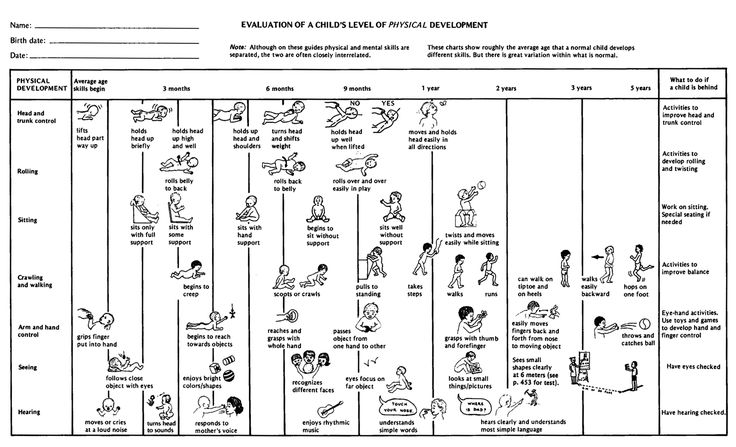
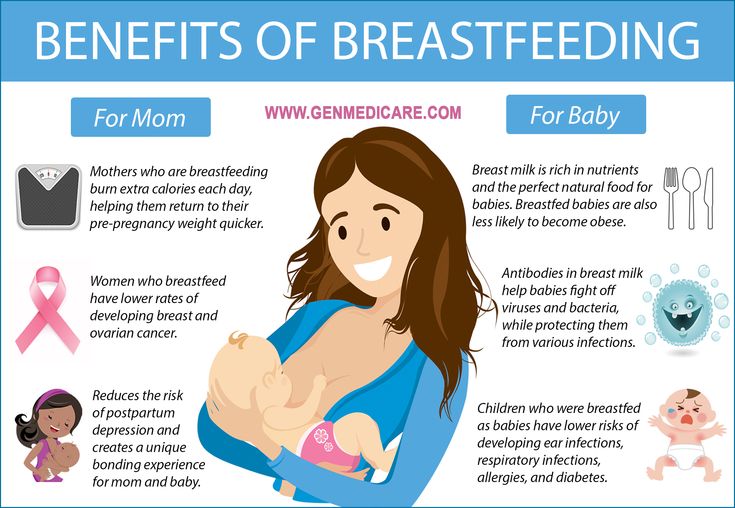
How can i help my child read and write better
Tips to Help Children Learn to Read
Written by Dayva Segal
In this Article
- Read Out Loud to Your Children
- Other Tips to Help Your Children Learn to Read
- What to Do if Your Child Is Having Trouble With Reading
Reading is an important skill that children will use daily for the rest of their lives. While many children learn to read at school, parents can enhance the experience by offering support at home. This support can begin as soon as your child is born.
Read Out Loud to Your Children
Experts agree that reading out loud to your children is the best way to help them learn to read. Start when your child is a newborn baby and continue throughout childhood. As a baby, your child is primed to learn the skills that will help them learn to read as they get older.
To make reading out loud as effective as possible, make sure to:
- Read age-appropriate books. Babies, for example, enjoy board books that they can touch and play with.
Older children may enjoy "big books" that help them to see differences in words and letters.
- Use silly voices and voice effects. This helps your children to engage with the story and feel excited about reading time.
- Point to words as you read so your child can follow along. Doing this helps solidify the idea that words are where the story comes from.
- Talk about the pictures. Ask your child to name what they see in the pictures and talk about what the images show as it relates to the story.
- Relate the story to life. Show your child how things in the book relate to things that happen in real life.
- Answer questions. If your child asks a question, stop and answer it. That will keep them engaged and interested.
- Read more difficult books. Once your child learns to read, keep reading out loud to them. You can read books that are above their reading level to encourage further improvement in their reading level.

Other Tips to Help Your Children Learn to Read
Besides reading out loud to your children, there are other things you can do to encourage literacy.
- Listen to your child read out loud. Once they learn to read, encourage them to read to you. This helps them build confidence in reading. The goal with reading aloud is for your child to understand the story. So if they need help pronouncing a word, tell them how it's said instead of making them sound it out — that way, they don't lose their place or the meaning of the sentence. If your child accidentally uses a word that doesn't make sense, have them go back and reread the sentence.
- Praise your child's reading. As your child learns reading, offering praise helps them gain confidence.
- Make reading time part of your daily routine. Daily reading time creates a routine that lets your child know reading is part of everyday life. Many families choose bedtime as their preferred reading time.

- Leave books in your kid's bedroom. That way, they can look at them and enjoy them whenever they want.
- Let your child complete sentences. If your child learns the words in their favorite books, let them finish the sentences or "read" the whole book out loud.
- Read books your child likes. This helps them to engage with reading time and enjoy it more.
- Remember, anyone can teach reading. Some parents think that only teachers can teach reading to children. But parents can, too. Reading is an essential life skill.
- Be patient. If your child shows no interest in a book, don't force it. If your child tries to write a word and gets a letter wrong, they still deserve praise. Patience and praise are more helpful for a child's learning to read than getting frustrated or yelling.
- Talk to your children. Exposing your child to new words and language can help their literacy skills.
 Talking to your baby a lot, for example, can help them become better readers later on.
Talking to your baby a lot, for example, can help them become better readers later on. - Encourage writing. Writing is part of literacy. Provide writing tools like crayons, pencils, and markers. Encourage your child to write, even if it's just scribbling. One idea is to write your child a letter and ask them to write one back.
- Have your child tell you a story and write it down. Ask your child to tell you a simple story. Write it down and then read it back to them while pointing at the words.
- Teach your child phonics. There are countless products available that help children learn the sounds that are associated with letters. This helps them to sound out words as they are learning to read. You can also just use paper and a pencil to help them learn this skill. Research shows that when children don't know phonics, they struggle more with reading.
- Avoid "leveled" reading programs.
 Some people believe that children who get frustrated by reading difficult material will get turned off by reading. But experts say that children learn more when they're exposed to more challenging reading material. Easy-level books often train children to rely on word memorization because they often use the same words over and over. They also train children to rely more on pictures. That can lead to slower reading development. It's best if children are exposed to a variety of challenges in their reading materials.
Some people believe that children who get frustrated by reading difficult material will get turned off by reading. But experts say that children learn more when they're exposed to more challenging reading material. Easy-level books often train children to rely on word memorization because they often use the same words over and over. They also train children to rely more on pictures. That can lead to slower reading development. It's best if children are exposed to a variety of challenges in their reading materials. - Talk to teachers. Ask your child's teachers about their reading program and how they teach literacy. Look for them to include phonics, reading out loud in class, vocabulary, and writing practice.
What to Do if Your Child Is Having Trouble With Reading
If your child's reading is not progressing, you should work with their school to get testing done. That way, you can find out if your child has a learning difficulty or difference, or if it's simply that the reading program in their class doesn't work for them. If your child does get diagnosed with a learning difference, like dyslexia, they're entitled to receive extra services from their school for free.
If your child does get diagnosed with a learning difference, like dyslexia, they're entitled to receive extra services from their school for free.
You can also hire a tutor to help your child improve their reading. Free tutoring may be available for students from low-income families.
At home, provide ongoing emotional support to keep your child from getting discouraged.
11 Ways Parents Can Help Their Children Read
Parents often ask how they can help their children learn to read; and it’s no wonder that they’re interested in this essential skill. Reading plays an important role in later school success. One study even demonstrates that how well 7-year-olds read predicts their income 35 years later!
Here are 11 practical recommendations for helping preschoolers and school-age students learn to read.
1. Teaching reading will only help.
Sometimes, parents are told early teaching is harmful, but it isn’t true. You simply can’t introduce literacy too early. I started reading to my own children on the days they were each born! The “dangers of early teaching” has been a topic of study for more than 100 years, and no one has ever found any convincing evidence of harm. Moreover, there are hundreds of studies showing the benefits of reading to your children when they are young.
I started reading to my own children on the days they were each born! The “dangers of early teaching” has been a topic of study for more than 100 years, and no one has ever found any convincing evidence of harm. Moreover, there are hundreds of studies showing the benefits of reading to your children when they are young.
2. Teaching literacy isn’t different than teaching other skills.
You don’t need a Ph.D. to raise a happy, healthy, smart child. Parents have been doing it for thousands of years. Mothers and fathers successfully teach their kids to eat with a spoon, use a potty, keep their fingers out of their noses, and say “please.” These things can be taught pleasantly, or they can be made into a painful chore. Being unpleasant (e.g. yelling, punishing, pressuring) doesn’t work, and it can be frustrating for everyone. This notion applies to teaching literacy, too. If you show your 18-month-old a book and she shows no interest, then put it away and come back to it later. If your child tries to write her name and ends up with a backwards “D,” no problem. No pressure. No hassle. You should enjoy the journey, and so should your child.
If your child tries to write her name and ends up with a backwards “D,” no problem. No pressure. No hassle. You should enjoy the journey, and so should your child.
3. Talk to your kids (a lot).
Last year, I spent lots of time with our brand new granddaughter, Emily. I drowned her in language. Although “just a baby,” I talked — and sang — to her about everything. I talked about her eyes, nose, ears, mouth, and fingers. I told her all about her family — her mom, dad, and older brother. I talked to her about whatever she did (yawning, sleeping, eating, burping). I talked to her so much that her parents thought I was nuts; she couldn’t possibly understand me yet. But reading is a language activity, and if you want to learn language, you’d better hear it, and eventually, speak it. Too many moms and dads feel a bit dopey talking to a baby or young child, but studies have shown that exposing your child to a variety of words helps in her development of literacy skills.
4. Read to your kids.

I know everyone says this, but it really is a good idea — at least with preschoolers. One of my colleagues refers to this advice as the “chicken soup” of reading education. We prescribe it for everything. (Does it help? It couldn’t hurt.) If a parent or caregiver can’t read or can’t read English, there are alternatives, such as using audiobooks; but for those who can, reading a book or story to a child is a great, easy way to advance literacy skills. Research shows benefits for kids as young as 9-months-old, and it could be effective even earlier than that. Reading to kids exposes them to richer vocabulary than they usually hear from the adults who speak to them, and can have positive impacts on their language, intelligence, and later literacy achievement. What should you read to them? There are so many wonderful children’s books. Visit your local library, and you can get an armful of adventure. You can find recommendations from kids at the Children’s Book Council website or at the International Literacy Association Children's Choices site. [Reading Rockets also provides guidance and lots of themed booklists in our Children's Books & Authors section.]
[Reading Rockets also provides guidance and lots of themed booklists in our Children's Books & Authors section.]
5. Have them tell you a “story.”
One great way to introduce kids to literacy is to take their dictation. Have them recount an experience or make up a story. We’re not talking “Moby Dick” here. A typical first story may be something like, “I like fish. I like my sister. I like grandpa.” Write it as it is being told, and then read it aloud. Point at the words when you read them, or point at them when your child is trying to read the story. Over time, with lots of rereading, don’t be surprised if your child starts to recognize words such as “I” or “like.” (As children learn some of the words, you can write them on cards and keep them in a “word bank” for your child, using them to review later.)
6. Teach phonemic awareness.
Young children don’t hear the sounds within words. Thus, they hear “dog,” but not the “duh”-“aw”- “guh.” To become readers, they have to learn to hear these sounds (or phonemes). Play language games with your child. For instance, say a word, perhaps her name, and then change it by one phoneme: Jen-Pen, Jen-Hen, Jen-Men. Or, just break a word apart: chair… ch-ch-ch-air. Follow this link to learn more about language development milestones in children.
Play language games with your child. For instance, say a word, perhaps her name, and then change it by one phoneme: Jen-Pen, Jen-Hen, Jen-Men. Or, just break a word apart: chair… ch-ch-ch-air. Follow this link to learn more about language development milestones in children.
7. Teach phonics (letter names and their sounds).
You can’t sound out words or write them without knowing the letter sounds. Most kindergartens teach the letters, and parents can teach them, too. I just checked a toy store website and found 282 products based on letter names and another 88 on letter sounds, including ABC books, charts, cards, blocks, magnet letters, floor mats, puzzles, lampshades, bed sheets, and programs for tablets and computers. You don’t need all of that (a pencil and paper are sufficient), but there is lots of support out there for parents to help kids learn these skills. Keep the lessons brief and fun, no more than 5–10 minutes for young’uns. Understanding the different developmental stages of reading and writing skills will help to guide your lessons and expectations.
8. Listen to your child read.
When your child starts bringing books home from school, have her read to you. If it doesn’t sound good (mistakes, choppy reading), have her read it again. Or read it to her, and then have her try to read it herself. Studies show that this kind of repeated oral reading makes students better readers, even when it is done at home.
9. Promote writing.
Literacy involves reading and writing. Having books and magazines available for your child is a good idea, but it’s also helpful to have pencils, crayons, markers, and paper. Encourage your child to write. One way to do this is to write notes or short letters to her. It won’t be long before she is trying to write back to you.
10. Ask questions.
When your child reads, get her to retell the story or information. If it’s a story, ask who it was about and what happened. If it’s an informational text, have your child explain what it was about and how it worked, or what its parts were. Reading involves not just sounding out words, but thinking about and remembering ideas and events. Improving reading comprehension skills early will prepare her for subsequent success in more difficult texts.
Reading involves not just sounding out words, but thinking about and remembering ideas and events. Improving reading comprehension skills early will prepare her for subsequent success in more difficult texts.
11. Make reading a regular activity in your home.
Make reading a part of your daily life, and kids will learn to love it. When I was nine years old, my mom made me stay in for a half-hour after lunch to read. She took me to the library to get books to kick off this new part of my life. It made me a lifelong reader. Set aside some time when everyone turns off the TV and the web and does nothing but read. Make it fun, too. When my children finished reading a book that had been made into a film, we’d make popcorn and watch the movie together. The point is to make reading a regular enjoyable part of your family routine.
Happy reading!
Sources:
Ritchie, S.J., & Bates, T.C. (2013). Enduring links from childhood mathematics and reading achievement to adult socioeconomic status. Psychological Science, 24, 1301-1308.
Psychological Science, 24, 1301-1308.
Karass J., & Braungart-Rieker J. (2005). Effects of shared parent-infant reading on early language acquisition. Journal of Applied Developmental Psychology, 26, 133-148.
7 tips on how to help your child fall in love with reading (voluntarily!)
For one child, a book is really the best gift, while another will cringe at the sight of another volume. They force you at school, now at home too. But you don’t need to force it, even a school reading list for the summer. How to really captivate a child with books - says a specialist in children's reading and writer Yulia Kuznetsova.
1. Do not force a child to read
The desire to read is formed from within, so I am sure that forcing a child to read at five or six years old is a dangerous path. The word "should" should be applied to children's reading in general with caution and at a more serious age, from grade 5-6 and only in relation to school literature.
If a child does not feel like reading by himself, there is nothing wrong with that. My middle son did not take reading aloud until he was three years old. While I was reading to my eldest daughter, he was crawling around on the sofa, pinching our hair - it only annoyed me. Then suddenly, at the age of four, he fell in love with reading aloud. At the age of five, we began to teach him to read, at first he did not particularly like to do this either. And by the age of six, reading began, this is a spontaneous process.
Often parents are afraid that their child will go to school without being able to read. It all depends on the teacher. Now I hear about cases when teachers say: “I don’t need parents to bring the child to some level, otherwise he will be simply bored in the lessons.”
2. Surrounding children with books is good advice, but it doesn't always work
My experience is very different. When I came back from book festivals and brought bags of books to children, we had the following dialogue: "I brought you gifts" - "What gifts?" - "Books" - "I see, but did you bring normal gifts?"
When there are many books in the family, the following stories may come up. You ask: "Do you want to read a book?" - "No". They closed the book and put it in the fridge. After a while, you ask again, you get the same answer, and you put the book on the windowsill. It turns out that these “I don’t want” lie all over the apartment.
You ask: "Do you want to read a book?" - "No". They closed the book and put it in the fridge. After a while, you ask again, you get the same answer, and you put the book on the windowsill. It turns out that these “I don’t want” lie all over the apartment.
It seems to me that we should remember our book experience, when there were always not enough books in childhood. Especially the ones you really wanted to read. I run courses for children where we do group calculations, we have our own library that fits on a chair. These are books from my home library that have gone through a rigorous selection: they will definitely appeal to children who do not like and do not want to read. Children come, sit down, see some books, they are interested in taking them and looking at them, but I don’t let them do it. They say, “Please, please, can I? If I don’t take it now, then Petya will take this book later.” I say: "No, now we have a lesson, we are doing other interesting things." And when they see that the books cannot be freely approached, then after the lesson they scatter in a second. A mob runs up, they take everything apart and take it home. Moreover, the children know that next time I will ask what this book was about.
A mob runs up, they take everything apart and take it home. Moreover, the children know that next time I will ask what this book was about.
3. Talk with your children about the books you read yourself
Parents who read in front of their children are very rare. Use these moments to talk to him about the book you are reading right now, or even try reading out snippets. For example, my daughter once loved sheep very much, and I was reading Sheep Hunt by Haruki Murakami just at that time. When she found out about this, she said: “Sheep are being killed there, I feel sorry for them.” I offered to read a fragment of the book aloud to her so that she would see that no one was being killed there. I read the description of the pasture to her, and she was so delighted: her mother let her touch her book.
You can discuss books with other adults in front of children. I discuss books on the phone with my mother
We have similar tastes, my mother likes modern Russian women's prose, for example, Marina Stepanova. We call her and discuss some books, and the children hear it all.
We call her and discuss some books, and the children hear it all.
4. Read aloud. And record reading on a voice recorder
Parents spend the whole day at work, and if after that they read aloud to their children for at least ten minutes, this becomes a powerful lock that holds relationships together. You can also not only read aloud, but also record reading on a voice recorder. The phone is not suitable for this, because it will switch attention to itself all the time. There is only one button on the voice recorder - turn it on and off.
Dad sits down, reads aloud to them, all this is recorded on a dictaphone. One chapter in a children's book lasts an average of 10-15 minutes, this time is enough for the event called "evening reading" to take place. When dad leaves for a business trip, the children listen to the recordings. They turn it on when they eat, when they draw. This is not just a text, this is a memory of how good it was with dad in the evening.
5. Don't ignore audiobooks - they help with text
Audiobooks are a relief for children who are not very confident and see mostly letters, not images. They first get used to, and then return to a paper book. This mechanism also works with films (yes, yes). Children first watch the movie, find out how it all ends there, and then take the book and read it. It happens that children take the book even after performances. The host of the theater studio told how she staged "Uncle Vanya" with teenagers, and then a boy came to her and asked: "Is it possible to read this somewhere?" So a well-read audiobook, especially if you listen to it with your parents and discuss the plot, can also help instill a love of reading.
6. Write a book about your child - this is another way to help him start reading
Take a picture or draw your child, stick it on a piece of paper and write: "This is Kolya." Then take a picture of how he eats and write: "Kolya eats. " Then you can take a picture of how he sleeps, plays, and so on. Make such a book and show a child at the age of three - let him look at all this. When he is four years old, he will understand that letters can somehow be put together into words and will start trying to do it. Reading about yourself is always more interesting. My daughter is 12 years old, and she sits down with pleasure herself and reads a book about what she did nine years ago: she sculpted hedgehogs, kneaded the dough, molded cookies from it.
" Then you can take a picture of how he sleeps, plays, and so on. Make such a book and show a child at the age of three - let him look at all this. When he is four years old, he will understand that letters can somehow be put together into words and will start trying to do it. Reading about yourself is always more interesting. My daughter is 12 years old, and she sits down with pleasure herself and reads a book about what she did nine years ago: she sculpted hedgehogs, kneaded the dough, molded cookies from it.
In my lessons I set aside 15 minutes and we write a book about ourselves. I give simple phrases that need to be completed: "Once I went ...", "And suddenly I saw ...", "Here I meet ...". It takes a little time, but it works very well. Children can write whole volumes about themselves.
In fact, for students who have difficulty in reading, it can be like writing classes - this is a good way to overcome reading difficulties. It seems that the child is learning to write, but at the same time learning to read. I had a girl on the course who stuttered and skipped words when reading. But when I read my text, I did not miss a single word. For her it was very important.
I had a girl on the course who stuttered and skipped words when reading. But when I read my text, I did not miss a single word. For her it was very important.
7. Do not be afraid that the child will not read the school list of literature for the summer
Take the list of literature, a pen and first of all cross out the books that the child definitely does not need. During communication with the teacher, you can understand what he wanted, including this or that book in the list. For example, in the first grade in our textbook there was a fragment from The Hobbit. The teacher decided that since there is a piece from Tolkien, then you need to read the whole book. I say, "Sorry, guys," and cross it out. We tried to watch a movie based on the book, but the children didn't get it: they were just scared.
Then cross out all the books that the children know by heart. In the first grade, along with The Hobbit, we came across Little Red Riding Hood. I crossed out this book because we know it very well. Next, we select books that can be replaced with audiobooks and films. If the child is not drawn to reading Pinocchio, just show him the film. The plot will be postponed, and when the text from the book comes across to him in the textbook, the child will cope with it, because he will be six months or a year older.
Next, we select books that can be replaced with audiobooks and films. If the child is not drawn to reading Pinocchio, just show him the film. The plot will be postponed, and when the text from the book comes across to him in the textbook, the child will cope with it, because he will be six months or a year older.
Then choose the books you will read aloud. It was the same with Garin-Mikhailovsky's The Childhood of the Theme. My daughter got it in the second grade, and I realized that she would not pull it.
There remains a small sample of books that the child can read on his own. You take this list and say: “Look, here the teacher recommended these books. Which of these would be the most interesting for you to read?”. He chooses and you start reading. One summer, our son read one or two books, but at the very least, we replenished our cultural baggage. Often parents are afraid that they will come to school in September and they will be asked if the child has read the entire list. Just answer that you didn't read everything. There is nothing terrible in this.
Just answer that you didn't read everything. There is nothing terrible in this.
What else to read about children's reading:
- Marina Aromshtam "Read!" - a book that will give parents answers to many questions.
- Yulia Kuznetsova Calculation. How to help your child love reading ”- a book about how parents can help children love books.
- Aidan Chambers “Tell me. We read, think, discuss” - the author tells how to communicate with children through books. What questions can be asked to children so that they talk about what they read and at the same time do not feel that they are being examined ( an excerpt from the book read here ).
- Daniel Pennack "Like a Novel" - for parents who are worried that their child does not read.
- Papmambuk - is an excellent site with useful materials about children's reading.
Listen to the full interview with Yulia Kuznetsova here. The conversation took place on the air of "Radio School" - the "Mela" project and the radio station "Moscow Speaks" about education and upbringing. The guests of the studio are teachers, psychologists, scientists and other experts. The program airs on Sundays at 4:00 pm on the radio "Moscow Speaking".
The conversation took place on the air of "Radio School" - the "Mela" project and the radio station "Moscow Speaks" about education and upbringing. The guests of the studio are teachers, psychologists, scientists and other experts. The program airs on Sundays at 4:00 pm on the radio "Moscow Speaking".
Illustrations: Shutterstock (oriol san julian, Kat Buslaeva)
step-by-step instructions with expert advice
And now the first letter, the first word, appears on a sheet of paper. Uneven and uncertain. But long-awaited. How to teach a child to write? How can I help him develop writing skills at home? The answers are in our material
Alena Gerashchenko
KP author
Anna Shumilova
Methodist of the Uchi.ru platform
Almaz Marsov
Principal of the Ponyatno online school
Writing is an important skill that is learned in preschool and elementary school. The opinions of experts differ: someone thinks that it is better not to put a letter to the child at home, someone, on the contrary, is convinced that it is the parent who opens the world of writing to the child. We believe that you can start developing the skill of writing letters at home - learn to draw pictograms, connect dots on paper, draw - not write - letters. Leave the capital letters and intricate, ornate words to the schoolteachers. Teach your child the basics. Get him interested in drawing, help develop spatial perception of reality, teach hand-finger coordination. We will tell you step by step how to teach your child the basics of writing before school.
The opinions of experts differ: someone thinks that it is better not to put a letter to the child at home, someone, on the contrary, is convinced that it is the parent who opens the world of writing to the child. We believe that you can start developing the skill of writing letters at home - learn to draw pictograms, connect dots on paper, draw - not write - letters. Leave the capital letters and intricate, ornate words to the schoolteachers. Teach your child the basics. Get him interested in drawing, help develop spatial perception of reality, teach hand-finger coordination. We will tell you step by step how to teach your child the basics of writing before school.
Step-by-step instructions for teaching a child to write
Everything needs a system. In training, a systematic, everyday contribution to the development of skills is very important. Compliance with the following steps will lay the foundation for high-quality development of the child's writing.
Step #1. Get interested
Start telling children in an exciting way what writing is, why it is needed, how it originated and developed. The main thing is to present the story not with dry facts. Do it brightly, colorfully, picturesquely. Show your child photographs of the walls of the Egyptian pyramids, which depict various drawings and hieroglyphs. Tell your son or daughter the story of the Novgorod boy Onfim, who wrote birch bark letters in the 13th century, show his monument, and the letters and drawings. The emotional presentation of the story, coupled with illustrative material - all this will resonate with the child. Also invite the child to do the exercises during the stories. Here are a couple of activities to accompany stories that will help your child understand the nature of writing and want to learn to write on their own as soon as possible.
Exercise 1
Show your child pictograms (wall pictures that our ancestors used to communicate information to each other), invite him to fantasize and make up an oral story based on the pictures he saw.
Exercise 2
And vice versa: make up a story with the child and invite him to illustrate it in detail with the help of pictures. Such tasks, among other things, develop fantasy, speech and storytelling skills.
After the pictograms, go on to explain ideographic writing. It sounds complicated, but in fact, ideography uses simplified pictograms - symbols. The Chinese language is built on symbolism (principle 1 character = 1 word), designations in the transport sector. Acquaintance with the symbols will be interesting to the child if you pay attention to them during a walk.
You can teach a child to draw simple images with meaning: for example, two wavy horizontal lines symbolize a pond; crossed circle - prohibition, the word "no" and so on. Stories about ideographic writing and "practical ideography" will expand the horizons of the baby, teach him to perceive the world around him more sensitively, develop creative thinking, and teach spatial perception.
If you feel that the kid is ready for more (he asks questions, draws a lot), tell him about modern writing, about languages. Explain that the Egyptians wrote from right to left - it was inconvenient: hieroglyphs, drawings were smeared by hand. Show your child that writing like this is not very convenient. Tell us that we inherit the experience of the ancient Greeks - we write from left to right. Take a digression into history and tell the fidget that Latin was developed from the ancient Greek language, and it became the official language of the church. Latin formed the basis of many other languages (English, German). And our ancestors developed Slavic writing, the Russian language. Conclude that today we use the Russian script, an alphabet of 33 letters. Show the child a primer, study each letter with him. Invite the child to circle each of them with a finger.
Step #2: Practice Moderately
Spend no more than 15 minutes a day on letter-drawing. Let the child during this time repeat the outlines of the letters from the primer. Let him try to draw them. If the letters are crooked - it's not scary. It should not scare you that the signs crawling out from under the pencil of a novice writer do not quite look like letters. Transform the process of learning to write into a game - sit next to the baby and draw incomprehensible signs of eyes, smiles, legs and arms. So the child will have more fun. He will trust you, the process, the primer, and next time he will accurately draw a letter, and not a hippopotamus or a fat cat. The main rule is to learn to draw letters for a quarter of an hour. Let the child rest. Even the creativity that the kid is passionate about can exhaust him and discourage him from learning to write.
Let the child during this time repeat the outlines of the letters from the primer. Let him try to draw them. If the letters are crooked - it's not scary. It should not scare you that the signs crawling out from under the pencil of a novice writer do not quite look like letters. Transform the process of learning to write into a game - sit next to the baby and draw incomprehensible signs of eyes, smiles, legs and arms. So the child will have more fun. He will trust you, the process, the primer, and next time he will accurately draw a letter, and not a hippopotamus or a fat cat. The main rule is to learn to draw letters for a quarter of an hour. Let the child rest. Even the creativity that the kid is passionate about can exhaust him and discourage him from learning to write.
Spend no more than 15 minutes a day on letter-drawing. Photo: globallookpress.com
Step No. 3. “We wrote, we wrote, our fingers were tired!” Develop fine motor skills
Together with your child, sculpt from plasticine, build towers and wonderful animals from the designer, draw, color, make applications, lay out mosaics, embroider with a cross. Practice daily, captivate your child with creativity and at the same time help him develop fine motor skills of his hands. If he learns to manipulate various small objects, it will be easier for him to learn to write. Fine motor skills training allows you to develop the temporal regions of the brain that are responsible for speech. If the baby has good motor skills, he writes well, then it will also not be difficult for him to tell a poem beautifully or come up with a story and vividly present it to his family, classmates, teacher. In man, everything is very subtly interconnected.
Practice daily, captivate your child with creativity and at the same time help him develop fine motor skills of his hands. If he learns to manipulate various small objects, it will be easier for him to learn to write. Fine motor skills training allows you to develop the temporal regions of the brain that are responsible for speech. If the baby has good motor skills, he writes well, then it will also not be difficult for him to tell a poem beautifully or come up with a story and vividly present it to his family, classmates, teacher. In man, everything is very subtly interconnected.
See also
"Mom, buy": how to deal with children's requests in the shopping center, parental abuse in response: perhaps each of us was an unwitting witness to such heartbreaking scenes. Together with the teacher-psychologist Ekaterina Bolysheva, we learn to avoid mistakes that can lead to children's tantrums in the store0007
The child's back must not be bent by the wheel. Incorrect posture will negatively affect the health of the internal organs of the baby, his psychological state, even the activity of his thinking. Do sports with your child (gymnastics, swimming). Show him how to walk correctly - straight with a slightly raised chin, rushing the top of his head up. Teach him to sit at the table correctly: the child should bend in the lower back, the shoulders should be slightly relaxed, lowered. The kid should not lean heavily on the back of the chair and shift the entire body weight onto the table. The muscles of the upper body should be toned and slightly tense, but the neck should not be pulled forward. A slight tilt of the head is acceptable. In any case, consult with your pediatrician about how to properly seat your child at the table. He will suggest effective practices for controlling the muscles of the back, neck, arms and will talk in detail about why it is so important to develop the habit of sitting at the table correctly.
Do sports with your child (gymnastics, swimming). Show him how to walk correctly - straight with a slightly raised chin, rushing the top of his head up. Teach him to sit at the table correctly: the child should bend in the lower back, the shoulders should be slightly relaxed, lowered. The kid should not lean heavily on the back of the chair and shift the entire body weight onto the table. The muscles of the upper body should be toned and slightly tense, but the neck should not be pulled forward. A slight tilt of the head is acceptable. In any case, consult with your pediatrician about how to properly seat your child at the table. He will suggest effective practices for controlling the muscles of the back, neck, arms and will talk in detail about why it is so important to develop the habit of sitting at the table correctly.
Popular questions and answers
How to teach a child to write beautifully?
Anna Shumilova, methodologist of the Uchi. ru platform:
ru platform:
— Is it really necessary to demand beautiful handwriting and perfectly clean notebooks from a child? Some parents are worried when teachers lower their children's grades for the design of notebooks, and they believe that the main thing is to write down the exercise without errors, give the correct answer to the question, and find the right solution to the problem. Other parents, on the contrary, force the child to rewrite the work with blots and expect the teacher to spend enough time on calligraphy in the classroom. The truth, as always, lies somewhere in the middle. Any teacher knows from his own experience that in dirty, untidy notebooks there are rarely work without errors. Order and accuracy help to form a harmonious, logical thinking. If the student writes quickly and readably, this becomes a huge advantage for him in mastering the school material. We are of the opinion that the teacher should teach children to write. Any adult person knows for himself that it is quite difficult to change handwriting or the way letters are written. Incorrect spelling of letters will not help either the first grader or his teacher, but, on the contrary, will cause additional difficulties. However, a parent can help.
Incorrect spelling of letters will not help either the first grader or his teacher, but, on the contrary, will cause additional difficulties. However, a parent can help.
If you want to help your child prepare for writing, it is best to start with block letters and do no more than 20 minutes at a time. You should also explain to the future student the basic principles of writing.
1. The line is the letter house. It has a floor and a ceiling. You can not break through the floor and stick out the legs of the letters from there. You can't break through the ceiling and stick your head out like a giraffe. If such a nuisance nevertheless happened with the letters, you can give the child a colored pencil and ask them to underline the hooligan letters and ask what exactly is wrong with them. After that, be sure to underline the letters that turned out to be written correctly, and praise the child. Another great exercise is coloring. We select a small part of the picture and ask to color it without going beyond the outline of the figure. For little naughty fingers, it's not so easy.
For little naughty fingers, it's not so easy.
2. When we write letters, we imagine the rails on which the train travels. If the rails cross, the train will derail and fall. The letters should not dance on the line, but stand like soldiers. After the kid writes a line, you can take a ruler and draw vertical lines through the letters. If the rails are straight everywhere, then the train arrived wonderfully, and you can put a big fat plus on this line! Over time, the rails may become slanted, but should remain parallel.
3. Written letters consist of a certain set of elements: sticks, hooks, loops and ovals. As we wrote above, it’s better not to collect letters without a teacher, but it’s worth practicing writing sticks of different lengths. To work with an oval, we can draw a box. The oval should look out the window and not get stuck in it. If a child draws a circle, then his chubby cheeks will not crawl through the window. Cheeks will have to be erased. In addition to writing, we advise you to have an A4 lined notebook. If you don't have one, the regular one will do. First, the parent himself draws a large beautiful printed letter. The child paints its elements in different colors. Then we write giant letters (several centimeters high). At the beginning of the line, the parent puts dots, the child circles them, and only then appends the line on his own. Next come the middle letters and, towards the end of the page, the midget letters. While the child is writing, you can ask him to pronounce the sound of a capital letter in a rough voice, the sound of a middle letter in a normal voice, and squeak the sound of a midget letter. That will be much more fun!
In addition to writing, we advise you to have an A4 lined notebook. If you don't have one, the regular one will do. First, the parent himself draws a large beautiful printed letter. The child paints its elements in different colors. Then we write giant letters (several centimeters high). At the beginning of the line, the parent puts dots, the child circles them, and only then appends the line on his own. Next come the middle letters and, towards the end of the page, the midget letters. While the child is writing, you can ask him to pronounce the sound of a capital letter in a rough voice, the sound of a middle letter in a normal voice, and squeak the sound of a midget letter. That will be much more fun!
How to teach a child to write quickly?
Anna Shumilova:
— A quick letter is a continuous letter. He will be taught by a teacher at school. As soon as the literacy period ends (around February 1st grade) and the Russian language begins, you can dictate very short dictations to your child. You can use the collection of O. V. Uzorova. You can come up with short funny sentences about your child yourself. This will generate additional interest in the letter. Only practice and control over the maximum continuity of the hand while writing one word will help to write quickly. So that the child does not forget what this or that letter looks like (which happens up to grade 3), it is necessary to spend minutes of calligraphy.
You can use the collection of O. V. Uzorova. You can come up with short funny sentences about your child yourself. This will generate additional interest in the letter. Only practice and control over the maximum continuity of the hand while writing one word will help to write quickly. So that the child does not forget what this or that letter looks like (which happens up to grade 3), it is necessary to spend minutes of calligraphy.
Read also
How to teach a child to write at home?
Almaz Marsov, director of the online school "It's clear":
- Learning to write can be divided into 2 stages: preparing the hand for writing and writing itself. At the preparatory stage, you need to teach the child to coordinate brush movements. To do this, play and create with your child. Coloring pages, hatching tasks, as well as graphic exercises will help you: graphomotor tests, labyrinths, tasks of the series “connect by dots”, “connect by dotted lines”, “draw the second half” and so on. In a word, these are the tasks that will teach a child to use a pencil or pen - to set the direction of the lines, control the force of pressure, control the size of the image, the clarity of the lines and smoothness. After that, you can start writing letters and numbers.
In a word, these are the tasks that will teach a child to use a pencil or pen - to set the direction of the lines, control the force of pressure, control the size of the image, the clarity of the lines and smoothness. After that, you can start writing letters and numbers.
The main principle is to go from simple to complex. First, you can learn to write part of a letter or number, then the letter or number in full. It is important to show the child the correct sequence of writing letters and numbers: from left to right, from top to bottom. Too many children come to school with the wrong letter and are faced with the need to relearn. To avoid this, we recommend that you complete tasks with the children and control the correct spelling until they develop a writing skill.
Of course, the best helper is prescription. As soon as the child masters the letter with a hint, you can move on to a more difficult option - writing in a notebook. The more practice, the more confident and better the child's writing. Finally, the skill needs to be consolidated and improved. Write everywhere: sign drawings and crafts, write on asphalt with crayons, on misted glass with your finger - turn writing into a game and an interesting activity for a child. The more you practice, the faster and more beautiful the child will write.
Finally, the skill needs to be consolidated and improved. Write everywhere: sign drawings and crafts, write on asphalt with crayons, on misted glass with your finger - turn writing into a game and an interesting activity for a child. The more you practice, the faster and more beautiful the child will write.
What kind of games help children develop writing skills?
Anna Shumilova:
— Almost any exercise can be turned into a game. It depends on the submission of the material. You can draw letters with your nose in the air, collect letters from sweets. You can color the letters, circle them with dots, and then give them gifts. If the letter is oval, it is necessary to give objects that also contain an oval in their image. Write not only at the table, but also with chalk on the pavement, a marker on a blackboard, sand on glass or on a piece of paper, show letters on your fingers, ask you to guess which letter you are in.