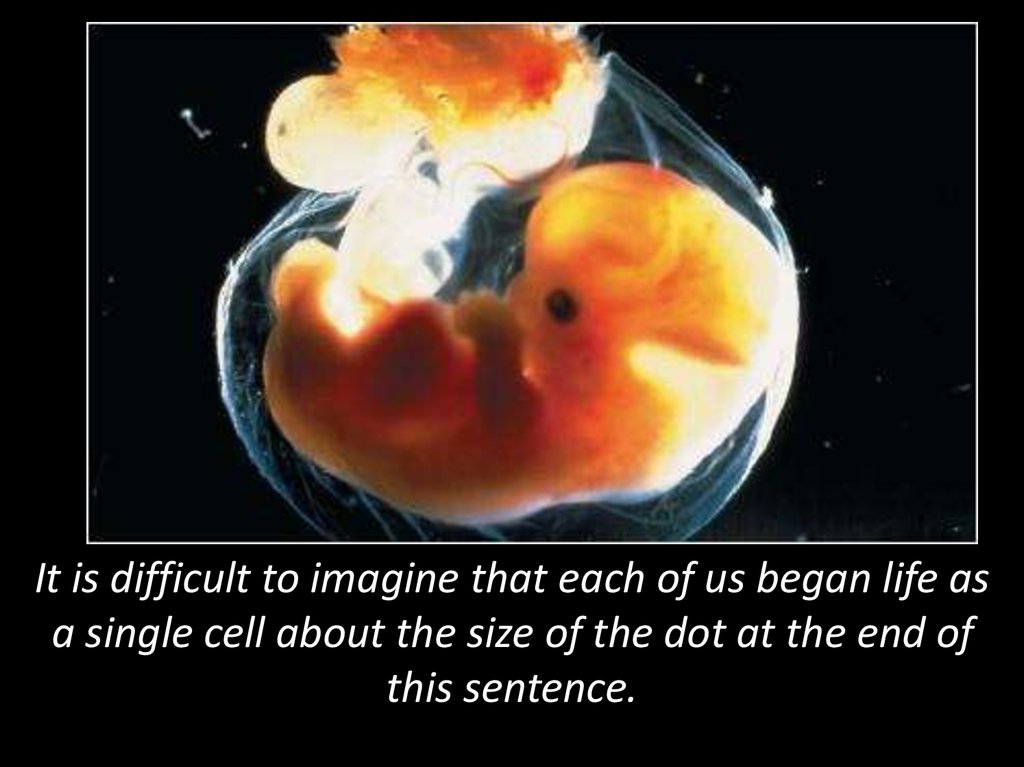
How big is a ten week old fetus
Pregnancy at week 10 | Pregnancy Birth and Baby
Pregnancy at week 10 | Pregnancy Birth and Baby beginning of content4-minute read
Listen
Your baby
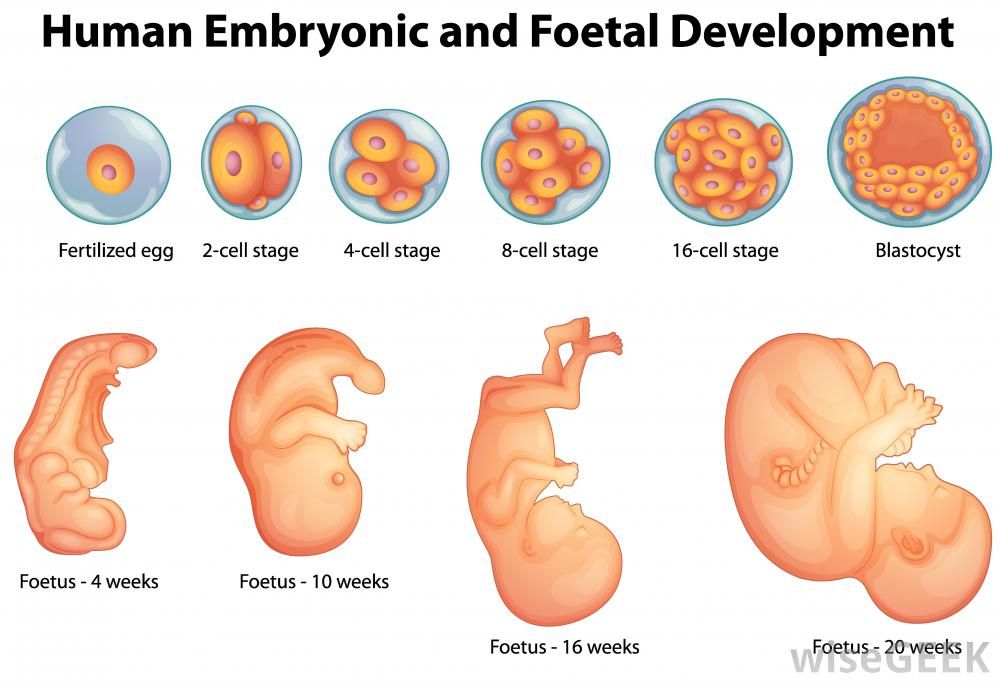
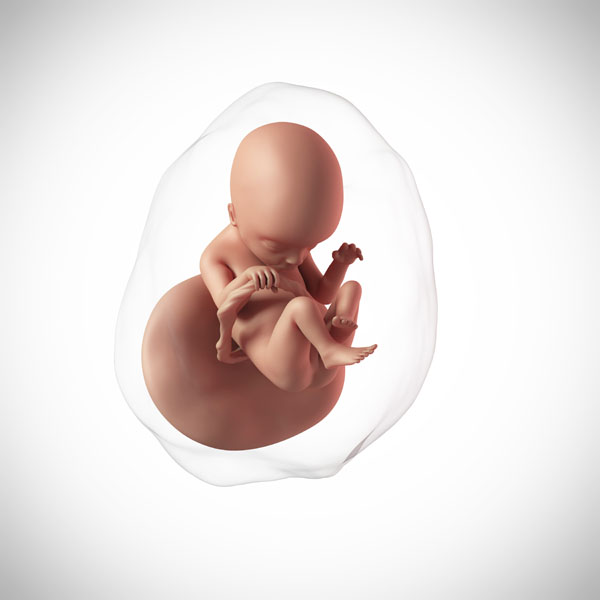
From 10 weeks, your baby is called a fetus. They are about 3.5cm long – around the size of a prune – and weight about 8g. The tadpole-like tail has disappeared.
All of the organs have formed but they aren’t working yet. The ears are developing and the nostrils are in place above the upper lip. The jaw bones already include all the milk teeth.
The baby has internal sex organs, their ovaries or testicles, but the external sex organs still haven’t developed. The brain is active and has brain waves. The heart has 4 separate chambers and is beating at about 180 beats per minute, 3 times faster than an adult heart.
The arms and legs have grown longer, and the baby has tiny fingers and toes. Their ankles, wrists, knees and elbows are forming.
Your baby at 10 weeks
| Length: | 3.5cm |
| Weight: | 8g |
Your body
Your womb (uterus) is now about the size of an orange. You may find your clothes are tighter and your stomach may be sticking out, but this can be due to changes in your bowel rather than your pregnancy.
Many women feel vulnerable and emotional when they are pregnant. This is completely normal. You may also be more hungry than usual. Try not to fill yourself up with unhealthy food – choose nutritious snacks as part of a healthy diet while you’re pregnant.
Things to remember
You may have already had an ultrasound scan to confirm your due date, but a dating scan is normally done at around 10 weeks.
From 10 weeks you can start thinking about prenatal screening.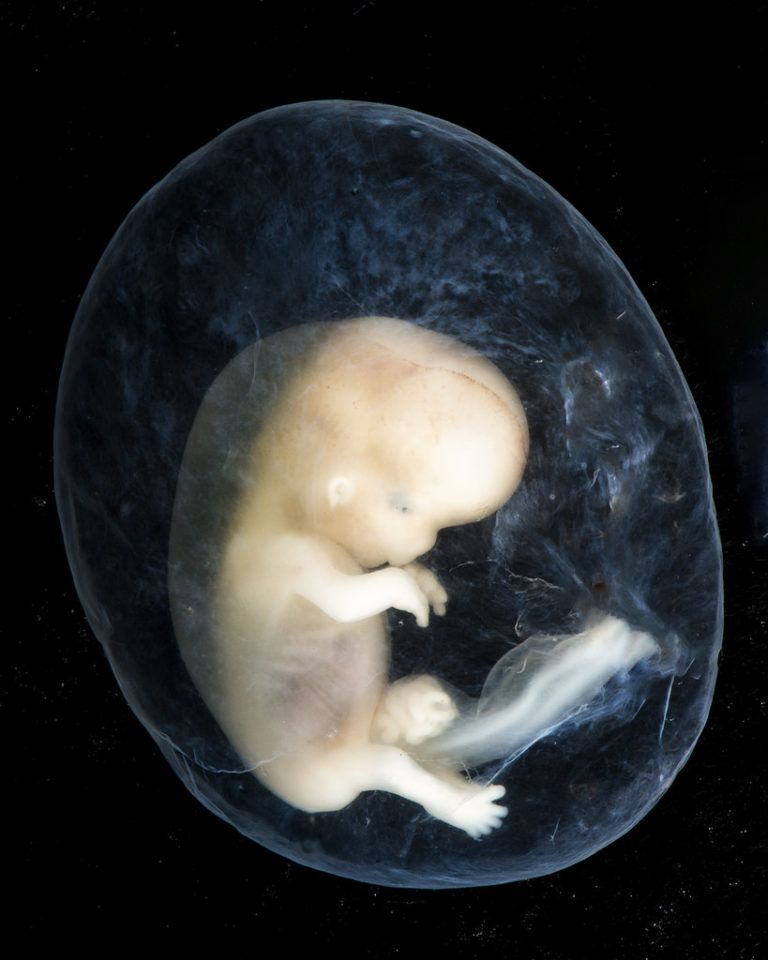 One screening test you can have now is a non-invasive prenatal test, or NIPT, to screen for Down syndrome and certain other abnormalities in the baby. This is a simple, very accurate blood test, but it’s quite expensive and it’s not for everyone. Most women who want to screen for Down syndrome have combined first trimester screening a little later in the pregnancy.
One screening test you can have now is a non-invasive prenatal test, or NIPT, to screen for Down syndrome and certain other abnormalities in the baby. This is a simple, very accurate blood test, but it’s quite expensive and it’s not for everyone. Most women who want to screen for Down syndrome have combined first trimester screening a little later in the pregnancy.
You do not have to have screening. It depends on your age, history and unique circumstances. Talk to your doctor or genetic counsellor about the best screening tests for you.
Read next
Your pregnancy at 11 weeks
Learn about your pregnancy journey and what is happening to you and your baby.
Speak to a maternal child health nurse
Call Pregnancy, Birth and Baby to speak to a maternal child health nurse on 1800 882 436 or video call. Available 7am to midnight (AET), 7 days a week.
Sources:
Raising Children Network (Pregnancy week-by-week), Better Health Channel (Pregnancy - week by week), Women's and Children's Health Network (The first 3 months of pregnancy: the first trimester)Learn more here about the development and quality assurance of healthdirect content.
Last reviewed: August 2020
Back To Top
Related pages
- Pregnancy week-by-week
Need further advice or guidance from our maternal child health nurses?
1800 882 436
Video call
- Contact us
- About us
- A-Z topics
- Symptom Checker
- Service Finder
- Linking to us
- Information partners
- Terms of use
- Privacy
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is funded by the Australian Government and operated by Healthdirect Australia.
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is provided on behalf of the Department of Health
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby’s information and advice are developed and managed within a rigorous clinical governance framework.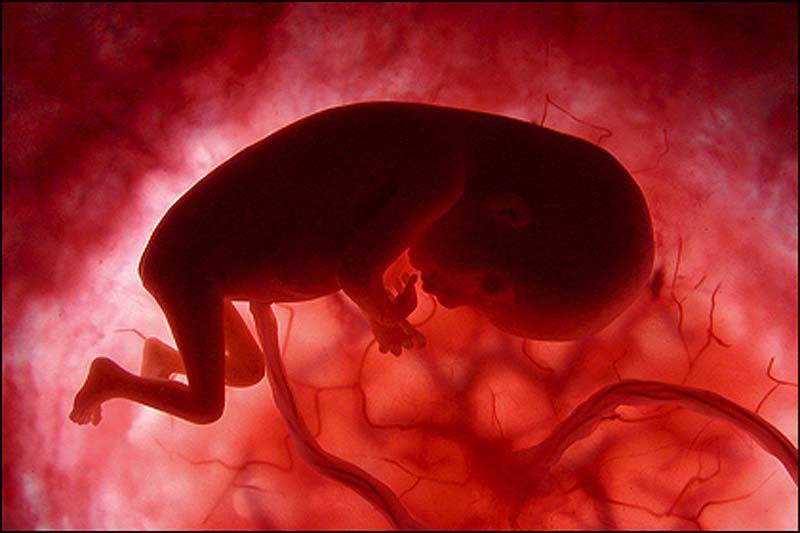 This website is certified by the Health On The Net (HON) foundation, the standard for trustworthy health information.
This website is certified by the Health On The Net (HON) foundation, the standard for trustworthy health information.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
This information is for your general information and use only and is not intended to be used as medical advice and should not be used to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any medical condition, nor should it be used for therapeutic purposes.
The information is not a substitute for independent professional advice and should not be used as an alternative to professional health care. If you have a particular medical problem, please consult a healthcare professional.
Except as permitted under the Copyright Act 1968, this publication or any part of it may not be reproduced, altered, adapted, stored and/or distributed in any form or by any means without the prior written permission of Healthdirect Australia.
Support this browser is being discontinued for Pregnancy, Birth and Baby
Support for this browser is being discontinued for this site
- Internet Explorer 11 and lower
We currently support Microsoft Edge, Chrome, Firefox and Safari.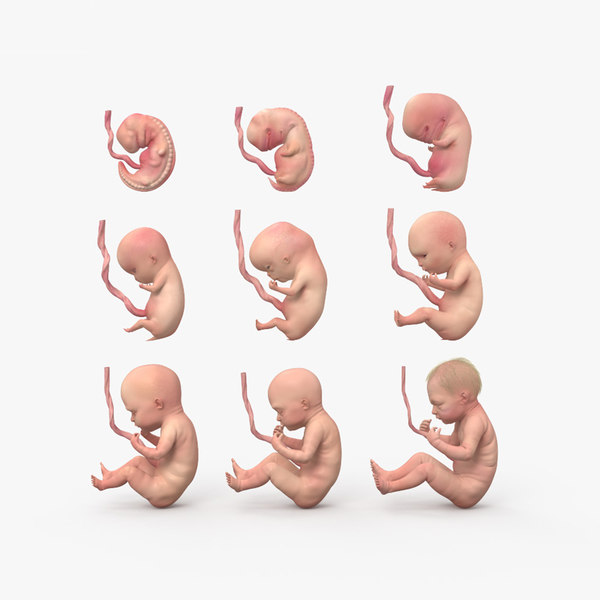 For more information, please visit the links below:
For more information, please visit the links below:
- Chrome by Google
- Firefox by Mozilla
- Microsoft Edge
- Safari by Apple
You are welcome to continue browsing this site with this browser. Some features, tools or interaction may not work correctly.
10 Weeks Pregnant: Symptoms and Baby Development
10 Weeks Pregnant: Your Baby's Development
Your baby has come a long way in just a few short weeks! That little head is taking on a rounder, more human shape, and by now all the internal organs should be in place and starting to work together.
Tiny tooth buds have begun to develop, too. Your baby’s fingers and toes are growing longer, and the webs that had been between each finger and toe are starting to disappear.
At the moment, your baby’s eyes, eyelids, and ears are continuing to develop, but they’ve still got some growing to do before they’re fully formed. What’s in store for both you and your baby until you’re able to look your little one in the eyes for real? Find out by checking out our Pregnancy Guide; it contains tips and insights to help you get through the rest of the first trimester and beyond.
What’s in store for both you and your baby until you’re able to look your little one in the eyes for real? Find out by checking out our Pregnancy Guide; it contains tips and insights to help you get through the rest of the first trimester and beyond.
The Size of the Fetus at 10 Weeks Pregnant
Your little one is still growing very quickly! At 10 weeks, the average fetus is about the size of a strawberry, measuring approximately an inch from crown to rump. Check out the illustration below for a look at how things are shaping up inside your belly as you head toward the end of the first trimester.
Mom's Body at 10 Weeks Pregnant
Your uterus is about the size of a large orange at this point, whereas before you became pregnant it was about the size of a small pear.
Around this time, you likely have had or will soon have a visit with your healthcare provider for a thorough examination.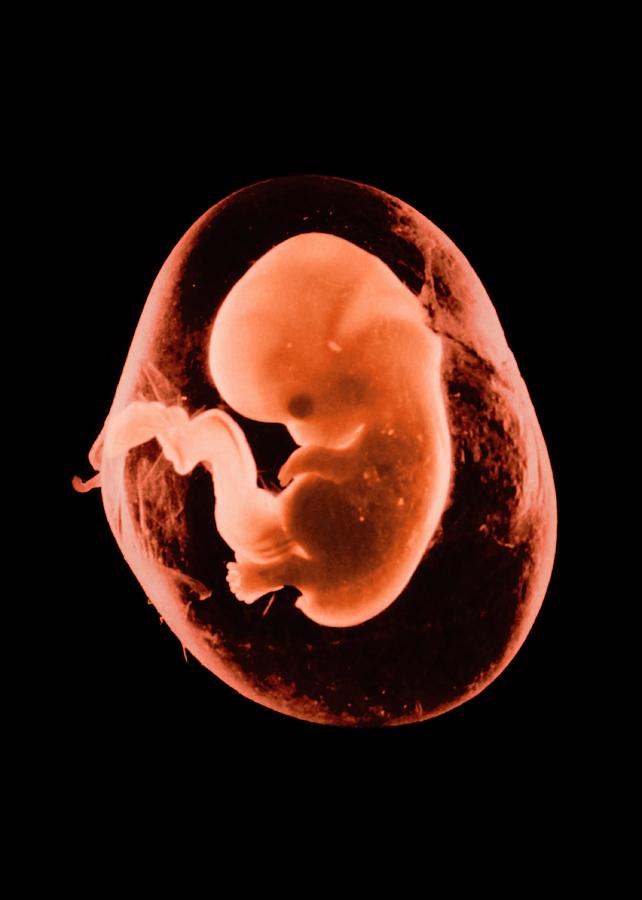 At this appointment, your provider may do an internal and external abdominal exam to determine the size and position of your baby, as well as take blood samples for a variety of other tests.
These blood tests may be used to determine if you have any infections, what your blood type and Rh factor are, and whether your own immunizations are up to date.
There’s a lot to do, but your provider will be able to walk you through the details and schedule future appointments and tests.
At this appointment, your provider may do an internal and external abdominal exam to determine the size and position of your baby, as well as take blood samples for a variety of other tests.
These blood tests may be used to determine if you have any infections, what your blood type and Rh factor are, and whether your own immunizations are up to date.
There’s a lot to do, but your provider will be able to walk you through the details and schedule future appointments and tests.
10 Weeks Pregnant: Your Symptoms
At 10 weeks pregnant, here are some of the symptoms you may be experiencing:
Morning sickness. You’re not alone if you’re 10 weeks pregnant and you're still suffering from morning sickness. The good news? You’re likely to start feeling better soon. Morning sickness often goes away after you enter the second trimester. Keep in mind, some moms-to-be experience a more severe form of morning sickness called hyperemesis gravidarum.
 If you suspect you may have this, speak to your healthcare provider.
If you suspect you may have this, speak to your healthcare provider.
Round ligament pain. Of all of the pregnancy symptoms you may be experiencing around this time, this one is among the most uncomfortable. Round ligaments are two of the ligaments in your pelvis that help support the uterus, and as your baby grows during pregnancy they stretch and soften. When these ligaments tighten, you may feel pain on one or both sides of your abdomen. Changing positions in bed or doing strenuous exercise may bring on this pain. Light stretching and gentle movements may help relieve the discomfort. If this symptom doesn’t go away on its own, or if you also have a fever, call your healthcare provider.
Minimal weight gain. Even though your clothes may be fitting a bit tighter, you may not have gained much weight, and you may even have lost a little if you've been dealing with morning sickness. Read pregnancy weight gain facts and advice here and be sure to talk to your doctor if you’re concerned.
 You can also try using our Pregnancy Weight Gain Calculator tool for an estimate of healthy weight gain based on your pre-pregnancy weight.
You can also try using our Pregnancy Weight Gain Calculator tool for an estimate of healthy weight gain based on your pre-pregnancy weight.
Exhaustion. You might feel like napping at every opportunity. This could be thanks to the increased levels of the hormone progesterone in your body. You can find tips on how to get a good night’s sleep here. You really do need it!
Headaches. Some moms-to-be get the occasional headache during pregnancy. If you're experiencing this symptom, try to rest in a darkened room and apply an ice pack to your head or neck to help relieve the pain. Contact your healthcare provider if the headache persists or is severe.
Mood swings. Hormonal changes may play a role in the highs and lows you feel when you’re about 10 weeks pregnant. You may find it helpful to distract yourself by chatting with friends, watching funny TV shows or movies, or treating yourself to a massage — just be sure to choose a trained masseuse who knows about safe massage techniques for pregnant women.

Vaginal discharge. You might be seeing more vaginal discharge than before, which is caused by your increased blood supply and higher hormone levels. This normal vaginal discharge is known as leukorrhea, and you can expect to see a clear to milky-colored, nearly odorless discharge that may appear slightly yellowish on your underwear. Contact your healthcare provider, though, if you notice a strong odor or color changes, or if you experience itching or bleeding around the vaginal area.
Acne. If you’re experiencing acne now and didn’t before you got pregnant, or if your acne is worse now than before, it may be one of your pregnancy symptoms. Read up on how you can combat some of those spots and blemishes in our article on pregnancy acne, and remember that it’s just one of those pesky pregnancy hormone-related symptoms that should clear soon after your baby is born.
10 Weeks Pregnant: Things to Consider
Reduce your caffeine intake, if you haven’t already done so.
 Many healthcare providers recommend reducing or eliminating caffeine from your diet so that you’re not having more than 200 mg per day (the equivalent of one 12-ounce cup of coffee). Cutting out caffeine can also help you sleep better.
Many healthcare providers recommend reducing or eliminating caffeine from your diet so that you’re not having more than 200 mg per day (the equivalent of one 12-ounce cup of coffee). Cutting out caffeine can also help you sleep better.
As your pregnancy progresses, the weight of your growing uterus can hinder blood flow to the lower parts of your body. When this happens, the veins in your legs can become swollen, sore, and blue. Varicose veins are not preventable, but you can take steps to ease the discomfort and prevent them from becoming worse. Don’t sit with your legs crossed or stand or sit for long periods of time. Try wearing support hose and propping your legs up whenever you can to help improve blood flow. Also, stay active, move around, and add some safe pregnancy exercise to your daily routine if your healthcare provider approves.
You may not be showing for a few weeks yet (although some moms-to-be start showing a little earlier than others), but you might like to think about starting a baby bump progression photo series – if this is something you might like to do.
 You could start as soon as you start showing, or even a little earlier. Pick a day of the week, where you’d like to stand and what to wear. Some wear a tight-fitting top, while others roll their singlet up to reveal their belly. Stand side-on and either take a selfie or have someone take a full-length photo of you. Once your baby is born you can even take a few postpartum shots with your baby in your arms. You’ll love being able to look back on how your belly grew as your pregnancy progressed.
You could start as soon as you start showing, or even a little earlier. Pick a day of the week, where you’d like to stand and what to wear. Some wear a tight-fitting top, while others roll their singlet up to reveal their belly. Stand side-on and either take a selfie or have someone take a full-length photo of you. Once your baby is born you can even take a few postpartum shots with your baby in your arms. You’ll love being able to look back on how your belly grew as your pregnancy progressed.
10 Weeks Pregnant: Ask Your Doctor
When can you hear your baby’s heartbeat?
When will you be able to know if you are pregnant with twins?
Are any genetic screening tests recommended? If so, when would these take place? Keep in mind: Genetic testing is completely optional. Talk to your doctor or consult a genetic counselor to decide whether these tests are right for you based on any risk factors, your family’s history, and any other considerations like your personal preferences.

What is chorionic villus sampling and is it recommended?
Is a nuchal translucency ultrasound recommended?
10 Weeks Pregnant: Your Checklist
Get a professional bra fitting and buy comfortable underwear and well-fitting bras if needed.
Start to plan a second trimester babymoon! You’re nearly in the trimester which is sometimes called the “honeymoon” period of pregnancy, when you may get your energy levels back, so this could be the right time to take a short break. Besides, after the second trimester, you may not have the chance to get away for a while, so this might be the perfect time to book a relaxing trip.
When you have a minute, read our article on pregnancy warning signs you should not ignore. You shouldn’t worry unduly, but it helps to be informed so you know what signs to look out for.
Sign up for even more pregnancy tips here:
Child development by week | Regional Perinatal Center
Expectant mothers are always curious about how the fetus develops at a time when it is awaited with such impatience. Let's talk and look at the photos and pictures of how the fetus grows and develops week by week.
Let's talk and look at the photos and pictures of how the fetus grows and develops week by week.
What does the puffer do for 9 whole months in mom's tummy? What does he feel, see and hear?
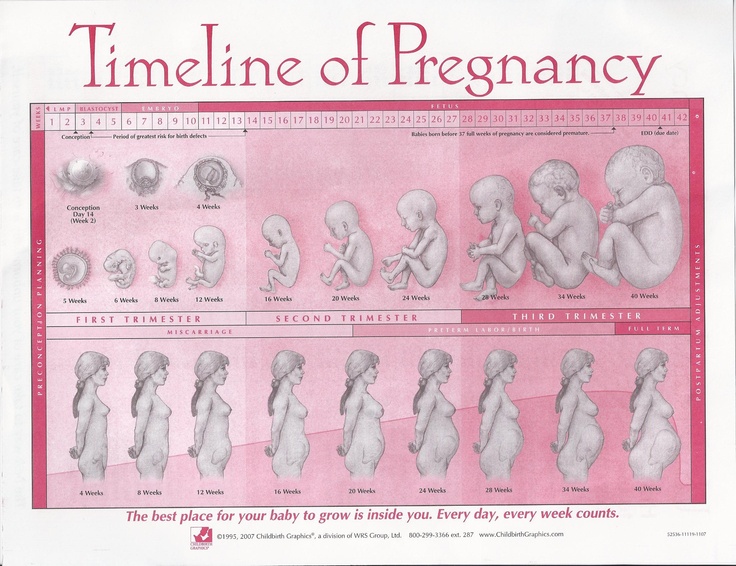
Let's start the story about the development of the fetus by weeks from the very beginning - from the moment of fertilization. A fetus up to 8 weeks old is called embryo , this occurs before the formation of all organ systems.
Embryo development: 1st week
The egg is fertilized and begins to actively split. The ovum travels to the uterus, getting rid of the membrane along the way.
On the 6th-8th days, implantation of eggs is carried out - implantation into the uterus. The egg settles on the surface of the uterine mucosa and, using the chorionic villi, attaches to the uterine mucosa.
Embryo development: 2-3 weeks
Picture of embryo development at 3 weeks.
The embryo is actively developing, starting to separate from the membranes.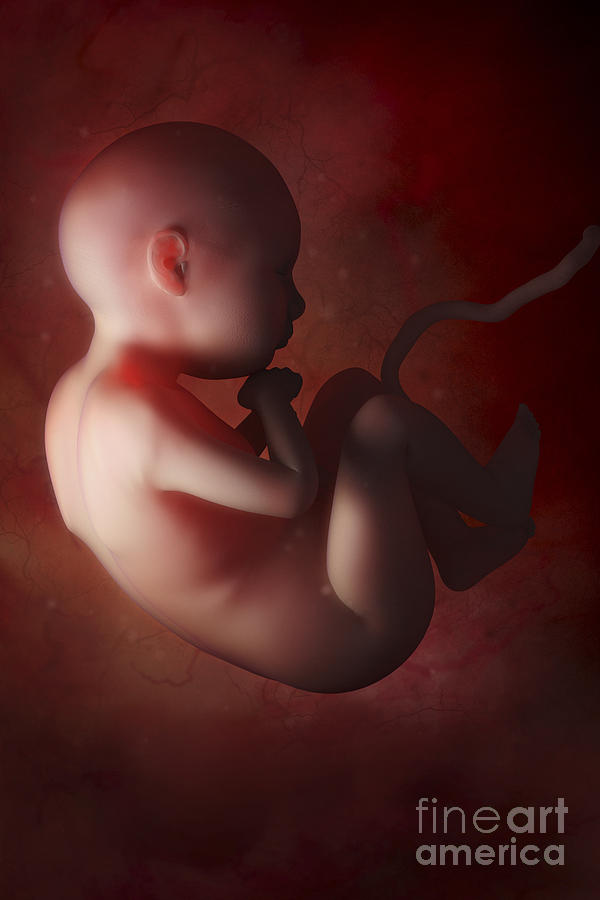 At this stage, the beginnings of the muscular, skeletal and nervous systems are formed. Therefore, this period of pregnancy is considered important.
At this stage, the beginnings of the muscular, skeletal and nervous systems are formed. Therefore, this period of pregnancy is considered important.
Embryo development: 4–7 weeks
Fetal development by week in pictures: week 4
Fetal development by week photo: week 4
Photo of an embryo before the 6th week of pregnancy.
The heart, head, arms, legs and tail are formed in the embryo :) . Gill slit is defined. The length of the embryo at the fifth week reaches 6 mm.
Fetal development by week photo: week 5
At the 7th week, the rudiments of the eyes, stomach and chest are determined, and fingers appear on the handles. The baby already has a sense organ - the vestibular apparatus. The length of the embryo is up to 12 mm.
Fetal development: 8th week
Fetal development by week photo: week 7-8
The face of the fetus can be identified, the mouth, nose, and auricles can be distinguished.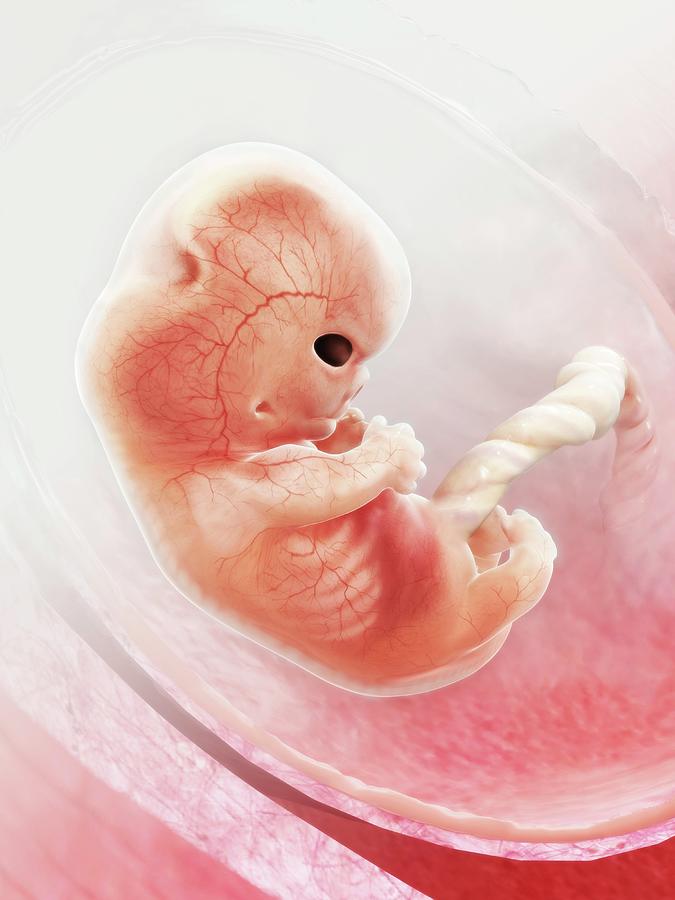 The head of the embryo is large and its length corresponds to the length of the body; the fetal body is formed. All significant, but not yet fully formed, elements of the baby's body already exist. The nervous system, muscles, skeleton continue to improve.
The head of the embryo is large and its length corresponds to the length of the body; the fetal body is formed. All significant, but not yet fully formed, elements of the baby's body already exist. The nervous system, muscles, skeleton continue to improve.
Fetal development in the photo already sensitive arms and legs: week 8
The fetus developed skin sensitivity in the mouth (preparation for the sucking reflex), and later in the face and palms.
At this stage of pregnancy, the genitals are already visible. Gill slits die. The fruit reaches 20 mm in length.
Fetal development: 9–10 weeks
Fetal development by week photo: week 9
Fingers and toes already with nails. The fetus begins to move in the pregnant woman's stomach, but the mother does not feel it yet. With a special stethoscope, you can hear the baby's heartbeat. Muscles continue to develop.
Weekly development of the fetus photo: week 10
The entire surface of the fetal body is sensitive and the baby develops tactile sensations with pleasure, touching his own body, the walls of the fetal bladder and the umbilical cord. It is very curious to observe this on ultrasound. By the way, the baby first moves away from the ultrasound sensor (of course, because it is cold and unusual!), And then puts his hands and heels trying to touch the sensor.
It's amazing when a mother puts her hand to her stomach, the baby tries to master the world and tries to touch with his pen "from the back".
The development of the fetus: 11–14 weeks
Development of the fetus in the photo of the legs: weeks 11
The baby, legs and eyelids are formed, and the genitals become distinguishable (you can find out the gender (you can find out the gender child). The fetus begins to swallow, and if something is not to its taste, for example, if something bitter got into the amniotic fluid (mother ate something), then the baby will begin to frown and stick out his tongue, making less swallowing movements.
The fetus begins to swallow, and if something is not to its taste, for example, if something bitter got into the amniotic fluid (mother ate something), then the baby will begin to frown and stick out his tongue, making less swallowing movements.
Fruit skin appears translucent.
Fruit development: Week 12
Photo of the fetus 12 weeks per 3D Uzi
buds are responsible for production for production urine. Blood forms inside the bones. And hairs begin to grow on the head. Moves more coordinated. The skin turns pink, the ears and other parts of the body, including the face, are already visible. Imagine, a child can already open his mouth and blink, as well as make grasping movements. Baby sucks his thumb, becomes more energetic. Pseudo-feces are formed in the intestines of the fetus - meconium , kidneys begin to work. During this period, the brain develops very actively. The auditory ossicles become stiff and now they are able to conduct sounds, the baby hears his mother - heartbeat, breathing, voice. The fetus intensively gains weight, fat deposits are formed. The weight of the fetus reaches 650 g, and the length is 300 mm. The lungs at this stage of fetal development are so developed that the baby can survive in the artificial conditions of the intensive care unit. Lungs continue to develop. Lips and mouth become more sensitive. The eyes develop, open slightly and can perceive light and squint from direct sunlight. In girls, the labia majora do not yet cover the small ones, and in boys, the testicles have not yet descended into the scrotum. Fetal weight reaches 900–1200 g, and the length is 350 mm. 9 out of 10 children born at this term survive. The lungs are now adapted to breathe normal air. Breathing is rhythmic and body temperature is controlled by the CNS. The baby can cry and responds to external sounds. Child opens eyes while awake and closes during sleep. The skin becomes thicker, smoother and pinkish. Starting from this period, the fetus will actively gain weight and grow rapidly. The fetus reacts to a light source. Muscle tone increases and the baby can turn and raise his head. On which, the hairs become silky. The child develops a grasping reflex. The lungs are fully developed. The fetus is quite developed, prepared for birth and considered mature. The baby has mastered over 70 different reflex movements. Due to the subcutaneous fatty tissue, the baby's skin is pale pink. The head is covered with hairs up to 3 cm. The baby perfectly mastered the movements of his mother , knows when she is calm, excited, upset and reacts to this with her movements. During the intrauterine period, the fetus gets used to moving in space, which is why babies love it so much when they are carried in their arms or rolled in a stroller. The nails protrude beyond the tips of the fingers, the cartilages of the ears and nose are elastic. In boys, the testicles have descended into the scrotum, and in girls, the large labia cover the small ones. The weight of the fetus reaches 3200-3600 g, and the length is 480-520 mm. After the birth, the baby longs for touching his body, because at first he cannot feel himself - the arms and legs do not obey the child as confidently as it was in the amniotic fluid. Therefore, so that your baby does not feel lonely, it is advisable to carry him in your arms, press him to you while stroking his body. And one more thing, the baby remembers the rhythm and sound of your heart very well . Therefore, you can comfort the baby in this way - take him in your arms, put him on the left side and your miracle will calm down, stop crying and fall asleep. Week by week BABY At the 9th week of pregnancy, the weight of the fetus is about 1 g, reaching 10 g by its end, and the length is about 30--45 mm. During this period, the embryonic tail disappears and the back straightens: the fetus acquires the usual “human” appearance. His head is pressed to his chest, his neck is bent, his arms are brought to his chest. The most important process is the continued intensive development of the brain. Two hemispheres are clearly formed, the cerebellum begins to function, which is responsible for the coordination of movements. From this moment on, the fetus feels the movements of its body, spontaneous movements are replaced by clear active movements. The heart of the future baby is divided into 4 chambers - 2 atria and 2 ventricles, and the heart rate is 120--150 beats per minute. Blood vessels are formed through which blood is driven, and the upper half of the fetal body is better supplied with blood, so its arms are more developed than legs. The fingers of the handles lengthen, the membranes disappear between them. By 9th week, the eyes are fully formed, they are closed, because they are tightly covered with eyelids. The facial bones are closed, the auricles with lobes, the nose with nostrils, the upper lip are clearly distinguishable: the face acquires the features inherent in a person. The tummy of the fetus becomes more rounded due to the intensive development of the digestive organs, of which the liver is especially important, since it is the main organ of hematopoiesis (formation of new blood cells) and produces "fetal" blood. At this time, a very important event occurs - the beginning of the production of hormones, including adrenaline. Expectant MOM A pregnant woman may experience fatigue, drowsiness, dizziness, and frequent mood swings. Manifestations of toxicosis (nausea and vomiting) can reach a maximum. At this time, it is advisable to visit a gynecologist and register for pregnancy. BABY This week of pregnancy is very significant, since from this period the fetal stage of development begins and the future baby can already be officially called not an embryo, but a fetus. By this period, the laying of all organs takes place, which in the future will only grow and develop. The fetus is located freely inside the uterus, practically without touching its walls. At this time, the nervous system is intensively developing, the neuromuscular pathways of impulse transmission are being improved. This is associated with the appearance of more intense fetal movements. From the 10th week, they are reflex, quite active and are associated with random touches on the wall of the uterus: at this time, the fetus makes clear movements with arms, legs or head. It is impossible to feel them, but with an ultrasound examination, the movements are clearly distinguishable. The diaphragm is completing its formation - a special flat muscle that separates the organs of the chest cavity from the abdominal cavity. Internal organs continue to develop. Expectant MOTHER A pregnant woman continues psycho-emotional lability, increased anxiety, nervousness at this period; she still owes this to changes in the hormonal background. The fact that the establishment of hormonal balance and the restoration of a good mood is not far off is a consolation. The situation with manifestations of toxicosis is changing. In most cases, vomiting stops completely, and nausea worries less and less, mainly in the morning. If toxicosis completely recedes, it may be replaced by an immoderate increase in appetite. During this period, it is important to monitor nutrition and prevent excessive weight gain due to overeating or eating high-calorie foods. This is harmful to the health of a pregnant woman, as it increases the load on the liver and kidneys, which can provoke the appearance of edema, shortness of breath and general poor health. Excess weight also leads to increased stress on the cardiovascular system. By the 10th week, expectant mothers may notice some body changes. The uterus increases, reaching the size of a grapefruit (or a large apple), but not so much as to change the shape of the abdomen, and the pregnancy is completely invisible to others. BABY At the 11th week, intensive growth of the fetus continues. It looks like this: a big head, a small torso, long arms and short bent legs pressed to the tummy. Such an unusual proportion is due to the fact that throughout the entire period of intrauterine development, the upper half of the fetal body receives the bulk of oxygen and nutrients, since it is there that the vital organs - the brain and heart - are located. Muscle growth continues, the formation of bones and joints, including small ones. The rudiments of nails appear on the fingers, and the rudiments of teeth appear in the jaws. By this time, fetal movements become more and more purposeful. The fetus begins to respond to external stimuli - loud sounds, sudden movements. Reflexes are actively developing: sucking is manifested by the movement of the lips of the fetus, grasping - by movements of the fingers. The formation of taste and olfactory receptors begins, when amniotic fluid enters the nasal passages or mouth, the fetus feels its taste. The iris is forming; it is she who will determine the color of the eyes after birth. In newborns, the eyes are predominantly blue or dark blue, less often brown. The true color of the eyes is due to the accumulation of melanin pigment in the iris. And its formation depends on genetic inheritance - how much of it is laid in the iris. The final eye color is formed by 5 months or a little later. Future MOM At this stage of pregnancy, as a rule, nausea, vomiting, increased susceptibility to smells almost completely disappear. Intensive growth of the fetus leads to an increase in blood volume. The body of a pregnant woman may react to this with increased sweating, as well as frequent urination due to increased kidney function. If frequent urination is not accompanied by pain or discomfort, then there is no cause for concern. 11 weeks is a significant period, since it is during this period that an important examination is carried out - the first prenatal screening aimed at identifying possible fetal defects (in particular, Down syndrome - the presence of an additional 21st chromosome). It is a combination of ultrasound and biochemical (blood test) research. In addition to identifying possible fetal malformations, the first scheduled ultrasound screening answers many other questions - about the duration of pregnancy, the growth and development of the baby, the state of the chorion, the future placenta, etc. BABY This week marks the end of the first trimester of fetal development. By the end of the 12th week, the fetus has a mass of about 20 g, and its body length is about 90 mm. During this period, many important events take place. The brain of the future baby develops very intensively, the large hemispheres form connections with the spinal cord. Another type of training is the rhythmic movements of the pectoral muscles, which imitate breathing. At the same time, amniotic fluid does not penetrate into the respiratory organs of the fetus, since the glottis is tightly closed. Fetal kidneys begin to function. They accumulate a small amount of fluid and periodically there is an exit of urine through the urethra into the amniotic fluid. At the 12th week, the placenta is finally formed; it begins its full independent functioning. This is the most important unique organ that not only ensures the exchange of nutrients between mother and baby, but also protects the fetus from the effects of external and internal toxins. Expectant MOTHER The general well-being of the woman improves; a period of 12 weeks is rightly considered the "golden" period of pregnancy. This is due to the fact that the corpus luteum, which produces progesterone (the culprit of many sufferings of pregnant women), finally transfers the “reins of power” to the placenta. The shape of the abdomen at this time does not change yet, but the uterus is already quite enlarged in size and reaches the edge of the pubis. In the first trimester, there may be no weight gain, more often it is lost due to toxicosis - poor appetite, vomiting. If the appetite of the expectant mother has not changed significantly, then it must be remembered that weight gain should not exceed 10% of the total for the entire pregnancy (approximately 1-2 kg). From 12 weeks of age, if there are no contraindications, sports activities are recommended. At earlier stages of pregnancy, they are not strictly contraindicated, but most often a period from 12 weeks is chosen to start classes, given the improvement in the general condition of the pregnant woman and the fetus overcoming critical periods of development, the number of which is maximum in the first trimester of pregnancy. The expectant mother can choose from swimming, fitness, yoga, dancing - any kind of activity designed specifically for pregnant women.
Development of the fetus for weeks: Week 14 9000 9000 Fetal development: 15-18 weeks
Fetal development by weeks photo: week 15  The fetus begins to actively push in the mother's tummy. The sex of the fetus can be determined by ultrasound.
The fetus begins to actively push in the mother's tummy. The sex of the fetus can be determined by ultrasound. Fetal development: 19-23 weeks
Fetal development by week photo: week 19
Fetal development by weeks photo: week 20 Fetal development: 24-27 weeks
 Now the baby is already falling asleep and waking up. Downy hairs appear on the skin, the skin becomes wrinkled and covered with grease. The cartilage of the ears and nose is still soft.
Now the baby is already falling asleep and waking up. Downy hairs appear on the skin, the skin becomes wrinkled and covered with grease. The cartilage of the ears and nose is still soft.
Fetal development by week photo: week 27 Fetal development: 28-32 weeks
 Almost all babies born prematurely at this time are viable. The weight of the fetus reaches 2500 g, and the length is 450 mm.
Almost all babies born prematurely at this time are viable. The weight of the fetus reaches 2500 g, and the length is 450 mm. Fetal development: 33-37 weeks
Fetal development by week photo: week 36 Fetal development: 38-42 weeks
Fetal development by weeks photo: week 40  For a baby, this is a completely natural state, so he will calm down and fall asleep when he is shaken.
For a baby, this is a completely natural state, so he will calm down and fall asleep when he is shaken.  And for you, finally, the time of bliss will come :) .
And for you, finally, the time of bliss will come :) . what happens, development of pregnancy and fetus
9-12 weeks pregnant
Elena Gevorkova
Obstetrician-gynecologist, Moscow 9th week

 This is due to the intensive growth of the adrenal glands of the fetus, the complication of their structure, the production of various hormones. They help the fetus to adapt to various extreme changes, to adapt to new conditions. It is under the influence of adrenaline that changes occur in the body that help to withstand stress. Adrenaline regulates a special “survival” mode that allows the fetus to withstand stress.
This is due to the intensive growth of the adrenal glands of the fetus, the complication of their structure, the production of various hormones. They help the fetus to adapt to various extreme changes, to adapt to new conditions. It is under the influence of adrenaline that changes occur in the body that help to withstand stress. Adrenaline regulates a special “survival” mode that allows the fetus to withstand stress. 10th week
 The 10th week is rightly considered the end of the first critical period: from this period, the teratogenic (leading to the occurrence of malformations) effect of various chemical factors (for example, drugs) is no longer as pronounced as before.
The 10th week is rightly considered the end of the first critical period: from this period, the teratogenic (leading to the occurrence of malformations) effect of various chemical factors (for example, drugs) is no longer as pronounced as before. 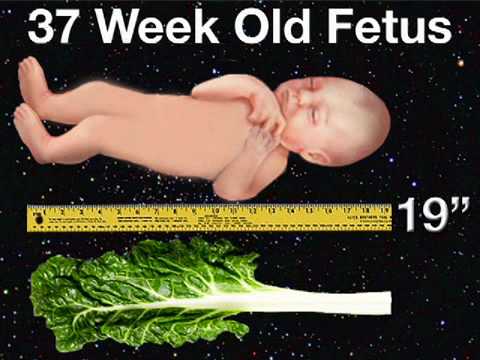
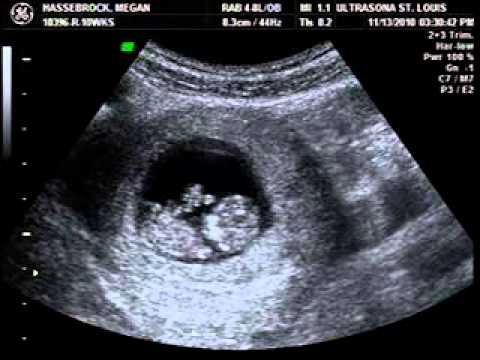 This may be due to both increased nutrition and muscle relaxation and redistribution of the subcutaneous fat layer due to the influence of progesterone, the main hormone of pregnancy.
This may be due to both increased nutrition and muscle relaxation and redistribution of the subcutaneous fat layer due to the influence of progesterone, the main hormone of pregnancy. 11th week

 A woman has the opportunity to control her diet; it is very important to pay attention to this: food should be varied, healthy and freshly prepared. Careful control of the diet will avoid problems that arise during this period. These include digestive disorders - bloating, heartburn, constipation, etc. A feature of the functioning of the digestive system of pregnant women is a decrease in motor skills, i.e. the muscles of the stomach and intestines contract "lazy" due to the relaxing effect of the main hormone of pregnancy, progesterone. This leads to slow progress of the food bolus and disorders of the digestive system. If you can not cope with the situation with the help of a diet, then it is worth discussing with your gynecologist the possibility of using medications.
A woman has the opportunity to control her diet; it is very important to pay attention to this: food should be varied, healthy and freshly prepared. Careful control of the diet will avoid problems that arise during this period. These include digestive disorders - bloating, heartburn, constipation, etc. A feature of the functioning of the digestive system of pregnant women is a decrease in motor skills, i.e. the muscles of the stomach and intestines contract "lazy" due to the relaxing effect of the main hormone of pregnancy, progesterone. This leads to slow progress of the food bolus and disorders of the digestive system. If you can not cope with the situation with the help of a diet, then it is worth discussing with your gynecologist the possibility of using medications.  Otherwise, you should consult a doctor, as these symptoms may indicate inflammation of the bladder - cystitis.
Otherwise, you should consult a doctor, as these symptoms may indicate inflammation of the bladder - cystitis. 12th week
 By their structure, the fetal brain is a small copy of the brain of an adult. Starting from the 12th week, not only erythrocytes are present in the blood of the fetus (as it was during the first three months), but also leukocytes - cells of the immune system that protect the body from infections. This period is characterized by the development of the digestive tract. Most of the abdominal cavity of the fetus is occupied by the liver, a new one is added to its former functions (hematopoiesis) - the production of bile. The intestine grows very intensively, from 12 weeks it begins to take shape in loops: this is exactly what the intestine of an adult looks like. From this period, the intestines begin to make the first peristaltic movements - muscle contractions that ensure the promotion of food. In the intrauterine period, amniotic fluid passes through the intestines, which the fetus swallows from 12 weeks throughout the entire gestation period. Such "trial" peristaltic waves are the training of the muscles of the digestive tract.
By their structure, the fetal brain is a small copy of the brain of an adult. Starting from the 12th week, not only erythrocytes are present in the blood of the fetus (as it was during the first three months), but also leukocytes - cells of the immune system that protect the body from infections. This period is characterized by the development of the digestive tract. Most of the abdominal cavity of the fetus is occupied by the liver, a new one is added to its former functions (hematopoiesis) - the production of bile. The intestine grows very intensively, from 12 weeks it begins to take shape in loops: this is exactly what the intestine of an adult looks like. From this period, the intestines begin to make the first peristaltic movements - muscle contractions that ensure the promotion of food. In the intrauterine period, amniotic fluid passes through the intestines, which the fetus swallows from 12 weeks throughout the entire gestation period. Such "trial" peristaltic waves are the training of the muscles of the digestive tract.
 Nausea, malaise disappear, expectant mothers become calmer and more relaxed.
Nausea, malaise disappear, expectant mothers become calmer and more relaxed.