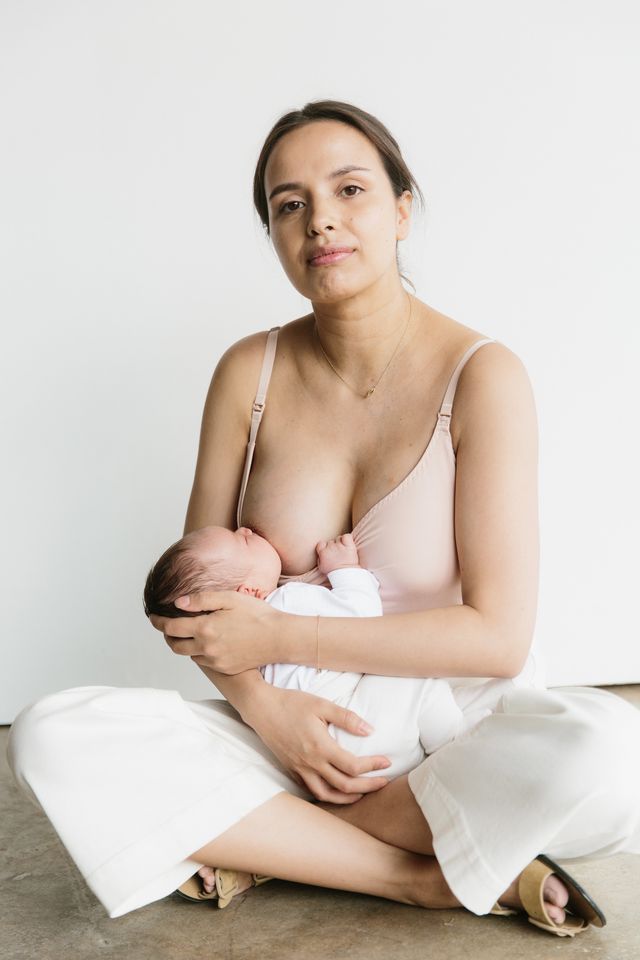
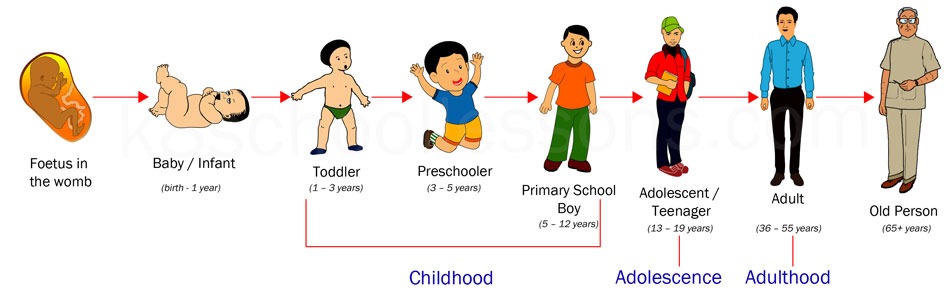
How do i claim child care on my taxes
Child and Dependent Care Credit
Editor’s note: This article has been updated to reflect updates to the Child and Dependent Care Credit from the American Rescue Plan Act of 2021. You’ll find those details near the bottom of this page.
If you’re a parent or caretaker of disabled dependents or spouses, listen up—you may qualify for a special tax credit used for claiming child care expenses. It’s called the Child and Dependent Care Credit, and with it, you might be able to get back some of the money you spent on these expenses by claiming it.
Learn more about this valuable tax credit and how it’s recently changed here.
Requirements for the Child Care Tax Credit
To claim the Child and Dependent Care Credit, all of these must be true:
- You and your spouse usually file as married filing jointly. (See Filing exceptions below.)
- You provide the care so you (and your spouse, if married) can work or look for work.
- You have some earned income. If you’re married and living together, both you and your spouse must have earned income. However, one spouse might be disabled or a full-time student at least five months of the year. If that’s the case, IRS assigns one of these earned income amounts to that spouse:
- $250 per month for one child
- $500 per month for two or more children
- You and the person(s) being cared for live in the same home for more than half of the year.
- The person providing the care can’t be:
- Your spouse
- Parent of your qualifying child under age 13
- Person you can claim as a dependent
- If your child provides the care, he or she:
- Must be age 19 or older
- Can’t be your dependent
Even if you’re not married filing jointly, you might be able to claim the credit if both are true:
- You paid more than half the cost of maintaining a household for the year.
 Both you and the qualifying person must have used the home as your main residence for more than half the tax year.
Both you and the qualifying person must have used the home as your main residence for more than half the tax year. - Your spouse wasn’t a member of the household during the last six months of the tax year.
Qualifying persons for the Child Care Credit
To claim a Child Care Credit for qualified expenses, you must provide care for one or more qualifying persons. (See Qualified expenses section below)
Qualifying persons include:
- A dependent who’s a qualifying child and under age 13 when you provide the care. Usually, you must be able to claim the child as a dependent to receive a credit. However, an exception applies for children of divorced or separated parents. In those situations, the child is the qualifying child of the custodial parent for purposes of this credit. This applies even if the noncustodial parent claims the child as a dependent.
- Spouse or dependent of any age who’s both of these:
- Physically or mentally incapable of self-care
- Has the same main home as you do when you provide the care
Qualified expenses for the Child and Dependent Care Credit
Qualified child- or dependent-care expenses are those you incur while you work or look for work. The main purpose of the expenses must be well-being and protection.
The main purpose of the expenses must be well-being and protection.
Qualified expenses for the Child and Dependent Care Credit include:
- Expenses for care provided outside the home. This applies if the qualifying person regularly spends at least eight hours each day in your home. If the qualifying person receives the care in a dependent-care center, the center must comply with all relevant state and local laws. A dependent-care center is one that cares for more than six people for a fee.
- Expenses for in-home care. This includes expenses for:
- Cooking
- Light housework related to the qualifying individual’s care
- The care itself
- Gross wages paid for qualified services, plus your portion of:
- Social Security
- Medicare
- Federal unemployment taxes
- Other payroll taxes paid on the wages
- Meals and lodging for the employee providing the services
What expenses don’t qualify for the Child and Dependent Care Credit?
These expenses don’t qualify for the Child and Dependent Care Credit:
- Transportation costs to and from the childcare facility
- Overnight camp expenses
- Expenses for the education of a child in kindergarten or higher
- Expenses for chauffeur or gardening services
The cost of before- or after-school programs might qualify if the program is for the care of the child. Education costs below kindergarten qualify if you can’t separate those costs from the cost of care. This includes nursery school.
Education costs below kindergarten qualify if you can’t separate those costs from the cost of care. This includes nursery school.
Calculating the Child and Dependent Care Credit until 2020
For tax years through 2020, the Dependent Care Credit is 20% to 35% of qualified expenses. The percentage depends on your adjusted gross income (AGI). The maximum amount of qualified expenses you’re allowed to calculate the credit is:
- $3,000 for one qualifying person
- $6,000 for two or more qualifying persons
How much you can claim phases out depending on your income.
Calculating the Child and Dependent Care Credit in 2021
Thanks to the American Rescue Plan Act of 2021, the amounts you can claim for this credit have increased. Starting with your 2021 taxes, you’ll be able to claim up to:
- $8,000 of expenses for a qualifying person
- $16,000 of expenses for two or more qualifying people
The percent of the expenses you can claim has also increased. You can now claim:
You can now claim:
- 50% of expenses if your AGI is below $125,000
- 50%-20%, if your AGI is $125,000-$185,000
- 20%, if your AGI is $185,000-$400,000
- 20%-0%, if your AGI is $400,000-$440,000
- 0%, if your AGI is $440,000 or more
How to claim the Child Care Credit
Complete Form 2441: Child and Dependent Care Expenses and attach it to your Form 1040 to claim the Child and Dependent Care Credit.
Bonus content: Employer-provided benefits
Some employers provide childcare benefits like:
- On-site care for their employees’ children
- Direct payment for third-party care
- Accounts earmarked for childcare expenses. Employees can put money from their salaries into these accounts.
If the value of the benefits is more than $5,000, your employer will report everything over $5,000 as taxable income. If the value is less than $5,000, it’s not taxable income.
For 2021 only, the maximum employer-provided dependent care benefit exclusion is increased from $5,000 to $10,500.
Some employers offer Section 125 plans. These are also called cafeteria plans or flexible spending accounts (FSAs). They allow employees to reduce their salaries for one or more nontaxable benefits. You can use common flexible spending accounts to pay childcare or medical expenses.
Your W-2, Box 10 will show the amount of child and dependent care benefits your employer provided. You can’t use expenses paid or reimbursed with these benefits to claim the childcare credit. Subtract the Box 10 amount from the amount of the child and dependent care credit you can claim. When your W-2 shows dependent care benefits, you must complete Form 2441 (Form 1040), Part III. This applies even if you’re not claiming a Child Care Credit.
Can you take a child care tax deduction?No, there are no tax deductions available for child care for individuals—just a credit. However, you might qualify for other credits or deductions. To learn more, read about the top five common tax credits.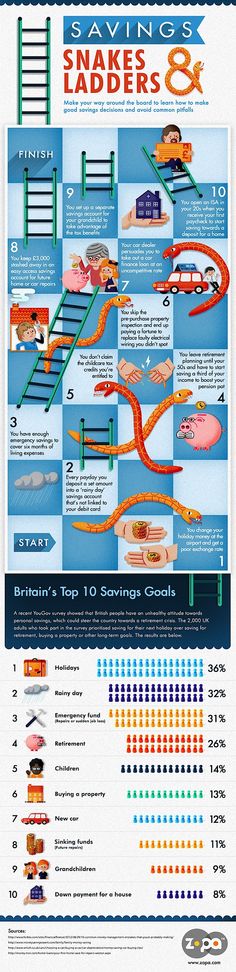
More help with claiming the Child Care Tax Credit
If you think you qualify for the Child Care Tax Credit or other tax credits or deductions, get help! With many ways to file your taxes with H&R Block, we can work with you in a way that best suits your needs to help maximize your tax credits and deductions.
Child and Dependent Care Credit – Get It Back
Child and Dependent Care Credit
The Child and Dependent Care Credit is a federal tax benefit that helps families pay expenses for child care needed to work or to look for work. The credit also is available to families that must pay for the care of an incapacitated spouse or an adult dependent.
NEW: The Child and Dependent Care Credit is fully refundable for tax year 2021 only (which you file taxes for in 2022). This means the credit can provide money back even if you don’t owe taxes.
Your family can claim this credit if you:
- Paid for care in 2021 for a qualifying child under age 13 claimed as a dependent*, or a spouse or dependent not able to care for themselves, who lived with your family for more than half of the year.
 AND
AND - Needed the child or dependent care to work or look for work. (In a two-parent family, both spouses must have needed the child or dependent care to work or to look for work unless one spouse was a full-time student or unable to care for themselves.) AND
- Spent less for dependent care during 2021 than your total income for the year. If taxpayers are married and filing a joint tax return, they must have paid less for care than the income of the spouse with the lowest earnings. There are special rules for calculating the income of a spouse who was a full-time student or disabled.
Types of care that qualify for this credit:
- Any kind of child or dependent care can qualify, including care at a center, a family day care home or a church, vacation day camps, or care provided by a neighbor or a relative (except if provided by a spouse, a dependent, or a child of the tax filer under 19).

- If a family receives free child care, such as from a state-subsidized program, that care cannot be used to qualify for the credit. Copayments by families for subsidized care, however, are an eligible expense.
The EITC and CTC do not affect a family’s eligibility for this credit. Claiming all three credits, when possible, may mean even more money back from the IRS.
* In general, the credit can only be claimed if a child is claimed as a tax dependent, but there are special rules for children of divorced or separated parents. See the IRS Publication 503, Child and Dependent Care Expenses, “Child of divorced or separated parents or parents living apart” section.
The size of the Child and Dependent Care Credit depends on the number of children or dependents in care, your family’s income, and the amount your family paid for care during the year.
| Number of Children | Amount of Qualified Expenses | Adjusted Gross Income (AGI) | Maximum Percentage of Expenses | Maximum Credit |
| 1 | Up to $8,000 | $0-$125,000 | 50% | $4,000 |
| $183,000-$400,000 | 20% | $1,600 | ||
| 2 | Up to $16,000 | $0-$125,000 | 50% | $8,000 |
| $183,000–$400,000 | 20% | $3,200 |
The CDCTC is unavailable to families with AGI greater than $438,000. For families earning between $125,000-$183,000 or between $400,000-$438,000, the credit rate decreases by one percent for each additional $2,000 in income and the maximum credit varies.
For families earning between $125,000-$183,000 or between $400,000-$438,000, the credit rate decreases by one percent for each additional $2,000 in income and the maximum credit varies.
Example: Ms. Lewis has one child and earned $30,000 in 2021. Ms. Lewis spent $8,000 during the year on child care and she is eligible for a Child and Dependent Care Credit up to 50 percent of what she spent on care, or up to $4,000. Her Child and Dependent Care Credit eliminates her tax liability. (She also qualifies for other tax benefits: she is eligible for a CTC refund worth $3,600 and her EITC is worth $2,099.)
Use the Bipartisan Policy Center’s calculator to help determine how much your credit is worth.
Families must file a federal income tax return and submit Form 2441, “Child and Dependent Care Expenses.” You will need to submit the provider’s name, address, and Taxpayer Identification number (TIN). To complete the tax form, you will also need to know how much you spent on care in 2021. You can refer to receipts or bank account statements depending on how you paid for the care.
You can refer to receipts or bank account statements depending on how you paid for the care.
Twenty-four states have state child and dependent care credits. Of these 24 states, 11 states provide a refundable credit: Arkansas (only for children under 6 in an approved child care facility), Colorado, Hawaii, Iowa, Louisiana, Maine, Minnesota, Nebraska, New Mexico, New York, and Vermont. In these states, low-wage earners that don’t owe income tax can still receive a refund. For more information, contact your state department of revenue.
Find out the 13 states with state child and dependent care credits that have adapted their credits based on the federal expansion.
- IRS Publication 503 “Child and Dependent Care Expenses”
- National Women Law Center’s 5 Things You Should Know About the Child and Dependent Care Tax Credit This Year
- National Women Law Center’s 2021 Child and Dependent Care Credit Fact Sheet (available in English & Spanish)
The latest
By Tysheonia Edwards, 2022 Get It Back Campaign Intern Identity theft happens when…
By Christine Tran, 2021 Get It Back Campaign Intern & Reagan Van Coutren,…
Internet access is essential for work, school, healthcare, and more. The Affordable Connectivity…
The Affordable Connectivity…
How to get child benefits as a self-employed person
I became self-employed in 2022. She is currently pregnant, the planned due date is 2023.
Can I receive maternity and childcare benefits as a worker? Do I need to pay contributions for voluntary pension insurance? If yes, then in what amount?
Another question: should a self-employed person have work experience? How many and what sales per month should it show?
Marina Sukhovskaya
lawyer
Author profile
The amount of sales that you pay in the My Tax application and voluntary contributions to the FIU will not affect child benefits. Pension contributions are transferred so that the seniority for a future pension goes on, benefits are not calculated on them.
If you do not have IP status, you will not receive maternity benefit. But you can count on a one-time allowance for the birth of a child and an allowance for caring for him up to a year and a half. You are also likely to be entitled to some regional payments. nine0003
You are also likely to be entitled to some regional payments. nine0003
How to make money with your business
The best business stories in your inbox every week. Free of charge
When a self-employed person can receive maternity allowance
Maternity allowance - as maternity allowance is commonly called - is paid on the basis of an electronic sick leave certificate. The doctor forms it:
- for a singleton pregnancy - for a period of 30 weeks. The duration of sick leave is 140 calendar days: 70 days before delivery and 70 days after; nine0028
- for multiple pregnancy - at 28 weeks. Sick leave will be given for 194 calendar days: 84 days before delivery and 110 days after.
clause 57 of the conditions for the formation of certificates of incapacity for work
Maternity payments are due to women insured in case of pregnancy and childbirth. As a rule, these women:
- work under an employment contract;
- do military service under a contract;
- are in the state or municipal service; nine0028
- study full-time at universities, colleges, technical schools, colleges and scientific organizations;
- were dismissed due to the liquidation of the organization or the termination of the activities of the individual entrepreneur and within a year were registered with the employment service.

st. 6 of the Law "On State Benefits for Citizens with Children"
The rule on compulsory social insurance does not apply to female entrepreneurs. If an entrepreneur wants the state to pay her sick leave, including in connection with a decree, she must:
- Register with the FSS as an insured. The easiest way to do this is on the public services portal, but you can personally come to any FSS client center and submit an application there. Some MFCs also provide this service.
- Pay voluntary contributions to the Social Insurance Fund until December 31 of the year preceding the year the sick leave was opened. In 2022, the amount of contributions is 4833.72 R.
Only self-employed people who have the status of an individual entrepreneur can register with the FSS and pay contributions for themselves. Self-employed without this status cannot be insured and receive sick leave: there is no such possibility by law. nine0003
nine0003
FSS letter dated February 28, 2020 No. 02-09-11/06-04-4346
Therefore, in order to receive maternity benefits, you need to register an individual entrepreneur and pay voluntary contributions before the end of the year.
What to do? 07/15/19
How can an individual entrepreneur receive maternity payments?
What benefits can a self-employed person receive per child? nine0003
Monthly allowance for early pregnancy registration. Its size is 50% of the regional subsistence minimum for the working-age population, on average 6,000 R. minimum in the region of residence.
The following conditions must also be met:
- The woman has Russian citizenship, a residence permit or a temporary residence permit in Russia. nine0028
- She was registered before the 12th week of pregnancy.
- After the 12th week, the woman applied for public services or the FIU if there is no account on the portal.
 An application cannot be submitted before this deadline.
An application cannot be submitted before this deadline. - A woman visits a medical facility at 10-14, 18-22, 30-32 weeks.
- The family's property is included in the established list. For example, if there is one apartment, one dacha, one garage and one car, the family fits into the norm. If there are two garages, there are no more.
So what? 07/01/21
Benefit for pregnant women in 2022: basic conditions
One-time allowance for the birth of a child is due to one of the parents and does not depend on employment, length of service and earnings.
From February 1, 2022, the allowance for each child is 20,472.77 R. It is not yet known how much the allowance will be indexed from February 2023.
/benefits/
Payments and child benefits in 2022
As a general rule, the allowance is paid to one of the parents at the place of work. From the second, a certificate is needed that he did not receive this payment.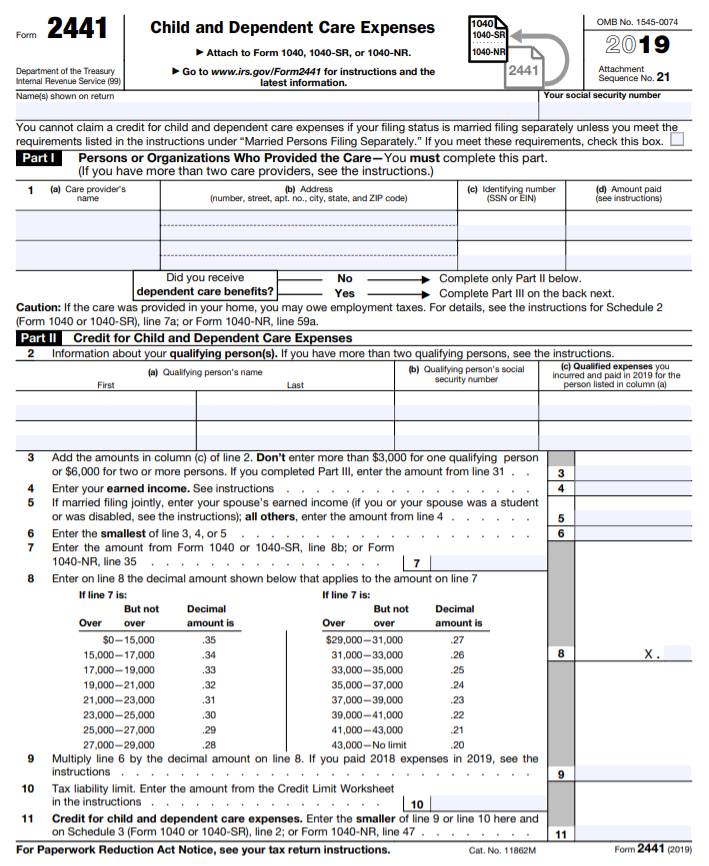 If both parents are unemployed or self-employed, the allowance is issued by one of them in the pension fund at the place of residence.
If both parents are unemployed or self-employed, the allowance is issued by one of them in the pension fund at the place of residence.
Additional payments exist in many regions. For example, Muscovites in 2022 can receive 6313 R for the first child or 16 642 R for the second and subsequent children.
And in St. Petersburg, parents are given a special children's card, to which 36,168 R is transferred for the birth of the first child, 48,227 R for the second, and 60,280 R for the third and subsequent children. This card can be used to pay for the purchase of children's goods in most big shops in the city. nine0003
Monthly allowance for caring for a child up to one and a half years old is due to both officially employed mothers and those who do not work or work for themselves.
The benefit is issued by the social security agency. If you register an individual entrepreneur and enter voluntary social insurance, you will need to apply to the Social Insurance Fund for childcare benefits.
/posobie-ip/
How an individual entrepreneur can apply for maternity benefits
You are entitled to the minimum allowance - 7677.81 R, since the length of service, if any, will not be taken into account. nine0003
As a result
In any case, you will receive a lump-sum allowance for the birth of a child and an allowance for caring for him up to a year and a half.
Early registration allowance for pregnancy is paid to the poor, subject to a number of conditions.
If you want to receive maternity allowance, you need to have time to register an individual entrepreneur and pay voluntary contributions before the end of the year.
Sales amounts reflected in the My Tax application and voluntary contributions to the Pension Fund do not affect the ability to receive child benefits, as well as their size. nine0003
What to do? Readers ask - experts answer
Ask a question
Monthly child care allowance for persons not subject to compulsory social insurance
The applicant has the right to file a complaint against the decisions and (or) actions (inaction) of the authorized body, its officials in the provision of public services (complaint), including in the pre-trial (out of court) procedure in the following cases:
- violation of the application registration deadline; nine0028
- violation of the term for the provision of public services;
- requirement from the applicant of documents, information or actions not provided for by the regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation for the provision of public services;
- refusal to provide a public service, if the grounds for refusal are not provided for by federal laws and other regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation adopted in accordance with them; nine0028
- refusal to accept documents, the submission of which is provided for by regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation for the provision of public services;
- requesting from the applicant, when providing a public service, a fee not provided for by the regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation;
- refusal of the authorized body, its officials to correct the misprints and errors made by them in the documents issued as a result of the provision of public services or violation of the deadline for such corrections; nine0028
- violation of the term or procedure for issuing documents based on the results of the provision of public services;
- suspension of the provision of public services, if the grounds for suspension are not provided for by federal laws and other regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation adopted in accordance with them, laws and other regulatory legal acts of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation, municipal legal acts.

nine0075 Subject of complaint
The subject of the complaint is a violation of the rights and legitimate interests of the applicant, unlawful decisions and (or) actions (inaction) of the authorized body, its officials in the provision of public services, violation of the provisions of the administrative regulations and other regulatory legal acts that establish requirements for the provision of public services.
A citizen has the right to file a complaint in writing on paper by mail or in person to any PFR Client Service, as well as in electronic form: nine0003
- on the official website pfr.gov.ru;
- portal vashkontrol.ru;
- portal do.gosuslugi.ru.
The reason for the appeal may be dissatisfaction with the quality of the provision of public services by the PFR, violation of the terms for the provision of services, violation of the terms for registering a request for a service, refusal to correct errors or typos, refusal to provide a public service, refusal to accept documents, demand for an additional fee. nine0003
nine0003
Procedure for filing and handling a complaint
The complaint must contain:
- name of the authorized body, last name, first name, patronymic (if any) of its officials providing public services, and (or) their leaders, decisions and actions (inaction) of which are being appealed;
- last name, first name, patronymic (if any) of the applicant, information about the place of residence, as well as contact phone number (numbers), e-mail address (s) (if any) and postal address to which the answer should be sent to the applicant; nine0028
- information about the appealed decisions and (or) actions (inaction) of the authorized body, an official of the authorized body, its head;
- arguments on the basis of which the applicant does not agree with the decisions and (or) actions (inaction) of the authorized body, an official of the authorized body, its head.
The applicant shall submit documents (if any) confirming his arguments or copies thereof.
When filing a complaint in electronic form, the documents specified in paragraph 106 of the administrative regulations may be submitted in the form of an electronic document signed with an electronic signature, the form of which is provided for by the legislation of the Russian Federation. In this case, an identity document of the applicant is not required.
In the authorized body, officials authorized to consider complaints are determined, who ensure:
- receiving and handling complaints; nine0028
- forwarding complaints to the body authorized to consider them.
Complaints against decisions and (or) actions (inaction) of an official of the authorized body are considered by the head of the authorized body or an official of the authorized body authorized to consider complaints. Complaints against decisions and (or) actions (inaction) of the head of the authorized body are considered by an official of the executive authority of the constituent entity of the Russian Federation authorized to consider complaints. nine0003
nine0003
If the complaint is filed by the applicant with a body whose competence does not include making a decision on the complaint, within 3 working days from the date of its registration, the said body sends the complaint to the body authorized to consider it and informs the complainant in writing about the redirection of the complaint.
The authorized body ensures:
- equipment for receiving complaints;
- informing applicants about the procedure for appealing against decisions and (or) actions (inaction) of the authorized body, officials of the authorized body by posting information on information boards in places where public services are provided, on the website of the authorized body, on the Single portal, service portal; nine0028
- advising applicants on the procedure for appealing against decisions and (or) actions (inaction) of the authorized body, officials of the authorized body at a personal appointment, by phone, using the website of the authorized body;
- conclusion of agreements on interaction between the multifunctional center and the authorized body in terms of the implementation by the multifunctional center of receiving complaints and issuing the results of consideration of complaints to the applicant;
- formation and quarterly submission to the Federal Service for Labor and Employment of reports on received and considered complaints (including the number of satisfied and unsatisfied complaints).
 nine0028
nine0028
Deadlines for considering a complaint
A complaint received by the authorized body shall be subject to registration no later than the working day following the day of its receipt.
The complaint is subject to consideration within 15 working days from the date of its registration, and in the event of an appeal against the refusal of the authorized body to accept documents from the applicant or to correct misprints and errors, or in the event of an appeal against a violation of the established deadline for such corrections - within 5 working days from the date of its registration. nine0003
Result of consideration of the complaint
The result of the consideration of the complaint is the adoption of one of the following decisions:
- satisfy the complaint, including in the form of cancellation of the decision made by the authorized body, correction of typos and errors in documents issued as a result of the provision of public services, return to the applicant of funds, the collection of which is not provided for by the regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation, regulatory legal acts of the subjects Russian Federation, municipal legal acts; nine0028
- refuse to satisfy the complaint.

When satisfying the complaint, the authorized body takes comprehensive measures to eliminate the identified violations, including the issuance of the result of the public service to the applicant no later than 5 working days from the date of the relevant decision, unless otherwise provided by the legislation of the Russian Federation.
A complaint may be denied in the following cases:
- availability of a court decision that has entered into legal force on a complaint about the same subject and on the same grounds;
- filing a complaint by a person whose powers have not been confirmed in the manner prescribed by the legislation of the Russian Federation;
- the presence of a decision on a complaint made earlier in accordance with the requirements of the Rules for filing and considering complaints against decisions and actions (inaction) of federal executive bodies and their officials, federal civil servants, officials of state non-budgetary funds of the Russian Federation, state corporations endowed with in accordance with federal laws, the powers to provide public services in the established field of activity, and their officials, organizations provided for by Part 1.
 1 of Article 16 of the Federal Law "On the organization of the provision of state and municipal services", and their employees, as well as multifunctional centers for the provision of state and municipal services and their employees, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 840 dated August 16, 2012, in respect of the same applicant and on the same subject of the complaint. nine0028
1 of Article 16 of the Federal Law "On the organization of the provision of state and municipal services", and their employees, as well as multifunctional centers for the provision of state and municipal services and their employees, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 840 dated August 16, 2012, in respect of the same applicant and on the same subject of the complaint. nine0028
A complaint may be left unanswered in the following cases:
- presence in the complaint of obscene or offensive language, threats to life, health and property of an official of the authorized body, as well as members of his family;
- the inability to read any part of the text of the complaint, the last name, first name, patronymic (if any) and (or) the postal address of the applicant indicated in the complaint.
In response to the results of the consideration of the complaint, the following shall be indicated: nine0003
- name of the body providing the public service that considered the complaint, position, surname, name, patronymic (if any) of the official who made the decision on the complaint;
- number, date, place of the decision, including information about the official of the authorized body, the decision and (or) action (omission) of which is being appealed;
- surname, name, patronymic (if any) of the applicant;
- grounds for making a decision on the complaint; nine0028
- decision made on the complaint;
- in the event that the complaint is found to be justified, the terms for eliminating the identified violations, including the term for providing the result of the public service;
- information on the procedure for appealing the decision taken on the complaint.
In the event that, during or as a result of consideration of a complaint, signs of an administrative offense or crime are established, an official of the authorized body authorized to consider complaints shall send the available materials to the prosecutor's office. nine0003
Procedure for informing the applicant about the results of the consideration of the complaint
A reasoned response based on the results of the consideration of the complaint is signed by the official authorized to consider the complaint and sent to the applicant in writing or, at the request of the applicant, in the form of an electronic document signed by the electronic signature of the official authorized to consider the complaint, the type of which is established by the legislation of the Russian Federation, no later than the day following the day the decision is made on the results of the consideration of the complaint. nine0003
Procedure for appealing a decision on a complaint
The applicant has the right to appeal the decision taken on the complaint by sending it to the Federal Service for Labor and Employment.
If the applicant is not satisfied with the decision made during the consideration of the complaint or the absence of a decision on it, then he has the right to appeal the decision in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation.
The applicant's right to receive information and documents necessary to substantiate and consider the complaint
The applicant has the right to receive comprehensive information and documents necessary to substantiate and consider the complaint.
Ways to inform complainants about the procedure for filing and handling a complaint
Information on the procedure for filing and considering a complaint is posted on information boards in places where public services are provided, on the website of the authorized body, on the Single Portal, Services Portal, and can also be communicated to the applicant orally and (or) in writing. nine0003
List of normative legal acts regulating the procedure for pre-trial (out-of-court) appeal against decisions and actions (inaction) of the authorized body, as well as its officials
The procedure for pre-trial (out-of-court) appeals against decisions and actions (inaction) of the body providing the public service, as well as its officials, is regulated by Federal Law No.