How do you know your child is autistic
Signs of autism in children
Autism in young children
Signs of autism in young children include:
- not responding to their name
- avoiding eye contact
- not smiling when you smile at them
- getting very upset if they do not like a certain taste, smell or sound
- repetitive movements, such as flapping their hands, flicking their fingers or rocking their body
- not talking as much as other children
- not doing as much pretend play
- repeating the same phrases
Autism in older children
Signs of autism in older children include:
- not seeming to understand what others are thinking or feeling
- unusual speech, such as repeating phrases and talking ‘at’ others
- liking a strict daily routine and getting very upset if it changes
- having a very keen interest in certain subjects or activities
- getting very upset if you ask them to do something
- finding it hard to make friends or preferring to be on their own
- taking things very literally – for example, they may not understand phrases like "break a leg"
- finding it hard to say how they feel
Autism in girls and boys
Autism can sometimes be different in girls and boys.
Autistic girls may:
- hide some signs of autism by copying how other children behave and play
- withdraw in situations they find difficult
- appear to cope better with social situations
- show fewer signs of repetitive behaviours
This means autism can be harder to spot in girls.
The National Autistic Society has more information about autistic women and girls.
Non-urgent advice: Get advice if:
- you think your child might be autistic
You could speak to:
- a GP
- a health visitor (for children under 5)
- any other health professional your child sees, such as another doctor or therapist
- special educational needs (SENCO) staff at your child's school
Getting diagnosed can help your child get any extra support they might need.
Find out how to get diagnosed
Page last reviewed: 11 November 2022
Next review due: 11 November 2025
Learn the Signs of Autism
One of the most important things you can do as a parent or caregiver is to learn the early signs of autism and become familiar with the typical developmental milestones that your child should be reaching.
The autism diagnosis age and intensity of autism’s early signs vary widely. Some infants show hints in their first months. In others, behaviors become obvious as late as age 2 or 3.
Not all children with autism show all the signs. Many children who don’t have autism show a few. That’s why professional evaluation is crucial.
The following may indicate your child is at risk for an autism spectrum disorder. If your child exhibits any of the following, ask your pediatrician or family doctor for an evaluation right away:
By 6 months
- Few or no big smiles or other warm, joyful and engaging expressions
- Limited or no eye contact
By 9 months
- Little or no back-and-forth sharing of sounds, smiles or other facial expressions
By 12 months
- Little or no babbling
- Little or no back-and-forth gestures such as pointing, showing, reaching or waving
- Little or no response to name
By 16 months
- Very few or no words
By 24 months
- Very few or no meaningful, two-word phrases (not including imitating or repeating)
At any age
- Loss of previously acquired speech, babbling or social skills
- Avoidance of eye contact
- Persistent preference for solitude
- Difficulty understanding other people’s feelings
- Delayed language development
- Persistent repetition of words or phrases (echolalia)
- Resistance to minor changes in routine or surroundings
- Restricted interests
- Repetitive behaviors (flapping, rocking, spinning, etc.
 )
) - Unusual and intense reactions to sounds, smells, tastes, textures, lights and/or colors
If you have concerns, get your child screened and contact your healthcare provider
The M-CHAT (Modified Checklist for Autism in Toddlers ™) can help you determine if a professional should evaluate your child. This simple online autism screen, available on our website, takes only a few minutes. If the answers suggest your child has a high probability for autism, please consult with your child’s doctor. Likewise, if you have any other concerns about your child's development, don't wait. Speak to your doctor now about screening your child for autism.
Resources
A diagnosis of autism is an important turning point in a long journey to understand your child's world. Autism Speaks has many resources for families whose children have recently received a diagnosis.
These include Autism Speaks First Concern to Action Tool Kit and First Concern to Action Roadmap.
Signs of autism in adults and teens
Do you suspect that your feelings and behaviors involve autism? Many people who have milder forms of autism go undiagnosed until adulthood. Find out more in our guide: "Is it Autism and If So, What Next?"
Please visit Treatment of Autism and our Autism Speaks Directory for more information. Have more questions? Autism Speaks' Autism Response Team can help you with information, resources and opportunities. Call us at 888-288-4762 (en Español 888-772-9050) or email [email protected].
Recent research confirms that appropriate screening can determine whether a child is at risk for autism as young as one year. While every child develops differently, we also know that early treatment improves outcomes, often dramatically. Studies show, for example, that early intensive behavioral intervention improves learning, communication and social skills in young children with autism spectrum disorders (ASD).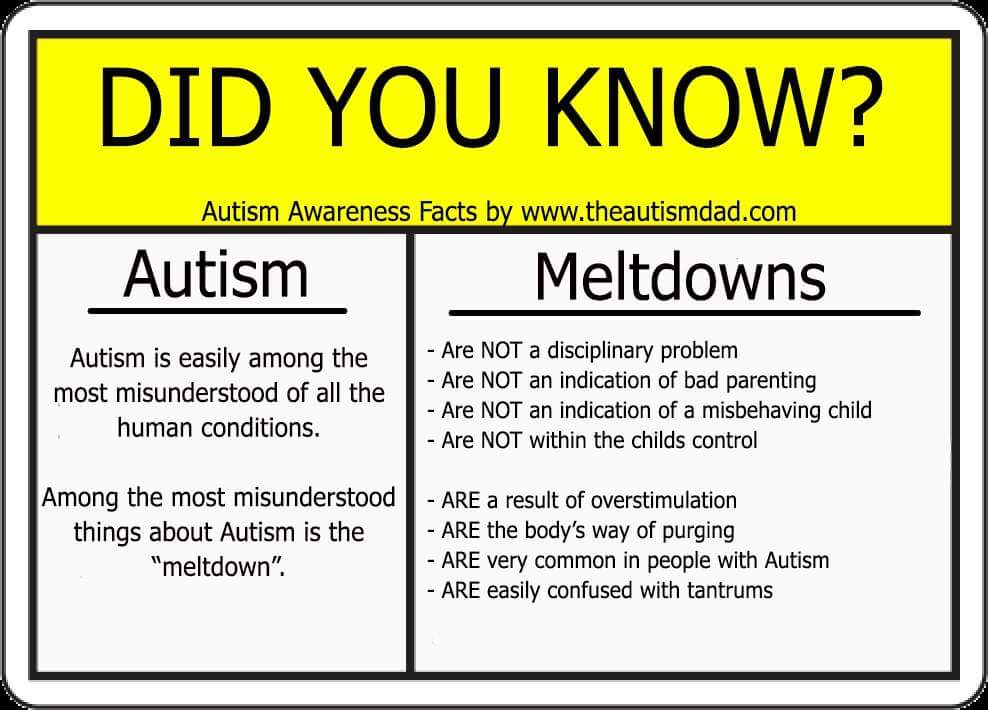
How to understand if your child has autism: six tips to parents
Fresh number
RG-week
Rodina
thematic applications
Union
Fresh number
04/11/2021 09:00
Category:
Society
Irina Ivoilova
How does the speech of autistic children change? Why are they often mistaken for deaf people? Do they have a pointing gesture? Is it possible to send such a child to a regular school? The readers of "RG" are told about this by the candidate of psychological sciences, leading researcher at the Moscow State Psychological and Pedagogical University, researcher at the University of Gothenburg Elena Orekhova.
iStock
Elena Vladimirovna, the parents of babies are most afraid of something going wrong with their child? Suddenly autism? How to recognize it?
Elena Orekhova: Autism is now diagnosed solely by behavior. Before the age of one, it is almost impossible to say with certainty whether a child has autism. Until that time, a small child can behave in exactly the same way as all other babies, look into the eyes, react to people. Scientists in the West are doing research trying to understand what are the earliest signs of autism. Parents who already have older children diagnosed with autism are invited to participate in such studies. The risk of autism in younger children in such families is increased, which gives scientists the opportunity to trace the early development of children with this diagnosis. At one time I worked in London in one of the laboratories where such research was carried out. There have been suggestions that children with autism do not need to communicate from birth. But it turned out that this was not the case. At three months, they looked into the eyes of another person even more than ordinary babies. As I got older, eye contact became less and less.
Until that time, a small child can behave in exactly the same way as all other babies, look into the eyes, react to people. Scientists in the West are doing research trying to understand what are the earliest signs of autism. Parents who already have older children diagnosed with autism are invited to participate in such studies. The risk of autism in younger children in such families is increased, which gives scientists the opportunity to trace the early development of children with this diagnosis. At one time I worked in London in one of the laboratories where such research was carried out. There have been suggestions that children with autism do not need to communicate from birth. But it turned out that this was not the case. At three months, they looked into the eyes of another person even more than ordinary babies. As I got older, eye contact became less and less.
What signs will tell moms and dads that something is wrong with a child?
Elena Orekhova:
1. An important symptom: speech delay, which is observed in almost all children with autism. Before a year, a child should be babbling, after a year he says separate words, a little later - sentences. If none of this is present before the age of two, it is not necessarily autism, but there is cause for concern. Most children with autism, although late, begin to speak, but their intonation suffers.
An important symptom: speech delay, which is observed in almost all children with autism. Before a year, a child should be babbling, after a year he says separate words, a little later - sentences. If none of this is present before the age of two, it is not necessarily autism, but there is cause for concern. Most children with autism, although late, begin to speak, but their intonation suffers.
2. Normal children raise or lower their tone to emphasize what is being said, while children with autism are often perceived as strange: they either speak monotonously or place accents incorrectly. At the MEG Center, we recently conducted a study in which we found that the left 'verbal' hemisphere of children with autism processes complex sounds differently from normal children. Now we want to find out how this disorder affects the development of speech. We invite both families of children with autism and children with typical development to participate in our study.
3. Another early sign of autism, oddly enough, is the suspicion of deafness. Parents often think that their child has a hearing impairment. They turn to him: "Kolya! Petya! Look ..." But he does not react. In a recent study conducted at the MEG Center, we found that half of the parents of autistic children during the first year and a half of life suspected that the child was not all right with hearing. In fact, his hearing is all right. But he does not respond, because he is completely immersed in the occupation that interests him.
Excuse me, but if a bucket falls with a roar next to an autistic child, will he react to this noise?
Elena Orekhova: Maybe yes, maybe no. These children often react in atypical ways to their environment.
4. The child may be annoyed by a slight noise outside the window, a light touch, a bright light. At the same time, he may not react to the roar, be insensitive to pain.
5. Another hint for parents: it is difficult for a child to ask you for something. Let's say he needs a pencil. He can take your hand and use it to try to get a pencil.
6. An autistic child does not have a pointing gesture. He won't point his finger at his favorite toy and ask for it.
It still happens that mothers in maternity hospitals are sometimes advised: abandon the child, he will not even recognize you. Does a child with autism understand that he has significant adults - parents, does he feel affection for them?
Elena Orekhova: Yes, the child is attached to his parents. He will feel sorry for his mother, because she is in pain, but it is difficult for him to understand feelings of a "higher order" - resentment, insult.
Can a child with autism be sent to a regular school?
Elena Orekhova: Such children often have sensory problems - the school environment can be simply unbearable for them. Flickering, screaming, noise, fuss: all this can cause a lot of stress, not at all contributing to normal learning. To calm down, the child may want to plug his ears, crawl under the desk.
Flickering, screaming, noise, fuss: all this can cause a lot of stress, not at all contributing to normal learning. To calm down, the child may want to plug his ears, crawl under the desk.
Another problem is the unpredictability of the environment. For a child with autism, it is important that he knows what follows what and in what order. If the daily routine or sequence of events is disturbed in an unpredictable way, this also causes stress. Being among people is also difficult for them because people are often unpredictable. It is difficult for such children to understand the school rules, and they may not behave as the teacher wants. Maybe parents are pleased when such a child goes to a regular school, but, in the final analysis, one must also think about the child himself, create sparing conditions for him. Although, of course, everything is individual. Some children with autism and good speech and cognitive abilities (formerly known as Asperger's syndrome) can go to a regular school. But you need to carefully monitor how the child feels at school. Often such children can be not only uncommunicative, but also clumsy, becoming the object of ridicule and bullying from classmates.
But you need to carefully monitor how the child feels at school. Often such children can be not only uncommunicative, but also clumsy, becoming the object of ridicule and bullying from classmates.
Children are cruel... And not only to special peers
Elena Orekhova: It is necessary to tell schoolchildren that people are different and that this is normal. In Sweden, for example, ordinary schools hold lessons where children are offered to try to ride in a wheelchair, read Braille texts for the blind, and learn some words in the language of the deaf and dumb. They are told that there are people with special needs and that everyone should be treated with respect and no one should be offended. At the same time, correctional classes and schools have been preserved there. And in Sweden, the diagnosis of autism is by no means a sentence. There was a case in Gothenburg when a girl graduated from a technical university, then a medical one, and got a job in an ambulance as a doctor. And then she had a nervous breakdown: it turned out to be extremely difficult for her to work with people. She went to a psychiatrist, who diagnosed her with autism. This turned out to be a great relief for her, as she finally understood the source of her problems. I must say that after that she successfully engaged in science, studying the work of the brain in people with mental disorders. Our brain is a real puzzle. This is what scientists have already figured out.
And then she had a nervous breakdown: it turned out to be extremely difficult for her to work with people. She went to a psychiatrist, who diagnosed her with autism. This turned out to be a great relief for her, as she finally understood the source of her problems. I must say that after that she successfully engaged in science, studying the work of the brain in people with mental disorders. Our brain is a real puzzle. This is what scientists have already figured out.
Family and the children's -heart
The main thing today is
-
In the center of Vienna hundreds of people went to a rally against Austria's participation in the conflict in Ukraine
-
WSJ: the Armed Forces of Ukraine lost several of the most prepared divisions
-
Zakharova, which said that Blinken's "talk" with Lavrov is an action before the US elections
-
Senator Klimov: the US will find a replacement for Scholz if he tries to "jump"
-
The Ministry of Foreign Affairs of the Russian Federation listed 11 countries that can become visa-free for Russians
-
Bloomberg: Britain has suspended gas supplies to Europe Clinic for children and adolescents
Clinical manifestations of childhood autism are variable: the symptoms in some cases may resemble mild forms of depression, in others they may resemble serious mental disorders.
 With careful attention to the baby, the earliest messengers of pathology can be seen already in infancy.
With careful attention to the baby, the earliest messengers of pathology can be seen already in infancy. The first signs of autism in children at an early age are:
- refusal of tactile contacts - the child cries when he is picked up, turns away, bends, and calms down only after he is returned to the crib;
- passivity in response to parents' appeal, lack of attention, interest during adult communication;
- a sharp reaction to loud noises;
- indifference to bright, rattling, whistling and squeaking toys with which adults try to entertain the child;
- indifference to standard toys, attempt to play with unsuitable objects.
As children grow older, symptoms of autism in children may include:
- absence of speech at the age of 1.5–3 years with a rich vocabulary and understanding of adult conversation;
- echolalia - uncontrolled copying and repeated repetition of sounds uttered by another person;
- perseveration - "getting stuck" on a phrase, word that the child constantly repeats, or emotions, or a task, while the child tirelessly ponders the idea that has swallowed him, but does not take any steps towards achieving the goal;
- refusal to comply with the game rules specified by adults or peers, and this refusal is not motivated by the child’s personal decision, his disagreement, he simply does not understand why some installations and restrictions are needed;
- difficulty in perceiving other people's emotions: children with autism do not understand why other children laugh at some teacher's phrase or why a girl who has been pulled by a pigtail is crying; such children may not have access to humor, sarcasm, irony;
- no response to own name;
- unwillingness to look directly into the eyes when communicating, answering or addressing, including in situations with parents or other close people;
- lack of fear, fear in life-threatening or health-threatening circumstances;
- tantrums, violent expressions of emotions when the usual environment changes, when strangers appear, etc.
 ;
; - restless, restless sleep with frequent awakenings.
Children with autism prefer to be alone, do not participate in group activities, it is difficult to force them to do something together with other children. They try to leave, hide where they will not be touched. Such children come up with their own games, incomprehensible to their peers, and constantly play them. From the side of people around, the movements of an autistic child may seem strange, devoid of meaning.
In many series and films that show the life of people with ASD, autistic characters are presented as strange but brilliant characters who avoid communication, offend others with their directness, but show excellent results in their professional activities. In life, unfortunately, everything is different: most often, children with autism develop mental retardation due to impaired functions of the cerebral cortex. Studying is given to them with difficulty, they are not able to understand the patterns, learn the rules, delve into the solution of the problem.