How do i find my docket number for child support
Family Court Overview | NYCOURTS.GOV
Help Center | Child Protective / Permanency Planning Office | Courtroom Activity Office (Hearings & Orders) | Docket Number System
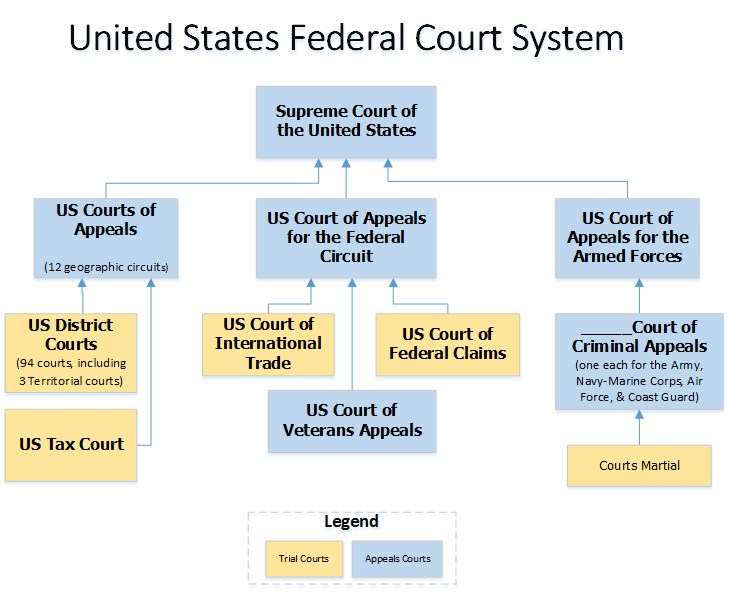
Overview
The Family Court of the State of New York was established to take action in the lives of children, parents and spouses. The court has a wide range of powers to fit the particular needs of the people who come before it.
The Family Court Act gives the Family Court power to hear certain types of cases. As each case is filed in the court, it is assigned its own identifying number, called a docket number. The docket number begins with a letter which tells the type of case filed. For example, a paternity case is given a docket number beginning with the letter "P".
In New York City, each of the five boroughs has its own Family Court. Generally, a case may be filed without fee in the county where one of the parties lives.
Most Family Court hearings (trials) are heard by judges. Support magistrates hear support and paternity cases. There are no juries in Family Court: the judge or support magistrate conducts a hearing and decides the case.
The Family Court is generally open to the public, in addition to those persons who are directly involved with a particular case. However, the judge or support magistrate presiding over each case has the authority to exclude the public from the courtroom depending upon the nature of the case or the privacy interests of the parties.
Persons who have been scheduled to appear in court are expected to arrive at the courthouse on time. If a party (a person who has a direct involvement with a case) is not present when the case is called into the courtroom, the judge or support magistrate may proceed and decide the case in that person's absence, or may dismiss it. Parties should understand that although they arrive early, they may be required to spend a lengthy period of time at the courthouse.
Each Family Court building has a child waiting area, where children may wait while a case is being heard in court. Indeed, in the Family courthouses in Bronx, Kings, New York and Queens counties, there are supervised Children's Centers which provide free drop in child care for parents who must use the court.
Indeed, in the Family courthouses in Bronx, Kings, New York and Queens counties, there are supervised Children's Centers which provide free drop in child care for parents who must use the court.
After a case has been completed and a final decision has been made, each party has the right to appeal the judge's decision, asking a higher court to review the evidence and any testimony presented at the Family Court hearing. (Decisions made by support magistrates are appealed first by filing an objection to the decision; a Family Court judge reviews the support magistrates' decision and order.) An appeal may result in a decision being affirmed (left as it is), or modified (changed somewhat), or reversed (changed entirely).
The court records of Family Court proceedings are not open to public inspection. However, the court may permit access to records where appropriate. Persons directly involved with a case who wish to obtain a copy of a court order may request a copy at the Record Room of the courthouse where the case was heard; proof of the person's identity is required.
Each Family Court in New York City is open all day from Monday through Friday, except on holidays. At lunchtime, the parts (hearing rooms) within each courthouse close for a lunch recess, but certain areas of each building remain open to the public. Specific information on hours may be obtained by calling the courthouse.
Additionally, each Family Court in New York City is comprised of three operational divisions, which are responsible for managing day to day operations. These divisions provide specific services to our court users as described below.
Help Center
The goal of the Help Center is to make it easier for the public to use the Family Court. Help Center staff provide legal information and other assistance--- but not legal advice --- to court users who do not have lawyers.
Help Center staff assist with the filing of certain types of petitions in NYC Family Court. These Family Court petitions include:
- Family Offense (Order of Protection)
- Visitation and Custody of Children
- Guardianship
- Child or Spousal Support
- Paternity
- Interstate Support (UIFSA)
The Help Center can also provide information on other court services, such as the Custody/Visitation Mediation Program and the Children's Center as well as other resources.
Child Protective/ Permanency Planning Office
The Permanency Planning office was created to manage and monitor the filing of Child Protective cases filed in the New York City Family Courts. Permanency Planning offices also monitor the Juvenile Delinquency and Persons In Need of Supervision cases filed in N.Y.C. Family Courts.
Additional functions include:
- Child Protective Proceedings
- Guide for parents for a child in foster care
- Foster Care Placement
- Family Treatment Court
- Termination of parental rights
- Adoptions
- Juvenile Delinquency/Designated felonies
- Persons In Need of Supervision
Hearings& Orders
The Courtroom Activity office manages the staffing needs of our trial court parts. It also monitors the scheduling of our courtroom's trial calendars and the completion of court orders.
Additional functions include:
- Court Reporter/Transcription Services
- Interpreting Services
- Appeals
- Subpoenaed records
Docket Number System
The NYC Family Court docket number system begins with a letter which tells the type of case filed:
- A: Adoption
- B: Permanent termination of parental rights
- D: Juvenile delinquency
- E: Designated Felony
- F: Child or spousal support
- G: Guardianship
- K: Foster Care Review
- L: Voluntary Foster Care Approval
- M: Marriage Application>
- NN and NA: Neglect / Abuse
- O: Family offense (order of protection)
- P: Paternity
- S: PINS (Person in Need of Supervision)
- U: Interstate support
- V: Visitation and custody of children
How to search court dockets
eAccess
The Details of How to search court dockets
What you need for How to search court dockets
You can access public electronic Trial Court case docket information in person or online. You can access electronic case information for SJC and Appeals Court cases here.
You can access electronic case information for SJC and Appeals Court cases here.
- To find judicial calendars, see view court calendars
- To get a copy of your divorce record, please see Get a copy of your divorce record
- To find old court records, please see Accessing Court Archives.
If you want to access information in person, you'll need a public terminal computer, which you can find at any Massachusetts courthouse or County Registry of Deeds sites.
If you want to access information at home, you'll need a supported browser:
- Microsoft Edge
- Firefox
- Chrome
How to view How to search court dockets
State Courthouses
Trial Court case information is available at designated public access computers located in District, Boston Municipal, Probate and Family, Superior, Housing, and Land Courts and County Registry of Deeds sites.
The public access PCs run the eAccess application and allow searches by name, case type, and case number. The search results display case information, including party, event, docket, and disposition details. However, you can't view case documents. Actual case documents are available for public inspection in the Clerk, Register, and Recorder's Offices.
Internet
Certain Trial Court case information is also available to the public online at www.masscourts.org. You don't need a log in. To access this information:
- Go to www.masscourts.org and click the button that says "Click here to search public records." You'll then select the court department and court division you're searching in. The court location will automatically fill for you.
- After you complete these fields, search tabs for name, case type, case number, and ticket/citation # will appear. You can choose which way you'd like to search for your case.
 Most criminal cases can only be searched by docket number. If you're searching by docket number, make sure you enter the number exactly how it appears. Please note that the ticket/citation # tab can only be used for Boston Municipal Court and District Court cases. For instructions on how to use each search tab, see Instructions for Massachusetts Trial Court Electronic Case Access.
Most criminal cases can only be searched by docket number. If you're searching by docket number, make sure you enter the number exactly how it appears. Please note that the ticket/citation # tab can only be used for Boston Municipal Court and District Court cases. For instructions on how to use each search tab, see Instructions for Massachusetts Trial Court Electronic Case Access. - Once you hit search, you will see a list of cases. Use the navigation bar at the bottom of the page to navigate through pages of results. Click the column headers to sort the search results. Each retrieved record represents a party in a case, therefore case numbers may appear multiple times in the search results. Please note that the system displays a maximum of 100 records for each search, so you'll need to narrow your search criteria if you can’t see all of the records in the selected range.
- To see more information about a case, click the desired case's hyperlink. You'll see public information about the case, including party, event, docket, and disposition details.
 However, you can't view case documents. Actual case documents are available for public inspection from the information counters of the courthouses. If you'd like to print a case, click the print icon in the upper-right corner.
However, you can't view case documents. Actual case documents are available for public inspection from the information counters of the courthouses. If you'd like to print a case, click the print icon in the upper-right corner. - If you'd like to find other cases, use the menu items at the top of the page. Choose:
- Results to return to the list of retrieved cases
- Search to change search criteria, choose a different search method, or to search for cases in a different court
- Home to return to the welcome page once you're finished searching
More info for How to search court dockets
Please email [email protected] with any questions.
Downloads for How to search court dockets
Contact for How to search court dockets
Feedback
Thanks, your message has been sent to Massachusetts Court System!
Join user panelFeedback
How to find out child support debt by last name - check child support debt online
There are several ways to see the amount of child support debt. To do this, you can contact the MFC or come to an appointment with a bailiff. In addition, you can find out the debt by last name via the Internet. To do this, you need to use the main website of the FSSP, the State Services portal or the State Payment service.
State payment
State payment online service offers the easiest and fastest way to find out the amount of alimony debt from yourself or another individual. The service does not require registration. To start checking:
- Go to the State Payments website;
- Enter the last name, first name and patronymic of the debtor, his date of birth and region of residence. Click "Check";
- Next, enter the code from the picture and wait for the verification results.
The service will check the FSSP database and provide information about the amount owed by a particular person.
With the help of "Gosoplata" you can not only find out, but also immediately pay the debt using any bank card.
The service has the following benefits:
- Instant payment of legal, tax and other debts;
- Simple and intuitive interface;
- Convenient mobile application;
- Payment information is automatically transferred to databases;
- All transmitted data is securely encrypted;
- Payment receipt is sent to the payer's e-mail immediately after the payment is made.
FSSP website
To find out the debt for alimony through the official website of the FSSP, you need:
- Go to the site at the link: fssp.gov.ru;
- In the site menu, select the "Service" section, the "Database of Enforcement Proceedings" category;
- Next, you need to fill in all the fields marked with an asterisk (*):
- Territorial bodies;
- Last name, first name;
- Click the "Find" button to start checking.
 Next, the system will ask you to enter the code from the picture to confirm that the request is made by a person and not a robot.
Next, the system will ask you to enter the code from the picture to confirm that the request is made by a person and not a robot.
If several debtors have the same first and last name, you need to enter the middle name and date of birth for a more accurate search.
As a result of the search, you will see a table where all the necessary information will be presented:
- amount of debt and enforcement fee;
- production number;
- court order number;
- territorial subdivision of the FSSP;
- surname and phone numbers of the bailiff.
On the main website of the bailiff service, you can not only find out the debt for alimony, but also pay it. If necessary, you can pay the debt online through the State Services portal or generate a receipt and pay it through any bank.
Public services
To find out the amount of alimony arrears through the Gosuslug portal, you must first register.
Attention! The search for accruals is carried out according to the data from your personal account.
To see if you have a legal debt, log into your personal account and follow these steps:
- Select the "Services" section, then the "Authorities" subsection and the "FSSP of Russia" category;
- Next, open the "Territorial authorities" tab and select the name of the desired department from the list;
- Select the electronic service “Providing information…”;
- Next, select the service "Law Debt";
- Click "Get Service";
You can pay your debt in several ways:
- With any bank card;
- Through Google Pay or Samsung Pay;
- Using an electronic wallet WebMoney, Qiwi, Yandex.Money;
- From a mobile phone account.
You can also generate a receipt and pay it at the bank or at the post office.
How quickly will an entry in the FSSP database be deleted?
If you have fully or partially paid the child support debt, the entry in the Database will be deleted or changed no earlier than 3-7 working days from the date of payment. This is due to the fact that first the funds go to the account of the bailiff unit, and then to the account of the claimant. It takes at least 3 days to process and transfer funds. If the workload is high, it can take up to 7 days to delete or change an entry.
If you have any additional questions, you can personally contact the territorial division of the FSSP. You can make an appointment for a personal appointment through the official website of the bailiff service - fssp.gov.ru.
Kontselidze Ednary Emzarievich Legal Expert
- The Supreme Court of the Republic of Belarus
Issues related to the recovery of alimony are of great public interest and are always in the area of close attention of the judiciary. Conflict situations related to non-fulfillment of maintenance obligations are resolved in court. Consideration by the court of disputes on the recovery of alimony guarantees their quick and correct resolution, ensuring the protection of the rights and legitimate interests of children. The relevance of the topic raised is also due to the rather high number of disputes related to the recovery of alimony considered by the courts.
Conflict situations related to non-fulfillment of maintenance obligations are resolved in court. Consideration by the court of disputes on the recovery of alimony guarantees their quick and correct resolution, ensuring the protection of the rights and legitimate interests of children. The relevance of the topic raised is also due to the rather high number of disputes related to the recovery of alimony considered by the courts.
June 12 this year The program “Actual Microphone” of the First National Channel of the Belarusian Radio was devoted to this topic with the participation of Vera Borisovna Krugova, Judge of the Judicial Collegium for Civil Cases of the Supreme Court of the Republic of Belarus .
The program aroused great interest among the listeners, and we additionally publish an interview of the judge on such a socially important topic.
In the photo: Judge of the Supreme Court of the Republic of Belarus Vera Borisovna Krugova
- Vera Borisovna, tell us what is the procedure established by law when applying to the court for the recovery of alimony, can a citizen independently draw up an application without seeking legal advice?
- Alimony for minor children can be collected in order order and order action proceedings . Recovery of alimony in the order of writ proceedings is carried out without holding a court session and calling the parties. By order, alimony can be recovered if this is not related to the establishment of paternity (maternity) or the need to involve third parties to participate in the case. In this case, the judge issues a ruling on a court order, which is also an executive document.
Recovery of alimony in the order of writ proceedings is carried out without holding a court session and calling the parties. By order, alimony can be recovered if this is not related to the establishment of paternity (maternity) or the need to involve third parties to participate in the case. In this case, the judge issues a ruling on a court order, which is also an executive document.
The statement of claim for the recovery of alimony is submitted in writing with a copy of the application to be sent to the defendant and must comply with the requirements of Art. Art. 109, 243 Code of Civil Procedure.
By the way, on the information stands of the courts and on our Internet portal there are samples of the most frequently filed statements of claim, including those on the recovery of alimony for a child in the order of action proceedings and on the recovery of alimony in the order of writ proceedings.
- Do I need to pay a state fee when applying to the court with an application for the recovery of alimony?
- No, you don't. In accordance with the requirements of the Tax Code, plaintiffs, applicants are exempted from paying the state fee when applying to the court with statements of claim and applications for initiating writ proceedings for the recovery of alimony. In this case, the obligation to pay the subsequent state duty rests with the defendant.
In accordance with the requirements of the Tax Code, plaintiffs, applicants are exempted from paying the state fee when applying to the court with statements of claim and applications for initiating writ proceedings for the recovery of alimony. In this case, the obligation to pay the subsequent state duty rests with the defendant.
- As you know, one of the results of the judicial and legal reform was the creation of a unified system of bodies for the enforcement of court decisions and other executive documents. Where should I go to claim child support? Where does the competence of the court end and the bailiffs begin?
- Proceedings on the recovery of alimony ends with the issuance of a court decision (decision on the recovery of alimony, ruling on a court order on the recovery of alimony).
In cases of writ proceedings on the recovery of alimony, if the debtor does not object to the court within the prescribed period, the judge issues to the exactor a ruling on the court order indicating the date of its entry into force for presenting it for execution. Business of action proceedings at the request of the recoverer, on the basis of a court decision on the recovery of alimony, a writ of execution is issued.
Business of action proceedings at the request of the recoverer, on the basis of a court decision on the recovery of alimony, a writ of execution is issued.
At the stage of issuing a court order to the recoverer, the competence of the court ends, and after presenting it for execution to the enforcement authorities, the competence of bailiffs begins.
- What if, in the opinion of the alimony collector, the bailiff is inactive or does not take all measures to collect alimony from the debtor?
- I believe that before appealing against the inaction of a bailiff, it is worth familiarizing yourself with the materials of the enforcement proceedings. It is likely that the bailiff is doing everything possible for this. But if the materials of the enforcement proceedings confirm the inaction of the bailiff, then the alimony collector has the right to appeal against the inaction of the bailiff in the manner prescribed by law. As for the procedure for appealing against the inaction of a bailiff directly to the court, it is regulated by Article 360-3 of the Code of Civil Procedure.
- Can the parties voluntarily settle this issue without going to court, in addition to the court order for the recovery of alimony?
- Of course, it is possible. Alimony may be paid on a voluntary basis by a person obliged to pay alimony, or by deduction from wages at the place of work or at the place of receipt of a pension, allowance, stipend, or other payments. An employer paying wages, an organization that pays pensions, allowances, scholarships and makes other payments, are obliged, on the basis of a written application of the person paying alimony , to monthly withhold from his salary, pension, allowance, scholarship and other payments amounts of money of established amounts, taking into account the restrictions provided for by the legislative acts of the Republic of Belarus, and pay (transfer to an account, transfer according to mail at the expense of the person paying the alimony) no later than three days from the date of payment of wages, pensions, allowances, stipends and other payments to the person specified in the application.
- What if the child support payer changes jobs?
- When a citizen, from whom alimony is withheld upon application, moves to another job or, for example, changes his place of residence, alimony is withheld on the basis of a newly submitted application. At the same time, alimony cannot be withheld on the basis of an application, if the total amount to be recovered on the basis of an application and executive documents exceeds 50 percent of the earnings and (or) other income due to the debtor, from which alimony is withheld, and also, if the debtor is recovered by a court order alimony for children from another mother, with the exception of the case of payment of alimony for minor children.
So, if alimony is paid for minor children, then on the basis of an application, alimony may be withheld and if the total amount of deductions on the basis of such an application and executive documents exceeds 50 percent of the earnings and (or) other income of the person obliged to pay alimony, but not more than 70 percent. That is, if the employee pays child support for minor children, which must be indicated in the application, the amount of alimony withheld can be more than 50 percent of earnings, but not more than 70 percent.
That is, if the employee pays child support for minor children, which must be indicated in the application, the amount of alimony withheld can be more than 50 percent of earnings, but not more than 70 percent.
At the same time, it should be noted that for able-bodied parents, the minimum amount of alimony per month should be at least 50 percent for one child, 75 percent for two children, 100 percent for three or more children of the subsistence minimum budget on average for per capita.
- Vera Borisovna, please explain how long it takes for alimony to be collected and is it possible to collect alimony for the past time? At the same time, alimony may also be collected for the past , but not more than for the previous three years, if the court establishes that before applying to the court, measures were taken to obtain funds for maintenance, but due to the evasion of the person obliged pay alimony, from their payment, alimony was not received.
- What can you say about the terms of consideration of cases of this category?
- Cases on claims for the recovery of alimony must be considered by the court of first instance no later than one month from the date of acceptance of the application. When considering cases by writ , a ruling on a court order for the recovery of alimony is issued within three days from the date of receipt of the application to the court. This means that by writ, alimony can be collected more quickly than in a lawsuit, however, writ order is permissible only if this is not related to the establishment of paternity (maternity) or the need to involve third parties to participate in the case.
- How to collect alimony if the parent who is obliged to pay them lives and works outside of Belarus? Where can I apply for alimony?
- In this case, the plaintiff (collector) with an application for the recovery of alimony can apply to the court both at his place of residence and at the place of residence of the defendant (debtor).
The jurisdiction of the courts of the Republic of Belarus in civil cases in disputes involving foreign citizens, stateless persons, foreign legal entities, as well as in disputes in which at least one of the parties resides abroad, is determined by the legislation of the Republic of Belarus, unless otherwise established by international treaties of the Republic of Belarus or a written agreement of the parties.
For example, regarding relations between the Republic of Belarus and the Russian Federation on the issue of alimony, the Convention on Legal Assistance and Legal Relations in Civil, Family and Criminal Matters applies, according to which cases on maintenance obligations fall within the competence of the court of the Contracting Party, in the territory in which parents and children have a permanent joint residence, and in the absence of a permanent joint residence of parents and children, the court of the Contracting Party of which the child is a citizen or, at the request of the claimant for maintenance obligations, the court of the Contracting Party in whose territory the child permanently resides.
It should be noted that on the issue of collecting alimony, the plaintiff can apply both to the Belarusian court at the place of his residence, and to the Russian court - at the place of residence of the defendant.
It is also important that on March 3, 2015, the Republic of Belarus and the Russian Federation signed an Agreement on the Procedure for the Mutual Execution of Court Orders in Cases of Recovery of Alimony, by virtue of which no special procedure is required for the recognition and execution of court decisions.
As for other states, in each specific case it is necessary to proceed from the terms of the international agreement (if any).
- But what should a parent do if he does not have information about the place of residence of the other parent?
- A claim against a defendant whose place of residence is unknown or who does not have a place of residence in the Republic of Belarus may be brought at the location of his property or at his last known place of residence in the Republic of Belarus. If the place of residence of the defendant in claims for the recovery of alimony is unknown, the judge is obliged to announce the search for the defendant through the territorial bodies of internal affairs. In this case, the court may suspend the proceedings for the recovery of alimony.
If the place of residence of the defendant in claims for the recovery of alimony is unknown, the judge is obliged to announce the search for the defendant through the territorial bodies of internal affairs. In this case, the court may suspend the proceedings for the recovery of alimony.
- If the child's birth certificate does not contain information about the father or if the child is not recognized as the father, where should the mother go to collect alimony?
- Mutual rights and obligations of parents and children (including the obligation of parents to support minor children) are based on the origin of children, certified in the prescribed manner.
The descent of a child from a father who is not married to the mother of the child is established on the basis of a joint application of the father and mother of the child for registration of the establishment of paternity, filed with the authorities registering acts of civil status.
If the parents of the child are not married to each other and the civil registration authorities do not submit applications for registering the establishment of paternity, and also if information about the father of the child is entered in the birth certificate at the direction of the unmarried mother, then paternity can be established in court.
Mutual rights and obligations between the father and the child, if the father and mother of the child are not married, arise from the moment the information about him as the father is entered in the record of the birth of the child in the prescribed manner or from the moment the court decision on establishment of paternity, with the exception of the obligation to maintain, which may be imposed from the moment of filing a claim for the establishment of paternity.
Establishment of paternity in court is carried out at the request of one of the parents or guardian, guardian of the child, as well as the child himself upon reaching the age of majority.
Thus, if in the child's birth certificate information about the father is indicated from the words of the unmarried mother, then the question of establishing paternity should first be raised, and then - the collection of alimony. The plaintiff has the right to state such requirements in one statement of claim. In this case, alimony can be collected from the moment of filing a claim to establish paternity.
For reference: with the decision in 2018, 20,625 cases on the recovery of alimony were considered, of which 20,227 cases (98%) were satisfied (in 2017, 20,670 cases on the recovery of alimony were considered, of which 20 In 267 cases (98%) the claims were satisfied. alimony to pay for this period?0090
- Of course, a parent of a child who is obliged by a court order to pay child support must, in accordance with the requirements of the Code of Civil Procedure, execute the court decision. At the same time, the parents of the child in this case, already within the framework of enforcement proceedings, can conclude an amicable agreement, which is approved by the court, on the issue of the fulfillment of maintenance obligations by the father during the specified period.
- What to do in cases when alimony is forcibly collected from a parent, since he did not pay money for the maintenance of the child, but it turns out that at the same time he provided the child with food and clothes. Does this count towards child support?
- Let's analyze the provisions of Chapter 11 of the Code of the Republic of Belarus on Marriage and Family (CoBS). They point out that alimony is usually a cash payment. The possibility of paying alimony in a non-monetary form, for example, by transferring property to the ownership of a child, can only be provided for by a notarized Agreement on the payment of alimony or a marriage contract. I want to note that a parent who is obliged to pay alimony has the right to provide his child with material maintenance and more than the amount determined by the court.
- Continuing on the subject of the Prenuptial Agreement, Alimony Agreement and Children's Agreement. What is the procedure to be followed in order to enter into a Marriage Agreement, Support Agreement and Children Agreement? How often do parents conclude them, because many of the parents do not even know about such an opportunity provided by law?
- Issues of maintenance, determination of the place of residence of children and other issues related to the upbringing of children can be settled by the spouses in the Marriage Agreement, Agreement on Children. In the Agreement on the payment of alimony, only questions about the amount, methods and procedure for paying alimony can be resolved.
In the Agreement on the payment of alimony, only questions about the amount, methods and procedure for paying alimony can be resolved.
A marriage contract is concluded in writing and is subject to notarization. If the Marriage Agreement contains conditions that are or may become the basis for the emergence, transfer, termination of rights, restrictions (encumbrances) of rights to real estate, then also requires mandatory state registration of the Marriage Agreement in the organization for state registration of real estate, rights to it and transactions with him. The legislator makes the same requirements for the Agreement on the payment of alimony. Spouses may conclude an agreement on children in accordance with the procedure established by the Code of Civil Procedure for amicable agreements upon dissolution of marriage in court.
The legislator does not exclude the possibility of specifying in the Marriage Agreement, Agreement on the payment of alimony, Agreement on children the payment of alimony in a fixed amount of money, in basic values, as a percentage of earnings.
An agreement on the payment of alimony cannot be concluded if the alimony is paid in accordance with the Marriage Agreement or the Agreement on Children concluded in accordance with the procedure established by the legislation of the Republic of Belarus, as well as a court decision that has entered into force, which resolves the issues of paying alimony for minors and (or) disabled adult children in need of assistance (part 7 of article 91 KoBS).
- Can any amount of maintenance for minor children be determined by the parties in the Marriage Agreement, Alimony Agreement, Agreement on Children?
- The terms of the Marriage Agreement, the Agreement on the payment of alimony or the Agreement on children must not violate the rights and legitimate interests of other persons, and must not contradict the legislation of the Republic of Belarus. That is, the amount of alimony specified in the Marriage Agreement, the Agreement on the payment of alimony or the Children's Agreement must not be less than the amount established by Article 92 of the Code of Civil Procedure, from which the courts proceed when collecting alimony in court.
For reference: according to the Ministry of Justice of the Republic of Belarus, in 2018 notaries of the republic certified 3,923 marriage contracts and 191 agreements on the payment of alimony.
- The issue of the possibility of paying alimony by transferring real estate to the child's ownership is topical. How does it work in practice?
- Legislator allows the possibility of paying alimony by transferring real estate to the ownership of the child. Such a procedure may be fixed in the Marriage Agreement or in the Agreement on the payment of alimony. If the alimony is collected by the court as a percentage of earnings or in a fixed amount of money or in basic units, then the issue of paying alimony for the future by transferring real estate to the child’s ownership can be resolved by the child’s parents by mutual agreement within the framework of enforcement proceedings by concluding a settlement agreement which is subject to court approval.
- There are cases when, according to several court decisions, child support was awarded from the defendant from different mothers or fathers, and in total the amount of child support exceeds the amount established by law. In this situation, is it possible to reduce the amount of alimony?
- Indeed, the legislator allows the possibility of reducing the amount of alimony by the court if the parent obliged to pay alimony has other minor children who, when collecting alimony, turned out to be less financially secure than the children receiving alimony, and also if such parent is a disabled person of 1 or 2 groups. In the event of such circumstances, the parent paying child support for minor children under a court order has the right to file a claim for a reduction in the amount of child support established by the court and collected for the maintenance of children.
It is also important that in exceptional cases the court may exempt a parent who is a disabled person of group I or II from paying alimony, as well as reduce the minimum amount of alimony collected from an able-bodied parent who, for objective reasons, cannot pay them within the established sizes.
- What kind of financial assistance from the father of a child can a mother who is on leave to care for a child under the age of three, if the parents do not live together, count on?
- A parent caring for a common child up to the age of three and in need of financial assistance has the right to receive maintenance from the other parent who has the necessary means for this, if they are married, and retains this right in case of divorce. In this case, the spouse in need of financial assistance and taking care of the child has the right to file a lawsuit against the second spouse (former spouse) for the recovery of funds for his maintenance until the child reaches the age of three. The amount of the amount awarded will depend on the need of the plaintiff, as well as take into account the financial and marital status of the other spouse who is obliged to provide material support, his obligations to other persons whom he is also obliged by law to help. If the conditions that are the basis for receiving maintenance have disappeared, and also if the divorced spouse receiving maintenance funds enters into a new marriage, then the spouse paying such funds by a court decision has the right to apply to the court to release him from their further payment .
- Is a parent obligated to support their child after they turn 18?
- The obligation to support children after they reach the age of 18 is enshrined in legislation in relation to disabled adult children in need of assistance. Also, the Marriage Agreement or the Agreement on the payment of alimony may provide for the payment of alimony for children even after they reach the age of majority (for example, until the child receives the first higher education after graduation from school).
- Vera Borisovna, could you explain what procedure a claimant must follow in order to directly execute a court decision after a court decision on the recovery of alimony has been issued?
- The recoverer must obtain from the court that issued the court order on the recovery of alimony, a writ of execution or a ruling on a court order, and apply with it to the enforcement authority with an application to initiate enforcement proceedings. It should also be noted that if a party under the Marriage Agreement, the Agreement on the payment of alimony, the Agreement on children does not fulfill its obligations to pay alimony, the exactor has the right to apply to the court for the issuance of a writ of execution and present it to the enforcement authority for the enforcement of alimony.
It should also be noted that if a party under the Marriage Agreement, the Agreement on the payment of alimony, the Agreement on children does not fulfill its obligations to pay alimony, the exactor has the right to apply to the court for the issuance of a writ of execution and present it to the enforcement authority for the enforcement of alimony.
- Parents often evade paying child support. What responsibility is provided by the legislation of the Republic of Belarus for parents evading the maintenance of their children?
- For parents evading more than three months during the year from paying, by court order, funds for the maintenance of minors or adults, but disabled and in need of assistance to children, criminal liability is provided.
In particular, the sanction of Part 1 of Art. 174 of the Criminal Code provides for punishment in the form of community service or correctional labor for up to two years, or arrest, or restriction of liberty for up to three years, or imprisonment for up to one year.
In the event of the commission of the specified act by a person previously convicted of evading the maintenance of children, Part 3 of Art. 174 of the Criminal Code provides for punishment in the form of correctional labor for a term of one to two years, or arrest, or restriction of liberty for a term of one to three years, or imprisonment for a term of up to two years.
- Summarizing all of the above, it is necessary to once again emphasize the importance of the topic discussed today and the increased interest in it from the public. And how important is it for the judiciary?
- Consideration of cases related to the protection of children is one of the priorities of the courts. When considering marriage and family disputes, including the recovery of alimony, the courts take comprehensive measures aimed at reconciling spouses, preserving the family and, most importantly, protecting the rights and interests of children.
 gov, join our user panel to test new features for the site.
gov, join our user panel to test new features for the site.