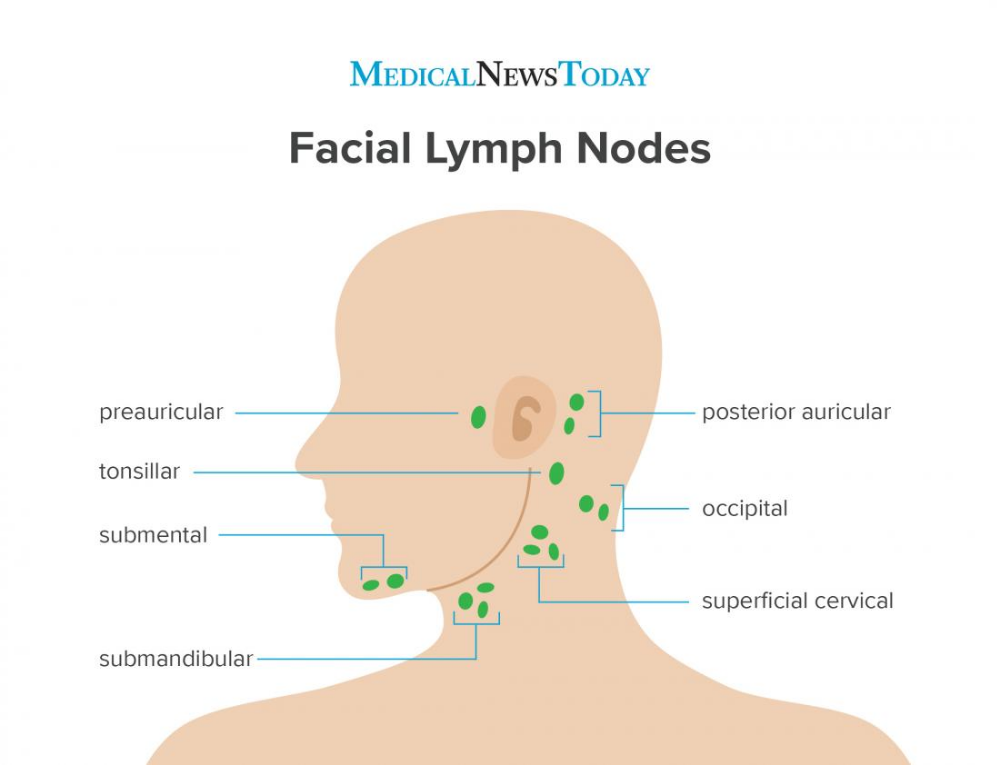
How do i know if child has ear infection
Ear Infections in Babies and Toddlers
Featured Expert:
Ear infections in babies and toddlers are extremely common. In fact, according to the National Institutes of Health, five out of six children will experience an ear infection before their third birthday.
"Many parents are concerned that an ear infection will affect their child's hearing irreversibly—or that an ear infection will go undetected and untreated," says David Tunkel, M.D., Johns Hopkins Medicine pediatric otolaryngologist (ENT). "The good news is that most ear infections go away on their own, and those that don't are typically easy to treat."
Childhood Ear Infections Explained
Ear infections happen when there is inflammation— usually from trapped bacteria—in the middle ear, the part of the ear connects to the back of the nose and throat. The most common type of ear infection is otitis media, which results when fluid builds up behind the eardrum and parts of the middle ear become infected and swollen.
If your child has a sore throat, cold, or an upper respiratory infection, bacteria can spread to the middle ear through the eustachian tubes (the channels that connect the middle ear to the throat). In response to the infection, fluid builds up behind the eardrum.
Children are more likely to suffer from ear infections than adults for two reasons:
- Their immune systems are underdeveloped and less equipped to fight off infections.
- Their eustachian tubes are smaller and more horizontal, which makes it more difficult for fluid to drain out of the ear.
"In some cases, fluid remains trapped in the middle ear for a long time, or returns repeatedly, even when there's no infection," Tunkel explains.
Ear Infection Signs and Symptoms
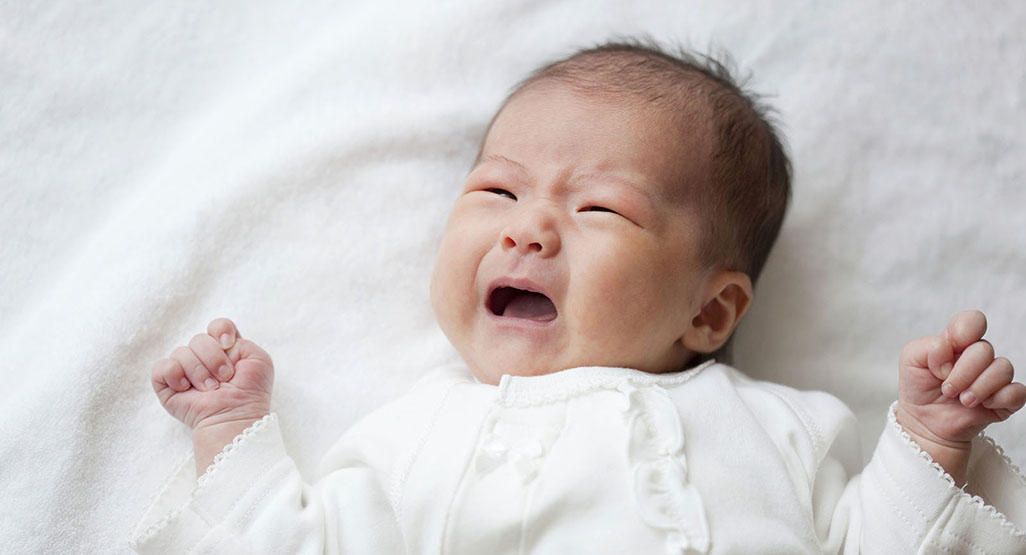
The telltale sign of an ear infection is pain in and around the ear. Young children can develop ear infections before they are old enough to talk. That means parents are often left guessing why their child appears to be suffering. When your child can't say "my ear hurts," the following signs suggest an ear infection could be the culprit:
Young children can develop ear infections before they are old enough to talk. That means parents are often left guessing why their child appears to be suffering. When your child can't say "my ear hurts," the following signs suggest an ear infection could be the culprit:
- Tugging or pulling the ear
- Crying and irritability
- Difficulty sleeping
- Fever, especially in younger children
- Fluid draining from the ear
- Loss of balance
- Difficulty hearing or responding to auditory cues
Signs that require immediate attention include high fever, severe pain, or bloody or pus-like discharge from the ears.
Pediatric Otolaryngology
Our pediatric otolaryngologists provide compassionate and comprehensive care for children with common and rare ear, nose, and throat conditions. As part of the Johns Hopkins Children's Center, you have access to all the specialized resources of a children's hospital.
Learn more about Pediatric Otolaryngology
Ear Infection Treatments
Most ear infections go away without treatment. "If your child isn't in severe pain, your doctor may suggest a 'wait-and-see' approach coupled with over-the-counter pain relievers to see if the infection clears on its own," Tunkel says.
The reason: Treating an infection with antibiotics may cause the bacteria causing the infections to become resistant to those antibiotics—and that makes treating future infections more difficult. Equally important, in most cases antibiotics aren't necessary. Otitis media tends to get better without them. While you may be tempted to treat your child's ear infection with homeopathic or natural medicine, Tunkel warns they aren’t well studied.
Your best bet is to work with your child's health care provider to determine the appropriate course of action. In nearly every case, treatment decisions depend on the child’s age, degree of pain and presenting symptoms.
Under 6 months
Babies under six months almost always receive antibiotics. At this age, children are not fully vaccinated. Equally important, there's no research about the safety of skipping antibiotics for babies under 6 months of age — and complications from ear infections can be more severe when they occur in young babies. Bacteria trapped behind the eardrum can spread to other parts of the body and cause serious infections.
6 months to 2 years
For children between the ages of 6 months and 2 years, the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) recommends shared decision-making between parents and providers about whether to treat ear infections that are not severe. The best course is often to watch the child for two to three days before prescribing antibiotic treatment. If the child is in pain, or the ear infection is advanced, your child's doctor may suggest immediate antibiotic treatment.
Over 2 years
With children over the age of 2, ear infections that are not severe are likely to clear on their own, without treatment. "In the meantime, you can treat pain with over-the-counter medications, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen," Tunkel says. If there's no improvement after two to three days, antibiotics may be warranted.
"In the meantime, you can treat pain with over-the-counter medications, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen," Tunkel says. If there's no improvement after two to three days, antibiotics may be warranted.
Unfortunately, some children suffer from recurrent ear infections, sometimes up to five or six a year. Kids who get repeated infections may benefit from a surgical procedure where doctors insert small tubes in the eardrums to improve air flow and prevent fluid buildup. "Tubes don't prevent all ear infections, but they make managing them significantly easier," Tunkel explains.
Ear Infection Prevention
There are several steps you can take to reduce your child's risk of developing ear infections, including:
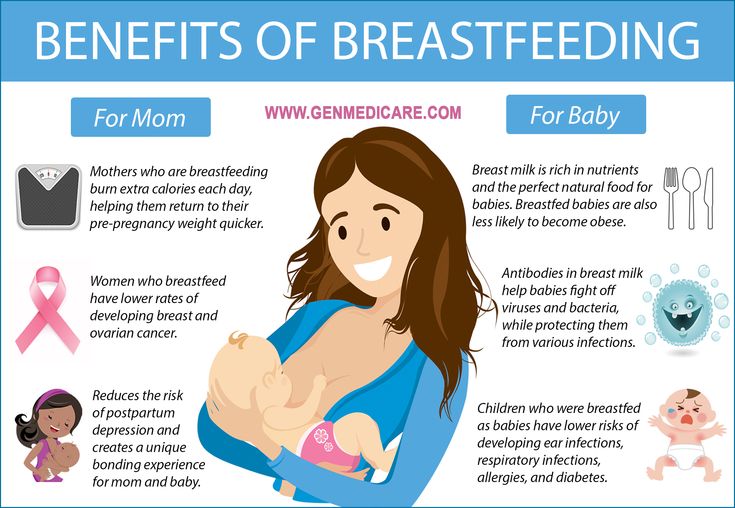
- Vaccinate your child: Children who are up-to-date on their vaccines get fewer ear infections than their unvaccinated counterparts. The 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV13) protects against 13 types of infection-causing bacteria.

- Consider breastfeeding: Breast milk contains antibodies that may help reduce the risk of ear infections and a host of other ailments. Whether you feed milk or formula, make sure your child sits up during feedings to prevent fluid from flowing into the middle ear.
- Wash your hands frequently: The best way to protect your child against cold and flu is to keep your hands clean. Wash your hands with soap and water and scrub them clean for a full 20 seconds each time you visit the sink.
- Steer clear of sick people: Don't allow your child to spend time with children or adults who are sick.
- Avoid secondhand smoke: Studies show that children who are exposed to secondhand smoke are up to three times more likely to develop ear infections than those who don't have those exposures.
Whether your child has ear infections or not, it's important to ensure they're able to hear well. "No child is too young to have a hearing test," Tunkel says. "We use a variety of techniques to test infant hearing and we can identify a hearing problem even in newborns."
"No child is too young to have a hearing test," Tunkel says. "We use a variety of techniques to test infant hearing and we can identify a hearing problem even in newborns."
Ear Infections in Children, Babies & Toddlers
What is an ear infection?
An ear infection is an inflammation of the middle ear, usually caused by bacteria, that occurs when fluid builds up behind the eardrum. Anyone can get an ear infection, but children get them more often than adults. Five out of six children will have at least one ear infection by their third birthday. In fact, ear infections are the most common reason parents bring their child to a doctor. The scientific name for an ear infection is otitis media (OM).
What are the symptoms of an ear infection?
There are three main types of ear infections. Each has a different combination of symptoms.
- Acute otitis media (AOM) is the most common ear infection. Parts of the middle ear are infected and swollen and fluid is trapped behind the eardrum.
 This causes pain in the ear—commonly called an earache. Your child might also have a fever.
This causes pain in the ear—commonly called an earache. Your child might also have a fever. - Otitis media with effusion (OME) sometimes happens after an ear infection has run its course and fluid stays trapped behind the eardrum. A child with OME may have no symptoms, but a doctor will be able to see the fluid behind the eardrum with a special instrument.
- Chronic otitis media with effusion (COME) happens when fluid remains in the middle ear for a long time or returns over and over again, even though there is no infection. COME makes it harder for children to fight new infections and also can affect their hearing.
How can I tell if my child has an ear infection?
Most ear infections happen to children before they’ve learned how to talk. If your child isn’t old enough to say “My ear hurts,” here are a few things to look for:
- Tugging or pulling at the ear(s)
- Fussiness and crying
- Trouble sleeping
- Fever (especially in infants and younger children)
- Fluid draining from the ear
- Clumsiness or problems with balance
- Trouble hearing or responding to quiet sounds
What causes an ear infection?
An ear infection usually is caused by bacteria and often begins after a child has a sore throat, cold, or other upper respiratory infection. If the upper respiratory infection is bacterial, these same bacteria may spread to the middle ear; if the upper respiratory infection is caused by a virus, such as a cold, bacteria may be drawn to the microbe-friendly environment and move into the middle ear as a secondary infection. Because of the infection, fluid builds up behind the eardrum.
If the upper respiratory infection is bacterial, these same bacteria may spread to the middle ear; if the upper respiratory infection is caused by a virus, such as a cold, bacteria may be drawn to the microbe-friendly environment and move into the middle ear as a secondary infection. Because of the infection, fluid builds up behind the eardrum.
Image
Source: NIH/NIDCDThe ear has three major parts: the outer ear, the middle ear, and the inner ear. The outer ear, also called the pinna, includes everything we see on the outside—the curved flap of the ear leading down to the earlobe—but it also includes the ear canal, which begins at the opening to the ear and extends to the eardrum. The eardrum is a membrane that separates the outer ear from the middle ear.
The middle ear—which is where ear infections occur—is located between the eardrum and the inner ear. Within the middle ear are three tiny bones called the malleus, incus, and stapes that transmit sound vibrations from the eardrum to the inner ear. The bones of the middle ear are surrounded by air.
The bones of the middle ear are surrounded by air.
The inner ear contains the labyrinth, which help us keep our balance. The cochlea, a part of the labyrinth, is a snail-shaped organ that converts sound vibrations from the middle ear into electrical signals. The auditory nerve carries these signals from the cochlea to the brain.
Other nearby parts of the ear also can be involved in ear infections. The eustachian tube is a small passageway that connects the upper part of the throat to the middle ear. Its job is to supply fresh air to the middle ear, drain fluid, and keep air pressure at a steady level between the nose and the ear.
Adenoids are small pads of tissue located behind the back of the nose, above the throat, and near the eustachian tubes. Adenoids are mostly made up of immune system cells. They fight off infection by trapping bacteria that enter through the mouth.
Why are children more likely than adults to get ear infections?
There are several reasons why children are more likely than adults to get ear infections.
Eustachian tubes are smaller and more level in children than they are in adults. This makes it difficult for fluid to drain out of the ear, even under normal conditions. If the eustachian tubes are swollen or blocked with mucus due to a cold or other respiratory illness, fluid may not be able to drain.
A child’s immune system isn’t as effective as an adult’s because it’s still developing. This makes it harder for children to fight infections.
As part of the immune system, the adenoids respond to bacteria passing through the nose and mouth. Sometimes bacteria get trapped in the adenoids, causing a chronic infection that can then pass on to the eustachian tubes and the middle ear.
How does a doctor diagnose a middle ear infection?
The first thing a doctor will do is ask you about your child’s health. Has your child had a head cold or sore throat recently? Is he having trouble sleeping? Is she pulling at her ears? If an ear infection seems likely, the simplest way for a doctor to tell is to use a lighted instrument, called an otoscope, to look at the eardrum. A red, bulging eardrum indicates an infection.
A red, bulging eardrum indicates an infection.
A doctor also may use a pneumatic otoscope, which blows a puff of air into the ear canal, to check for fluid behind the eardrum. A normal eardrum will move back and forth more easily than an eardrum with fluid behind it.
Tympanometry, which uses sound tones and air pressure, is a diagnostic test a doctor might use if the diagnosis still isn’t clear. A tympanometer is a small, soft plug that contains a tiny microphone and speaker as well as a device that varies air pressure in the ear. It measures how flexible the eardrum is at different pressures.
How is an acute middle ear infection treated?
Many doctors will prescribe an antibiotic, such as amoxicillin, to be taken over seven to 10 days. Your doctor also may recommend over-the-counter pain relievers such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen, or eardrops, to help with fever and pain. (Because aspirin is considered a major preventable risk factor for Reye’s syndrome, a child who has a fever or other flu-like symptoms should not be given aspirin unless instructed to by your doctor. )
)
If your doctor isn’t able to make a definite diagnosis of OM and your child doesn’t have severe ear pain or a fever, your doctor might ask you to wait a day or two to see if the earache goes away. The American Academy of Pediatrics issued guidelines in 2013 that encourage doctors to observe and closely follow these children with ear infections that can’t be definitively diagnosed, especially those between the ages of 6 months to 2 years. If there’s no improvement within 48 to 72 hours from when symptoms began, the guidelines recommend doctors start antibiotic therapy. Sometimes ear pain isn’t caused by infection, and some ear infections may get better without antibiotics. Using antibiotics cautiously and with good reason helps prevent the development of bacteria that become resistant to antibiotics.
If your doctor prescribes an antibiotic, it’s important to make sure your child takes it exactly as prescribed and for the full amount of time. Even though your child may seem better in a few days, the infection still hasn’t completely cleared from the ear.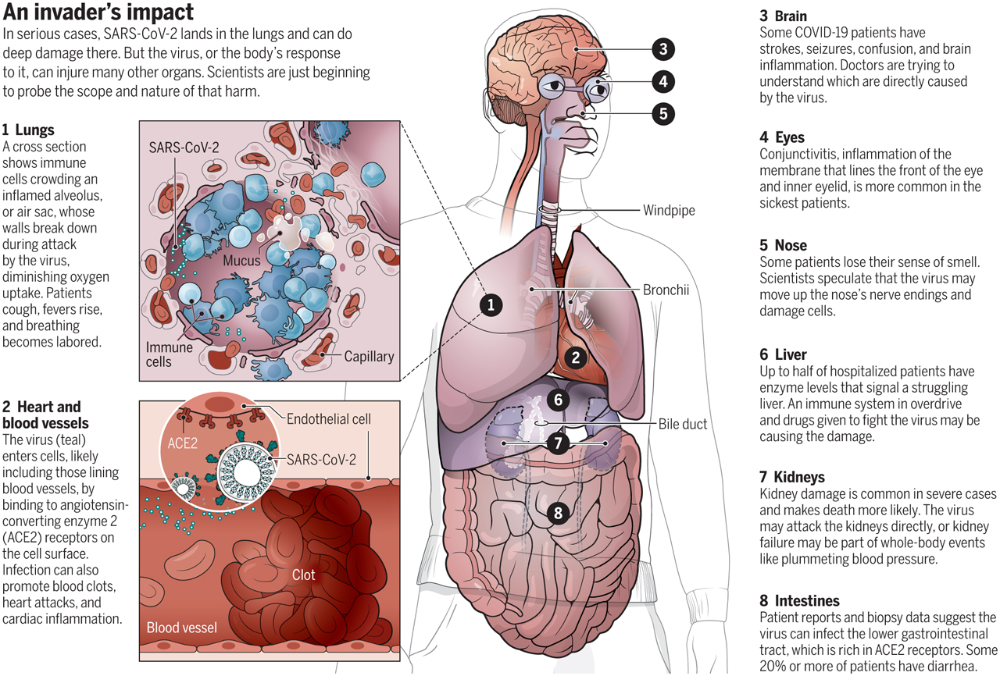 Stopping the medicine too soon could allow the infection to come back. It’s also important to return for your child’s follow-up visit, so that the doctor can check if the infection is gone.
Stopping the medicine too soon could allow the infection to come back. It’s also important to return for your child’s follow-up visit, so that the doctor can check if the infection is gone.
How long will it take my child to get better?
Your child should start feeling better within a few days after visiting the doctor. If it’s been several days and your child still seems sick, call your doctor. Your child might need a different antibiotic. Once the infection clears, fluid may still remain in the middle ear but usually disappears within three to six weeks.
What happens if my child keeps getting ear infections?
To keep a middle ear infection from coming back, it helps to limit some of the factors that might put your child at risk, such as not being around people who smoke and not going to bed with a bottle. In spite of these precautions, some children may continue to have middle ear infections, sometimes as many as five or six a year. Your doctor may want to wait for several months to see if things get better on their own but, if the infections keep coming back and antibiotics aren’t helping, many doctors will recommend a surgical procedure that places a small ventilation tube in the eardrum to improve air flow and prevent fluid backup in the middle ear. The most commonly used tubes stay in place for six to nine months and require follow-up visits until they fall out.
The most commonly used tubes stay in place for six to nine months and require follow-up visits until they fall out.
If placement of the tubes still doesn’t prevent infections, a doctor may consider removing the adenoids to prevent infection from spreading to the eustachian tubes.
Can ear infections be prevented?
Currently, the best way to prevent ear infections is to reduce the risk factors associated with them. Here are some things you might want to do to lower your child’s risk for ear infections.
- Vaccinate your child against the flu. Make sure your child gets the influenza, or flu, vaccine every year.
- It is recommended that you vaccinate your child with the 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV13). The PCV13 protects against more types of infection-causing bacteria than the previous vaccine, the PCV7. If your child already has begun PCV7 vaccination, consult your physician about how to transition to PCV13. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends that children under age 2 be vaccinated, starting at 2 months of age.
 Studies have shown that vaccinated children get far fewer ear infections than children who aren’t vaccinated. The vaccine is strongly recommended for children in daycare.
Studies have shown that vaccinated children get far fewer ear infections than children who aren’t vaccinated. The vaccine is strongly recommended for children in daycare. - Wash hands frequently. Washing hands prevents the spread of germs and can help keep your child from catching a cold or the flu.
- Avoid exposing your baby to cigarette smoke. Studies have shown that babies who are around smokers have more ear infections.
- Never put your baby down for a nap, or for the night, with a bottle.
- Don’t allow sick children to spend time together. As much as possible, limit your child’s exposure to other children when your child or your child’s playmates are sick.
What research is being done on middle ear infections?
Researchers sponsored by the National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders (NIDCD) are exploring many areas to improve the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of middle ear infections. For example, finding better ways to predict which children are at higher risk of developing an ear infection could lead to successful prevention tactics.
Another area that needs exploration is why some children have more ear infections than others. For example, Native American and Hispanic children have more infections than do children in other ethnic groups. What kinds of preventive measures could be taken to lower the risks?
Doctors also are beginning to learn more about what happens in the ears of children who have recurring ear infections. They have identified colonies of antibiotic-resistant bacteria, called biofilms, that are present in the middle ears of most children with chronic ear infections. Understanding how to attack and kill these biofilms would be one way to successfully treat chronic ear infections and avoid surgery.
Understanding the impact that ear infections have on a child’s speech and language development is another important area of study. Creating more accurate methods to diagnose middle ear infections would help doctors prescribe more targeted treatments. Researchers also are evaluating drugs currently being used to treat ear infections, and developing new, more effective and easier ways to administer medicines.
NIDCD-supported investigators continue to explore vaccines against some of the most common bacteria and viruses that cause middle ear infections, such as nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae (NTHi) and Moraxella catarrhalis. One team is conducting studies on a method for delivering a possible vaccine without a needle.
Where can I find additional information about ear infections?
The NIDCD maintains a directory of organizations that provide information on the normal and disordered processes of hearing, balance, smell, taste, voice, speech, and language.
Use the following keywords to help you search for organizations that can answer questions and provide printed or electronic information on ear infections:
- Otitis media (ear infection)
- Speech-language development
- Early identification of hearing loss in children
NIDCD Information Clearinghouse
1 Communication Avenue
Bethesda, MD 20892-3456
Toll-free voice: (800) 241-1044
Toll-free TTY: (800) 241-1055
Email: nidcdinfo@nidcd. nih.gov
nih.gov
Ear inflammation in a child: how to prevent complications
Otitis media is one of the most common diseases in childhood. According to international statistics, 98% of children suffer from ear inflammation at least once, 60% experience the disease twice. What is effective prevention and how otitis is treated, said the otorhinolaryngologist of the Morozov Children's Hospital, Candidate of Medical Sciences, holder of the status of "Moscow Doctor" Alexander Mikhailovich Ivanenko.
Why does otitis occur?
Depending on the location of the inflammatory process, otitis can be external, medial or internal. Otitis externa is caused by microbes and fungi, most often manifested by damage to the skin of the ear canal and boils in the auricle.
Acute otitis media is an acute inflammation of the mucous membrane of the middle ear cavity. It develops against the background of respiratory infections. Ear infection occurs through the auditory tube, when mucus from the nasopharynx enters the middle ear and viruses, bacteria, fungal flora freely penetrate from the nasopharynx through the mouth of the auditory tube into the tympanic cavity.
Due to anatomical features, the smaller the child, the shorter and wider the auditory tube connecting the ear cavity with the nasopharynx. Therefore, in an infant who spends most of his time lying down, and in a younger child who does not know how to clean his nose, mucus can flow at any time. In adolescent children, the auditory tube is a tortuous narrow tube, so the infection from the nasopharynx to the middle ear is less likely to pass.
Adenoid vegetations also contribute to the development of ear inflammation. This is an overgrowth of the nasopharyngeal tonsil, which is the main focus of bacterial infection in the nasopharynx.
How does the disease manifest itself?
The main symptom of otitis media is pain in the ear. Children under one year old, as a rule, refuse to eat, because sucking movements cause pain. Babies often touch their ears, rub them, and cry. You can suspect otitis media by pressing on the tragus of the child's auricle.
The key method for diagnosing otitis media is otoscopy - an examination by a doctor of the external auditory canal and eardrum using a special instrument.
How to treat otitis?
If the inflammatory process is at the initial stage, outpatient treatment is carried out. The therapy is selected by a pediatrician or an otorhinolaryngologist depending on the child's condition. Be sure to use vasoconstrictor drops in the nose.
If medical assistance is not provided in a timely manner, the inflammatory process turns into acute catarrhal otitis media, and then into acute purulent otitis media, characterized by the appearance of purulent discharge from the ear. In some cases, with inadequate outflow of contents or its absence, the child in the hospital undergoes paracentesis - an incision in the eardrum. The intervention is performed under anesthesia. Then medical conservative treatment continues.
Which preventive measures are most effective?
There is an opinion among many parents that otitis media can be prevented by “covering the ears with cotton wool in the street” or “putting a few hats on the child”. Such recommendations will not insure against otitis media.
Such recommendations will not insure against otitis media.
Due to the fact that ear infection occurs through the auditory tube that communicates with the nasopharynx, it is necessary to carefully care for the nasal cavity if the child has a runny nose. Otherwise, mucus flows from the nasopharynx into the middle ear, which leads to an inflammatory process in the ear.
In case of excessive growth of the nasopharyngeal tonsil, its removal is recommended.
Otitis ear in a child - symptoms and treatment of otitis 2019.
Otitis media is the medical name for inflammation of the middle ear caused by an infection. The disease is most common in young children, this is due to the peculiarity of the structure of the ENT organs in babies (shorter and wider ear canal than in older children or adults). Acute otitis media is an infection that usually develops due to the accumulation of fluid in the middle ear. Otitis can be caused by viruses or bacteria. Most children with otitis media first develop an acute respiratory viral infection or acute respiratory disease, which then progresses to otitis media, causing inflammation and swelling in the nasal passages and the Eustachian tube. The risk of recurrent middle ear infections is increased in children who:
The risk of recurrent middle ear infections is increased in children who:
- Attending a nursery or kindergarten
- Exposed to cigarette or stove smoke in the home
- Have enlarged adenoids that may obstruct the drainage of the Eustachian tube
Symptoms of acute otitis media usually include ear pain and fever. Otitis media with effusion (fluid or pus), also known as adhesive otitis media, occurs when there is fluid in the middle ear after the infection has cleared. This condition usually does not cause pain, but it can cause hearing loss in a child.
Children with acute otitis media usually get better quickly with anti-inflammatory medication and proper care. Sometimes, if the doctor is sure that the disease is caused by bacteria, the child may be given antibiotics. Children who develop adhesive otitis media and other complications may need additional treatment with physical therapy.
Symptoms of otitis in children
Most children with acute otitis media will complain of ear pain.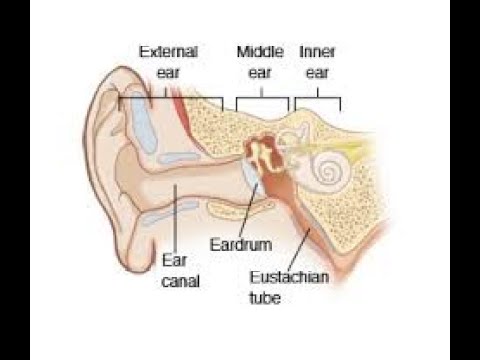 If the child is still small and does not know how to speak, otitis may be indicated by a long aching cry, the refusal of the child to breastfeed. Other symptoms may include:
If the child is still small and does not know how to speak, otitis may be indicated by a long aching cry, the refusal of the child to breastfeed. Other symptoms may include:
- Irritability, capriciousness
- "forced" position (if the pain is on one side, the child can put his hand to the ear or try to lie on the sore ear)
- Lethargy, weakness
- sleep disorders
- fever
- decreased or lack of appetite
- vomiting
Because many cases of otitis media are caused by a viral infection, other symptoms associated with the infection, such as runny nose, watery eyes, or cough, can often be present.
Diagnosis of otitis media
If your child has had an earache for more than 2 days, or if your child is under 2 years old and you suspect that they have an earache, you should urgently seek help from an otolaryngologist, pediatrician, or general practitioner. Delay can threaten the fact that the child will lose his hearing or become completely deaf.
The doctor will examine the child's ears and eardrums with an instrument called an otoscope. In acute otitis media, the eardrum will be inflamed and bulging due to a buildup of fluid in the middle ear. The doctor will take the temperature and examine the child for other infections (such as bronchitis). There are no specific tests to diagnose otitis media. One of the effective diagnostic methods is ENT endoscopy using a flexible ENT endoscope, which is successfully carried out in our medical center by experienced ENT doctors. Such diagnostics are absolutely painless and can be performed according to the doctor's indications in the youngest children, from the age of 9months.
Treatment of otitis media
Your child's treatment will depend on his age and health.
It is generally assumed that children over 6 months of age who have mild otitis media initially receive only anti-inflammatory drugs. If symptoms persist for more than 48 hours or if they worsen, then broad-spectrum antibiotics may be needed. it is extremely important to prevent complications of the disease in any way. The first antibiotic of choice for the treatment of acute otitis media in children is amoxicillin. An alternative antibiotic will be given if the child is allergic to penicillin. Antihistamines and corticosteroids have not been shown to be of any benefit in the treatment of acute otitis media.
it is extremely important to prevent complications of the disease in any way. The first antibiotic of choice for the treatment of acute otitis media in children is amoxicillin. An alternative antibiotic will be given if the child is allergic to penicillin. Antihistamines and corticosteroids have not been shown to be of any benefit in the treatment of acute otitis media.
Possible complications
Perforation (rupture) of the eardrum is a common complication of acute otitis media in children. This can lead to leakage of fluid from the ear, while fluid or pus begins to flow from the middle ear cavity, which alleviates the child's condition: pain in the ear decreases due to reduced pressure on the eardrum. By itself, the rupture of the eardrum does not lead to deafness; in the process of treating otitis media, the integrity of the membrane is quickly restored. Treatment is the same as for acute otitis media. The child should not be immersed in water or go to the pool until the eardrum is healed.
Otitis media sometimes develops after an acute ear infection. This means that there is fluid in the middle ear (otitis media with effusion), which can cause temporary hearing loss. Most children with this complication recover within 3 months without the need for special treatment. In the chronic form of the disease, treatment with a tympanostomy may be required - inserting a small drainage tube into the eardrum to drain fluid and allow air into the middle ear to restore hearing.
Chronic suppurative otitis media is a middle ear infection with perforation of the tympanic membrane and discharge of fluid from the ear lasting for at least 6 weeks. In this case, the ear canal must be sanitized several times a day, and an antibiotic should be dripped into the ear (for example, Otipax). It may also be necessary to take antibiotics by mouth.
Acute mastoiditis is an infectious inflammation of the bone behind the ear (the mastoid process of the temporal bone) that is treated with antibiotic therapy.