How big is a baby at 1 month
Fetal development: Month-By-Month Stages of Pregnancy
When does a pregnancy start?
The start of pregnancy is actually the first day of your last menstrual period. This is called the gestational age, or menstrual age. It’s about two weeks ahead of when conception actually occurs. Though it may seem strange, the date of the first day of your last period will be an important date when determining your due date. Your healthcare provider will ask you about this date and will use it to figure out how far along you are in your pregnancy.
How does conception work?
Each month, your body goes through a reproductive cycle that can end in one of two ways. You will either have a menstrual period or become pregnant. This cycle is continuously happening during your reproductive years — from puberty in your teen years to menopause around age 50.
In a cycle that ends with pregnancy, there are several steps. First, a group of eggs (called oocytes) gets ready to leave the ovary for ovulation (release of the egg). The eggs develop in small, fluid-filled cysts called follicles. Think of these follicles as small containers for each immature egg. Out of this group of eggs, one will become mature and continue on through the cycle. This follicle then suppresses all the other follicles in the group. The other follicles stop growing at this point.
The mature follicle now opens and releases the egg from the ovary. This is ovulation. Ovulation generally happens about two weeks before your next menstrual period begins. It’s generally in the middle of your cycle.
After ovulation, the opened (ruptured) follicle develops into a structure called the corpus luteum. This secretes (releases) the hormones progesterone and estrogen. Progesterone helps prepare the endometrium (lining of the uterus). This lining is the place where a fertilized egg settles to develop. If you don’t become pregnant during a cycle, this lining is what is shed during your period.
On average, fertilization happens about two weeks after your last menstrual period. When the sperm penetrates the egg, changes occur in the protein coating of the egg to prevent other sperm from entering.
When the sperm penetrates the egg, changes occur in the protein coating of the egg to prevent other sperm from entering.
At the moment of fertilization, your baby’s genetic make-up is complete, including its sex. The sex of your baby depends on what sperm fertilizes the egg at the moment of conception. Generally, women have a genetic combination of XX and men have XY. Women provide each egg with an X. Each sperm can be either an X or a Y. If the fertilized egg and sperm is a combination of an X and Y, it’s a boy. If there are two Xs, it’s a girl.
What happens right after conception?
Within 24 hours after fertilization, the egg begins rapidly dividing into many cells. It remains in the fallopian tube for about three days after conception. Then the fertilized egg (now called a blastocyte) continues to divide as it passes slowly through the fallopian tube to the uterus. Once there, its next job is to attach to the endometrium. This is called implantation.
Before implantation though, the blastocyte breaks out of its protective covering. When the blastocyte makes contact with the endometrium, the two exchange hormones to help the blastocyte attach. Some women notice spotting (slight bleeding) during the one or two days when implantation happens. This is normal and isn’t something you should worry about. At this point, the endometrium becomes thicker and the cervix (the opening between your uterus and birth canal) is sealed by a plug of mucus.
When the blastocyte makes contact with the endometrium, the two exchange hormones to help the blastocyte attach. Some women notice spotting (slight bleeding) during the one or two days when implantation happens. This is normal and isn’t something you should worry about. At this point, the endometrium becomes thicker and the cervix (the opening between your uterus and birth canal) is sealed by a plug of mucus.
Within three weeks, the blastocyte cells ultimately form a little ball, or an embryo. By this time, the first nerve cells have formed.
Your developing fetus has already gone through a few name changes in the first few weeks of pregnancy. Generally, it's called an embryo from conception until the eighth week of development. After the eighth week, it's called a fetus until it’s born.
How early can I know I’m pregnant?
From the moment of conception, the hormone human chorionic gonadotrophin (hCG) will be present in your blood. This hormone is created by the cells that form the placenta (food source for the growing fetus). It’s also the hormone detected in a pregnancy test. Even though this hormone is there from the beginning, it takes time for it to build within your body. It typically takes three to four weeks from the first day of your last period for the hCG to increase enough to be detected by pregnancy tests.
It’s also the hormone detected in a pregnancy test. Even though this hormone is there from the beginning, it takes time for it to build within your body. It typically takes three to four weeks from the first day of your last period for the hCG to increase enough to be detected by pregnancy tests.
When should I reach out to my healthcare provider about a new pregnancy?
Most healthcare providers will have you wait to come in for an appointment until you have had a positive home pregnancy test. These tests are very accurate once you have enough hCG circulating throughout your body. This can be a few weeks after conception. It’s best to call your healthcare provider once you have a positive pregnancy test to schedule your first appointment.
When you call, your healthcare provider may ask you if you are taking a prenatal vitamin. These supplements contain folic acid. It’s important that you get at least 400mcg of folic acid each day during a pregnancy to make sure the fetus's neural tube (beginning of the brain and spine) develops correctly. Many healthcare providers suggest that you take prenatal vitamins with folic acid even when you aren’t pregnant. If you weren’t taking prenatal vitamins before your pregnancy, your provider may ask you to start as early as possible.
Many healthcare providers suggest that you take prenatal vitamins with folic acid even when you aren’t pregnant. If you weren’t taking prenatal vitamins before your pregnancy, your provider may ask you to start as early as possible.
What’s the timeline for fetal development?
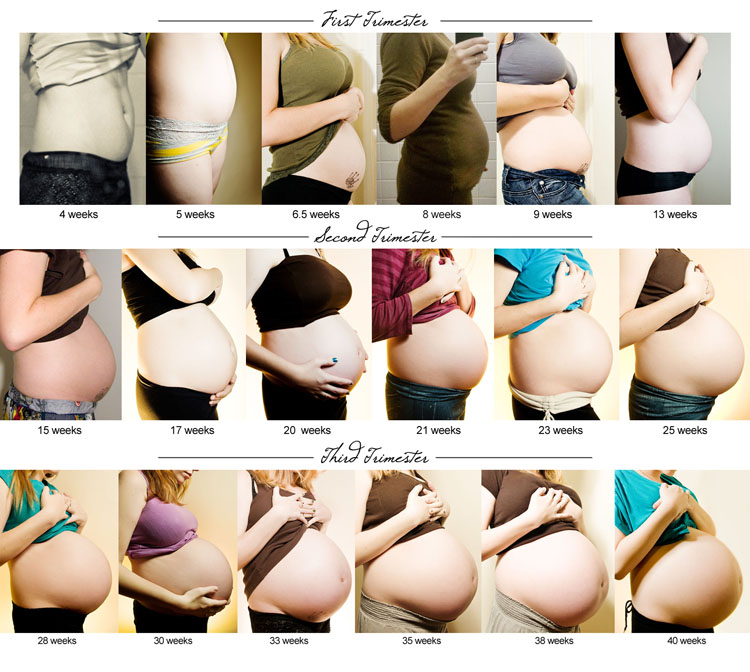
The fetus will change a lot throughout a typical pregnancy. This time is divided into three stages, called trimesters. Each trimester is a set of about three months. Your healthcare provider will probably talk to you about fetal development in terms of weeks. So, if you are three months pregnancy, you are about 12 weeks.
You will see distinct changes in the fetus, and yourself, during each trimester.
Traditionally, we think of a pregnancy as a nine-month process. However, this isn’t always the case. A full-term pregnancy is 40 weeks, or 280 days. Depending on what months you are pregnant during (some are shorter and some longer) and what week you deliver, you could be pregnant for either nine months or 10 months. This is completely normal and healthy.
This is completely normal and healthy.
Once you get close to the end of your pregnancy, there are several category names you might hear regarding when you go into labor. These labels divide up the last few weeks of pregnancy. They’re also used to look out for certain complications in newborns. Babies that are born in the early term period or before may have a higher risk of breathing, hearing or learning issues than babies born a few weeks later in the full term time frame. When you’re looking at these labels, it’s important to know how they’re written. You may see the week first (38) and then you’ll see two numbers separated by a slash mark (6/7). This stands for how many days you currently are in the gestational week. So, if you see 38 6/7, it means that you are on day 6 of your 38th week.
The last few weeks of pregnancy are divided into the following groups:
- Early term: 37 0/7 weeks through 38 6/7 weeks.
- Full term: 39 0/7 weeks through 40 6/7 weeks.
- Late term: 41 0/7 weeks through 41 6/7 weeks.
- Post term: 42 0/7 weeks and on.
Talk to your healthcare provider about any questions you may have about gestational age and due date.
Stages of Growth Month-by-Month in Pregnancy
First trimester
The first trimester will span from conception to 12 weeks. This is generally the first three months of pregnancy. During this trimester, the fertilized egg will change from a small grouping of cells to a fetus that is starting to have a baby’s features.
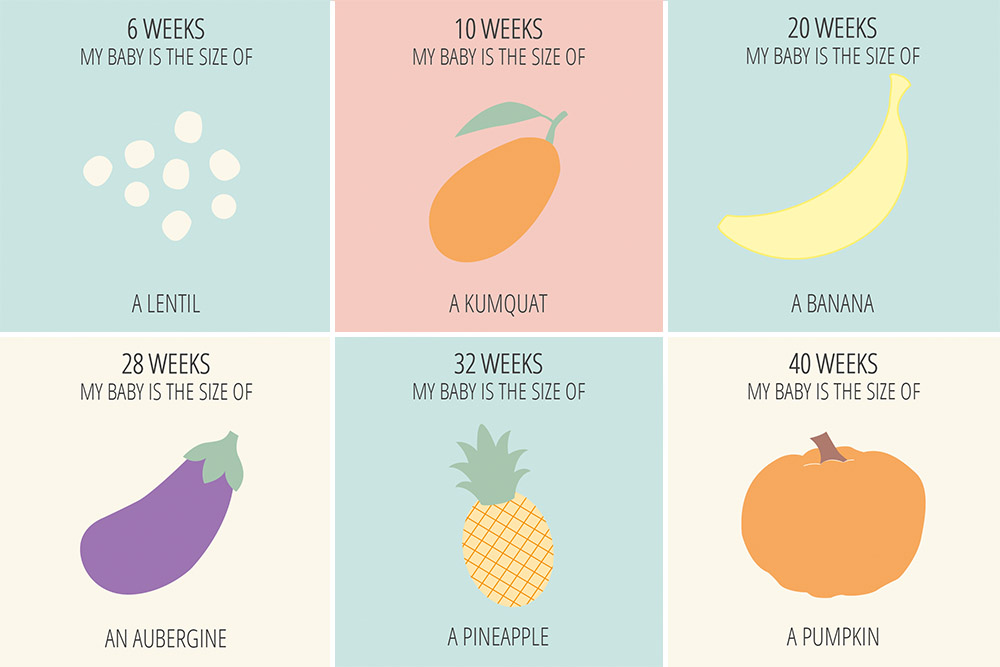
Month 1 (weeks 1 through 4)
As the fertilized egg grows, a water-tight sac forms around it, gradually filling with fluid. This is called the amniotic sac, and it helps cushion the growing embryo.
During this time, the placenta also develops. The placenta is a round, flat organ that transfers nutrients from the mother to the fetus, and transfers wastes from the fetus. Think of the placenta as a food source for the fetus throughout your pregnancy.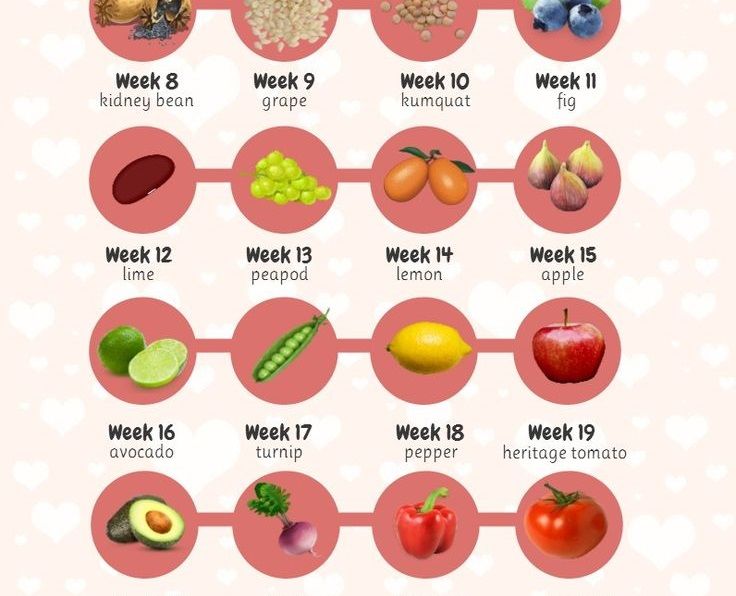
In these first few weeks, a primitive face will take form with large dark circles for eyes. The mouth, lower jaw and throat are developing. Blood cells are taking shape, and circulation will begin. The tiny "heart" tube will beat 65 times a minute by the end of the fourth week.
By the end of the first month, the fetus is about 1/4 inch long – smaller than a grain of rice.
Month 2 (weeks 5 through 8)
Facial features continue to develop. Each ear begins as a little fold of skin at the side of the head. Tiny buds that eventually grow into arms and legs are forming. Fingers, toes and eyes are also forming.
The neural tube (brain, spinal cord and other neural tissue of the central nervous system) is well formed now. The digestive tract and sensory organs begin to develop too. Bone starts to replace cartilage.
The head is large in proportion to the rest of the body at this point. At about 6 weeks, a heartbeat can usually be detected.
After the 8th week, healthcare providers refer to it as a fetus instead of an embryo.
By the end of the second month, the fetus is about 1 inch long and weighs about 1/30 of an ounce.
Month 3 (weeks 9 through 12)
The arms, hands, fingers, feet and toes are fully formed. At this stage, the fetus is starting to explore a bit by doing things like opening and closing its fists and mouth. Fingernails and toenails are beginning to develop and the external ears are formed. The beginnings of teeth are forming under the gums. The reproductive organs also develop, but sex is still difficult to distinguish on ultrasound.
By the end of the third month, the fetus is fully formed. All the organs and limbs (extremities) are present and will continue to develop in order to become functional. The circulatory and urinary systems are also working and the liver produces bile.
At the end of the third month, the fetus is about 4 inches long and weighs about 1 ounce.
Since the most critical development has taken place, your chance of miscarriage drops considerably after three months.
Second trimester
This middle section of pregnancy is often thought of as the best part of the experience. By this time, any morning sickness is probably gone and the discomfort of early pregnancy has faded. The fetus will start to develop facial features during this month. You may also start to feel movement as the fetus flips and turns in the uterus. During this trimester, many people find out whether their baby will be designated male or female at birth. This is typically done during an anatomy scan (an ultrasound that checks physical development) around 20 weeks.
Month 4 (weeks 13 through 16)
The fetal heartbeat may now be audible through an instrument called a doppler. The fingers and toes are well-defined. Eyelids, eyebrows, eyelashes, nails and hair are formed. Teeth and bones become denser. The fetus can even suck his or her thumb, yawn, stretch and make faces.
The nervous system is starting to function. The reproductive organs and genitalia are now fully developed, and your doctor can see on ultrasound if the fetus will be designated male or female at birth.
By the end of the fourth month, the fetus is about 6 inches long and weighs about 4 ounces.
Month 5 (weeks 17 through 20)
At this stage, you may begin to feel the fetus moving around. The fetus is developing muscles and exercising them. This first movement is called quickening and can feel like a flutter.
Hair begins to grow on the head. The shoulders, back and temples are covered by a soft fine hair called lanugo. This hair protects the fetus and is usually shed at the end of your baby's first week of life.
The skin is covered with a whitish coating called vernix caseosa. This "cheesy" substance is thought to protect fetal skin from the long exposure to the amniotic fluid. This coating is shed just before birth.
By the end of the fifth month, the fetus is about 10 inches long and weighs from 1/2 to 1 pound.
Month 6 (weeks 21 through 24)
If you could look inside the uterus right now, you would see that the fetus's skin is reddish in color, wrinkled and veins are visible through translucent skin. The finger and toe prints are visible. In this stage, the eyelids begin to part and the eyes open.
The finger and toe prints are visible. In this stage, the eyelids begin to part and the eyes open.
The fetus responds to sounds by moving or increasing the pulse. You may notice jerking motions if the fetus hiccups.
If born prematurely, your baby may survive after the 23rd week with intensive care.
By the end of the sixth month, the fetus is about 12 inches long and weighs about 2 pounds.
Month 7 (weeks 25 through 28)
The fetus continues to mature and develop reserves of body fat. At this point, hearing is fully developed. The fetus changes position frequently and responds to stimuli, including sound, pain and light. The amniotic fluid begins to diminish.
If born prematurely, your baby would be likely to survive after the seventh month.
At the end of the seventh month, the fetus is about 14 inches long and weighs from 2 to 4 pounds.
Third trimester
This is the final part of your pregnancy. You may be tempted to start the countdown till your due date and hope that it would come early, but each week of this final stage of development helps the fetus prepare for birth. Throughout the third trimester, the fetus gains weight quickly, adding body fat that will help after birth.
Throughout the third trimester, the fetus gains weight quickly, adding body fat that will help after birth.
Remember, even though popular culture only mentions nine months of pregnancy, you may actually be pregnant for 10 months. The typical, full-term pregnancy is 40 weeks, which can take you into a tenth month. It’s also possible that you can go past your due date by a week or two (41 or 42 weeks). Your healthcare provider will monitor you closely as you approach your due date. If you pass your due date, and don’t go into spontaneous labor, your provider may induce you. This means that medications will be used to make you go into labor and have the baby. Make sure to talk to your healthcare provider during this trimester about your birth plan.
Month 8 (weeks 29 through 32)
The fetus continues to mature and develop reserves of body fat. You may notice more kicking. The brain developing rapidly at this time, and the fetus can see and hear. Most internal systems are well developed, but the lungs may still be immature.
The fetus is about 18 inches long and weighs as much as 5 pounds.
Month 9 (weeks 33 through 36)
During this stage, the fetus continues to grow and mature. The lungs are close to being fully developed at this point.
The fetus has coordinated reflexes and can blink, close the eyes, turn the head, grasp firmly, and respond to sounds, light and touch.
The fetus is about 17 to 19 inches long and weighs from 5 ½ pounds to 6 ½ pounds.
Month 10 (Weeks 37 through 40)
In this final month, you could go into labor at any time. You may notice that less movement because space is tight. At this point, The fetus's position may have changed to prepare for birth. Ideally, it's head down in your uterus. You may feel very uncomfortable in this final stretch of time as the fetus drops down into your pelvis and prepares for birth.
Your baby is ready to meet the world at this point. They are about 18 to 20 inches long and weigh about 7 pounds.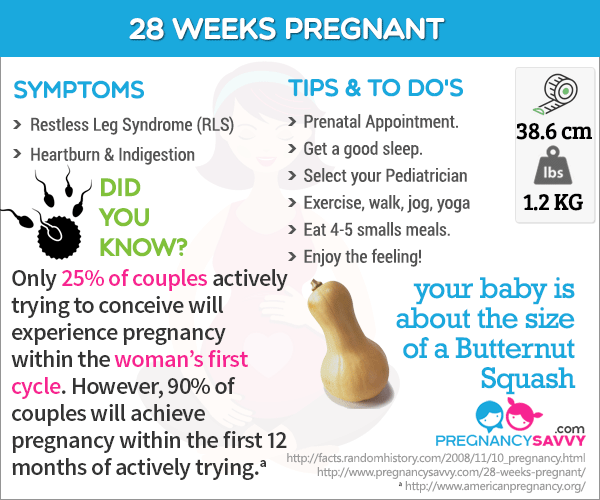
First Month: Physical Appearance and Growth
Log in | Register
Ages & Stages
Ages & Stages
When your baby was born, her birth weight included excess body fluid, which she lost during her first few days.
Most babies lose about one-tenth of their birth weight during the first five days, then regain it over the next five, so that by about day ten they usually are back to their original birth weight. Most babies grow very rapidly after regaining their birth weight, especially during growth spurts, which occur around seven to ten days and again between three and six weeks. The average newborn gains weight at a rate of 2⁄3 of an ounce (20–30 grams) per day and by one month weighs about ten pounds (4.5 kg). She grows between 1 1⁄2 and 2 inches (4.5 to 5 cm) during this month. Boys tend to weigh slightly more than girls (by less than 1 pound, or approximately 350 grams). They also tend to be slightly longer than girls at this age (by about 1⁄2 inch, or 1.25 cm).
They also tend to be slightly longer than girls at this age (by about 1⁄2 inch, or 1.25 cm).
Your pediatrician will pay particular attention to your child’s head growth, because it reflects the growth of her brain. The bones in your baby’s skull are still growing together, and the skull is growing faster during the first four months than at any other time in her life. The average newborn’s head circumference measures about 13 3⁄4 inches (35 cm), growing to about 15 inches (38 cm) by one month. Because boys tend to be slightly larger than girls, their heads are larger, though the average difference is less than 1⁄2 inch (1 cm).
During these first weeks your baby’s body gradually will straighten from the tightly curled position she held inside the uterus during the final months of pregnancy. She’ll begin to stretch her arms and legs and may arch her back from time to time. Her legs and feet may continue to rotate inward, giving her a bowlegged look. This condition usually will correct itself gradually over the first year of life. If the bowlegged appearance is particularly severe or associated with pronounced curving of the front part of the foot, your pediatrician may suggest a splint or a cast to correct it, but in most instances these circumstances are extremely unusual.
If the bowlegged appearance is particularly severe or associated with pronounced curving of the front part of the foot, your pediatrician may suggest a splint or a cast to correct it, but in most instances these circumstances are extremely unusual.
If your baby was born vaginally and her skull appeared misshapen at birth, it soon should resume its normal shape. Any bruising of the scalp or swelling of the eyelids that occurred during birth will be gone by the end of the first week or two. Any red spots in the eyes will disappear in about three weeks.
To your dismay, you may discover that the fine hair that covered your child’s head when she was born soon begins falling out. If she rubs the back of her head on her sleep surface, she may develop a temporary bald spot there, even if the rest of her hair remains. This loss is not medically significant. The bare spots will be covered with new hair in a few months.
Another normal development is baby acne—pimples that break out on the face, usually during the fourth or fifth week of life. They are thought to be due to stimulation of oil glands in the skin by hormones passed across the placenta during pregnancy. This condition may be made worse if the baby lies in sheets laundered in harsh detergents or soiled by milk that she’s spit up. If your baby does have baby acne, place a soft, clean receiving blanket under her head while she’s awake and wash her face gently once a day with a mild baby soap to remove milk or detergent residue.
They are thought to be due to stimulation of oil glands in the skin by hormones passed across the placenta during pregnancy. This condition may be made worse if the baby lies in sheets laundered in harsh detergents or soiled by milk that she’s spit up. If your baby does have baby acne, place a soft, clean receiving blanket under her head while she’s awake and wash her face gently once a day with a mild baby soap to remove milk or detergent residue.
Your newborn’s skin also may look blotchy, ranging in color from pink to blue. Her hands and feet in particular may be colder and bluer than the rest of her body. The blood vessels leading to these areas are more sensitive to temperature changes and tend to shrink in response to cold. As a result, less blood gets to the exposed skin, causing it to look pale or bluish. If you move her arms and legs, however, you should notice that they quickly turn pink again.
Your baby’s internal “thermostat,” which causes her to sweat when she’s too hot or shiver when she’s too cold, won’t be working properly for some time. Also, in these early weeks, she’ll lack the insulating layer of fat that will protect her from sudden temperature shifts later on. For these reasons, it’s important for you to dress her properly—warmly in cool weather and lightly when it’s hot. A general rule of thumb is to dress her in one more layer of clothing than you would wear in the same weather conditions. Don’t automatically bundle her up just because she’s a baby.
Also, in these early weeks, she’ll lack the insulating layer of fat that will protect her from sudden temperature shifts later on. For these reasons, it’s important for you to dress her properly—warmly in cool weather and lightly when it’s hot. A general rule of thumb is to dress her in one more layer of clothing than you would wear in the same weather conditions. Don’t automatically bundle her up just because she’s a baby.
Between ten days and three weeks after birth, the stump from the umbilical cord should have dried and fallen off, leaving behind a clean, well-healed area. Occasionally a raw spot is left after the stump is gone. It may even ooze a little blood-tinged fluid. Just keep it dry and clean (using a cotton ball dipped in rubbing alcohol) and it will heal by itself. If it is not completely healed and dry in two weeks, consult your pediatrician.
- Last Updated
- 8/1/2009
- Source
- Caring for Your Baby and Young Child: Birth to Age 5 (Copyright © 2009 American Academy of Pediatrics)
The information contained on this Web site should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your pediatrician. There may be variations in treatment that your pediatrician may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
There may be variations in treatment that your pediatrician may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
Weight and height of a child by months up to a year - Table of weight norms for babies up to a year
A young mother often worries about whether her baby is developing correctly. And the weight of the child is one of the “sick” questions that often comes up on the playground.
Undoubtedly, how much a newborn is gaining weight is really important to know. But remember that the height and weight of the child are individual indicators. And they may not always fit into beautiful statistics. Although the approximate norm for the weight of a newborn is calculated based on general values. Doctors who carry out regular weighing of a newborn also have their own guidelines. nine0003
The table below shows the height and weight of the newborn by month. The figures take into account statistical data and recommendations of pediatricians (the discrepancy, by the way, is only 3%).
| Child's age, months | Boy, weight, g | Boy, height, cm | Girl, weight, g | Girl, height, cm nine0012 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Newborn | 3 600 | fifty | 3400 | 49.5 |
| 1 month | 4 450 | 54.5 | 4 150 | 53.5 |
| 2 month nine0026 | 5 250 | 58 | 4 900 | 56.8 |
| 3 month | 6050 | 61 | 5 500 | 59.3 |
| 4 month | 6 700 | 63 nine0026 | 6 150 | 61. 5 5 |
| 5 month | 7 300 | 65 | 6 650 | 63.4 |
| 6 month | 7 900 | 67 | 7 200 | 65.3 nine0026 |
| 7 month | 8 400 | 68.7 | 7 700 | 66.9 |
| 8 month | 8 850 | 70.3 | 8 100 | 68.4 |
| 9 month nine0026 | 9 250 | 71.7 | 8 500 | 70 |
| 10 month | 9 650 | 73 | 8 850 | 71. 3 3 |
| 11 month | 10,000 | nine0031 74.39 200 | 72.6 | |
| 12 month | 10 300 | 75.5 | 9 500 | 73.8 |
To use the table, you should know how to weigh a newborn correctly. Before turning on the scales, you need to remove all foreign objects from the bowl, otherwise you will get distorted data. Although you can leave a diaper on it and then press the "Tara" button to reset the result. It is necessary to put the baby in the scales at rest in order to fix the exact numbers, which can then be compared with the “ideal”. nine0003
Modern electronic scales for weighing newborns are proactive. A smart device “knows” the weight of a healthy baby in advance and compares the norm with the result. Just wait a few seconds and you will see the result. Home scales with a built-in height meter will allow you to control the physical development of your baby without visiting the clinic.
Home scales with a built-in height meter will allow you to control the physical development of your baby without visiting the clinic.
Remember that the proper weight of the child is growing in dynamics. You can follow this indicator through a mobile application that collects the results of each weigh-in. nine0003
Height and weight of the baby - Motherhood in Khabarovsk
Height and weight of the baby, from 1 day before 7 days
Weight loss in an infant: norms
In the first year of life, the child grows at the fastest rate. Its development should be under the constant supervision of a pediatrician.
Its development should be under the constant supervision of a pediatrician.
In the first week of life, a baby can lose 5-7% of its weight. The main reason for this is the decrease in the amount of fluid in his body. While in the womb, the baby did not lose moisture with breath, through the skin, with urine and stool. Having passed from the aquatic environment to the air, he first encountered these "expenditures". That is why he loses weight, and this is not bad for health, as long as the weight loss does not go beyond 7-10%. nine0003
Baby's height and weight, from 1 day before 14 days
Baby height and weight at birth
According to the standards of the World Health Organization at birth, the baby's body weight is 2. 800-3.900 g. Height is 47-52 cm.
800-3.900 g. Height is 47-52 cm.
Baby's height and weight, from 1 day before 1 month
Baby weight gain
In the first month, your baby will gain about 600 g of weight, although some may add about 1000 g. If this is the first birth and the baby is breastfed, it will not be terrible if he gains 400 g - this is a mutual adaptation of mother and baby.
Baby's height and weight, from 1 month before 1 month 25 days
Baby height and weight: 1 month
According to the standards of the World Health Organization, by the end of the first month, the baby's body weight is 3. 600-5.100 g. Height is 52-57 cm.
600-5.100 g. Height is 52-57 cm.
Baby's height and weight, from 2 months before 2 months 25 days
Baby height and weight: 2 months
According to the standards of the World Health Organization at two months, the baby's body weight is 4. 500 - 5.800 g. Height is 55-59 cm.
500 - 5.800 g. Height is 55-59 cm.
Baby's height and weight, from 3 months before 3 months 25 days
Baby height and weight: 3 months
According to the standards of the World Health Organization, at three months the baby's body weight is 5. 200-7.200 g. Height is 58-64 cm.
200-7.200 g. Height is 58-64 cm.
Baby's height and weight, from 4 months before 4 months 25 days
Baby height and weight: 4 months
According to the standards of the World Health Organization at four months, the baby's body weight is 5. 700-7.800 g. Height is 60-66 cm.
700-7.800 g. Height is 60-66 cm.
Baby's height and weight, from 5 months before 5 months 25 days
Baby height and weight at 5 months
According to the standards of the World Health Organization at five months, the baby's body weight is 6. 100 - 8.400 g. Height is 62-68 cm.
100 - 8.400 g. Height is 62-68 cm.
Baby's height and weight, from 6 months before 6 months 25 days
Baby height and weight: 6 months
According to the standards of the World Health Organization at six months, the baby's body weight is 6.![]() 500-8.800 g. Height is 64-70 cm.
500-8.800 g. Height is 64-70 cm.
Baby's height and weight, from 7 months before 7 months 25 days
Baby height and weight: 7 months
According to the standards of the World Health Organization at seven months, the baby's body weight is 6. 800-9.200 g. Height is 65-71 cm.
800-9.200 g. Height is 65-71 cm.
Baby's height and weight, from 8 months before 8 months 25 days
Baby height and weight: 8 months
According to the standards of the World Health Organization at eight months, the baby's body weight is 7. 000-9.600 g. Height is 66-73 cm.
000-9.600 g. Height is 66-73 cm.
Baby's height and weight, from ninemonths before 9 months 25 days
Baby height and weight: 9 months
According to the standards of the World Health Organization at nine months, the baby's body weight is 7. 300-9.900 g. Height is 68-74 cm.
300-9.900 g. Height is 68-74 cm.
Baby's height and weight, from 10 months before 10 months 25 days
Baby height and weight: 10 months
According to the standards of the World Health Organization at ten months, the baby's body weight is 7. 500-10.200 g. Height is 69-76 cm.
500-10.200 g. Height is 69-76 cm.
Baby's height and weight, from 11 months before 11 months 25 days
Baby height and weight: 11 months
According to the standards of the World Health Organization at eleven months, the baby's body weight is 7.