Discharge and spotting during pregnancy
Bleeding and spotting from the vagina during pregnancy
Bleeding and spotting from the vagina during pregnancy are common
If you bleed or spot during pregnancy, it doesn’t always mean there’s a problem but in some cases they may be signs of a problem for you or your baby’s health
If you have heavy bleeding, call your health care provider right away
Tell your provider about any bleeding or spotting you have during pregnancy
Bleeding and spotting from the vagina during pregnancy are common. Up to 1 out of 4 (up to 25%) of all pregnant women have some bleeding or spotting during their pregnancy.
Bleeding and spotting in pregnancy don’t always mean there’s a problem, but they can be a sign of miscarriage or other serious complications. Miscarriage is when a baby dies in the womb before 20 weeks of pregnancy.
Call your health care provider if you have any bleeding or spotting, even if it stops. It may not be caused by anything serious, but your provider needs to find out what’s causing it.
What’s the difference between bleeding and spotting?
Bleeding or spotting can happen anytime, from the time you get pregnant to right before you give birth. Spotting is light bleeding. It happens when you have a few drops of blood on your underwear. Spotting is so light that the blood wouldn’t cover a panty liner. Bleeding is when the blood flow is heavier, enough that you need a panty liner or pad to keep the blood from soaking your underwear and clothes.
What should you do if you have bleeding or spotting during pregnancy?
Call your health care provider if you have any kind of bleeding during pregnancy and do these things:
- Keep track of how heavy your bleeding is, if it gets heavier or lighter, and how many pads you are using.
- Check the color of the blood. Your provider may want to know. It can be different colors, like brown, dark or bright red.
- Don’t use a tampon, douche or have sex when you’re bleeding.

Call your health care provider right away at any time during pregnancy or go to the emergency room if you have:
- Heavy bleeding
- Bleeding with pain or cramping
- Dizziness and bleeding
- Pain in your belly or pelvis
What causes bleeding or spotting early in pregnancy?
It’s normal to have some spotting or bleeding early in pregnancy. Bleeding or spotting in the first trimester may not be a problem. It can be caused by:
- Having sex
- An infection
- Implantation. When a fertilized egg (embryo) attaches to the lining of the uterus (womb) and begins to grow.
- Hormone changes. Hormones are chemicals made by the body.
- Changes in your cervix. The cervix is opening to the uterus that sits at the top of the vagina.
- Certain types of testing during pregnancy like an amniocentesis or Chorionic villus sampling (CVS). These are tests that are done to check for genetic abnormalities in your baby.
 Genetic abnormalities are changes in the genes that are passed down to a baby from mom or dad. These genetic changes can cause health problems for a baby.
Genetic abnormalities are changes in the genes that are passed down to a baby from mom or dad. These genetic changes can cause health problems for a baby. - Problems related to smoking. If you smoke, it’s best to stop before pregnancy or as soon as you know you’re pregnant.
Sometimes bleeding or spotting in the first trimester is a sign of a serious problem, like:
- Miscarriage. Almost all women who miscarry have bleeding or spotting before the miscarriage.
- Ectopic pregnancy. This is when a fertilized egg implants itself outside of the uterus and begins to grow. An ectopic pregnancy cannot result in the birth of a baby. It can cause serious, dangerous problems for the pregnant woman.
- Molar pregnancy. This is when a mass of tissue forms inside the womb, instead of a baby. Molar pregnancy is rare.
What causes bleeding or spotting later in pregnancy?
Bleeding or spotting later in pregnancy may be caused by:
- Labor
- Having sex
- An internal exam by your health care provider
- Problems with the cervix, like an infection, growths, inflammation or cervical insufficiency.
 This is when a woman’s cervix opens too early. Inflammation of the cervix is when it may be painful, swollen, red or irritated.
This is when a woman’s cervix opens too early. Inflammation of the cervix is when it may be painful, swollen, red or irritated.
Bleeding or spotting later in pregnancy may be a sign of a serious problem, like:
- Preterm labor. This is labor that happens too early, before 37 weeks of pregnancy.
- Placenta previa. This is when the placenta lies very low in the uterus and covers all or part of the cervix.
- Placenta accreta. This is when the placenta grows into the wall of the uterus too deeply.
- Placental abruption. This is when the placenta separates from the wall of the uterus before birth.
- Uterine rupture. This is when the uterus tears during labor. This happens very rarely. It can happen if you have a scar in the uterus from a prior cesarean birth (also called c-section) or another kind of surgery on the uterus.
 A c-section is surgery in which your baby is born through a cut that your doctor makes in your belly and uterus.
A c-section is surgery in which your baby is born through a cut that your doctor makes in your belly and uterus.
How are bleeding and spotting treated?
Your treatment depends on what caused your bleeding. You may need a medical exam and tests.
Most of the time, treatment for bleeding or spotting is rest. Your provider may also suggest treatments like:
- Take time off from work and stay off your feet for a little while
- You may need medicine to help protect your baby from Rh disease. Rh disease is when your blood and baby’s blood are incompatible (can’t be together). This disease can cause serious problems — even death — for your baby.
- Don’t have sex, douche or use tampons
- If you have heavy bleeding, you may need a hospital stay or surgery
Last reviewed April 2020
Vaginal bleeding in early pregnancy: MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia
Vaginal bleeding during pregnancy is any discharge of blood from the vagina. It can happen any time from conception (when the egg is fertilized) to the end of pregnancy.
It can happen any time from conception (when the egg is fertilized) to the end of pregnancy.
Some women have vaginal bleeding during their first 20 weeks of pregnancy.
Spotting is when you notice a few drops of blood every now and then on your underwear. It is not enough to cover a panty liner.
Bleeding is a heavier flow of blood. With bleeding, you will need a liner or pad to keep the blood from soaking your clothes.
Ask your health care provider more about the difference between spotting and bleeding at one of your first prenatal visits.
Some spotting is normal very early in pregnancy. Still, it is a good idea to tell your provider about it.
If you have had an ultrasound that confirms you have a normal pregnancy, call your provider the day you first see the spotting.
If you have spotting and have not yet had an ultrasound, contact your provider right away. Spotting can be a sign of a pregnancy where the fertilized egg develops outside the uterus (ectopic pregnancy). An untreated ectopic pregnancy can be life-threatening for the woman.
An untreated ectopic pregnancy can be life-threatening for the woman.
Bleeding in the 1st trimester is not always a problem. It may be caused by:
- Having sex.
- An infection.
- The fertilized egg implanting in the uterus.
- Hormone changes.
- Other factors that will not harm the woman or baby.
- A threatened miscarriage. Many threatened miscarriages do not progress to pregnancy loss.
More serious causes of first-trimester bleeding include:
- A miscarriage, which is the loss of the pregnancy before the embryo or fetus can live on its own outside the uterus. Almost all women who miscarry will have bleeding before a miscarriage.
- An ectopic pregnancy, which may cause bleeding and cramping.
- A molar pregnancy, in which a fertilized egg implants in the uterus that will not come to term.
Your provider may need to know these things to find the cause of your vaginal bleeding:
- How far along is your pregnancy?
- Have you had vaginal bleeding during this or an earlier pregnancy?
- When did your bleeding begin?
- Does it stop and start, or is it a steady flow?
- How much blood is there?
- What is the color of the blood?
- Does the blood have an odor?
- Do you have cramps or pain?
- Do you feel weak or tired?
- Have you fainted or felt dizzy?
- Do you have nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea?
- Do you have a fever?
- Have you been injured, such as in a fall?
- Have you changed your physical activity?
- Do you have any extra stress?
- When did you last have sex? Did you bleed afterward?
- What is your blood type? Your provider can test your blood type.
 If it is Rh negative, you will need treatment with a medicine called Rho(D) immune globulin to prevent complications with future pregnancies.
If it is Rh negative, you will need treatment with a medicine called Rho(D) immune globulin to prevent complications with future pregnancies.
Most of the time, the treatment for bleeding is rest. It is important to see your provider and have testing done to find the cause of your bleeding. Your provider may advise you to:
- Take time off work
- Stay off your feet
- Not have sex
- Not douche (NEVER do this during pregnancy, and also avoid it when you are not pregnant)
- Not use tampons
Very heavy bleeding may require a hospital stay or surgical procedure.
If something other than blood comes out, call your provider right away. Put the discharge in a jar or a plastic bag and bring it with you to your appointment.
Your provider will check to see if you are still pregnant. You will be closely watched with blood tests to see if you are still pregnant.
If you are no longer pregnant, you may need more care from your provider, such as medicine or possibly surgery.
Call or go to your provider right away if you have:
- Heavy bleeding
- Bleeding with pain or cramping
- Dizziness and bleeding
- Pain in your belly or pelvis
If you cannot reach your provider, go to the emergency room.
If your bleeding has stopped, you still need to call your provider. Your provider will need to find out what caused your bleeding.
Miscarriage - vaginal bleeding; Threatened abortion - vaginal bleeding
Francois KE, Foley MR. Antepartum and postpartum hemorrhage. In: Landon MB, Galan HL, Jauniaux ERM, et al, eds. Gabbe's Obstetrics: Normal and Problem Pregnancies. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 18.
Salhi BA, Nagrani S. Acute complications of pregnancy. In: Walls RM, Hockberger RS, Gausche-Hill M, eds. Rosen's Emergency Medicine: Concepts and Clinical Practice. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2018:chap 178.
Updated by: John D. Jacobson, MD, Professor of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Loma Linda University School of Medicine, Loma Linda Center for Fertility, Loma Linda, CA. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
Browse the Encyclopedia
articles of the Oxford Medical clinic Kyiv
Contents:
-
What discharge during pregnancy is considered normal?
-
When should you see a doctor for discharge?
-
Discharge during early pregnancy
-
Discharge during late pregnancy
-
Discharge during pregnancy by color0005
During pregnancy, a woman's body undergoes a number of physiological changes - her body changes, adapts to carrying a baby and future childbirth. Changes can also occur with vaginal discharge. After conception, their number or color may become different, which often makes a woman worry. In order not to worry for no reason, but also not to miss a possible reason to see a doctor, you need to know which discharges are normal and which are not.
After conception, their number or color may become different, which often makes a woman worry. In order not to worry for no reason, but also not to miss a possible reason to see a doctor, you need to know which discharges are normal and which are not.
What discharge during pregnancy is considered normal?
The nature of the discharge at different stages of pregnancy may vary slightly. Standard variant are:
-
transparent or white discharge;
-
odor free;
-
not exceeding the usual volume;
-
not accompanied by itching, burning or other painful symptoms.
At the same time, in the first 2-4 weeks, the daily discharge may increase slightly and become thicker.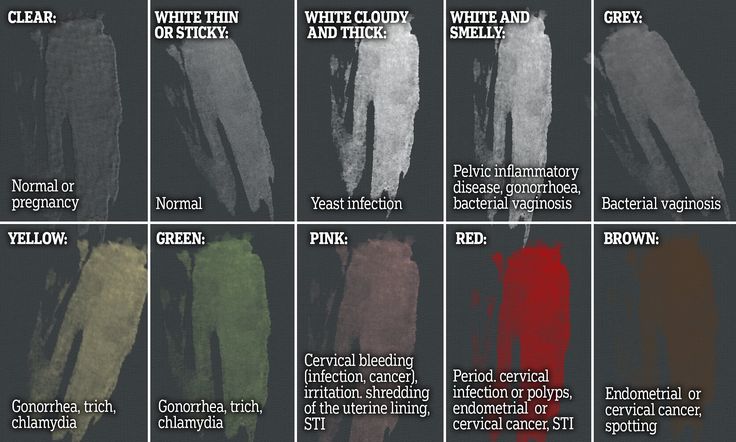 It is also possible the appearance of light spotting within a few hours or a day, which occurs as a result of the implantation of the embryo to the uterine wall.
It is also possible the appearance of light spotting within a few hours or a day, which occurs as a result of the implantation of the embryo to the uterine wall.
When should you see a doctor for discharge?
During pregnancy, a woman is advised to visit a gynecologist regularly for examinations and tests. First, consultations are prescribed once a month, and then once every 2 weeks. This allows you to carefully monitor the health of the pregnant woman and the development of the fetus. But, if discomfort appears, you need to see a doctor as soon as possible.
One of the alarming symptoms is the appearance of atypical discharge:
-
yellow, green, brown;
-
bloody;
-
thick;
-
too abundant;
-
slimy;
-
malodorous;
-
accompanied by itching, burning and other symptoms.

Such a change in the nature of the discharge may be associated with the development of an inflammatory or infectious disease, as well as complications of pregnancy. To find out the exact cause, you need to do tests, conduct an ultrasound and, if necessary, other studies.
Discharge during early pregnancy
When conception occurs, changes begin in the body. First of all, the synthesis of the hormone progesterone increases and blood flow to the pelvic organs increases. These processes are often accompanied by profuse vaginal discharge. They can be translucent, white or with a slight yellowish tint. There should be no unpleasant odor or skin irritation.
Shortly thereafter, progesterone levels decrease and estrogen levels rise. At this time, a mucous plug is formed that covers the cervix. Its formation can also cause increased secretion, but gradually it should decrease and become more liquid and transparent.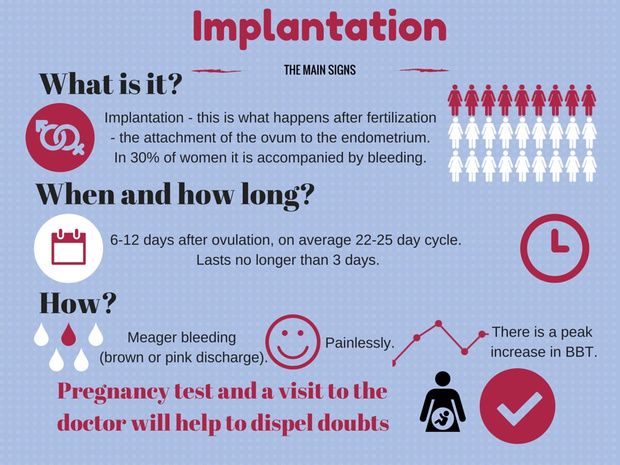
In addition, in the first weeks, the ovum attaches to the wall of the uterus, which can cause light brown discharge. As a rule, they are scarce and quickly stop - within a few hours or a day. If heavy bleeding has begun, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Approximately from 5 to 20 weeks, the discharge should be the same - transparent or whitish, in small volume, odorless.
Discharge in late pregnancy
From 20 to 40 weeks of pregnancy, the discharge is normally white, free of impurities and unpleasant odor.
In the last week before childbirth, the discharge may become thinner. If they are very abundant, leakage or discharge of amniotic fluid is possible, which requires a visit to a doctor.
Characterization of pregnancy discharge by color
Normal discharge should be colorless or white. A change in color and consistency may indicate the development of a disease or complications of pregnancy.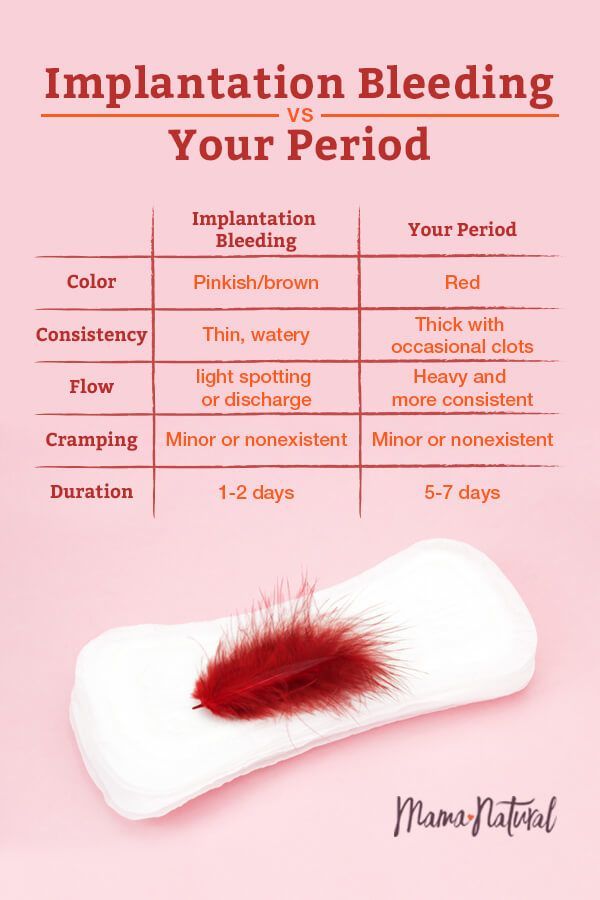
Bright or dark yellow discharge most often occurs when inflammation develops. Grey-green and green may result from infection. Thick white discharge speaks about it - as a rule, candidiasis manifests itself. Brown discharge may be due to slight bleeding.
Oxford Medical says it is important to consider not only the color of the discharge, but also its smell, volume and consistency. A sharp and unpleasant odor appears only with bacterial or fungal diseases, so it should by no means be ignored. Also, an alarming signal is a strong increase in the volume of secretions, a change in structure, foaminess and other deviations from the norm.
There can be many reasons for abnormal discharge. To find them out, you need to conduct examinations, and then, if necessary, treatment.
Bloody discharge during pregnancy
The appearance of bloody discharge at any stage of pregnancy is a reason to immediately consult a doctor.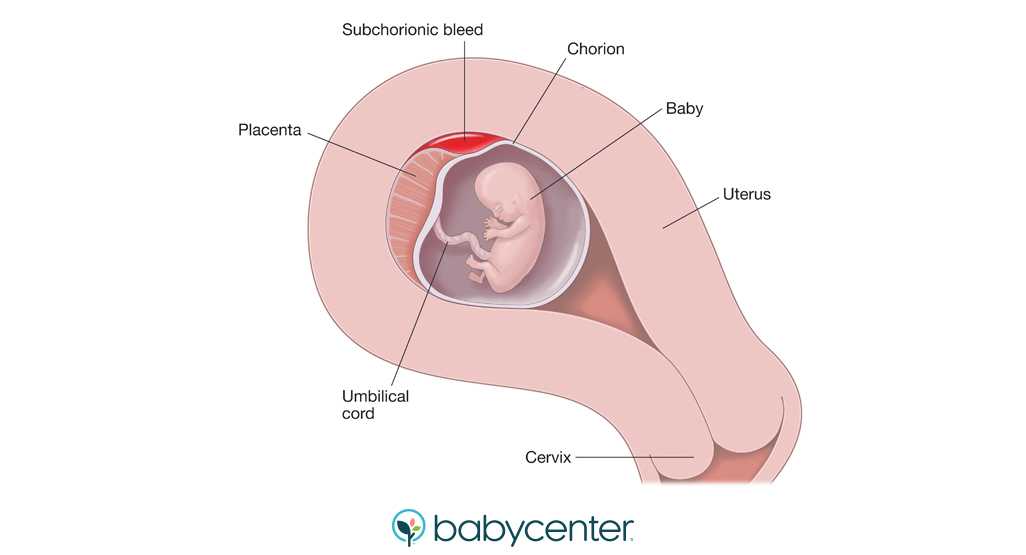
The exception is small spotting in the first weeks (usually the date of the expected menstruation), which indicates the implantation of the embryo. At this point, capillaries and small vessels can be injured, which causes light bleeding. Normally, it is very weak, not accompanied by pain or other unpleasant symptoms.
Blood-streaked discharge may also occur on the eve of childbirth as a result of cervical dilatation. This is normal, but a doctor's consultation is required.
In other cases, both in the first and last trimester, any discharge from pale pink and brown to red is a dangerous symptom. The violation may be minor, but it is necessary to conduct an examination.
Bleeding can be caused by:
-
hormonal disorders;
-
cervical erosion;
-
cysts;
-
fibroids;
-
inflammatory and infectious diseases;
-
ectopic pregnancy;
-
miscarriage;
-
placental abruption;
-
threatened miscarriage or premature birth.

Regular follow-up with an experienced obstetrician-gynecologist and the implementation of all recommendations will help to avoid possible complications and concentrate on the most important thing - the joyful expectation of the baby and preparation for meeting him.
In early pregnancy, bleeding occurs in 25% of women. In most cases, they are associated with the implantation of the fetal egg to the wall of the uterus. Also, scanty spotting may appear on the dates of the expected menstruation. If they end quickly, are not accompanied by pain, and the woman has not had miscarriages or pregnancy complications before, most likely she has nothing to worry about. However, it is necessary to consult an obstetrician-gynecologist and undergo an examination.
Why bloody discharge can appear and when it is dangerous, said the doctor of the highest category obstetrician-gynecologist, gynecologist-endocrinologist, ultrasound specialist of the ADONIS Medical Center Elena Petrovna Domnich.
Elena Nikolaevna, tell me, can a woman have periods during pregnancy?
- Sometimes during pregnancy, a woman may experience spotting, but this should not be interpreted as menstruation. Menstruation occurs at the end of the menstrual cycle, during which the endometrium changes, first proliferative, then secretory. During the cycle, the endometrium prepares for pregnancy, and if it does not occur, then menstruation begins.
In the event of a pregnancy, menstruation is not possible, although spotting may occur at the expected time. Because of this, some women do not immediately know that they are pregnant. However, when the obstetrician-gynecologist at the reception asks them about the nature of the discharge, it always turns out that they are different from menstrual. As a rule, they are more scarce, pass faster and are not accompanied by other symptoms. Sometimes a woman says that her period was very recent, but at the time of examination and examination, we find that she is already 8 or 12 weeks pregnant.
How often does this happen? Is spotting during pregnancy an exception or a fairly common occurrence?
- Bleeding occurs infrequently in pregnant women, but still it cannot be said that these are exceptional cases.
Tell me, if a woman is planning to conceive a child, and during the expected period she has atypical discharge, does she need to take a pregnancy test?
- Yes, but it's better to visit an obstetrician-gynecologist. There are cases when a woman is pregnant, but the test strip shows a negative result. To accurately determine whether there is a pregnancy, allows a blood test for the level of hCG.
So bleeding during pregnancy is not menstruation, but bleeding? Why can it appear and why is it dangerous?
- Yes, that's right. This is bleeding, not menstruation. It can be a symptom of a miscarriage, ectopic pregnancy, or other pathology. For diagnosis, you must consult a doctor.
For diagnosis, you must consult a doctor.
Tell me more, if a woman has a discharge and thinks she is menstruating, but the previous pregnancy test came back positive, could it be wrong?
- A pregnancy test is sometimes positive even if it is not. This happens if a woman has formed luteal cysts or developed a thyroid disease.
Bloody discharge during pregnancy requires contacting the antenatal clinic or the medical center where the woman was registered for pregnancy management. Sometimes they may not be dangerous, but without diagnosis, it cannot be ruled out that this is a symptom of a serious disorder.
Bleeding may occur with:
- threatened miscarriage;
- ectopic pregnancy;
- infectious diseases of the reproductive system;
- cysts;
- myomas;
- cervical erosion;
- placental abruption;
- the threat of premature birth.
You can watch the video version of Elena Petrovna Domnich's interview here.