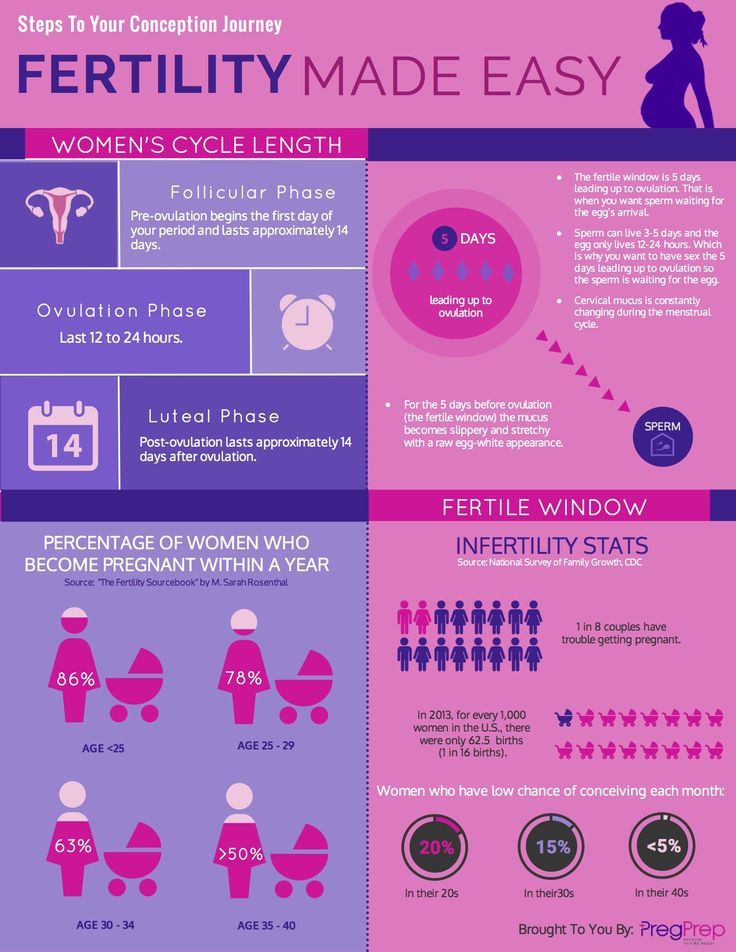
Do you have cervical mucus when pregnant
Cervical Mucus: An Early Pregnancy Sign?
Cervical Mucus: An Early Pregnancy Sign?Medically reviewed by Debra Sullivan, Ph.D., MSN, R.N., CNE, COI — By Erica Cirino on June 13, 2019
We include products we think are useful for our readers. If you buy through links on this page, we may earn a small commission. Here’s our process.
Healthline only shows you brands and products that we stand behind.
Our team thoroughly researches and evaluates the recommendations we make on our site. To establish that the product manufacturers addressed safety and efficacy standards, we:
- Evaluate ingredients and composition: Do they have the potential to cause harm?
- Fact-check all health claims: Do they align with the current body of scientific evidence?
- Assess the brand: Does it operate with integrity and adhere to industry best practices?
We do the research so you can find trusted products for your health and wellness.
It’s normal for cervical mucus (vaginal discharge) to change in color, consistency, and amount throughout your menstrual cycle. It may also change during the early stages of pregnancy.
While it may be possible to notice changes in cervical mucus during the early stages of pregnancy, these changes are usually subtle. They can also vary a lot from person to person.
Read on to learn about cervical mucus changes and whether it’s a reliable method of detecting early pregnancy.
During early pregnancy, changes in cervical mucus can be subtle. There is usually an increase in the amount of cervical discharge. However, the change may be so slight that it may be barely noticeable.
Early on in a pregnancy, you may feel more wetness in your underwear than usual. You may also notice a larger amount of dry whitish-yellow discharge on your underwear at the end of the day or overnight.
Cervical mucus, also called leukorrhea, is a normal part of a woman’s cycle. It helps keep the vaginal tissues healthy by protecting them against irritation and infection, and it also keeps the vagina lubricated.
It helps keep the vaginal tissues healthy by protecting them against irritation and infection, and it also keeps the vagina lubricated.
During your menstrual cycle, you may notice that your cervical mucus changes. One day it may be white and sticky, for example, and the next day it may be clear and watery.
When you get pregnant, your body’s hormone levels will begin to rise dramatically. These hormonal changes help prepare your body to grow, and they also help protect and nourish the baby.
The changes to your hormones can lead to an increase in vaginal discharge as your pregnancy progresses. This happens naturally, as your body works to prevent vaginal infections, especially during more advanced stages of pregnancy.
Healthy cervical mucus is thin, white or clear, and has a mild odor. While cervical mucus changes throughout your cycle, and also during pregnancy, it should continue to have these qualities.
The following characteristics of discharge are not typical:
- smells foul
- is bright yellow, green, or gray
- causes itching, swell, burning, or irritation
Cervical discharge with any of these traits could be a sign of an infection. It’s important to see your doctor if you notice any of these changes or symptoms.
It’s important to see your doctor if you notice any of these changes or symptoms.
A slight increase in cervical mucus is just one of many early signs of pregnancy. Because it’s so subtle, it’s often overlooked. Other common, more noticeable early signs of pregnancy include:
- a missed period; however, several other conditions, including stress, extreme exercise, eating disorders, hormone imbalance, and other health issues may cause you to miss a period
- cramping
- food cravings and increased hunger, as well as avoidance of certain foods
- frequent urination caused by the pregnancy hormone chorionic gonadotropin, which triggers frequent urination
- fatigue, caused by an increase in the hormone progesterone
- light spotting called “implantation bleeding,” which may occur 6 to 12 days after conception, not lasting more than 24 to 48 hours
- nausea, often in the morning (morning sickness)
- breast changes that typically include tender, sore, swollen breasts
- metallic taste in the mouth
- headaches and dizziness
Most women’s bodies produce a very specific kind of mucus right before ovulation.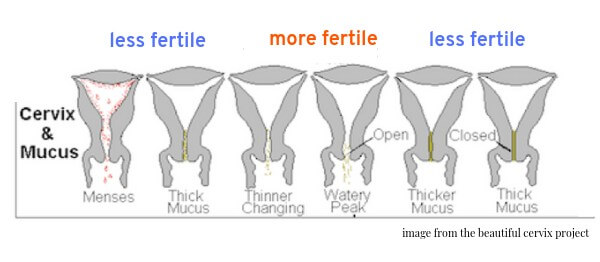 If you carefully track your discharge, it may be possible to track the days when you are most fertile.
If you carefully track your discharge, it may be possible to track the days when you are most fertile.
When your cervical mucus is clear and slippery, you’re probably about to ovulate. This is the time when you’re most likely to get pregnant. You’re less likely to get pregnant when you notice cloudy and sticky mucus, or when you feel dry.
Recording the characteristics of your cervical mucus throughout the month may reveal patterns in your ovulation, helping you determine when you’re most fertile.
While it’s possible to track your fertility by focusing on your cervical mucus throughout the month, it may be challenging to rely on this method to determine when you’re at your most fertile.
That’s why experts usually recommend using a more accurate method of fertility tracking, such as fertility monitoring. There are different types of ovulation tests and fertility monitoring kits you can buy. Some involve taking urine tests to check for hormonal spikes that occur during ovulation.
With other kits, you need to take your temperature in order to check where you are in your menstruation cycle. Your body temperature usually drops a little before you ovulate, and then goes up and stays a little higher for a few days.
Purchase ovulation tests and fertility tracking kits online.
You may notice slight changes in your cervical mucus during early pregnancy. However, it’s not the most reliable way to determine whether or not you are pregnant. Taking a pregnancy test at home or at your doctor’s office is a much more reliable method.
While changes in cervical mucus may not help you know whether or not you are pregnant, paying attention to your cervical mucus throughout your cycle can help you keep an eye on your reproductive health.
Consult your doctor if you have questions about your fertility or getting pregnant.
Last medically reviewed on June 13, 2019
- Parenthood
- Pregnancy
- Pregnancy Complications
- Cat 1
- vaginalhealth
How we reviewed this article:
Healthline has strict sourcing guidelines and relies on peer-reviewed studies, academic research institutions, and medical associations. We avoid using tertiary references. You can learn more about how we ensure our content is accurate and current by reading our editorial policy.
We avoid using tertiary references. You can learn more about how we ensure our content is accurate and current by reading our editorial policy.
- Basal body temperature (BBT) charting.(2018).
uofmhealth.org/health-library/hw202058 - Bouchard TP, et al. (2018). Achieving pregnancy using primary care interventions to identify the fertile window. DOI:
10.3389/fmed.2017.00250 - Kumar P, et al. (2012). Hormones in pregnancy. DOI:
10.4103/0300-1652.107549 - Mayo Clinic Staff. (2018). Cervical mucus method for natural family planning.
mayoclinic.org/tests-procedures/cervical-mucus-method/about/pac-20393452 - Mayo Clinic Staff. (2019). Symptoms of pregnancy: What happens first.
mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/getting-pregnant/in-depth/symptoms-of-pregnancy/art-20043853 - Vaginal discharge. (2015).
my.clevelandclinic.org/health/symptoms/4719-vaginal-discharge - Vaginal discharge in pregnancy.
 (2018).
(2018).
nhs.uk/conditions/pregnancy-and-baby/vaginal-discharge-pregnant/
Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information becomes available.
Share this article
Medically reviewed by Debra Sullivan, Ph.D., MSN, R.N., CNE, COI — By Erica Cirino on June 13, 2019
Read this next
Guide to Cervical Mucus
Cervical mucus can provide important clues to vaginal health, ovulation, pregnancy, and more. Here’s how to check it and what your mucus is telling…
READ MORE
What Causes White Discharge Before Your Period?
Vaginal discharge is the body's way of protecting the vagina from infections. Here’s more about why you might see white discharge before your period.
READ MORE
Everything You Want to Know About Vaginal Yeast Infections
Medically reviewed by Valinda Riggins Nwadike, MD, MPH
A vaginal yeast infection is common and has several causes, but treatment is typically simple.
 Learn more here.
Learn more here. READ MORE
Everything You Should Know About pH Balance Pills and the Best Options to Take
By Melissa Lee
pH balance pills and probiotics may help balance your vagina's natural pH level. Here are our top picks.
READ MORE
Replens Review: Why Users Love These Vaginal Moisturizers and Lubes
Medically reviewed by Valinda Riggins Nwadike, MD, MPH
Replens vaginal moisturizers and lubes claim to help with symptoms of vaginal dryness — but do these products actually work?
READ MORE
What Causes Brown Vaginal Discharge and How Is It Treated?
When blood leaves the body quickly, it's usually a shade of red. But if the flow slows, the blood has time to oxidize and turn brown or even black in…
READ MORE
The Ultimate Guide to Menstrual Cup Sizing
Not only do menstrual cup brands have different sizes, but it can also be hard to work out what’s best for your body without some experimenting.

READ MORE
How to Get Rid of Vaginal Odor
Medically reviewed by Carolyn Kay, M.D.
A change in vaginal odor can be a sign of a larger condition, one that you may be unable to treat on your own. Here's what you need to know.
READ MORE
Chart, Stages, Tracking & Fertility
Overview
Checking cervical mucus for fertility using your fingers.What is cervical mucus?
Cervical mucus is a fluid produced by and released from the cervix (the opening to uterus). Hormones cause your cervical mucus to change in texture, volume and color throughout your menstrual cycle. It can be used to identify when you are most fertile.
Your mucus is thick, white and dry before ovulation (when your ovary releases an egg). Just before ovulation, your cervical mucus will turn clear and slippery. This consistency makes it easy for sperm to swim up to meet an egg at ovulation. If you want to get pregnant, this type of discharge tells you it's time for sex.
If you want to get pregnant, this type of discharge tells you it's time for sex.
Some people chart their cervical mucus to tell them where they are in their cycle. Cervical mucus can tell you when you are fertile or most likely to conceive. It can also indicate when you are not fertile and pregnancy is less likely. This process is called the cervical mucus method of natural family planning.
Function
What does cervical mucus do?
Cervical mucus, or cervical fluid, has two jobs depending on where you are in your cycle. The first is to help sperm move through the cervix so it can fertilize an egg during ovulation. The second job is to prevent sperm or other substances from getting into the cervix.
What are the different types of cervical mucus?
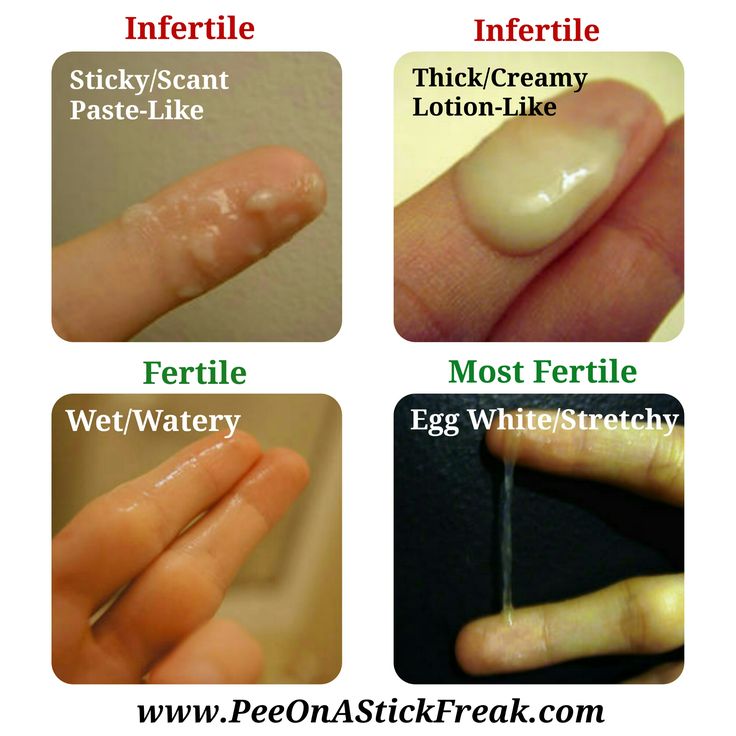
Not every person will be the same, but your cervical mucus will resemble all or most of the following during your menstrual cycle:
- Dry or no cervical fluid.
- Sticky like paste. It can be white or yellow.
- Creamy like yogurt. Smooth in texture and usually white.
- Slippery, stretchy. Resembling raw egg whites.
- Wet, watery and clear in color.
The type or texture of your cervical mucus will depend on what stage of your menstrual cycle you're in. Your mucus generally starts as dry or pasty before moving to a creamier texture. As ovulation nears, your discharge will become wet, stretchy and slippery. The most common analogy used for super fertile cervical mucus is looking and feeling like raw egg whites. If you see that texture, you will know you're at your most fertile time. After ovulation, your cervical mucus goes back to thick and dry.
How does cervical mucus help with conception?
Cervical mucus plays a key role in conception. The hormone estrogen peaks just before ovulation. This causes cervical mucus to change from pasty or creamy to resembling stretchy, raw egg whites. This wet, slippery discharge makes it easier for sperm to swim up the vagina and into the uterus to meet an egg.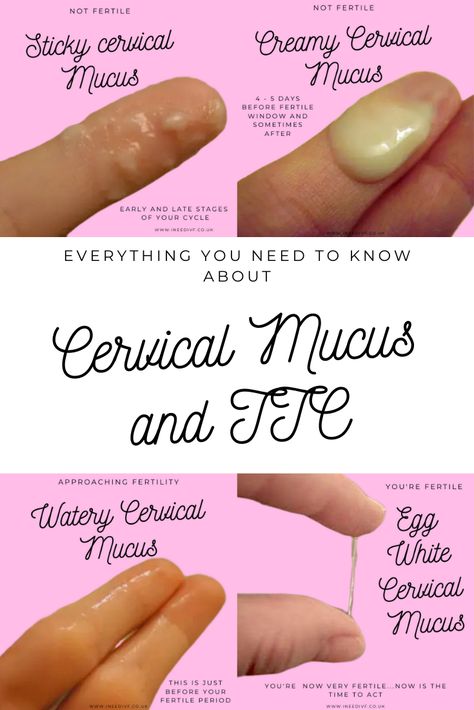 If you have sex at this time, you increase your chances of getting pregnant.
If you have sex at this time, you increase your chances of getting pregnant.
Think of your uterus as a swimming pool, your cervical mucus as water and the sperm as a person trying to swim. If the water was thick or mud-like, there's no way a person could swim through it to reach the other side of the pool. This is how hard it is for sperm to reach your fallopian tubes if your cervical mucus isn't fertile. It's easier for sperm to swim up the uterus to meet an egg for conception in thin, wet, egg white mucus.
How does cervical mucus change throughout my menstrual cycle?
The changes in cervical mucus happen as a result of hormones shifting throughout your menstrual cycle. Estrogen increases before ovulation and makes your cervix produce the fertile, egg white mucus. It's your body's way of making it easy for sperm to reach the egg it's about to release. After ovulation, estrogen levels drop and progesterone levels rise. This rise in progesterone helps the fertilized egg implant into your uterus if conception occurs.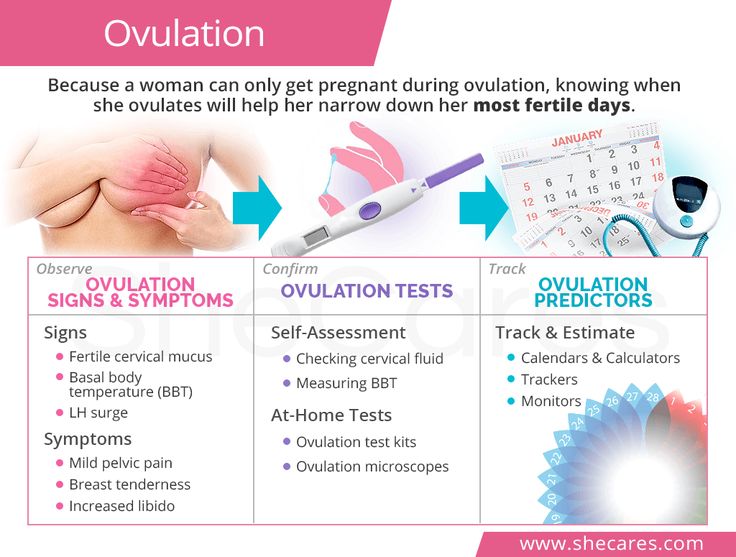 However, this causes your cervical mucus to begin to dry up.
However, this causes your cervical mucus to begin to dry up.
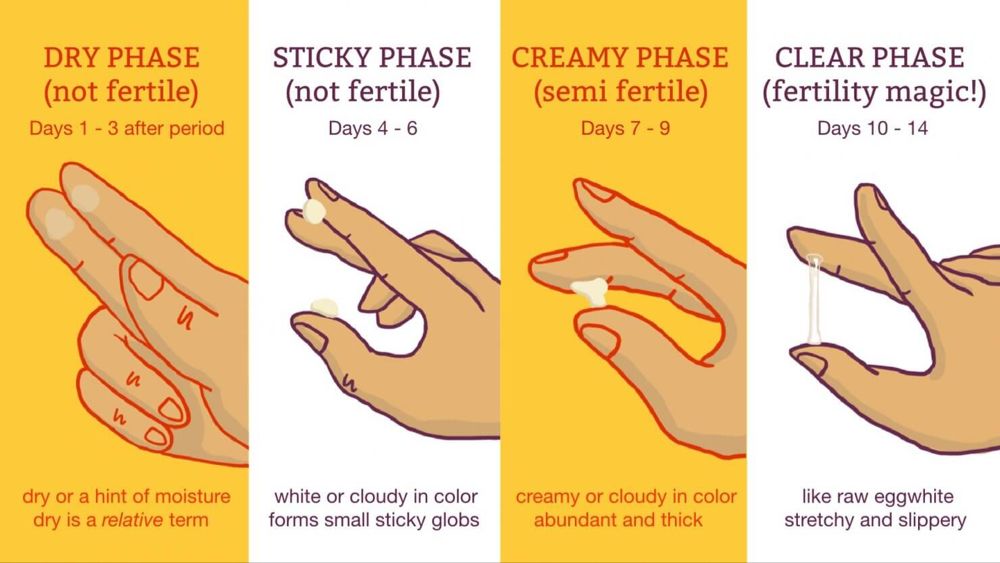
If you have a 28-day menstrual cycle, your cervical mucus will generally follow this pattern:
- Days 1-4 after your period ends: Dry or tacky. It can be white or yellow-tinged.
- Days 4-6: Sticky. Slightly damp and white.
- Days 7-9: Creamy, yogurt-like consistency. Wet and cloudy.
- Days 10-14: Stretchy and resembles raw egg whites. Slippery and very wet.
- Days 14-28: Dry until menstruation occurs.
Most women with a 28-day cycle ovulate around day 14. This is why your cervical mucus is slippery, stretchy and highly fertile just before the egg is released.
How long will I have egg white cervical mucus?
The egg white discharge lasts about four days. If your cycle is 28 days, the fertile cervical mucus occurs around days 10 to 14.
How does cervical mucus change during early pregnancy?
Changes in cervical mucus can be a sign of early pregnancy. After ovulation, your cervical mucus thickens or dries up, then you eventually get your period. However, if you conceived at ovulation, you may still produce some cervical mucus. This can indicate to some women that they might have conceived. In other cases, implantation bleeding occurs. Implantation cervical mucus is tinged brown or pink. This happens around your period, leading some people to think they didn't become pregnant.
However, if you conceived at ovulation, you may still produce some cervical mucus. This can indicate to some women that they might have conceived. In other cases, implantation bleeding occurs. Implantation cervical mucus is tinged brown or pink. This happens around your period, leading some people to think they didn't become pregnant.
It's important to note that every person is different and not everyone has implantation bleeding or noticeable changes in cervical mucus.
Anatomy
Where does cervical mucus come from?
Cervical mucus is produced by your cervix when the hormone estrogen rises. Your estrogen level begins low, then climbs to its peak at ovulation before dropping again. This is why you see the changes in your mucus instead of it being the same all the time.
What can cervical mucus look like?
Cervical mucus can look sticky, creamy, pasty, watery, stretchy or slippery. At your most fertile time, your mucus is slippery and watery. When you're not fertile, the mucus will be thick or pasty.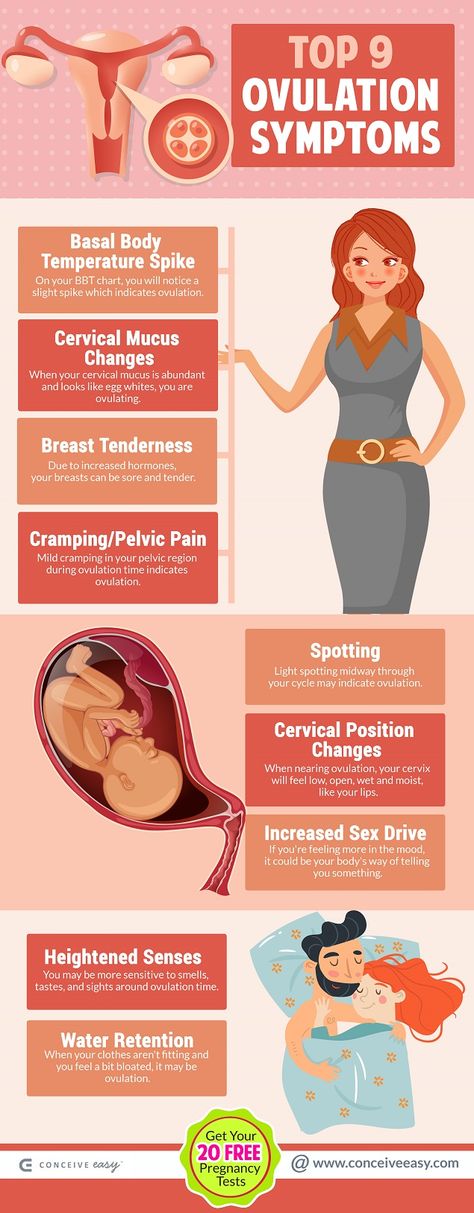 Your cervical mucus is generally odorless. If it's foul-smelling, it could mean you have an infection. It's common for your mucus to be white, off-white or clear in color.
Your cervical mucus is generally odorless. If it's foul-smelling, it could mean you have an infection. It's common for your mucus to be white, off-white or clear in color.
At certain times, especially if implantation has occurred, your discharge might be tinged with pink or brown. If this happens regularly, talk to your healthcare provider as it could be spotting between periods or signs of a problem.
Conditions and Disorders
What can cause changes to cervical mucus?
Certain factors can play a role in the amount of cervical mucus you have or what it looks like. Things that can affect your cervical mucus are:
- Breastfeeding.
- Sexual lubricants.
- Hormonal birth control.
- Sexually transmitted infections (STIs).
- Other vaginal infections like yeast infections or bacterial vaginosis.
- Surgery on your cervix.
- Medications.
- Stress and diet.
How do you know if you have a problem with your cervical mucus?
If you check your cervical mucus and don't believe you see the slippery, fertile cervical mucus, it could be a sign of ovulatory problems, infection or other issues. Your healthcare provider will diagnose cervical mucus problems by performing a pelvic exam and discussing your health history and any medications you take. They'll examine your cervix for signs of infection, scarring or other conditions that could impact vaginal discharge.
Your healthcare provider will diagnose cervical mucus problems by performing a pelvic exam and discussing your health history and any medications you take. They'll examine your cervix for signs of infection, scarring or other conditions that could impact vaginal discharge.
Care
Are there medications to take to increase cervical mucus?
To naturally increase your cervical mucus, try increasing your water intake and eating more fruits and vegetables. Certain medications and vitamins are available that claim to increase cervical mucus. Before taking any supplements for cervical mucus production, talk to your healthcare provider. They will want to discuss issues you are having with conception and rule out any problems.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do I check my cervical mucus?
You can check your cervical mucus a few different ways:
- Use your fingers: With clean hands, place a finger in your vagina. Remove your finger and look at the mucus.
 You may need to use another finger to see if it stretches.
You may need to use another finger to see if it stretches. - Check your underwear: Look at your underwear when you go the bathroom and note the discharge you see.
- Use toilet paper: Using toilet paper is probably the least reliable method to check cervical mucus, but it can still be helpful. After urinating and wiping, check your toilet paper for cervical mucus.
Pay attention to how your cervical mucus looks and feels. Is it sticky, creamy, watery or dry? If it's dry or sticky, you're probably not fertile yet. If it's wet, slippery or soaking your underwear, you are likely fertile.
How do I start charting cervical mucus to get pregnant?
Charting or tracking your cervical mucus is called the cervical mucus method of family planning. Determining ovulation is one of the best tools you can have in your toolbox if you want to conceive.
To chart your cervical mucus, keep track of the changes you see each day — the amount, texture and color. It might be helpful to use a calendar and label days as pasty, creamy, wet or dry. You're most fertile around the time your mucus becomes slippery and wet, like raw egg whites. Once you see this type of mucus, it's time to have sex if conception is your goal. To prevent pregnancy, you should abstain from sex or use another method of birth control.
It might be helpful to use a calendar and label days as pasty, creamy, wet or dry. You're most fertile around the time your mucus becomes slippery and wet, like raw egg whites. Once you see this type of mucus, it's time to have sex if conception is your goal. To prevent pregnancy, you should abstain from sex or use another method of birth control.
If you need help recognizing patterns or think your cervical mucus never reaches a fertile stage, talk to your healthcare provider for guidance.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Tracking your cervical mucus is a helpful way to track your menstrual cycle and identify when you're fertile. Learn how to check your vaginal discharge and note your findings, especially if you're trying to conceive. Cervical mucus alone isn't a reliable form of contraception, so if you don't wish to become pregnant, talk to your healthcare provider about more effective contraception. If you notice any foul-smelling discharge, speak with your healthcare provider so they can rule out any issues.
why they appear in the early and late periods, in the 1st, 2nd and 3rd trimester, what to do at home
While carrying a child, any changes in a woman's body can be alarming and cause concern. Including mucous secretions that occur during different periods of pregnancy. Together with gynecologists, we will figure out which of them are considered the norm, and which indicate the development of serious pathologies.
Obstetrician-gynecologist, gynecologist-endocrinologist of the Institute of Reproductive Medicine REMEDI Nina Antipova tells what is discharge in women. They consist of:
- secretion of the vaginal mucosa;
- cervical mucus, cervical mucus;
- a secret that is released from the uterine cavity (during menstruation - blood, on the days of the beginning and end of menstruation - mucous secretions that are produced by cells of the endometrium, the mucous membrane of the uterus).

- Discharge from the genital tract - an individual story, so the norm here is ambiguous. As such, the concept of mucous discharge during pregnancy does not exist, emphasizes Nina Antipova. nine0003
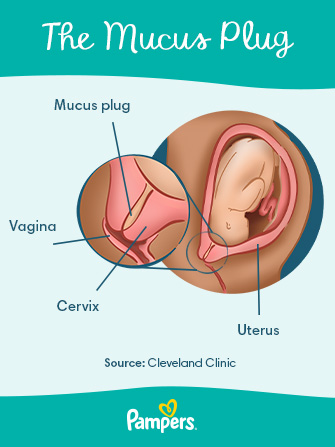
Pregnancy mucus discharge
Pregnancy mucus may vary in color, texture, smell, quantity and feel. The norm is considered to be discharges that meet the following characteristics.
| Color | colorless or white, without bloody interspersed |
| Consistency | Not dense |
| Number | Moderate, not abundant |
| Smell | None |
| Feel | No itching, burning or pain |
Clear discharge
900 But in the second and third trimester, they can be confused with amniotic fluid. Therefore, if abundant colorless discharge occurs, you should be wary.Learn more
White discharge
White mucus that is not accompanied by odor, itching or discomfort is normal (1). The main reason for their appearance is the formation of a mucous plug that prevents the occurrence of infections. nine0003
The main reason for their appearance is the formation of a mucous plug that prevents the occurrence of infections. nine0003
Learn more
Yellow discharge
Yellow mucus may be a symptom of severe inflammation. The most likely cause of their appearance is a bacterial infection (2). In such cases, additional symptoms appear: smell, burning and itching.
Learn more
Bloody discharge
The appearance of bloody mucous discharge during pregnancy can signal serious processes, such as a threatened miscarriage. In such a situation, immediate medical attention is needed. nine0003
Learn more
Brown discharge
Brown color indicates blood in the discharge. This is not always a dangerous symptom, for example, discharge with a brown tint can be observed with cervical erosion. But you should not lose vigilance. In the first months of pregnancy, brown discharge can mean the presence of serious pathologies, and in the last, among other things, the onset of the birth process.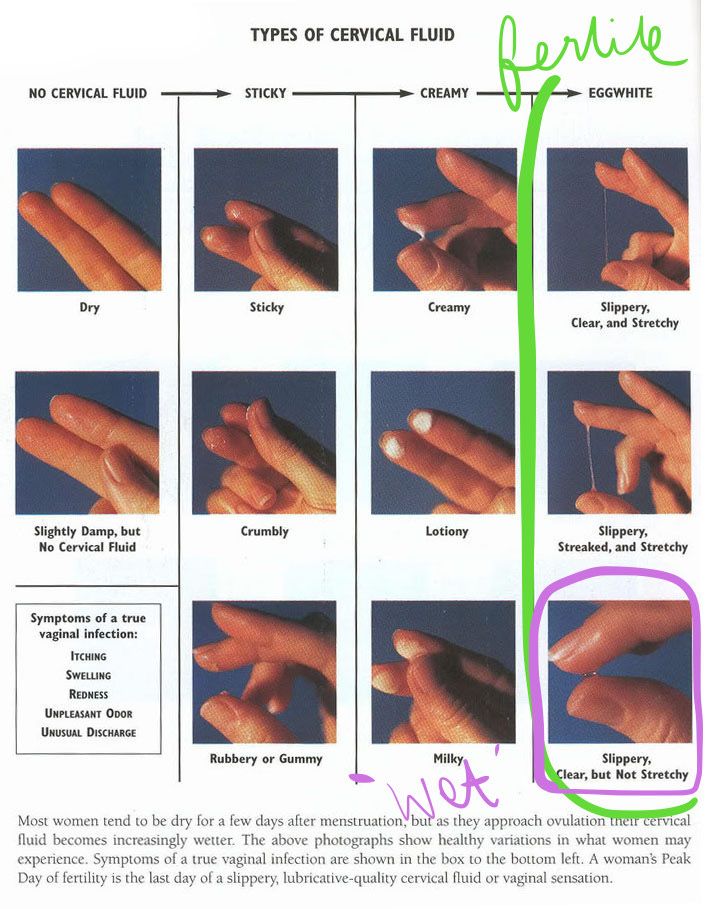
Learn more
What causes mucous discharge during early pregnancy
Mucus discharge in a woman can occur for various reasons, which depend on the stage of pregnancy.
1st trimester
Abundant mucous discharge at the beginning of pregnancy may be one of the signs of its onset. In this case, they are painted white, do not smell and do not cause discomfort. Discharge with an unpleasant odor, accompanied by itching, may indicate a violation of the microflora. The treatment of this problem should be entrusted to a doctor.
Brown discharge may indicate an ectopic or miscarriage, or a threatened miscarriage. The symptom is dangerous, so you need to act immediately. nine0003
Why there is mucous discharge during late pregnancy
Any discharge during pregnancy should not go unnoticed. The closer the date of birth, the more closely you need to monitor your well-being and the changes that occur in the body.
2nd trimester
Mucous discharge in the second trimester of pregnancy, which is colorless and odorless, is most often associated with the action of hormones (3). But sometimes they can be a signal of problems. For example, abundant mucous discharge may be amniotic fluid. To understand whether this is true or not, you should consult a doctor and pass the necessary analysis. nine0003
But sometimes they can be a signal of problems. For example, abundant mucous discharge may be amniotic fluid. To understand whether this is true or not, you should consult a doctor and pass the necessary analysis. nine0003
If the discharge is white, itchy and painful, a fungal infection (eg thrush) may have flared up. It is impossible to treat it on your own with the help of pills during pregnancy, so you must definitely see a doctor.
3rd trimester
Mucus discharge in the third semester of pregnancy may indicate the following processes:0014
If heavy discharge occurs in the last months of pregnancy, you should immediately consult a doctor. Any of these causes is a pathology and can lead to serious consequences.
How to deal with mucus discharge during pregnancy at home
If the discharge does not increase and does not cause concern, then it is usually not necessary to treat it. It is important to visit the gynecologist on time, monitor any changes and observe intimate hygiene. nine0003
It is important to visit the gynecologist on time, monitor any changes and observe intimate hygiene. nine0003
- A pregnant woman often perceives mucous discharge as a minor symptom that she herself can eliminate. But in no case should this be done, because self-medication can negatively affect the development of the fetus, - notes obstetrician-gynecologist, doctor of the highest category Elena Kollerova . - Doing anything at home is not necessary categorically, because this can lead to dangerous consequences.
Popular questions and answers
Any discharge, including mucous, can provoke a lot of questions from a woman carrying a child. Our experts answer the most popular ones. nine0003
How dangerous is mucous discharge during pregnancy?
- The causes of mucous discharge can be very diverse - from harmless to dangerous. Such discharge may appear, for example, due to changes in the hormonal background, with the threat of miscarriage or premature birth. The degree of danger depends on the period at which they appeared, says Elena Kollerova. - If, for example, at 25 weeks or earlier, a woman has found abundant mucous discharge, this may indicate a threat of miscarriage. If you do not take action and do not consult a doctor, the consequences can be unpredictable. For both mom and baby. If such discharge appeared at 38-40 weeks of pregnancy, you should also immediately consult a doctor. Mucous discharge in late pregnancy can signal the release of the mucous plug from the cervix, and this may be a harbinger of childbirth. nine0003
The degree of danger depends on the period at which they appeared, says Elena Kollerova. - If, for example, at 25 weeks or earlier, a woman has found abundant mucous discharge, this may indicate a threat of miscarriage. If you do not take action and do not consult a doctor, the consequences can be unpredictable. For both mom and baby. If such discharge appeared at 38-40 weeks of pregnancy, you should also immediately consult a doctor. Mucous discharge in late pregnancy can signal the release of the mucous plug from the cervix, and this may be a harbinger of childbirth. nine0003
- Discharge from the genital tract is a mixed discharge consisting of vaginal secretions and cervical mucus. In every woman, under the influence of hormones during pregnancy, the nature of the discharge from the genital tract changes. For many, the amount of discharge increases, for someone they can become thicker or thinner, acquire a pronounced milky tint or remain transparent, says Nina Antipova. - During pregnancy, secretions from the genital tract are represented by the secretion of the glands of the cervix (cervical mucus) and vaginal secretions. The appearance of scarlet, brown, yellow-beige spotting during gestation is a reason to contact an obstetrician-gynecologist for an examination on the chair and ultrasound. Sometimes bleeding from the genital tract occurs during the normal course of pregnancy and does not require treatment and hospitalization. However, in some cases, they can be a wake-up call that requires emergency medical attention. nine0003
The appearance of scarlet, brown, yellow-beige spotting during gestation is a reason to contact an obstetrician-gynecologist for an examination on the chair and ultrasound. Sometimes bleeding from the genital tract occurs during the normal course of pregnancy and does not require treatment and hospitalization. However, in some cases, they can be a wake-up call that requires emergency medical attention. nine0003
A change in discharge patterns may be associated with threatened miscarriage or preterm labor, amniotic fluid leakage, shortening of the cervix, and premature dilatation. In such situations, the doctor, if necessary, conducts tests for leakage of amniotic fluid, rupture of the membranes and premature birth, sends an ultrasound to determine the condition of the cervix and prevent complications.
When do I need to see a doctor urgently?
— Pregnant women should pay attention to any symptoms that may even seem harmless, recommends Elena Kollerova. - Having noticed mucous secretions, in no case should you self-medicate: insert candles, take any drugs, and even more so use folk remedies. Instead, you should immediately consult a doctor to find out the cause of the discharge. This should be done immediately if heavy discharge occurs in late pregnancy. nine0003
- Having noticed mucous secretions, in no case should you self-medicate: insert candles, take any drugs, and even more so use folk remedies. Instead, you should immediately consult a doctor to find out the cause of the discharge. This should be done immediately if heavy discharge occurs in late pregnancy. nine0003
- At a certain stage of pregnancy, a woman may feel that her usual secretions from the genital tract have become more mucus streaked with brown, scarlet or pink. This may lead to thoughts about the release of the mucous plug. At home, it is impossible to assess such a situation. To do this, you should consult a doctor for examination in the chair, - Nina Antipova answers.
What measures are there to prevent mucus during pregnancy?
- There is no specific prevention of mucous secretions during pregnancy. Because they can be a variant of the norm - in case they are associated with changes in the hormonal background and epithelium.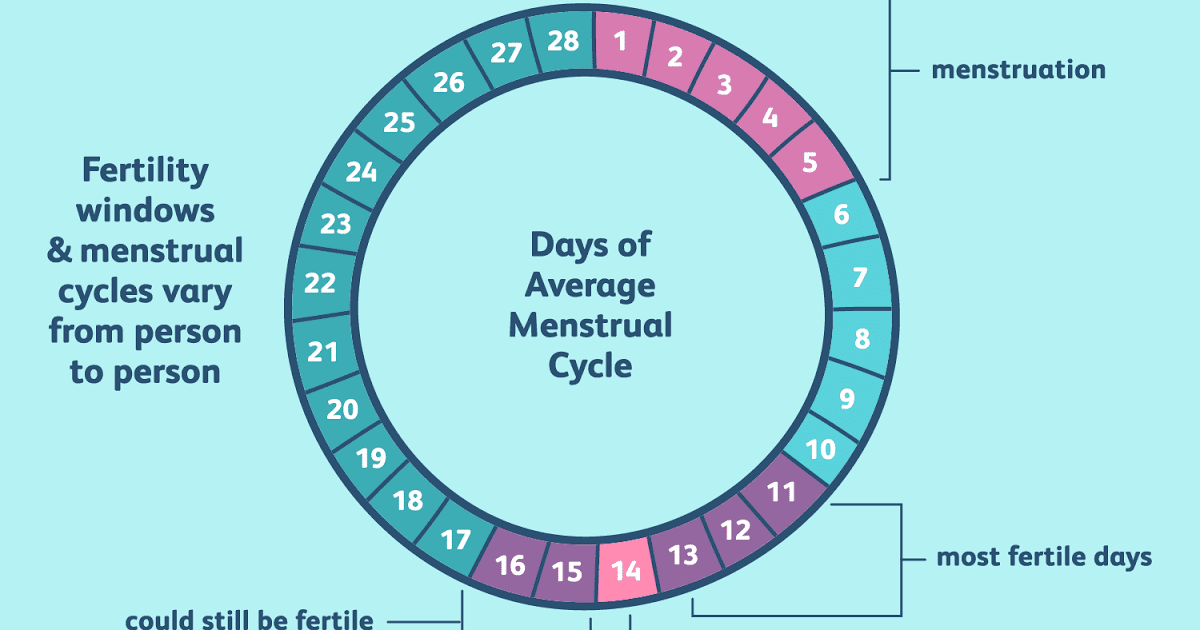 But only a doctor can determine whether they are harmless,” explains Elena Kollerova. - In the later stages, you should especially vigilantly monitor their number. This will help prevent miscarriage or premature birth. The best prevention is an attentive attitude to changes in the body and a timely visit to the doctor at all stages of pregnancy. nine0003
But only a doctor can determine whether they are harmless,” explains Elena Kollerova. - In the later stages, you should especially vigilantly monitor their number. This will help prevent miscarriage or premature birth. The best prevention is an attentive attitude to changes in the body and a timely visit to the doctor at all stages of pregnancy. nine0003
— The main prevention of complications during pregnancy associated with a change in the nature of secretions from the genital tract is aimed at detecting infections. They are the main risk factor for preterm birth and prenatal rupture of amniotic fluid, says Nina Antipova. - Regular observation by an obstetrician-gynecologist, control of smears and compliance with hygiene rules is recommended. The first smears are made when a woman is registered during pregnancy. After - in case of complaints. The last smear is taken a month before delivery - at 36 weeks. nine0003
Sources
- E.A. Burmistrov. Pregnancy, childbirth, motherhood.
 M., 2012
M., 2012 - Rebecca Malachi. Yellow Discharge During Pregnancy: Causes And Treatment. 2022. URL: https://www.momjunction.com/articles/yellow-discharge-during-pregnancy_00477970/
- A.E. Kasparova, I.I. Mordovina, L.A. Sus. Modern approaches to diagnosis and complex treatment of vaginal discharge syndrome. Algorithm for sanitation of urogenital infection during pregnancy (literature review). M., 2010
2nd week of pregnancy what happens to the fetus
Contents
The second obstetric week is ovulation and conception. The egg, ready for fertilization, is released from the ovary. Fertilization will take place only if the sperm meets the egg. What happens next?
What happens in a woman's body?
The production of hormones by the pituitary and ovaries regulates the release of the egg and initiates ovulation.
At this time, the discharge from the vagina is like egg white, clear and stringy. They are called "cervical mucus". It is she who promotes the passage of spermatozoa and their filtration. nine0003
It is she who promotes the passage of spermatozoa and their filtration. nine0003
After fertilization of the egg, these secretions will become transparent, less viscous, odorless and colorless, and will soon disappear. A sharp jump in basal temperature will also indicate successful ovulation. During the day, it will drop and return to the same indicator as it was before, or even increase.
What other symptoms does the woman have in the second week?
- There may be an increase in libido, breasts begin to swell.
- In some women, taste preferences may change, drowsiness and fatigue may occur. nine0014
- Small rashes may appear on the face as a reaction to hormonal changes.
- Sometimes disturbed by unpleasant sensations in the lower abdomen or pulling pains in the lower back.
- Often there is a decrease in blood pressure.
- Urination may also become more frequent.
- And of course, the ovulation test will show a positive result.
These symptoms are typical of the second week of pregnancy, but are not at all obligatory for each individual woman. nine0003
What happens after fertilization?
After fertilization occurs, the hormonal background changes dramatically in the woman's body. At the end of the third week of pregnancy, the fertilized egg attaches to the wall of the uterus. Attachment of the embryo may cause slight pain and be accompanied by some bleeding.
It is worth remembering that all of the listed symptoms are not accurate indicators of pregnancy. The same signs can indicate stress, overheating, overwork. Therefore, there are no signs that guarantee the fact of conception. nine0003
Recommendations for future parents
General recommendations remain the same as in the first week:
- Give up bad habits, do not drink alcohol, stop smoking, even passive. Avoid visiting places where they smoke.
- Do not lift heavy things to avoid miscarriage.