How long can a child be on your health insurance
Dependent Health Coverage and Age for Healthcare Benefits
Table of Contents
- Table: State Laws Relating to Dependent Coverage
- Coverage Beyond the Federal ACA (7 states)
Contact
- Health Program
The Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (ACA) mandates that all health insurance carriers in every state that offer coverage to both adults and their dependents must allow dependents to remain on their parents or guardians’ “family” plans until the dependents are 26 years old.
The issued regulations state that young adults are eligible for this coverage regardless of any, or a combination of any, of the following factors: financial dependency, residency of the young adult, student status, employment status, or marital status. This applies to all plans in the individual market and to almost all employer plans (small group, large group, including self-funded or so-called ERISA plans) created after March 23, 2010.
PPACA & HCERA; Public Laws 111-148 and 111-152: Consolidated Print
‘‘SEC. 2714. EXTENSION OF DEPENDENT COVERAGE.
‘‘(a) IN GENERAL.—A group health plan and a health insurance issuer offering group or individual health insurance coverage that provides dependent coverage of children shall continue to make such coverage available for an adult child until the child turns 26 years of age. Nothing in this section shall require a health plan or a health insurance issuer described in the preceding sentence to make coverage available for a child of a child receiving dependent coverage. [As revised by section 2301(b) of HCERA]
‘‘(b) REGULATIONS.—The Secretary shall promulgate regulations to define the dependents to which coverage shall be made available under subsection (a).
‘‘(c) RULE OF CONSTRUCTION.—Nothing in this section shall be construed to modify the definition of ‘dependent’ as used in the Internal Revenue Code of 1986 with respect to the tax treatment of the cost of coverage.”
- NCSL Fact Sheet
- White House Fact Sheet
- Commonwealth Fund: Rite of Passage: Young Adults and the Affordable Care Act of 2010
- Kaiser Family Foundation Summary
The States’ Role
The extension of coverage for young adults under their parents’ or guardians’ health insurance plans, like many of the ACA’s provisions, originated in state legislatures. Prior to the implementation of the ACA, at least 31 states required carriers to extend coverage to young adults. The age at which insurers were no longer required to provide coverage to young adults under their family plans varied by state. Additionally, some states required certain conditions to be met by young adults in order to be eligible for coverage under their guardians’ plans. For example, a number of states required that young adults be unmarried in order to qualify.
Prior to the implementation of the ACA, at least 31 states required carriers to extend coverage to young adults. The age at which insurers were no longer required to provide coverage to young adults under their family plans varied by state. Additionally, some states required certain conditions to be met by young adults in order to be eligible for coverage under their guardians’ plans. For example, a number of states required that young adults be unmarried in order to qualify.
States may continue with current state law requirements for extended dependent coverage unless they prevent the application of the ACA. As with other state health insurance statutes, the state mandate language enables the state insurance departments to educate the public, and to implement and enforce those laws directly, including use of state courts and state-specific penalties.
State and local governments, as employers and sponsors of coverage plans, are required to notify those under the age of 26 whose coverage has ended or who were denied coverage under their plans before turning 26, of enrollment opportunities.
State Actions
The federal ACA law applies to young adults in all states.
As of 2012, (before the ACA was fully in effect) the following 37 states had already extended the age that young adults can remain on their parents' health insurance plan: Colorado, Connecticut, Delaware, Florida, Georgia, Idaho, Illinois, Indiana, Iowa, Kentucky, Louisiana, Maine, Maryland, Massachusetts, Minnesota, Missouri, Montana, Nevada, New Hampshire, New Jersey, New Mexico, New York, North Dakota, Ohio, Oregon, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, South Carolina, South Dakota, Tennessee, Texas, Utah, Virginia, Washington, West Virginia, Wisconsin and Wyoming.
There is considerable variation among state laws in terms of eligibility requirements. At least 30 states have extended dependent coverage, regardless of student status. Most states require that a young adult be unmarried and financially dependent on their parents in order to qualify for extended dependent coverage.
States may continue to apply current state law requirements for extended dependent coverage except to the extent that the requirements prevent the application of the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (ACA). [Reviewed/updated 2016]
The box allows you to conduct a full text search or type the state name.
| State | Laws |
|---|---|
| Colorado | Colo. Rev. Stat. § 10-16-104.3 states that a child is considered a dependent for insurance purposes up to age 25 (even if they are not enrolled in an educational institution) as long as they are unmarried and are financially dependent or share the same permanent address as the insurance provider. |
| Connecticut | C.G.S.A. § 38a-497 requires that group comprehensive and health insurance policies extend coverage to unwed children until the age of 26 provided they remain residents of Connecticut or are full-time students. |
| Delaware | Del. Code Ann. Tit. 18, § 3354 requires insurance providers to cover policyholder's dependent children until age 24. Dependents must be unmarried and a resident of Delaware or, if living outside the state, a full-time students. Insurance companies may charge more for dependent coverage past age 18, but it may not exceed 102 percent of the policyholder's cost before the child turned 18. |
| Florida | Florida 627.6562 allows for dependent children up to 25, who live with their parent or are a student, and up to 30 years old, who are also unmarried and have no dependent child of their own, to remain on their parents' insurance. |
| Georgia | Ga. Code § 33-30-4 allows dependent children up to age 25 who are enrolled as a full-time student at least five months during the year or are eligible to enroll but are prevented due to illness or injury to remain on their parents' insurance. Ga. Code § 33-24-28 requires that a health services plan or health insurer exempt dependent children incapable of self-sustaining employment due to disability from dependent age limits. |
| Idaho | Idaho Stat. § 41-2103 allows for any unmarried dependents to remain on their parents' health insurance until age 21; any full-time, unmarried student until age 25; or a dependent with a disability without regard to age. |
| Illinois | 215 ILCS 5/356z.12 provides parents with the option of keeping unmarried dependents on their health care insurance up to age 26. Parents with dependents who are veterans can keep them on their plans up to age 30. |
| Indiana | IC 27-8-5-2,28 and IC 27-13-7-3 require commercial health insurers and health maintenance organizations to cover children until age of 24 or without regard to age if they are incapable of self-sustaining employment due to disability. |
| Iowa | Iowa Code § 509.3 and Iowa Code § 514E.7 requires that health insurance providers continue to cover unmarried children under their parents' coverage provided that the child 1) is under the age of 25 and a current resident of Iowa, 2) is a full-time student, or 3) has a disability. |
| Kentucky | Ky. Rev. Stat. § 304.17A-256 allows parents to keep their unmarried children on their health plans until the age of 25. Parents may have to pay extra for their adult children. |
| Louisiana | La. Rev. Stat. Ann. § 22:1003 allows an unmarried, dependent child to remain on parent's insurance up to age 24 if they are a full-time student. |
| Maine | 24-A MRSA § 2742-B requires individual and group health insurance policies to continue coverage for a dependent child up to 25 years of age if the child is dependent upon the policyholder and the child has no dependents of the his/her own. |
| Maryland | MD Code, Insurance § 15-418 requires that health insurance be extended to, at the request of the policy holder, unmarried dependents under the age of 25. |
| Massachusetts | Mass. Gen. Laws Ann. Ch. 175 § 108 allows dependents to stay on their parent's coverage for two years past the age of dependency or until age 26, whichever occurs first, or without regard to age if they are incapable of self-sustaining employment due to disability. Young adults ages 19-26 are eligible for lower-cost insurance coverage, tailored to meet their needs, offered through the Commonwealth Health Insurance Connector. Reform summary and fact sheet, PowerPoint presentation. |
| Minnesota | Minnesota Chapter 62E.02 Defines "dependent" as a spouse or unmarried child under age 25, or a dependent child of any age who is disabled. |
| Missouri | Mo. Rev. Stat. § 354-536 defines dependent as an unmarried child up to age 26. If a health maintenance organization plan provides that coverage of a dependent child terminates upon attainment of the limiting age for dependent children, such coverage shall continue while the child is and continues to be both incapable of self-sustaining employment by reason of mental or physical handicap and chiefly dependent upon the enrollee for support and maintenance. |
| Montana | MCA 33-22-140 provides insurance coverage under a parent's policy for unmarried children up to age 25. |
| Nevada | NRS 689C.055 allows an unmarried, dependent child who is a full-time student to remain on his or her parent's insurance up to age 24 if parent is covered by small group policy. NRS 689B. |
| New Hampshire | N.H. Rev. Stat § 420-B:8-aa defines dependent as those who are unmarried up to age 26 and either a full-time student or resident of New Hampshire for purposes of health insurance coverage. 2009 SB 115 allows those up to age 26 to buy-in to coverage through the state's CHIP program, Healthy Kids. |
| New Jersey | N.J.S.A. 17B:27-30.5 states that, at the option of the insured person, a dependent may be covered up to the age of 31, as long as they are unmarried and have no dependents of their own. |
| New Mexico | NM Stat. Ann. § 13-7-8 states that health insurance for dependents may not be terminated based on age up to age 25. |
| New York | N.Y. Insurance Code, sec. 3216. (2009 AB 9038) allows an unmarried adult child to remain on parent's insurance through age 29 (up to age 30) if they are a resident of New York. [link updated 4/2015] |
| North Dakota | N.D. Cent. Code § 26.1-36-22 allows an unmarried, dependent child to remain on parent's insurance up to age 22 if they live with parents. If they are a full-time student, they can remain on parent's insurance from age 22 up to age 26. |
| Ohio | Ohio Rev. Code § 1751.14, as amended by 2009 OH H 1 allows an unmarried, dependent child that is an Ohio resident or a full-time student to remain on parent's insurance up to age 23, or without regard to age if they are incapable of self-sustaining employment due to disability. |
| Oregon | O.R.S. § 735.720 defines dependent as an unmarried child up to 23, elderly parents and disabled adult children for the purpose of insurance coverage. |
| Pennsylvania | 2009 SB 189 states that an unmarried child may remain on parent's insurance up to age 30 if they have no dependents and are residents of PA or are enrolled as full-time students. 51 Pa.C.S.A. § 7309 states that full-time students whose studies are interrupted by service in the reserves or the National Guard must be extended health care benefits as a dependent of their parent beyond the terminating age equal to the length of their deployment.. |
| Rhode Island | R.I. Gen. Laws § 27-20-45 and Gen. Laws § 27-41-61 requires insurance plans which cover dependent children to cover unmarried dependent children until age 19 or, if a student, until age 25. |
| South Carolina | S.C. Code Ann. § 38-71-1330 allows an unmarried, dependent child who is a full-time student to remain on parent's insurance up to age 22 if parent is covered by small group policy. S.C. Code Ann. § 38-71-350 requires that a dependent child who is not capable of self-sustaining employment be allowed to remain on his or her parent's insurance, without regard to age. |
| South Dakota | SD Codified Laws Ann. § 3-12A-1 states that any insurance provider offering benefits to a dependent may not terminate those benefits by reason of age before the dependent's 19th birthday. If the dependent is enrolled in an educational institution, they are not to be terminated until they reach age 24 and not terminated if unable to seek self-support due to disability. SD Codified Laws § 58-17-2.3 states that if the dependent remains a full-time student upon attaining age 24 but not exceeding age 29, the insurer shall provide for the continuation of coverage for that dependent at the insured's option. |
| Tennessee | Tennessee Code Ann. § 56-7-2302 allows for dependent coverage for children under their parents' health insurance plan up to age 24 provided the child is unmarried and financially dependent on the parents. |
| Texas | V.T.C.A. Insurance Code § 846.260 and V.T.C.A. Insurance Code § 1201.059 make dependent status available for an unmarried child up to age 25 for insurance purposes. |
| Utah | Utah Code Ann. tit. 31A § 22-610.5 requires that coverage for unmarried dependents continue up to age 26, regardless of whether or not the dependent is enrolled in higher education. |
| Virginia | Va. Code Ann. § 38.2-3525 makes dependent status available to any child up to age 19 or who is a dependent up to age 25 who resides with the parent or is a full-time student. |
| Washington | West's RCWA 48.44.215 states that, at the option of the insured person, an unmarried dependent may be covered up to age 25. |
| West Virginia | W. Va. Code § 33-16-1a defines dependent for health insurance coverage as a child or stepchild up to age 25. |
| Wisconsin | Wis. Stat. § 632.885 requires that coverage for unmarried dependents through a parent's insurance be offered up to age 27 if they are not offered insurance through an employer. Full-time students called to active duty in the armed forces can be covered beyond age 26 depending on various factors. |
| Wyoming | Wyo. Stat. § 26-19-302 states that if child is unmarried and a full-time student, they can remain on parent's insurance up to age 23 if parent is covered by small group policy. |
Coverage Beyond the Federal ACA | 2016 update
Six states, including Florida, Illinois, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, South Dakota and Wisconsin have enacted laws that require or authorize carriers to cover young adults beyond age 26. New York and Ohio previously enacted such laws, however those provisions are no longer in effect.
| State | Required Coverage Age Cut-off | Citation |
|---|---|---|
| Florida | 30 (must be unmarried and have no dependents of their own) | West's F. |
| Illinois | 30 (applies to Veterans only) | 215 ILCS 5/356z.12 |
| New Jersey | 31 | N.J.S.A. 17B:27-30.5 |
| New York | 29* (unmarried and not eligible for employer-based insurance) | McKinney's Insurance Law § 3216 |
| Pennsylvania | 30 | 40 P.S. § 752.1 |
| South Dakota | 29* | SDCL § 58-17-2.3 |
| Wisconsin | Full-time students, regardless of age | Wis. Stat. § 632.885 |
Who Pays?
The cost of notifying families about new enrollment opportunities is shared between insurance providers and employers. The cost of covering the young adults who take advantage of the extension is shared between employers and the families of newly covered young adults. For families with no employer health coverage, the cost may fall on the parents. Those families that qualify for States, as sponsors of coverage plans for state employees, also share the costs with families. A qualified young adult cannot be required to pay more for coverage than similarly situated individuals who did not lose coverage due to the loss of dependent status.
The cost of covering the young adults who take advantage of the extension is shared between employers and the families of newly covered young adults. For families with no employer health coverage, the cost may fall on the parents. Those families that qualify for States, as sponsors of coverage plans for state employees, also share the costs with families. A qualified young adult cannot be required to pay more for coverage than similarly situated individuals who did not lose coverage due to the loss of dependent status.
IRS Notice 2010-38 provides guidance to extend the general exclusion from gross income for the reimbursements for medical care under an employer provided accident or health plan to any employee's child who has not yet attained age 27 as of the end of the taxable year, making the benefit tax-free.
*The information on this page is intended for state policy makers. It is not intended as legal or medical advice or guidance to individual insurance enrollees. .
.
Source: NCSL legal research, 2016; State Health Facts by KFF. Legal review, 2011-2015: Richard Cauchi, NCSL Health Program.
Update 2016 research: Ashley Noble, J.D., NCSL Health Program
How Long Can You Stay on Your Parent's Insurance?
Under current laws, you can stay on your parent’s health insurance policy until you turn 26 years old.
In some states, it’s even longer.
When the time comes for you to get your own insurance, it’s important to know what your health insurance choices are and how to choose the right plan.
It can be a confusing topic, and sometimes it is difficult to know what your best options are.
This article breaks down what you need to know about your health insurance options, how to choose a plan that’s right for you, and if you even need insurance.
When You Lose Health Insurance Through Your Parents
Currently, the Affordable Care Act (ACA) requires your parent’s insurance plan to cover you until your 26th birthday.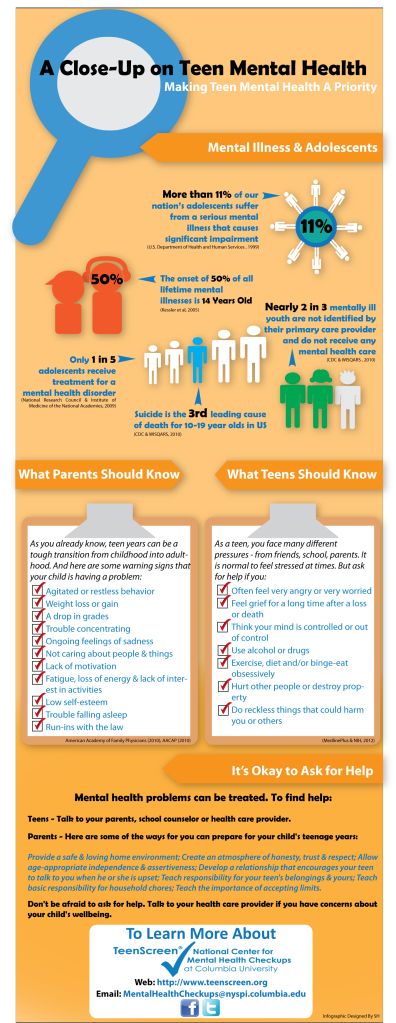
You qualify for coverage under your parents even if you are:
- Married
- Attending school
- Not living with your parents
- Not financially dependent on your parents
- Eligible to enroll in your employer’s plan
If your parents have their insurance plan through an employer, you usually have coverage until the end of your birthday month.
Check with your individual plan to know for sure, as some states and plans have different rules.
If your parents have a Marketplace insurance plan, you have until December 31of the year you turn 26 to get your coverage.
States with an extended age limit
Some states have an extended age limit to remain on your parent’s policy if you meet specific criteria.
To be eligible for extended dependent coverage, you typically can’t be eligible for any other form of comprehensive health coverage.
For example, if you are eligible for your own employer’s health insurance, you may not be able to extend your parent’s coverage. (This does not apply to individuals who have a disability.)
(This does not apply to individuals who have a disability.)
Following are the states that offer exceptions; however, laws are always subject to change, so check with your own state’s laws.
| State | Dependent Age Limit Exceptions |
| Florida | Through age 29 for those who are unmarried, have no dependents, and are residents of the state or enrolled as a part-time or full-time student |
| Georgia | No age limit for persons with a disability incapable of self-support |
| Idaho | No age limit for unmarried persons with a disability |
| Illinois | Through age 29 for unmarried veterans No age limit for persons with a disability incapable of self-support |
| Indiana | No age limit for persons with a disability incapable of self-support |
| Massachusetts | No age limit for persons with a disability incapable of self-support |
| Minnesota | No age limit for persons with a disability |
| Missouri | No age limit for persons with a disability incapable of self-support |
| Nevada | No age limit for persons with a disability incapable of self-support |
| New Jersey | Through age 30 for those who are unmarried, have no dependents, and are residents of the state or full-time students |
| New York | Through age 29 for those who are unmarried and residents of or workers in the state No age limit for persons with a disability who are unmarried and incapable of self-support |
| Ohio | No age limit for persons with a disability incapable of self-support |
| Oregon | No age limit for persons with a disability |
| Pennsylvania | Through age 29 for those who are unmarried, have no dependents, and are residents of the state or enrolled as a full-time student |
| Rhode Island | No age limit for persons with a disability |
| South Carolina | No age limit for persons with a disability incapable of self-support |
| South Dakota | Through age 29 for full-time students No age limit for persons with a disability incapable of self-support |
| Wisconsin | No age limit for full-time students; for full-time students who are National Guard or reservists called into active duty; for those called for federal active duty; or for persons with a disability incapable of self-support |
Health Insurance Options
If you are about to age out of your parent’s insurance policy, you have a few options to choose from.
If you or your spouse are currently employed full-time, you may be able to get health insurance coverage through an employer.
You must request special enrollment within 30 days of your loss of coverage.
Health insurance marketplace
For individual coverage, you may qualify for special enrollment through the Health Insurance Marketplace.
To purchase a Marketplace plan, you must special enroll within 60 days of aging out of your plan. You can find more information here.
You may even qualify for subsidies that can make your coverage more affordable.
COBRA
If your parent’s employer sponsors 20 or more employees on its plan, you may be eligible to purchase a temporary extension of health coverage for up to 36 months under the Consolidated Omnibus Budget Reconciliation Act (COBRA).
Be sure to notify your parent’s employer in writing within 60 days before you turn 26 if you want to elect COBRA coverage.
Medicaid
If you apply for insurance through your state health insurance marketplace, you will be asked to enter your income amount.
Depending on how much you make per year, you may qualify for your state’s Medicaid program.
If you are currently attending a university as a full-time student, you may be able to get health coverage through your school’s insurance policy.
This is a great option for graduate students who are getting older and aging out of their parent’s plan.
Check your symptoms using K Health and talk to a medical provider for a low cost.
Get StartedChoosing the Right Health Insurance
The health insurance plan you choose depends somewhat on your health status.
If you are in good health and don’t require monthly prescriptions or need to have a procedure done, you will want a different plan than someone who does.
Types of plans
Here are the most common types of health insurance plans.
Exclusive provider organizations (EPO): An EPO plan requires you to seek healthcare services from doctors and hospitals within their defined network if you want your costs to be covered, with exceptions for emergency care.
Health maintenance organizations (HMO): HMO plans typically contract with doctors within a specific area to provide services, including preventative measures. Except for an emergency, this type of plan only covers the cost of services provided by in-network healthcare providers.
Point of Service (POS): POS plans offer reduced-cost physician and hospital care when you seek care from their in-network providers. If you need an appointment with a specialist, you’ll need to get a referral from your primary care physician.
Preferred provider organization (PPO): With a PPO, you pay less for healthcare services when you only use in-network providers. This plan does not require a referral to see a specialist.
Marketplace: The health insurance Marketplace offers a few different levels of coverage plans. The plans are broken down by tier:
- Gold and Platinum: These plans have the most expensive premiums (monthly payments), but they also have the lowest deductibles (the amount you need to pay out of pocket).
 This means you will have access to coinsurance benefits quickly. If you are in great health, this policy might end up costing more compared to the benefits you will receive. However, if you require monthly medications, this plan would be a great money-saving plan for you.
This means you will have access to coinsurance benefits quickly. If you are in great health, this policy might end up costing more compared to the benefits you will receive. However, if you require monthly medications, this plan would be a great money-saving plan for you. - Silver: These plans have average premiums, deductibles, and out-of-pocket maximums. It is more expensive than the cheapest plan, but it’s a great plan if you are preparing to start a family. In addition, Silver plans offers cost-sharing discounts if your income is below 250% of the federal poverty level.
- Bronze: These plans have low premiums and high deductibles but are only available for people under 30. If you are eligible for subsidies, you can apply them to get a Bronze plan for a low monthly rate. This type of plan is good if you don’t think you’ll have many medical expenses throughout the year.
- Catastrophic: These plans are also only available for people under 30.
 They are the cheapest plans available on the Marketplace, but they have the highest deductibles and out-of-pocket maximums. This type of cheap plan is great if you are healthy and don’t expect to have substantial medical costs. You cannot apply subsidies to Catastrophic plans.
They are the cheapest plans available on the Marketplace, but they have the highest deductibles and out-of-pocket maximums. This type of cheap plan is great if you are healthy and don’t expect to have substantial medical costs. You cannot apply subsidies to Catastrophic plans.
Costs
Whatever plan you choose, there is a required monthly premium (how much you pay for the plan each month).
If you don’t require any medical care, your premium is the only payment you can expect.
However, if you do require healthcare services, you will have to pay other costs as well.
- Deductible: This is the amount of money you pay out of pocket before the benefits of the policy start covering costs. For example, if you have a deductible of $2,000, you will need to pay the first $2,000 of any healthcare bills yourself before your insurance starts to pay.
- Copayment: Also called a copay, the copayment is typically a fixed cost for a service (e.
 g., $25 to see your primary care physician). Once the deductible has been met, you will only be asked to pay your copay when you visit your doctor.
g., $25 to see your primary care physician). Once the deductible has been met, you will only be asked to pay your copay when you visit your doctor. - Out-of-pocket maximum: This is the maximum amount of money you will pay out of your own pocket for healthcare services in a single year. Until you reach this maximum, you are responsible for all of the out-of-pocket costs.
Check your symptoms using K Health and talk to a medical provider for a low cost.
Get StartedDo I Need Health Insurance?
If you are healthy, you might think that you don’t need health insurance coverage.
But consider that accidents happen all the time, and healthcare services can be expensive without the help of insurance.
According to the U.S. Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services, the average hospital stay can cost $10,000 per day.
While that may be an extreme case, injury and illness can come as a surprise, and signing up for health insurance is one simple way to help avoid high medical bills if an issue does arise.
It’s always best to plan ahead—you’ll be happy you did.
How K Health Can Help
Need to go to urgent care but no insurance?
Check your symptoms, explore conditions and treatments, and if needed, text with a healthcare provider in minutes all through K Health.
K Health’s AI-powered app is HIPAA compliant and is based on 20 years of clinical data.
K Health articles are all written and reviewed by MDs, PhDs, NPs, or PharmDs and are for informational purposes only. This information does not constitute and should not be relied on for professional medical advice. Always talk to your doctor about the risks and benefits of any treatment.
K Health has strict sourcing guidelines and relies on peer-reviewed studies, academic research institutions, and medical associations. We avoid using tertiary references.
-
Why Bother with Health Insurance? (n.
 d.)
d.)
https://www.healthcare.gov/young-adults/ready-to-apply/ -
Young Adults and the Affordable Care Act: Protecting Young Adults and Eliminating Burdens on Businesses and Families. (2020.)
https://www.cms.gov/CCIIO/Resources/Files/adult_child_fact_sheet -
How to Get or Stay on a Parent’s Plan.
 (n.d.)
(n.d.)
https://www.healthcare.gov/young-adults/children-under-26/ -
Health Insurance Marketplace. (n.d.)
https://www.healthcare.gov/glossary/health-insurance-marketplace-glossary/ -
The 2021 Florida Statutes.
 (2021.)
(2021.)
http://www.leg.state.fl.us/statutes/index.cfm?App_mode=Display_Statute&Search_String=&URL=0600-0699/0627/Sections/0627.6562.html -
Life Events – Child Turns 26. (n.d.)
https://team.georgia.gov/life-events-child-turns-26/ -
Idaho Statutes.
 (2021.)
(2021.)
https://legislature.idaho.gov/statutesrules/idstat/title41/t41ch31/sect41-2103/ -
Dependent Coverage. (2017.)
https://www2.illinois.gov/cms/benefits/trail/state/Pages/AddingaDependent.aspx -
Eligibility requirements to enroll.
 (n.d.)
(n.d.)
https://www.in.gov/spd/benefits/eligibility/eligibility-requirements-to-enroll/ -
Section 108. (n.d.)
https://malegislature.gov/Laws/GeneralLaws/PartI/TitleXXII/Chapter175/Section108 -
Family Eligibility.
 (n.d.)
(n.d.)
https://mn.gov/mmb/segip/family-eligibility/ -
Title XXIII Corporations, Associations and Partnerships. (2008.)
https://revisor.mo.gov/main/OneSection.aspx?section=354.536 -
Chapter 689b - Group and Blanket Health Insurance.
 (n.d.)
(n.d.)
https://www.leg.state.nv.us/NRS/NRS-689B.html#NRS689BSec035 -
Coverage of Young Adults in New Jersey Up to Age 31. (n.d.)
https://www.state.nj.us/dobi/division_consumers/du31.html#du31 -
Coverage Expansion Through Age 29.
 (n.d.)
(n.d.)
https://www.dfs.ny.gov/consumers/health_insurance/faqs_age29_young_adult_option -
Disabled Dependent 26 Years of Age or Older. (2018.)
http://www.cs.ny.gov/employee-benefits/hba/shared/manuals/pa/pdfs/2.3_disabled_dependent_26_or_older.pdf -
Section 1751.
 14. Termination of coverage of child. (2016.)
14. Termination of coverage of child. (2016.)
https://codes.ohio.gov/ohio-revised-code/section-1751.14 -
Eligibility and Dependent Eligibility. (2022.)
https://www.oregon.gov/oha/OEBB/Pages/Eligibility.aspx -
Senate Bill No.
 189. (2009.)
189. (2009.)
https://www.legis.state.pa.us/CFDOCS/Legis/PN/Public/btCheck.cfm -
Chapter 41. Health Maintenance Organizations. (2012.)
http://webserver.rilin.state.ri.us/Statutes/TITLE27/27-41/27-41-61.HTM -
Title 38 - Insurance.
 (2019.)
(2019.)
https://www.scstatehouse.gov/code/t38c071.php -
58-17-2.3. Dependent coverage termination--Age--Full-time students. (2011.)
https://sdlegislature.gov/Statutes/Codified_Laws/2074932 -
58-17-30.
 1. Continuation of coverage for child with intellectual or physical disability--Proof of dependency. (2013.)
1. Continuation of coverage for child with intellectual or physical disability--Proof of dependency. (2013.)
https://sdlegislature.gov/Statutes/Codified_Laws/2074966 -
632.885. Coverage of dependents. (2011.)
https://docs.legis.wisconsin.gov/statutes/statutes/632/vi/885 -
Young Adults and the Affordable Care Act: Protecting Young Adults and Eliminating Burdens on Businesses and Families FAQs.
 (n.d.)
(n.d.)
https://www.dol.gov/agencies/ebsa/about-ebsa/our-activities/resource-center/faqs/young-adult-and-aca -
Enroll in or change 2022 plans — only with a Special Enrollment Period. (n.d.)
https://www.healthcare.gov/coverage-outside-open-enrollment/special-enrollment-period/ -
Subsidized Coverage.
 (n.d.)
(n.d.)
https://www.healthcare.gov/glossary/subsidized-coverage/ -
COBRA Continuation Coverage Questions and Answers. (n.d.)
https://www.cms.gov/CCIIO/Programs-and-Initiatives/Other-Insurance-Protections/cobra_qna
Insurance for a child for a trip abroad and in Russia 2022
Updated July 26, 2022
Reading time ≈ 7 minutes
Author Christina
Views 17914
Travel health insurance for a child is an important point in which many nuances must be taken into account.
How fast and qualified assistance will be provided to the child will depend on the chosen insurance.
In this article we will tell you which insurances will really help you when traveling abroad and in Russia, and which ones are not even worth spending money on.
ORDER INSURANCE
What should be included in travel insurance for a child
It is important to understand that children are more exposed to all sorts of risks and diseases. Even climate change can have a negative impact on the child's body. Therefore, insurance must necessarily include the most necessary options.
- Injuries. One of the most frequent claims under the insurance policy are various injuries. Most often, children are injured in water parks, on children's attractions and playing active games. This item in the insurance is called "Active rest".
- Sunburn. In hot countries, situations with heat stroke and sunburn are not uncommon.
 Sometimes, even with all precautions, such an unpleasant situation can occur.
Sometimes, even with all precautions, such an unpleasant situation can occur. - Poisoning. Food poisoning is also among the most common insurance claims. Abroad, you should try to feed your child with the simplest and most familiar food. But, nevertheless, such a risk should be in the policy.
- Dentistry. Emergency dentistry is a necessary item, because medicine abroad is very expensive, and it will be expensive to treat a child's teeth.
- Bites of insects and animals. In this case, the option may not always work, it all depends on the specific situation.
- Allergies. This item is related to the previous one. In some cases, bites may be accompanied by a rash and itching, suggesting an allergic reaction.
- Coronavirus. In the current circumstances, this item is required for any insurance.
- Evacuation. This paragraph provides for sending the child to their home country if the parents need hospital treatment or urgent medical care.

- Unlimited doctor visits. Please note that there is such a note in the policy. Some insurance companies provide only 2 visits to the doctor, but in some cases a week's treatment may be necessary. Then all subsequent receptions will have to be paid independently.
What kind of insurance to choose for a child - the best companies
In this article we will consider only two insurances that really work and are suitable in all respects for children.
If you come across advertisements from various insurance companies, we recommend that you do not waste time and money on buying such insurance. Most likely, you will not get help from such policies.
So, there are 2 insurances that really work: Euroins (formerly ERV) and Polis Oxygen . We note right away that these are the most expensive, but at the same time the most reliable insurance.
In this case, the price is fully consistent with the quality.
Why don't we consider policies from other companies? Other insurers do not have a set of necessary options, more negative reviews, less reliable assistance.
Assitance is a company that provides assistance to tourists abroad. It is this company that will send you to the clinic and give recommendations for further actions. The best assistance is European. ERV - SAVITAR Group, Polis Oxygen - AXA Assistance (Oxygen Assistance).
The assistance phone number is on your insurance policy.
Euroins children insurance
Euroins insurance benefits
- One of the best travel insurance companies is Euroins (formerly ERV). This insurance is in the lead in all ratings.
- Euroins has the most positive reviews
- Reliable assistance SAVITAR Group has branches in Europe, Asia and America.
 The company cooperates with thousands of clinics around the world, thanks to which you can count on help right away, and not collect checks and seek payments from the insurance at home.
The company cooperates with thousands of clinics around the world, thanks to which you can count on help right away, and not collect checks and seek payments from the insurance at home. - This policy is suitable for a variety of categories: pregnant women (the only company that insures pregnancy complications up to 31 weeks), people with chronic diseases, children (including babies).
- The insurance does not provide for coefficients that increase the price of the policy for children.
Things to consider when applying for a Euroins policy
Please note that if you are buying a package tour, another company may be the assistance (this should be clarified with the tour operator). Therefore, it is better to buy insurance on your own online.
Insurance programs
There are two packages in the Euroins policy: Standard Plus and Optima. The Standard is suitable for a child, since the Optima program includes risks - pregnancy complications and help with alcohol intoxication.
This insurance can be obtained on POLIS812 or other sites.
Polis Oxygen for Children
Benefits of Polis Oxygen
- Many good comments about AXA Assistance (Oxygen Assistance).
- You can choose a clinic for assistance yourself.
- It is possible to call a doctor at home.
- "Online doctor" option thanks to which you can be in touch with doctors around the clock.
- Child care is a priority. If the child needs medical assistance, assistance will deal with this situation first.
Things to consider when applying for Polis Oxygen
The cost of insurance for a child under 8 years old will be twice as expensive.
Insurance programs
Polis Oxygen has three basic packages: a, b, c. They are suitable for adults. For children, you should choose the Premium program.
Polis Oxygen is a unique insurance product that can only be purchased on our POLIS812 website.
Should a child be insured against COVID-19
According to statistics, only 2% of the total number of cases of COVID-19 are children. Therefore, the likelihood of injury or getting another disease is much greater. But the meaning of insurance is not only in common risks, but in protection even from the most unpredictable circumstances.
If you purchase Euroins or Polis Oxygen , they already cover coronavirus treatment. If you buy another policy, you should pay attention to this risk.
How to get insurance abroad for a child
- Buying travel insurance is more convenient and more profitable online. The POLIS812 website presents both the policies described in the article and other insurances. You can familiarize yourself with the terms of each policy by calculating the preliminary cost on the online calculator.
- Fill in the fields of the insurance search form - indicate the country of travel, dates, age of the child (if more than one child is insured, indicate the age of each child separated by a comma). Use the promo code for a 15% discount.
- Select the appropriate policy, fill out the form with personal data and pay for the service.
- The finished document will be sent to your e-mail. The insurance must be printed out, this version of the document has the same legal force as the one purchased at the office of the insurance company.
GET INSURANCE
Useful articles
June 2, 2022 8163
Rating of Sberbank mortgage insurance companies 2022
How to choose a mortgage insurance company How to compare the cost of insurance: online calculator Mortgage insurance companies rating 2022 How to get insurance…
Recently you searched:
Travel insurance Countries: - Dates: - Tourists: — Continue calculation
Send a link to the mail
How to get a tax deduction for treatment under VHI
My family does not rely on free medicine, so all family members have VHI. The husband's insurance is paid by the employer: this is part of the social package. We buy a policy for me and the child with our own money. I learned that you can get a tax deduction for the costs of voluntary health insurance. Tell us on what conditions they give a deduction for VHI and how to issue it.
The husband's insurance is paid by the employer: this is part of the social package. We buy a policy for me and the child with our own money. I learned that you can get a tax deduction for the costs of voluntary health insurance. Tell us on what conditions they give a deduction for VHI and how to issue it.
In 2019, we have already spent: on my policy - 48,000 R, on the child's policy - 13,000 R, the husband's insurance costs 64,000 R, but only 20,000 R is deducted from the salary, the rest is at the expense of the company. We work officially. How much money can be returned?
Vika
Vika, in 2019 your family can return 10,530 R from the budget. Moreover, without a declaration and right now, without waiting for the next year. Here's how to do it.
Ekaterina Miroshkina
economist
Author profile
What is VHI?
VHI is voluntary health insurance. Such programs are offered by insurance companies. A client who has bought a VHI policy can receive medical services in paid clinics or in public ones, but faster than under a regular policy. The set of these services depends on the insurance program. Sometimes VHI includes only medical consultations, but may include vaccinations, x-rays, hospital treatment, and even dentistry.
A client who has bought a VHI policy can receive medical services in paid clinics or in public ones, but faster than under a regular policy. The set of these services depends on the insurance program. Sometimes VHI includes only medical consultations, but may include vaccinations, x-rays, hospital treatment, and even dentistry.
You can buy a VHI policy with your own money - for yourself or your child. Sometimes health insurance is included in the social package from the employer: the company can pay the policy in full or withhold part of the costs from the employee's salary.
It is not necessary to buy a VHI policy. Every employer still pays contributions to the compulsory health insurance fund. Even the unemployed, pensioners and newborns have MHI policies. They guarantee that the policyholder can contact the clinic for free, call an ambulance, go to the hospital or take an x-ray if a fracture is suspected. But not on the terms of a specific insurance company or a paid clinic, but under the basic program at the expense of the budget.
You cannot get a deduction from compulsory contributions to CHI, but you can from the cost of a VHI policy.
/dms/
What is VHI
Who can get a deduction for VHI expenses
The cost of a VHI policy is the expenses for which you can get a tax deduction. That is, to return the paid personal income tax from the budget - 13% of the amounts spent on insurance.
A tax deduction can be received by a resident of the Russian Federation who pays personal income tax at a rate of 13% and paid VMI for himself, his spouse, children or parents with his own money.
Example. Vika paid for the VHI policy for herself and her minor child. Two policies cost 61,000 R. Both contracts - both in their favor and in favor of the child - will be taken into account in the amount of the deduction. If you pay for a VHI policy for a mother or husband, these amounts can also be taken into account for the return of personal income tax.
para. 2 pp. 3 p. 1 art. 219 Tax Code of the Russian Federation
Conditions for social tax deduction under VHI
Insurance premiums under a voluntary medical insurance agreement are included in the social tax deduction. Here are the conditions that must be met at the same time for the return of personal income tax:
- A resident of the Russian Federation is claiming a deduction. That is, you need to stay in Russia for at least 183 days within 12 consecutive months.
- The insurance company from which the VHI policy was purchased has a license for this particular type of activity.
- The contract states that the insurance company only pays for medical services under it.
- The clinic, which provides medical services, has a Russian license.
- There are documents that confirm the payment of insurance premiums with your own money.
- If the employer pays for VMI, then the deduction can be received only if some amounts are withheld from the employee's salary towards contributions.
 The tax will be refunded only on these withheld amounts.
The tax will be refunded only on these withheld amounts.
The amount of the deduction for the purchase of VHI
The tax deduction for VHI expenses is equal to the amount of the actual expenses for such a policy. But since this is a social deduction, it has a limit - 120,000 R per year. You can spend more on voluntary health insurance, but you can return a maximum of 13% of 120,000 R, that is, 15,600 R of tax per year.
The annual limit includes all social deductions : for treatment, education, medical insurance, pension contributions and life insurance. That is, 120,000 R is the maximum for all such expenses. Only the costs of educating children are not included - they have a separate limit of 50,000 R per year - and the cost of expensive treatment - it has no limit at all and the tax is returned from the entire amount.
If less than 120,000 R was spent in a year, 13% of this amount can be returned. And the rest that is not used is burned: it cannot be transferred to the next year.
So what? 07/18/17
How to receive deductions for an apartment, treatment and education at work
How to calculate the amount of deduction and tax to be returned
Example of calculation with exceeding the limit. In 2019, Vika spent 61,000 R on her and her children's policies. Let's say that in the same year she also paid for her education at a driving school - 50,000 R and treatment at the dentist for her mother - 30,000 R. Also, Vika paid for English language courses for a child - 28,000 R. She will declare these amounts as a tax deduction.
The total amount of Vika’s expenses for VHI, education and treatment in 2019 will be 141,000 RUR. This is more than the annual limit, so the tax will be refunded only from 120,000 RUR — 15,600 RUR. taken into account, and indicated in the declaration as a separate line. Therefore, Vika will be able to return 13% of 28,000 R - another 3640 R. In total, Vika will return 19,240 RUR from the budget with such expenses.
Example of calculation with expenses less than the limit. In 2019Vika spent 61,000 RUR on VHI policies for herself and her child. Vika had no other expenses for treatment, training or insurance. The social deduction for 2019 will be 61,000 R, which is less than the annual limit. Vika will be able to return 13% of this amount - 7930 R. The unused balance of the maximum possible deduction in the amount of 59 000 R will be burned. It cannot be transferred to 2020 and added to the new annual limit. Next year, the maximum amount of the social deduction will again be 120,000 R, and so every year.
Spouse's expenses example. If Vika paid the policy for herself and the child, she will claim 61,000 R for deduction and return 7930 R of tax from the budget. Vika's husband spent only 20,000 R on his policy - this is the amount of contributions that the employer deducted from his salary for insurance. He will be refunded 2600 R, that is, 13% of the actual costs of VHI, and not of the entire cost of the policy, since the employer paid part of the money. In total, Vika and her husband will be able to return 10,530 rubles from the budget.
In total, Vika and her husband will be able to return 10,530 rubles from the budget.
/edumed-vychet/
Social deductions calculator
Documents for deduction
To receive a tax deduction for VMI expenses, you will need copies of the following documents:
- Agreement with an insurance company or insurance policy. It must be drawn up in favor of the person who pays for the policy and claims the deduction, or in favor of his spouse, children or parents.
- Insurance company license. If these licenses are in the contract, you don’t have to attach a copy: the tax authorities will check it themselves.
- Documents for payment of insurance premiums: checks, receipts, payments.
- Birth or marriage certificate, if the policy is for family members.
- Certificate 2-NDFL on salary for the year in which the policy was paid.
These documents can be attached to an electronic declaration or sent along with an application for confirmation of the right to a deduction.
How to get a deduction from an employer
You can get a social tax deduction for VHI expenses during the current year at work. But only if there is an employment contract, according to civil law, this will not work.
To do this, you need to take a tax notice of the right to deduct. This can be done right in the middle of the year, right after purchasing the policies. The notice will be ready in a month. It must be taken to work - next month, when calculating the tax, the tax base will be reduced by the amount of the deduction, and personal income tax will be calculated only from the difference. If the deduction is more than a monthly salary, the balance will be transferred to the next month and personal income tax will be reduced again - and so on until the deduction ends.
So what? 27.02.19
How to get a tax deduction through an employer without a declaration
An application can be submitted through a personal account or go to the tax office in person. If you have the right to a property deduction, determine in advance the order in which the deductions will be received so as not to lose money.
If you have the right to a property deduction, determine in advance the order in which the deductions will be received so as not to lose money.
How to return tax on a declaration
If you do not have an employment contract or you do not want to bring deduction documents to your employer, the tax can be returned on a declaration next year. Then the employer will not be aware of the return, and the money will come to the card directly from the budget.
You can receive a deduction on the declaration only when the year in which you paid for VHI ends. The tax office will check the documents for three months and return the money for another month. It happens earlier, but according to the law, these are the maximum terms. If you submit a declaration in January, you should wait for the money around May.
/zapolneno/
How to fill out a medical deduction declaration
If you have a question about personal finances, rights and laws, health or education, write to us.



 035 requires that dependents retain coverage beyond age of policy termination if they are incapable of self-sustaining employment due to disability.
035 requires that dependents retain coverage beyond age of policy termination if they are incapable of self-sustaining employment due to disability.

 If the dependent child is mentally or physically impaired, the plan must continue their coverage after the specified age.
If the dependent child is mentally or physically impaired, the plan must continue their coverage after the specified age. 


 S.A. § 627.6562
S.A. § 627.6562