general rule, if the parent-debtor already pays child support, then they should be collected on other children through the district court. The mother of twins needs to apply to the district court at her place of residence or the defendant.
You can file a claim with an attorney. In addition, sample applications are often placed in courts. You can use this sample, detailing your situation and attaching supporting documents.
nine0078 (Answers to other questions of alimony recipients and their payers can be found in the articles “On child support - in detail”, “On the payment of alimony - on real examples”, “Cross-border alimony”).
What threatens a parent for non-payment of alimony?
For late payment or non-payment of alimony in full, the debtor parent may be held liable - administrative (Article 5.
35.1 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation) or criminal (Article 157 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation). nine0003
Bailiffs bring to administrative responsibility negligent parents. This is possible in the event of non-payment without good reason of funds for the maintenance of children according to a judicial act, a court order or an agreement on the payment of alimony. The court already attracts criminal liability for malicious evasion from the fulfillment of maintenance obligations of parents.
On April 27, 2021, the Plenum of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation approved a resolution stating that “violation of a judicial act or agreement on the payment of alimony should be understood as non-payment of alimony in the amount, on time and in the manner established by this decision or agreement.” Partial payment of alimony cannot exclude the application of liability measures (read about this also in the news "The Plenum of the Supreme Court clarified the nuances of administrative responsibility for non-payment of alimony") .
In which case will the debtor parent be released from liability despite the child support debt?
If the parent-debtor has good reasons for which he cannot pay child support in the prescribed amount, he has the right to go to court and ask to change the procedure for collection. In the presence of such reasons, the debtor may be released from liability. nine0003
Valid reasons may be recognized such circumstances in which non-payment of alimony occurred regardless of the will of their payer: his illness (incapacity for work), his military service on conscription, force majeure circumstances, the fault of other persons, for example, non-payment of wages by the employer, delay or incorrect transfer bank of funds to the recipient of alimony.
The list of reasons that may be recognized as valid for exemption from liability is not exhaustive. In all cases, the judge must assess whether specific circumstances can be attributed to the number of good reasons for non-payment of alimony.
nine0003
How do bailiffs force persistent non-payers to fulfill maintenance obligations?
If the parent does not just evade the payment of alimony, but hides and prevents their collection, i.e. becomes a malicious defaulter, the bailiffs start the procedure for searching for the debtor. But they can do this only if there is a statement from the alimony claimant. During the search, bailiffs try to locate the debtor and his property in order to bring him to justice and force him to fulfill maintenance obligations. How do they do it? nine0003
Bailiffs are endowed with special powers. They have the right:
- receive personal data from the internal affairs authorities, tax authorities, the Pension Fund, registry offices, traffic police;
- check information through the customs authorities;
- check in banks information about accounts, deposits, securities;
- to interview relatives, friends, colleagues - everyone who has information about the non-payer; nine0014
- carry out a visit to the location of the debtor's property for its examination and evaluation;
- use information obtained through the involvement of a private detective bureau or from open sources, including those posted on personal pages on social networks.